Genital psoriasis is one of the types of the classic form of psoriasis, which can occur in both women and men. Characteristic psoriatic rashes can affect not only the genitals, but also nearby areas (buttocks, anal area, abdomen, groin area, etc.).
The disease causes suffering to the patient, however, due to the specific location of the symptoms, many patients are embarrassed to go to a medical institution for help, as a result of which treatment begins in the later stages of development, when psoriasis has already become severe.
Sometimes psoriasis on the genitals can occur atypically, not accompanied by characteristic symptoms, which is most often found in patients who are overweight. This course greatly complicates the timely diagnosis of psoriasis.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Some people mistakenly consider a rash in the perineal area to be infectious, suggesting that it can be sexually transmitted. This opinion is fundamentally incorrect, since the nature of the disease excludes direct infection through sexual contact. Psoriasis in the genital area is not transmitted this way.
The main reason for the development of negative symptoms is the genetic factor, when psoriasis is transmitted from parents to children. Moreover, if one of the parents is sick, then the probability of transmitting psoriasis to the child is 50%, and if both parents have psoriasis, the probability of transmission is 99%.
In addition, a common cause that leads to psoriatic symptoms in the genital area is a malfunction of the immune system, stressful and emotional situations, poor diet and disruption of the daily routine.
Treatment
Let us next consider the most effective treatment methods.
Medicines
The prescription of various medications depends on the severity of the disease. So, with a mild form, the basis of treatment is external symptomatic treatment. This includes ointments and creams.
Main groups of drugs for external use:
- antibacterial;
- antifungal;
- anti-inflammatory;
- moisturizing;
- healing;
- calming;
- decongestants.
Ointments with the addition of tar, sulfur or vitamin D, with glucocorticosteroids, and hormonal ones are often prescribed.
With a wide variety, they are never used simultaneously, but in alternation, since all remedies have different mechanisms of action, and therefore they are suitable for different periods of the disease. Thus, hormonal ointments are prescribed for severe symptoms for a short period of time, moisturizing ointments are prescribed for the speedy healing of cracks and moisturizing the skin, and healing ones are used with them.
Examples of topical medications: Cortisone, Salicylic ointment. These products are relatively cheap, but they are effective and quick to act.
In addition to local external treatment, oral medications are added if necessary. Main groups:
- immunosuppressants;
- antifungal;
- antibiotics;
- vitamins;
- sedatives;
- painkillers;
- retinoids;
- hormonal;
- normalizing liver function.
Examples of oral medications: Suprastin, Cetrin. Both drugs are accessible and inexpensive. They have a quick effect, effectively relieving unwanted symptoms. It is important to remember that Suprastin has contraindications and side effects, but doctors choose it to provide quick help.
Effective non-hormonal ointments in the treatment of psoriasis throughout the body; more about this in our material.
ethnoscience
Although drug treatment is the main one, experts themselves do not deny the benefits of some folk remedies. It is only important to note that in no case should they replace the main one, ignoring the doctor’s recommendations.
As an auxiliary treatment the following is used:
- Products based on golden mustache . This could be an alcohol tincture. But it is not applicable for acute forms, as it takes about 2 weeks to prepare. Use golden mustache juice for external use or ointments based on it. Has anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous effect.
- Propolis . Propolis-based tinctures have bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and other effects. Use a tincture with alcohol or water.
- Celandine . Tinctures are prepared with celandine and used both externally and internally. This remedy also has anti-inflammatory and bactericidal properties.
- Oats . Oat tinctures have a calming, antipruritic effect; they soften the skin, preventing the further spread of the disease.
- Herbal decoctions . Decoctions based on chamomile, celandine, nettle and other herbs are used in the form of medicinal baths to relieve symptoms.
More details about treatment of psoriasis using traditional methods at home can be found in our material.
Procedures
The treatment package includes physiotherapeutic procedures. They help reduce the manifestation of symptoms, prevent the formation of complications, and improve metabolic processes in the body. Physiotherapy is indicated not only during an exacerbation, but also during remission, to prevent the return of the disease.
For genital psoriasis, the following procedures are used:
- selective phototherapy;
- cryotherapy;
- electrophoresis;
- treatment with magnets;
- electrosleep;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- ultrasound treatment;
- X-ray therapy;
- Spa treatment.
The duration of therapy depends on the dynamics of treatment. The doctor evaluates it, and he also sets the boundaries of treatment.
