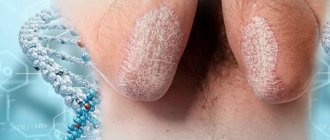
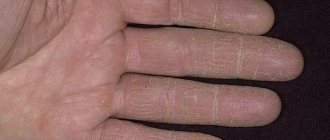
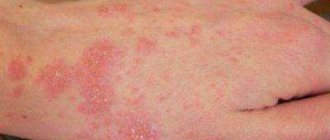
When communicating with a person who has any defect on the skin, the question arises: is eczema contagious or not? To get the answer, it is important to study information about what this dermatological disease is.
The chronic disease, which causes flaky, weeping red patches, can affect a person's skin regardless of age.
Causes of eczema on the hands and feet
The exact cause of the disease has not yet been established, however, due to the presence of many studies in this area, there is a reasonable answer to the question of whether it is possible to contract eczema from another person. The pathology is non-infectious in nature, so there is no danger of becoming infected through contact.
The reasons for the manifestation of pathology are the following circumstances:
- increased anxiety, frequent exposure to stressful situations, neuroses;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- metabolic disorders;
- consequences of insect bites;
- sudden change in temperature;
- excessive use of cosmetics and detergents that contain chemically aggressive components;
- hormonal disorders in the body. As a rule, this is characteristic of women during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy, as well as adolescents during puberty;
- reduced immunity;
- reaction to external irritants (allergens);
- infection of the epidermis by fungi;
- heredity;
- skin injuries, mechanical effects on the epidermis.
Note! Eczema can appear in any person, regardless of age and gender, so when the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. This is especially true for children, since the disease is accompanied by continuous burning and itching, causing increased discomfort in the baby.
Due to the fact that the disease is autoimmune in nature, the statement that eczema is transmitted by contact is fundamentally incorrect; the disease is not contagious.
Mechanism of disease development
The development mechanism is similar to any other allergic reaction, that is, foreign bodies (in this case, microbes) interact with the cells of the body’s immune system.
As a result, these cells begin to produce active compounds that, through chemical reactions, cause inflammation of the epidermis.
The pathology is more intense than a normal allergy due to the fact that the immune response is more violent due to increased sensitivity to the antigen. An autoimmune reaction may also occur.
Externally, the development of pathology goes through the following stages:
- an area of skin becomes covered with red spots;
- bright papules form on the spots;
- bubbles filled with pus form on the surface of the nodules;
- the bubbles burst, revealing damaged skin, which is colored bright red and oozes serous fluid;
- the epithelium dries out and becomes covered with a dense crust;
- healthy epithelial cells are actively dividing, and the skin begins to peel off.
If left untreated, the disease becomes chronic, and the process begins to go in circles.
At the same time, periods of subsidence of the disease are observed, and the source of inflammation may not enter the moistening stage for quite a long time.
Typically, all stages of the development of the disease are accompanied by severe itching. It may not be present only when redness begins in a poorly innervated area of the skin.
Types of eczema, its manifestations
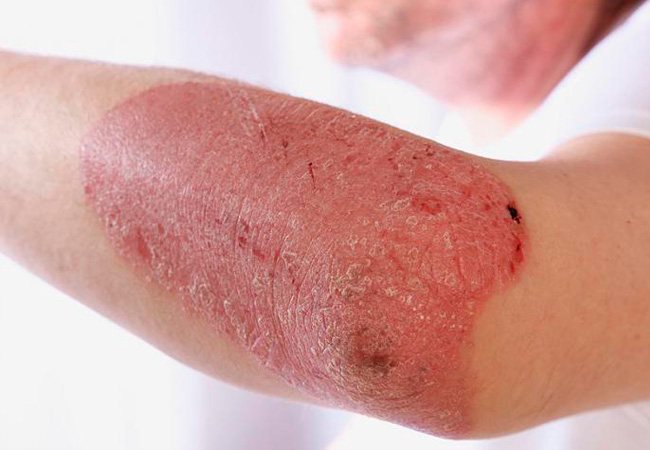
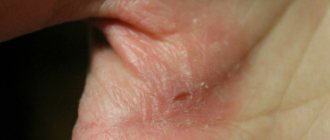
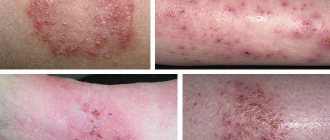
The main symptoms of the disease are rashes that appear on the skin and are accompanied by constant itching and burning. Over time, the skin in problem areas begins to peel off, the vesicles that formed earlier crack and weeping appears in their place. In the event of a bacterial infection, which is quite likely in the absence of treatment, pustules may form in the affected areas.
