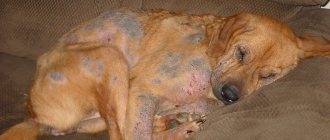
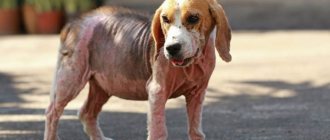
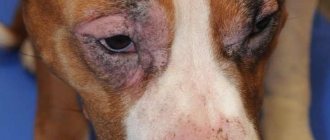
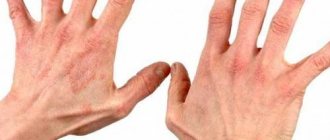
The most common signs of skin dermatitis are rash, itching, redness, blisters and crusts. In general, weeping dermatitis develops in the same way, but in the process the affected area begins to ooze ichor or exudate, which creates excellent conditions for the development of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora.
Predisposing factors
Dermatitis can be caused by various factors. Physical (insect bites), chemical (skin contact with acids or alkalis), psychosomatic (stress), biological (infections).
Other predisposing factors include:
- Allergies, including intolerance to some food components.
- Mites (dermatitis often occurs due to infection with Sarcoptes scabei or Cheyletiella mites).
- Ear infections.
- Poor care.
- Splinters, including grass stubble getting into the thick skin.
- Interestingly, weeping dermatitis often develops in animals suffering from joint dysplasia. Most likely, this is due to serious metabolic disorders, which is normal for such pets.
- Inflammation of the anal glands.
If there are disturbances in the functioning of vital organs such as the kidneys or liver, as well as interruptions in the functioning of the lymphatic or immune systems, the skin will begin to react first. Very often (and quickly) with such disorders, an infection joins the pathological process. A general deterioration in the condition of the skin, due, among other things, to an insufficient amount of vitamins and microelements in food, will only contribute to this.
Risk group
All dogs are susceptible to dermatitis. There are only predisposing factors that can contribute to the development of inflammation:
- heredity (it has been proven that Labradors have a predisposition to atopic dermatitis that is inherited);
- young age up to 3 years (and the earlier the disease begins, the more difficult it will be to treat and go away over the years);
- breeds prone to skin problems: West Highland Terrier, German Shepherd, Jack Russell, Boxer, Shar Pei, Spaniel, Yorkshire Terrier;
- the presence in the diet of components such as beef, dairy products, wheat, chicken.
Causes of pathology
Atopy is a dog's body's reaction to exposure to a specific allergen. When it enters the respiratory tract or skin, the immune system produces antibodies to eliminate the irritant, which causes a characteristic reaction of the skin. Depending on the origin of the allergen, the disease may be seasonal or non-seasonal. It is inherited, but the causative allergens may differ among puppies of the same litter.
The most common provoking factors are:
- Home microclimate (household dust, indoor plants, changes in room temperature and humidity, changes in region of residence).
- Incorrect approach to the care and maintenance of a pet (inappropriate food, lack of anti-parasitic treatment).
- Concomitant diseases (urolithiasis, giardiasis, hypothyroidism, etc.).
- Heredity and breed characteristics. Atopy most often occurs in Shar-Peis, Pugs, Labradors, Boxers, Bulldogs, Spaniels and Dalmatians.

Clinical features
Lesions most often appear in hot, humid weather. Animals constantly lick or scratch separate areas of the skin, which can vary in size and are usually sharply demarcated. The most commonly involved areas are the dorsal or dorsolateral parts of the lumbosacral region and the parotid region. The damaged skin is erythematous, moist and, in most cases, with exudation. In a typical case, there is alopecia or thinning hair. However, fur may still remain in the lesion if the lesion is discovered early or if its location makes licking and scratching difficult. Excoriation due to licking and scratching is sometimes present. The surrounding skin should be carefully examined for associated disorders, including superficial folliculitis and, less commonly, deep pyoderma with fistulous tracts.
Secondary symptoms
Often the owner misses the primary symptoms of the development of the disease and pays attention to it only when the condition worsens significantly. Allergies often cause the development of a bunch of related ailments. Here is their list:
- Pyoderma. This disease is often attributed to scabies or other ailments caused by parasites. Consequently, incorrect treatment regimens are prescribed. Pyoderma develops with the participation of specific microorganisms. Usually these are staphylococci and streptococci. Microbes enter wounds when scratching and lead to an inflammatory reaction. This complication is characterized by baldness and purulent lesions on the skin. It becomes bloated and lumpy.
- Purulent conjunctivitis. Often provoked by the activity of purulent microflora. Therefore, specific treatment is prescribed, using antibiotics.
- Acute moist dermatitis. Outwardly, it looks like a collection of wet wool. But when you cut it off, you can see how severe the overall clinical picture is. Most often, dermatitis is combined with pyoderma, scabies, lichen and deep, complex infections.
- Otitis externa. The ear area is so affected that the hearing aid canal is completely blocked.
- Pododermatitis. This is a purulent infectious disease of the soles of the extremities.
- Acral dermatitis. Appears on the forelimbs, in the area of the wrist joint. Initially, hair disappears from this area, the skin darkens and the affected area increases in size. It becomes visible above the surface of the entire coat.

Routes of infection
Hereditary and autoimmune forms of the disease are not contagious to other animals and appear when an allergic agent enters the body. The atopic form manifests itself upon contact with house dust, microscopic mites, mold spores, and epithelial components. In seasonal phenomena, the main cause may be pollen from various plants.
The flea form develops when a dog is infected with fleas. These parasites can get onto your pet from other animals. There is also a higher risk of flea infestation if the dog’s home is located close to the basement.
Fungal contamination usually occurs when yeast microorganisms develop excessively in areas of inflammation. Most often, these are representatives of Malassezia. The predominant bacteria are staphylococcal lesions.
Important! There is no need to create perfectly clean conditions for small puppies. The more sterile the environment, the worse the body will react to the allergens encountered later.
Symptoms of weeping diathesis
Weeping diathesis has a second name - scrofula. With this skin disease, the surface of the skin becomes dry and golden-yellow crusts appear on it. It was from the color of the crusts that the disease began to be called scrofula.
A small child experiences discomfort during the period of illness, as the spots spread quite quickly, itching appears, and the affected areas begin to itch. When the crust is removed, a wet spot of a reddish hue is formed. If treatment is not started in time, scrofula develops into a more serious disease.
Kinds
There are several types of dermatitis in dogs, each of which manifests itself differently..
Flea
Caused by flea bites. The parasite's saliva contains a large amount of specific substances that reduce blood clotting.
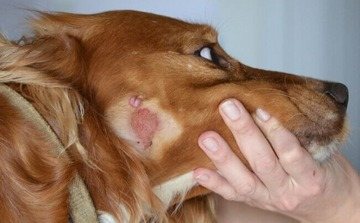
Penetrating into the bloodstream, one of the components activates the allergen, which appears instantly. Just one bite is enough for an animal to become infected.
Redness appears in the affected area, hair falls out, forming a bald patch, and the four-legged friend is bothered by constant itching. Lack of treatment leads to massive baldness, weakness of the animal, and weight loss.
