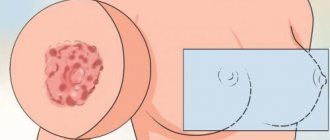
Seborrheic dermatitis does not pose a serious danger to the patient, but from an aesthetic point of view, seborrhea looks unpleasant.
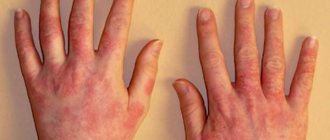
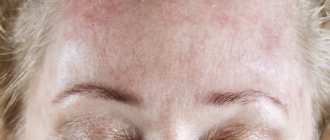
As a rule, it is chronic and appears not only on the scalp, but also on the face. In this case, redness of the skin, rash and the formation of seborrheic crusts are observed. The rash is characterized by severe itching, so many patients have a completely natural question: is seborrheic dermatitis contagious? In order to find out the routes of infection, it is necessary to know the etiology, development factors and symptoms of the disease.
Mechanisms of development and symptoms of the disease
The main causes of seborrheic dermatitis include:
- individual susceptibility of the body;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- emotional and nervous stress;
- eating disorders;
- unfavorable environmental situation in the patient’s region of residence;
- hereditary predisposition;
- increased sensitivity of the immune system.

It should be noted that any dermatitis has typical symptoms, regardless of the factors that caused its exacerbation.
How to treat seborrhea of the scalp?
Due to the multifactorial nature of the presented pathology, its therapy should be individualized and fully consistent with the physiological characteristics of the patient. Comprehensive general treatment of seborrhea of the scalp:
- renunciation of any harmful addictions;
- diet correction;
- elimination of stress and depressive conditions, stabilization of the psychological background;
- limiting negative effects on curls, including thermal styling;
- selection of suitable hygiene and care cosmetics;
- physiotherapy.
Sometimes seborrhea of the scalp improves and even disappears for a long time after applying the listed recommendations. If the above tips do not work, you need to contact a dermatologist and trichologist, undergo an examination and strictly follow the doctors’ instructions. Depending on the form of seborrhea and its severity, doctors prescribe complex therapy:
- systemic medications;
- local remedies;
- special shampoos;
- alternative recipes.
Classification of dermatitis
The most common are contact (simple), allergic, atopic and seborrheic dermatitis.
CONTACT. This type of disease is caused by aggressive exposure to external irritants (acid, alkali, ultraviolet radiation, etc.). It is NOT SPREAD from person to person.
ALLERGIC. Develops as a result of exposure to an irritant on an organism predisposed to allergies. Like other forms of dermatitis, allergic dermatitis CANNOT BE TRANSMITTED BY CONTACT, and therefore does not pose a danger to other people.
ATOPIC. Atopic dermatitis is an allergic disease and is TRANSMITTED BY INHERITANCE. However, it should be understood that it is not the disease that is transmitted genetically, but the tendency to develop it. Atopic dermatitis does not have an infectious path of development, therefore it is not transmitted through direct contact.
INFECTIOUS. This form of the disease, like others, despite being classified as infectious dermatitis, is safe for healthy people. The question is that this type of disease is quite often provoked by various infections, which can easily be transmitted from person to person. In other words, when a healthy person comes into contact with a patient who has been diagnosed with infectious dermatitis, TRANSMISSION OF VIRUSES AND INFECTIONS of the immediate cause of the disease MAY OCCUR.
Prevention of seborrhea of the scalp
If there is a genetic predisposition to this pathology, it is difficult to prevent or completely cure. Adequate prevention of seborrhea consists of minimizing any factors that can disrupt the normal functioning of the sebaceous glands. Experts advise:
- Eat a balanced diet, giving preference to foods high in vitamins.
- Introduce brewer's yeast into the diet (in courses).
- Choose high-quality, hypoallergenic and non-comedogenic care cosmetics for the scalp.
- Avoid emotional turmoil.
- Monitor the balance of estrogens and androgens.
Can you get seborrheic dermatitis?
Despite the fact that medicine does not stand still, today there is no single factor contributing to the development of the seborrheic form of the disease.
This form of the disease is provoked by endocrine and trophic disorders associated with hypersecretion of the sebaceous gland, which is manifested by rashes in the face and scalp. The main factors in the appearance of the seborrheic form of the disease are fungal spores pityrosporum. However, for negative symptoms to occur in the head area, first of all, the patient’s immune system must be weakened. This is the main condition for the development of this disease.
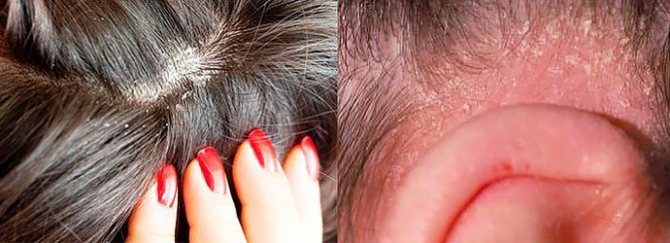
Patients with seborrheic dermatitis who are wondering whether the dermatitis is contagious should know that this disease has NO CONTACT ROUTES OF TRANSMISSION. It is not able to move from a sick person to a healthy one during a handshake, kiss, etc., so it does not involve isolating the patient from the people around him. The patient should only adhere to a hypoallergenic diet and strictly follow medical prescriptions.
Treatment methods
You can treat seborrhea at home. But it is advisable to first confirm the diagnosis and differentiate the disease from systemic lupus erythematosus, rosacea, psoriasis, and dermatophytosis. Only a dermatologist can do this. Based on the initial examination and laboratory tests (microscopic examination of scale scrapings and bacteriological culture), he will accurately determine the patient’s health status. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment is selected taking into account the localization of the pathological process.
A set of measures for the treatment of the scalp:
- The patient is recommended to adhere to a restrictive diet and consume foods high in zinc, selenium, vitamin A, PP, B and C).
