Causes
The mechanism for the development of such a powerful allergic reaction has not yet been fully studied. It is assumed that this condition is a consequence of the repeated entry of the allergen into the body, which releases a huge amount of histamines. These are biologically active substances that cause such an extraordinary clinical picture.
Doctors name the following causes of anaphylactic shock in children:
- injections of drugs (very often antibiotics);
- use of local anesthetics;
- administration of a contrast reagent before x-ray;
- a bite of an insect;
- consumption of certain foods;
- entry of a chemical into the body;
- intradermal tests for allergic reactions;
- vaccination, administration of gamma globulin or serum agents.
Sometimes anaphylactic shock develops in an infant who previously seemed absolutely healthy and did not react to anything with any rashes. In such cases, the first contact with a harmful allergen could occur during pregnancy - through the placenta.
The speed at which symptoms of anaphylactic shock spread depends on how the allergen entered the child’s body:
- intravenous administration - instant anaphylaxis;
- the use of tablets or ointments is a gradual development as the medicine is absorbed;
- through food - the clinical picture appears only after a few hours.
The faster adults respond to such a condition, the greater the chance of saving lives. But to do this, you need to know how anaphylactic shock manifests itself in a child - what symptoms indicate that an allergen has entered his body.
How does anaphylactic shock develop in children?
The insidiousness of the disease lies in the appearance of dangerous symptoms suddenly, in an absolutely healthy child. Factors predisposing to the development of shock include frequent manifestations of allergies in the baby and a hereditary predisposition to anaphylactic reactions. Parents who have themselves encountered a dangerous condition should be wary of anaphylaxis in a child.
The culprit in the development of a serious illness is an immediate allergic reaction. In the case of the first contact with the allergen, specific immunoglobulins of class E are produced in high concentration. If the substance enters the body again, even after a lapse of time, the allergen and antibody bind to form immune complexes.
These compounds settle on mast cells and damage their membrane, the protective shell. As a result of cell destruction, a huge amount of biological substances are produced that cause shock. The release of the mediator, histamine, increases the permeability of the vascular walls, causing redness of the skin, swelling and itching.
Depending on the amount of immunoglobulin produced by the immune system, the body’s reaction and the severity of allergy symptoms will differ. In anaphylactic shock, changes occur throughout the body simultaneously and lead to the development of life-threatening conditions.
It is believed that the frequency and severity of the development of the disease are related to age. The older the child, the more at risk he is of developing anaphylaxis.
Symptoms
Depending on the allergen, the signs of anaphylactic shock can be very different, since in this condition almost any internal organs can be affected. For ease of diagnosis, specialists identify several forms of anaphylaxis, each of which is accompanied by characteristic symptoms.
Asphyxial:
- acute respiratory failure due to laryngeal edema and bronchospasm;
- a sharp drop in pressure to a minimum, which leads to loss of consciousness;
- painful cough;
- wheezing;
- angioedema of the face;
- sudden onset of symptoms with their subsequent increase.
Hemodynamic:
- acute heart failure;
- sharp pain behind the sternum;
- decrease in pressure;
- pale skin;
- thready pulse;
- weakness;
- noise in ears;
- pouring sweat.
Cerebral:
- epileptic seizure;
- convulsions;
- foam at mouth;
- heart failure;
- cessation of breathing.
Abdominal:
- acute abdominal pain;
- intra-abdominal bleeding.
Food:
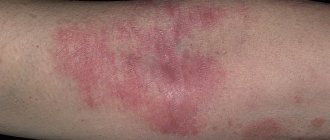
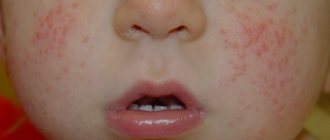
- characteristic redness of the skin;
- rashes on the body;
- swelling.
Moreover, the severity of anaphylactic shock does not depend on the dose of allergen that enters the body.
Sometimes it happens. In medical practice, there are cases when this condition develops in a baby suffering from penicillin intolerance, when communicating with a doctor who has previously had contact with this drug.
The clinical picture is further complicated by the fact that anaphylactic shock is difficult to differentiate from other similar painful conditions.
Diagnosis in such life-threatening cases should be carried out exclusively by a specialist. But since at such moments every minute is precious, it is necessary to know the algorithm of actions for anaphylactic shock in order to provide first aid to a small patient.
The main symptoms of anaphylaxis in babies
In its development, the disease goes through several stages. Their duration and severity depend on the type of allergen and the sensitivity of the body.
Shock begins with the appearance of excitement or, conversely, sudden weakness, tinnitus and dizziness. The condition is accompanied by abdominal pain, a feeling of pressure behind the sternum and a pronounced fear of death. A rash appears suddenly in the form of hives, which quickly spreads throughout the body, the baby complains of skin itching and burning.
Edema often develops and spreads to the subcutaneous tissue. Lips, eyelids, ears, and tongue increase in size. Changes occur very quickly, and the child’s condition can worsen literally before our eyes. Blood pressure at this stage remains within normal limits, and therapeutic manipulations carried out at this time are most effective.