Medication
Some topical medications can cause skin irritation and localized rashes in dogs. The areas to which the drug was applied turn red, become painful, become covered with a small rash or crusts, and the hair on them may fall out. Due to severe itching, the animal constantly licks and scratches the skin, aggravating the situation.
Seborrheic
The cause of this type of dermatitis is disruption of the sebaceous glands. A typical sign of seborrhea is oily hair with dandruff. The skin is inflamed, peels, and sometimes acquires an unpleasant odor due to the presence of colonies of the yeast-like fungus basidomycete Pityrosporum ovale.
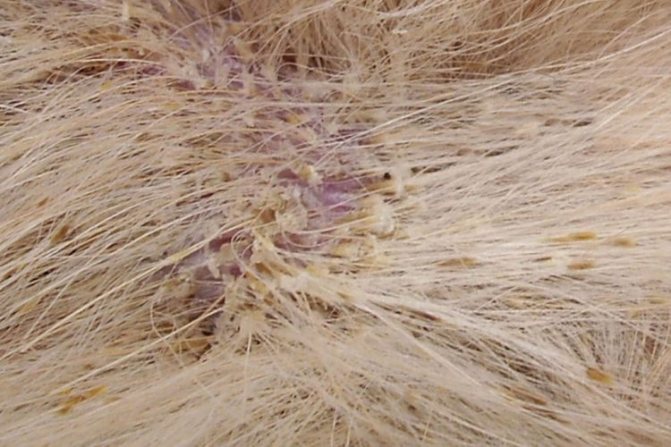
Malassezia (Malassezia) dermatitis
The pathogen (fungus Malassezia pachydermatis.) is an opportunistic microflora that lives on the skin of a dog. With good living conditions, food, and a strong dog’s immunity, the fungus does not make itself felt. It's not contagious. Malassezia prefers the area around the ears, eyes, under the lower jaw; in severe cases of the disease, external otitis develops. Seborrheic dermatitis develops as a response to increased secretion of the sebaceous glands.
Sometimes Malassezia fungus indicates a serious internal pathology. A typical feature of opportunistic microflora is to become activated when the immune system is severely weakened or when there is infection or viral diseases. In cases where the dog’s body is severely weakened.
Folded dogs and brachycephalics are more likely to be hostage to Malassezia dermatitis. Poor treatment of folds and anatomical depressions leads to the fact that the skin begins to get wet; increased humidity and temperature provoke increased development of fungus. Redness and an unpleasant odor appear in the folds; the pet licks the damaged area, scratches it, and introduces bacteria. If the disease is not treated, then healing does not go away on its own.
Papular dermatitis
Described as pemphigus foliaceus, it is an autoimmune skin disease in animals. Due to the production of antibodies and their deposition in the intercellular spaces, detachment of epidermal cells occurs. The disease occurs in dogs of any age and breed, but is most often diagnosed in Chow Chows and Akitas. Sometimes papular dermatitis develops as a reaction to medications or chronic skin diseases.
Food
Occurs due to an allergy to some food. It could be anything, from an unsuitable component in the finished food, to regular cereals and even meat.
It is difficult to identify an allergen even after taking a sample for analysis. The problem causes a lot of trouble for the pet: scratches appear on the skin in different places, hair falls out, sometimes pimples appear on the dermis, mucus and blood streaks are present in the feces.
Food allergies manifest themselves in different ways among animals.
Atopic

The disease occurs in response to an irritant. The allergen cannot be identified.
Thermal
The development of this type of dermatitis is caused by exposure to high or low temperatures. The disease most often affects the animal's paws (pododermatitis) or head. The affected area swells, hurts, erosions, microcracks and wounds formed on the skin cause itching and can fester.
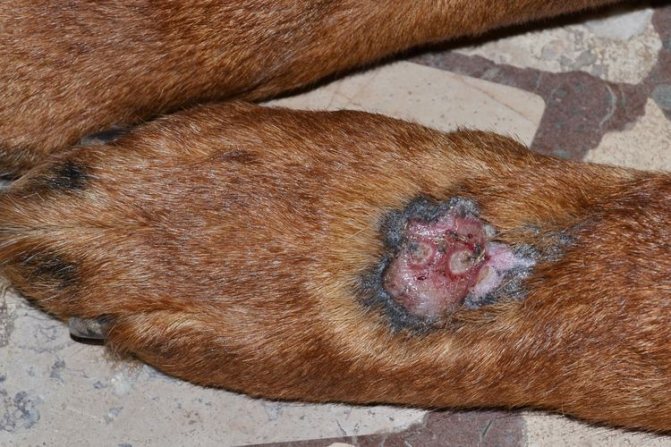
Contact
With this type of dermatitis, the process involves not only the superficial layers of the skin, but also the deep ones. The signs are the same as for other types.
The skin becomes hot, itches, and wounds appear.
Contact dermatitis causes the skin of a shaggy friend to interact with chemical or physical irritants: the collar has rubbed, there has been contact with detergents, cleaning products, etc.
It is not difficult to identify the irritant if desired.
Weeping
This skin lesion is manifested by hyperemia (redness), swelling, small itchy and painful cracks, from which transparent exudate (ichor) is released. Weeping dermatitis in dogs is often the result of food allergies, tick infestations, ear infections, skin damage (cuts, abrasions, scratches), or develops due to improper grooming.
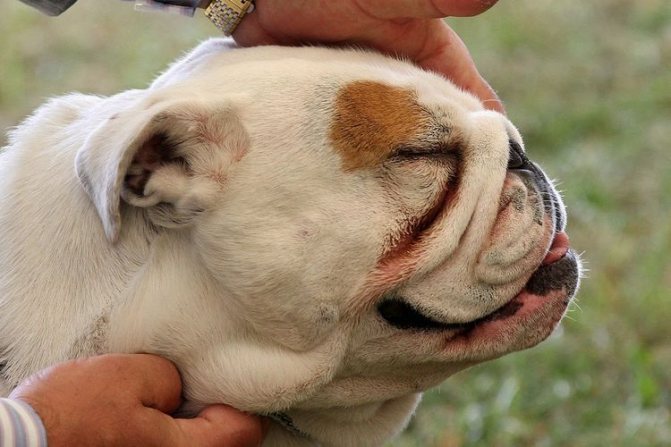
The risk group for developing weeping dermatitis includes dog breeds with long hair or thick undercoat: Newfoundland, St. Bernard, collie, Tibetan mastiff, Afghan hound.
Infectious
It is caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Most often we are talking about staphylococcal dermatitis.

If the barrier function is weak, infections can enter microcracks, leading to disease.
Acral
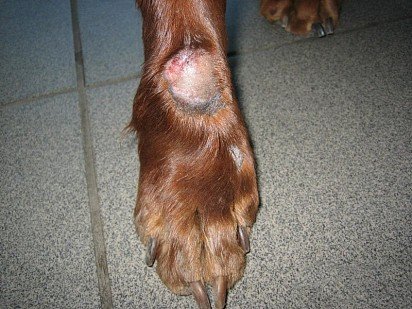
Symptoms of acral dermatitis include thick, ulcerated patches of skin caused by your dog licking the area excessively. Pathological behavior of an animal can be caused by allergies, parasites, infection and other factors that must be detected and eliminated before treating the skin.
