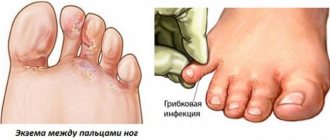
Currently, various skin diseases are not uncommon. Ostiofolliculitis can occur in the presence of an environment favorable to it and bring a lot of discomfort. If you recognize the disease at an early stage and take measures to eliminate it, you can achieve good results.
- 2 Types of ostiofolliculitis
- 3 Why does the disease occur?
3.1 Causes of ostiofolliculitis - video
- 6.1 Medicines for the treatment of ostiofolliculitis - photo gallery
6.4.1 Folk remedies for the treatment of ostiofolliculitis - photo gallery
What is the disease
Ostiofolliculitis, or staphylococcal impetigo, is a pathology of infectious origin. In this case, the inflammatory process occurs in the hair follicle. This disease is caused by the proliferation of staphylococci. When the infection spreads through the follicle, a papule is formed. It may not be unique. Quite often multiple ulcers form. The disease can occur at any age, regardless of gender.
Ostiofolliculitis is a consequence of the proliferation of bacteria in the hair follicle
What is ostiofolliculitis and is it dangerous?
Ostiofolliculitis refers to pyoderma diseases, which are distinguished by a purulent-inflammatory course. This dermatological disease can develop on the skin of any person, regardless of his age group, but most often the pathology is diagnosed in children under 12 years of age. Such medical morbidity statistics are justified by the fact that at this age the child does not yet have such a strong immune system capable of resisting the strain of Staphylococcus aureus.
The adult category of patients with ostiofolliculitis encounters this disease after receiving mechanical injuries to the skin as a result of shaving, bites of blood-sucking insects, scratching, and various types of irritation. This dermatological disease is not classified as a particularly dangerous pathology, but ostiofolliculitis still carries a certain degree of threat. The danger lies in the fact that after Staphylococcus aureus penetrates the skin, the infection first affects the hair follicle, the surface layer of the epithelium, nearby sebaceous glands, and then, along with the blood flow, spreads throughout the body. As a result, the risk of developing secondary foci of inflammation in any part of the body is not excluded.
Types of ostiofolliculitis
The disease can occur in different parts of the human body. The classification of the disease depends on the location:
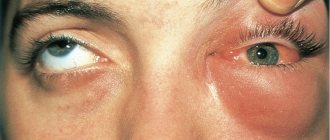
- Cervicofacial ostiofolliculitis. It often causes unpleasant painful sensations and is more severe than in other places. Affects the neck and face area.
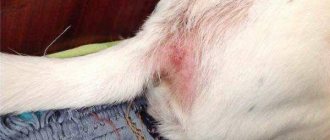
- Pathology covering the area of the upper and lower extremities. The formation appears on the thighs, calves, arms, and buttocks.
- Ostiofolliculitis of the scalp. Occurs extremely rarely.
In men, the disease often occurs in the beard and mustache area.
Diagnosis of ostiofolliculitis
For an experienced specialist in the field of dermatology, the diagnostic process is not difficult. Diagnostics includes a whole range of measures.
First of all, the clinician needs to:
- get acquainted with the medical history - to identify the most characteristic predisposing factor for the patient with a pathological basis;
- collect and analyze life history - to establish the influence of one or another physiological source;
- assess the condition and palpate the problem area of the skin or scalp;
- examine papular neoplasms using a dermatoscope;
- interviewing the patient in detail regarding the first time of onset and severity of symptoms will make it possible to draw up a complete symptomatic picture.
Laboratory research:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- biochemistry of blood and urine;
- tests to determine glucose concentration;
- immunological tests;
- blood culture for sterility;
- bacterial culture of skin scrapings;
- microscopic examination of the fluid filling the papules.
Instrumental procedures are of an auxiliary nature and are limited to the following studies:
- radiography;
- ultrasonography;
- CT;
- MRI.
Ostiofolliculitis should be differentiated from the following pathologies:
- deep folliculitis;
- prickly heat;
- pseudofurunculosis.
Why does the disease occur?
Ostiofolliculitis develops when Staphylococcus aureus or white staphylococcus enters a healthy follicle. This microorganism can be present on the skin of almost every person. It does not cause harm when the immune system is functioning normally. But when for some reason the body’s defenses weaken, this kind of inflammatory process can develop.