If after first aid the condition does not improve, the disease moves to the next stage. Blood pressure decreases and consciousness is impaired. The heart rate increases, but the pulse is weak in filling, and low cardiac output syndrome develops. Shortness of breath occurs, harsh wheezing can be heard even from a distance. The skin becomes pale and cold sweat appears.
The third stage is manifested by the baby’s extremely difficult condition and lack of consciousness. The child breathes frequently, but shallowly. Blood pressure is sharply reduced, and the pulse is practically undetectable. Tissue bleeding occurs, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome develops, and kidney function is disrupted to the point of complete loss of function.
But the development of shock does not always follow this principle; there are several clinical forms of the disease:
The pathology of the respiratory system comes to the fore, swelling of the larynx and an attack of bronchospasm develop. The baby's voice becomes hoarse, difficulty breathing appears, and the baby cannot take a breath. The condition quickly worsens, blood pressure drops to the lowest levels, and the child loses consciousness. This form of shock is more common in children suffering from bronchial asthma and allergic bronchitis.
In the case of acute damage to the cardiovascular system, they speak of a hemodynamic form of anaphylactic shock. Manifestations of the disease begin with pain in the chest, pale skin, and a drop in pressure. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, heart failure increases, it becomes difficult to determine the pulse due to poor filling of the blood vessels, and collapse occurs.
In this case, damage to the central nervous system plays a major role in the development of the disease. The first and leading sign of pathology is agitation or retardation, confusion. The baby ceases to navigate what is happening and answer simple questions. In case of severe shock, loss of consciousness, cerebral edema, convulsions, and breathing problems occur.
The main symptom of this form of the disease is abdominal pain. The baby complains of pain in the stomach or intestines, the intensity of which is increasing. These manifestations are not only unpleasant, but also dangerous due to the development of intra-abdominal bleeding.
First aid
So, what to do if your child has anaphylactic shock? What emergency care is provided in such cases? First, you need to urgently call an ambulance and describe all the symptoms to the dispatcher in detail.
While waiting for the doctor, you should try to resuscitate the patient on your own:
- Lay him on a horizontal surface, raise his legs, turn his head to the side, push out his lower jaw so that his tongue does not sink into his throat.
- Remove the trays.
- Clear your mouth of vomit.
- Talk to your doctor by phone about using antihistamines or adrenaline.
- Provide access to oxygen: unbutton your collar, take off your scarf, open the window.
- Monitor your pulse and blood pressure.
- Remember the exact time of anaphylaxis, application of a tourniquet, and names of medications used.
In parallel with this, you need to try to stop the entry of the allergen into the child’s body:
- When injecting, apply ice to the injection site, make the bandage a little higher for half an hour;
- if bitten, remove the sting, apply ice to the skin puncture site;
- when instilling medicine into the nose or eyes, rinse them thoroughly with running water;
- If you are using pills or have food anaphylactic shock, immediately rinse the child’s stomach and give him activated charcoal.
If first aid for anaphylactic shock in children was carried out correctly and in a timely manner, there is a chance of recovery with minimal risks to life and health.
Since it is impossible to predict the onset of such a dangerous condition, parents should always keep on hand a first aid kit stocked with medications that will be useful in such situations:
- ampoule solution of adrenaline;
- antihistamines (Tavegil, Diphenhydramine, Suprastin);
- Prednisolone solution;
- medical alcohol for disinfection;
- saline;
- tourniquets;
- bandages, cotton wool, gauze;
- syringes.
Dosages and methods of use of medications must be agreed upon with your doctor. This is especially true when you are treating anaphylactic shock in children under one year of age, since most drugs are contraindicated for them.
Pre-medical methods of assistance
If a child has symptoms of shock, call an ambulance. When providing first aid, the algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Calm and comfortably lay the child (on his back). Your legs should be slightly elevated.
- Turn your head to the side.
- Remove foreign objects from the oral cavity (food debris, dentures).
- Open a window or door to allow oxygen to flow in.
- Stop the entry of the allergen into the body. If necessary, apply a tourniquet above the insect bite or injection site.
- If there is no pulse (cardiac arrest), perform an indirect cardiac massage.
- Start artificial respiration when it stops.
Treatment
Medical treatment of anaphylactic shock in children is carried out depending on the severity of the little patient’s condition:
- Injection of adrenaline to restore the body.
- Intravenous injections of antiallergic drugs.
- For bronchospasms and acute respiratory failure - bronchodilators.
- To avoid side symptoms, administer steroid hormones.
- If a child is allergic to penicillin, the enzyme penicillinase is given to the child.
- When blood pressure drops, periodic administration of norepinephrine is recommended.
- If the situation is out of control and threatens to be fatal, artificial ventilation and chest compressions are performed.
If everything went well, the anaphylactic shock was stopped, and the child spent 10 days in hospital treatment. He continues to be given hormonal medications and is given IV drips to restore his water-salt balance.
In the future, to avoid such situations, you need to protect it from contact with the allergen. After all, one day anaphylaxis can result in death or serious health consequences.
Diagnostics
Correctly carried out diagnostic measures make it possible to provide timely first aid for anaphylactic shock in children. The clinical picture of the disease plays a huge role in determining shock, since there is no time left for an instrumental examination of the patient.
