What is urticaria?
This is a dermatological disease caused by a certain irritant, which is accompanied by the following symptoms: the skin turns red and swells, blisters 0.1-1.0 cm in size appear on it. The lesions resemble nettle burns, they bother the patient: they hurt, burn, itch.
Urticaria is a common disease. In children it is more often acute, while adults suffer from a chronic form.
Mechanisms of disease occurrence
There are 2 ways of developing pathology:
- Immune. Ordinary substances upon first contact with the body, due to improper functioning of the immune system, are perceived by it as hostile - it begins to produce antibodies. Upon repeated contact, the antibodies begin to fight the irritant, causing harm to the person himself - characteristic allergy symptoms appear.
- Non-immune. Antigens (for example, antibiotics) in this case do not require repeated contact, they will immediately provoke antibodies to attach to mast cells and release histamine.
Types of pathology
There are several types depending on the factor that provokes the reaction.
Types of urticaria
| View | Provocateur of reaction |
| cold | low temperatures |
| solar | ultraviolet radiation: sun, solarium |
| thermal | heated object |
| cholinergic | overheating of the body, heavy physical activity, stress |
| aquagenic | water |
| contact | natural fabrics, wool and particles of animal epidermis, some plants, cosmetics, topical medications |
| medicinal | medications, in particular antidepressants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetylsalicylic acid, antibiotics |
| food | products |
| dermographic | mechanical effect on the skin |
| idiopathic | unknown origin: the irritant can be cold, heat, stress, medications, foods |
Allergy in the form of scratches: why does it occur and how to get rid of it?
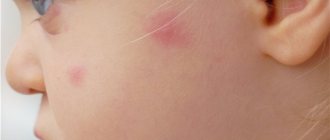
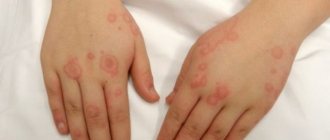
Allergic manifestations can be of different types. They are most commonly seen as a rash on the skin or a raised spot that resembles a burn. But allergies can also manifest themselves in the form of scratches. In this case, it is called demographic urticaria. What the disease may be associated with and how to get rid of such reactions, read on.
General characteristics of the disease
The disease is characterized by an abnormal reaction of the skin due to mechanical stress on it. In response to pressure, various manifestations appear on the epidermis, repeating the shape of the irritant, and often they take the form of a scratch.
The allergen that provokes such a reaction is often:
- element of clothing (zipper, collar, label, seam on clothing);
- decoration, accessories (belt, bag, chain, bracelets);
- contact with chemical solutions, medications for external application;
- other mechanical influence (for example, a jet of water).
Symptoms usually occur spontaneously, immediately after exposure to an irritating factor. In the area of mechanical pressure, the skin changes color, and this is due to a change in the width of the lumen of the vascular walls.
Typically, allergy symptoms last for several hours. But they can last a couple of days. Then they gradually subside, provided there is no exposure to the stimulus. A similar abnormal reaction occurs in both adults and children. It can be an independent disease or a secondary sign of various pathological processes in the body.
Causes and signs of allergies in the form of scratches
Why the skin reacts sharply to seemingly harmless objects and things is not fully understood. However, doctors identify several predisposing factors to such an abnormal reaction:
- The presence of another allergic disease (food allergy, drug allergy, insect allergy, hay fever, etc.).
- Hypersensitivity of the skin to the irritant.
- Genetic predisposition to allergic reactions.
- Weakened body defenses, untreated diseases, recent infections.
- Chronic stress, heavy physical activity.
- Endocrine (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism), skin (eczema, dermatitis) pathologies.
- Malignant processes.
- Worm infestation.
- Impaired reactivity of body tissues.
- Blood transfusions.
Symptoms
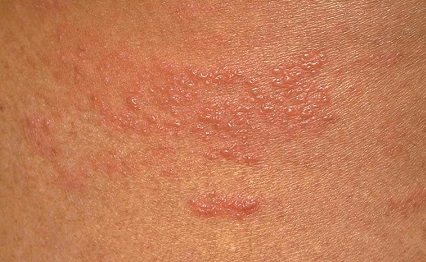
In the area of exposure to the irritant, the epidermis swells, repeating the shape of the element that provoked the abnormal reaction in the form of a stripe and a blister. Externally, the reaction resembles a nettle burn with clear boundaries and shape. The color also changes - the stripes take the form of red or pale spots.
