Rhinosinusitis is an inflammatory process that develops on the mucous membrane of the nose and its paranasal sinuses. The disease has several varieties, depending on its etiology. One of them is allergic rhinosinusitis.
The development of the allergic form of rhinosinusitis occurs due to the entry of various allergens into the nasal cavity, which the immune system begins to perceive as foreign agents. This disease has recently become increasingly widespread, like other types of allergies. If rhinosinusitis is not treated promptly, serious complications can develop. It is important to recognize the symptoms of the disease in time and consult a specialist.
Causes and allergens
The causes of this disease are:
- Nasal polyps.
- Pathologies of the development of nasal septums.
- Damage to the nasal mucosa.
- Presence of caries.
- Weakened immunity.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Acute viral infections leading to complications such as rhinosinusitis.
- Hypothermia.
- Flu, which caused complications.
- Inhalation of chemicals.
Most often, the appearance of characteristic symptoms is provoked by the following allergens:
- smell of flowers;
- perfume aroma;
- the smell of honey;
- animal hair;
- household allergens (detergents, powders, bleach, window cleaners, etc.);
- the smell of chemical compounds in shampoos, soaps, etc.;
- the smell of citrus fruits;
- dust;
- inhalation of pollen from plants and flowers.
Rhinosinusopathy
Rhinosinusopathy of the brain (or rhinosinusitis) is an unpleasant and debilitating disease. The disease has a chronic course, and the paranasal sinuses are affected by the pathological process. The patient experiences discomfort and suffers from chronic runny nose, which in most cases has an allergic etiology. Rhinosinusitis – allergic rhinitis.
What is rhinosinusopathy of the brain?
Chronic runny nose of allergic origin is called rhinosinusopathy. The disease is based on inflammation of the paranasal appendages and mucous membrane of the nasal cavity for several reasons.
The sinuses of the nose are lined with several layers of epithelium, in particular glandular and ciliated. Inflammatory processes lead to various disorders of the endothelium: allergens provoke an immune response, as a result of which nasal breathing is disrupted and mucus accumulates.
Due to constant itching, the number of sneezes increases. Rhinosinusopathy indicates the occurrence of rhinitis (runny nose) due to decreased functioning of the sinus system.
Due to the close proximity of the nasal appendages, the disease is considered a brain pathology, however, this is a strong misconception.
There are several forms of chronic sinusitis:
- Polypous rhinosinusopathy – characterized by the formation of polyps. Polyps are capsule-like growths of mucous membranes. They increase in size and block the path of air at the entrance, and also complicate its circulation in the accessory cavities.
- Allergic rhinosinusopathy is a runny nose that develops as a result of contact with the mucous layers of a provoking allergen.
- Vasomotor rhinosinusopathy is a peculiar reaction of nerve endings to external irritating factors: hormonal imbalance, heat, cold and viral infection.
There is also a purulent and catarrhal form of the disease. The disease also differs in severity, cause of the pathological phenomenon and clinical picture.
The purulent and catarrhal forms have only an acute course and differ in the severity of symptoms.
To identify the disease, it is necessary to establish the cause and conduct a diagnosis.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of rhinosinusitis is the effect of allergens on the mucous layers of the paranasal appendages. The causes of allergies are:
- bad habits, especially nicotine addiction;
- alcohol abuse;
- hereditary predisposition;
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- professional factor: flour for bakers, chemicals for laboratory workers, etc.;
- ecological situation;
- Diagnosed allergy to animal dander or plant pollen.
Forms
Pathology has the following forms:
- Seasonal. It develops during certain seasons of the year (most often spring and summer). It occurs in an acute form, causing quite severe symptoms. It is caused by flowering plants and dust.
- Acute is characterized by severe intoxication of the sick person’s body. This form of the disease lasts for five to ten days. In this case, the person loses his ability to work, his temperature rises and pus flows from his nose. If not treated promptly, acute rhinosinusitis can cause serious complications.
- Chronic allergic rhinosinusitis occurs in humans over several months. However, it is less pronounced when comparing it with acute rhinosinusitis. Its symptoms are not as strong, and the sick person tolerates it more easily. The danger of this form of the disease is that it can return due to exposure to allergens.