Therefore, it is very important to know the first signs of shock development. The manifestations of the disease are varied; parents and medical workers need to be wary when carrying out vaccinations, treatment with antibiotics and immunobiological drugs.
It should be understood that signs of shock do not always occur suddenly. Thus, with a delayed form, symptoms of the disease may appear several hours after contact with the allergen. But, fortunately, these types of disease are less malignant.
At the stage of emergency medical care, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- collecting complaints and identifying predisposition to anaphylaxis;
- physical examination: examination of the patient, determination of the frequency and nature of heartbeats, respiratory movements;
- blood pressure measurement.
This list is enough to make a dangerous diagnosis and immediately begin emergency care. After therapy, the patient is sent to the hospital, where examinations continue:
- 24-hour monitoring and recording of blood pressure, heart rate, diuresis, blood oxygen saturation;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram;
- determination of the acid-base state of the blood;
- instrumental methods - ECG, chest x-ray, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis;
- determination of immunoglobulin E in blood serum.
Complications
One of the most serious complications during the onset of anaphylactic shock is collapse. The child cannot breathe, the heart can stop at any moment, the pressure drops. In the absence of resuscitation measures, death is possible.
After anaphylactic shock, for some time the baby may suffer from muscle pain, fever, severe itching, and allergic skin rashes.
Possible consequences of shock:
- glomerulonephritis;
- bronchial asthma;
- non-infectious jaundice;
- inflammation of the heart muscle.
You need to understand that anaphylactic shock in children does not occur out of nowhere. If there is a tendency to allergies, parents should know as much information as possible about this dangerous condition and be able to prevent it at the first symptoms.
You can put a memo with the algorithm of actions in a visible place so that at the right time you don’t get confused and do everything as quickly and correctly as possible.
source: www.vse-pro-detey.ru
In pediatric practice, there are quite a lot of different emergency conditions that require emergency care. Delay in providing therapy can lead to the most severe consequences and even death of the child.
What it is?
A sharp decrease in systemic blood pressure and loss of consciousness when exposed to allergic causes is called anaphylactic shock. It is impossible to predict the onset of this dangerous condition - every person has a risk of its occurrence throughout his life.
Causes
The development of anaphylactic shock is caused by the entry of various allergens into the child’s body. But not all allergenic substances can cause such a reaction - a special predisposition and hypersensitivity to a specific allergen is also required.
How to provide emergency assistance for anaphylactic shock can be found in the following video.
There is currently no single theory that would explain the development of a pronounced drop in pressure and disturbances of consciousness during the action of an allergenic substance. Scientists believe that the impetus for anaphylactic shock can be disturbances in the functioning of the immune system with high sensitivity to a specific allergen.
The most common reasons that can cause the development of this dangerous condition in children are:
- Traumatic skin injuries resulting from bites of various insects and animals. The most common dangers are: bees, bumblebees, wasps, mosquitoes, snakes, lizards. When swimming in the sea, anaphylaxis can be caused by contact with a jellyfish. When touching a sea creature, a child often experiences a burn on the skin, which can cause the development of anaphylaxis.
- Use of medicines. The method of administration of drugs does not matter. Most often, anaphylaxis occurs with new medications that have not been previously prescribed to the child. If there is a cross-allergy, the baby may develop intolerance to certain components of the medications. If a similar substance enters the body, anaphylaxis may develop.
- Chemical burn from plants. The leaking juice, which contains a huge amount of various biologically active substances in high concentrations, can cause shock. If they come into contact with a child's delicate skin, they quickly penetrate the dermis and can cause anaphylaxis.
- Allergenic foods. Most often, children develop anaphylaxis to nuts, chocolate, citrus fruits and seafood. Also, tropical fruits can lead to the development of a dangerous condition.
- Detergents and household chemicals. Perfume additives included in such products contribute to the development of anaphylaxis in children.
- New clothes and shoes made from low-quality materials. Brightly colored products pose the greatest danger. In their production, unscrupulous manufacturers use poor quality dyes.
- Vaccination. All vaccines and immunobiological preparations are quite allergens and reactogens. In pediatric practice, there are quite a lot of cases where vaccination caused anaphylactic shock in the baby. Taking this into account, vaccination should be carried out only in a specially equipped room. It contains a kit or first aid kit to provide the necessary assistance in a critical situation.
How does it arise?
When an allergenic substance enters the body, a violent allergic reaction develops. It only takes a few minutes to get started. In response to the entry of a foreign biological agent into the body, the cells of the immune system are activated. They begin to produce a huge amount of biologically active substances.
These components cause a strong constriction of blood vessels, which, in turn, leads to a decrease in pressure and impaired consciousness. This reaction is primarily defensive in nature. The body seems to be trying to limit the systemic spread of the allergen through the bloodstream. However, with severe sensitivity to the allergenic substance, a critical condition may develop.
During an allergic systemic response, the body produces a huge amount of a specific protein - immunoglobulin E. The higher its content in the body, the more pronounced and rapidly the symptoms will increase.
In newborns, adverse symptoms of shock develop rapidly. This condition is very dangerous and requires immediate hospitalization of the baby in a hospital.