This is explained by the activation of mast cells (mast cells) of the epidermis, the release of histamine and other biologically active substances. They expand the vascular walls, increase their permeability, and disrupt the outflow of tissue fluid, which leads to local edema. In addition, skin receptors are irritated, which is accompanied by obsessive itching and burning.
Demographic allergy in the form of scratches photo:
If the abnormal reaction is a secondary sign of other pathologies, then general malaise may additionally be a concern: aches, weakness, dizziness, low physical and mental performance. Other general allergic symptoms are also possible: cough, lacrimation, rhinitis, etc.
Diagnostics
As a rule, diagnosis is not difficult. A dermatologist, allergist or immunologist conducts a survey and examination. Instrumental studies are usually carried out with the aim of differentiating demographic urticaria from other types of urticaria.
The diagnostic test involves exposing the epidermis to a special solid object—a dermographometer. It helps to regulate the degree of pressure and thereby identify the sensitivity threshold. After a certain period of time (usually 2, 12, 48 hours), the condition of the skin is assessed. Also, for diagnostic purposes, a stream of cold or hot water can be used.
As for laboratory tests, they are rarely prescribed, since they do not reflect any special changes in blood parameters (if the disease is independent and not occurring against the background of another pathology). It is often only in severe and protracted cases that eosinophil levels increase slightly. Sometimes this indicates a helminthic infestation, which can act as a provoking factor.
If the patient cannot find the cause of the abnormal skin reaction, then it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis from different specialists: endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, therapist, etc.
Depending on the irritant, urticarial demography is classified into:
- mechanical (occurs as a result of stimulus pressure);
- toxic (develops after contact with chemicals, drugs);
- thermal (if the reaction appeared after exposure to heat);
- cold (if the reaction occurred after exposure to cold).
Treatment methods for allergic skin diseases
If urticaria is mild and occurs rarely, then specific drug treatment is not required. You just need to eliminate exposure to the allergen. To make the symptoms go away faster, apply a cool compress (of course, provided that the irritant is not cold).
For a compress, you can use a decoction of herbs with a calming effect (lemon balm, chamomile, string, rose hips, plantain). You can combine them with each other, or you can brew them separately. To prepare, just pour 1 tbsp. l. crushed dry plant with a glass of boiling water and let it brew for half an hour. Then wipe the problem area with this decoction.
If the disease takes a severe form, bothers you with severe itching, and does not go away for several days, then medications are needed. In this case, it is recommended to use antihistamines for external use: Dermadrin ointment, Fenistil gel.
The drugs have a complex effect: they relieve allergies, itching, swelling, and also gently anesthetize and soothe the problem area.
They act quite quickly, have a prolonged effect that lasts for several hours after use, but much depends on the intensity of the manifestations of urticaria.
They should be applied to the affected area 2-5 times a day. The duration of use is until the urticaria improves.
In advanced cases, when allergy scratches develop in parallel with Quincke's edema, more serious medications are needed. As first aid, glucocorticoids (for example, Prednisolone), antihistamines (first generation: Diphenhydramine, Tavegil, Suprastin), diuretics (Furosemide), infusion therapy, enterosorption can be used.
Prevention and prognosis
Primary prevention will help prevent the development of an allergic reaction. It consists of excluding exposure to factors that may affect the development of skin hypersensitivity.
To do this, it is recommended to have less contact with household chemicals or use gloves, carefully choose skin care products, and avoid cosmetics with a large number of components of synthetic origin.
It is necessary to monitor the immune system, especially in the cool season, and promptly treat diseases of any origin. You should take medications only as prescribed by your doctor and avoid stress.
If such an allergic reaction has already occurred once and acquired a chronic form with periodic subsidence and exacerbation of symptoms, then it is allowed to take certain drugs of the second generation antihistamine group with a preventive effect: Loratadine, Zodak, Cetirizine, etc. To stop the release of histamine and other mediators from mast cells, basophils, it is recommended to take Ketotifen.
If an allergy in the form of scratches occurs against the background of another pathology, then all efforts must be directed toward a cure.
The prognosis is generally favorable. Most often, urticarial demography disappears without a trace after a couple of hours, and the person does not even understand that it was an allergic reaction. In the case of the chronic form, it is necessary to promptly and correctly treat the underlying diseases that led to the abnormal skin reaction. Then a complete recovery is possible.