- Infectious-allergic occurs when an infection enters the pathogenic microflora of the nose. As a result, pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply in the nasal cavity, causing a severe inflammatory process in a sick person, which is accompanied by purulent nasal discharge and fever. This form of rhinosinusitis requires serious medical treatment with antibiotics and other drugs.
Features of the disease in children
Allergic rhinitis usually develops during childhood and is the most common chronic allergic disorder seen in children. Research has shown that affected children may experience significant impairment as a result of numerous physical and psychological aspects. Symptoms of rhinosinusitis negatively affect social interaction and put the child at risk of accidental injury.
Nasal congestion is associated with sleep disturbances and daytime fatigue. Two studies concluded that untreated allergic rhinosinusitis in children has a marked negative impact on children's learning and test scores.
Symptoms of allergic rhinosinusitis
This disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- A sick person experiences headaches that are not relieved by conventional analgesic medications.
- A cough develops.
- A person feels a loss of strength and general malaise.
- Body temperature rises to 38 degrees.
- Mucus discharge comes out of the nasal cavity, which over time (in the absence of proper therapy) becomes purulent in nature.
- Nasality.
- Constant or periodic nasal congestion.
- Ear congestion.
- Tinnitus.
- Complete or partial loss of smell.
- Frequent sneezing.
- Nasal breathing.
- Itching in the nasal cavity.
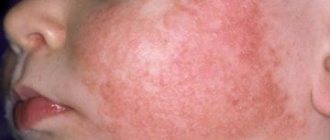
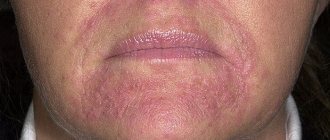
- Swelling of the face.
- Tearing.
- Feeling of tightness in the nose.
- Redness of the eyes and nose.
- Fever.
- Drowsiness.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Muscle pain.
- Unpleasant odor from the mouth and nose.
- A sore throat.
Rhinosinusitis: symptoms, treatment features, prevention
Rhinosinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membranes of the paranasal sinuses and nasal cavity. The disease is typical for people over 45 years of age and more often affects women than men. Sometimes the disease occurs in children.
The term rhinosinusitis has been used in medicine for only 2 decades, so many patients often ask questions about what rhinosinusitis is, what its symptoms are, how the disease differs from the more familiar sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, etc.
, what are the methods of diagnosis and treatment, how long does the disease last, what is rhinosinusopathy.
What is rhinosinusitis?
The upper respiratory tract is a collection of cavities (sinuses) in the facial part of the skull, connected by the nasal passages. There are sinuses: frontal, maxillary, sphenoid and ethmoidal labyrinth. The entry of a virus or infection into the respiratory tract most often leads to inflammation of the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses and the rapid development of unpleasant and severe symptoms.
The mucous membrane swells and thickens. The cavities between the sinuses and nose overlap, forming a closed space. Negative pressure develops inside the sinus, resulting in reduced oxygen supply. The cilia lining the surface of the sinus lose their mobility, which leads to impaired mucociliary clearance. Mucus stagnation develops.
All these changes together create favorable conditions for the development of pathogenic microflora.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses is called sinusitis. The term comes from the Latin word sinus, which translates to “sinus,” and sinusitis means inflammation of the sinus. However, the virus or infection never strictly affects 1 sinus.
They penetrate into the nasal passages, causing inflammation of the nasal mucosa, which is already called rhinitis (from the Latin rhino - nose), and into other cavities of the facial part of the skull, so it was decided to generalize the terminology and call the inflammatory processes of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses with a more precise term - rhinosinusitis.
Reasons for the development of rhinosinusitis
Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose and paranasal sinuses can develop due to a number of factors and their combinations, which include:
- hereditary predisposition;
- congenital or acquired defects in the structure of the nose, for example, a deviated nasal septum, obstruction of the nasal passages;
- facial injuries;
- dental procedures and infections;
- weakened immune system or immunodeficiency states;
- the habit of blowing your nose incorrectly, freeing both nostrils from mucus at the same time;
- the presence of adenoids in children and polyps in adults;
- allergic reactions;
- systematic inhalation of irritants such as chemicals, dust, etc.;
- viral infections of the upper respiratory tract;
- bacterial pathologies caused by strains of streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc.;
- fungal infections;
- bronchial asthma;
- diseases of nearby organs.