- Antifungal agents are prescribed: gels or shampoos (Dermazol, Nizoral, Cynovit, Danex).
- When washing your hair, it is advisable to use tar soap or tea tree oil.
- It is imperative to eliminate the provoking factors that gave impetus to the development of pathology.
Such treatment reduces the number of fungi and sebum produced, and removes scales. To achieve an effect, the duration of treatment should be two weeks.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the skin of the face and back begins with eliminating the provocateur factor. Then therapeutic tactics are applied that eliminate the main symptoms of skin pathology.
For oral administration the following are prescribed:
- antibacterial drugs (Doxycycline),
- antihistamines (Telfast, Loratadine),
- multivitamin complexes (Multitabs, Alphabet).
For external treatment the following is prescribed:
- antifungal ointments (Ketodine, Bifasam),
- hormonal creams (Elocom),
- immunomodulators (Protopic, Elidel).
If seborrheic dermatitis affects the skin of the eyelids, wash the eyes with antiseptic solutions and treat the affected areas with antibacterial ointments.
Next entry »
- antibacterial drugs (Doxycycline);
- antihistamines (Telfast, Loratadine);
- multivitamin complexes (Multitabs, Alphabet).
- antifungal ointments (Ketodine, Bifaces);
- hormonal creams (Elocom);
- immunomodulators (Protopic, Elidel).
Prevention of dermatitis
Of no small importance in preventing unpleasant manifestations in the head and face area is the prevention of the development of seborrheic dermatitis. As a rule, there are no special obstacles or difficulties to comply with it.
- The patient must maintain personal hygiene and give up the bad habit of squeezing pimples. If the skin is oily, especially in the scalp area, it is recommended to use drying cosmetics. Men should give up beards and mustaches.
- It is important to follow a diet, consuming large amounts of plant fiber and vitamins. Perform hardening procedures accompanied by an active lifestyle. In addition, it is important to avoid nervous tension in the body, as very often this leads to an exacerbation of the process.
It must be remembered that treatment and timely prevention of the disease should be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician, which allows for a longer remission.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a harmless disease. It brings other problems, in particular, aesthetic and psychological ones. The rashes appear on the neck, face and scalp and are very noticeable. People around perceive the external symptoms of seborrheic lesions with caution and often try to reduce contact with patients for fear of becoming infected. Therefore, both the patient and the people around him are concerned about the question of whether seborrheic dermatitis is contagious or not.
How to recognize dermatitis
Seborrhea is localized in the scalp, flaking or forming a dense, scaly crust. Bacteria also affect the hair itself, thinning it and ultimately leading to baldness. In an advanced stage, dermatitis begins to progress, the size of the red areas increases, the scales become denser and begin to flake more strongly.
The disease often occurs in children aged 3-6 months. Symptoms subside after the baby stops receiving breast milk. The reason for this is simple - a large amount of hormones in mother's milk.
Rashes with childhood dermatitis have clear boundaries, the skin is diffuse, covered with crusty red flaky scales. They usually do not cause itching or discomfort and can be treated well. The main thing is to adjust the baby’s diet, and in a couple of months the dermatitis will go away.
According to some people, dermatitis is preceded by a fungal infection. These facts should be refuted. The fungus is not contagious and is normal for everyone. With stress, hormonal imbalances, and decreased immunity, a favorable environment appears for the proliferation of this fungus, which begins to actively develop in places where the sebaceous glands accumulate. The disease is not transmitted through contact of another person with the affected areas.
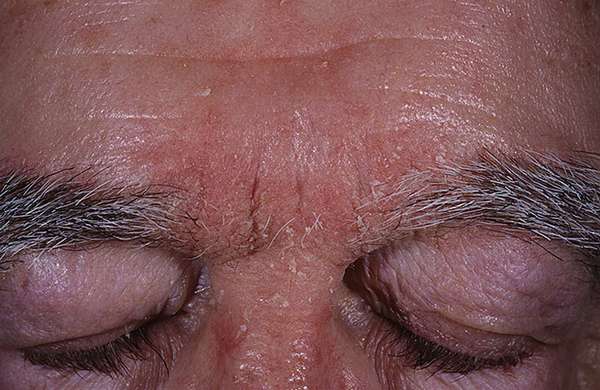
Infection does not occur through contact with other types of dermatitis; this is just the body’s predisposition to its development.
The fungus cannot be transmitted by airborne droplets and is not contagious by shaking hands.
- unfavorable ecology;
- unhealthy diet, lifestyle;
- individual characteristics of the body;
- constant stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- features of the immune and nervous system.
The fungus spoils a person’s appearance, and strangers are afraid to come into contact with the sick person. But the disease is not transmitted in any way.
Dermatitis is treated individually, since the nature of its occurrence is different, and it also all depends on the course of the disease; with the wrong approach, this threatens a person with baldness. It is important to identify the source of excitation of this infection and treat existing stomach diseases.
To normalize the nervous system, the patient is prescribed bromine and valerian. To strengthen the protective functions - vitamins A, B, C. It is possible to prescribe female sex hormones and other drugs to suppress male hormones, the predominance of which often leads to an outbreak of the disease.
Preference should be given to water procedures, ultraviolet irradiation, and exposure to the sun. As an antifungal therapy, human hair is treated with shampoos containing zinc, tar, and ketoconazole. You should wash your hair 2 times a week and use shampoo for 1-2 months until the unpleasant symptoms disappear.
Antibiotics can only be used with the permission of a doctor. Taking them can lead to disruption of the microflora, colonization of spores, and atrophy of the epidermis.
It is important to eliminate the causes that provoked the development of the disease. In case of increased cholecystitis, it is recommended to drink Essentuki mineral water, and Allochol for a month.

For oily dermatitis, patients are prescribed valerian, motherwort tincture, bromine, calcium chloride, vitamin B, B12.