Symptoms
Signs of anaphylactic shock develop rapidly and appear quite clearly. Usually, after a few minutes, the baby experiences a severe disturbance in his general well-being. You can recognize anaphylactic shock at home.
The following symptoms are typical for this critical condition:
- Severe weakness or complete loss of consciousness. The manifestation of this symptom depends on the initial condition of the child and the level of his individual susceptibility to the allergen.
- Dizziness. The child's gait is disturbed. In some cases, the baby is not even able to take a few steps. Being in a horizontal position somewhat reduces dizziness.
- Fall in blood pressure. The measurement results are significantly below the norm. In some critical situations, blood pressure can drop to almost 60/40 mm. rt. Art. and even lower.
- Pronounced pallor of the skin. The nasolabial triangle may be bright blue.
- Hands and feet are cold to the touch.
- Very weak pulsation in the peripheral arteries when trying to measure the pulse. It is practically not palpable or difficult to detect. The first stage of anaphylactic shock is characterized by an increase in heart rate. A decrease in this indicator is an unfavorable sign.
- Swelling of the face and eyes. May not occur in all cases. This is the most characteristic symptom of Quincke's edema. This sign may precede the development of anaphylaxis.
Treatment
When the first signs of a critical condition are detected, the baby needs to immediately begin therapy. Untimely treatment can lead to dangerous complications in the child, cardiopulmonary failure, and in especially severe cases, even to the development of a coma.
If the baby has had contact with an allergen and signs of anaphylaxis appear, there should be no delay. First of all, immediately call an ambulance and be sure to tell the dispatcher that the child has signs of anaphylaxis. But saving the child must begin even before the doctor arrives.
First aid
In order to prevent the development of dangerous consequences of an allergic critical condition, use the following algorithm of actions:
- Lay the baby horizontally and elevate the legs. This position will help improve blood flow to vital organs: the heart and brain.
- If your child has dental guards, remove them as they may cause aspiration if they vomit.
- Open doors and windows wide to improve the flow of fresh air into the room.
- If the baby loses his breath and is not breathing, begin artificial respiration.
- Monitor your pulse. If there is no pulsation in the carotid arteries, which are located in the neck, place your hands on the chest and begin artificial heart massage.
Urgent Care
Children with anaphylactic shock are treated immediately. Emergency treatment begins with the ambulance team. The child is given humidified oxygen. If there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure, children are given cardiopulmonary resuscitation measures.
In difficult cases, when the heart rhythm is not efficient enough or there are signs of vascular insufficiency, adrenaline is used. The dosage of this drug is selected taking into account the baby’s age and weight.
To eliminate adverse symptoms, injectable forms of antihistamines are used. To normalize blood pressure and stop the allergic reaction, prednisolone is administered. To stabilize the baby’s condition, intensive infusion therapy is administered with the introduction of large amounts of isotonic solutions or glucose.
The provision of qualified assistance is carried out in a hospital setting. If the baby is in a critical or serious condition, go to the intensive care unit. If the child is unconscious or in a coma, then he is given massive infusion treatment using a whole complex of various medications.
Prevention
In order to reduce the risk of possible anaphylactic shock in a child, use the following recommendations:
- Get your child regularly examined by an allergist. The doctor will prescribe all the necessary tests that will help identify possible allergens. When identifying such provoking substances, care should be taken to ensure that they do not enter the child’s body. Any contact with an allergen in the future can lead to the development of anaphylaxis.
- Plan your children's diet carefully. All children with allergic diseases must follow a hypoallergenic diet throughout their lives. Such therapeutic nutrition implies a complete rejection of possible foods that can cause exacerbations of the disease.
- Strengthen your immune system. Weak children often react more acutely to allergens entering the body. A proper daily routine, quality nutrition and active walks in the fresh air will help the immune system work better.
- Use repellent creams. Such products will help protect the child from possible bites of various insects.
When the first signs of anaphylactic shock appear, you should never panic!
Only consistent implementation of first aid measures will help prevent the development of dangerous conditions that can occur during anaphylaxis. Timely emergency treatment will definitely save the baby’s life.
source: www.o-krohe.ru
Anaphylactic shock (anaphylaxis) is a painful condition. It is accompanied by a sharp increase in the sensitivity of the body. The sensations appear when the allergen substance is reintroduced. These include any type of foreign protein. In addition, anaphylactic shock can be caused by:
- Medications.
- Insect bites.
Etc. Anaphylactic shock is life-threatening for adults and children. It is one of the most severe manifestations of allergic reactions.
It takes very little time for the manifestations to become critical - starting from a few seconds, but not more than 2 hours. It does not matter how the allergen came into contact with the patient. The more it is, the worse the patient’s condition will be.
Causes of anaphylactic shock in children
- Use of certain medications.
- Contact with radiopaque substances.
- Allergy diagnostic technique.
- Taking antibiotics (especially penicillin).
- Food allergies.
- Insect bites.
- The use of gamma globulin, a number of vaccines, and serums.
There are quite rare cases - for example, when the body reacts to cold in this way. It is very difficult to identify the exact allergen, especially if these are medications and the patient does not take them in single quantities.