Development of the disease among women
Among the fair sex, psoriasis on the labia and vulva is observed very often. Primary signs of the disease appear during hormonal age-related changes in the body.
An important factor in the occurrence of psoriasis is hormonal changes in the body, especially in pregnant women and during menopause. At this time, many women often confuse similar symptoms with genitourinary diseases that are sexually transmitted and begin to be treated on their own. Delaying contact with a medical institution leads to the fact that the patient’s condition sharply worsens and in the future it is no longer enough to simply correct psoriatic manifestations, but more serious medical intervention is required.
In women, typical locations for psoriatic rashes are the intergluteal region, armpits, chest and pubic area, vaginal mucous membranes, labia minora and labia majora (pictured). In addition, a psoriatic rash is noted in the groin, where pinkish papules appear, covered with silvery-whitish scales. The symptoms of the disease are very similar to vulvitis, so you should definitely seek advice from a medical institution.
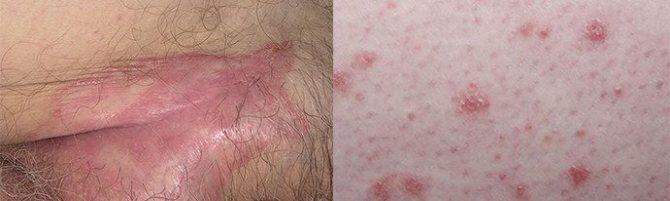
Symptoms
Genital psoriasis can cause constant discomfort due to increased sensitivity.
Inverse psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis in the groin and genital area. This results in smooth, dry, red patches on the skin. Inverse psoriasis is often more painful than other types of psoriasis, and the areas may be tender and itchy.
Psoriasis causes different symptoms in different parts of the pelvis and thighs, as shown below:
- Pabis: This refers to the area just above the genitals. The skin here is more sensitive, so doctors advise caution when applying procedures to the pubic area.
- Upper thighs: Psoriasis on the upper thighs consists of small, round, red patches and scales. With psoriasis, this area can become irritated, especially in people whose thighs stick together when they walk or run.
- Folds between the thigh and groin: Psoriasis appears as non-scale, red and white in the folds between the thigh and groin. The skin may also have cracks or fissures. People who are overweight or underweight may also develop an infection in the folds of their skin, similar to a yeast infection. It can occur on the genitals of both men and women.
- Vulva: Vulvar psoriasis is often smooth, unscaled, and red. Although this may cause itching, it is important not to scratch the area as this can cause infection and dryness. This infection can lead to thickening of the skin and additional itching. Genital psoriasis usually does not affect the mucous membranes and remains on the outer layer of the vaginal skin.
- Penis: Penis psoriasis takes the form of many small red spots on the shaft. The skin may appear scaly or smooth and shiny. This condition can affect all men, whether they are circumcised or not.
- Anus and surrounding area: Psoriasis on or near the anus is red, non-scaling, and may be itchy. Symptoms may be similar to those of yeast infections, itching hemorrhoids, and club worm infestations.
Genital psoriasis of the anus can also cause rectal bleeding, pain when passing stool, and dryness. The folds of the buttocks may have severe deposits and redness, although the skin is less sensitive and difficult to treat.
Development of the disease among men
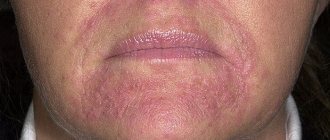
In men, psoriatic manifestations include a rash on the glans penis, pubis and groin. Psoriasis on the penis is characterized by hyperemic spots with clear boundaries, slightly rising above the surface of the skin. The surface of psoriatic spots is covered with white scales. Extremely rarely, psoriasis in the penis area can manifest itself on the inner surfaces of the foreskin, resembling the development of subacute balanoposthitis.
However, it should be remembered that psoriasis on the penis is almost always accompanied by other manifestations characteristic of all forms of psoriasis. Therefore, psoriatic manifestations in men can be observed not only on the head of the penis (pictured), but also on the surrounding tissues.
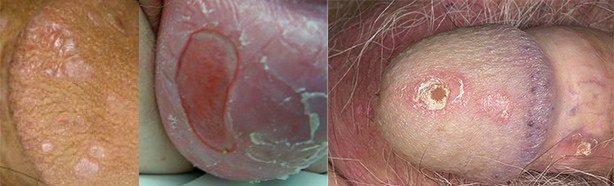
What is psoriasis on the genitals
The disease causes not only physical but also psychological discomfort. This problem is difficult to treat with medication, and, as a rule, has a recurrent nature. Psoriasis on the genitals is considered the most severe form of the disease.
