The possibilities of medicine are limitless, the patient's capabilities are limited.
Today I want to talk about the types of molecular diagnostics: ImmunoCap, Immulite, Allergochip, Alex Allergy Explorer. I will try to list the advantages of such diagnostics over other types of research in the field of allergology. I will consider the options in which cases molecular diagnostics are prescribed and in which laboratories you can donate blood for analysis. I will answer the question - why in Moscow they take blood from a finger, and in other cities only venous blood
Types of molecular diagnostics:
ImmunoCap is the name of the diagnostic type. Allergochip is the name of the analysis itself. An allergy chip is made using the ImmunoCap method.
ImmunoCAP ISAC (Phadia) (Sweden)
This is a very accurate and fully automated test system for measuring IgE antibodies, developed by Phadia. The result is measured in units (kU/l).
ImmunoCAP - does not display the proteins themselves, it displays the presence of antibodies to the suspected allergen and does this at the molecular level. The method diagnoses allergies at the earliest stage.
ImmunoCAP does not require discontinuation of medications taken (antihistamines, hormones and Montelukast - Singulair, Singalon, Montelar, etc.).
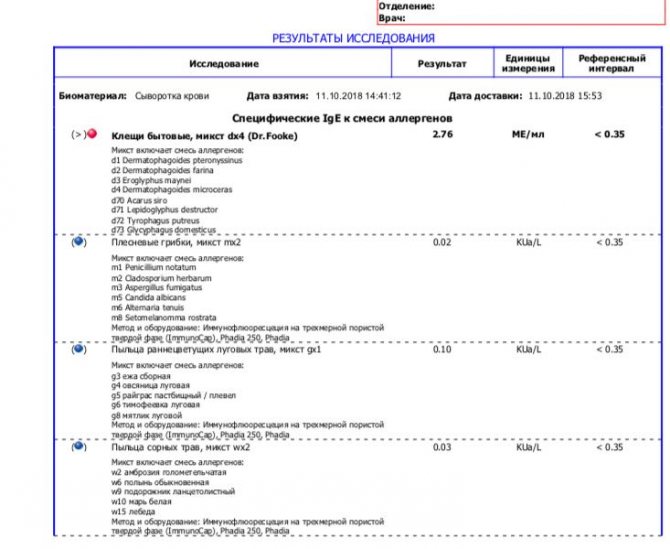
The IMMUNOCAP method is excellent at searching for inhalant allergens, but for food allergens this method often produces false results.
To identify true food allergies, you can test:
- Allergochip, where minor and major proteins of the suspected allergen are identified.
- Prick - tests with exactly those products that you suspect (bring them with you).
- Provocative tests (the most dangerous type of diagnosis, which I will discuss in a separate article).
ALEX Allergy Explorer
The Austrian molecular allergy test determines the presence of a reaction to 282 allergens. Distributed in Europe and the post-Soviet space. In Russia you can take it remotely.
Does not require medication withdrawal.
Separate article about the ALEX test
IMMULITE (England)
IMMULITE, like ImmunoCap, is a molecular diagnostic option performed on a precision immunochemical analyzer that looks for the lowest concentrations of IgE. It differs from Immunocap in the country of origin of the equipment.
IMMULITE does not require discontinuation of antihistamines before the examination.
Allergochip (ImmunoCAP ISAC method)
The most informative method for diagnosing allergies from infancy.
The analysis examines 112 allergen components and 51 proteins of common allergens. The allergy chip results show the presence of a reaction to minor and major proteins.
Major protein is an indicator of a true allergy. Minor protein is an indicator of cross-reaction.
This data will help determine the sources of allergies: one single one, several closely related ones, or many different ones.
The allergy chip does not require discontinuation of any medications before taking the test.
If you do not need information on all 112 components, you can separately take a major-minor test for the desired allergen using the ImmunoCAP method.
Separate article about allergochip
What is an allergy?
Allergy is the increased sensitivity of the body to certain substances, expressed by a pathological reaction. The meaning of the state is as follows. Some substances are allergens to the human immune system. At the first meeting, the protective system seems to “remember” them, and when they meet again, it releases a large amount of biologically active substances (histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins), causing damage to body tissues and disruption of their functioning. This is the so-called pathophysiological stage of allergy. It can result in Quincke's edema and the death of a person from suffocation, all this can develop within just a few minutes.
Class E immunoglobulins are of particular importance in the development of an allergic reaction . It is they who react when they encounter allergens again and are fixed together with them on the surface of the membranes of basophils and mast cells, causing the release of biologically active substances.

There are different groups of allergens:
- Food products.
- Waste products of animals and plants.
- Medicines.
- Household (the most common is dust).
- Substances that enter the body through direct contact with insects.
- Chemical industrial compounds.
Diagnosis of allergies is important because it allows you to identify the body’s hypersensitivity to a particular product or animal or plant before the manifestation of pathology and avoid a repeat encounter.
Advantages of molecular diagnostics:
- Allows you to conduct research on a wide range of allergens, without risk to health - unlike scratching and provocative tests.
- A huge advantage of molecular diagnostics is that in most cases there is no need to discontinue medications.
- A small amount of blood is required for analysis.
- The test has no age restrictions and is prescribed even to infants.
