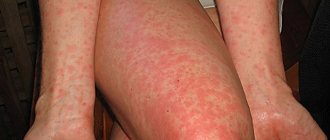
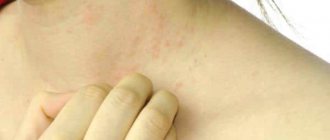
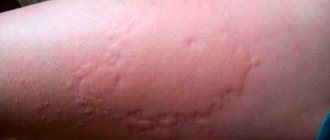
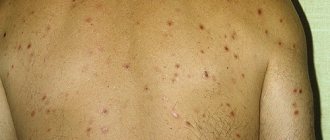
It is difficult for any doctor to tell what to do if ear pain or swelling occurs without specifying the diagnosis. Such pain is just a manifestation of symptoms, but the otorhinolaryngologist needs to find out the cause of their occurrence, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Possible causes may be viruses, bacteria or fungi, manifestations of allergic reactions, various types of eczema, previous injuries, penetration of foreign bodies into the auricle and much more.
Ear diseases that may be accompanied by swelling:
- Otitis.
- Allergies, Quincke's edema.
- Perichondritis.
- Othematoma.
- Barotraumatic edema.
- Erysipelas.
The occurrence of an ear tumor and inflammation can be caused by external otitis (in rare cases - middle, internal). Symptoms of perichondritis include pain and swelling on the outside of the ear. With hematomas, the top of the auricle in front becomes blue-cherry in color.
Erysipelas manifests itself in the form of peeling, wounds appear that are covered with a thin crust. As a result of barotrauma, in addition to swelling, peeling and redness may also appear.
The main task for the doctor is to determine the type of inflammation in the patient and the tumor that has arisen, to find the difference between bacterial causes and allergic or mechanical ones, and only then to make a diagnosis and choose an effective treatment method.
Puncture
Ear piercing is the most common cause of hearing damage. Moreover, after a puncture, an inflammatory process in the tissues can develop in both a child and an adult.
The causes of the pathological condition are as follows:
- Use of non-sterile instruments by a specialist. Due to this, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the wound.
- Insufficient treatment of the puncture site at home. If your earlobe is swollen, this may indicate that the unhealed wound has become infected. The master always warns that at home it is necessary to treat it with antiseptic agents until complete healing. If a child’s earlobes are swollen after a piercing, most likely he touched the wounds with dirty hands.
- Local lipid metabolism disorder. Against the background of this condition, the sebaceous glands become blocked around the wound, which triggers the development of the inflammatory process in them.
If your earlobe is swollen after a puncture, you should contact the specialist who performed the procedure. He will examine the affected area and recommend anti-inflammatory ointments.
In order to speed up the healing process and prevent the re-development of the pathological process, it is necessary to treat the earlobe with medical alcohol and hydrogen peroxide as often as possible. If swelling and pain do not disappear with home treatment, you need to consult a surgeon. The doctor will open the soft tissues and clear them of purulent accumulations.
Swollen earlobe: photos, causes, treatment
The earlobe is a projection of the internal organs, as Chinese doctors say, and the appearance of a tumor reflects the condition of the corresponding part of the body. Therefore, when starting ear treatment, it is recommended to pay attention to the body as a whole.
The direct cause of the tumor is both disease and external factors. Seeing a doctor is the best thing to do if your earlobe is swollen. Prescribing effective treatment is possible only based on the results of the examination and analysis of negative effects.
Possible diseases
The diagnosis of the origin of swelling is influenced by:
- location: internal or external side is affected;
- color: white, bluish or red;
- shape: are there any pronounced thickenings or is the swelling widespread;
- traces of damage: punctures, scratches, bites, bruises.
Analysis of this information will allow us to localize the range of possible causes and establish the main one.
Furunculosis
Purulent inflammation of a fungal nature, which occurs in an acute form. It appears as a tumor and a conical elevation with a white central core. Characterized by pain, redness, increased temperature during exacerbation.
A boil is a secondary disease that occurs against the background of internal infectious inflammation, such as otitis. Immunity weakened by resistance to the disease acts as a trigger for the activation of pathogenic microflora.
