Category: ABC of health
Today we will understand what an allergy to insect bites looks like and how to treat it, we will look in detail on the website alter-zdrav.ru the causes and symptoms of an allergic reaction on the skin after an insect bite, and we will cover the issues of diagnosis and prevention of the disease.
A person is not always able to perceive the poison that he receives as a result of insect bites. It penetrates the bloodstream and promotes the production of antibodies, which lead to the development of allergic reactions.
The disease develops after contact with stinging insects such as bees, hornets, wasps, and bumblebees. Symptoms can also appear after being stung by mosquitoes or fleas, ticks or lice, or ants.
Allergies to insect bites can occur in both children and adults.

Insects that can cause allergies
Insects that live in the vicinity of a person, when bitten, can cause allergic reactions that differ from each other in severity.
- Spiders.
After their bite, a small area of swelling forms on the human body with a pronounced red dot in the center (it is shaped like a lump).
People with hypersensitivity to this poison may experience swelling at the site of the bite, pain, and fever within 15 minutes.
- Fleas.
These insects cause very painful bites, and are often accompanied by large hemorrhages on the skin. Flea bites are usually accompanied by very severe itching.
- Bedbugs.
The most common type of “home invaders” is bed bugs; they attack the human body at night. After their bite, you can observe the appearance of red dots that itch very much, but do not have swelling and do not hurt.
These parasites can cause Chagas disease. It is accompanied by feverish conditions and causes hypertrophy of the lymph nodes.
- Lice and their larvae - nits.
Symptoms of skin damage by lice are very similar to bedbug bites, but the location of the bite is the head (its scalp).
- Bees, wasps, bumblebees.
These insects cause painful bites. They are always accompanied by pain and swelling. Very often a sting remains in the wound; it must be removed immediately.
- Mosquitoes.
After their bite, a swelling remains, which is accompanied by severe itching, while intense hyperemia and a local increase in temperature are noted.
What causes the reaction?
Severe allergies can occur to the bites of a wide variety of insects. The most striking responses of the body are observed after attacks by bees and wasps. You can also get a response from the immune system from any of the blood-sucking insects. There may be many reasons, but the main one is the individual characteristics of the body and the strength of the immune system as the main defender.
The main reasons also include a hereditary predisposition to allergies. Additionally, poor ecology, nutritional disorders and some diseases, especially if they are in a chronic stage, contribute to the development of the problem.
For wasp venom
One of the most powerful is wasp allergy.
The reasons for the violent reaction of the body lie in the composition of the injected liquid (poison).
The main toxic component - the allergen contained in aspen venom, belongs to the category of substances - neurotoxins. All of them are capable of causing paralysis of various muscle groups, including the heart, difficulty breathing, and effects on the muscles.
The main reason for the negative response is the presence of deviations in health - malfunctions of the body (weakened immunity, the presence of complex/chronic diseases, genetic predisposition). It is important to pay attention and consult a doctor immediately if:
- pregnancy occurs (at all stages);
- age under 18 or over 60 years;
- have allergies (of various types);
- the medical history records chronic or complex diseases.
If there are no health problems or other special conditions, then in 90% of cases the reaction is expressed in mild swelling and a feeling of pain in the place where the sting was inserted. Redness may also appear. All symptoms disappear within 3-5 hours, sometimes within a day.
The reasons are also related to the fact that in addition to toxins, insect venom contains special protein compounds - serotonin and bradykinin, which are highly allergenic, as well as a large number of additional biologically active substances that can provoke a reaction:
- peptides;
- histamine;
- norepinephrine;
- some amino acids.
All these substances together can become the main mechanism that triggers allergies. Complicating the situation is the fact that the wasp venom enters the blood almost instantly, that is, the type of allergy in this case is immediate.
To the bee's venom
The reaction to bee stings and poison entering the blood is recorded in 3% of all calls and cases. Causes:
- the presence of special antibodies in the body (they can accumulate if contact with bees is prolonged - work in an apiary);
- intolerance to the components that make up bee venom.
Composition of bee venom:
- histamine;
- organic acids – formic, hydrochloric, orthophosphoric;
- acetylcholine;
- melitin (causes inflammation and destroys red blood cells);
- norepinephrine;
- peptides (protein components) - reduce blood clotting.