The main factors provoking the occurrence of ostiofolliculitis are:
- flu;
- ARVI;
- diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract;
- diabetes;
- hypothermia;
- prolonged stress;
- tuberculosis;
- renal failure.
Additional reasons for the development of pathology are:
- increased sweating;
- excessive activity of the sebaceous glands;
- skin injury;
- lack of hygiene;
- violation of the acid-base balance of the skin.
Infection in ostiofolliculitis is concentrated in the upper part of the hair follicle
Causes of ostiofolliculitis - video
Causes
Normally, the human body contains saprophytic microflora, which includes the causative agents of osteofolliculitis white and Staphylococcus aureus.
The cause of ostiofolliculitis is a general decrease in immune status caused by hypothermia, frequent colds or serious illnesses:
- tuberculosis;
- measles;
- meningitis;
- hepatitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- renal failure;
- bronchitis;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity, other endocrine disorders;
- pneumonia.
People with dermatological diseases - contact and atopic dermatitis, eczema, seborrhea - are susceptible to the disease.
Staphylococcal impetigo develops with poor body hygiene, increased sweating, increased acid balance of the skin, constant overheating, and increased secretion of the sebaceous glands.
The trigger point can be minor skin injuries - shaving cuts, scratches, abrasions, softening of the skin due to a chronic runny nose or conjunctivitis.
Harmful production factors also have an impact - contact with fuels and lubricants, varnishes, and chemicals.
Ostiofolliculitis can develop as a side reaction during therapy with hormonal external agents or a complication after scabies (Bockhart's ostiofolliculitis).
The cause of staphylococcal impetigo is sometimes pseudofolliculitis - ingrowth of hair into the skin.
Impaired hair growth leads to suppuration of the root part of the follicle and the spread of infection.
In rare cases, the causative agents of the disease are dermatophytes, candida, herpes and molluscum contagiosum viruses, demodex mites, treponema pallidum, gonococci, and pseudomonas.
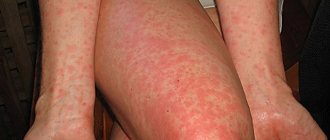
Symptoms of the disease
The first signs of ostiofolliculitis are the appearance of slight redness at the site of the lesion. Any touch causes pain. Next, a formation appears around the hair, which is filled with pus. The pustule does not change its size, and after a few days it dries out, forming a crust. Without the necessary treatment, the infection can penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin. When the crust falls off, a slight scar remains in its place.
Mature ostiofolliculitis is expressed by redness and a purulent vesicle around the hair
In quite rare cases, the formation can be large, the size of a pea. As a rule, pustules appear in groups and are localized in different places. Favorable soil for the development of infection is the areas of the body that are most often exposed to contamination.
Symptoms
The signs of the disease are very similar to most dermatological diseases, the development of which is associated with an infectious nature of origin.
Therefore, during the initial examination, a dermatologist can only suspect the presence of this disease and prescribe the patient a bacterial culture from the skin at the site of the lesion. In general, the symptoms of ostiofolliculitis are as follows.
Skin redness
At the entrance to the mouth of the sebaceous gland duct, slight swelling and inflammation appears. Without special equipment, it is difficult to determine that this particular element of internal secretion is located under the skin and only local irritation is visible on the skin. After this, within 3-4 hours, a cone-shaped pustule is formed, which forms around the hair, and its root system is shrouded in the purulent contents of the capsule of the inflammatory neoplasm.
Transition of pustules to chronic form
Without drug treatment within 3-5 days, the acute phase of the inflammatory process ends and the surface of the abscess dries out, becoming covered with a thin layer of crust. In this case, purulent inflammation does not stop completely, but only goes into the deeper layers of the epidermal tissue. So Staphylococcus aureus tries to penetrate deep into the body in order to expand its range of existence. Periodically, as soon as a person’s immune system becomes more weakened, a dried pimple becomes active again and breaks out.
The appearance of multiple rashes
As the total amount of bacterial microflora increases in its population, skin rashes become more numerous. At the same time, the density of pustule formation also becomes more saturated, but the ulcers never merge into a single inflammatory abscess. Each such formation has its own pustule, which is localized directly around the hair follicle. The largest accumulation of acne with staphylococcal filling is located in the area of the neck, lower leg, inner thigh, temporal region of the head, and upper extremities.