Source: https://allergia.expert/allergicheskie-zabolevaniya/kozhnye-zabolevaniya/allergiya-v-vide-tsarapin-pochemu-voznikaet-i-kak-izbavitsya.html
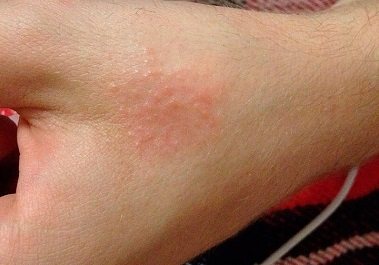
Features of dermographic urticaria
Dermographism develops according to this scenario: after a slight physical impact on the skin, mast cells are activated and release histamine and bradykinin, which dilate small arteries. As a result, vascular permeability increases, tissue fluid absorption slows down, skin receptors in the area of contact with the allergen are irritated, the body itches and red stripes and blisters appear.
The big question is: why and how do mast cells become hyperactive? The exact answer to science is not yet known; scientists believe that due to genetic or metabolic factors, they become unstable, they degranulate, and a lot of histamine is released into the blood. Degranulation causes the formation of an “autoallergen” directly due to mechanical impact on the skin, which provokes the formation of specific IgE antibodies designed to fight it.
When a mechanical effect is applied to the skin of a healthy person, mast cells are also activated, but no reaction occurs due to their small number. In 2-5% of the population, significant physical impact causes redness and blistering, but no itching. This is a simple dermographism caused by a physiological hyperreaction of the dermis and does not require therapy.
Also distinguished are urtical and non-urtical dermographism . The first is characterized by the appearance of erythema, blisters and itching, the second - the appearance of white or red stripes. Their color depends on the spasm or expansion of venous and arterial vessels.
The stripes on the skin can be red or white, this is explained by the different activity of the nervous system in people.
There are 3 types of dermographism:
- immediate: the reaction appears almost instantly (literally 3 minutes) after physical impact and lasts 30 minutes;
- medium: skin response is delayed for 0.5-2 hours, lasts 3-9 hours.
- late: the body reacts 4-6 hours late, lasts 2 days (rarely diagnosed).
Causes of stretch marks in teenagers
Why can girls and boys develop stretch marks? Adolescence is a time when rapid weight gain and body growth are also accompanied by a hormonal surge. Due to the fact that the skin quickly stretches, the epithelium ruptures. The result is the appearance of red and purple stripes on the teenager’s body, which are called stretch marks (striae). After some time, the color of the stretch marks changes to white, but against the background of tanned skin they are very noticeable.
Stretch marks are equally likely to appear in girls and boys. They most often occur on the abdomen, thighs, legs and butt due to increased muscle mass. In girls during this period, the mammary glands begin to grow, which contributes to the formation of stretch marks on the chest.
The reasons for the appearance of stretch marks on the body can be different. The main ones:
- A sudden weight gain or growth spurt leads to thinning of the skin and cracks. These cracks are then filled with connective tissue and red and purple stripes appear.
- Weight gain, caused by hormonal changes or a sedentary lifestyle, also contributes to the appearance of stretch marks on the legs, thighs, butt or abdomen.
- A weakened immune system will sooner or later cause the skin to become less elastic and tears to occur.
- Heredity. The predisposition to developing stretch marks in a child can be passed on from parents. In this case, it is worth taking preventive measures as early as possible.
- Lack of muscle mass with rapid bone growth is the cause of the formation of stretch marks on the back. If a teenager feels pain, then it is worth seeing a doctor as soon as possible. Displacement of the vertebrae may occur.
If your child begins to grow rapidly, be sure to warn him about the possibility of stretch marks appearing on his legs, stomach or butt.
You can, for example, show a photo so that he knows what they look like and immediately turns to you the first time he appears. Explain that there is nothing wrong with this and stretch marks can be treated.
Causes and factors for the development of pathology
Stripes and other patterns on the body arise for the following reasons:
- tight clothes (the seams chafe);
- heavy bags or city backpacks with narrow harnesses on the shoulders;
- rubbing the body: massage, rough washcloth or towel;
- scratching after insect bites, scabies, dermatomyositis, mastocytosis.
Children are more susceptible to reactions due to their activity and carelessness: they often receive minor injuries while playing, and then scratch the damaged areas.