It also contains amino acids. The danger of penetration of the substance is that it causes severe swelling.
The bee sting often remains in the wound, which leads to an increased negative reaction from the body.
On bloodsucking
A negative reaction can also occur from blood-sucking insects. For example, these include:
- mosquitoes;
- fleas
Substances dangerous to a weakened body are contained in saliva, which penetrates the blood. The main reason is the content of special enzymes that interfere with the process of blood clotting.
General factors
In order for a reaction to substances received from insects to occur, there must be a coincidence of several factors that weaken the body and immunity. These include:
- hereditary factors;
- living in a large city;
- genetic predisposition;
- low environmental quality in the area of residence;
- the presence in food products included in the daily menu of a large number of carcinogens, dyes, and impurities.
You also need to take into account the presence of diseases or age characteristics - in children and the elderly, the body and its protective functions are weak, so the reactions are much brighter and longer lasting. Feature: each subsequent insect sting leads to increased allergies.
When to be especially careful
According to biologists and doctors, the most severe allergic reactions can be caused by the bites of bees, wasps, and ants; their poison is fast-acting, and the entire symptom complex can unfold in a quarter of an hour.
As part of a normal reaction to an insect bite, all signs and manifestations should go away within 24 hours, but if the situation only gets worse, then we are dealing with a classic allergy.
You need to be especially careful and seek medical help in situations with multiple bites.
This should also be done in case of bites on the face, neck, tongue, adding to the symptoms a serious deterioration in the general condition - difficulty breathing and swallowing, convulsions, general increase in body temperature, increased drowsiness, swelling of the throat.
IMPORTANT! The more developed the initial allergic reaction to insect venom, the more likely it is that the situation will recur if the incident occurs again.
How to distinguish a problem from normal consequences
It is important to distinguish and understand whether it is bites from various insects or an allergy. If there are no abnormalities in the human body, there are no peculiarities in genetics, then in 90% of cases the symptoms correspond to a normal reaction. After injecting poison or saliva into the bloodstream, a person feels:
- itching;
- the appearance of a compaction at the site of the lesion;
- pain (can be acute or not very strong - depends on the insect and the threshold of pain sensitivity).
Swelling and redness also appear. All these reactions are natural, as the body begins to fight the problem. After a few hours, the manifestations will pass, there will be no health consequences.
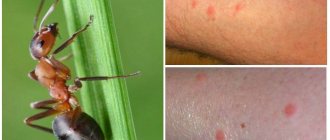
The photo shows a common reaction in children and adults to bites of blood-sucking and other insects:
bee wasp mosquito
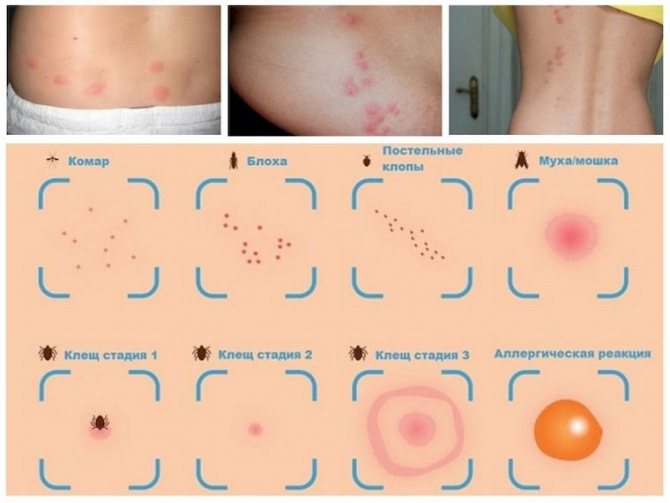
Causes of an allergic reaction to bites
This pathological process is based on a hereditary predisposition. In addition, there may be an increased sensitivity limit; the higher it is, the greater the likelihood of developing this pathology.
Insects have the ability to carry various types of carcinogenic and dye substances, and they can also cause the development of an allergic reaction.
Increased susceptibility is the main reason for the ongoing pathological process in adults. Children suffer from this much more often due to a genetic predisposition.
