Swelling of the tongue due to dehydration
Dry mouth is a sign of dehydration, when organs and systems lack fluid. This happens if the body temperature rises or infectious diseases develop. This condition is typical for vomiting, diarrhea, runny nose, and poisoning. When the nose is stuffy, the patient breathes through the mouth. This causes drying of the mucous tissues. It happens that the tongue swells during sleep. This increase in size can cause suffocation. It is imperative to find out the cause in order to get rid of the pathology. To do this, you need to contact your dentist.
Causes of tongue swelling
Language has long been considered an indicator of human health. Any abnormalities, such as the appearance of teeth marks on the side surfaces, changes in color and size, or pain, may indicate health problems. Edema is no exception. An organ can swell for various reasons: trauma, allergies, infection, endocrine diseases. Determining the cause is important for further treatment.
Acute trauma
The most common reason why the tongue swells is due to thermal, chemical or mechanical damage. Thermal damage can occur when eating food that is too hot, and chemical damage can occur when drinking strong alcoholic beverages. In this case, only the oral cavity is affected (rarely also the esophagus); in addition to swelling, other symptoms occur: pain, which is especially disturbing during meals, numbness, tingling.
Mechanical damage often occurs, for example:
- as a result of biting the mucous membrane while eating, an attack of epilepsy;
- when filling teeth;
- when the mucous membrane is injured with a knife, fork, or bone.
Swelling and hyperemia with such a lesion usually persists for 2-3 days. A deep wound increases the risk of infection.
Symptoms
Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue as a result of a bacterial, viral infection, injury, or other origin. Symptomatically manifested by swelling of the tongue, burning, difficulty chewing food, swallowing, speech, pain.
Injury due to piercing
The tongue is a very delicate and sensitive organ, so it is natural for it to swell after any injury, including after piercing. It usually goes away within 3-5 days. If the swelling is accompanied by pain, twitching, increased body temperature, and weakness, then an infection may have occurred. The cause may be either unsterile instruments used during piercing, or an infection in the saliva.
Hypothyroidism
When there is a lack of thyroid hormones in the blood, hypothyroidism develops. In addition to weakness, drowsiness, and fatigue, this disease is characterized by impaired hearing function and voice changes. This occurs due to developing swelling of the tongue and larynx.
Acromegaly
Acromegaly belongs to the group of severe neuroendocrine diseases. The reason for its development is the chronic excessive production of growth hormone during the period of completed physiological growth. In this case, pathological disproportionate growth of bones, cartilage, and internal organs occurs. Increased sweating occurs, joints hurt, and the tongue swells.
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a systemic disease in which amyloid, a protein polysaccharide complex, is formed and deposited in tissues. In addition to swelling of the tongue, this disease also causes problems with the kidneys and intestines.
A bite of an insect
If after an insect bite it becomes difficult to breathe, your face and tongue are swollen, then most likely the cause is an allergic reaction to an insect bite. The bite site becomes swollen, turns red, and begins to itch.
Stomatitis
Inflammation of the oral mucosa (stomatitis) is sometimes also accompanied by swelling of the tongue, multiple or single. In their place, wounds and ulcers may appear afterwards.
Infectious nature
The tongue may swell in some diseases of infectious origin, for example, with sore throat. Sometimes swelling is a side effect of scarlet fever.
Mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis is an acute viral disease. It occurs with an increase in body temperature, damage to the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. The pharynx is also affected, and the tongue increases in volume.
The main route of transmission is airborne droplets, less commonly through blood transfusion.
Pathological formations in the mouth
Injuries and inflammatory processes can lead to the formation of oral fibromas, which are sometimes localized on the tongue.
Tongue cancer is the most common tumor among malignant tumors of the oral cavity. The most common provoking factors for its development are:
- chronic traumatization of the tongue (incorrectly installed crowns, fragments of teeth);
- exposure to tobacco smoke, namely its carcinogenic effect;
- alcohol abuse;
- leukoplakia, tongue papilloma.
In addition to swelling of the tongue, cancerous tumors are accompanied by pain when eating, numbness of the tongue, and enlarged lymph nodes.
Round or flat formations with clear boundaries and different etiological origins can be benign tumors of the tongue. These include papillomas, hemangiomas, angiomas, fibromas, cysts, adenomas, etc.
Rupture of blood vessels
When the blood vessels of the tongue rupture, a hematoma, or bruise, appears at the tip of the tongue. Reasons may be:
- traumatic origin (fall, blow, biting, surgery and others);
- dental nature (incorrectly placed filling or its absence, wounding fragments of teeth);
- cardiovascular diseases;
- hemophilia, hemorrhagic vasculitis (very rare);
- eating food that is too hot or too cold;
- consumption of hot spices and seasonings, coarse unprocessed food.