The treatment process becomes more complicated if the rash spreads to the groin folds, because in these areas there is a suitable level of temperature and humidity for the further development of the pathological process.
The likelihood of successful treatment for psoriasis is much lower than the risk of complications. In the absence of therapeutic measures, the rashes affect the mucous membranes of the intimate area, which excludes the possibility of using physiotherapeutic procedures in this case.
Stages of the disease
Psoriasis of this form occurs in several stages:
- Exacerbation stage - characterized by the appearance of new plaques on the organs. In addition, the spread of psoriatic plaques over a large area is quite often observed;
- Stabilization - at this stage, the inflamed area does not change, and the symptoms of pathological changes remain;
- Stage of remission (regression) - at this stage there is a decrease in psoriatic symptoms and a decrease in the size of psoriatic plaques.
It is important to consider that exacerbation of any form of psoriasis is characterized by seasonality (spring and autumn).
Nutrition
Proper nutrition has a positive effect not only during treatment, enhancing the effect of medications, but also during remission, reducing the risk of negative symptoms.
Desirable products for consumption include:
- all types of cereals;
- fruits and vegetables;
- dairy products;
- boiled, baked or stewed dishes;
- honey.
Doctors include the following on the list of foods that should be excluded from the daily diet:
- eggs;
- oranges and other citrus fruits;
- beans and products with them;
- sweets;
- flour products;
- alcohol;
- coffee;
- carbonated sweet drinks.
Atypical development of symptoms
With the development of an atypical form of psoriatic manifestations, brightly shiny red spots with clearly defined boundaries may appear in the area of natural skin folds. As a result of increased humidity in the folds of these spots, white scales, characteristic of the typical development of the disease, are not observed.
Such symptoms are possible in both women and men. As a result of systematic friction, the skin is subject to irritation, severe burning and unbearable itching occurs. In addition, psoriatic spots often crack, abrasions and ulcerative growths appear on them. In especially severe cases, secondary bacterial infection is observed.
As a result, the atypical development of symptoms is difficult to diagnose. A number of laboratory tests are recommended, including histological examination of tissue from the affected area.
Features of the treatment of psoriasis in the groin
Below we will consider popular external remedies for improving the condition of the skin.
Elokom
The drug is a hormonal ointment. Apply to affected areas of the body. The active substance remains mometasone furoate. Treatment is based on a number of effects of the drug:
- Anti-inflammatory. The activity of the corresponding mediators decreases. Itching and redness are reduced.
- Decongestant. Glucocorticosteroids constrict blood vessels. This leads to a decrease in exudation into the interstitial space.
- Immunosuppressive. The autoimmune factor in the development of the disease is suppressed.
During treatment with Elokom, the rashes quickly regress. The patient's condition returns to normal, itching and discomfort disappear. The medicine can be used only as prescribed by a doctor.
Triderm
Combined product with triple action. It is especially effective if genital psoriasis is combined with bacterial or fungal infection of the epidermis. Active components of the drug:
- betamethasone – glucocorticosteroid;
- gentamicin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic;
- Clotrimazole is an antifungal agent.
Due to the action of these substances, it is possible to comprehensively influence the pathological process. Inflammatory activity decreases. Before using Triderm, consultation with a doctor is required.
Diagnostics
It should be noted that diagnostic methods are the same for men and women.
They provide:
- visual inspection of affected skin areas;
- collection of anamnestic information;

- collection of material for laboratory diagnostics;
- conducting a detailed blood examination.
In addition, a smear is often taken to identify a sexually transmitted infection, which is transmitted directly through sexual contact.
ethnoscience
In order to defeat inguinal psoriasis, you can additionally use folk recipes. They are of an auxiliary nature and are used to improve the effectiveness of basic therapy.

Popular products for improving skin condition:
- Baths with sea salt. They reduce the inflammatory process, cleanse the epidermis, and accelerate the rejection of keratinized skin.
- Birch tar. It is applied to the affected areas in the groin. A lot of recipes have been developed for creating ointments based on it. Good results are demonstrated by tar soap, which is used for intimate hygiene, but with caution.