An independent autopsy is unacceptable; this can lead to the spread of infection, and in some cases, blood poisoning. Within a week, the abscess comes out on its own, the pain and swelling disappear. If during this period there is a deterioration in the condition or new tumors appear, then you need to consult a doctor to examine the body and treat the underlying disease.
Atheroma
This is the name of a benign formation in the form of a dense ball with a pronounced center on the earlobe, which is filled with dead cells and fat mass. Occurs in places where fat and sebaceous glands accumulate due to blockage of skin pores. Metabolic disorders in the body increase the likelihood of their occurrence.
Atheroma can quickly increase in size, become inflamed and degenerate into a dangerous type of cyst. In the normal state, the color matches the shade of the skin tissue, and in the acute stage it changes to brown. This formation requires surgical removal in the clinic; independent attempts to get rid of the growth are undesirable.
Herpes
An infectious disease provoked by viruses that are constantly in the human body at rest and are activated at the time of weakening of the immune system or other negative influences.
It manifests itself in the form of a tumor, blistering rash, ulcers, which over time form flaky scabs. As herpes spreads, it causes pain and discomfort. Affection of the earlobe by this disease indicates damage to the facial nerve and requires immediate treatment.
Dermatitis
A skin disease that manifests itself in the ears as an inflammatory process that, if left untreated, can spread from the outer surface of the shell and lobe to the inner parts.
Manifestations of dermatitis include redness, swelling, itching, peeling, and weeping areas. These symptoms occur due to metabolic disorders, allergic reactions, chronic diseases and decreased immunity. A situation where the earlobe is swollen from an earring may indicate the first signs of contact dermatitis and indicate the need for a medical examination.
Dermatitis requires an integrated approach to treatment, since its external manifestations often function as a symptom of an internal imbalance in the body. In most cases, eliminating the allergen irritant is enough to solve the problem.
Swollen earlobe photo
The most common cases of direct infection occur when ears are pierced for jewelry. Signs of a negative process include pain, redness and swelling of the impact site, purulent discharge and elevated temperature.
If the earlobe is swollen after a piercing and accompanying symptoms appear, then you need to urgently seek medical help, remove the jewelry and disinfect the wound. There are also other reasons:
- Lipoma. A benign subcutaneous formation that looks like an atheroma, but without a central point. The popular name for lipoma is wen. It is small in size, not subject to inflammation, and is able to move through the subcutaneous space. The reason for the appearance of these formations is not fully understood. In practical medicine, it is customary to monitor the formation without surgical intervention.
- Allergy. Interaction with allergens and the subsequent reaction of the body often leads to swelling and redness of the earlobes. Contact form is often observed due to poor quality metal on jewelry. Eliminating contact with irritants and anti-allergy therapy will restore the skin and relieve swelling.
- A bite of an insect. Leads to local toxicity of the bite site, which is accompanied by swelling and redness of the lobe. If the situation is not complicated by infection or an allergic reaction, then the inflammation quickly passes.
- Hematoma. The situation when the earlobe is swollen and blue is the result of a domestic injury or severe bruise. The danger is that with local injury there is a risk of internal inflammation and hematomas. Diagnosis of damage will eliminate possible consequences.
- Decorations. Injury to the earlobe as a result of accidentally pulling on an earring causes swelling and redness. This situation can be complicated by infection of the tear site, so it is necessary to thoroughly disinfect the painful area and temporarily remove the jewelry.
Thus, if the earlobe is swollen and painful, then the right action would be to consult a doctor to determine the true cause, since in most cases this phenomenon accompanies or can cause an internal disease that requires complex treatment.
Source: https://nakozhe.com/opuhla-mochka-uha.html
Insect bites
Mosquitoes, gadflies, midges, etc. often choose sensitive parts of the body. After their bites, the soft tissues swell and turn red. If your earlobe hurts and is swollen, you should always pay attention to the accompanying symptoms. As a rule, after a bite a person feels itching and burning of the skin in the affected area.
In most cases, swelling and other unpleasant conditions go away on their own in a short period of time. To make you feel better, you can use medications. Currently, a large number of products are produced on the pharmaceutical market to alleviate symptoms after insect bites. The most popular are: “Moskitol”, “Fenistil”, “Nezulin”, “Psilo-balm”.