Allergy
The tongue can greatly increase in volume if an acute allergic reaction occurs when consuming medications or food to which there is an individual intolerance. In this case, the swelling can quickly spread to the larynx, disrupting respiratory function.
This life-threatening condition requires immediate cessation of exposure to the allergen and emergency medical care.
Bite disorders
Most often, malocclusions are observed in childhood. The presence of teeth marks on the tongue is one of the signs of this problem. Sometimes the tongue may become swollen.
Mechanical damage to the tongue is the most common cause of swelling. It could be a harmless little biting of the tongue. Or there may be severe compression as a result of a fall or blow to the jaw, disrupting blood circulation and rupturing blood vessels. With mechanical damage, disruption of innervation can lead to sensory and motor disorders.
A swollen tongue due to dehydration may indicate insufficient fluid intake in the body. In addition, cracks appear in the corners of the lips, the skin becomes loose, the urine is saturated yellow in color, little of it is excreted, dry mouth and severe thirst appear.
Conditions in which a central nervous system disorder occurs, accompanied by swelling of the tongue:
- damage to the central nervous system as a result of traumatic brain injury with severe damage to the brain and/or its membranes;
- circulatory disorders of the cerebral vessels (stroke, ischemia, aneurysm);
- severe poisoning with alcohol or drugs;
- hereditary gene diseases (Down syndrome);
- infectious diseases (measles, untreated influenza, tick-borne encephalitis).
Chronic damage
Long-term exposure to traumatic factors leads to the development of chronic glossitis. Chronic glossitis is caused mainly by the following factors:
- carious teeth;
- poor quality fillings and dentures;
- tartar;
- bad habits.
The process develops over a long period of time – months, years. Swelling, hyperemia, and pain occur. Over time, erosions and ulcers may form.
Other diseases
Often, swelling of the tongue is one of the signs of diseases of the internal organs.
| Group of diseases | Explanation |
| Thyroid diseases | An enlarged and swollen tongue may be signs of hypothyroidism. Symptoms occur due to the accumulation of mucopolysaccharides, which retain water. |
| Pathology of the stomach and intestines | Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are often accompanied by damage to the oral cavity. The tongue may swell and marks appear on its side surface. |
| Vitamin deficiency | The symptom appears especially often with a deficiency of B vitamins (B1, B12). |
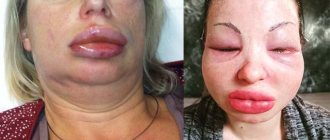
Quincke's edema
Quincke's edema is an acute allergic condition in which areas with well-developed subcutaneous tissue swell. These are the oral cavity, face, neck, genitals. Swelling can involve the entire facial area, but it can also develop in isolation, for example, when only the tongue swells.
An allergic reaction occurs in response to the action of an allergen, which can be:
- food products (especially citrus fruits, honey, chocolate, nuts);
- plants;
- medications;
- insect poison.
Quincke's edema is a dangerous condition, as swelling of the root of the tongue or pharynx can lead to acute respiratory failure. An enlarged tongue leads to blockage of the airways; if medical assistance is not provided in time, a person may suffocate.
- Symptoms develop quickly, within a few minutes after contact with the allergen:
- the tongue increases significantly in size;
- surrounding tissues swell;
- breathing becomes difficult;
- aphonia (loss of voice) occurs.
Causes of tongue allergies in adults and children
› Allergies on the body
Many people on the planet suffer from allergic reactions, and their manifestations can be very different. This common disease affects both adult patients and children.
The onset of the disease is associated with individual hypersensitivity to a particular substance and intolerance by the body, which begins to produce a large amount of histamine in order to suppress the action of the allergen. This leads to a number of unpleasant and sometimes dangerous consequences.
Particular discomfort is caused by rashes on the tongue and in the oral cavity of an allergic nature.
Is it possible to have allergies in the tongue area?
As a result of contact with an allergen, a reaction occurs in the body, which can affect different human organs and systems. Therefore, it is not surprising that the language is often subject to such influence.
However, many patients ignore the symptoms - changes in the color of the tongue, the appearance of rashes. Although, even having discovered them, people cannot always associate them with the root cause (the effect of the allergen), so they begin to treat themselves.
This behavior is dangerous and can cause a number of complications.
Glossitis and its varieties
Inflammatory processes that occur in the tongue area and are the result of injuries, microorganisms and other factors are described by the concept of glossitis. This condition is associated both with systematic changes in the tongue, for example, vitamin deficiency, acute infections, dermatoses, and with disturbances in the nature of the structure.
With high frequency, glossitis is provoked by microorganisms - bacteria, viruses, fungi. Sometimes caused by a complex infectious effect of pathogens, for example, simultaneously viruses and fungi. If a person does not have problems with immune defense, then the likelihood of glossitis occurring is minimal.
