Classification of the disease
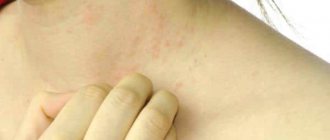
Seborrheic dermatitis or seborrhea is a common disease. Although it is caused by a yeast-like fungus, it is not infectious. This skin disease is associated with the inflammatory process of that area of the human body where many glands that produce subcutaneous sebum are located. Most often these are areas covered with hair: the head, eyebrows, behind the ears, upper lip, axillary, cervical, inguinal folds. Less often - between the shoulder blades, on the surface of the chest.
When a large amount of sebum is suddenly secreted by the glands, the number of microorganisms in this area increases, the skin becomes inflamed, causing peeling and itching.
The origin of seborrheic dermatitis can be:
- Inherited - transmitted from parents or one of them, the tendency of the sebaceous glands to produce excess amounts of fatty secretion;
- Acquired - a malfunction of the immune system, deviation from the norm in the functioning of the digestive system, brain vessels, leads to activation of the sebaceous glands, with a simultaneous deterioration in the quality of the secretion produced.
Reasons for appearance
In rare cases, seborrheic dermatitis is a congenital pathology, that is, a consequence of genetic predisposition. But more often, dermatologist patients become people with acquired disease. Various factors can provoke a decrease in immunity and excessive secretion of sebum. These include:
- puberty,
- hormonal disruptions accompanied by a decrease in estrogen levels while maintaining or increasing the concentration of androgens and progestins (ovarian inflammation, menopause, seminoma, androsteroma, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, obesity),
- unhealthy diet with excess fat, salt and spices,
- smoking and drinking alcohol in large quantities,
- infectious processes in the body,
- immunodeficiency states (with HIV infection, helminthic infestations, diabetes mellitus),
- taking medications (immunosuppressants, Cimetidine, Fluorouracil),
- stress,
- lack of sleep, overwork,
- sweating, wearing warm clothes,
- pathologies of the endocrine system and gastrointestinal tract, metabolic disorders,
- mental disorders accompanied by malfunctions of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus (schizophrenia, epilepsy, MDD).
External factors can also contribute to the manifestation of seborrhea on the body: low temperature and humidity, climate change, irregular hygiene procedures, the use of alkaline skin care products, laser and acid peeling.
Types of seborrheic dermatitis
Human sebum is a specific mixture secreted by special fatty glands, consisting of carboxylic acids with various radicals, fats and proteins that ensure the normal functionality of the skin. When the glands are functioning stable, the secreted secretion performs a protective function: it softens and moisturizes the skin, creates a protective film with antibacterial properties, and protects the skin from drying out.
Traditional medicine distinguishes 3 types of seborrheic dermatitis.
Oily seborrheic dermatitis
The disease most often occurs during puberty in boys and girls due to an imbalance of male and female sex hormones in the body, and can manifest itself in thick and liquid form.
The thick form is more typical for males. The scalp of teenagers thickens, loses its childhood elasticity, and the hair becomes coarser. During this period, in boys, the secretion of the sebaceous glands and the exfoliated part of the skin form a layer of thick, oily dandruff, which clogs the glands and sticks to the hair. By the age of 28, the symptoms of oily seborrheic dermatitis in men disappear.
The liquid form is typical for girls during puberty. Hair always feels damp and greasy even after daily washing. Itchy skin and thinning hair appear.
Dry seborrheic dermatitis
It is more common in children and adolescents under 15 years of age. Deviation of sebum production by the sebaceous glands due to the viscosity of the secretion helps to slow down its release from the sebaceous ducts. In this case, insufficiently moisturized areas of skin appear on the face or head, which itch and flake. Hair loses its natural elasticity, shine, becomes brittle and brittle.
Mixed seborrheic dermatitis
This form of dermatitis most often affects adult men. The disease has symptoms of both dry and oily forms. The scalp visually has an oily appearance, while the face has the complete opposite: dry, cracked and flaky skin.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of dermatitis are as follows:
- Dandruff. This is the main sign of the disease, which signals that something is wrong with the scalp. Hair loss occurs due to dandruff. Some scales may stick to the skin, while others may remain on the hair.