For dry dermatitis, hormonal drugs and vitamin A are prescribed.
When seborrhea appears, it is important to eat right. You should not eat chocolate, sweets, honey, sugar, hot or spicy foods. It is better to eat vegetables, fruits, and boiled meat. The diet should not contain a large number of calories, which lead to increased sebum secretion and skin rashes.
It is good to wipe the skin with alcohol solutions that contain sulfur, resorcinol, and salicylic acid.
When the disease subsides, physiotherapy, cryomassage, and darsonvalization are effective for drying the skin under the influence of high-frequency currents. Under the influence of current, the nervous system calms down, adrenaline and testosterone return to normal. Ultraviolet irradiation can achieve stable, long-term remission.

The patient's clothing should be cotton, which does not cause skin irritation.
In case of skin rashes, especially in children, you should immediately consult a doctor, who will prescribe treatment that is more effective and correct, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the causative agents of infection.
Seborrheic dermatitis is not an infectious disease; it can be avoided by following the rules of personal hygiene and choosing special products for the care of oily and problematic skin. The body needs hardening, vitamin A, the skin needs exposure to ultraviolet rays. You need to learn how to properly care for your skin and such problems can be avoided.
The emergence and spread of fungus can be triggered by many factors: consumption of fatty and concentrated foods, sugar, spices, bad habits, hereditary characteristics of subcutaneous fat, hormonal changes, infections and decreased immunity, stress and chronic fatigue, metabolic disorders, psychological and emotional instability .
With sudden changes for the worse, conditions are created in the human body for the development of a fungus that causes disease. Teenagers are most susceptible to seborrheic dermatitis, since at their age the sebaceous glands work very actively, thereby creating favorable conditions for the development of fungus. Seborrhea is not difficult to diagnose; it is determined by a number of symptoms:
- excessive peeling of the skin;
- itching and burning;
- the appearance of dandruff;
- if the disease progresses, the scales have a characteristic yellowish color;
- red spots appear on the body and face;
- exacerbation in the autumn-spring periods.
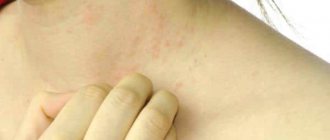
This type of dermatitis manifests itself throughout the body and in the scalp, mainly in places where hair grows on the eyebrows, eyelids, nasolabial folds, in men in the place of the beard and mustache, chest, and can extend into the ears inside and outside. Often found in the groin, abdomen, armpits, and in women on the mammary glands.
On the scalp, dermatitis looks like ordinary transmitted dandruff, only larger in size, so those infected mistakenly believe that it is dry skin and do not resort to treatment. The main difference between seborrhea and ordinary dandruff is constant itching of the skin and bright red spots at the site of the lesion.
Seborrheic dermatitis begins with itching and flaking
Mechanism of development and symptoms
The disease is chronic and affects areas of the skin and scalp where the sebaceous glands actively work (usually the face and upper body). The exact mechanism of seborrheic type dermatitis has not yet been determined; existing assumptions require proof.
It is believed that the cause is the lipophilic (fat-eating) yeast-like fungus Malassezia, which is found on human skin and is not contagious. According to statistics, these fungi are found in the skin microflora of more than 78% of people. Settled around the sebaceous glands, they use the sebum secreted by the skin as food for their own development.
With normal skin condition and normal functioning of the sebaceous glands, the fungi are kept in an inactive state and do not cause harm to humans. But if the functioning of certain systems is disrupted, the lifestyle is incorrect, as well as some individual characteristics of the body, the fungi are activated, and the immune system ceases to limit their development.
As a result, increased work of the sebaceous gland begins, which is manifested by rashes, peeling, and dandruff (if it is the hairy part). When the microflora is disturbed, the vital activity of fungi is activated. By processing sebum, they release components that irritate the skin.
Internal factors leading to activation of fungi:
- frequent and severe stress;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems, the digestive tract;
- HIV;
- weakening of the immune system.
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- folds on the skin due to excess weight;
- increased sebum production (therefore, people with oily skin have a greater risk of developing the disease).
The disease can also develop under the influence of external irritants (acid, alkali from detergents), and alcohol consumption.
The human body can control the growth of fungi. However, due to weakened immune defenses, frequent stressful situations, endocrine disorders, and nervous diseases, this natural ability is lost. Yeast-like fungi begin to grow and multiply.
- Peeling of the skin and dandruff.
- Inflammation with itching.
- The rash is pink and noticeably different in color from normal skin. The lesions are usually large and merge with each other. If symptoms appear behind the ears, on the chest or between the shoulder blades, the spots may be separate, round in shape, and small in size.
- Formation of a greasy seborrheic crust, which is easily removed. In severe cases of dermatitis, pus may accumulate under the crust.
Since the patient scratches the itchy areas, dermatitis can be complemented by another infectious disease that penetrates through the scratched wounds.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious or not, is it transmitted from person to person?
.
Seborrheic dermatitis, or as this disease is popularly called, seborrhea, is a disease of the scalp and face, namely the scalp, the disease is caused by a fungus. Most people are carriers of the fungus, but the disease does not manifest itself in any way. It is localized in places where the sebaceous glands actively work: the face (nose, cheeks, forehead), back, namely the interscapular area, chest.
Seborrheic dermatitis is an unpleasant disease
How to recognize the disease?
The emergence and spread of fungus can be triggered by many factors: consumption of fatty and concentrated foods, sugar, spices, bad habits, hereditary characteristics of subcutaneous fat, hormonal changes, infections and decreased immunity, stress and chronic fatigue, metabolic disorders, psychological and emotional instability .
With sudden changes for the worse, conditions are created in the human body for the development of a fungus that causes disease. Teenagers are most susceptible to seborrheic dermatitis, since at their age the sebaceous glands work very actively, thereby creating favorable conditions for the development of fungus.