Inflammatory processes in the tongue (glossitis) are the result of the interaction of various factors that lead to damage to the mucous membrane and suppress the immune system.
Along with allergic glossitis, caused by the action of an allergen and manifested by redness and swelling of the tongue, other types are also distinguished:
- desquamative (exfoliative) – manifests itself due to vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal disorders, and the presence of parasites in the body;
- Gunterovsky (Hunterovsky) - caused by anemia, which occurs as a result of a deficiency in folic acid;
- candidiasis – associated with changes in microflora in the oral cavity;
- atrophic, resulting from the action of various infections;
- herpetic, caused by the action of the herpes virus, etc.
Causes of manifestation
Factors that play an important role in the occurrence of allergic manifestations in the oral cavity usually include a reduced degree of the body's immune defense and smoking. However, the dominant position among the causes of the disease is the penetration into the body of a number of components that can provoke allergies, i.e. a reaction of the immune system that is pathological in nature.
An allergic reaction during development forces the immune system to activate at the cellular level, in particular, the order to work is given to T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes.
They stimulate the production of antibodies against the action of foreign components. The manifestation of an allergic reaction usually occurs after the second penetration of the allergen substance.
At the same time, the process of saturating the blood with histamines, which play the role of inflammatory mediators, is also activated.
Causes
Tongue allergies can be caused by the following factors:
- weakened immunity for various reasons;
- heredity, genetic predisposition to a specific reaction to an allergen;
- excessively high psycho-emotional stress and nervous ailments;
- diseases that last a long time in a chronic form.
Irritation of the mucous membranes can occur under the influence of components penetrating the body:
Symptoms
A rash on the tongue of an adult is the main sign of an allergic reaction to irritating factors. In general, such manifestations are purely individual. Patients may complain of the following:
- rashes on the mucous membranes of varying shapes and intensity;
- decreased general health, lethargy, drowsiness;
- change in the color of the tongue;
- manifestation of dry mouth;
- pain, discomfort, burning sensation in the tongue area;
- itching of varying intensity on the tongue;
- inflammatory changes on the mucous membranes;
- active salivation, causing severe discomfort;
- the appearance of damage to the mucous membranes - various cracks, ulcers, erosions;
- persistent swelling in the mouth and tongue.
Manifestation of allergies in children
Allergies in a child’s tongue can have different manifestations, so parents should monitor the condition of this organ, its color shade, and structure. Geographic tongue syndrome, accompanied by the appearance of asymmetrical spots and stripes on the mucous membrane, requires serious attention.
In some cases, it indicates disorders in the baby’s body, diseases of an infectious, inflammatory or allergic nature.
If newborns and babies in their first year of life develop spots and rashes on the tongue, then in most cases we can talk about problems with breastfeeding.
Mom needs to pay more attention to her diet and remove allergenic foods from the menu. Teenagers abuse foods saturated with carcinogens - chips, crackers, soda. These products, as well as some medications, can cause changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue.
Subsequently, there is a high probability of changes in taste, pain and burning sensation while eating. In any case, if suspicious changes appear, you should rinse your mouth with warm water and consult a doctor.
Often redness of the tongue, pain on it or under it occur due to allergic stomatitis. It is especially common among children. The cause is caries, interaction with the material when filling teeth or brackets to straighten the bite. In adults, this reaction is observed upon contact with dentures. The main signs of this form of stomatitis are as follows:
- change in tongue color, redness of the surface;
- violation of the integrity of the cover - the formation of ulcers and cracks;
- the formation of plaque, the layer of which gradually increases;
- soreness of the tongue, both at rest and during eating;
- the appearance of edema on the mucous membrane.
Swelling on the tongue
A peculiarity of the body's reaction to irritating factors is that with allergies the tongue swells. In this case, the swelling can be located in one area of the organ or cover its entire surface. If it is expressed only slightly, then after a couple of hours or days it usually disappears.
However, in a severe form of allergy, swelling can be immediate, for example, after an insect bite, an anesthetic injection in dental practice, or when taking antibiotics. Then the situation is complicated by the swelling of the tongue, in which the swelling will be very strong.
Therefore, the likelihood of anaphylactic shock is quite high.
During anaphylactic shock provoked by an allergen, the following signs are observed:
- sudden increase in heart rate;
- the occurrence of painful shortness of breath, which is difficult to cope with;
- increase in general body temperature, deterioration in health;
- problems with the functioning of the respiratory system, complicated inhalation and exhalation;
- the appearance of swelling on the facial surface and in the larynx area;
- presyncope with the possibility of loss of consciousness;
- low blood pressure;
- excessive sweating, which causes serious discomfort;
- a feeling of numbness in the tongue, lips, and fingers;
- violation of the natural shade of the skin - its excessive pallor, and sometimes cyanosis;
- dizziness accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Important! If symptoms of anaphylactic shock occur, immediate medical attention and hospitalization are required.