In children, such manifestations are often caused by certain vaccines and serums. Shock is usually evident upon secondary exposure to the allergen. Often, in children whose mothers used a dangerous drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding, anaphylactic shock occurs as a result of the first contact with the drug. The method of administration and dose are not important for a sensitized (allergenic) patient.
Anaphylactic shock due to food ingestion is quite rare. Often among children there is intolerance to milk (sensitization to beta-lactoglobulin), fish dishes, and egg whites.
Symptoms of childhood anaphylactic shock
Symptoms of anaphylactic shock in children are related to how the disease develops. First, the allergen enters the body. Upon skin contact, itching, swelling, etc. occur. If the disease develops due to the product, then the corresponding symptoms begin. Some manifestations of the disease can be identified:
- Signs of anxiety, fear.
- Throbbing headache.
- Dizziness.
- Numbness of lips and facial muscles.
- Noise in ears.
- Cold sweat.
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Quincke's edema.
- Hives.
- Attacks of shortness of breath.
- Bronchial spasm.
- Tightness in the chest area.
- Nausea.
- Stomach ache.
- Vomit.
- Cramps.
- Foaming at the mouth.
- Low blood pressure.
- Uncontrolled urination.
- Bloody formations discharged from the vagina (in adults).
- The pulse becomes threadlike.
- Loss of consciousness.
If the latter symptom is observed, there is a risk of death. It is necessary to immediately provide first aid and bring the patient to his senses. From suffocation, death occurs in 5-30 minutes. Vital organs decompose within 24-48 hours. These are irreversible changes that must be prevented immediately. There are cases when death occurs as a result of changes in the kidneys (glomerulonephritis), which require more time to develop pathology. Also, after a long time, damage can be diagnosed:
- gastrointestinal tract (intestinal bleeding),
- heart pathology (myocarditis),
- death of brain cells (swelling, hemorrhage)
In most cases, shock occurs in two phases. First, there is some improvement in well-being, and then blood pressure drops sharply. Patients who have suffered such a shock spend at least 12 days in the hospital.
There are situations when children can preliminarily notice certain manifestations of the disease. They are observed immediately after contact with an allergen (hives, itching, dizziness, etc.) They are called “anxiety” symptoms.
Found an error in the text? Select it and a few more words, press Ctrl + Enter
What to do if a child has anaphylactic shock?
You need to call an ambulance immediately. This is done at the first symptoms. This is especially important when you know in advance about an atypical reaction to an allergen. In such a case, the ambulance dispatcher is warned that he needs to send a specialized team to the call.
Detailed article on the topic of first aid for anaphylactic shock
When the allergen is known, the patient needs to be isolated from it and preventative measures taken: ventilate the room, or treat the wound, depending on its nature. If it is a bite, a tourniquet and something cooling are applied over it. The patient should take a horizontal position as soon as possible.
You should give your child a dose of antihistamines according to the instructions. Give him one of the antihistamines (tavegil, suprastin, claritin). If you do not know what kind of medicine is usually given to your child, give what is available.
Tavegil (syrup) is not given to children 1-3 years old more than 2-2.5 ml. twice a day. Patients aged 3 to 6 are given no more than 5 ml, and those aged 6 to 12 years require 5-10 ml. Also, at the age of 6 to 12 years, you can give tablets - one half twice a day; adolescents and adults are given a whole tablet.
Suprastin is given to those aged 1–12 months, 5 mg (0.25 ml), at the age of 2–6 years, the dose increases to 10 mg (0.5 ml), and patients aged 7–14 years need 10–20 mg (0.5–1 ml). The daily dose should not exceed 2 mg/kg.
Next you will have to monitor the child. It is imperative to regularly measure pulse and pressure, frequency and rhythm of breathing.
You need to remember the exact time of onset of anaphylactic shock and report it to your doctor. It is necessary to say as accurately as possible when the manifestations of the disorder began and mention the names of the medicine that was given to the patient before the specialist arrived.
How to treat anaphylactic shock in children?
When anaphylactic shock is diagnosed, a child urgently requires an injection of adrenaline. This will help relieve allergies. Typically, patients suffering from such attacks are well aware of their problem. The child can rarely use the necessary medicine on his own.
If a reaction occurs for the first time, you must immediately call an ambulance. Before their arrival, it is necessary to achieve patency of the airway. It is necessary to eliminate mucus and vomit from the oral cavity and prevent tongue retraction. If the victim is conscious, you should not show him your anxiety. The tone should remain even. If an aerosol inhaler is available, it must be used. It stops an attack of bronchial asthma; a corticosteroid hormone tablet (prednisolone, dexamethasone) will also help with this. This will help alleviate the symptoms of shock a little, and therefore wait for the doctors to arrive.
The child is immediately placed lying down, with his limbs raised. Then the fluid will not leak out of the heart pump. Whenever possible, use an oxygen therapy mask of two to four liters per minute.
Adrenaline, given intramuscularly or subcutaneously, is the first step in emergency treatment. Depending on the conditions of care, different forms of the drug are used - standard injections in ampoules, intravenous administration, etc. After hospital treatment, it is necessary to eliminate the risk of contact with allergens.