The etiology of dermorgaphism has not been fully studied, but it has been established that its occurrence is influenced by the following factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- frequent stress and post-stress states;
- blood transfusions;
- frequent infectious diseases;
- endocrine disorders;
- malignant neoplasms;
- parasitic infestations;
- taking certain medications: anti-inflammatory, analgesics.
Also, stripes on the body can appear on their own, without the influence of other factors. This issue is the object of study by scientists.
Such symptoms can be either a separate disease or a manifestation of another. In the second case, the main symptom is transient scars due to mechanical impact.
Symptoms
This type of urticaria is often manifested by abnormal redness of the skin (erythema), the appearance of blisters, and local itching. Sometimes these symptoms occur with a light blow or rubbing of some object on the skin. After some time, the stripes turn red and swell - red or white scars appear on the skin, which rise slightly.
The manifestations pass quickly, from a couple of hours to 2 days, after which they disappear, leaving no traces even after frequent relapses. Therefore, patients often prefer to do without treatment.
Dermographism does not affect general well-being. Its peculiarity is that the usual manifestations of allergies (runny nose, watery eyes, sneezing) are not observed.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, you need to consult a therapist. After collecting an anamnesis, he will conduct a test, applying a hard object, cold, heat, water to different areas of the skin, in order not only to confirm assumptions about dermographism, but also to exclude the possibility of other types of urticaria.
The doctor also prescribes a stool test for parasites and a general blood test using a detailed formula. However, in most cases with dermographic urticaria, all indicators will be normal, only in severe forms the number of eosinophils will increase. Severe eosinophilia with such skin symptoms indicates the presence of helminths, which can provoke similar symptoms.
Dermographometer
You may need to consult a dermatologist, allergist, gastroenterologist, or endocrinologist to eliminate other pathologies.
A dermographometer, a device that determines the strength of skin irritation and the magnitude of the skin reaction, will help to accurately establish the diagnosis. It looks like a pen with a steel tip. This device measures the force with which the skin is pressed and determines the threshold of irritation that leads to the appearance of marks and blisters.
Red spots on the body - photos and descriptions of the main diseases
When a rash appears, many people begin to panic, suspecting the most terrible diseases. Neoplasms may not manifest themselves in any way, but may itch, hurt and cause severe discomfort.
You shouldn’t immediately make a dangerous diagnosis. When you notice the first symptoms, it is recommended to consult a doctor, he will conduct a diagnosis, find out what it could be, and tell you how to cure the disease.
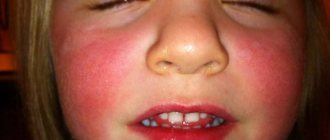
Allergy
Depending on the type of allergic reaction and the cause that caused it, hypersensitivity manifests itself as red, scaly spots or white blisters against a background of reddened skin (urticaria).
READ ALSO: Urticaria from eutirox - Treating the Skin
Such spots are located asymmetrically with a predominant localization on the face, neck or limbs. They are accompanied by itching, especially at night - the peak occurs at 3-4 am, when the concentration of glucocorticosteroids in the blood is minimal, and the body cannot suppress the immune reaction taking place in this area.
The size of the spots varies: they can be large single ones or appear as small confluent ones. They usually do not cause pain.
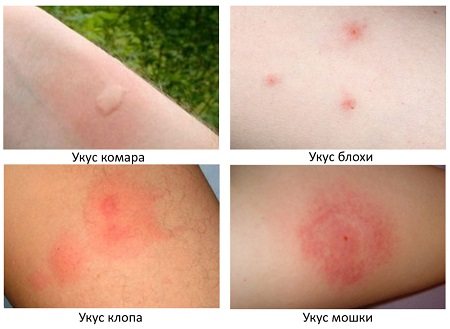
Insect bites
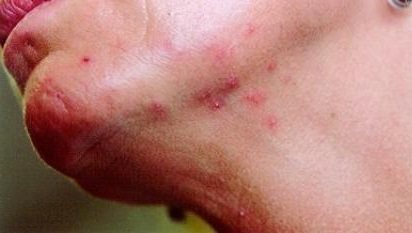
You have been walking outside barefoot or wearing open-toed sandals and may have been bitten by insects such as ants or mosquitoes. Bites from any of these insects can cause one to several red spots on the skin.