Diagnostics
If a negative reaction to an allergen occurs, subsequent contact with the irritant must be avoided. Before starting therapy, diagnostic tests are carried out in order to accurately identify the allergen responsible for the occurrence of the disease.
Allergic problems must be differentiated from infectious stomatitis and autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus. If a patient suffers from autoimmune diseases, then not only the oral cavity is affected, but also other organs, and the symptoms of intoxication are observed throughout the body.
Exudative erythema multiforme, which can be confused with an allergic disease, occurs in addition to stomatitis and a rash in the upper extremities.
Sometimes the root cause is determined based on a conversation between the doctor and the patient. In more complex and ambiguous cases, tests to determine allergens are organized.
To differentiate allergies from diseases of a bacterial nature, saliva or mucous membrane components are submitted for biochemical testing.
Anamnesis and the presence of previously recorded allergy situations in the past are taken into account.
The necessary tests include:
- A smear, scraping from the surface of the area of the tongue or oral cavity where the inflammatory process is observed. It allows, through bacteriological examination, to determine the pathogen present.
- Histological examination of samples that are removed from abscesses that are previously subject to autopsy.
- A general blood test to determine the state of immune defense, the nature of inflammatory changes, and the presence of anemia.
- Biochemical analysis to assess the functioning of the kidneys and liver.
- Test for the presence of HIV or syphilis.
Features of treatment
Based on the data obtained, a course of therapy will be determined, aimed at suppressing allergic reactions and eliminating inflammatory manifestations.
Complex therapeutic effects include:
- Elimination of intoxication that the body experiences under the influence of allergens. For this, activated carbon or other drugs are prescribed - Enterosgel, Polysorb, Sorbex, Smecta.
- Treatment of the oral cavity and surface of the tongue with an antiseptic. For example, oil solutions with sea buckthorn and rose hips are used as a preparation.
- Rinse the mouth using herbal decoctions with a medicinal effect. Oak bark is suitable, and it is also possible to use sage and calendula. It is important to take into account possible restrictions on contraindications.
- Taking antihistamine medications, which have a positive effect by relieving swelling and inflammation. Doctors prescribe Claritin, Zyrtec, Tavegil, Chlorpyramin.
To exclude the manifestation of a bacterial infection, it is necessary to rinse your mouth with antibacterial solutions - a solution of chlorhexidine or miramistin.
If the pain is excessively high, doctors prescribe painkillers. All medications are taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
In this case, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of a specialist, both in terms of dosage parameters and regarding the duration of the course of therapeutic effects.
Causes of tongue allergies in adults and children Link to main publication
in social networks
Source: https://allergy-med.ru/allergiya-na-tele/allergiya-na-yazyke
Diagnostics
The initial diagnosis is made on the basis of an external examination of the tongue and oral cavity, but in order to accurately identify the cause of discomfort, a comprehensive examination is performed.
Diagnostic methods:
- biochemical, hormonal, general blood test;
- test for tumor markers, tissue biopsy;
- bacterial culture of an oral smear;
- PCR and ELISA to identify the type of pathogen;
- Ultrasound of the digestive system;
- X-ray, CT, MRI of the jaw.
Frequent manifestations of thrush in the mouth are a signal for a more thorough examination of the body
Which doctor should I go to to diagnose edema?
It is recommended to seek help from an otolaryngologist . This specialist will examine the patient’s tongue, paying attention not only to its size, but also to its color.
These indicators can tell you why your tongue is swollen.
If the patient's condition worsens, you should visit a therapist who will consult the patient and prescribe certain medications.
Diagnosis is carried out in the hospital. First, the doctor examines the patient and then begins to collect anamnesis.
To correctly establish the cause of edema, the following are prescribed:
Treatment
An integrated approach is used in the treatment of pathology. At home, you can use rinses with antiseptics or decoctions of medicinal herbs, and follow a diet. After identifying the cause, the doctor prescribes specific drug treatment.
What to do at home
The main thing that is used at home is rinsing. You need to rinse your mouth with plain water every time after eating, since the accumulation of food debris in the swollen tissue can lead to infection.
Additionally, rinses with medications and folk remedies are used. The following solutions have an antiseptic effect:
- Chlorhexidine;
- Furacilin;
- chamomile decoction;
- calendula decoction.
To reduce swelling, antihistamines can be used, for example, Loratadine, Suprastin. In case of severe pain, local painkillers are prescribed: Pyromecaine ointment, Bumecaine solution.
In case of infectious inflammation, a swollen tongue can be treated with Chlorhexidine
Emergency care for Quincke's edema
The first thing to do is to stop contact with the allergen that caused the swelling (cancel the administration of the drug, stop eating food, eliminate the insect).
If possible, you need to slow down the absorption of the allergen:
- if an insect bites, apply a tourniquet above this place;
- When administering the causative drug intramuscularly, apply a cold compress or ice.