- Skin irritation. Spots with distinct edges appear on the head. As the disease develops, these islands gradually begin to dry out, heal, and crusts form on them. This phenomenon is caused by the activity of a fungal infection.
- Swelling. When the disease moves to those areas where there are folds, swelling appears. With scalp dermatitis, this manifestation is observed when the skin in the ear area is affected.
- Peeling. As the skin heals, severe peeling begins. It is accompanied by itching that does not stop even for a short time. This happens due to the rapid rejection of cells.
- Scales. This symptom is observed from the first days of the onset of dermatitis. The scales gather on the head like a crown. This clinical sign is observed due to the impregnation of dry areas with sebum. With the onset of pathology, there are few scales, they are white. As the disease progresses, they become more numerous and turn yellow.
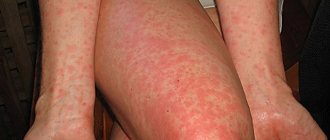
- Skin rashes. When an infection occurs, a rash appears on the scalp. It usually has watery contents, but purulent pimples are not uncommon.
The root causes of the development of seborrheic dermatitis
The fungus that provokes the development of the disease is inherent in every person. And only under favorable circumstances for its reproduction, a decrease in human immunity, does it begin to actively develop, provoking the evolution of seborrheic dermatitis of the skin. The decrease in the immune defense of the human body is influenced by external and internal circumstances.
| Circumstances | Relapse |
| Domestic | Inherited pathogenesis |
| Violation of fat metabolism in the body as a result of liver disease, digestive system | |
| Obesity, diabetes | |
| Chronic diseases | |
| Specific diseases of the nervous system | |
| HIV AIDS | |
| External | Poor nutrition (abuse of spicy foods, spices, smoked meats, marinades, sweets) |
| Severe, frequently repeated stress | |
| Abuse of alcohol-containing cosmetics | |
| Overheating, visiting countries with hot climates, alcohol abuse | |
| Damage to the skin by scratching, abrasions with the possibility of dust and dirt getting into the wounds |
If the main cause of the disease is correctly identified, seborrheic dermatitis on the head and face is cured completely, with a small percentage of reoccurrence.
Seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious, since the disorders are caused by internal factors of the proper functioning of organs and systems.
Course and prognosis
Seborrheic dermatitis occurs cyclically. The period of exacerbation of the disease is replaced by a period of relative well-being, after which the patient’s condition worsens again.
Despite the possibility of reappearance of rashes caused by a fungal infection , in most cases the prognosis is favorable, since with the help of modern techniques and effective medications the patient has the opportunity to prolong remission as much as possible and reduce the severity of symptomatic manifestations.
Pathology of seborrhea of facial skin
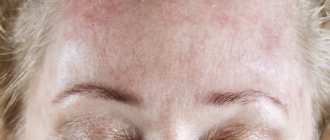
Symptoms of the disease on the face appear gradually, the initial sign is the appearance of small foci of scales on the face with a gradual increase in their number. The skin in these places becomes pink, and the scales become white with a grayish or yellowish tint.
In a more serious clinical case, peeling skin with profuse redness is observed on the forehead, eyebrows, around the nose and is accompanied by itching.
As noted above, seborrheic dermatitis is characteristic of adolescence during puberty. But often adults are also susceptible to this disease, in whom the functioning of the sebaceous glands occurs due to:
- Malignant and benign neoplasms in the endocrine system, when changes in the endocrine balance occur in the human body;
- Schizophrenia, epilepsy or infection of the nervous system;
- Excessive use of hormonal drugs;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Overwork and being in a prolonged state of stress;
- Acute gastrointestinal disease;
- Vitamin deficiency, violation of diet and caloric intake;
- Long-term infectious diseases.