Symptoms of rhinosinusitis
The disease has several types, differing in their own symptoms. However, most symptoms are general signs of rhinosinusitis. These include:
- nasal congestion;
- stuffy ears;
- swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose and paranasal cavities;
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- sneezing;
- loss of smell;
- copious mucous discharge from the nasal cavities;
- lacrimation;
- disturbance of taste sensations;
- toothache.
Types of rhinosinusitis
There are several types of disease. To know how to treat rhinosinusitis, it is necessary to distinguish the symptoms of each type and the reasons for its development.
There are unilateral and bilateral pathologies.
Due to the development of the disease, it happens:
- viral;
- fungal;
- bacterial;
- mixed.
There are 3 forms of severity of the disease:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
According to the course, rhinosinusitis can be acute, chronic and recurrent.
Spicy
The acute form of the pathology develops rapidly. The cause is a viral infection or complications resulting from the flu. Symptoms of the acute form of the disease are:
- temperature increase;
- headache;
- swelling of the face;
- feeling of squeezing in the sinuses;
- ear pressure;
- weakness;
- nasal congestion and difficulty breathing;
- copious mucous discharge.
If treatment is untimely or incorrect, a bacterial component may be added to the viral form of the disease, which is a complication requiring hospitalization and antibacterial therapy.
Chronic
Regularly untreated acute nasal diseases can cause the development of a chronic form of the disease. The provoking factors are:
- smoking;
- regular inhalation of dust, smoke, chemicals, etc.;
- congenital anomalies of the aging nose;
- tendency to allergic reactions.
Symptoms of this type of rhinosinusitis are less pronounced. These include:
- constant nasal congestion;
- decreased sense of smell;
- nasal voice;
- distension in the sinuses;
- purulent discharge.
This form of the disease is dangerous due to the development of complications such as a decrease in the supply of oxygen to the body, the growth of the mucous membrane and its transformation into polyps.
Polyposis
Polypous rhinosinusitis is the result of chronic. Its symptoms are:
- pain in the head and sinuses;
- stuffy ears;
- chronic fatigue;
- problems with swallowing (if the disease is advanced);
- sensation of a foreign body inside.
This form of the disease is dangerous due to complications such as damage to the eyeballs and meningitis and requires surgical treatment.
Purulent
Purulent, or bacterial, rhinosinusitis is life-threatening and therefore requires immediate hospitalization. The reason for its development is bacterial microflora, the spread of which can quickly lead to an abscess, meningitis, empyema of the brain or orbits. The symptoms of this form of the disease are easily identified. This:
- elevated temperature;
- fever;
- purulent nasal discharge;
- headaches and facial pain;
- swelling of the face;
- pain in muscles and joints.
Allergic
Signs of rhinosinusitis of allergic origin are:
- redness of the eyes;
- sneezing;
- lacrimation;
- headache;
- copious clear discharge from the nose.
The cause of the allergic form of the disease is any of the allergenic factors to which a person reacts. It could be:
- plant pollen;
- animal hair;
- chemicals;
- fungal spores;
- dust.
Treatment consists of identifying and eliminating the allergen and taking antihistamines.
Catarrhal
The catarrhal form of the disease occurs without purulent discharge, but with a large amount of transparent exudate. The provoking factors are:
- allergies;
- dental infections;
- deviated nasal septum;
- hypothermia;
- polyps and other neoplasms in the nasal cavity;
- viral and fungal infections.
The clinical symptoms are:
- nasal congestion;
- loss of smell;
- temperature increase;
- headache;
- sleep disturbance;
- swelling of the face;
- conjunctivitis;
- lacrimation.