The following actions are aimed at facilitating the victim's breathing. It is necessary to loosen tight clothing and provide access to fresh air.
In addition, be sure to call an ambulance and follow the instructions of the medical personnel.
Treatment depending on the cause
Further treatment depends on what caused the swelling.
| Cause | Treatment tactics |
| Acute trauma | It is recommended to apply ice or a cold compress immediately after the injury. Specific treatment is usually not required; it is enough to use rinses with antiseptics and follow a gentle diet. If necessary, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are used to reduce pain and inflammation. |
| Infectious lesion | Antibacterial, antiviral or antifungal drugs are used. |
| Chronic damage | Treatment consists of eliminating the influence of the damaging factor and sanitation of the oral cavity. |
| Angioedema | Drug treatment is used to eliminate swelling. Adrenaline is administered subcutaneously to normalize the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Glucocorticoids are also used - Dexamethasone, Prednisolone; these drugs have a strong anti-allergic and anti-edematous effect. Additionally, antihistamines (Diphenhydramine, Loratadine) and diuretics (Furosemide) can be used. |
| Diseases of internal organs | The underlying disease should be treated. For diseases of the stomach and intestines, it is necessary to follow a diet; antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and probiotics are often prescribed. For hypothyroidism, hormone replacement therapy is prescribed - Levothyroxine. For hypovitaminosis, B vitamins are prescribed. |
Manifestation of allergies in the tongue and its treatment
An allergic reaction can occur on any part of the body, the tongue is no exception. One of the main symptoms of allergies is swelling of the tongue, both completely and some part of it. Allergy to the tongue is a fairly common phenomenon, since allergens primarily affect the respiratory organs and digestive system, of which the tongue is an integral part.
Causes of tongue allergies
Allergies can be triggered by various factors. The most common causes of irritation are:
- pollen;
- Food;
- dust and mold spores;
- medications;
- cosmetics and perfumes, household chemicals;
- pet hair;
- sun and frost;
- insect bites.
However, a completely unexpected substance can also be an allergen, therefore, to identify it, it is necessary to carefully analyze all contacts with possible allergens a day before the reaction occurs.
Allergic reactions are especially common in patients:
- with weakened immunity;
- having a genetic predisposition;
- nervous disorders;
- chronic diseases.
Most often, an allergy on the tongue is allergic stomatitis. In children it appears due to caries while wearing braces.
Often the cause of allergic stomatitis in adults is a reaction to the materials from which dentures are made. The disease is diagnosed by characteristic changes in the tongue.
It becomes swollen, shiny and smooth, pustules and ulcers are possible, and in more severe forms - erosion.
Manifestation of an allergic reaction
Allergies in the tongue can be different and depending on the form of the disease, the symptomatic picture changes somewhat. However, the most commonly observed are:
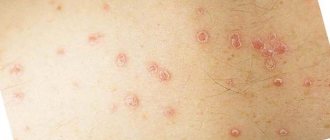
- various rashes. The first sign of an allergy is the appearance of a small pimple on the tongue, later the rashes become multiple;
- general weakness;
- change in tongue color. Most often, the tongue becomes burgundy-red, sometimes brown or white;
- itching, pain and burning;
- inflammatory process on the mucous membranes;
- increased salivation;
- ulcers, erosions and cracks;
- swelling of the tongue.
Eating and drinking become especially difficult during the acute period of the disease; in more complex forms, it is difficult and painful for a person to talk. An alarming symptom is an increase in temperature, especially in children.
Tongue allergies in children
Allergies are often diagnosed in children. Manifestations can be observed on the face and other parts of the body, but the area of particularly acute pain and discomfort remains the oral cavity. The causes of the disease may vary depending on the age of the child.
In infants, an allergic reaction occurs due to the mother eating foods that are an allergen for the child. Through milk, the irritant enters the baby's body. Therefore, if an infant has spots on the tongue, then the mother needs to reconsider her diet.
Older children may have a reaction to chips, crackers, sweet carbonated drinks, fast food, or a long course of antibiotics.
An allergy in a child’s tongue often manifests itself in the form of “geographic tongue.” The surface and walls of the organ become covered with spots, stripes, and its color changes. In general, parents should constantly monitor the condition of their children’s tongue, since its external changes may indicate not only allergic diseases, but also the presence of infections, inflammation and disorders of the digestive system.
Any alarming changes in a child’s oral cavity are a reason to consult a doctor.
Complications
If during an allergy symptoms such as fever and swelling of the mucous membranes appear, then urgent medical attention is required, since they may be signs of a serious disease such as Quincke's edema. This is the most dangerous form of allergy. In this case, the tongue swells, turns red and can block the airways.
Also, with Quincke's edema, the face swells, tearing, wheezing, suffocating cough, and intermittent breathing appear.
