A rash is the presence of pathological elements on the skin or mucous membranes, the appearance of which differs from healthy skin and mucous membranes in color, appearance and structure. Many diseases (more than 100) appear in children with rashes, including not only harmless prickly heat, but also life-threatening meningococcal infection.
Photo: depositphotos.com
If the cause of a child’s skin rash is blood and vascular diseases
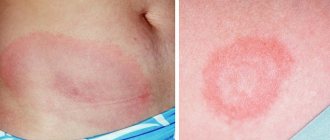
In diseases of the blood and blood vessels, the rash can be either pinpoint or resemble one large bruise. This rash is a hemorrhage into the skin. The color of the elements may change (as happens with bruises) over the course of several days. The appearance of such a rash can be triggered by even minor trauma or pressure on the skin.
If parents notice the unreasonable appearance of bruises on the child’s body “here and there,” it is necessary to contact a hematologist for a thorough examination and identification of blood pathologies.
Diagnostics
Sometimes the cause of an allergic rash can even be a new toy bought by parents, if it is made of low-quality materials.
In most cases, based on the nature and type of the rash, the doctor quickly determines its origin. In doubtful cases, additional tests are prescribed - blood, urine, feces. Sometimes, if a bacterial infection is suspected, samples of the contents of the pustules can be taken for bacterial culture to establish the type of pathogen and its resistance to certain types of antibiotics.
If the cause of a rash on a child’s body is insect bites
Insect bites are a very common cause of rashes. In the morning, you may notice small red or pink spots on those parts of the body that were exposed during sleep, including on the face. Perhaps these are mosquito bites. Flea and bedbug bites can become more dangerous.
Usually the bite sites are slightly itchy, but many children may be allergic to these insects, which results in severe swelling and irritation. In this case, it is necessary to urgently give an antiallergic drug and lubricate the bite sites with antiallergic gel.
To protect against mosquitoes, you need special nets on the windows; you can use a fumigator (for children). If fleas or bedbugs are detected, the premises should be thoroughly disinfested and treated with a special pet product.
Another parasite on human skin that causes rashes and itching (at night) is the scabies mite. This rash is localized on the child’s stomach, on the palms of the hands and between the fingers. It consists of paired elements at a distance of 2-3 mm from each other. Scabies is a contagious disease, so treatment of patients must be carried out carefully, in compliance with quarantine and under the supervision of a doctor. Scabicidal substances (which have a detrimental effect on ticks) are used for treatment.
Watery
A watery rash may indicate the following diseases:
- herpes;
- impetigo;
- angulitis (streptococcal);
- initial stage of chickenpox;
- allergic reaction to insect bites;
- presence of molluscum contagiosum;
- presence of fungus;
- contact with toxic substances.
The appearance of watery blisters on the skin, resembling droplets of water, can also be a consequence of a sunburn. It is contraindicated to pierce the blisters and start treatment on your own.
Allergic rash in a child
Allergic rashes on the body in children appear quite often, this is due to the immaturity of the immune system. The cause of such a rash can be not only food, but also detergents (powders, soaps), toys, clothes or plants.
The appearance of an allergic rash is associated with the immune system's response to something new entering the body. The child develops irregularly shaped spots on his body, gradually merging with each other and accompanied by severe itching. Sometimes the child can be very excited or, conversely, apathetic. In rare cases, there is an increase in temperature.
An allergic reaction can be associated with the introduction of complementary foods or the inclusion of exotic seafood and fruits in the diet.
Toys with a strong chemical smell and bright colors are dangerous, the same goes for clothes and any new household items. Even one touch of the allergen may be enough. This is the so-called contact dermatitis. This group also includes a rash from touching certain plants.
I would especially like to mention medications and vitamins. Many of these products are chemical in nature and can cause an allergic rash in a child.
If an allergic reaction occurs, the child should immediately be given an antiallergic agent and adsorbents (activated carbon).
It is necessary to consult a doctor and together identify the cause of the disease. It is mandatory to exclude from the diet a product that is not tolerated by the child, or remove a toy or clothing, i.e., contact with the allergen is excluded.