Vasomotor
Vasomotor rhinosinusitis develops as a result of swelling of the nasal mucosa and sinuses, which occurs due to impaired tone of blood vessels. The disease begins against the background of acute respiratory viral infections or colds and has symptoms such as:
- constant nasal congestion;
- sneezing;
- nasal voice;
- impaired sense of smell;
- lack of appetite;
- sleep disturbance;
- copious watery discharge from the nose.
The likelihood of developing the disease increases against the background of such negative factors as:
- anatomical pathologies of the nose;
- smoking;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- stressful situations;
- frequent use of nasal drops;
- hypothermia.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is made using:
- Visual examination by an otolaryngologist with identification by palpation of places with pain.
- Instrumental studies, which include:
- rhinoscopy, which allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the nasal passages;
- endoscopy, which allows us to identify physiological disorders in the structure of the internal parts of the nose;
- radiography, which gives an idea of the condition of the sphenoid and frontal sinuses;
- Ultrasound, with the help of which the presence of polyps, cysts, inflammations in the frontal sinuses is diagnosed;
- computed tomography, revealing the structural features of the nose;
- Magnetic resonance imaging to detect tumors.
- Laboratory research, which includes:
- blood analysis;
- microbiological examination of nasal secretions, allowing to identify the causative agents of the disease;
- bacteriological culture.
Treatment of rhinosinusitis
Treatment of rhinosinusitis includes a set of measures: the use of antibacterial agents, rinsing of the nasal passages, and physiotherapy.
The list of necessary medications, the choice of which depends on the type of disease and the patient’s susceptibility, necessarily includes broad-spectrum antibiotics. Most often prescribed:
- Amoxicillin;
- Azithromycin;
- Clarithromycin.
Depending on the accompanying symptoms, other medications for rhinosinusitis are additionally prescribed:
- To reduce the temperature and relieve the patient from pain, Ibuprofen and Paracetamol are used.
- Inflammation is relieved with Loratadine and Hydrocortisone.
- Vibrocil and Rinofluimucil are used to relieve nasal congestion.
- Sinupret is prescribed to thin mucus and remove fluid from the sinuses.
- Nazivin, Tizin, Rinonorm drops help relieve swelling and narrow blood vessels.
- Aquamaris spray is used for excessive dryness of the nasal mucosa.
- To rinse the nose, use solutions of Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
- In order to increase immunity, IRS-19, Immunal or Imunorix are prescribed.
When treating rhinosinusitis in children, they try to do without antibiotics. Doctors prescribe nasal rinsing with herbal decoctions and sea salt solutions, treatment with antiseptic drops, inhalations using Borjomi mineral water, and other physiotherapy procedures:
- UHF;
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- diadynamic currents.
The same physiotherapy procedures are prescribed for adults. Dental sanitation is important, since the odontogenic factor often causes relapse of rhinosinusitis, as well as strengthening the immune system.
ethnoscience
Traditional medicine is an effective addition in the treatment of inflammation of the nasal mucosa. The most popular home remedies are:
- rinsing the nasopharynx with sage decoction, beet or lemon juice, previously diluted by ½ with clean water and salted;
- instillation into the nose of a mixture consisting of potato juice, onion and liquid honey, mixed in equal proportions;
- instilling 2 drops of aloe or Kalanchoe juice into each nostril;
- warming up the areas of the facial sinuses with salt heated in a frying pan and placed in a linen bag;
- inhalation using a decoction consisting of chamomile flowers, calendula, sage, eucalyptus leaves and valerian, taken in equal proportions.
Surgical intervention
If treatment of rhinosinusitis with conservative and folk remedies does not bring results, you have to resort to a last resort - surgical intervention. There are several surgical treatment methods:
- Sinus puncture (puncture). During the operation, the surgeon pierces the thinnest part of the bone, washes out the accumulated pus with an antiseptic and injects an antibiotic.
- Endoscopy of polyps. Such growths can appear due to an advanced form of the disease and at the same time become the cause of chronic recurrent rhinosinusitis. Therefore, polyps must be removed.
- Sinusotomy is the most complex operation with a long rehabilitation period, which is used as a last resort. The operation involves removing part of the facial bone by opening it.