Staphylococcal impetigo
This symptom of ostiofolliculitis is also called Bockhart's spot. With this symptomatology, purulent pustules increase to the size of a pea; in the center of each such neoplasm, vellus hair begins to grow, which was not there in principle before the skin was infected with Staphylococcus aureus. In some cases, this is how a complication of scabies manifests itself.
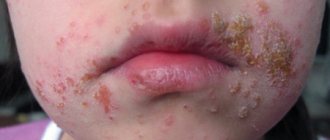
Sycosis
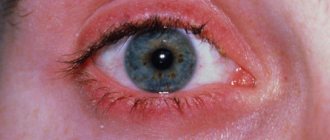
This symptom differs from all others in that the inflamed pustules described above appear exclusively on the surface of the skin of the face, in the circumference of the hair of the eyebrows, and the place where the mustache and beard grow. If these symptoms are present, there is a high risk that the disease will spread over the entire surface of the face and neck.
All the described signs of the disease enable an experienced dermatologist to put forward a theory about the possible infection of the epithelial surface of the patient’s skin with Staphylococcus aureus. If, as a result of a laboratory study of smears taken from the patient’s skin, the presence of the specified microflora is confirmed, then the patient is given a final diagnosis - osteofolliculitis.
Diagnostic tests
At the first suspicion of ostiofolliculitis, you should consult a dermatologist. As a rule, diagnosing this pathology is not difficult. First of all, the doctor examines the rash. They are very easy to identify using optical equipment. Pustules are cone-shaped and always filled with pus. They never merge into one formation, which is their distinctive feature.
However, it is important to differentiate this disease from others: prickly heat, deep folliculitis and other skin pathologies. For this purpose, bacterial culture of pus from pustules is carried out, and the pH in the area of localization of formations is determined. In addition, a blood test is prescribed to rule out dangerous generalized infections.
Prevention and prognosis
Preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of ostiofolliculitis include the following recommendations:
- complete cessation of bad habits;
- regular implementation of hygiene measures;
- proper and balanced nutrition;
- prevention of frequent skin injury;
- wearing protective equipment when working with chemicals and toxic substances, gases and dust;
- strengthening the immune system;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of any pathologies that can lead to the development of ostiofolliculitis;
- Regularly undergoing a complete preventive examination at a medical institution.
The prognosis for osteofolliculitis is mostly favorable - complete recovery can be achieved. Complications develop extremely rarely.
If you think you have ostiofolliculitis
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: a dermatologist, a pediatrician, a therapist.
Source
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Treatment of ostiofolliculitis
Drug treatment of osteofolliculitis involves the use of local antibacterial agents. Ulcers should be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, brilliant green and fucorcin at least 2 times a day, using a cotton swab and applying one of the selected products pointwise. The course of treatment is at least 5 days. Antiseptic ointments are often used: tetracycline and erythromycin, which should also be applied at least 2 times a day to the lesions for a week.
Medicines for the treatment of osteofolliculitis - photo gallery
To treat rashes you need a very weak solution of potassium permanganate
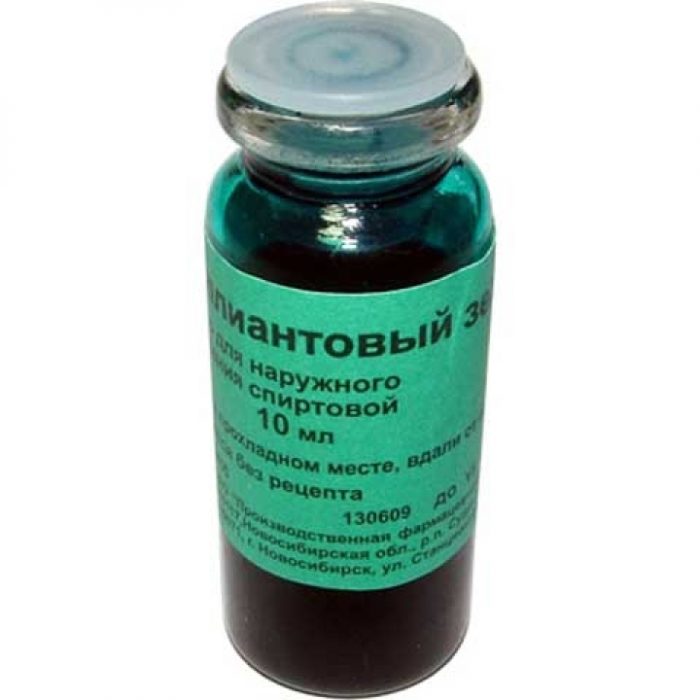

Zelenka is best used on areas with thicker skin.