Seborrhea is not difficult to diagnose; it is determined by a number of symptoms:
- excessive peeling of the skin;
- itching and burning;
- the appearance of dandruff;
- if the disease progresses, the scales have a characteristic yellowish color;
- red spots appear on the body and face;
- exacerbation in the autumn-spring periods.
This type of dermatitis manifests itself throughout the body and in the scalp, mainly in places where hair grows on the eyebrows, eyelids, nasolabial folds, in men in the place of the beard and mustache, chest, and can extend into the ears inside and outside.
Often found in the groin, abdomen, armpits, and in women on the mammary glands. Does not apply only to the palms and armpits. Red spots characteristic of seborrhea are accompanied by itching and peeling, sometimes burning, and the appearance of papules that combine into plaques.
These growths have clear boundaries and are covered with yellow, greasy scales.
If the disease progresses, you can notice bright yellow crusts on the skin, the area of which increases noticeably. They are also accompanied by a bacterial infection.
On the scalp, dermatitis looks like ordinary transmitted dandruff, only larger in size, so those infected mistakenly believe that it is dry skin and do not resort to treatment. The main difference between seborrhea and ordinary dandruff is constant itching of the skin and bright red spots at the site of the lesion.
Seborrheic dermatitis begins with itching and flaking
Is it possible to catch seborrhea?
Many people are tormented by the question, is seborrheic dermatitis contagious? Since the fungus that causes the disease is found on the skin of healthy people, seborrhea is absolutely not contagious.
Various factors, such as infections and bacteria or active sebaceous glands, contribute to the appearance of spots and scales.
This disease is not transmitted from person to person, even through direct contact with the patient’s skin, because everyone has a fungus - this is a normal state of human microflora.
If there are no factors that provoke changes in the human body, namely metabolic disorders or hormonal imbalances and similar prerequisites, the disease will not progress.
Dermatitis is absolutely not contagious, and moreover, it cannot be inherited; only a predisposition to increased activity of the sebaceous glands can be inherited.
Stress contributes to the activity of the disease, so protect yourself from stress, and if someone from your environment is sick, then you should not avoid him.
You simply cannot get sick even if you use the same hygiene and household items. The disease is not transmitted through:
- hugs or handshakes;
- kisses;
- airborne or tactile, etc.
You don’t have to be afraid to come into contact with an infected person. If you adhere to a healthy lifestyle, then such problems will not arise.
Proper nutrition and minimizing stress helps prevent illness or cure if symptoms appear.
Basically, medications treat symptoms, so a relapse is possible in the future; comprehensive measures will be needed to strengthen the immune system and the body as a whole.
Seborrhea is not transmitted through hugs
Treatment of seborrhea
Modern medicine does not offer remedies that cure seborrheic dermatitis, since it is impossible to regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands with the help of medications. The proposed treatment is symptomatic.
During an exacerbation, doctors prescribe antifungal drugs; the course of treatment lasts one to two weeks. For seborrhea of the scalp, shampoos are prescribed, which can be purchased at the pharmacy; they contain antimycotic components.
Shampoos reduce itching, relieve swelling and inflammation. If the disease is not treated, there is a possibility of complications developing. These include:
- baldness;
- furunculosis;
- the appearance of dandruff in large quantities;
- conjunctivitis;
- otitis.
Dermatologists prescribe treatment depending on the type of seborrhea. There are three types in total.
- The fatty type has two forms: liquid and thick. In the liquid form, a fatty secretion is observed in the area of the wings of the nose and head. Girls under 14 years of age are susceptible to this form of the disease. In the thick form, an infection gets into the sebum, causing acne and pimples to appear; the thick form affects men and boys under 20 years of age.
- The dry type develops in adolescents before puberty. This is due to the fact that the secretion of the sebaceous glands is reduced, which causes the skin to crack and dry out.
- Mixed type of seborrhea affects men. It manifests itself differently in both dry and oily skin. On the cheeks, nose, forehead there is mostly dry and cracked skin with characteristic redness, on the scalp it is oily, but it can be the other way around.
Baldness is one of the consequences of seborrhea
Is there a risk of getting sick and how to avoid it?
Seborrhea of the head is absolutely not contagious; it is treated comprehensively, going through several stages. First you need to adjust your diet and eat foods that contain zinc and vitamins A, B, C, PP. Apply antifungal drugs or antiseptics in the form of shampoos, creams or gels to the scalp. There are also treatment methods from the field of traditional medicine.
When eliminating a disease from the skin of the face, a complex treatment approach is used, reducing the manifestations of symptoms and treating the causes that provoked the active production of sebum.
Redness or suppuration on the face seriously spoils your appearance. Therefore, when self-treating, in order not to aggravate the situation, you should not use cleansers with active ingredients or alcohol-based ones. It is recommended to use antiseptic agents that relieve inflammation and cleanse the skin of bacteria and fungi.
Specialists can also prescribe antibacterial, antihistamine, vitamin and mineral components. Depending on the root cause of the disease, you can resort to other drugs that treat the digestive tract, hormonal levels, etc.
If you are prone to seborrheic dermatitis, you can prevent it in the following ways:
- take care of yourself and maintain personal hygiene;
- do not squeeze pimples;
- do not use cosmetics that dry out the skin;
- men should not wear a beard or mustache;
- proper nutrition;
- rejection of bad habits;
- hardening;
- systematic rest;
- avoiding overwork and stress;
- add plenty of fruits and vegetables to your diet to avoid vitamin deficiencies.
You should not ignore the disease, because failure to treat seborrhea of the scalp leads to premature baldness. There is also no need to be afraid of contacting patients, because seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious.
Solving the problem of skin dermatitis is not difficult; you can get rid of constant itching, cosmetic defects and tightness. If you follow the prevention recommendations, your face will shine with health and beauty.
Source: https://kozhmed.ru/dermatit/seborejnyj-zarazen-ili-net.html
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious?