The pathology is characterized by a recurrent nature and seasonal exacerbations, which once again confirms the negative answer to the question: is microbial eczema contagious or not?
Type of eczema:
- True eczema. The primary location of the pathology is the skin of the face; small bubbles filled with clear liquid appear here. In the absence of timely treatment, the symptoms of the disease become more noticeable, itching appears, the rash grows and spreads to the epidermis of the upper and lower extremities. The vesicles crack and oozes form in their place;
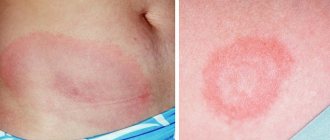
- Varicose eczema. Varicose eczema or so-called stasis dermatitis develops in patients suffering from varicose veins;
- Microbial eczema. Eczema occurs in problem areas of the skin where a fistula or ulcer has previously formed. The affected area is usually covered with a crust, which subsequently cracks and weeping remains in its place. The main cause of the development of microbial eczema is considered to be dysfunction of the immune system and malfunctions of the nervous system. A factor contributing to the manifestation of this type of dermatitis is the body’s predisposition to fungal infections and microbes;
- Eczema of the lips. It appears around the lips; this form is characterized by the appearance of scales, crusts and cracks in the affected areas. Weeping does not form;
- Seborrheic eczema. The localization of the disease is the scalp, axillary area, and shoulder blade area.
What should you do to avoid getting sick (especially if there is a hereditary predisposition)?

If a person experiences itching and redness of the skin, you should definitely see a doctor, especially if close relatives have had cases of eczema. The doctor will prescribe a course of treatment, which mainly includes corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory drugs. Flucinar is considered an effective ointment for eczema. This is an anti-inflammatory drug with antibacterial action. Be sure to first read the instructions for using Flucinar ointment).
Do not be afraid of this disease; it is well corrected with hormonal drugs with anti-inflammatory effects, which are aimed at eliminating the main symptoms of eczema. After the exacerbation is relieved, the doctor selects the necessary diet and eliminates factors that lead to allergic reactions in the body, which may result in the development of the disease.
Given that eczema can still be contagious if fungi or germs are present, it is worth protecting yourself, especially in public places:
- When visiting public baths and saunas, use only personal household items, towels, slippers, etc.
- When visiting, you should not wear the hosts' slippers.
- People who have a predisposition to eczema and work in hazardous industries will have to change their profession.
- Those who abuse spicy, salty and fatty foods need to reconsider their diet.

Thus, answering the question of whether eczema is contagious, we can safely say that it is not. For a person with a good immune system, this disease is not terrible, even with a hereditary predisposition. But given the fact that in the modern rhythm of life, not many can boast of good immunity, and with the tendency of eczema to turn into a microbial variety, it is worth taking care of preventive measures and observing the rules of personal hygiene. Eczema can be a serious problem for a person, because it looks aesthetically unsightly. This circumstance, in turn, leads to problems at work and in personal life.
Is eczema contagious or not: the scientific basis for the issue
The main causes of the disease are dysfunction of the endocrine and nervous systems, reduced immunity, so the infectious nature of the pathology is completely excluded. This indicates that it is impossible to contract eczema through contact, in particular by shaking hands.
The risk group includes patients whose mother or father has previously encountered the disease, since the fact that a genetic predisposition to dermatoses, including eczema, is inherited is scientifically substantiated and has been proven repeatedly in practice.
Heredity
It was previously believed that eczema was inherited. This is also not an entirely true statement. Eczema cannot directly spread to children, grandchildren and great-grandchildren. The only thing that ancestors can bestow is a predisposition to the development of eczema.