If you have been outside or near an animal that has fleas, you may also have been bitten by them. Corticosteroid creams or lotions will help relieve the itching because in most cases you will not need any other treatment.
Eczema
Also known as atopic dermatitis, eczema is a condition characterized by dry, sensitive skin, itching, and dark, scaly, wet or dry patches. Eczema is usually very itchy, itchy and can become inflamed.
It is very important not to confuse eczema with other types of dermatitis - seborrheic, for example, since these are different diseases, although they all have the same essence - inflammation of the skin. Favorite places for eczema are the inner bends of the elbows and knees. However, this skin condition is controllable. Stress and allergens can worsen attacks, but daily bathing and regular hydration can reduce it.
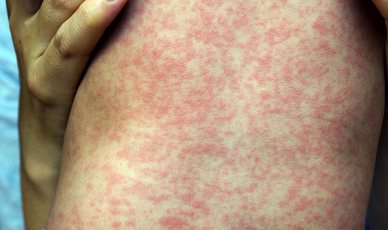
This childhood viral disease has recently become increasingly common due to neglect of vaccination. It all starts with fever, runny nose, cough, conjunctivitis and headache.
After 2–3 days, pink-red spots appear behind the ears and on the head. They merge with each other and gradually descend lower along the body to the very lower extremities. Complications are especially dangerous for a child, from which 3% of patients died before the introduction of mandatory vaccinations.
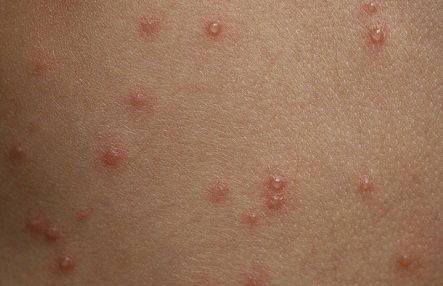
Chickenpox
Chickenpox also has an infectious origin. It begins with red spots, in place of which bubbles up to 5 mm in size later form.
After three days they become covered with dry crusts. With chickenpox, both spots and pimples are present on the skin at the same time. If you comb them, they will leave behind small pits, so-called pockmarks, which are difficult to get rid of.
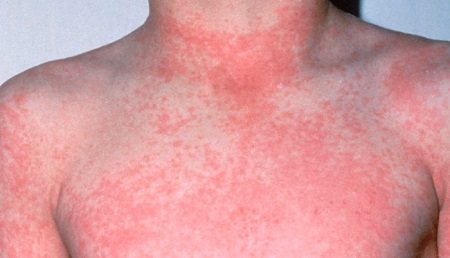
Scarlet fever
This infectious pathology is accompanied by small red spots measuring 1-2 mm. They appear after a sore throat occurs and are usually localized in the groin area and lower abdomen.
Due to densely located spots, the skin appears reddened and inflamed.
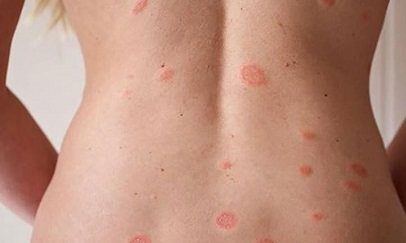
Pityriasis rosea
On the body, medium-sized scarlet-colored plaques with a diameter of 30–50 mm are found, which are otherwise called “mother spots.”
Then they are surrounded by others, smaller ones. The causes of the disease include general weakened immunity and herpespirus. The treatment is quite lengthy.
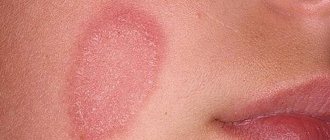
Ringworm
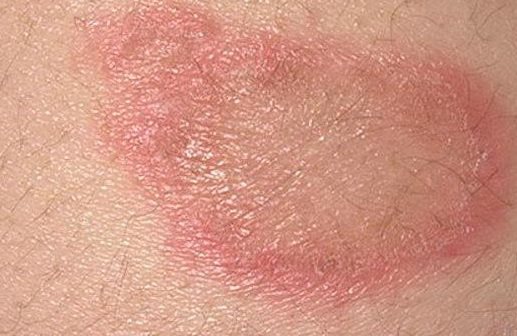
In dermatology it is known as microsporia. This is a contagious disease of fungal origin. Its causative agent is a mold fungus of the genus Microsporum, which parasitizes the keratinized layer of the epidermis.