The appearance of acne, including white subcutaneous acne, rapid greasy hair, even after washing, abundant secretion of sebum on the face, increased sweating of the hands - the first signs of oily seborrheic dermatitis.
Unstable functioning of the sebaceous glands of the face leads to dry skin, increased drying out, and the protective layer of the skin disappears. The outer layer of skin begins to burst, small scales appear, which are called dandruff on the face, they cause redness, constant itching and burning. Excessive dryness of the facial skin provokes a decrease in the supply of nutrients to the hair, which begins to fall out. Such signs indicate a dry form of seborrheic dermatitis.
In the described cases, it is recommended not to take any medications or procedures on your own, but to consult at a medical institution with an endocrinologist or dermatologist, who, based on the tests performed, will prescribe treatment.
Prevention
In order to prolong the period of remission and prevent the development of seborrhea, it is worth taking preventive measures. First of all, you need to maintain personal hygiene and not harm your hair by washing too often. It is also important to eat right, trying to include as many fiber-rich vegetables and fruits into your diet as possible and limiting sugary and canned foods. Fermented milk products allow you to maintain a healthy intestines and stomach every day. Since it is gastrointestinal diseases that provoke seborrheic dermatitis, this is a good prevention.
Do not overheat the scalp or overcool it. This can trigger the development of dandruff. It is also worth fighting chronic foci of infection.
It is worth giving up alkaline shampoos with fragrances and dyes and choosing hypoallergenic hygiene products. The comb should have round, blunt teeth. You cannot use other people's combs, towels, or hats. After washing, it is best to blot your hair rather than vigorously dry it.
It is extremely important to deal with stress. Yoga, sports, daily walks, meditation, and relaxing treatments will help. In some cases, psychotherapy is indicated.
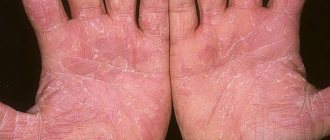
Dry seborrheic dermatitis on hands
Dry seborrheic dermatitis on the hands is a fairly common disease. Damage to the sebaceous ducts on the hands causes excessive dryness of the skin, which in turn leads to cracking. This may be the result of the use of household chemicals, exposure to changes in outside air temperatures, or the lack of a sufficient number of sebaceous glands on the hands.
The main cause of the disease is yeast fungi, which penetrate into the cracks formed in the dermis and enter an environment favorable for development. They begin to actively multiply, causing inflammation of the skin. Under natural conditions, the human immune system prevents their development. But under the influence of certain factors, it weakens, which is immediately used by yeast-like fungi.
Factors that contribute to a decrease in the action of the human immune system and an increased risk of dry seborrheic dermatitis on the hands:
- Diseases of the system regulating the activity of human internal organs (thyroid gland, obesity of any kind, insufficiency of insulin production in the body);
- Disorder of the metabolic process in the body at the cellular level;
- Pregnancy, menopause – in women, puberty – in adolescents;
- The period after surgical treatment of the abdominal cavity, when there is a decrease in the action of the immune system;
- Ovarian diseases in women;
- Immunodeficiency diseases caused by a violation of the body's defense mechanisms (HIV, cancer, tuberculosis).
Women are more susceptible to this disease. And not only because they wash dishes or do laundry using household chemicals more often. The World Health Organization believes that a stressful condition, nervous shock or depression, even an emotional outburst, contribute to a short-term loss of the body and its immune system’s ability to resist yeast-like fungi, which quickly multiply and disrupt the functioning of the fat glands on the hands. Winter temperature changes (frost outside - warmth in the apartment) contribute to inflammation of the skin of the hands.
Excessive and unusual dryness of the hands, a constant feeling of discomfort, should be alarming. And if severe itching appears, redness on the back of the hands, peeling of the skin, ever-increasing red spots and lesions, the first sign is to consult a dermatologist. In some cases, self-medication leads to the formation of ulcers on the hands and the prospect of unpleasant complications.