Fukortsin is harmful to staphylococci
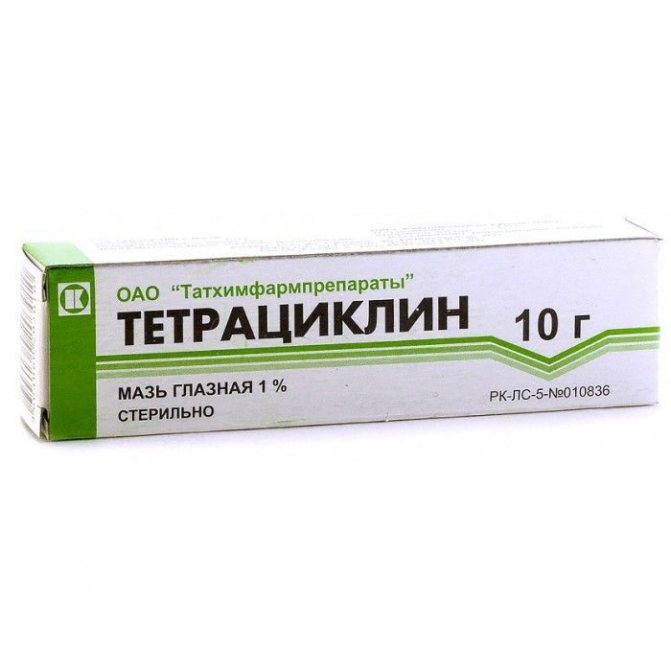

Tetracycline ointment belongs to the group of antibiotics
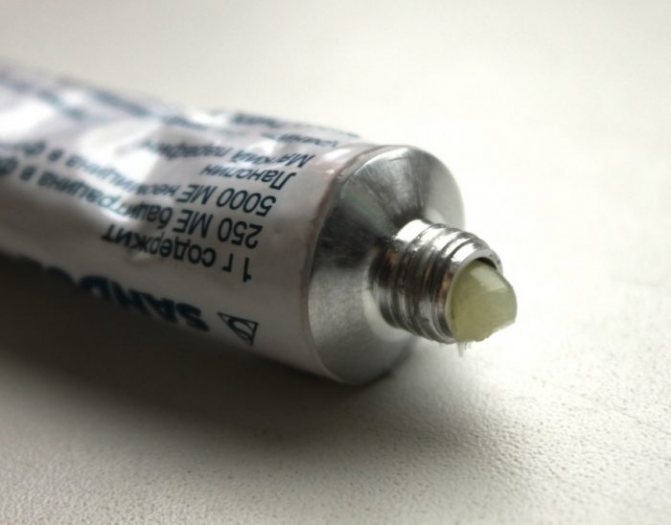

Erythromycin ointment quickly relieves ulcers
Physiotherapeutic treatments
If ostiofolliculitis steadily progresses and new lesions appear, then physiotherapeutic treatment is additionally indicated. Ultraviolet and laser effects on blood are most often used. This kills bacteria, speeds up metabolism and improves the body's immune response. A slight irradiation of the blood occurs, which restarts the oxidation processes in the cells, renewing them.
Nutrition for ostiofolliculitis
There is no special diet for this disease. However, in order to reduce sebum secretion, you need to exclude from the diet for the duration of treatment everything that clogs the intestines, namely: fatty and fried foods, fast food. It is recommended to consume more dairy products, fresh vegetables and fruits, which have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the immune system.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treatment boil down to treating lesions with herbal decoctions and propolis, which has an antibacterial effect. Sage decoction has a powerful antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. You will need 2 tbsp. l. dry herbs, which need to be poured with 500 ml of boiling water and boiled for 10 minutes. Then close the lid tightly and let stand for another 30 minutes. After this, strain the liquid and treat the affected areas with it using a cotton pad 3-4 times a day for a week.