Treatment consists of the initial elimination of the provoking factor and a therapeutic effect on the damaged epidermis. Limiting your pet's access to the itchy area is of great importance. In addition, antidepressant and psychotropic drugs are used in therapy.
Psychogenic
Dogs with a sensitive nervous system develop a psychogenic form of the disease. It is observed when a dog experiences separation from its owner, stressful situations, or a change of place of residence.
In this case, the doctor prescribes sedatives that normalize the state of the dog’s nervous system.
The disease is easier to eliminate when the causes are identified. If they are not detected, the rash between the fingers will reappear.
Causes of neurodermatitis. How to treat a disease at home!
Have you been struggling with WRINKLES for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to get rid of wrinkles by taking every day...
Read more "
Neurodermatitis is a skin disease that manifests itself as tissue inflammation.
It occurs chronically with alternating frequent exacerbations and remissions. In most patients, the pathology develops against the background of allergies or nervous disorders, but there are other factors that provoke the appearance of symptoms of the disease.
Why does neurodermatitis develop?
Experts believe that common causes of neurodermatitis are:
- weakened immunity;
- intoxication of the body;
- inflammatory processes;
- metabolic disease;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- hereditary predisposition;
- mental or physical exhaustion;
- poor nutrition and irregular daily routine;
- neuropsychological disorders, neuroses, stress, depression.
Despite the variety of factors that provoke the development of neurodermatitis, dermatologists believe that the disease triggers an allergic mechanism. At the first meeting with an allergen, the body produces antibodies to a new compound, but the second time the antibodies combine with the body and are carried through the bloodstream to all tissues and organs and destroy the membranes of their cells.
During the process of degranulation, active substances are released, among which is histamine. This substance causes redness and thickening of the skin, an increase in local temperature and a feeling of itching or burning. In case of secondary infection, body temperature rises.
Scientists explain damage to the nervous system as the cause of neurodermatitis by dysfunction of peripheral nerve fibers. Therefore, the patient begins to experience severe itching, and rashes appear on the body. The desire to scratch the skin leads to injury, increased intensity of itching and swelling of the tissue.
Neurodermatitis is not a contagious disease. Often its root cause is a genetic predisposition to allergies. The human body can react with illness to any irritant - from the fur of a pet to your favorite cosmetic product.
Neurodermatitis - types and symptoms
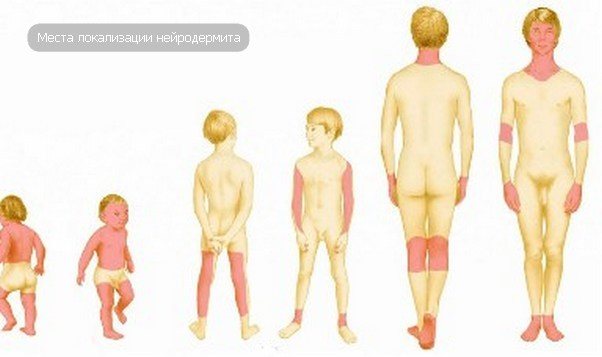
Neurodermatitis is divided into several varieties. The classification was developed according to the criteria of “location of rash localization” and “degree of prevalence of the process.”
Based on this, the disease is diagnosed by type:
- Limited. The most common form of neurodermatitis, affecting small areas of the skin.
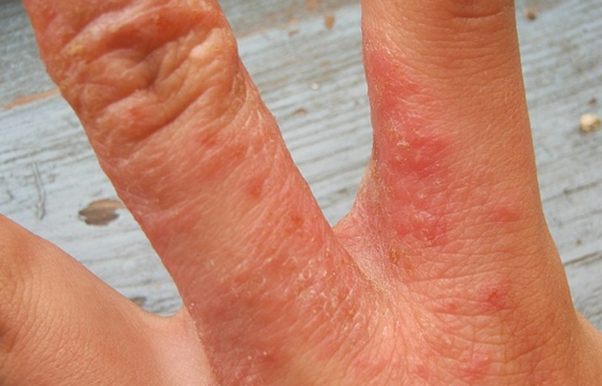
- Diffuse. Pathological elements appear multiple and occupy large areas of the body. Usually the rash is localized on the face, neck, knee-elbow cavities, and arms. Neurodermatitis on the hands is a subtype of diffuse neurodermatitis, its symptoms can be seen in the photo (above), and the principles of treating the disease will be described below.
- Linear – affects the upper and lower extremities.
- Follicular – affects the scalp.
- Psoriasiform - appears on the neck and head.
- Hypertrophic - localized in the groin area.
- Decalvating - a rash forms on the hairy areas, subsequently the affected hairs fall out.
The main symptom of the acute stage of the disease is unbearable itching, which intensifies at night. Other signs appear later. At first, the rash resembles red spots, papules and plaques that tend to merge. Due to scratching, the body is affected by a secondary infection, which turns the elements into pustules - vesicles with contents. The skin tissues swell and appear puffy.
External signs of neurodermatitis in adults are shown in the photo.
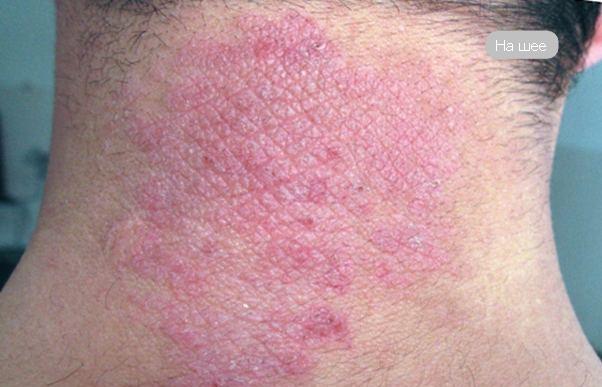
Doctors see 3 zones on a patient’s body:
- The first is the lichenification zone. It is located in the center of the affected tissue.
- The middle zone is located around the central zone. It is identified by isolated papules.
- The third zone is called “peripheral”. It is determined by hyperpigmentation.
In chronic patients in remission, a zone of lichenification appears due to irritation of the skin, because it is difficult for a person to resist scratching. Multiple papules form on the scalp of the body. The skin of the fingers, palms and soles cracks.
If neurodermatitis develops on the face, the patient notices increased eyebrow loss and an abnormal shade of the eyelids. Skin color changes due to constant scratching. Pale pink papules form on the forehead and cheeks. Itching at the site of their localization intensifies periodically. If bright spots appear on the cheeks, they do not have clear boundaries, but constantly itch and begin to peel off.
The photo clearly demonstrates what neurodermatitis looks like on the face.