Prevention
Prevention of the disease consists of strengthening the body’s immune system in order to create a powerful barrier to external viruses and infections. To do this you should:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- do hardening;
- support the body with courses of vitamins;
- During periods of epidemics of viral diseases, try not to contact patients, avoid crowded places if possible, avoid hypothermia, and wash your nose daily using special means.
If the disease cannot be avoided, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Find out the disease by its symptoms
Source: https://nosoved.ru/zabolevanija-nosa/rinosinusit/lechenie-rinosinusita-narodnye-sredstva.html
Treatment methods
This pathology is treated using the following methods:
- use of nasal drops;
- drug therapy;
- use of folk recipes.
Drops
Nasal drops are prescribed to those patients who have been diagnosed with a mild form of allergic rhinosinusitis.
The most effective drugs that have a vasoconstrictor effect are the following drops:
- naphthyzin;
- sanorin;
- xylene
The duration of treatment with these drugs is five to seven days.
Effective antihistamine drops that contain hormones are:
- erius;
- claritin;
- Zyrtec.
Antiallergic drops are also often used:
- cromoglin;
- cromolyn sodium.
Drugs
Drug treatment of this pathology involves taking the following medications:
- Taking antiviral drugs (Anaferon, Arbidol).
- The use of antibacterial drugs (antibiotics), such as Azithromycin, Bioparox or Augmentin. The duration of treatment is up to seven days. These medications are prescribed only when the patient has a severe inflammatory process (high fever, purulent nasal discharge).
- Use of corticosteroids (Loratadine).
- Taking vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
- Use of creams and ointments if the patient has an allergic rash on the face.
- Taking mucolytic drugs.
- Prescribing antipyretic medications when the patient has a high temperature. The most commonly used are Nurofen, Panadol and Paracetamol.
- Taking multivitamins (Vitrum, Biomax, Complivit).
Folk recipes
Treatment of this disease using traditional methods is quite effective. It helps relieve inflammation and allergies.
Aloe recipe:
- squeeze juice from aloe plant;
- Instill this product into your nose every day (4 times a day), two drops into each nostril.
Beetroot recipe:
- squeeze juice from fresh beets;
- Apply two drops of this juice to your nose twice a day.
Garlic remedy:
- finely chop a few garlic cloves;
- put them in a deep bowl and pour boiling water over them;
- do inhalations (breathe over the steam for ten minutes).
Chamomile recipe:
- pour two tablespoons of dry chamomile into a glass of boiling water;
- leave for two hours;
- strain and rinse your nose with the resulting infusion.
Tatarnik recipe:
- squeeze the juice from the tartar;
- Place five drops in each nostril for ten days.
Herbal recipe:
- take equal amounts of sage, chamomile and calendula;
- mix everything and pour in a liter of boiling water;
- boil;
- strain and use for inhalation.
Celandine remedy:
- take chamomile and celandine tincture from the pharmacy;
- mix these tinctures in equal quantities;
- put two drops into the nose three times a day.
Herbal remedy (for the treatment of chronic form):
- take ten grams of dry plantain, five grams each of immortelle and yarrow;
- pour a glass of boiling water over the herbs;
- leave for an hour;
- strain;
- use the prepared infusion for inhalation.
Potato recipe:
- boil a few potatoes;
- remove the vegetables from the water and place them in a separate deep bowl;
- cut potatoes;
- breathe in the hot steam from the potatoes for at least fifteen minutes, covering your head with a towel on top.
Egg recipe:
- hard boil five eggs;
- wrap them in cloth;
- apply to the sinuses as a hot compress for a couple of minutes.
Read whether toxicerma is dangerous in children.
What does hand dyshidrosis mean? The answer is here. Sea salt remedy:
- heat a glass of sea salt in a steam bath;
- wrap the salt in a small towel;
- apply to the sinuses as a warm compress for two to three minutes.
Black radish recipe:
- squeeze juice from black radish;
- mix it with vegetable oil;
- lubricate the paranasal sinuses with the prepared liquid;
- cover them with film on top and wrap your face with a woolen cloth (leaving room for normal breathing through your nose or mouth);
- keep for up to twenty minutes. If a burning sensation occurs, remove the compress.