Description
The risk of the disease directly depends on two factors: immunity and sebum secretion . This dependence determines the fact that seborrheic dermatitis cannot be classified as an infectious disease. Fungi that provoke an inflammatory reaction and peeling of the epidermis (Pityrosporum orbiculare and Pityrosporum ovale from the genus Malassezia) are opportunistic and are part of the normal microflora of human skin.
Active reproduction of yeast fungi leads to the fact that they concentrate around the ducts of the sebaceous glands and use the secreted secretion as a source of nutrients. Excessive sebum secretion aggravates the problem.
By processing triacylglycerides from the secretions of the glands, fungi leave waste products - unsaturated fatty acids. Some of them can cause inflammation, irritation and peeling of the skin. As a result, the protective function of the skin is weakened, facilitating the further spread of pathogens.
If the epidermis is damaged and cracks appear, a bacterial infection can join the fungal infection, causing even greater irritation and damage to the skin.
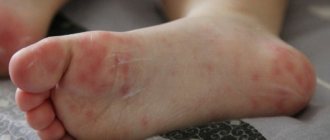
Seborrheic dermatitis in children
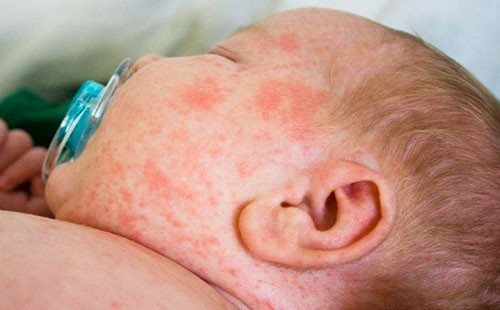
Flaky or greasy, “milky” crusts – childhood seborrheic dermatitis. It can appear quickly after birth not only on the baby’s head, but also on other parts of the body rich in sebaceous glands. There are several reasons for the occurrence of the disease: genetic predisposition or improper hygiene.
Features of the appearance of seborrheic dermatitis in children
Most pediatricians are inclined to believe that the remaining maternal hormones in the child’s body after birth provoke increased activity of the glands, including the sebaceous ones. The result of their active activity is a rash, redness and greasy crusts. In this case, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician for timely initiation of treatment. The advanced form is much more difficult to treat, and complications may arise.
One of the main causes of skin inflammation is yeast, which can become active on children's skin when the immune system is not yet fully formed.
In addition to the above reasons, the appearance of inflammation of the skin of a child of any age is caused by:
- Unnatural increased sweating caused by excessively wrapping the child or taking a certain category of medications;
- Problems with the digestive system due to poor nutrition;
- Poor child hygiene: infrequent washing, use of detergents for personal use (soap) and for washing (powders), which have an irritating effect;
- Genetic inheritance, when one or both parents have dermatitis.
As a rule, childhood seborrheic dermatitis is completely cured in the first months of life. In some cases, the disease recurs at 3-4 years of age, but much less frequently.
There is a good expression in the medical community: a disease is a missed opportunity for its prevention. It is perfect for newborn babies. After all, the prevention of childhood seborrheic dermatitis must be addressed from the first days of pregnancy for the expectant mother. To do this, you just need to give up bad habits, be attentive to your health and that of your unborn baby, regularly undergo examinations by qualified doctors, and lead a healthy lifestyle. After the birth of a child, strict adherence to hygiene rules by all family members; the baby should be examined daily. At the first visual deviation, visit a doctor and follow all his recommendations for care. There are certain periods for the start of feeding with vegetable and meat compositions. Their implementation is the key to the child’s health, including good skin condition.
Rough skin on the elbows: photos, possible diseases
The skin performs a protective function, protecting the human body from adverse external influences.
And the stronger this impact, the more the skin suffers. In addition, the deterioration of his condition is caused by various diseases, both systemic and skin. The condition and functioning of internal organs and their systems is also reflected in the quality of the skin.
Therefore, rough skin on the elbows may be the result of such reasons as:
- dermatological diseases;
- fungal and bacterial infections;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- metabolic disorders;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- anemia;
- dehydration;
- irritation;
- high load on the elbow bends.