It happens that food allergies go away over time, but the prevention of this condition is the gradual and careful introduction of complementary foods into the baby’s diet.
How to treat?
It is not recommended to apply ointments that you think should help or alleviate hives . Treatment is prescribed and monitored by a dermatologist and an allergist .
Before prescribing treatment the doctor finds out when and how the disease began. It is important to tell what else the child is sick or was sick the day before, what medications he took. Then the doctor asks about your diet and the absence of gastrointestinal or autoimmune diseases.
Treatment first of all eliminates the influence of a factor that can cause a rash on the child’s skin. To find the causative agent of the disease, analyze what new the child ate at home, at grandma’s, in kindergarten. Think about what powder you used to wash your clothes last time.
The reason may be hidden even in the basic socks that you put on your child for the first time. Check if the room is too hot. Perhaps the air is too dry.
This is the most difficult part of treatment, but if you do not find the allergen, then taking medications will be pointless.
Interesting ! According to pediatricians, every fourth child . The risk of the disease most often occurs at ages from 0.5 months to 3 years .
The doctor prescribes antihistamines , which relieve itching and reduce swelling.
If the disease is caused by a food product, which most often concerns the appearance of urticaria in children, sorbents are prescribed to cleanse the intestines - Enterosgel, Smecta.
Proper nutrition plays an important role in treatment . All “dangerous” foods are excluded from the children's diet.
To identify the allergen, doctors recommend an elimination diet. Products that can provoke hives are removed from the menu one by one.
If the rash appears during another illness, pay attention to drugs that can cause it - Aspirin, Codeine, Capoten, Enap.
If medical help is not needed immediately and the child’s health is not in danger, before consulting a doctor, parents can eliminate the allergen, limit food, and give the child a compress .
If the cause of a rash on a child’s body is an infection
Most infectious diseases in children are accompanied by symptoms other than rash, such as fever, malaise, chills, loss of appetite. Possible abdominal pain, diarrhea, sore throat, cough, runny nose. And the rash has its own characteristics (localization, appearance, nature of spread) for each disease.
Varicella (chickenpox) appears as a rash after 2-3 days of fever and malaise. The amount of rash is small at first, then new elements appear in the form of spots, gradually turning into a tubercle, then a blister, which gradually dries out and becomes covered with a crust. Rashes appear everywhere, even on the scalp, and cause severe itching.
A measles rash on a child’s body appears on the 4th-5th day of illness with spots that tend to merge. And it all starts with fever, runny nose, conjunctivitis and cough. A characteristic feature of measles rashes is that they appear on the face and chest on the 1st day, on the torso on the 2nd day, and on the legs on the 3rd day, and the spots on the face disappear without a trace.
Rubella differs from measles by a profuse skin rash that appears all over the body simultaneously, as well as enlarged occipital lymph nodes. The spots also disappear without a trace, and the disease is accompanied by signs of a mild cold.
These 3 diseases (measles, rubella and chickenpox) do not require hospitalization or specific treatment. Good child care is important. For chickenpox, an antiallergic gel can be used to eliminate itching, and for measles, bright light is not advisable due to conjunctivitis.
Pregnant women should avoid contact with children with rubella.
To prevent measles and rubella, children under one year of age are recommended to be vaccinated. It does not give a 100% guarantee that the child will not get sick, but he will not have a violent manifestation of infection. Everything can be done without conjunctivitis and high fever.
Scarlet fever is considered a more severe illness and begins with a high fever, sore throat and sore throat. And after a few hours, a pinpoint pink rash appears on the child’s body (there is especially a lot of it in the natural folds of the skin). In the second week of the disease, severe peeling appears on the palms and soles after the rash. A characteristic feature of the disease is a “grainy” bright red tongue - this symptom appears on days 2-4 of the disease.
Scarlet fever must be treated; you must definitely call a doctor, because with this disease, antibacterial therapy is prescribed to prevent complications on the heart and kidneys. Drinking plenty of fluids and bed rest are recommended.
Infantile roseola (sudden exanthema) is a viral disease that begins with an increase in temperature; loose stools with mucus are possible. But the child’s condition does not suffer. After 3-4 days, the child develops a rash on his face and goes down to his stomach and below. After the rash disappears, no traces remain and no specific treatment is required.