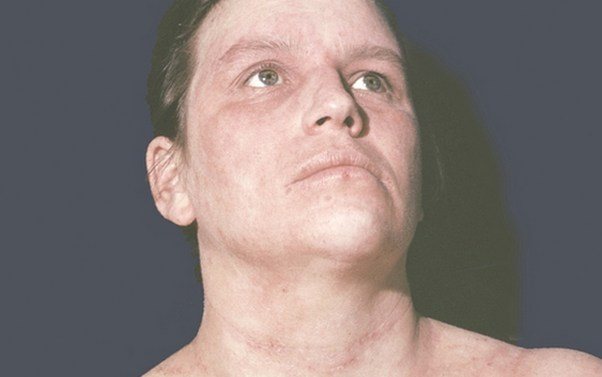
Scratching the skin of the face is dangerous due to the addition of pyococcal infection. Infection with pyococcus is recognized by a pronounced gray tint to the face. The skin becomes dry and flaky. It itches in both problem and healthy areas.
Features of neurodermatitis in children
Neurodermatitis most often affects children with allergies. The disease develops not only due to allergies to food, wool or pollen. In some babies, a predisposing factor is congenital intolerance to certain substances. Children with an unstable psycho-emotional background and problems with the nervous system are also susceptible to the disease.

How neurodermatitis in children will be treated depends on the specific symptoms. The traditional variant of the pathology is one inflamed focus (a larger number of zones are observed less frequently).
Pharmacies are hiding a cheap anti-wrinkle trick! -15 years instantly, if green...
Rotaru admitted why at 68 years old she has no wrinkles! It turns out the singer...
In the acute period, an erythematous area is detected on the skin, which subsequently transforms into a bizarre papule with a diameter of up to 3 mm. Several papules merge into a single lesion of any shape. As the pathology progresses, weeping begins.
Important signs of neurodermatitis in children are:
- dry skin;
- white dermographism;
- the severity of the skin pattern (the lines are drawn most strongly on the palms).
The hyperpigmentation zone reaches several centimeters and smoothly transitions into normal tissue. At different ages of children, neurodermatitis behaves differently. In infants, a rash forms on the neck, face, extensor parts of the limbs and scalp. By the age of 3, the disease is usually cured.
After 2 years, inflammatory changes in the skin of children are observed in the elbow and popliteal cavities. The rash forms on the neck and on the joint surfaces - ankle or wrist. In adolescents, foci of neurodermatitis are localized on the flexor areas of the limbs, hands, lips and eyes.
Dermatologists are developing a treatment regimen for neurodermatitis for children from the following groups of drugs:
- sedatives;
- complexes with vitamins A, E, B;
- glucocorticosteroid ointments (Advantan, Afloderm, Elokom);
- antihistamines (Cetirizine, Loratadine);
- histamine receptor blockers (Cyproheptadine).
During the treatment of neurodermatitis, it is useful to feed the child with fermented milk products, fish, poultry, quail eggs, soybean oil, avocados, and multivitamin juices. It is forbidden to give sweets to the baby.
Treatment of adult patients for neurodermatitis
Drug treatment of neurodermatitis at home is based on the internal use of antihistamines - Citrine, Erius, Fexofenadine. They are taken once a day. The drugs do not cause side effects; they make skin receptors insensitive to the effects of histamine.
Antiallergic medications also include calcium gluconate and sodium thiosulfate. For the general health of the body, vitamins of groups E, A, B are prescribed. Systemic hormones are offered to the patient in advanced stages of neurodermatitis or when other means have been unsuccessful.
Local therapy is based on the use of ointments - resorcinol ointment and ointments with tannin and boric acid are good for neurodermatitis.
If these medications do not have an effect, doctors recommend weak hormonal ointments - Dermovate, Sinaflan, Celestoderm B, hydrocortisone. A steroid drug with prednisolone quickly penetrates the bloodstream and relieves inflammation. Use prednisolone ointment up to 3 times a day. per day, occlusive dressings are applied with it as prescribed by the doctor.
If exudate is released from the pustules, dermatologists suggest treating the body with Fluorocort. Based on triamcinolone, this ointment quickly relieves inflammation and itching. The hormonal drug is distributed in a thin layer over the skin, and sometimes bandages soaked in the substance are applied. The procedure is performed 2 - 3 times. per day, but not more than 4 weeks.
When neurodermatitis is complicated by a bacterial/viral infection, adult patients are prescribed antibacterial ointments:
- Symbicort;
- Oxycort;
- Hyoxyzone;
- Corticomycin.
Patients with dry, actively flaking skin are prescribed Prednicarb. The combination drug contains urea and prednisolone. The ointment softens the skin and prevents keratinization, relieves inflammation and slows down the release of fluid that accumulates in pustules.
Video: treatment of neurodermatitis.
Treatment of neurodermatitis: folk remedies and diet
Traditional treatment of skin diseases is allowed after the approval of a doctor. How to treat neurodermatitis at home? For external use, experts advise preparing ointments. According to the first recipe, the drug is obtained from petroleum jelly and propolis (1: 10). First, Vaseline is liquefied on the stove until it boils, then mixed with propolis and cooled. The product is rubbed into the affected areas.
Ointment with natural fat is prepared as follows:
- 0.5 kg of pork lard is heated in a frying pan, strained and poured into a porcelain container;
- 250 g of purified sulfur is mixed with warm fat;
- the body is treated with baby soap, and then ointment is applied.
Liquid for compresses for neurodermatitis is prepared from oak bark. Take it in an amount of 5 parts and combine it with nettle, coriander, birch leaves, wormwood, mint, and flaxseeds. The collection is infused in boiling water for 1 day. The next day, moisten gauze with the infusion and apply a compress.
If pustular elements are scattered throughout the body, baths will help speed up the treatment. For example, you can mix potato starch, crushed birch leaves and walnut partitions (1 tbsp each). Throw the mixture into water and take a bath for 20 minutes.
A herbal bath for neurodermatitis is prepared from the following components:
- oak bark – 50 g;
- sage – 15 g;
- rowan berries – 40 g;
- horsetail – 30 g;
- scumpia leaves – 40 g.
Boil half a glass of the resulting mixture for 15 minutes. in 3 liters of water. The broth is filtered and added to the bath.
Healing liquid for baths can also be prepared with a decoction of oregano, yarrow, coltsfoot, and plantain. But regardless of the recipe, after taking a bath you should always lubricate the affected areas with olive/sunflower oil or rendered pork fat.
Video: folk remedies for treatment.
In the process of treating skin pathologies, it is important to adhere to nutritional rules. The diet for neurodermatitis in adults is based on portioned meals without overeating. The diet must include fresh vegetables with plenty of fiber. Consumption of meat and fish should be limited. It is recommended to eat meat boiled with the addition of herbs - it makes the dishes easier to digest.
Approved products for patients with neurodermatitis are:
- rice;
- kefir;
- goat milk;
- fruits – fresh and baked;
- lean varieties of fish and meat;
- vegetables – stewed and steamed;
- mineral water, green tea, mint infusions.
Here is a list of foods that are prohibited for patients with neurodermatitis:
- honey;
- chocolate;
- fast foods;
- chicken eggs;
- spicy cheeses;
- citrus juices;
- butter;
- herbs and spices;
- semi-finished products;
- fresh cow's milk;
- marinades and canned food;
- snacks and fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- baking and bakery products;
- concentrated juices;
- black tea and coffee, alcohol;
- vegetables and fruits with bright skins - apples, carrots, beets, raspberries, citrus fruits, strawberries.