The main question for others is: is this disease transmitted from person to person? In short: no, it is not transferable. Most people have this fungus on their skin in a healthy state, that is, theoretically, almost all of us can get sick anyway. The cause of dermatitis is abnormalities in the functioning of the immune system and the hormonal system, so the disease is not transmitted through contact from person to person through any transmission route (airborne, through touch, through clothing, sexual contact).
If your own health is in order, you will not become infected even if you touch the affected area of a sick person. If you have any disorders and your skin is prone to excessive oiliness, seborrheic dermatitis may develop, even if you have never seen anyone with this disease.
The only amendment: if the patient has some additional infectious disease, for example, a staphylococcal infection, others can become infected with it through blood from scratched wounds.
Is there a risk of getting sick and how to avoid it?
Seborrhea of the head is absolutely not contagious; it is treated comprehensively, going through several stages. First you need to adjust your diet and eat foods that contain zinc and vitamins A, B, C, PP. Apply antifungal drugs or antiseptics in the form of shampoos, creams or gels to the scalp. There are also treatment methods from the field of traditional medicine.
When eliminating a disease from the skin of the face, a complex treatment approach is used, reducing the manifestations of symptoms and treating the causes that provoked the active production of sebum.
Redness or suppuration on the face seriously spoils your appearance. Therefore, when self-treating, in order not to aggravate the situation, you should not use cleansers with active ingredients or alcohol-based ones. It is recommended to use antiseptic agents that relieve inflammation and cleanse the skin of bacteria and fungi. Specialists can also prescribe antibacterial, antihistamine, vitamin and mineral components. Depending on the root cause of the disease, you can resort to other drugs that treat the digestive tract, hormonal levels, etc. If you are prone to seborrheic dermatitis, you can prevent it in the following ways:
- take care of yourself and maintain personal hygiene;
- do not squeeze pimples;
- do not use cosmetics that dry out the skin;
- men should not wear a beard or mustache;
- proper nutrition;
- rejection of bad habits;
- hardening;
- systematic rest;
- avoiding overwork and stress;
- add plenty of fruits and vegetables to your diet to avoid vitamin deficiencies.
You should not ignore the disease, because failure to treat seborrhea of the scalp leads to premature baldness. There is also no need to be afraid of contacting patients, because seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious.
Solving the problem of skin dermatitis is not difficult; you can get rid of constant itching, cosmetic defects and tightness. If you follow the prevention recommendations, your face will shine with health and beauty.
Inflamed sores on the face cause many people a feeling of disgust and fear of catching an infection through contact. Most people don't know whether seborrheic dermatitis is contagious or not.

Seborrhea can be of mechanical, chemical, temperature, light, animal or plant origin. Red spots appear on the body, the skin itches, becomes swollen and swollen. The symptoms of the disease directly depend on the state of the human nervous system, microbial or fungal pathogenesis.
If the skin is healthy, it secretes 5-6 grams of sebum per week, sweat and sebum form a thin water-fat layer on the skin, giving the skin elasticity, protecting it from the effects of microorganisms, but when sick, the antibacterial component of sebum is lost, fats begin to decompose, and itching appears skin.
The adrenal glands, endocrine and nervous systems, as well as pituitary hormones and gonads influence the condition of the sebaceous glands. It is due to excess sebum in the layers of the skin that the pores become clogged, the water-fat balance is disrupted, and the skin becomes available for the proliferation of fungi and bacteria.
Similar but contagious diseases
Many dermatological diseases manifest themselves with symptoms that can easily be confused with seborrheic dermatitis. This is why people fear for their health if they see patients with problem skin (rashes, redness, peeling). An ordinary person cannot recognize at first glance whether a disease is contagious or not.
In terms of symptoms, the following infectious diseases are similar to seborrheic (oily and dry) dermatitis:
- Scabies. The skin becomes covered in rashes, peels, and is very itchy. The rashes look different in appearance - brighter in color, small and frequent.
- Tinea versicolor. Rashes are localized not only where the sebaceous glands are actively working. The rash comes in different shades and can spread over a large area.
- Dermatomycosis. The disease also occurs due to fungi, but is contagious. The rashes are round in shape and large in size, so they can be distinguished visually from the seborrheic type of dermatitis. The disease is highly contagious, so patients diagnosed with infectious dermatomycosis need to observe hygiene measures so as not to spread the infection.
Is seborrhea contagious?
Everyone has a fungus, the activity of which leads to the development of seborrhea. Increasing its amount with strong immunity and normal functioning of the sebaceous glands is not dangerous.
This disease is not inherited, but there is a predisposition to increased activity of the sebaceous glands. If there is such a factor in the anamnesis, any external or internal irritant will give impetus to the active synthesis of sebum.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp is not transmitted by airborne droplets or tactile contact; it cannot be contracted through hugs, kisses, or handshakes.
The main question for others is: is this disease transmitted from person to person? In short: no, it is not transferable. Most people have this fungus on their skin in a healthy state, that is, theoretically, almost all of us can get sick anyway. The cause of dermatitis is abnormalities in the functioning of the immune system and the hormonal system, so the disease is not transmitted through contact from person to person through any transmission route (airborne, through touch, through clothing, sexual contact).
If your own health is in order, you will not become infected even if you touch the affected area of a sick person. If you have any disorders and your skin is prone to excessive oiliness, seborrheic dermatitis may develop, even if you have never seen anyone with this disease.
Many dermatological diseases manifest themselves with symptoms that can easily be confused with seborrheic dermatitis. This is why people fear for their health if they see patients with problem skin (rashes, redness, peeling). An ordinary person cannot recognize at first glance whether a disease is contagious or not.
In terms of symptoms, the following infectious diseases are similar to seborrheic (oily and dry) dermatitis:
- Scabies. The skin becomes covered in rashes, peels, and is very itchy. The rashes look different in appearance - brighter in color, small and frequent.