Furuncle
Often, abscesses cause changes in the size of the hearing organ and the occurrence of uncomfortable and painful sensations. If the earlobe is swollen in a child or adult, it is necessary to rule out the presence of a boil, since this pathological process most often requires medical intervention.
The following symptoms are alarming:
Even if the clinical manifestations have disappeared, a small amount of pathological content still remains within the soft tissue. In this regard, it is necessary to continue to use topical medications.
The treatment regimen includes the following points:
- Treat the affected area with chlorhexidine, boric alcohol or zinc ointment. These products have an antiseptic effect.
- Use of antibacterial ointments. Examples of products: “Gentaxan”, “Levomekol”.
- Treating the earlobe with anti-inflammatory drugs. Most often, doctors recommend using the following products: “Diklak”, “Desitin”, “Sinaflan”.
- Treatment of the lesion with nystatin-based ointments. This is necessary in order to prevent the addition of other pathogenic flora.
If conservative treatment methods do not lead to a positive result, surgical intervention is indicated. During the operation, the doctor opens the soft tissues, cleans them of pus, performs sanitation and sutures the lobe.

Complications of otitis externa
Complications from external otitis are rare. However, in some cases it is possible.
We recommend reading: Eye color in newborns: table showing what eye color the child will have
Abscesses
- These are usually painful, pus-filled growths that appear in and around the sore ear after an infection. They usually go away on their own, but in some cases your doctor may need to drain the pus out of them.
Stenosis (narrowing) of the ear canal -
a growth of thick, dry skin in the ear canal that can form due to chronic otitis externa. This can impair your hearing as the skin growth causes your ear canal to become narrower. In rare cases, this can lead to deafness. Ear canal stenosis is treated with ear drops.
Inflammation or perforation of the eardrum.
Any infection can spread to your eardrum. In some cases, the infection can cause pus to build up in the inner ear, causing your eardrum to perforate (rupture). This is called perforation of the eardrum. Symptoms:
- temporary hearing loss;
- pain or discomfort in the ear;
- discharge of mucus from the ear;
- ringing or buzzing in the ear (“tinnitus”).
In many cases, a damaged eardrum heals without treatment in about 2 months. If there are no signs of improvement during this time, you may need surgery.
Hypodermatitis
is a bacterial skin infection that can develop after otitis externa. This happens when bacteria that normally lives on the surface of your skin and doesn't cause any harm penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin through damaged areas, such as as a result of otitis externa.
The areas of skin affected by hypodermitis become red, sore, inflamed and sensitive to touch. Other symptoms include:
- nausea;
- shiver;
- chills;
- general feeling of malaise.
Most cases of hypodermatitis can be cured with a 7-day course of antibiotics. If hypodermatitis is found in a person who already has a serious illness or is extremely susceptible to infection, they may be admitted to the hospital as a precaution.
Malignant otitis externa
is a severe but very rare complication of otitis externa, in which the infection spreads to the bone surrounding the ear canal.
Malignant otitis externa is more common in adults than in children. Adults who are immunocompromised (those who have a weakened immune system) are especially susceptible to this disease. This includes people who have undergone chemotherapy or have a chronic illness such as diabetes, HIV or AIDS.
If you have malignant otitis media, you may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
- severe ear pain and headaches;
- exposed bone visible through the ear canal;
- paralysis of the facial nerve, when the facial skin sags on the side of the affected ear.
Without treatment, malignant otitis externa can be fatal. However, it can be effectively treated with antibiotics and surgery.
Treatment of external otitis with a doctor
Otitis externa may go away on its own, but without treatment it may take several weeks. Your doctor may prescribe medicated ear drops to speed up the healing process. There are four main types of ear drops used to treat otitis externa:
- antibiotics - can cure the bacterial infection that causes otitis media;
- corticosteroids - help relieve inflammation;
- antifungal - can cure fungal infection;
- acidic - acid can help kill bacteria.
In some cases, you may be prescribed treatment that is a combination of the above, such as antibiotics and corticosteroids.
If instilled incorrectly, the effectiveness of ear drops may be reduced. It's better if someone helps you drip into your ears. You (or your assistant) will need to do the following:
- Gently remove any discharge, earwax, or debris from your outer ear and ear canal using a cotton swab (do not use Q-tips).