Ways to combat the disease
If there is a suspicion of allergic rhinosinusitis, then you cannot hesitate, you should immediately contact a specialist, otherwise it will very quickly turn from acute to chronic. In addition, ignoring the disease leads to a weakening of the protective functions of the entire body.
If treatment is started with a delay, then diseases of other organs may begin to develop, such as an inflammatory process in the auricle, regular conjunctivitis. The fight begins with eliminating the source of inflammation.
First of all, the most severe symptom – inflammation – is relieved. Antibacterial therapy is used for this. But there is no universal remedy for treating inflammation, so it is prescribed by a doctor after a laboratory examination. The most effective drug is taking an antibiotic:
- Amoxicillin;
- Clavulanate;
- Ceforuxime;
- Levofloxacin;
- Moxifloxacin;
- Sparfloxacin.
The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician.
After which the pathogenic secretion is removed. That is, the nasal cavity is cleansed and pathogenic bacteria are eliminated. Otherwise, taking antibiotics will not help. To do this, rinse the nose with preparations containing sea salt - Aquamaris, Aqualor and others. Vasoconstrictor nasal drops and antibacterial agents help relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane.
The disease can actively develop against the background of weakened immunity. For this reason, drugs that strengthen the immune system are used for treatment. A common drug is IRS-19. It contains bacterial lysates that help improve the body's protective functions. It is not addictive even with long-term use, and does not aggravate natural immunity. Its effect is local, it allows the body to recover and begin to fight viruses on its own. In addition to this drug, the patient may be prescribed:
- Xylometazoline;
- Naphazoline;
- Oxymetazoline.
But do not forget that during treatment you should follow a proper diet, enriched with healthy vitamins and minerals.
A special word for prednisolone
Prednisolone is an antiallergic and anti-inflammatory hormonal agent.
Treatment of allergic rhinosinusitis with prednisolone is carried out when the patient's condition is classified as moderate to severe.
The duration of taking prednisolone tablets is four to seven days.
The attending physician can adjust the dose and general treatment regimen depending on the patient’s condition, his symptoms and the presence of contraindications.
Why is allergic rhinosinusitis dangerous?
Nasal congestion and a runny nose can cause difficulty sleeping, daytime sleepiness, irritability, and trouble concentrating. Allergic rhinosinusitis can also worsen asthma symptoms.
The consequences of allergic rhinosinusitis can be:
- nasal polyps;
- middle ear infection;
- chronic inflammation;
- the addition of a bacterial infection and the formation of pus;
- conjunctivitis;
- bronchial asthma.
Interesting fact! It has been estimated that up to 90% of patients with allergic rhinosinusitis are untreated or treated inappropriately.
Prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of this pathology and its complications, it is necessary to adhere to the following rules of prevention:
- Engage in physical activity (swimming, running, taking dance lessons, etc.).
- Strengthen the immune system (harden yourself, take vitamin complexes, drink fruit juices).
- Immediately after the first symptoms of rhinosinusitis appear, you should consult a doctor before the disease becomes chronic, since in this case it will be much more difficult and longer to treat.
- Visit the dentist regularly and treat tooth decay.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Give up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Eliminate congenital or acquired defects and anomalies of the nasal septum.
Find out how microbial eczema manifests itself on the hands. What do the symptoms of weeping eczema look like? Details in the article.
What are the causes of dry eczema on the hands? See below.
What is rhinosinusopathy of the brain: signs, symptoms and treatment
Those patients who are diagnosed with rhinosinusopathy deserve sympathy - this is an extremely unpleasant, debilitating disease.
Moreover, it often occurs through no fault of the person himself, even if he leads a healthy lifestyle and monitors the condition of his body.
The patient is constantly worried about:
- Liquid discharge from the nasal passages;
- Severe swelling and itching of the nasal mucosa;
- Recurrent runny nose, sometimes up to 10 times a year.
Treatment of the pathology is quite simple and successful if started in the early stages. If the disease is advanced, it can be very difficult to cure. Therefore, everyone, even people not prone to rhinitis, should know what it is, why it occurs and how it manifests itself, so that at the first symptoms they can consult a doctor and begin adequate treatment.