Urgent hospitalization will help get rid of a dangerous disease literally within a few hours, otherwise asphyxia may occur.
The main treatment for angioedema is to identify the allergen and isolate the patient from it, as well as taking antihistamines. In addition, any allergy, if left untreated, becomes chronic.
How to treat tongue allergies?
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause of the allergy. To do this, a number of diagnostic measures are carried out, including tests and laboratory tests. Only if the allergen is identified is effective treatment possible.
Complex treatment is aimed at suppressing the reaction and relieving inflammation. It includes:
- Eliminating the impact of the allergen on the body.
- Gastric lavage, if the allergy is caused by taking medications.
- Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity by rinsing with warm water or herbal decoction and treatment with sea buckthorn oil or rosehip oil.
- Taking absorbent drugs, such as activated carbon, Enterosgel, Smecta, to relieve intoxication.
- Taking antihistamines. Rapid-acting antihistamines include Claritin and Zodak. They will help relieve swelling and inflammation in case of tongue allergies. Drugs in this group block the production of histamine, but do not treat allergies; this requires complex therapy.
- Carrying out immunotherapy, which will reduce sensitivity to the irritant.
- Conducting sublingual therapy. It consists of treatment with medications based on the most common allergens. This way the body gradually gets used to the stimulus and stops reacting to it.
All procedures and medications must be prescribed by a doctor based on the diagnostic results.
Treatment with folk remedies
Folk remedies can help the body fight allergies. But their effect is quite small, so they must be used in combination with drug treatment, after consulting a doctor. In the case of herbal treatment, it is important to take into account the presence of individual intolerance, so as not to aggravate the disease.
Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs will help eliminate symptoms and inflammation:
- rinsing the mouth with chamomile decoction will help relieve inflammation;
- sage infusion has an antibacterial effect;
- the astringent properties of oak bark heal wounds on the mucous membranes;
- Oregano has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects;
- Rinsing with potato juice helps relieve swelling of the tongue.
You need to rinse your mouth with herbal infusions at least 5-6 times a day for a week.
You should not try to cleanse your tongue of plaque and rashes mechanically on your own, since in the process you can cause injury, which will only aggravate the development of the disease.
Prevention
To prevent new manifestations of an allergic reaction, it is necessary to avoid contact with the allergen. To do this you will have to endure some restrictions:
- For those who have a reaction to plant pollen, it is necessary to limit walks during flowering.
- If you are allergic to food, you should exclude it from your diet.
- If the disease is caused by medications, you must consult a doctor to change the drug.
- Regular and frequent wet cleaning of the premises and ventilation are also important.
- Cleaning carpets with special products.
- Avoid contact with animals.
- Cleaning air conditioner filters and using it with the air ionization function.
Following the rules will help you forget about allergies for a long time, and over time, completely get rid of them.
In fact, getting rid of tongue allergies is quite possible. To do this, you must strictly follow all doctor’s prescriptions and try to avoid contact with the allergen.
Tongue allergies are a particular problem for children. The disease prevents the child from communicating normally with peers, from proper speech development, and from receiving normal, nutritious nutrition.
This is also an unpleasant aesthetic defect, due to which a child may develop a complex.
Therefore, as a preventive measure, parents should constantly support a healthy lifestyle for the child, monitor what he eats and his daily routine.
It is important to pay attention to the condition of the tongue, its color. Normally, the tongue should be pink, and any changes in color may indicate problems with the gastrointestinal tract, infection, or allergies.
The cause of allergies can be various factors, the disease can also progress differently, but in any case, you should not self-medicate. Only a doctor can find out the cause of the disease and prescribe effective treatment. Proper therapy can not only eliminate symptoms and prevent complications, but also help get rid of allergies forever.
Source: https://allergiya03.com/simptomy/allergiya-na-yazyke.html
Additional symptoms
The reason to visit a doctor may be the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms that accompany a swollen tongue:
- Runny nose.
- Constant sneezing.
- Dermatological rashes.
- Pain or itching in the mouth.
- The appearance of a white coating.
- Darkening of the tongue.
- Problems with taste buds.
- Pain in the tongue and entire oral cavity.
- A sharp jump in body temperature, fever.
- Problems with the swallowing reflex.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Sensation of a foreign object in the mouth.
Why does the tongue swell due to allergies?
Due to an allergic reaction, the tongue may increase significantly in size. This is explained by the effect of any allergen on the body.
These particles enter the oral cavity with food or inhaled air and begin to irritate the surface of the tongue. Then, they penetrate into the deep tissues of the organ, which leads to irritation and provokes swelling.
Swelling due to allergies appears almost immediately. To eliminate non-dangerous symptoms , it is recommended to rinse your mouth thoroughly with boiled water, drink activated charcoal, and use herbal infusions as a rinse.