- Tinea versicolor. Rashes are localized not only where the sebaceous glands are actively working. The rash comes in different shades and can spread over a large area.
- Dermatomycosis. The disease also occurs due to fungi, but is contagious. The rashes are round in shape and large in size, so they can be distinguished visually from the seborrheic type of dermatitis. The disease is highly contagious, so patients diagnosed with infectious dermatomycosis need to observe hygiene measures so as not to spread the infection.
Seborrheic dermatitis, or as this disease is popularly called, seborrhea, is a disease of the scalp and face, namely the scalp, the disease is caused by a fungus. Most people are carriers of the fungus, but the disease does not manifest itself in any way. It is localized in places where the sebaceous glands actively work: the face (nose, cheeks, forehead), back, namely the interscapular area, chest.
Seborrheic dermatitis is an unpleasant disease
Reading time: 2 min.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by a rash with the formation of crusts on the scalp or torso, where the sebaceous glands are located.
The development of the pathological process is provoked by yeast-like fungi of the Malassezia species; more details about the reasons can be found in this article. Skin papular rash is accompanied by itching, burning and peeling. It can merge into large spots and become covered with yellow, greasy scales.
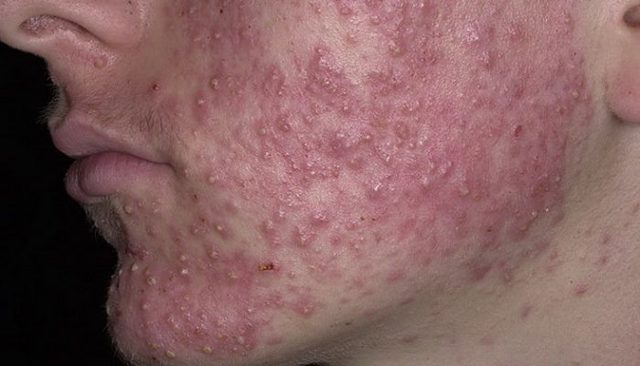
The diagnosis of seborrhea or seborrheic dermatitis is often encountered in the practice of a dermatologist. Can these diseases be transmitted between people?
Seborrhea
Seborrhea is a skin disease in which the amount of sebum secreted increases sharply. In addition, its chemical composition also changes.
The first option is more common in men; it debuts after 16–18 years. Most often caused by disruption of the endocrine system, androgen imbalance. Thick seborrhea is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Thickening of the skin in the affected areas.
- Porosity.
- A large number of comedones.
As the disease progresses, atheromas, papulopustular elements, nodes and cysts can form, after which noticeable scars remain on the skin. It is impossible to become infected with thick seborrhea from each other.
Liquid seborrhea affects mainly women and is caused by autonomic disorders, neuroses, and changes in the estrogen-androgen ratio. The first signs of the disease appear at the beginning of puberty, after 10 years.
The scalp and face are usually affected. At the same time, patients experience greasiness of the skin and hair, oily sheen, comedones, and acne. Complaints of severe itching in the scalp and dandruff are common. Over time, hair may fall out rapidly.
In the mixed form, signs of both variants of the disease occur. Seborrhea is extremely characterized by the appearance of acne on the face and body, which often becomes inflamed due to the activation of the microorganisms Propionibacterium acne.
Is scalp seborrhea contagious or not? Its main cause is hormonal and autonomic disorders; the disease is not transmitted through contact.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin lesion. The reasons for its development are:
- seborrhea;
- altered composition of sebum and sweat;
- fungal infection.
Dermatologists are often asked, “If seborrheic dermatitis is diagnosed, is that person contagious?”
The disease has two forms - infant and adult. The first one regresses on its own at the age of three months, rarely later. Its main signs are the formation of dense yellow crusts on the head and rashes in the crown area and fontanelle.
The adult form tends to become chronic. Characteristic signs appear after 40 years, more often in men.
These include:
- The appearance of clearly defined spots on the skin.
- Plaques are yellow, pink, orange.
- Peeling of the affected lesions according to the pityriasis type.
- Oily scales on the skin.
- Dandruff.
Sometimes an eczematous reaction appears on the skin - a rash of small blisters. Most often this is due to external irritation. The symptoms are most pronounced on the head, chest, back, and in large folds of the body.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious or not? Although the provoking factor is the activation of the fungi M. furfur, the disease is not transmitted from person to person. These fungi are opportunistic microflora and normally live on everyone’s skin. They can grow and multiply under the influence of certain triggering factors, which vary for each patient.
That is why it is completely wrong to say that seborrheic dermatitis is contagious and the disease was transmitted through contact or sharing a towel. People with such skin lesions do not pose a danger to others and are not a source of infection.
Seborrheic dermatitis does not pose a serious danger to the patient, but from an aesthetic point of view, seborrhea looks unpleasant.
As a rule, it is chronic and appears not only on the scalp, but also on the face. In this case, redness of the skin, rash and the formation of seborrheic crusts are observed. The rash is characterized by severe itching, so many patients have a completely natural question: is seborrheic dermatitis contagious? In order to find out the routes of infection, it is necessary to know the etiology, development factors and symptoms of the disease.
Despite the fact that medicine does not stand still, today there is no single factor contributing to the development of the seborrheic form of the disease.
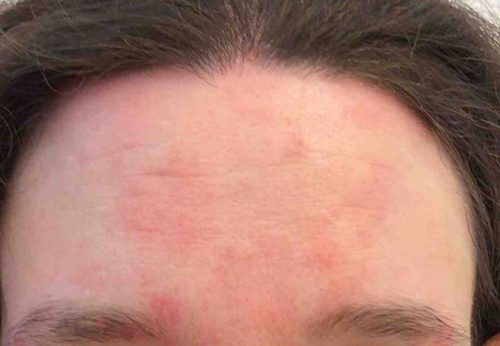
Based on the known causes and mechanism of action of other forms of dermatological diseases, it has been PROVEN that some people's belief that seborrheic dermatitis is contagious is completely incorrect.