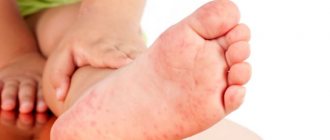
Symptoms of an allergy to insect bites
The clinical picture usually develops very quickly, but sometimes the first signs can be observed after several hours or days.
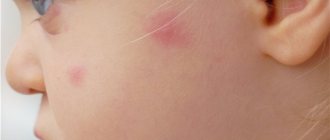
The very first signs of an allergy to insect bites are swelling and swelling in the area of the bite, which is accompanied by redness and itching. These manifestations, in favorable cases, disappear after a couple of days.
But sometimes a skin allergy after an insect bite is accompanied by large swelling. An adult is able to control his actions and understands that this area should not be combed. The child very often begins to scratch the wound, which leads to infection.
An allergy to insects is often accompanied by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, an increase in temperature, and the appearance of weakness.
If the patient experiences shortness of breath, difficulty swallowing, rapid heartbeat, convulsions, or a sharp drop in blood pressure, you should consult a doctor. These signs are characteristic of the development of Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock.
Insects can not only be a source of allergens, but also carry dangerous infections. For example, mosquitoes can carry the malaria pathogen.
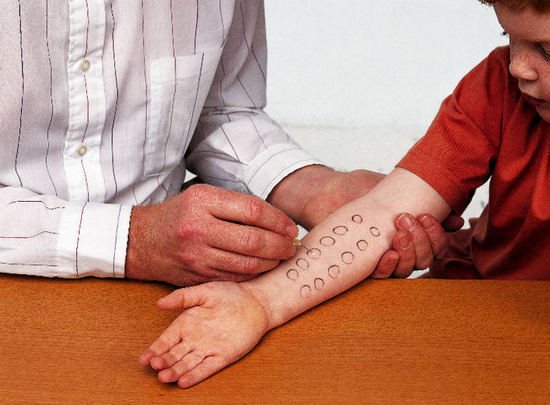
Main features
With a normal immune response, symptoms are temporary. After time, clinical manifestations in the form of itching and swelling disappear on their own. In the presence of predisposing factors, saliva or insect venom enters the bloodstream, a number of other symptoms appear:
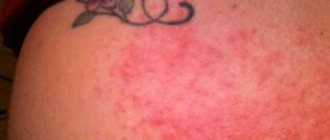
- local manifestations with intense swelling, erythema;
- swelling persists for more than 2-10 days;
- general malaise, muscle weakness;
- anaphylactic shock;
- toxicogenic manifestations (with simultaneous stinging);
- vascular collapse;
- shock reactions.
The latter complications can be fatal. Muscle or joint pain, fever, and deterioration in general condition without specific symptoms are often observed.
Important! Manifestations of anaphylaxis are expressed by a sharp drop in blood pressure, involuntary bowel movements or urination due to disruption of the innervation of the pelvic organs, respiratory arrest, and acute heart failure.
Organ manifestations are rare, developing as hemorrhagic vasculitis, dysfunction of the myocardium, tissue of the renal structures, and brain. Complications associated with damage to the nervous system, which occurs after the bite of hornets, bees, and ticks, are considered dangerous. Upon contact with stinging bodies, signs of rhinoconjunctivitis, bronchospasm, and intestinal disorders appear.
Diagnosis of allergies to insect bites, ICD 10
A visual examination is sometimes not enough to determine the diagnosis. For a more accurate diagnosis, you need to contact a medical laboratory for analysis using skin allergy tests . This allows a diagnosis to be made.
, you can test your blood for immunoglobulin E. This method, although not as reliable, is safe.
In children, diseases are much easier to identify, due to the fact that their body reacts more violently to foreign antibodies.