Any allergy is an aggressive reaction of the body to an external irritant, which begins at the stage of division of a fertilized egg in a woman’s body, that is, at the genetic level. It is believed that if one of the parents is allergic, then the probability of identifying a similar illness in the child is about 25-30%. If both parents have immune disorders, then this probability increases to 70-75%.
Some women experience eczema on their nipples during lactation. Is this kind of eczema contagious for a child? It is eczema that is not transmitted to the baby in any way, but it brings a lot of discomfort to the woman during the feeding process. Severe pain forces many mothers to switch their babies to artificial feeding, which is also wrong.
If this delicate problem occurs, you need to adhere to the diet and doctor’s recommendations, avoid contact of the affected areas with water, and increase the time between feedings. You can express milk and bottle feed your baby, alternating with the natural process.
Is microbial eczema contagious and how to protect yourself from the disease?
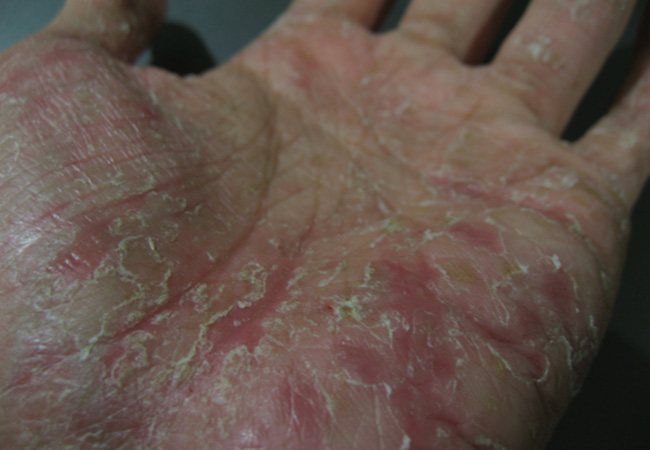
Doctors say that eczema is not transmitted from person to person through contact, so there is no chance of becoming infected during close contact with a patient affected by the disease.
It is believed that microbial eczema can be transmitted through contact. However, this is not entirely true, since it is not the disease itself that is transmitted, but only the bacteria accompanying it. In addition, the risk of infection is negligible, only in the case of very close contact.
To avoid the possibility of injury, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of hygiene, follow the advice of dermatologists and nutritionists, and use various antiseptics as a preventive measure.
Treatment methods
If timely treatment is not carried out, the microbial form may transform into its true form.
Therapy is carried out in two directions:
- elimination of foci of inflammation;
- treatment of the disease that caused the infection with eczema.
Due to the allergic nature of the disease, a complete cure is impossible - the body will not stop reacting acutely to the allergen. But the manifestations can be stopped quite successfully.
Treatment consists of local treatments, systemic treatments and general lifestyle changes to reduce stress, improve nutrition and maintain hygiene.
Local therapy includes:
- antiseptic gauze compresses – 2% boric acid solution, 1% resorcinol solution, brilliant green, lead water;
- drying ointments: zinc, ichthyol, naphthalan;
- antibacterial ointments: erythromycin, tetracycline;
- for large foci of inflammation - drugs with corticosteroids.
Systemic treatment consists of taking the following medications:
- antihistamines - reduce allergic signs of the disease, including swelling and itching (suprastin, loratidine);
- injections of desensitizing drugs;
- immunomodulators – reduce the activity of the immune response;
- antibiotics – kill microorganisms that cause the disease;
- sedatives – valerian, sleeping pills;
- B vitamins.
Various methods of physiotherapy are also used:
- UV lamp;
- magnetic therapy;
- saturation of the skin with ozone;
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UHF irradiation.
What is dyshidrosis? The answer follows.
allergycentr.ru
Treatment of the disease
The main therapy consists of eliminating the allergen and using medications in the form of ointments, gels, and antifungal tablets.
Treatment alone is not enough, and in order to protect yourself from the spread of the inflammatory process throughout the body and ease the course of the disease, preventive measures should be taken:
- Don't forget about personal hygiene. If there are pustular rashes, cracks and ulcers on the skin, they need to be treated with iodine or other disinfectants.