Author of the article: Alekseeva Maria Yurievna, general practitioner
source: www.ayzdorov.ru
Hello, dear readers! Today we will tell you about what anaphylactic shock in children is and why it is dangerous.
Together with you, we will understand the causes of its occurrence, learn about the symptoms and learn how to provide emergency care for this phenomenon.
Why can a child experience anaphylactic shock, and what should parents do?
27.02.2019
Anaphylactic shock (anaphylaxis) is the occurrence of an immediate allergic reaction that develops when an allergen re-enters the body, which is always accompanied by a sharply increased sensitivity.
Causes and risk factors
Anaphylactic shock can occur when:
- Use of certain medications.
- Contact with radiopaque substances.
- Insect bites.
- Consumption of foods rich in allergens (milk, fish, eggs, etc.).
- Taking antibiotics.
- The use of gamma globulin, a number of vaccines and serums.
- Carrying out allergy diagnostics (intradermal tests for allergens).
In rare cases, anaphylactic shock may occur as a response to low temperatures.
The following diseases are considered risk factors:
Also, emotional stress and travel should be added to the risk factors, as a result of which the body’s defense systems are reduced due to exhaustion or constant exposure to strong allergens.
Severity and shape
There are 4 degrees of severity of anaphylactic shock:
- Easy. Accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure by 30-40 mm Hg. Art. below normal, while the heart rate reflexively increases. Affected children are often agitated, restless, or inactive due to increasing weakness. These guys have retained their consciousness.
- Moderate weight. Systolic blood pressure ranges from 60-90, while diastolic blood pressure drops to 40 or less mmHg. Art. In children, a detailed clinical picture is observed, characterized by Quincke's edema, decreased hearing and vision, ringing and noise in the head. Gastrointestinal and renal syndromes appear. Consciousness may be clouded, and in rare cases there is loss of consciousness.
- Heavy. Systolic pressure drops to 40-60 mmHg. Art., diastolic may not be determined. The child's pulse is small and frequent, signs of acute respiratory failure appear, and loss of consciousness is possible.
- Very heavy. Blood pressure is not determined, as is the pulse, which often accompanies cardiac arrest and cessation of breathing. The child immediately loses consciousness, during which involuntary acts of defecation and/or urination occur. The child's skin is pale, cyanotic. The pupils are dilated and do not respond to light.
Of considerable importance in determining the severity of anaphylactic shock in children is the effect of anti-shock therapy, which is relevant and has a positive effect in mild to moderate anaphylaxis. Therapeutic measures are ineffective or may have virtually no effect in severe and extremely severe shock, respectively.
Forms of anaphylactic shock:
- The typical one is manifested by arterial hypotension, respiratory failure, impaired consciousness, convulsions, urticaria, Quincke's edema, redness of the skin (if the allergen affected the area directly), itching.
- Asphyxia is characterized by severe respiratory failure, which developed as a result of swelling of the larynx, bronchioles, lungs, and bronchospasm.
- Hemodynamic. There is a predominance of cardiovascular symptoms: substernal pain in the heart area, rhythm disturbances, weak pulse, significant drop in blood pressure; upon auscultation, doctors determine that the child has a decrease in the sonority of heart sounds.
- Cerebral occurs with characteristic disorders of the central nervous system, including: loss of consciousness, convulsions, respiratory rhythm disorders, cerebral edema.
- Abdominal – the symptoms of an “acute” abdomen progress. The child is diagnosed with vomiting, abdominal pain, and the urge to defecate.
With the abdominal form of anaphylactic shock, problems often arise with the correct diagnosis.
Which doctor is treating you?
The first medical procedures are carried out by an ambulance team, and their actions depend on the severity of anaphylactic shock, which determines the child’s condition.
If necessary, doctors also carry out resuscitation measures (artificial respiration, closed heart massage), after which they deliver the victim to the hospital. In a hospital, a child can be treated by a pediatrician or an allergist.
Diagnostics
Making a diagnosis is usually not difficult due to the characteristic clinical picture and usually a burdened allergic history.
Differential diagnosis can be carried out with myocardial infarction, intestinal obstruction, pulmonary embolism, cerebral hemorrhage, systemic mastocytosis, however, all of the above conditions are usually accompanied by an uncomplicated allergic history.
In the hospital, the child undergoes the following tests:
- collecting an allergy history;
- skin and patch tests (Path-test);
- blood test for total immunoglobulin;
- provocative tests.
The studies carried out make it possible to accurately determine the causative agent of the allergic reaction.
Complications and consequences of anaphylactic shock in children
The consequences of anaphylaxis in children are determined by how severe the process was and how long it lasted. The sooner first aid was provided, the better. Anaphylactic shock affects many organs, and complications in children may include:
- Non-infectious jaundice.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Arrhythmia and other myocardial disorders.
- Malfunctions in the central nervous system and vestibular apparatus.
- Swelling, bleeding in the brain.
- Intestinal bleeding.
Prevention measures
Predicting the development of anaphylactic shock is not easy, which requires:
- Prescribe medications with pronounced antigenic properties with caution.