PS In the treatment of neurodermatitis, it is important not only to follow a diet and take medications, but also to set yourself in a positive mood. If nervous scratching occurs during sleep, go to bed wearing cosmetic gloves.
Hypersensitivity disorders that can cause allergic dermatitis
The clinical signs of all allergic hypersensitivity reactions are similar: itching, erythema, hair loss, papules and, over time, hyperpigmentation and lichenification. Differentiation between reactions is based on a careful history, the nature of the clinical signs and, most often, assessment of response to clinical trials.
Hives
Urticaria is a classic type 1 hypersensitivity disorder. Clinical signs tend to be acute at onset and include itchy blisters or large areas of swelling. Clients commonly refer to these lesions as urticaria. It can be local or generalized.
Hypersensitivity to intestinal parasites
Hypersensitivity to intestinal parasites is a poorly documented and somewhat controversial reaction. Various intestinal parasites (roundworms, coccidia, hookworms, tapeworms or dicotyledonous worms) can cause pruritus, urticaria, seborrhea or generalized papular crusting dermatitis. Hookworm larvae can penetrate the skin and cause inflammation and itching as they migrate. But the pathophysiology of itch caused by internal parasitism is unclear. This may be due to a byproduct of the parasite, an immune reaction on the part of the patient, or another mechanism. The diagnosis is confirmed by excluding other causes of itching, finding parasites on stool examination, and observing resolution of clinical signs after parasiticidal therapy.
Hormonal hypersensitivity
Hormonal hypersensitivity is another poorly documented and somewhat controversial hypersensitivity reaction that is believed to be caused by reactions to sex hormones. It is unclear whether it actually exists in dogs or cats. Clinical signs mimic those of other hypersensitivity reactions and coincide with the onset of estrus in females. For men, seasonality is not observed. Surgical castration helps treat this problem.
Hypersensitivity to bacteria and Malassezia. Many animals with secondary staph infections or Malassezia fungal overgrowth are itchy. It can be caused by an underlying disease, as well as an allergic reaction to antigens secreted by these organisms. Antimicrobial therapy and identifying the trigger that predisposes an animal to overgrowth are the keys to successful treatment.
Otodectosis
Hypersensitivity reactions to ear mites (otodectosis) are most common in cats. But they also occur in dogs. In typical ear mite infestations, the itching is usually limited to the face, head and ears and all stages of the mites are easily detected. Itching associated with ear mite hypersensitivity may also be localized to the scalp or may be generalized. Diagnosing this disease can be difficult because, unlike common infestations, mites are less common. Diagnosis is usually made after observing a positive response to treatment for otodectosis. Read more about ears on the page: treatment of ears in dogs.
Main symptoms and signs
It's easy to spot the problem. Symptoms vary somewhat depending on the type of allergen, but the main ones remain the same:
- Constant skin itching, causing a lot of inconvenience to the animal, which itches almost incessantly.
- Redness in the problem area.
- Peeling of the skin, in some places it becomes rough, resembling large calluses.
- Hair loss.
- Release of exudate from the surface of the skin.
- Soreness.
- General deterioration of the dog's condition: it may lie down more, eat and play less.
Many owners begin to think about how to treat their pet, although the first step is to find out the type of dermatitis.
Even a veterinarian will not always be able to tell from a photo or external signs what led to the development of the problem.
General symptoms
Symptoms of dermatitis of any etiology include:
- erythema (redness of the skin);
- subcutaneous swelling;
- local hyperthermia (skin temperature in the affected areas is increased);
- dryness, rough skin,
- alopecia (“bald patches” on the affected areas);
- formation of skin rashes in the form of papules (nodules) and pustules (pustules);
- itching (the dog constantly tries to scratch the skin);
- if the dermatitis affects the dog’s limbs, it may limp due to pain and swelling;
- change in behavior - the animal may lose appetite, become restless, aggressive, and sleep poorly.
First aid
Sometimes it is not possible to take your dog to the vet immediately. To alleviate the animal’s condition, it is necessary to eliminate the external irritant. Before starting treatment, the affected areas must be prepared. Places where there are wounds are first washed with water and treated with boric acid. Then the hair is cut, exudate and dead tissue are removed, and treated with an antiseptic. Most often, a 1% solution of chlorhexidine or Zooderm is used. Do not pick off dried crusts. They need to be soaked with an antiseptic, and only then removed from the wound surface.
Antiseptic sprays can be applied to small and shallow wounds . They also have a drying effect. However, if used frequently, these products can cause irritation, so it is not recommended to use them more than once a week.
If eczema occupies a large area or affects deep layers, a drying ointment is applied to the wound surface. In addition, you can use products that promote regeneration. Itching can be reduced with a solution of novocaine, which is added to the treatment compositions.

It is important that the dog does not lick or scratch the affected areas. They need to be protected with bandages or a special collar.
Treatment of secondary infection
As a rule, its appearance leads to blurring of the clinical picture. At first glance, it is not clear what kind of illness it is, and the owners do not know where to start treatment. In addition to the injectable antibiotic, it is also necessary to use topical agents. They are an auxiliary, but very important part of the course of treatment.
- The first step is to clean the surface of wool, soggy crust and pus. To do this, it is best to use a swab moistened with any antiseptic solution.
- In addition, Levomekol and wet lotions of the affected areas with Chlorhexidine can be used externally.
- Antibacterial drugs such as streptomycin ointment and its analogues are widely used.
- Often, in addition to a bacterial infection, animals also develop a fungal infection. Most often, a complicated course of pyodermatitis of the paw pads occurs. Products based on clotrimazole have proven themselves well. When treating, you need to make sure that the animal will not lick the product.
There are no special ointments for allergic dermatitis for dogs. Veterinarians analyze the animal’s condition, do the necessary tests and, based on this, select the most effective treatment.

Veterinary assistance
At the clinic, the dog will first undergo the necessary tests to identify the type of dermatitis. The owner will be interviewed in detail about the circumstances surrounding the condition.

Then procedures will be carried out aimed at:
- relieving itching;
- local anesthesia; in case of severe pain, a novocaine blockade will be given;
- anti-inflammatory treatment of damaged skin areas.
Flaky areas are lubricated with special creams. Drying solutions and antimicrobial powders are applied to weeping or purulent ulcers.
If necessary, the dog may be given an antibiotic or detoxifier. At the end of the appointment, the doctor will prescribe the necessary medications for home treatment of dermatitis in a dog. Dosages are selected individually. They must be strictly followed so as not to provoke complications and side effects.
In some cases, the pet is indicated for physical therapy. Ultraviolet and infrared radiation are highly effective. These procedures help accelerate skin regeneration, destroy pathogenic microflora, and activate local immunity. The best result is ensured by the combined use of physiotherapeutic and pharmaceutical treatment methods.
The owner will also be advised on proper care of the animal to prevent skin problems.