Meningococcal infection is accompanied by a small rash (there may even be single elements). However, high temperature and the child’s condition worsening every hour come first. Vomiting and impaired consciousness appear. In this condition, it is necessary to call an ambulance and urgently hospitalize the child.
Other types of rash
There is a rash similar to prickly heat - both scarlet fever and rubella are a possibility. If this is accompanied by a small rash similar to goosebumps and fever, this is still the same meningitis, and you need to quickly seek help.
There are many diseases that go away without fever.
If the rash appears without fever, this is a signal to assume that your child has:
- Scabies is a contagious skin disease, acariasis from the group of acarodermatitis, caused by a microscopic parasite - the scabies mite or scabies itch.
- Urticaria is a lesion of the epidermis characterized by pale pink inflammation. If the nature of the symptom is not related to allergies, it is a sign of some kind of illness.
- Pyoderma is the penetration of pyogenic bacteria into the body. More than 110 million children are infected every year.
- Eczema is an inflammation of the epidermis, accompanied by burning, itching and peeling. Eczema is not contagious, but is prone to relapses, so it is better to approach treatment responsibly.
READ ALSO: How to treat heat rash in a newborn at home and what does it look like?
You need to understand that this is not a reason to treat at home if your person does not have a fever. All diseases affecting the skin have a complex and dangerous etiology that must be determined.
Even if your child only has a small white rash, like an allergic reaction, it is better to prevent and prevent all possible consequences in advance.
Finally, there is a separate, unrelated type of rash that appears as small pimples on the skin.
This is not an infection or an allergy - this is what is left of the baby from the mother. It appears for the reason that in children's blood, especially when it comes to a newborn, there are still a lot of maternal hormones that come into slight conflict with their own hormonal system. In order to eliminate this, certain therapy is prescribed.
Conclusion
So, if you find certain spots or rashes in children, you should contact a specialist. The rash can be associated with both meningitis and hyperkeratosis. You can’t let such symptoms go by chance, relying on your own carelessness in not observing children’s hygiene.
The body of a newborn or one-year-old child is a very fragile system that can be undermined even by the most serious illness. And it’s better to visit the pediatrician one more time than to pay for the consequences later.
News MirTesen
Treatment of eczema
If a rash appears in a child, then antihistamines are given. Cooling gels and antiallergic ointments are used externally.
Dermatologists recommend combining oral administration of an antihistamine with external use of a cream or gel with the same active ingredient. Parents are afraid that such treatment will cause drowsiness in the child and reduce academic performance.
Antihistamines Fenistil, Claritin, Erius, Zyrtec have almost no sedative effect and are better tolerated.
Histamine is released by mast cells in the blood and tissues to help the immune system protect the body from pathogens and toxins. However, in some people, allergies lead to an overprotective reaction directed at harmless substances. Antihistamines block histamine receptors, preventing or reducing itching, swelling, redness of the skin, and lacrimation.
Antihistamines are the most effective for eliminating rashes in acute forms of urticaria. For chronic urticaria, such drugs help only 50% of patients.
Corticosteroid ointments have antiallergic and anti-inflammatory effects. The drugs Fenistil-gel, creams and ointments Elokom, Lokoid, Advantan, Sinaflan, and Flucinar are used externally. Children are given enterosorbents to drink, for example, Enteros-gel or Laktofiltrum. Dietary supplements with lacto- and bifidobacteria are also taken internally.
READ MORE: Vegetative vascular dystonia in adults, clinical recommendations
The translation of the name of the disease from ancient Greek sounds very simple - “skin rash.” Infantile eczema or atopic dermatitis appears before 6 months of age. Dense red spots form on the child’s cheeks without clear boundaries. The disease manifests itself as itching, inflammation and dry skin on the face, wrists, and under the knees
Redness, blisters, crusts, and cracks in the skin are observed in all types of eczema.
The acute phase of the idiopathic form of the disease is manifested by the formation of many blisters. They open, they begin to get wet, after which crusts and stains remain. Typical localizations of true eczema are the face, hands, forearms, feet and knees. Rashes appear symmetrically on the body.