If these methods do not help, then you need to start identifying the causes of the swelling.
Macroglossia in newborns
Macroglossia in newborns It is advisable to identify the disease at an early stage, since in this case treatment will be easier, and the likelihood of the disease becoming chronic is much lower. Therefore, detection of macroglossia in newborns becomes a particularly important task.
Causes
In newborns, macroglossia often takes on a local character. Typically this disease occurs for the following reasons:
- adverse effects on the mother's body during pregnancy;
- for idiopathic diseases;
- due to the presence of cavities or cysts during the formation of the tongue;
- due to improper development.
Manifestations
If macroglossia occurs in a newborn, in addition to the symptoms already listed, you may notice:
- general deterioration in health;
- fever due to infection;
- blocking of the larynx with the tongue, causing the child to refuse food;
- drying of the surface of the tongue;
- tuberosity of the tongue;
- attacks of asphyxia.
Diagnostics
Ultrasound helps to identify macroglossia before the baby is born, which facilitates treatment and prevents possible complications. The ideal option would be to detect the disease in utero. To date, a number of standards have been developed for the size of the child’s organs at different stages of pregnancy. Ultrasound helps to identify abnormalities. The final diagnosis is usually made by the thirtieth week of pregnancy.
Newborn children with macroglossia should undergo consultations with several specialists: an ENT doctor, a geneticist, an infectious disease specialist, an oncologist and an endocrinologist. Only after this can treatment tactics be developed.
Manifestation of allergies in children
Allergies in a child’s tongue can have different manifestations, so parents should monitor the condition of this organ, its color shade, and structure. Geographic tongue syndrome, accompanied by the appearance of asymmetrical spots and stripes on the mucous membrane, requires serious attention. In some cases, it indicates disorders in the baby’s body, diseases of an infectious, inflammatory or allergic nature.
If newborns and babies in their first year of life develop spots and rashes on the tongue, then in most cases we can talk about problems with breastfeeding. Mom needs to pay more attention to her diet and remove allergenic foods from the menu. Teenagers abuse foods saturated with carcinogens - chips, crackers, soda. These products, as well as some medications, can cause changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue. Subsequently, there is a high probability of changes in taste, pain and burning sensation while eating. In any case, if suspicious changes appear, you should rinse your mouth with warm water and consult a doctor.
Swelling after puncture
Many people complain of a swollen tongue after getting a piercing. You can view photos of the piercing below. In this case, this phenomenon is not a malfunction of the body.
Piercing traumatizes the tongue, so increasing its size is a completely natural process. After the puncture, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations, rinse on time, keep the mouth clean and ensure that no purulent formations appear.
If the swelling does not disappear within a week or new inflammation appears, then it makes sense to go to the hospital. Normally, the swelling should go away within 5-7 days, and discomfort may appear for about two weeks from the moment of puncture.
What diseases cause the tongue to swell? Causes of a swollen tongue
The causes of macroglossia can be congenital or acquired. For newborns, large swelling and swelling is especially dangerous (the child loses weight, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, and there is a risk of suffocation).
Congenital causes:
- infectious or somatic diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy;
- alcoholism;
- radiation exposure;
- benign formations in the fetus;
- development of hypertrophy of muscles or blood vessels during embryonic development.
External symptoms of the disease are very characteristic. They are immediately noticeable if you compare the tongue of a healthy and a sick person in a photo.
Main symptoms:
Causes of tongue swelling on one or both sides
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to find out from me how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free
!
The following factors lead to tongue enlargement in adults and later children:
Open bite in children
Open bite – non-occlusion of the upper and lower jaws. Chronic pathology leads to impaired diction, changes in microflora, dry mouth, difficulties with chewing and swallowing food. Over time, this structure of the jaw bones leads to an enlargement of the tongue.
Timely diagnosis at an early age and qualified treatment provide a good chance of correcting the bite. The swollen tongue also returns to normal over time after therapy.
Allergic edema
Allergies are a common cause of a swollen tongue. Extensive swelling of the mucous membranes leads to obstruction of the airways (Quincke's edema).
In most cases, an allergic reaction occurs to foods or medications. Common irritants include nuts, citrus fruits, fruits, honey, mustard, artificial preservatives and colors.
If the allergen gets on the mucous membrane, the person immediately feels that it is swollen.
Other causes of swelling
The tongue may become swollen due to internal causes. Some malfunctions in the body's functioning lead to pathology in the oral cavity, as a result of which the tissues become swollen and swollen. An enlarged tongue will be a consequence of the course of a certain disease.
- If there is a hormonal imbalance and an excess of growth hormone, you may notice that the organ is swollen and enlarged.
- Hypertrophy of muscle tissue or the network of blood vessels also leads to an increase in soft tissue.