Summer dermatitis of dogs
Inflammation in the dermis, the deep layer of skin - dermatitis - is common in dogs. The disease can be of a different nature, have a different cause, and occur in animals of different breeds, ages and conditions of detention. A pet can be completely cured only if the diagnosis is carried out correctly, mainly in the laboratory. Self-medication of dermatitis in dogs without going to the clinic leads to the disease becoming chronic and developing complications. Dermatitis in dogs is often a consequence of the simultaneous influence of several factors.
In summer, even minimal damage to the skin provokes acute weeping dermatitis, which most often occurs in dogs with a highly developed coat or sensitive skin: chow chows, Caucasian shepherd dogs, malamutes, Newfoundlands, golden retrievers, shar-peis.
.
VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: eczema-wetting tihvinskiyhram.ru new methods of treatment.1
Diagnostics
Diagnosis comes down to a series of measures aimed at determining the etiology of the disease.
We are talking about:
- General examination and history taking of a shaggy patient. The doctor examines the animal and assesses the degree of damage to the skin. The veterinarian will definitely ask how quickly the disease developed, when the first symptoms appeared, and what preceded this condition. You should definitely talk about all chronic pathologies, if any, about nutrition.
- Flea and contact dermatitis are excluded if the dog is regularly treated against pests with reliable and effective means. Contact - the same, if nothing new happened, the dog did not walk anywhere, nothing was washed, cleaned, or turned on in the house.
- Research.
Diagnostic measures:
- urine and blood analysis;
- coprogram;
- microscopic examination of scraping of the dermis;
- bacteriological culture;
- laboratory tests for possible associated infection.
In some cases, the veterinarian may prescribe additional procedures.
Preventive actions
It is not difficult to prevent the occurrence of dermatitis - owners need to carefully approach the issue of keeping and feeding the animal. At home, it is necessary to carry out regular inspection, treatment for parasites, use of vaccines and other methods of general prevention. The use of various drugs should be carried out as prescribed by the attending physician, as they can cause allergies and contact dermatitis.
The diet should be compiled independently, and if problems are detected, on the recommendation of a veterinarian. The use of prepared foods should be limited as they are a common cause of atopy. You also need to use any medications carefully - a local reaction to medications for fleas and ticks also often leads to dermatitis, like the parasites themselves.
There is no universal means of preventing skin inflammation, since the pathogenesis of this disease has a wide variety of causes. Pododermatitis in dogs develops with most local irritations, so the owner needs to protect the pet from them. And if a pathological condition is detected, contact a veterinarian immediately.
Treatment
Each type of interdigital dermatitis requires a different approach to treatment.
- With traumatic dermatitis, the main task is to accelerate the healing process of damaged skin. To do this, use zinc ointment, Chemi spray, Kubatol spray or Baldecchi wound-healing zinc powder. Sore paws of the animal should be protected from water.
- If the cause of the disease is stress, the signs of dermatitis, as a rule, disappear on their own after the dog is treated with sedatives Vet Expert Calm Vet, Antistress Bifar, NoviPet, Sanal.
- Pododermatitis caused by subcutaneous mites is treated with antiparasitic agents. In veterinary medicine, Ivermectin or Ivermec is used. These drugs are toxic, so they are not prescribed to pregnant and lactating bitches, and in the case of external use of these drugs, measures must be taken to prevent the dog from licking the medicine from the paw.
- The allergic form of the disease is more difficult to treat than others. Here it is important to completely eliminate the possibility of contact of the animal with the allergen. And if it is a food product, the dog has to be put on a hypoallergenic diet for 2-3 months. Chlorhexidine, Kubatol or tar shampoo are used as symptomatic treatment.
- Bacterial dermatitis (
pyoderma) develops when there is damage as a result of a secondary infection. Its treatment requires long-term use of antibiotics, sometimes several at the same time. Veterinarians usually prescribe drugs with the active ingredient enrofloxacin: Baytril, Enroxil; Enroflon, Enroflox. For better healing and relief of itching, agents are prescribed that have a drying, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect: Baldecchi zinc powder, Canina wound healing balm or alum solution.
Attention! During treatment, conditions must be ensured for unhindered healing of the affected skin. Its surface must always be clean and dry. It is also important to exclude the possibility of the dog licking its sore paws. For this purpose, it is recommended to use a special protective collar.
Physiotherapy
Among physiotherapeutic procedures, ultraviolet and infrared irradiation are popular. UV and infrared rays accelerate skin restoration, kill pathogenic microorganisms, and strengthen local immunity. The combined use of physiotherapy and drug therapy helps to obtain a more lasting therapeutic effect.
Therapeutic techniques
Let us immediately describe the main provisions of all therapeutic methods actively used in the treatment of this disease:
- It is necessary to completely get rid of the irritating factor and protect the pet from the action of the identified allergen (only a doctor can determine it in an equipped clinic).
- Treatment of damaged dermatitis with chlorhexidine. This is a good and inexpensive antiseptic that will help prevent bacterial contamination.
- The use of antibacterial drugs, of which the most accessible to the “mere mortal” is the usual chloramphenicol.
- To relieve skin itching, it is necessary to use antihistamines. If the dog is completely unbearable, the pet is literally tearing the skin, you can use half a tablet of Suprastin. But it’s better to take your pet to the vet right away.
- Nutritional adjustments are required. Again, we strongly advise you to talk to your veterinarian for this.
- If there is a sharp deterioration in the condition of the skin, it is necessary to urgently contact a veterinary dermatologist or allergist.
Treatment should be aimed at immediately eliminating the cause, and only then at suppressing the clinical manifestations of the disease. In many dogs, fleas are the primary predisposing factor. In addition, you need to look at the localization of skin lesions. If they are located near the ears, one may suspect the presence of otitis media when there are foci of inflammation near the anus - inflammation of the anal glands, etc. Regardless of the type of identified root cause, it should be eliminated simultaneously with the elimination of the dermatitis itself, since otherwise the treatment may be completely ineffective.
List of drugs against the disease
There is no specific therapy for dermatitis in dogs. All medications are selected individually, depending on the type and degree of development of the disease.
During the acute period, the skin is treated with antiseptics. For this use:
- streptocide preparations;
- Syntomycin ointment;
- Levomekol;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- Dexamethasone cream mixed with vitamin PP, B6.
If the ulcers fester, the affected area should be rinsed well with hydrogen peroxide (or 0.05% chlorhexidine solution) and covered with antimicrobial powder.
Usually prescribed:
- Norsulfazole;
- Streptocide (with the addition of an antibiotic if necessary);
- Iodoform with boric acid.
Apply external agents as follows: apply a thin, even layer on a clean cotton cloth, apply to the affected area of the skin, and secure with a bandage. The dressing should be changed twice a day (for weeping wounds - up to four times).
When treating allergic dermatitis in dogs, antihistamines are prescribed to relieve itching:
- Suprastin;
- Allervet;
- Tavegil.
In severe cases, it is recommended to take glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone and others). They are given in short courses under constant veterinary supervision due to the large number of side effects and contraindications.
Purulent dermatitis is treated with antibiotics. Most often used:
- Cephalexin;
- Baytril;
- Enrofloxacin.