With this pathology, the red spots have a round shape with a lighter center. Most often appear on the head and limbs.
Herpes zoster (shingles)
Adults who have had chickenpox in childhood are usually affected. There is a high temperature, a strong burning sensation at the site of future spots and blisters under the arms, as well as along the intercostal nerves.
READ ALSO: Polycystic ovary syndrome and Acne
In severe cases, it is necessary to take antibiotics and apply combination ointments to the affected areas of the body. Shingles is most severe in the groin and genital areas.
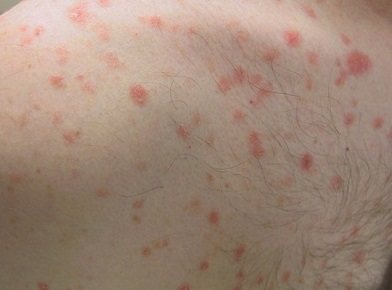
Psoriasis
Psoriasis rashes can come in different shapes and sizes. Regardless of this, plaques develop according to a certain principle:
- Scaly rashes appear. They are grayish-white in color. Easily scraped off the skin. The scales look like paraffin shavings.
- After complete scraping of the plaques, a thin, terminal film forms on the rash.
- The next stage is characterized by the symptom of “blood dew”. If you remove the film, the papillae bleed. The bleeding itself is drip in nature.
Typically, with psoriasis, plaques are localized on large extensor joints - the knees, and red spots appear on the elbows. The scalp and areas subject to frequent injuries are severely affected. But this symptom cannot be considered final when making a diagnosis, since atypical forms of psoriasis are very different.
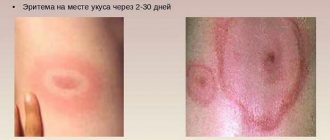
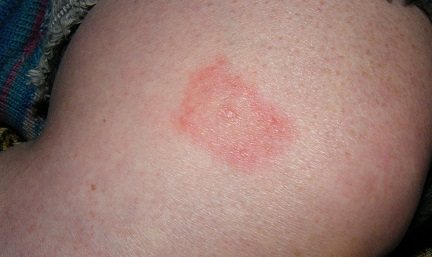
Borreliosis
The disease is caused by bacteria that are spread by ixodid ticks. First, red round spots appear on the body in the place where the ticks bit. Sick people are bothered by itching and symptoms of intoxication.
The spots increase in diameter by 2–10 times and become similar to a target. Treatment in a hospital is carried out with antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and desensitizing agents.
Hives
After exposure of the body to seafood, chocolate, and certain medications, an allergic response occurs with red spots and itchy blisters.
Spots of an allergic nature are eliminated gradually, taking into account factors such as the nature of the rash, its location and the etiology of the disease. The doctor prescribes an allergen-free diet. Thanks to enterosorbents: activated carbon, Lactofiltrum and Enterosgel, it is possible to clean the digestive canal, after which existing stains disappear.
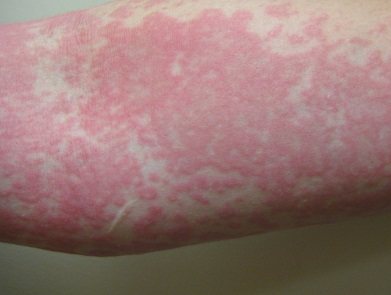
Photodermatitis
UV exposure can also cause rashes, redness and swelling of the skin due to increased sensitivity to sunlight.
To treat the disease, drugs with photoprotective properties are prescribed.
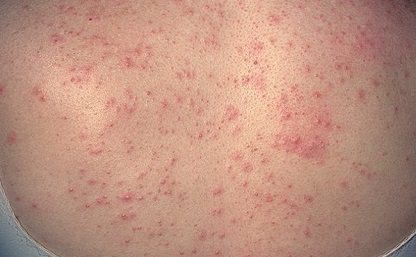
Keratosis follicularis
Keratosis pilaris appears as small red bumps. The condition is thought to be caused by a genetic disorder, and the severity of symptoms can fluctuate depending on the season. Typically, the worsening will go away or improve in the summer, but worsen during the winter months.
The bumps are red in color and are located mainly near the hair follicles. They do not cause any particular health concern, but are a serious cosmetic problem. A specific trigger for the onset of the disease is a deficiency of vitamins A, C, K or any allergic reactions.
Regular moisturizing may relieve symptoms slightly, but there is no known cure.