- Warm the ear drops by holding the bottle in your hands for a couple of minutes—the cold drops may make you feel dizzy.
- Lie on your side with your affected ear facing up and place the drops directly into the outer ear, then gently pull and rub the outer ear so that the drops flow deeper into the ear and the air trapped under the drops comes out.
- Lie in this position for 3-5 minutes to ensure that the drops do not flow back out of the ear canal.
- Do not cover the ear canal to allow it to dry.
Other treatments your doctor may suggest include:
- prescription painkillers such as codeine for severe cases;
- antibiotic tablets or capsules to treat a severe infection - flucloxacillin is usually the best option in this case;
- treating underlying skin conditions that may worsen otitis externa, such as seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, or eczema;
- If a boil forms inside your ear, your doctor may decide to prick it with a sterile needle and drain the pus; Do not under any circumstances try to do this yourself.
To make treatment more effective, your doctor may remove earwax. This can be done in several ways, for example:
- douching or rinsing, when water is injected into the ear canal with a syringe without a needle to wash out the wax present in the ear;
- microsuction, when using a small suction device, the outer ear and ear canal are freed from wax, secretions and dirt particles;
- dry rubbing, in which wax is gently removed from the ear canal.
Sometimes, for better effect of the medicine, it is injected into the ear on a small gauze swab - turunda. Turunda ensures deep penetration of the therapeutic agent. It should be changed every 2-3 days.
Dermatitis
With this skin disease, the shell and area behind the ears may also swell. If you have dermatitis, you should immediately consult a doctor. If the earlobe is swollen during the course of the disease, only a specialist can tell you what to do about it. This is due to the fact that the development of the disease can be triggered by the activity of viruses, fungi and bacteria. Depending on the infection, the treatment regimen may also be different.
Symptoms of dermatitis include the following conditions:
To identify the pathogen, the doctor collects cells from the affected area by scraping. Based on the results of laboratory diagnostics, the dermatologist draws up an antibacterial, antifungal or antiviral treatment regimen.

Symptoms of External Otitis in children:
Clinical symptoms have a specific picture. The onset of external otitis is characterized by a feeling of severe itching in the ear canal, turning into pain. With a limited form, the boil increases, which leads to compression of the nerve receptors and the rapid onset of pain. Pain in otitis externa can radiate (spread) to the temporal and occipital zones, upper and lower jaws, and cover half the head on the side of the affected ear. The pain intensifies when chewing, which leads to the child refusing to eat. The pain becomes intense at night, so with otitis externa, children often have restless sleep. The resulting boil in some cases can completely block the lumen of the ear canal, resulting in hearing loss.
When the boil opens, pus flows out of the ear, resulting in a sharp decrease in pain. Sometimes, when it is opened, nearby hair follicles in the ear canal are seeded, which leads to the formation and development of multiple boils, which can result in furunculosis, which has a severe course and does not respond well to therapy. Furunculosis with external otitis leads to complete closure of the auditory lumen and increased clinical symptoms. Otitis externa is accompanied by swelling in the area behind the ear, as well as protrusion of the auricle.
The disease is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms: inflammation of the ear canal, filling the lumen with a large amount of serous infiltrate.
In the acute form, patients experience severe pain, so during examination, even the slightest touch causes discomfort and pain to the patient. Pain also manifests itself upon palpation in the area where the tragus is located.
With an uncomplicated form of otitis externa, children may experience slight hearing loss. This sign allows you to differentiate external otitis media from otitis media.
In some cases, with external otitis, keratinization and peeling of the epithelium occurs.
If external otitis appears against the background of immunodeficiency, then the patient experiences a general toxic reaction of the body, increased body temperature, weakness and chills. With such symptoms, patients are urgently hospitalized.
Diffuse external otitis is manifested by a feeling of fullness, itching and increased body temperature, followed by a pain syndrome that covers half of the head and intensifies with chewing. Patients experience significant swelling of the walls of the ear canal, which narrows the lumen in the ear and leads to hearing loss. With diffuse external otitis, the discharge from the ear is insignificant, at first it is serous in nature, and as the disease develops it becomes purulent. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner and in case of a severe course of the disease, the inflammatory process can spread to the auricle and soft tissues of the parotid area. The acute period of the diffuse form of acute otitis lasts from 14 to 21 days. Diffuse external otitis can become chronic with a protracted course, which is accompanied by the formation of scars.