In the treatment of acral dermatitis in dogs, psychotropic drugs (Phenobarbitone, Diazepam, Hydroxyzine) or tricyclic antidepressants (Amitriptyline, Clomipramine) are sometimes used.
Giving any medications to a dog without a veterinarian's prescription is prohibited!
To stimulate the animal's immune system, use:
- Immunofan;
- Cycloferon;
- Gamavit.
Parasitic dermatitis is treated with antifungal (Fungin, Zoomikol) or antiparasitic (Skalibor, Sanofly) medications.
Vitamins of group B, E, A, PP are used as general strengthening agents. When there is a need to accelerate the removal of toxins from the body, the dog is given the diuretic drug Furosemide in tablets.
Treatment can be supplemented with traditional medicine. Lotions made from grated raw potatoes or decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, calendula, witch hazel) will help alleviate the dog's condition.
If drug treatment is ineffective (in rare cases), radiation therapy or surgery is required.
Traditional medicine
Traditional medicine can be used as an additional remedy for the treatment of dermatitis in dogs. Ointments, compresses and lotions based on chamomile, celandine, fireweed, burdock, and plantain will help ease the course of the disease and reduce the severity of symptoms. For example, a compress based on raw potato pulp or a decoction of pear leaves, from which lotions are made, are popular.
To prepare a medicinal ointment from herbs, take 1 tbsp. l. the necessary plants (for example, chamomile, fireweed and plantain), mixed with hay dust in a volume of 400 ml, poured boiling water, kept in a “bath” for 5 minutes. The pulp is removed from the resulting broth, mixed with 15 g of butter and kept on fire until the mixture reaches a homogeneous consistency. After adding the same amount of glycerin, the ointment is ready for use. It should be applied to damaged areas of the skin four times within a month.

Regular hygiene measures when soiled are good prevention of dermatitis
Treatment of neurodermatitis in dogs
Neurodermatitis (atopic dermatitis) in dogs is a chronic disease.
It is characterized by dry skin, itching and various rashes. Modern lovers of four-legged friends have to deal with such trouble more and more often. Through scientific analysis, experts were able to prove that neurodermatitis cannot be transmitted from one dog to another.
However, the occurrence of the disease may occur due to genetic predisposition.
Which breeds are more likely to be affected by the disease?
- Labrador.
- German Shepherd.
- Irish, English setters.
- American, French, English bulldogs.
- Golden retriever.
- Dalmatian.
- Dachshund.
- Chow-chow.
Causes of neurodermatitis in dogs
Atopic dermatitis may first appear in a pet between the ages of one and three years. It has been proven that the gender of the dog does not affect the acquisition of the disease. Let's look at the most common causes of neurodermatitis in dogs:
- Genetics.
- Microclimate of the habitat.
- The climate of the area where the dog lives.
- The presence of allergens (dust, grass, human skin, trees, pollen, flea excrement, fungal spores).
- Chronic diseases that contribute to the development of neurodermatitis.
It is important to understand that animals that are not properly cared for by their owners are more likely to suffer from flea dermatitis.
How to recognize the disease
The following symptoms of neurodermatitis in dogs are observed:
- Skin pigmentation increases noticeably.
- The dog is constantly itching.
- Excessive hair loss.
- Thickening and redness of your pet's skin.
Diagnosis of neurodermatitis
Before making a diagnosis, the doctor will need to find out the medical history and use it to find out the cause of the disease. To do this, the pet owner needs to provide specific information:
- Are there other animals in the house?
- How and what does a dog eat?
- Has it ever happened that the dog lived on the street?
- How often do you walk your dog?
- Features of animal bedding.
The next step will be to conduct laboratory tests:
- Skin scraping is examined.
- An analysis of stool, blood and urine is done.
- The blood is examined for biochemistry.
- Fungal microflora is determined.
How to treat atopic dermatitis
You should understand: it is very difficult to completely cure a dog and deprive it of the chance to get sick again. Treatment should take a long time and be complex. This should be approached with all seriousness, because the health of the four-legged animal is at stake.
Ideally, of course, it is possible to determine exactly which allergens are likely to affect a dog, although this often becomes difficult to do. You need to eliminate the allergen from your animal's environment as soon as possible. In this case, you should change the microclimate of your pet's habitat. The bowl, leash, collar, shampoos, all grooming items, etc. are changed.
It would be good to treat the area where the dog lives with antibacterial agents and install a device to purify the air in the room. The owner must regularly carry out wet cleaning of the house, monitor the humidity of the room, and wipe off dust in a timely manner to avoid the spread of dust mites.
It is recommended to take your pet to a veterinary clinic every two weeks for an examination.
The specialist will determine whether continued treatment with current medications is required or whether it is worth changing them, whether there are side effects, and you will also be able to assess how effective the treatment is and find out the prognosis for your pet’s recovery. When the disease goes away, visits are reduced. Typically, a veterinarian will schedule an examination every 4-6 months.
Often dog owners notice redness on the skin of their pets. If the animal constantly scratches and bites the affected area, most likely it is dermatitis.
What is dermatitis: nature of the disease and symptoms
Dermatitis is a disease that belongs to the category of allergic and can be caused by factors of various natures.
In the general understanding, the principles of nosology are most often taken as the basis for classifying the nature of the disease.
According to this doctrine, various disorders of the functioning of the body are united based on kinship. In this vein, dermatitis refers to skin diseases.
The main clinical picture is all kinds of skin lesions. Dermatitis is of infectious, inflammatory or hereditary origin. In this case, the course of the disease goes through two stages, and treatment is carried out taking this factor into account.
The acute phase is characterized by pronounced symptoms, which usually disappear if the animal is isolated from the source of the pathogen. The chronic stage occurs if the pet is constantly in contact with factors that cause irritation.
However, the symptoms of the disease at both stages are similar, although they have different degrees of manifestation. The presence of dermatitis can be diagnosed if the following skin changes are visually observed:
- Redness;
- Swelling of the affected area;
- Severe itching, burning;
- Hair loss;
- An increase in temperature at the site of inflammation, and throughout the body as a whole;
- Blisters, ulcers.
How does dermatitis manifest?
First of all, dermatitis manifests itself in the deterioration of the dog’s physical condition. Often this factor is supplemented by deviations in the behavior of the animal as a whole.
In the case of deterioration in physical condition, we are talking about visually observable changes - the affected areas become inflamed, red, covered with blisters and hematomas. In places of damage, hair often falls out and suppuration forms. Body temperature rises.
Characteristic violations of the behavioral aspect of animal functioning are:
- Obvious anxiety - the dog constantly scratches painful areas, aggravating the situation; moves from place to place;
- Changes in eating behavior - refusal to eat;
- Transformation of the animal’s character – reluctance to make contact with the owner or, conversely, aggressive reactions;
- Depression, apathy.
Factors provoking the development of dermatitis
Factors that cause the appearance and development of dermatitis can be divided according to their qualitative component. The nature of their occurrence may be:
Physical factors
This group includes damage to the skin that occurred as a result of:
- Mechanical shock from an external object - stick, stone, sharp objects;
- Falls from a height;
- Exposure to high temperature (burn followed by dermatitis);
- Improper maintenance of the animal - lack of daylight or proximity to a source of electricity.