- Be attentive to contraindications in the child. For example, if a child requires treatment with antibiotics, and the child is allergic to penicillin, semi-synthetic penicillins and cephalosporins should never be prescribed.
- Be careful when introducing complementary feeding and supplementary feeding to children with hereditary allergies. Each new product should be introduced every 5-7 days.
- Protect your child from swimming in cool water and prolonged exposure to low temperatures if he or she has a cold allergy.
- Cover the windows with mesh or install a mosquito net, keep the child away from apiaries to avoid insect bites.
- Carry out specific antiallergic treatment within the walls of a medical institution as a prevention of shock from diagnostic allergens.
The medical record of a child with a history of allergies should be kept at hand in order to remember all the substances that cause a hypersensitivity reaction in the child and to exclude contact with them.
about anaphylactic shock in a child
We present to your attention a video that explains what anaphylactic shock is, what statistics say about the prevalence of this condition, by what signs it can be recognized, and also how to properly provide first aid to the victim:
If you know that children and other family members have a tendency to immediate allergic reactions, it is recommended to have disposable syringes and anti-shock medications, and brief dosage notes in your home and travel first aid kit. Knowing first aid techniques can save your child's life.
Source: https://telemedicina.one/allergiya/anafilakticheskiy-shok-u-detey.html
What causes the development of anaphylaxis in a child?
Most often, anaphylaxis in children develops under the influence of contrast agents and chemicals. The reaction is caused by a weakness of the immune system and digestive tract.
Less commonly, shock indicates a food allergy or an insect bite. There are known cases of illness from cold.
Any drug can increase the body's sensitivity to the effects of an irritant and cause anaphylactic shock in a child.
Antibiotics are the first on the list of those drugs that provoke a reaction. Even the smallest and permissible dose can provoke a violent reaction in the body.
Introducing whey proteins or vaccines into the baby's body can provoke a negative reaction.
And their repeated use can cause severe anaphylactic shock. Mothers who took serious medications while carrying a child or breastfeeding increase the risk of developing allergies in their baby.
A child may have a reaction at the first interaction with an allergen. In this case, it does not matter at all what dose enters the body.
Genetic predisposition and the state of the immune system play a major role in the occurrence of anaphylaxis.
Food allergy shock is quite rare. In children, it occurs when there is an intolerance to certain foods, such as egg whites, milk or fish.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of developing anaphylactic shock, you need to follow some recommendations:
Parents of children with allergies should understand the danger of developing an emergency condition. Even if a child has other types of allergies - hay fever, eczematous dermatitis, you need to be wary of anaphylactic shock.
To prevent contact with an allergen, it is worth undergoing examinations with a specialist and identifying which substances cause an increase in the body’s sensitivity. Then you should avoid contact of the baby with a potentially dangerous allergen.
Children prone to allergies must adhere to a certain diet. Consumption of highly allergenic foods can provoke the development of sensitization and dangerous conditions. When introducing new products to the menu, it is worth maintaining a weekly interval, during which the portion of the dish is gradually increased. Parents should monitor the baby and at the first manifestations of an allergy, exclude the product from the diet.
Currently, there are many means that can drive away intrusive insects. But do not forget that an allergic child may react to the product itself, so it is better to put mosquito nets on the windows and not walk with the baby near apiaries.
Daily walks, exercise, hardening and proper nutrition will stimulate the normal functioning of the immune system and keep the baby healthy.
Signs of illness in your baby
When anaphylactic shock occurs in children, symptoms can manifest as anxiety, pain in the head and neck, and loss of balance.
Additional signs of an acute reaction:
- pale skin on the face;
- low blood pressure;
- noise in ears;
- excessive sweating;
- loss of consciousness.
Sometimes accompanied by urticaria. Abdominal pain, rapid and difficult breathing, a sensation preceding vomiting, and diarrhea appear. Foaming at the mouth and paroxysmal muscle contractions are possible.
Fainting during anaphylaxis can cause death within the next half hour. And if the functions of vital organs are impaired within 24-48 hours.
Quite often, a state of shock is accompanied by two phases. After the patient's condition improves, blood pressure decreases again.
There are several types of anaphylaxis. They depend on which organs suffered the most. The first is the typical form.
With it, blood pressure decreases, there is a disorder of consciousness, itching of the skin, shortness of breath and convulsions.
The hemodynamic form entails disorders of the cardiovascular system. Symptoms such as decreased blood pressure, chest pain and muffled heart sounds are observed.
The asphyxial variant has the following clinical picture: swelling of the upper part of the windpipe, bronchospasm, pulmonary edema. Shock develops due to food allergies.
Much less common is the cerebral type of acute allergic reaction. It affects the central nervous system.
It is characterized by an excited state of the patient, epileptic seizures, convulsions, and often the breathing and heart stop.
The clinic of an “acute” abdomen refers to the abdominal type of anaphylaxis. The patient is urgently taken to the operating table. With this type of anaphylactic shock in children, emergency care is an extremely important measure.
Prevention
Of course, it is much better to prevent a child from going into shock than to urgently correct a situation that could end tragically. Prompt and timely therapeutic measures aimed at the root cause of the disease will significantly reduce the risk of developing a serious form of shock.