This form of the disease is provoked by endocrine and trophic disorders associated with hypersecretion of the sebaceous gland, which is manifested by rashes in the face and scalp. The main factors in the appearance of the seborrheic form of the disease are fungal spores pityrosporum. However, for negative symptoms to occur in the head area, first of all, the patient’s immune system must be weakened. This is the main condition for the development of this disease.
Therefore, we can confidently say that seborrheic dermatitis does not belong to that part of infectious diseases that are transmitted through direct contact between people. In addition, this type of dermatitis is not only NOT INFECTIOUS, but also NOT TRANSMISSED BY INHERITANCE! The offspring inherits only a predisposition to dermatitis, manifested by hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands.
Patients with seborrheic dermatitis who are wondering whether the dermatitis is contagious should know that this disease has NO CONTACT ROUTES OF TRANSMISSION. It is not able to move from a sick person to a healthy one during a handshake, kiss, etc., so it does not involve isolating the patient from the people around him. The patient should only adhere to a hypoallergenic diet and strictly follow medical prescriptions.
Reasonable prevention measures
To prevent dermatitis, you need to properly and regularly take care of yourself. Rules and recommendations:
- Using products to care for oily skin. Skin prone to excessive sebum production requires special cosmetics. Not every remedy is suitable for it. They should be used on an ongoing basis (if sebum is secreted constantly, regardless of the weather) or during periods of heavy secretion (in summer, winter under warm clothes).
- Dieting. You should avoid foods with a lot of glucose (sweets, confectionery, baked goods), fatty foods, and fried foods. If there are any problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you need to follow a diet appropriate for your illness.
- Regular change of bed and underwear.
- Avoiding stress and moral overload.
- Timely treatment of problems with the immune system, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system.
- Prevention of obesity, and if you are overweight, regular hygiene and careful care of the areas in the folds.
- If the scalp is oily, choose a suitable shampoo (it is recommended to seek the help of a trichologist or dermatologist) or a short haircut.
All people with oily skin and intensively working sebaceous glands need to adhere to preventive measures. Teenagers are most susceptible to the seborrheic type of skin inflammation. During adolescence, the sebaceous glands function more actively than in a healthy adult. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the number of hygiene procedures.
Many in adolescence suffered from oily hair, dandruff and a shiny forehead. These are the initial signs of seborrhea.
Gradually, hormonal levels improve, which means sebum production returns to normal.
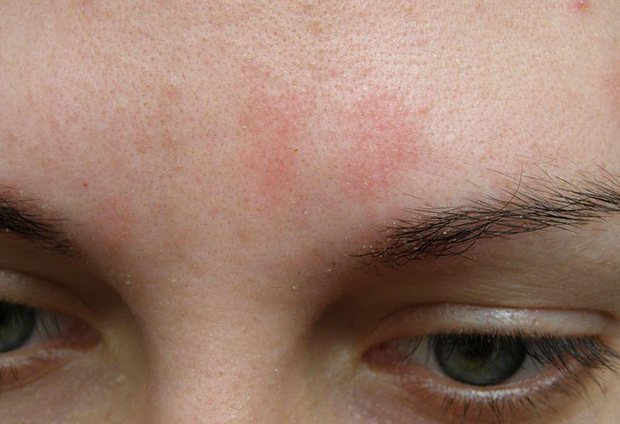
However, this disease can make itself felt at absolutely any age.
Treatment of seborrhea
Modern medicine does not offer remedies that cure seborrheic dermatitis, since it is impossible to regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands with the help of medications. The proposed treatment is symptomatic. During an exacerbation, doctors prescribe antifungal drugs; the course of treatment lasts one to two weeks. For seborrhea of the scalp, shampoos are prescribed, which can be purchased at the pharmacy; they contain antimycotic components. Shampoos reduce itching, relieve swelling and inflammation. If the disease is not treated, there is a possibility of complications developing. These include:
- baldness;
- furunculosis;
- the appearance of dandruff in large quantities;
- conjunctivitis;
- otitis.
Features of the disease
Disease of the scalp is associated with increased sebum secretion and can occur in two types - dry and oily.
- With dry seborrhea, the hair becomes very fragile and brittle, a large amount of dandruff appears on the skin, and unpleasant itching occurs.
- If seborrhea is of the oily type, then the hair always looks untidy and shiny. Dandruff appears in the form of yellow plaques. Hair may begin to fall out, sometimes quite severely.
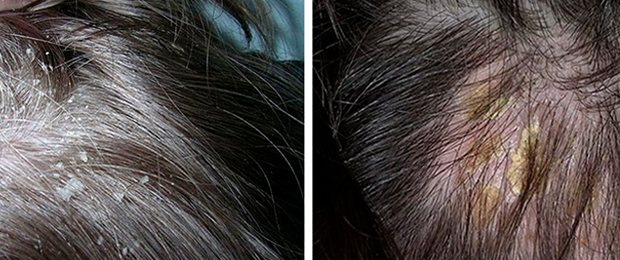
If no measures are taken, the sebaceous glands will begin to work more and more actively and will constantly affect new areas. Irregular hair washing aggravates the situation. Complications are expressed by red spots and plaques. If you scratch these skin lesions, they may bleed.
Is scalp seborrhea contagious? How can you get rid of this disease?
Seborrhea of the scalp (photo, description of the disease is presented below) is a chronic pathology , which is included in the extensive list of dermatological diseases caused by disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
In general, the term “seborrhea” is translated from Latin as “seborrhea,” which means it is excessive secretion of subcutaneous sebum.
This disease develops due to changes in the secretory option of the sebaceous glands, as well as the chemical composition of the secretion that they produce.