- In Moscow, you can donate capillary blood (from a finger) for molecular analysis. In other cities, this is difficult to do due to the nuances of transporting and storing blood. For now, diagnostic equipment is only available in Moscow, where blood is delivered for analysis.
- Molecular allergy diagnostics allows you to distinguish true allergies from cross-reactions.
- Molecular diagnostics is necessary in selecting the correct allergen for ASIT (allergen-specific immunotherapy) in people with multiple (polyvalent) allergies.
- It has been proven that the use of molecular diagnostic methods forces a change in ASIT, selected based on the results of skin prick tests.
Allergic respiratory diseases
Allergic diseases of the respiratory system can have serious consequences and therefore require increased attention.
Bronchial asthma
The disease is associated with chronic damage to the respiratory system. When an allergen enters the body, a sharp narrowing of the bronchioles and small bronchi occurs, which leads to bronchial obstruction. Bronchial asthma can be identified by frequent shortness of breath, persistent cough, wheezing, and a feeling of tightness in the chest. The greatest danger is posed by status asthmaticus, when the bronchos swell and sputum accumulates in them, causing hypoxia.
Bronchitis
The disease is associated with an inflammatory process in the bronchi. The following can provoke it: pollen of flowering plants, fluff, wool, dust. Since it is mainly diagnosed in the cold season, doctors are confident in the infectious factor of development. The disease manifests itself in attacks of choking cough, which can intensify during sleep.
Allergic rhinitis
The pathology has an allergic and infectious nature of development. Occurs against the background of an inflammatory process in the mucous membranes. In addition to nasal congestion and discharge from it, it may be accompanied by itching, swelling of the eyelids, and lacrimation. The disease occurs after contact with pollen, components of cleaning products, dust, and food.
Allergic alveolitis
The provocateur is fungal spores. The reaction occurs in the smallest bronchioles, alveoli and blood capillaries. As a result, an inflammatory process develops, which leads to the appearance of granulomas and fibrosis of the affected tissues.
Leffer syndrome
Pathology occurs in the lungs. As a result of the development of the syndrome, an eosinophilic infiltrate appears. Pathology develops against the background of helminthiasis. Allergens include pollen, fungal spores and some medications. The cause of the appearance of infiltrate in the lungs often remains unknown.
Table of contents
Chapter 1. Pathogenetic mechanisms of allergy formation in children Chapter 2. Specific diagnosis of allergies in children 2.1. Basic principles and methods of specific diagnosis of allergies 2.2. Features of specific diagnostics of various types of allergies 2.2.1. Specific diagnosis of household allergies 2.2.2. Specific diagnosis of epidermal allergy 2.2.3. Specific diagnosis of pollen allergy 2.2.4. Specific diagnosis of food allergies 2.2.5. Specific diagnosis of bacterial allergy 2.2.6. Specific diagnosis of drug allergies Chapter 3. Age-related patterns of allergy formation in children Chapter 4. Basic principles and methods of treatment of allergic diseases in children 4.1. Specific treatment of allergic diseases 4.1.1. Method of individual diet therapy 4.1.2. Specific immunotherapy 4.2. Nonspecific therapy of allergic diseases Chapter 5. Features of the etiology, clinical picture and treatment of major allergic diseases in children 5.1. Atopic dermatitis 5.2. Bronchial asthma 5.3. Hay fever 5.4. Urticaria and Quincke's edema Applications Questionnaire for a children's allergy clinic Methods of allergological examination Skin allergy tests Provocative allergy tests Laboratory methods of allergological examination Laboratory tests for diagnosing immediate B-dependent allergies Direct basophil test according to Shelly Indirect basophil test according to Shelly Mast cell destruction reaction ( RDTK) Radioallergosorbent test (RAST) Specific leukocytolysis reaction (RLL) modified by A. M. Potemkina Laboratory tests for the diagnosis of delayed, T-dependent type allergies Neutrophil damage index (NDI) according to V. A. Fradkin Leukocyte migration inhibition reaction (RTML) ), micromethod by A. G. Artemova Rosette reaction test (according to Zalberg) modified by R. A. Pospelova Blast transformation reaction of lymphocytes (RBTL) Literature
Detailed question
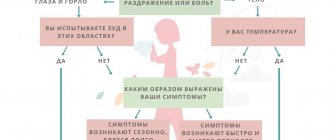
The first stage of diagnosis will be a detailed questioning to find out the causes of the allergy. Parents should be told the following:
- presence of allergies in other family members;
- dependence of allergy manifestations on the time of year;
- influence of climate on allergies;
- the effect of physical activity or stress on the course of allergies;
- connection between allergies and viral diseases;
- influence on the manifestations of allergies to food products, drugs or cosmetics;
- exposure to harmful factors.
Prevention of allergic diseases
To achieve long-term remission, patients must follow some preventive rules:
- try to completely avoid contact with substances that can provoke an allergic reaction;
- carry out wet cleaning of the premises daily;
- exclude from the diet foods that can cause a negative reaction in the body;
- prevent the development of chronic ailments, and if they exist, carry out timely therapy;
- exclude sources of development of inflammatory processes;
- treat caries promptly;
- during the flowering of plants that cause disease, try to be outside less often;
- strengthen the immune system.
Allergic processes can have serious consequences. Therefore, if any of their signs appear, it is important to immediately consult a doctor, undergo an examination and begin proper treatment.