II generation antihistamines
Fenkarol.
The sedative effect of fenkarol is either weak or not manifested at all. Side effects, such as dry mucous membranes, are not characteristic of fenkarol. Diazolin. This drug also causes little hypnotic effect and has a prolonged (long-lasting, continuing even after drug withdrawal) effect.
Suprastin. The hypnotic effect of this drug is quite strong. Additionally, the drug also has an antispasmodic effect, so it is often used as part of a lytic mixture when it is necessary to quickly reduce the temperature, for example, during an acute respiratory infection.
Tavegil. Among all the drugs in this group, tavegil has the most pronounced antipruritic effect. For bronchial asthma and respiratory infections, tavegil is prescribed with caution or not prescribed at all, as it leads to thickening of sputum.
Fenistil has the mildest effect, which is why this drug is often used in children under one year of age. When applied topically, fenistil (fenistil gel) easily relieves itching and redness characteristic of allergic skin reactions.
Zyrtec - the drug does not have a sedative effect, so it is often prescribed to people whose professional activities require quick reactions - for example, drivers. In addition, Zyrtec has zero drug interactions - that is, it does not interact with any medications, therefore it is most often prescribed as part of complex therapy for diseases - both allergic and infectious.
Claritin. The drug is approved for use in children starting from 2 years of age. It does not cause drowsiness and is considered one of the most effective antihistamines. The disadvantages of Claritin include its ability to create toxic combinations with some antifungal drugs (for example, Nizoral) and some antibiotics (for example, Sumamed).
Kestin. A long-acting drug, well suited for the control of seasonal allergic rhinitis. It is usually started to be used 10-15 days before the expected start of flowering in order to negate the symptoms of allergic rhinitis at the beginning of flowering.
Telfast. This drug is considered safe, as it is quickly eliminated from the body and does not cause symptoms of cardiac arrhythmia, which are characteristic of many second-generation antihistamines. The drug begins to act fairly quickly after use and within an hour after use it relieves almost all symptoms of allergic rhinitis.
Xizal. The effect of the drug begins within 12 minutes after ingestion and lasts for 24 hours after use. Xyzal is approved for use in children over 6 years of age.
Allergodil is a topical antihistamine (nasal spray). It is characterized by a rapid onset of action with very small administered doses. Ineffective for nasal congestion.
Description of the disease
Allergic rhinitis (rhinitis), or hay fever, is a common disease that develops when the body is hypersensitive to certain irritants. With direct contact with them, a wide range of symptoms appears - itching, sneezing, profuse nasal discharge, decreased sense of smell and conjunctivitis.
Depending on the course of the disease, seasonal and year-round rhinitis are distinguished. Allergies have been confirmed in both children and adults; most often, the pathology develops between the ages of 10 and 20 years. There is no effective treatment; therapy is only symptomatic and supportive.
Allergic rhinitis occurs upon contact with an irritant.
Provoking factors may include:
- plant pollen;
- medications;
- animal hair;
- cosmetics;
- household chemicals;
- dust;
- insects.
There are 3 forms of allergic rhinitis:
- Seasonal. It usually develops in spring or summer. The seasonal form is characterized by the presence of individual intolerance to plant pollen.
- Persistent (year-round). Occurs upon contact with other pathogens (food, medicines, etc.).
- Professional. This form occurs with constant contact with an irritant, due to the characteristics of a person’s specialization. In particular, bakers often develop an allergy to flour, and carpenters often develop an allergy to formaldehyde.
Each of the listed forms of the disease is characterized by the same symptoms, the intensity of which varies depending on the degree of sensitivity of the body to a particular pathogen.
How often can you inject Diprspan if you have allergies? Read the link.
Why is it necessary to use drops?
The effect of drops for nasal congestion is determined by the type of drug used. For allergic rhinitis, antihistamines, vasoconstrictors and hormonal medications are mainly prescribed. Irrigating medications based on sea water are also used to eliminate congestion and moisturize the mucous membrane.
The effect of antihistamines is due to the fact that the drugs inhibit the functions of a special substance (histamine) synthesized by the body in response to exposure to an allergen. Thanks to the activity of these medications, the symptoms of rhinitis disappear.