- For varicose eczema that develops against the background of vascular diseases, it is recommended to use special compression garments.
- In case of exacerbation of the disease, it is prohibited to take hot water treatments; during this period it is better to bathe in a bath with a diluted decoction prepared from medicinal plants: dandelion, yarrow, wheatgrass, burdock, violet, viburnum, nettle, milk thistle, string, etc.
- Treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in a timely manner, consume all the necessary vitamins.
- Eat right, avoid overeating or undereating.
- Any skin lesions: cuts, burns, ulcers, rashes must be eliminated as quickly as possible.
- Stop taking medications that provoked an allergic reaction (upon prior consultation with a doctor).
- Avoid contact with chemicals used in everyday life (wash dishes only with rubber gloves).
- Do not stay in the sun for a long time (direct ultraviolet rays have a negative effect on the skin).
- Try not to wear synthetic and woolen clothing.
Bacterial infections
The vast majority of cases of eczema are associated with the active activity of microbes in foci of chronic infection.
Agents that cause inflammation have actively multiplied and become dangerous due to disruptions in the immune system, endocrine and nervous regulation.
Such disorders are individual in nature and do not imply the transmission of bacteria to others - especially since we are usually talking about opportunistic agents that live in the body constantly, but are activated when the immune system fails.
At the same time, relapse, that is, repetition of the symptoms of chronic eczema, can occur during the period of infection associated with exogenous (external) intake of an unfavorable agent. Simply, with infection.
And patients can spread the pathogen - for example, with discharge from the nose, throat, or bronchi.
However, the bacteria in a contact person will not cause an eczematous process - only the same acute infection as the source of the microbes.
Are viruses dangerous?
This group includes a huge number of pathogens of various diseases. They can also provoke changes characteristic of eczema - an example is Kaposi's syndrome, caused by the herpes virus. This is an infectious-allergic process caused by the action of a pathogenic agent against the background of primary disorders:
- Autoimmune pathologies.
- Chronic dermatoses.
- Allergy.
- HIV infection.
- Immunodeficiency.
Since the exudate contained in blisters on the skin may contain a virus, the disease is considered dangerous to others and requires compliance with safety rules to prevent transmission of the pathogen.
But you need to keep in mind that we are not talking about classic eczema, but about a pathology that copies its symptoms. After the herpes infection subsides, even if there are inflammatory changes in the skin, there is no risk of infection.
An infection that occurs in combination with eczema can pose a danger to others.
When should you not worry?
Pathology is divided into many forms, which only specialists can distinguish. For a general overview, it’s worth listing them:
- True eczema, also called idiopathic, initially occurs in the facial area. Then it moves to the arms, legs and feet. At first it is a small rash consisting of blisters with a watery filling. When they are opened, erosive areas are formed. Often the disease is chronic and characterized by long-term relapses.
- Allergic eczema is the body’s response to external irritants if there are internal systemic failures. Often this eczema is hereditary in nature and manifests itself already in the first years of a child’s life. In adults, professional costs become a trigger.
- Varicose eczema. Develops against the background of impaired venous outflow.
- Tilotic type is one of the forms of true eczema.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Ointment for eczema on the head
Are these types of eczema contagious? All these species are non-infectious in nature and develop as a result of systemic disorders in the human body, and therefore are not contagious.
Proper nutrition
Diet plays a huge role in preventing eczema.
First of all, you need to exclude alcohol and citrus fruits from your diet (they contribute to exacerbation of the disease). In addition, it is not recommended to use:
- honey;
- chocolate;
- baked goods;
- marinades;
- pickles;
- canned food;
- lamb and pork meat;
- spicy and fatty foods;
- seasonings;
- coffee;
- red berries.
Will be useful:
- boiled or steamed meat;
- fish;
- dairy products;
- porridge;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- natural juices.
Eczema is not contagious and does not pose a potential threat to others or to the patient himself, but it brings a lot of inconvenience and significantly reduces the standard of living, so you need to start therapy immediately after the first signs are detected. The sooner treatment begins, the easier and more effective it will be.
thepsorias.ru