Allergic reaction
As soon as swelling of the earlobes appears (after a piercing or changing jewelry), you must immediately prevent contact of soft tissues with jewelry. Many women suffer from contact allergies, which forces them to constantly wear gold, platinum or silver.
An undesirable reaction to jewelry manifests itself as follows:
The main treatment measure is changing jewelry to earrings made of precious metals. If the discomfort does not subside, it is recommended to take an antihistamine for 5 days, for example, Zyrtec, Zodak, Claritin.

What other reasons can cause itching?
If the outside of your ears itch, the causes and treatment may vary. Among them also:
- weather conditions (rain, wind, sun rays, severe frost);
- hormonal disorders in women;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- food allergy (one-time or repeated, due to the consumption of undesirable foods);
- diathesis;
- increased blood sugar (diabetes mellitus);
- excessive consumption of sugar;
- foreign object entering the ear.
Atheroma
This term refers to a pathological process accompanied by the growth of a cyst against the background of clogging of the sebaceous ducts. Atheroma is very easy to confuse with a boil. The main difference is that the growth of the cyst is not accompanied by painful sensations. Upon palpation, you can feel a small capsule. For a long time it does not cause any discomfort to a person.
If the atheroma becomes inflamed, the clinical manifestations are as follows: swelling, redness, pain.
Unlike a boil, a cyst cannot open on its own. It is possible to get rid of it only through surgery. The doctor opens the soft tissue, cuts out the atheroma, sanitizes the cavity of the pathology and sutures the lobe.

Acne
Pimples occur when excess oil and dead cells begin to accumulate in the pores. Pathological contents are a favorable environment for the life of bacteria. In this regard, acne often becomes inflamed, which is accompanied by swelling and pain.
The patient may be confused: what to do if the earlobes are swollen due to acne? First of all, pay special attention to these places when carrying out hygiene procedures. In addition, the earlobes should be regularly treated with salicylic acid. In severe cases, you should consult a therapist. He will prescribe retinoids and antibiotics.
Injuries
The earlobe may swell as a result of a violation of the integrity of the skin. Bruises, cuts and abrasions often cause swelling and pain.
In most cases, unpleasant symptoms disappear on their own within a few days. If the wound is deep, it is necessary to regularly treat it with medications or go to the hospital to avoid the development of an inflammatory process. As it heals, you need to treat the earlobe with antimicrobial and antibacterial drugs.
Bruises should also not be ignored. If the resulting hematoma is not treated, it can lead to disruption of normal blood circulation and deformation of the lobe and cartilage tissue. The natural result is a change in the appearance of the auricle. If, after receiving an injury, the lobe is not only swollen, but also becomes too red or, on the contrary, white, rush to the clinic.
How can you alleviate your condition?
If your ears itch on the outside and are burning, you can try to reduce the discomfort. First of all, you need to calm down. The more nervous you are, the more likely it is that your skin will itch more. You can also try one of the following methods:
- Purchase an itching reliever from your local pharmacy.
- Take an antihistamine.
- If you have boric alcohol in your medicine cabinet, drop a few drops into your ear.
- Follow a strict diet or exclude allergenic foods (chocolate, citrus fruits, honey).
- Take a course of medications whose action is aimed at restoring intestinal microflora.
If we talk about preventing itchy ears, the main thing is not to forget to devote time to basic hygiene and not allow water to remain in the ears. Consider strengthening your immune system.
You should not use other people's headphones to avoid infection.
What do people say
Elderly people often say that today everyone runs to the doctor for any reason or without reason. In their opinion, such a sign as the outside of the ear itching can be easily explained by folk beliefs. The most common explanation is that your ears itch when someone remembers you. And the more they burn and itch, the “stronger” the well-wisher’s word is.
There is an opinion that the left ear itches if gossip is spread about you, and the right ear, on the contrary, if you are praised.
Itchy ears can also indicate an imminent change in the weather.
If you yourself could not determine why the outside of your ear itches, a general practitioner or otolaryngologist after an examination will be able to do this for you. The main thing is not to delay going to the clinic.