One of the indirect causes of local coarsening of the epidermis is also improper skin care. When applying emollient creams and moisturizers, attention is often paid to the hands and face, bypassing the neck, décolleté and elbow creases. Meanwhile, nutrition is necessary for all parts of the body, without exception.
Symptoms and signs of dermatitis
Dermatitis is a general concept that represents irritation of the epidermis. This process may be based on various reasons, depending on which one or another type of dermatitis is determined, for example:
- allergic – occurs in response to contact with an allergen;
- contact – is a consequence of irritant (physical, chemical or biological) effects;
- seborrheic – has a fungal nature;
- atopic – chronic, the most complex form.
Of course, the method of treatment and its prognosis entirely depend on the form of dermatitis. To determine it, it is necessary to conduct a series of laboratory tests.
However, external signs and the nature of the process can also help a lot.
For example, if the skin on one elbow is rough and the other is completely normal, it means that the impact was directed, most likely external, since a violation of internal processes would have a bilateral reflection.
Dermatitis in the elbow area, as in other parts of the body, is characterized by a change in the condition of the skin.
Signs of peeling appear on the affected areas, itching, sometimes burning, and swelling may occur. This type of phenomenon often exhibits a cyclical pattern.
For example, in the cold season, dermatitis worsens, but in the summer, on the contrary, it is almost unnoticeable. Appearing in the elbow area, dermatitis usually has the following symptoms:
- severe itching and burning of the affected area;
- sometimes papules and scars remaining after them;
- pain, necrosis;
- red spots on the body;
- rough skin on the elbows;
- thickening of the epidermis;
- cyanosis.
The chronic course of dermatitis can lead to partial or complete loss of sensitivity of the affected area, in the most severe cases even to skin atrophy. In many ways, the severity of this reaction depends on the hereditary predisposition to it.
It is impossible to remove such a reaction by peeling and applying emollients. In this case, treatment is required, which is selected individually. The primary condition for its effectiveness is the elimination of the irritating factor. Then the patient is prescribed conservative therapy, including the use of local and, if necessary, systemic drugs.
Rough skin on elbows photo
Another disease that causes rough skin on the elbows is psoriasis. At the initial stage, this disease is localized mainly in the area of the elbows, knees, feet, palms, and scalp. However, if left untreated, the disease can spread over large areas, affecting other parts of the body.
In addition to a hereditary predisposition to this disease, as well as some individual characteristics of the body, psoriasis can occur for the following reasons:
- decreased immunity;
- use of certain medications;
- severe/prolonged stress;
- traumatic effect on the skin.
Treatment of psoriasis in each individual case is prescribed individually. The same drugs can be extremely effective for some patients and completely useless for other patients. Therefore, the principle of treatment depends on the individual skin reaction to the drug used.
It is also important to remember that self-medication for psoriasis can lead to complications of the situation, especially with regard to the use of hormonal drugs. In this case, it is necessary to strictly follow the established treatment regimen and not stop it too abruptly. You should also know that, unfortunately, it is impossible to cure psoriasis completely.
The disease will periodically make itself felt. But it is quite possible to increase the remission period.
Source: https://nakozhe.com/shershavaya-kozha-na-loktyah.html
How to get rid of seborrheic dermatitis
The effect of seborrhea treatment is not always achieved quickly, but with some effort after an accurate diagnosis. Since seborrheic dermatitis is easily visually confused with other dermatological diseases, it is necessary to conduct appropriate analyzes of the scraped crust or husk.
Simultaneously with the determination of the pathogenic bacteria, it is necessary to analyze the “population” of the intestines for the presence or absence of beneficial microflora. The fact of the presence of stagnant infectious foci in the body, stagnation of bile, is being studied. In some cases, it is necessary to conduct a blood test for hormones.