- Solid oil. Base for medicinal ointments. The main thing is to choose the right recipe.
These and other types of alternative treatments for psoriasis can improve the results of drug therapy. Without it, genital and inguinal psoriasis is difficult to overcome. Particular attention needs to be paid to intimate hygiene, perhaps more than with other types of psoriasis.
Complications
Untreated genital psoriasis has dangerous complications. In addition to the fact that it tends to spread, affecting other parts of the body, it can negatively affect the condition of joints and internal organs.
The most dangerous complications of psoriasis are psoriatic erythroderma, arthritis, generalized pustular psoriasis, diabetes, hypothyroidism, muscular dystrophy, anemia, secondary infections, and heart damage.
How psoriasis occurs on the eyes, eyelids and how you can cure it in more detail in our material.
Medical characteristics of the disease
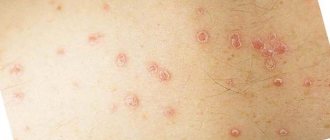
Recognizing psoriasis is very simple. The disease manifests itself first as single, and then as multiple inflamed, convex raised reddish-pink spots, the surface of which, moreover, is abundantly strewn with small flaky elements - silver-gray scales. The spread of rashes throughout the body is associated with a lot of unpleasant sensations - itching, burning, pain in the affected areas. Covered with psoriatic plaques - this is what the characteristic rash elements are called - areas of the epidermis are hyperemic, swollen, and dried out.
The uncertainty of the causes of psoriasis explains the absence of a single universal treatment regimen for this disease, which could help patients with the appropriate diagnosis to forget forever about the hated psoriatic plaques. Any therapeutic measures that a dermatologist selects for patients with psoriasis are exclusively symptomatic in nature and are designed to stop the inflammatory process on the skin, cope with unpleasant “local” sensations, prevent further spread of the rash throughout the body and prevent complications of the disease.
How to deal with the disease
Diagnosis of genital psoriasis involves the use of the following methods:
- Visual examination and assessment of the condition of the genital organs;
- Taking skin samples for further laboratory study;
- General clinical blood test;
- Examination of smears to exclude the presence of sexually transmitted viruses.
Genital psoriasis should be treated comprehensively. It is possible that the help of a gynecologist (urologist) may be needed to draw up a correct therapeutic regimen. The methods of combating the inflammatory process on the skin are identical in both women and men.
Thus, to treat mild (initial) forms of the disease, exclusively local medications (creams, gels, ointments) with antibacterial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory effects are used. Thus, formulations with vitamin D, tar, sulfur, as well as hormonal agents (those containing glucocorticosteroids) are popular in the fight against genital psoriasis.
In the case of a complicated course of genital psoriasis, systemic drugs are also added to external therapy. So, these can be immunosuppressants, retinoids, medications with vitamin D, and, if necessary, antibiotics and antifungal compounds (to exclude provoking factors).
Among the physiotherapeutic methods used to combat the manifestations of genital psoriasis, it is necessary to mention selective light therapy and the use of low-frequency laser beams.
Traditional medicinal and physical therapy for genital psoriasis is supplemented with medicinal baths with the addition of decoctions of medicinal plants (chamomile, nettle, string, yarrow). So, 2 tbsp. dry crushed raw materials are poured with a glass of boiling water, left for half an hour, then filtered and poured into warm water prepared for bathing. The procedure should last no more than 15-20 minutes, the manipulations are repeated daily for two weeks.
As you can see, the treatment of male and female genital psoriasis is complex and symptomatic. It will not be possible to get rid of this unpleasant disease once and for all, as in the case of any other form of psoriasis, but getting rid of unpleasant sensations and delaying the period of exacerbation as much as possible are quite feasible tasks.
Use of medications
For psoriasis of the genital organs, products intended for external use are actively used:
- Salicylic ointment;
- "Zinocap";
- Ointment containing vitamin D.
In the treatment of genital psoriasis, ointments made on the basis of corticosteroids or antibiotics are also used. When a bacterial infection occurs, the use of antimycotic agents is indicated.
There are also effective internal medications used for genital psoriasis:
- "Methotrexate";
- Cyclosporine."
In some situations, medications belonging to the group of antidepressants are used:
- "Pyrazidol";
- "Amitriptyline."
Antidepressants improve the condition of the nervous system and normalize sleep. Such drugs help get rid of irritability, which often occurs with psoriasis.