Biological factors
Biological causes of dermatitis represent the most common category of skin disease in dogs. Among the main pathogens:
- Pathogenic viruses (parvovirus, plague, hepatitis);
- Bacteria (streptococci, helminths);
- Some mushrooms and plants are poisonous if they enter the stomach of an animal.
Chemical factors
The list of chemicals that can lead to dermatitis is long. We are mainly talking about toxic aerosols, paints and varnishes, household chemicals and medicines.
Psychogenic factors
Stressful situations - a change of owner, place of residence or changes in feeding regimen - can lead to the appearance of dermatitis.
Differences from pododermatitis
Pododermatitis is a disease of an animal's paws. The clinical picture has some similarities with dermatitis: redness, sores, bloody boils and swelling.
The causes, as in the case of dermatitis, can be mechanical (trauma), biological (viruses, infections) or allergic in origin (contact with a contaminated object, food intolerance to certain products).
The main difference from dermatitis is the fact that the disease affects the pads and paws of the animal. Failure to contact a veterinary clinic promptly can lead to lameness in your pet. Preventive measures consist of following hygiene procedures (washing paws after every walk, cleaning off dirt that accumulates between the animal’s toes, daily inspection of the pads).
Source: https://why-why.ru/info/lechenie-nejrodermita-u-sobak/
Interdigital dermatitis in dogs: types and methods of treatment
Interdigital dermatitis in dogs is an inflammatory disease. When it occurs, the skin layers between the animal’s toes are damaged. Inflammation can also be observed on the pads and in the nail area. Some animals suffer from a skin disease localized on the top of the paws.
Many owners, after comparing the symptoms with the photo, begin to treat the disease on their own. However, this should be done only after examining the dog. Your veterinarian can prescribe treatment, which depends on the cause of the disease.
Interdigital dermatitis in dogs is characterized by inflammation of the skin between the toes.
Acute wet dermatitis of dogs and cats (pyotraumatic dermatitis)
Dogs can laugh. Their laughter is a repeated snort. Let your beautiful pet win a prize for you! Weeping dermatitis in dogs is most common among animals with long hair or a thick undercoat, although the delicate sensitive skin of short-haired dog breeds is also susceptible to this problem. The main cause of weeping dermatitis in dogs is a local allergy to a specific antigen. The most common cause of a local allergic reaction is insect bites, especially fleas.
Does a sick pet need special care?
Living conditions affect the effectiveness of treatment for this disease. To quickly rid your dog of flea dermatitis, the animal owner must:
- Walk your dog outdoors regularly. Walks with your pet should be long - from 0.5 to 2.5 hours a day. To prevent an animal from picking up fleas on the street, you need to put a special collar on it and treat its fur with anti-flea drugs before leaving. To reduce the risk of re-infection, it is recommended to choose uncrowded places for walking, where you can rarely see other animals.
- Protect your pet from contact with other animals. It is necessary to ensure that while walking he does not have contact with other dogs, especially animals living on the street. Otherwise, your pet may be infected again.
- Carry out insecticidal treatment of the room in which the dog lives, as well as its personal belongings - bedding, toys. For this purpose, you can use specialized drugs - imported products “Frontline” and “Bolfo” or domestic “Bars”. If it is not possible to purchase such chemicals, you can use folk remedies instead, for example, tansy decoction.
- Provide your pet with a nutritious diet consisting of foods familiar to the animal. During the treatment period, it is forbidden to take new food or give the animal new products, as they can cause allergic reactions that complicate treatment.
Your dog can be given vitamin supplements to strengthen its immune system. However, such drugs must be selected by a veterinarian. Violation of this rule can negatively affect the dog's condition. It is possible that your pet will develop a severe allergy to an incorrectly selected complex, which will also require long-term complex treatment.
First aid and subsequent treatment for a dog
Weeping eczema is very painful, therefore, before carrying out any manipulations, it is advisable to numb these areas.
Air access must be provided to the affected areas of the skin. To do this, trim the hair around the eczema. Then the wounds need to be treated with an antiseptic. This could be a tincture of St. John's wort, calendula, or a solution of chlorhexidine. After this, treat the eczema with some kind of drying agent. Zinc ointment, zinc powder, and talc are suitable for this. If the dog suffers from severe itching, then you can give it an antihistamine - Tavegil, Suprastin, Loratadine.
In addition, it is necessary to monitor the dog and not give it the opportunity to scratch its wounds. If the eczema does not heal, then the animal should be shown to a veterinarian as soon as possible. Your pet may need antibiotics to recover. In rare cases, a dog may be prescribed a hormonal drug.
Diet
Nutrition is an important component of therapy. This is especially important when the allergy is related to food. You need to feed your dog tightly, but with high-quality foods rich in vitamins.

The diet must include meat. It could be beef, chicken or turkey. Sea and river fish, also low-fat, are useful.
For cereals, it is better to give bulgur, oatmeal, buckwheat, rice in small quantities (to avoid constipation), and polenta. Be sure to include vegetables and fruits, dairy products.
When feeding an animal with dry food, they switch to hypoallergenic super-premium lines. A diet is a transition to proper nutrition.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of interdigital dermatitis, it is recommended to provide the dog with high-quality, nutritious feeding, ensure a comfortable mental state and constant moderate physical activity. After each walk, be sure to thoroughly wash and wipe your paws dry, and if even minor damage to the skin is detected, treat the wounds with an antiseptic. The owner must ensure that the animal does not have access to aggressive chemicals used at home.

To prevent infectious and parasitic diseases that can cause dermatitis, the best means are regular vaccination and treatment with insecticidal and anthelmintic drugs.
Sources
- https://vashipitomcy.ru/publ/sobaki/bolezni/moknushhij_dermatit_u_sobaki_priznaki_simptomy_lechenie_profilaktika/26-1-0-1997
- https://mybarbos.com/dermatit-u-sobak/
- https://veter96.ru/dermatologicheskij-atlas/piotravmaticheskij—dermatit
- https://vashbarbos.ru/zdorove/zabolevanija/allergicheskiy-dermatit-u-sobak.html
- https://usatiki.ru/dermatit-u-sobak/
- https://Bobik.online/healf/disease/dermatit-u-sobak.html
- https://lapkins.ru/p/dermatit-u-sobak/
- https://jota.su/dermatit/mezhpaltsevyj-dermatit-u-sobak.html
- https://veterinar-dermatolog.ru/allergii-u-sobak/allergicheskij-dermatit/
- https://allergiya03.com/zhivotnye/moknushhaya-yekzema-u-sobak.html
- https://www.PorodiCobak.ru/zdorove-i-bolezni/dermatit-u-sobaki
- https://usatiki.ru/mezhpaltsevyj-dermatit-u-sobak-prichiny-i-lechenie/
- https://dogworry.ru/veterinariya/bloshinyj-dermatit-u-sobaki-simptomy-lechenie.html
[collapse]