Few parents do not know about allergic reactions and have not seen their manifestations in practice. Allergies can occur in various forms and can be expressed by a small rash, runny nose or a serious condition - anaphylactic shock, requiring immediate treatment.
Although an emergency condition is rare, all parents should know the signs indicating the development of a terrible disease. It is important to understand what actions can protect the baby from serious consequences or even death. After all, it is difficult to predict anaphylaxis, and the situations in which it occurs can be non-standard and unpredictable.
How to help your baby with anaphylaxis
What to do in case of anaphylactic shock in a child and how to provide first aid? This question primarily worries parents who are faced with trouble.
At the first symptoms of anaphylaxis, emergency care must be provided.
The first step is to stop administering the drug that caused the negative reaction. The area above the injection or bite should be tied with a tourniquet.
Inject a 0.1% solution of adrenaline into the area of the bite or injection. The dose depends on the age of the child. For one year of a child’s life there is 0.1 ml of the substance. You need to place a cold object on this area.
One of these drugs is immediately administered: Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone or Dexasone. It is necessary as a hormone of the adrenal cortex.
Any medical institution has anti-shock kits in its arsenal. Just as the baby’s life depends on eliminating shock.
If there is no medical center nearby, the patient should be laid down and his legs elevated. Accordingly, lower your head a little and turn it to the side so that the victim does not swallow vomit.
A mandatory measure is to provide the child with warmth and fresh air.
In cases where medications are powerless, a number of important measures must be taken.
These include inserting an endotracheal tube into the trachea, maintaining air circulation through the lungs using artificial respiration, and performing resuscitation measures.
The prognosis depends on the prompt provision of medical care and the form of anaphylaxis. With the right algorithm of actions, it is much easier to cope with the disease.
But it is worth remembering that you should not rely on such an indicator as high blood pressure. It is necessary to provide anti-shock measures until blood circulation is restored.
How does it arise?
When an allergenic substance enters the body, a violent allergic reaction develops. It only takes a few minutes to get started. In response to the entry of a foreign biological agent into the body, the cells of the immune system are activated. They begin to produce a huge amount of biologically active substances.
These components cause a strong constriction of blood vessels, which, in turn, leads to a decrease in pressure and impaired consciousness. This reaction is primarily defensive in nature. The body seems to be trying to limit the systemic spread of the allergen through the bloodstream. However, with severe sensitivity to the allergenic substance, a critical condition may develop.
During an allergic systemic response, the body produces a huge amount of a specific protein - immunoglobulin E. The higher its content in the body, the more pronounced and rapidly the symptoms will increase.
In newborns, adverse symptoms of shock develop rapidly. This condition is very dangerous and requires immediate hospitalization of the baby in a hospital.
Preventing a possible negative reaction
It is very difficult to prevent the development of a negative reaction of the body. The prescription of antigen drugs should be accompanied by great caution.
If a child has a reaction to penicillin, then the use of drugs in this category is strictly prohibited.
Every parent must know that a baby with a hereditary allergy must adhere to a special diet. During the complementary feeding period, each new product should be introduced no more than once a week.
If children have a cold allergy, they are prohibited from swimming in cool water and staying outside for long periods of time in winter.
If your child may have anaphylaxis from an insect bite, then a necessary preventive measure will be to limit the child from places where flowering plants and apiaries accumulate.
As well as protecting windows and vents with special mosquito nets.
If there is an allergy sufferer in the house, the first aid kit should always contain means to relieve acute symptoms.
These include syringes, anti-shock drugs and antihistamines to help a child with anaphylactic shock.
You can partially stop the attack yourself; at the same time, it is recommended to call an ambulance.
First aid
In order to prevent the development of dangerous consequences of an allergic critical condition, use the following algorithm of actions:
Lay the baby horizontally and elevate the legs. This position will help improve blood flow to vital organs: the heart and brain.
If your child has dental guards, remove them as they may cause aspiration if they vomit.
Open doors and windows wide to improve the flow of fresh air into the room.
If the baby loses his breath and is not breathing, begin artificial respiration.
Monitor your pulse. If there is no pulsation in the carotid arteries, which are located in the neck, place your hands on the chest and begin artificial heart massage.

Urgent Care
Children with anaphylactic shock are treated immediately. Emergency treatment begins with the ambulance team. The child is given humidified oxygen. If there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure, children are given cardiopulmonary resuscitation measures.
In difficult cases, when the heart rhythm is not efficient enough or there are signs of vascular insufficiency, adrenaline is used. The dosage of this drug is selected taking into account the baby’s age and weight.
To eliminate adverse symptoms, injectable forms of antihistamines are used. To normalize blood pressure and stop the allergic reaction, prednisolone is administered. To stabilize the baby’s condition, intensive infusion therapy is administered with the introduction of large amounts of isotonic solutions or glucose.
The provision of qualified assistance is carried out in a hospital setting. If the baby is in a critical or serious condition, go to the intensive care unit. If the child is unconscious or in a coma, then he is given massive infusion treatment using a whole complex of various medications.