Idiopathic, true eczema is the same as weeping lichen, a chronic itchy dermatosis. A rough rash on the body of a one-year-old child is located on the face, arms and legs, chest and buttocks. There are such stages of the eczematous process as erythema, blisters, erosions, and crusts.
Causes:
- allergies to substances in food, mite secretions, dust, mold, climate change;
- diseases of the digestive system, endocrine system;
- hereditary predisposition;
- stress, psycho-emotional trauma.
As the disease becomes chronic, the skin thickens and peels. Symptoms worsen in climates unsuitable for the child, with excessive dry air. The influence of constant or seasonal action of allergens is noted.
Therapeutic methods and means:
- Antihistamines that relieve itching and inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Resorcinol solution for cooling and astringent lotions.
- Antiallergic ointments, antiseptic solutions.
- Valerian tincture and other sedatives.
- Enterosorbents to cleanse the body of allergens.
- Oral diuretics to reduce swelling.
- Hormonal ointments (GCS).
- Physiotherapy.
Corticosteroids for external use have anti-inflammatory and antitoxic effects. GCS is included in the ointments "Lokoid", "Dermozolon", "Ftorokort" and "Sikorten". Combined products contain corticosteroids and an antibiotic and are used for microbial eczema. Ointments “Cortomycetin” and “Gioxizon” belong to this group.
If the child is taking any medications at this moment, you should definitely inform the doctor about this and, if it is impossible, stop the medications and choose analogues.
In 80% of cases, these measures are more than enough for the non-infectious rash to first begin to fade, and then completely disappear without a trace.
However, sometimes treatment is unavoidable. An allergic rash may require treatment with antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil, Loratadine, Cetrin and others), as well as hormonal ointments (Advantan, Triderm). Such treatment is not always prescribed and not for everyone; the decision on the use of such drugs must be made by a doctor.
Neonatal rash in newborns does not require treatment at all, since it goes away on its own as the level of maternal hormones decreases. Heat rash requires correction of both the microclimate in the apartment and the hygienic principles and approaches that exist in the family.
The child benefits from air baths, bathing without soap with a decoction of string, chamomile, treating weeping diaper rash with baby powder or drying cream (Sudokrem), and treating dry crusts with softening creams with a healing effect, for example, Bepanthen or Dexpanthenol.
If the rash itches, you should avoid scratching, as this increases the risk of a secondary infection. It is necessary to ensure that the child has comfortable clothes and soft bedding so that additional mechanical irritation does not occur.
If the rash intensifies on one cheek on the side on which the baby slept, this may indicate that the child sleeps on linen that has been washed with allergenic substances or mechanically irritates the skin.
By and large, there is no need to treat an infectious rash. It goes away as the child recovers from the underlying disease.
It is only important to prevent scratching, and also to treat with an antiseptic those fragments of the rash that the baby managed to scratch in order to avoid bacterial infection. Aniline dyes – “zelenka” or “Fukortsin”, as well as the drug “Chlorophyllipt” – are suitable for processing.
To achieve results, it usually takes at least 7-10 days of taking these drugs. The first positive effect, as a rule, is noticeable already 2-3 days after the start of using the medicine.
Treatment of urinary rash: drugs and remedies
| Active substance | Examples of drugs | Release form | At what age are they used? |
| Azelastine | "Allergodil", "Azelastine" | Eye drops, nasal spray | Eye drops - from 4 years, nasal spray - from 6 years |
| Cetirizine | "Zyrtec", "Zodak", "Cetirizine" | Tablets, drops, syrup | From 6–12 months |
| Desloratadine | "Desloratadine-Teva", "Erius" | Tablets, syrup | After 12 months |
| Levocetirizine | "Levocetirizine Sandoz" | Syrup | From 2 years |
| Loratadine | "Loratadine-Hemofarm", "Claritin" | Pills | After 2 years |
The rash goes away quickly when the allergen is eliminated, antihistamines are taken, and hormonal ointment is applied. Antiallergic drugs reduce the level of histamine in tissues.
Antihistamines are used in almost all cases of rash to reduce itching and swelling. New generations of drugs in this group do not cause drowsiness and are well tolerated by children.