Propolis tincture effectively fights infectious foci. It is better to purchase it at a pharmacy and lubricate each pustule with a cotton swab 2 times a day for 5 days. A water tincture will be less effective.
Cranberry juice also has excellent antiseptic properties. To prepare it, you will need 1 cup of fresh berries, which must be thoroughly rinsed under water and crushed with a mortar. Then squeeze out the juice using gauze. The finished product should be stored in the refrigerator for no longer than 24 hours. Wipe the affected areas 2 times a day for 3 days.
Folk remedies for the treatment of ostiofolliculitis - photo gallery

Propolis is a natural antibiotic

Sage has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect

Cranberry juice has antiseptic properties
Traditional medicine recipes
Decoctions with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects shorten the treatment period and help survive its unpleasant manifestations.

Alternatively, you can prepare:
- A decoction of sage, calendula and string, which are mixed in equal proportions. 1 tbsp. l. The mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water and left for 40 minutes. Taken orally to boost immunity and reduce inflammation.
- Chamomile decoction, which is used to treat inflamed, purulent areas of the hair. The decoction relieves irritation and itching, promotes rapid healing of inflamed skin areas.
- A decoction of St. John's wort, rose hips and calendula. 2 tbsp. l. pour ½ liter of herbal mixture. water, boil and let it brew. Used as lotions, applied to areas of inflammation.
- Celandine juice, which is applied pointwise to ulcers. The product heals inflamed areas well and has an antibacterial effect.
For your information! If ostiofolliculitis has a progressive course, then antibacterial therapy is needed, and traditional medicine is used as an auxiliary one.
Treatment prognosis
With a timely approach to treatment, the prognosis is good. If you prevent damage to the deep parts of the hair follicle, then recovery comes fairly quickly. It is especially important to carry out therapy carefully in young children. It is necessary to maintain hygiene and prevent pustules from being picked off, otherwise the course of ostiofolliculitis can be aggravated.
If the infection is generalized, treatment will be delayed. Multiple rashes are accompanied by painful sensations, which significantly worsens the quality of life. In addition, ulcers spoil the appearance, so treatment must be approached with full responsibility.
Causes of ostiofolliculitis
The main factor in the occurrence of the disease is staphylococcus, which is present in the microflora of a healthy person and lives on the skin. Penetration into the sebaceous glands and infection can be facilitated by a decrease in immunity due to frequent hypothermia or due to diseases such as tuberculosis, hepatitis or acute respiratory diseases, in which bronchitis or pyelonephritis is observed. The barrier function of the skin in diabetes mellitus also decreases.
Also, the development of ostiofolliculitis can be facilitated by heavy sweating, lack of hygiene, or increased activity of the sebaceous glands.
In case of insect bites, injuries, or itchy skin, small wounds can serve as an entry point for infectious pathogens with subsequent infection of other areas of the skin.
Some other professions involve frequent contact and work with harmful substances, such as kerosene, gasoline or acid. Such factors have a harmful effect on the skin and the entire body as a whole.
If the compress is applied incorrectly, you can also create conditions for the proliferation of bacteria and viruses.
Classification or clinical forms of ostiofolliculitis
The infectious process in osteofolliculitis is caused by various pathogens. Most often this is a staphylococcal infection caused by different strains of bacteria, therefore the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Staphylococcal folliculitis is a classic variant of the disease with all its manifestations. The pathology is clearly visible after shaving the hair on the head and face. More often diagnosed in men.
- Ostiofolliculitis decalvans has a chronic course and develops in the temporal and parietal region. Atrophic changes in the skin and persistent baldness occur.
- Hoffmann's undermining folliculitis is rare, so its etiology is poorly understood. It lasts for a long time and destroys the growth zone of the hair shaft, which leads to complete and irreversible baldness.
- Candida form - manifests itself under the influence of fungi of the genus Candida and is characterized by large pustular rashes in the area of the hair follicle. More often seen in people with limited mobility.
- Herpetic form - occurs under the influence of the herpes virus and is noticeable in the form of a finely blistered rash in the hair follicle, which turns into scabs. It usually develops in men on the chin and nasolabial area.