- Advanced purulent inflammation (abscess) in the mouth destroys and infects neighboring tissues. The inflammatory process leads to severe swelling. The patient notes that the organ is swollen and enlarged.
- Fungal infection causes a lot of unpleasant symptoms (plaque, fever, pain, rash, inflammation). Severe disease sometimes leads to extensive swelling. The mucous membrane becomes swollen and swells greatly.
- Serious diseases (tuberculosis or syphilis) affect the entire body over time. The immune system is significantly weakened, the microflora of the mouth changes. Even minor infections can cause the tongue to swell in size.
Swollen throat
If the tongue and throat are swollen at the same time, this condition is life-threatening for the patient. In the vast majority of cases, this condition occurs during anaphylactic shock (the most severe manifestation of allergies). Only an experienced doctor can remove a patient from a state of anaphylactic shock, therefore, at the first signs of swelling of the tongue and throat, you should immediately call an ambulance, especially if the patient has other dangerous symptoms - such as difficulty swallowing, bluish coloration of the lips and nails, swelling of the eyes and lips, small rashes, low blood pressure, nausea, shortness of breath or choking.
Most common reasons
There are quite a few reasons that lead to swelling of the tongue, in particular these may be:

- allergy;
- infections;
- mechanical trauma of the tongue;
- inflammation;
- anaphylactic shock;
- improper metabolism;
- trauma caused by a denture;
- thyroid diseases;
- piercing;
- pernicious anemia;
- pituitary disorders.
In this article we will consider the most popular type of edema - allergic .
First aid
If in your presence a person’s tongue is swollen to such an extent that it is difficult for him to breathe, then you need to take the following steps to provide first aid:
- Call an ambulance.
- Give the patient antihistamines.
- Elevate the patient's head slightly to prevent choking.
After the ambulance arrives, the doctor will take appropriate measures and prescribe treatment. Before this, you need to act quickly, clearly and harmoniously, since the patient can suffocate in a matter of minutes.
Thus, a swollen tongue can indicate dangerous diseases that cannot be ignored. The best solution is to consult a doctor, but if you are sure that this phenomenon is caused by minor reasons, then you can carry out treatment yourself.
What can cause swelling under the tongue?
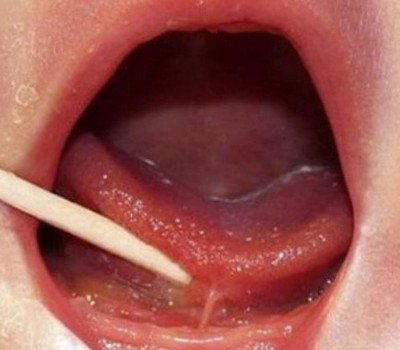
Swelling under the tongue (in the area shown in the photo on the right) rarely occurs due to allergic reactions.
Most often the reasons are:
- dental problem;
- angina;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes, tonsils;
- mechanical damage;
- entry of foreign bodies into the glands;
- past viral diseases;
- stones in the salivary ducts.
Treatment methods
After examining the mouth area, the doctor will prescribe a treatment that is right for you.
Without knowing the exact cause of the disease, self-medication is very dangerous.
In addition, allergic reactions can cause so-called Quincke's edema .
In this situation, the patient urgently needs to take medications that relieve swelling and call an ambulance, otherwise the consequences can be disastrous.
How to quickly relieve swelling?
To get rid of this unpleasant phenomenon, you need to take the following medications:
- Suprastin, Tavegil . Suitable if swelling is caused by allergies.
- Activated carbon . It will help cleanse the body of allergens, infections, and toxic substances.
It is recommended to rinse your mouth thoroughly with boiled water . It should be warm. If this does not help, prepare infusions of chamomile, yarrow, and plantain sage.
Rinse the mouth with prepared infusions of medicinal herbs one to three times a day.
Experts advise using potato juice to relieve swelling.
To do this, a small tuber is washed, peeled, and grated. Juice is squeezed out of the pulp, which is used as a mouth rinse.
This is one of the most effective remedies. The result appears within a few minutes .
What can I do to prevent my tongue from swelling in the future?
To avoid such a problem in the future, you need to follow some rules .
- There should be careful and regular oral hygiene .

Why is a swollen tongue dangerous?
This symptom may indicate serious illnesses or dangerous reactions, such as:
If action is not taken promptly, a swollen tongue can lead to suffocation. Air will not flow in the required quantity, oxygen starvation will occur.
A swollen tongue is often a symptom of angioedema . This phenomenon occurs due to the body's reaction to the allergen. With this disease, not only the tongue swells, but also the subcutaneous tissue and mucous membranes.
Swelling requires immediate treatment and specialist help. If this is not done, the patient begins to cough deeply and choke .
Thus, swelling of the tongue is a dangerous phenomenon. This may indicate serious illness. Self-medication can be very dangerous for the body .