Reasons for the development of rhinosinusopathy
Currently, the problem is a common disease among all categories of the population, the fault of which is not the person himself, but the external factors to which he is exposed every day.
The reasons why allergic rhinosinusopathy may develop are as follows:
- Living in an ecologically bad area.
- Work in hazardous industries - for example, a chemical plant.
- Uncontrolled use of medications, in particular antibacterial ones.
- Bad habits – smoking.
- Hereditary predisposition to allergic reactions.
- Intestinal dysfunction, dysbacteriosis.
- Neoplasms in the nasal passages - adenoids or polyps.
- Chronic diseases of various types.
It should be noted that although almost every person has to deal with such factors in their life, a disease such as rhinosinusopathy does not occur in everyone.
Therefore, we can say that the main factor provoking its development is still genetic predisposition.
If a patient has a tendency to allergies, he is primarily at risk. Such people need to be careful and, if possible, avoid those factors that could become an impetus for the progression of the disease.
Long-term use of certain medications is especially dangerous - in this case, treatment of rhinosinusopathy can last for many years.
How to recognize rhinosinusopathy
The symptoms of rhinosinusopathy are similar to those of the onset of flu or a cold. Therefore, many patients begin to take medications specifically for these diseases, and only when the condition does not improve even after several weeks, they begin to understand that rhinitis has become chronic and they require completely different treatment.
Typical symptoms of rhinosinusopathy:
- Constant nasal congestion.
- Runny nose.
- Labored breathing.
- Sore throat and mild cough.
These signs can be observed constantly, or occur periodically if the patient comes into contact with an irritating allergen.
The patient's general well-being also worsens. Due to a constantly stuffy nose, a person’s appetite and night sleep are disrupted, as a result of which headaches, irritability, and lethargy occur due to chronic lack of sleep.
Accordingly, the patient’s performance, concentration and speed of reactions decrease, and advanced allergic rhinitis is to blame.
Methods for diagnosing rhinosinusopathy
Diagnosis of the disease in the early stages is often difficult, since the symptoms are very similar to those of a common cold or seasonal ARVI.
Even an experienced doctor will not be able to immediately identify rhinosinusopathy based solely on signs such as sneezing, coughing, swelling of the nasal mucosa, and lacrimation.
To identify rhinosinusopathy, special laboratory tests are required. They are prescribed if, despite the treatment, treatment occurs again and again at intervals of several weeks. To make an accurate diagnosis, the following measures are taken:
- Interview and examination of the patient;
- X-ray of the nasal sinuses;
- Rhinoscopy is a procedure that allows you to determine the extent of the disease and its severity.
After comparing all the results obtained, the otolaryngologist will select the appropriate treatment.
Sometimes you can hear a diagnosis such as rhinosinusopathy in the brain. But in fact, brain tissue is not affected by this pathology.
The patient suffers from severe headaches due to stagnation of purulent discharge in the sinuses, which puts pressure on neighboring organs. An MRI of the brain will show which areas of the nasal cavities are affected.
Useful tips
By following the tips below you can minimize the risk of developing the disease:
- During the flowering period of allergenic plants, when going outside, you need to wear a protective mask so as not to inhale pollen and odor.
- Regularly do wet cleaning in the house to prevent dust collection.
- People prone to rhinosinusitis are advised to wear protective rubber gloves and a mask when using cleaning chemicals. It is also advisable to completely replace artificial cleaning products with natural ones that do not contain strong aromas.
Allergic rhinosinusitis has a favorable prognosis. It can be successfully treated, especially in the early stages of manifestation. As a result, it is very important to seek medical help on time.
Previous article: Eczema what is it Next article: Eczema on the face
Diagnostics
The accuracy of the diagnosis is established by analyzing the medical history, the manifestation of clinical symptoms, the causes, and the allergic reaction that occurs.
A diagnostic examination of the nasal cavities is prescribed: there is noticeable blueness of the mucous membrane, swelling of the turbinates and copious mucous discharge. An x-ray shows thickening of the paranasal sinuses and a decrease in their airiness.