Effective vasoconstrictor drops eliminate swelling of the mucous membrane, thereby restoring nasal breathing. This result is achieved due to the fact that drugs of this group reduce the lumen of blood vessels, as a result of which the speed of blood circulation decreases and the inflammatory process is suppressed.
Read how to do inhalations correctly for allergic rhinitis here.
Hormonal drops and sprays affect mediators that trigger the inflammatory process. Medicines in this group provide a quick effect: nasal breathing is restored within a few minutes.
Reviews from doctors and allergy sufferers about nasal drops
There is no drug that would be characterized by all people in the same way. Each medicine has its own audience of “fans” and “detractors”. There are a large number of negative reviews of anticongestants from patients, especially xylometazoline - sneezing, increased rhinorrhea, the appearance of conjunctivitis when using products based on this substance. But many of them are associated more with errors in use (overly frequent or prolonged use, leading to addiction, lack of effect from the drug and the development of side effects).
Doctors, for their part, for the most part complain about the uncontrolled use of drugs for the common cold, which leads to the difficulty of selecting therapy when an allergy sufferer goes to the hospital.
Thus, nasal drops for allergies is a very broad topic. More and more new drugs are appearing on the market every day, and advertising is becoming more aggressive. However, the basic postulates remain unchanged - the selection of a drug should be based on the mechanism of development of the disease, the severity of symptoms and the general condition of the allergic person’s body.
II generation antihistamines
Antihistamines are the most commonly prescribed group of drugs for allergic rhinitis. Tablet forms are divided into three generations, which differ in composition, mechanism of action and number of side effects:
- first generation. This group includes Suprastin, Tavegil, and Diazolin. Their advantage is the rapid relief of the general condition by relieving tissue edema, reducing itching, reducing the frequency of sneezing and facilitating breathing. They are considered “first aid” drugs. Despite this, tablets are used quite rarely compared to medications of other generations. The fact is that they have a strong sedative effect, which is why they are limited in use by people whose profession requires concentration. The disadvantages also include a short-term therapeutic effect (no more than 5 hours). The risk of changes in psycho-emotional state, aggression, agitation, and hysteria cannot be excluded. Due to the high likelihood of addiction, it is recommended to select a different treatment regimen every three weeks;
- second generation (Loratadine, Claritin, Cetrin). Clear advantages include the absence of drowsiness after taking the drug. Tablets for allergic rhinitis have a prolonged effect, so that after a single dose the effect lasts for a day. Over the next few days, the person continues to be under medicinal protection from allergens. Restrictions on use apply to people with severe cardiac pathology.
Claritin has a minimal number of side effects, so it is often prescribed even to infants.
- third generation (Telfast, Zirtek, Tsetrilev). These drugs for allergic rhinitis are the best in the fight against the disease. They do not have a negative effect on the nervous system, and also do not affect the myocardium. Some representatives of this group are capable of accumulating in the body, which must be taken into account when drawing up a treatment regimen. The drugs can be used for several months.
Tsetrin
The active ingredient of the drug is cetirizine. It reduces the severity of symptoms and prevents their reappearance during hay fever. Regular use provides a decongestant, antipruritic effect, blocks the action of histamine, and also reduces vascular permeability.
Cetrin is prescribed as a tablet once a day. Children over six years old are recommended to take half a tablet twice a day. The drug should be taken with water in a small volume. The duration of the course can be 1-4 weeks, but if necessary it can be extended to six months.
The medicine has some side effects, among which it is worth highlighting:
- tremor, dizziness, insomnia, migraine, headache, agitation;
- change in taste sensations;
- dry mouth, tongue discoloration, liver dysfunction;
- stomatitis;
- rapid heartbeat, increased blood pressure;
- joint, muscle pain; inflammation of the throat mucosa.
Contraindications include pregnancy, lactation period, hypersensitivity to cetirizine.
Cromoghlin
A spray for allergic rhinitis blocks the release of biologically active substances that stimulate the development of allergies. The drug is prescribed for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes.
Among the contraindications we highlight:
- individual intolerance;
- polypous formations in the nasal passages;
- severe renal, liver failure;
- pregnancy (first trimester);
- age up to five years.