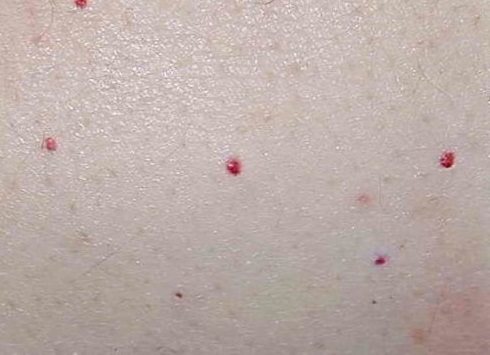
Angioma
If you notice a tiny mark that looks like a red speck of blood, it's most likely a cherry angioma.
Cherry angioma is a firm red, blue or purple papule with a diameter of 0.1-1 cm. When thrombosed, they may appear black in color until diagnosed with a dermatoscope, when the red or purple color is more easily seen. Cherry angioma can develop on any part of the body, but most often appears on the scalp, face, lips and torso.
This phenomenon is quite common and most often occurs in people over 30 years of age. Their red color comes from a damaged blood vessel under the skin.
Experts are not entirely sure what causes the anomaly, but genetics is considered the leading theory today. Typically, these small red dots are harmless, but contact your doctor if you see them growing or changing shape or color.
Scabies
Scabies is caused by a female mite. It penetrates under the skin and, moving parallel to the surface layer, forms an itch in which it lays eggs. The disease manifests itself as red itchy spots located in the interdigital folds, on the flexor surfaces of the wrist joints, the extensor surface of the forearm, shoulders, on the skin of the thighs and abdomen.
READ ALSO: Can a wen develop into a malignant tumor (cancer)
Between the rashes, scabies are observed - dirty gray lines slightly raised above the skin, 1 mm to 2 cm long. A characteristic symptom is a rash on the sacrum in the shape of a triangle with the apex down.
Neuroses
Pink spots can also appear with neurosis, often appearing on the face, neck and décolleté.
With neurosis, the appearance of red spots is accompanied by a feeling of either cold or heat, and possible pain in the limbs and internal organs (heart, stomach). Pain and discomfort may increase under the influence of stress, shortness of breath may appear and the heart rate may increase.
With neuroses, redness of the skin appears, especially during anxiety, panic or phobias.
Skin cancer
The appearance of any neoplasms on the skin (ulcers, moles, rashes, scars) not previously presented becomes a reason to think about skin cancer. Changes in the skin include changes in color, thickening, and the appearance of new elements.
Depending on the type of cancer, formations acquire specific characteristics. Initially, almost imperceptible red spots with a brown tint are formed, characterized by compactions, which later change and become dense nodes.
Therapy
In mild cases (90%), there is no need to treat such a disorder. Marks on the skin disappear on their own after some time and do not leave scars. To relieve symptoms, take sedative antihistamines of the 1st generation: suprastin, diphenhydramine.
But in severe chronic forms, non-sedating antihistamines of the 2nd generation (loratadine) or 3rd generation (cetirizine) are prescribed. They are taken once when manifestations occur or regularly for persistent relapses. For prevention, ketotifen is prescribed; it prevents histamine from entering the tissue.
Ways to combat stretch marks [edit | edit code]
Treatment of stretch marks is a difficult task, but with an integrated and methodical approach it is completely solvable; stretch marks can be made less noticeable, although it cannot be made completely invisible. [ source not specified 1379 days
] The earlier treatment for stretch marks is started, the greater the likelihood of getting proper results.
Stretch marks can be completely removed only through surgery, but you can reduce the intensity of their coloring and make them less noticeable using various cosmetic procedures:
Prevention and prognosis
You can prevent the development of symptoms if you adhere to the following rules:
- choose soft washcloths for hygiene procedures;
- refuse massage;
- dry yourself with soft (preferably bamboo) towels;
- wear clothes that fit properly and without tight seams;
- do not scratch your body after bites or other injuries;
- choose backpacks with wide straps and bags with comfortable handles;
- give up woolen clothes and clothes made from thick materials, give preference to cotton;
- adhere to a certain daily routine and healthy diet;
- wash fruits, berries and vegetables thoroughly before eating;
- Avoid stressful situations if possible.
The prognosis of dermographism is often favorable. With proper treatment of it and associated diseases, absolute recovery is possible.