ICD-10 code for allergies to insect bites - set to either W57 or T78.4
W57 Bite or stinging by a non-venomous insect or other non-venomous arthropod T78.4 Allergy, unspecified
Kinds
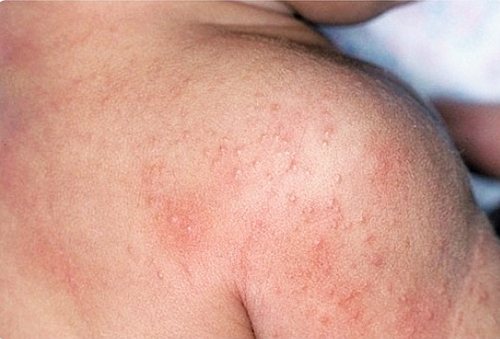
Allergic dermatitis (ICD-10 code - L23) is divided into several types:
- allergic contact dermatitis - occurs as a response to external irritants. The history of the disease begins with skin contact with an irritant (household, food, epidermal). May be caused by an insect bite.
- toxic-allergic dermatitis - manifests itself in the form of toxicoderma. Irritation appears in response to the penetration of an allergen into the respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, when administered intravenously or subcutaneously. Toxic-allergic dermatitis manifests itself in the form of a rash that occupies a large area of the skin. Unlike other dermatitis, allergic toxicderma manifests itself quickly.
- Atopic allergic dermatitis is the result of a combination of a respiratory disease and chronic skin lesions in the form of eczema. It can appear in adults and children, as well as in pregnant women. Unlike classic eczema, the history of allergic atopic dermatitis stops immediately after eliminating the allergen. This disease is characterized by less extensive symptoms in the form of a rash and irritation on the skin. Often it does not even require treatment with ointments and creams.
- fixed erythema - having a local form. Manifests itself in the form of local inflammation on the skin. Allergic dermatitis on the hands, face, neck, and other parts of the body occurs as a response to sulfonamide drugs. In essence, this type of dermatitis is a type of toxicerma.
All types of dermatitis can have different stages. There are acute, subacute and chronic forms. Treatment for each stage of the disease is expected to be different from the others. Mostly ointments and creams are used. It is certainly much easier to cure the acute form.
First aid and treatment of allergies to insect bites
Treatment should be comprehensive, but sometimes it is carried out with one drug. The most important thing in the treatment of this pathological manifestation is the correct provision of assistance to the victim.
- First you need to remove the sting from the wound, since it is this part that releases the largest amount of poison.
- After that, apply something cooling (a bag filled with ice or a container with cold water) to the bite area and apply a sterile bandage.
- Inject Prednisolone 75 mg intramuscularly. This remedy reduces the level of histamine in the bloodstream.
- The use of antihistamines (Tavegil, Suprastin) is also recommended. But their dose must be agreed with your doctor.
If the disease is not pronounced, then before going outdoors you can use external antihistamine medications (Fenistil gel).
In severe cases it is recommended:
- Epinephrine is given to block allergies.
- Phys. the solution is used to normalize blood pressure.
- Calcium chloride makes the immune system immune to poison.
- Theophylline helps with heavy breathing and shortness of breath.
the method of specific immunotherapy (ASIT) is currently widely used .
It consists of a long course of subcutaneous injection of poison in very small doses, which in turn ensures the development of stable immunity. The effectiveness of treatment with this method is 97%.
Also worth a look on this topic:
Insect bite - swelling and redness, what to do and how to treat, first aid.
Encephalitis tick bite: symptoms, treatment, consequences.

Prevention
To avoid the development of an allergic process, you must follow simple rules and norms of behavior in nature.
- Avoid contact with insect nests; they are most often found in earthen embankments, logs, tree crevices, and bushes.
- When walking outside the city or in forests, it is advisable to wear long sleeves and avoid wearing bright, multi-colored clothing.
- You should not approach the apiary, and you should not walk through flowering fields and gardens, especially with loose hair, where plant-pollinating insects can easily become entangled, and the floral smell of perfume can provoke them into aggressive actions.
- When a flying insect approaches, try to avoid panic and fussy quick actions; it is better to simply retreat slowly.
- At picnics, it is better not to consume sweets - aromatic fruits, ice cream; after eating, quickly remove everything to prevent further spread of odors. You should wash your hands and face after drinking sweet juice or fruit.
- At home, place insect screens on windows and doors, and spray a small amount of insect repellent aerosol before going to bed.
- Garbage waste bins must be treated with a special aerosol.
- It is advisable to remove climbing plants from an apartment or house; they can attract blood-sucking parasites.