After laboratory determination of the name of the bacterium, guided by additional research, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Modern treatment methods comprise a complex of measures:
- Use of antifungal drugs. As it turned out from the results of the practice of using hormonal antifungal ointments, which provide a quick but short-term cure, with subsequent resumption of the disease in a more severe form;
- Preparations based on birch tar, salicylic acid, zinc and selenium give positive results, but require strict use as prescribed by a doctor;
- Strengthening the immune system through dosed sunbathing, playing certain sports, and replenishing the body with vitamins of natural origin;
- Strict adherence to the diet, excluding sweets as much as possible;
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules. The use of moisturizing creams, lotions with aloe extract, eucalyptus has a beneficial effect on well-being.
In some cases, seborrhea is allergic in nature. Therefore, by eliminating the consumption of chocolate, nuts, cow's milk, strong tea and coffee, the intake of natural allergens into the human body is significantly reduced. It is not recommended to eat spicy, fried foods, spices and smoked foods.
A separate line should be noted about the effect of drinking alcoholic beverages during an exacerbation of the disease. As practice shows, it is alcohol that is responsible for a sharp exacerbation of the disease and interferes with effective treatment.
Share with friends
Rate this article
Treatment
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis is long-term, since the disease is chronic. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor after making a diagnosis and excluding other diseases. Diagnostics includes dermatoscopy, spectral examination, assessment of the patient’s hormonal status, and blood tests. The following diseases need to be excluded:
- atopic dermatitis,
- psoriasis,
- pityriasis versicolor,
- impetigo,
- candidiasis,
- dermatophytosis.
Therapeutic measures are aimed at restoring the skin and eliminating the main cause of the disease. Treatment involves normalizing the food intake, following a hypoallergenic diet, using antihistamines, antifungal drugs, and glucocorticoids. Keratolytic medications in the form of ointments, creams or gels are very often used.
For dermatitis of the scalp, antifungal drugs are used (Ketoconazole, Nizoral, Skin-Cap).
They are recommended to be used in the form of shampoos or ointments. These medications allow you to suppress the activity of fungi, reduce the production of sebaceous secretions, and remove crusts from the surface of the skin. Local antiseptics (tea tree oil, zinc paste) have a good effect.
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. Shampoos are used for 2-4 weeks. To soften and better remove crusts, exfoliating agents are prescribed. This group includes salicylic and zinc ointments. Treatment of facial skin dermatitis includes the use of medicinal cosmetics, antifungal ointments or lotions (Mikospor, Nizoral), immunostimulants. In severe cases, hormonal ointments are prescribed.
Elokom is a hormonal drug. If external medications are ineffective, systemic drugs are used. These can be antifungal drugs based on ketoconazole, clotrimazole, itraconazole and fluconazole, antihistamines (Loratadine, Zyrtec, Clemastine), steroids (Beclomethasone, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone). In case of penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the skin, antibiotics (tetracyclines, Metronidazole) are indicated.
Shampoos for dry seborrhea
Treatment of dry seborrhea on the scalp will not be effective without proper hygiene. Today there are a lot of anti-dandruff shampoos, some advertised and some not so well advertised. For seborrhea, several types of detergents are used.
- Antifungal (contains ketoconazole, ciclopirox, zinc pyrithione).
- Keratolytic (contain salicylic acid, ichthyol and sulfur).
- Antibacterial (contains octoprirox and crimbazole).
- Anti-inflammatory (contain zinc pyrithione, mint or menthol extracts).
Medicinal anti-dandruff shampoo should be purchased at a pharmacy. The concentration of the active compound in it should not be less than 2%. The most famous effective shampoos against seborrhea:
- Nizoral and Dermazol with ketoconazole.
- "Sebipirox" with ciclopirox.
- "Keto-plus" with ketoconazole and zinc pyrithione.
- "Sulsena" with selenium sulfide. This component affects cell regeneration processes.
To achieve a positive effect, the detergent is used at least twice a week for two months.
Products do not have to be applied over the entire length of the hair. It is important to thoroughly wash the scalp and roots with a medicated shampoo. The rest of your hair can be treated with regular mild shampoo.

"Keto-plus" contains ketoconazole and zinc pyrithione