Factors that influence the development of seborrhea are as follows:
- genetic predisposition;
- endocrine disorders;
- disorders of a neurogenic nature (such as chronic stress and various diseases of the central nervous system);
- disorders in the digestive tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- lack of vitamins;
- immunodeficiency states;
- chronic pathologies of internal organs.
To determine the specific cause that provoked the disease, you need to consult a trichologist.
Many people are interested in whether scalp seborrhea is contagious ? Fortunately, this disease is not contagious, but it is caused by the activity of fungi, but they can be transmitted to another person.
Such fungi live on the skin of any person, albeit in small quantities; their active activity begins with a decrease in immunity and systemic disorders in the body.
Interesting on the web:
What is oily seborrhea of the scalp? Photo and description of the disease
This disease begins to manifest itself as excess sebum secretion caused by increased production of sebaceous gland secretion. The most common is oily seborrhea of the scalp. It has the following symptoms :
- With oily seborrhea, the scalp is greasy, it becomes easily inflamed, itching often appears, and sometimes red spots form. The skin also appears thickened and takes on a yellowish tint. If you don’t react in any way to your hair getting greasy too quickly and don’t go see a dermatologist, the disease will progress.
- As a rule, oily seborrhea begins on the face, after which it moves to the scalp. The disease can be recognized by yellowish, easily scraped, greasy scales. Very quickly, even on the day of washing, hair becomes covered with grease, sticks together and forms greasy strands. You may notice increased hair loss, while seborrhea is sometimes accompanied by unbearable itching.
The most serious complication of oily seborrhea is baldness. It is difficult to restore normal hair growth after complete recovery. If you consult a specialist in time, you can quickly and without consequences get rid of the disease.
Causes of occurrence on the scalp

Seborrhea can develop at any age, but most often it is detected during puberty in adolescents. The disease can be caused by:
- situations of stress;
- endocrine system disorders;
- overwork;
- lack of vitamins A and B;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- prolonged exposure to the sun.
During illness, the amount and composition of sebum changes. This leads to a decrease in the functions of the skin and sebaceous glands. The development of the disease in the human body is closely related to environmental conditions - temperature and humidity.
Seborrhea of the scalp - symptoms
The clinical picture of the described pathology corresponds to its form, degree of progression and activity of the sebaceous glands. A common feature of all types of the disease is alopecia. Seborrhea and hair loss accompany each other due to the following changes:
- disruption of root nutrition processes, their weakening;
- deterioration of the structure of the rods;
- lack of protection of curls from destructive influences;
- decreased local immunity;
- fragility, tendency of strands to split.
Oily seborrhea of the scalp
Hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands leads to excessive sebum secretion and rapid contamination of curls. The following problems are associated with such seborrhea of the scalp:
- constant itching;
- sebaceous surface of the epidermis;
- presence of an oil film on the skin;
- dandruff in the form of dense balls or sticky flakes, lumps;
- thinning strands;
- lack of volume in the hairstyle.
The considered seborrhea of the scalp without adequate therapy begins to spread to smooth skin. Symptoms of the pathological process:
- thickening of the epidermis;
- comedones;
- enlarged and contaminated pores;
- shiny face;
- acne.
Dry seborrhea of the scalp
With hypofunction of the sebaceous glands, there is a lack of hydration of the epidermis, follicles and rod structures. Dry hair seborrhea is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- intense itching, mainly after washing your hair;
- dull and fragile curls;
- copious, fine and light dandruff;
- the presence of red scaly plaques on the epidermis;
- end section;
- feeling of tightness in the scalp.
Additional clinical manifestations of seborrhea are noticeable on the skin of the neck, shoulders, face and back:
- dryness;
- cracking;
- peeling;
- red or pinkish spots.
Treatment of this seborrhea of the scalp involves contacting a trichologist and dermatologist. Specialists will be able to establish the causes and trigger factors of the disease, develop a unique therapeutic regimen and recommend prevention methods to prevent relapses of the pathology. It is difficult to completely get rid of the symptoms of the disease, but it is possible to achieve a stable and long-term remission.
Purulent seborrhea of the scalp

Sometimes, during the active progression of a fatty or mixed type of disease, the sebaceous ducts become clogged. They gradually accumulate a large amount of secreted secretion. If bacterial infection occurs, purulent seborrhea develops. It is characterized by the following problems:
- boils;
- subcutaneous, painful, inflamed comedones;
- abscesses.
How is the disease transmitted?
It is impossible to contract a disease from another person through tactile contact. Seborrhea is not transmitted through shared objects or by airborne droplets. So don't be afraid to communicate with people who have been diagnosed with this condition.
This disease cannot be inherited; The only thing that can be passed on to you genetically is a predisposition to excessive sebum production.
If one of your relatives has encountered such problems, then, if possible, protect yourself from the causes of the development of the disease. Try not to be nervous and lead a healthy lifestyle.
If someone close to you suffers from seborrhea, do not under any circumstances exclude this person from your social circles and do not show in any way that this situation causes you discomfort. On the contrary, explain that you shouldn’t refuse contact with people and be ashamed of your appearance.
For what reasons does dermatitis develop?
To understand whether seborrheic dermatitis is contagious, you need to know the reasons for its development.
Dermatitis develops due to streptococci and staphylococci, which are in the ducts of the glands in a spore state. When the fungal microflora is disturbed, the secretion of the sebaceous glands immediately develops and, as a result, seborrheic dermatitis. The scalp is especially severely affected, but lesions can be anywhere where the sebaceous glands are located. Under the influence of unfavorable conditions, the body's control over the growth of spores is disrupted, the skin ceases to function normally, and the secretion of sebum increases in volume. The course of dermatitis is complicated by existing diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, caries, otitis media, sinusitis, climate change, stress, and physical activity.
The disease can be triggered by paralysis, paresis, Parkinson's disease or spinal cord pathologies. The risk group includes children with a genetic predisposition to eczema or any other type of seborrheic dermatitis.