A blood test is performed to check for the presence of eosinophilia. Radioimmunoassay studies reveal the concentration of IgE in mucus and blood serum. Differential diagnostic studies are aimed primarily at excluding an infectious nature.
Possible complications
If the treatment is incorrectly selected, the patient develops complications and consequences; prevention of sinusitis helps strengthen the immune system: the body tries to fight the infection on its own. Possible complications include:
- chemosis - swelling of the conjunctiva and eyelids;
- bulging eyes (exophthalmos);
- periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum) - accompanied by severe pain in the corners of the eye and bridge of the nose;
- mucocele - a cyst grows in the paranasal sinuses against the background of obstruction of the nasal ducts;
- cholesteatoma - accompanied by the formation of a cavity filled with dead cells;
- sepsis;
- cavernous sinus thrombosis - characterized by the accumulation of blood in the dura mater of the brain;
- inflammation of the meninges, abscess;
- pathologies of the organs of vision and hearing (otitis media, conjunctivitis, purulent inflammation of the eye sockets).
Complications from the visual organs can lead to complete loss of vision. With adequate therapy, the risk of developing negative consequences is reduced. . Previously untreated pathology. Untreated infectious etiologies (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis), accompanied by swelling of the nasopharynx and larynx, can provoke oxygen deficiency due to congestion. Oxygen starvation affects concentration and memory. Stopping breathing during sleep (apnea) develops due to systematic blockage of the nasal passages.
Medicines from a folk pharmacy
To some, concepts such as rhinosinusitis and treatment with folk remedies seem incompatible. However, for many diseases of the nose, doctors recommend turning to traditional medicine. Medicines based on medicinal plants - valerian, eucalyptus, sage, calendula, chamomile - have proven themselves well. They have antibacterial properties and can reduce inflammation and swelling.
According to one of the recipes, a decoction of calendula, valerian, sage, and eucalyptus leaves is prepared. All components are taken in equal parts and placed in a three-liter pan so that they occupy a third of the container. The raw materials are poured with water to the top of the pan and boiled for 10 minutes. When the broth has cooled to room temperature, it is filtered and used for washing. The procedure is carried out 3 times a day. This decoction can be dropped into the nose. Products based on St. John's wort, chamomile, and marshweed are also prepared.
You can make drops at home. You need to take celandine and aloe juice in a 1:1 ratio, and then add honey. It should occupy 1/3 of the volume of the entire product. The mixture is instilled 6 drops into each nostril 3 times a day. For treatment, cyclamen juice extract (2 drops each) and linden liquid honey (2 drops each) are also used.
Healers advise preparing oil drops based on propolis. You need to dissolve a small piece of propolis in 100 ml of olive oil, and then drip the resulting product into your nose twice a day. Patients claim that with the help of this medicine almost all symptoms of the disease are relieved.
What is rhinosinusitis?
Rhinosinusitis is a collective name for various diseases of the nose. It is usually indicated as a preliminary diagnosis. Depending on the duration of the inflammatory process, acute and chronic rhinosinusitis are distinguished. After an examination involving the use of various methods, patients are found to have:
- sinusitis, in which the inflammation was localized in the maxillary (maxillary) sinus;
- ethmoiditis with edema in the ethmoidal labyrinth;
- frontal sinusitis with damage to the frontal sinus;
- sphenoiditis (pathology of the sphenoid sinus);
- pansinusitis - inflammation of all sinuses at once;
- hemisinusitis, in which several sinuses are affected, but on one side.
The impetus for the development of the disease is often given by ARVI. With a viral infection of the nasopharynx, microorganisms intensively develop in the paranasal sinuses. Due to severe swelling, the passage of air through the nose and the outflow of secretions worsen, creating conditions for the spread of infection.
The cause of rhinosinusitis may be untreated vasomotor rhinitis, accompanied by a runny nose and a feeling of complete blockage of the nose.
Bacteria can cause the disease. Allergies and weakening of local/general immunity contribute to damage to the mucous membrane.
Pathology affecting several nasal sinuses is also caused by the growth of polyps. If the tumors are not removed, conservative treatment will not give the desired result, and the inflammation will spread.