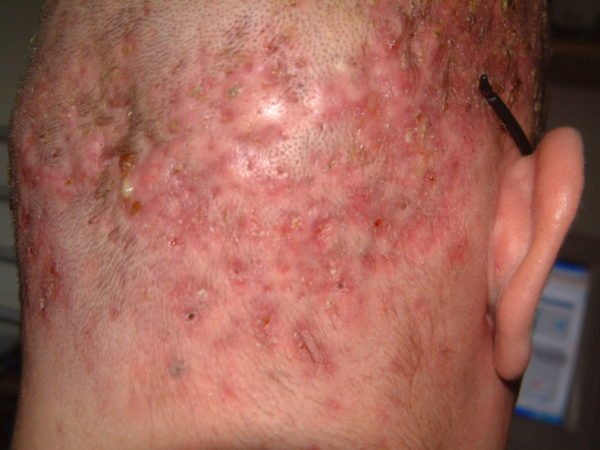
The disease sometimes manifests itself as a secondary infection during the development of syphilis (papular rash) or when Demodex folliculorum parasites penetrate the skin. Papules and pustules of a purulent nature form on the affected areas.
Important! Typically, ostiofolliculitis is mild and does not have serious consequences. But in advanced cases, in the absence of treatment and neglect of personal hygiene, complications arise in the form of serious skin pathologies.
Drug therapy
If the disease is mild, it goes away on its own and does not require drug therapy. In the acute form, antibacterial treatment is practiced. Most often it is local in nature: the use of tetracycline, syntomycin, heliomycin ointments. For severe purulent inflammations, ichthyol ointment helps well.
Pustules are treated with solutions:
- potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate);
- methylene blue;
- brilliant green (greenery);
- salicylic alcohol.

The solution must contain the active substance in a concentration of no more than 1-2%.
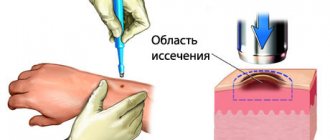
Important! In case of numerous purulent rashes, the pustules are opened and treated with hydrogen peroxide. The cavities forming are drained (pus is removed) and treated with disinfectants to prevent re-infection.
In case of relapse of pathology (recurrent infection), broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. First, a bacterial culture is done and not only the pathogen is determined, but also its resistance to antibiotics. The drug is selected taking into account the sensitivity of staphylococci to a specific drug.
Immunostimulating therapy is important, since the proliferation of bacterial colonies occurs against the background of weakened immunity. In parallel, courses of ultraviolet irradiation - ultraviolet blood purification and laser therapy are conducted, which can enhance the effect of conservative treatment.
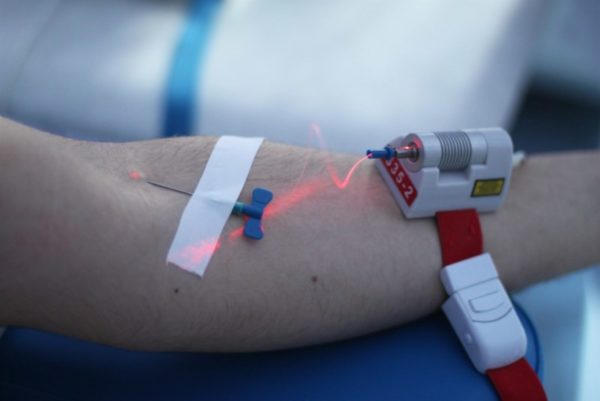
For your information! During treatment, it is unacceptable to take any water procedures. During this period, the sauna, pool or shower is canceled.
Complications of folliculitis
Treatment can have serious consequences if the pathology develops severely. The risk group includes newborns whose immune system is imperfect and whose skin is very delicate and easily affected by staphylococcal infection.
In adults, the infection can penetrate into deep tissues, causing serious complications in the form of abscesses, carbuncles or boils. Such consequences lead to an increase in temperature, general intoxication of the body, and local painful manifestations. After healing, scars most often remain on the skin.
Differential diagnosis
The nature of the rash is clearly visible according to dermatoscopy (examination under magnification). The presence of an abscess at the base of the follicle and redness of the skin around it indicate an infection on the epidermis.
To clarify the diagnosis, you need to find out:
- skin acidity level;
- blood sterility;
- nature of infection (bacteria culture is carried out).
Differential diagnosis involves comparison with similar pathologies: prickly heat, deep folliculitis, pseudotuberculosis, streptococcal impetigo.