The remedy for allergic rhinitis must be used daily, otherwise the therapeutic effect will be incomplete. The recommended dosage is one spray up to four times a day. If necessary, the frequency of administration can be increased to six.
The drug is prescribed for a long course. Even after symptoms have reduced, its use should be continued, reducing the frequency of administration. The medicine is mainly prescribed in combination with a vasoconstrictor to obtain a quick effect.
Adverse reactions include:
- lacrimation;
- increased tissue swelling;
- unpleasant taste;
- nausea, vomiting;
- irritation, dryness of the nasopharynx.
It is believed that in cases of mild allergic rhinitis, the use of antihistamines alone may be quite sufficient to relieve all symptoms of allergic rhinitis. If the use of antihistamines is not enough (they really do not have a significant effect on nasal congestion and nasal discharge), then in this case they already speak of a moderate or even severe course of allergic rhinitis.
In such cases, along with antihistamines, doctors have to prescribe drugs from other groups - primarily topical hormonal agents (topical steroids).
Antihistamines are divided into first generation drugs, which have a sedative (hypnotic) effect, and second generation drugs, which do not have this effect. We will look at some drugs of the first and second generations, which are most often used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis in children.
Ketotifen. Ketotifen has virtually no side effects. The effect of the drug begins 2 hours after administration and lasts for 12 hours. Ketotifen is approved for use in young children.
Cromohexal. The drug is available in the form of a nasal spray, a solution for inhalation (used for bronchial asthma) and in the form of eye drops. Cromohexal for allergic rhinitis effectively reduces the amount of nasal discharge, nasal itching and sneezing, but has virtually no effect on nasal congestion. Due to the fact that cromohexal, in addition to the release of histamine, also blocks the release of almost all inflammatory mediators, it is widely used by doctors in Europe as an anti-inflammatory drug for acute rhinitis.
The age limit (up to 5 years), which is in the instructions for the drug, is only valid for inhalation through a compressor inhaler. Inhalation of cromohexal in children under 5 years of age can cause bronchospasm. At the same time, cromohexal nasal spray can be used from 2.5 years.
General principles of therapy for allergic rhinitis
Treatment of allergic rhinitis has one feature. Medical prescriptions usually include a complex of drugs with different directions of action. It is necessary to follow the general principles of their use:
- Before instilling the main medicine, you must first rinse your nose with saline solution.
- When simultaneously prescribing several groups of drugs, instillation should begin with vasoconstrictor compounds (if such are prescribed in the prescription). They relieve swelling of the mucous epithelium, and it is easier for healing substances to reach their destination.
- To instill the allergic rhinitis spray, you need to take an upright position. After administering the drug, turn your head slightly to the side and lie in this position for 10-15 minutes.
- If indicated, antihistamines in tablet form are used along with local remedies for allergic rhinitis.
- If an allergy is just making itself known, drugs that create a natural oil barrier in the nose (Prevalin) or sorbents (Polyorb, Enterosgel, Activated Carbon) can cope with it. The latter bind toxins and allergens that have gotten inside and are removed in the classical way.
On a note! Allergy patients believe that in order to be cured, it is enough for them to exclude the cause of the allergy, i.e. contact with a provocateur of pathological nasal congestion. This is partly true, but in most cases it is impossible to do this in reality (for example, if you are allergic to ragweed or dust). Therefore, you cannot do without the recommendations of otolaryngologists.
The complex of drugs against allergic rhinitis is divided into 3 groups:
- barrier agents;
- symptoms;
- drugs to control the disease.
Treatment of a runny nose of allergic etiology is possible only with drugs of the third group. Barrier agents are effective when the disease has not yet begun to manifest itself. Symptoms temporarily eliminate the signs of pathology without providing any therapeutic effect.
Cheap analogues
Cheap drops used for allergic rhinitis cost no more than 100 rubles. Such drugs include:
- Xylene. Has a vasoconstrictor effect. The price is about 30 rubles.
- Rhinostop. Constricts blood vessels, eliminating swelling. The medicine costs more than 35 rubles.
- For the nose. Stimulates vasoconstriction. The price reaches 100 rubles.
- Naphthyzin. Used to eliminate swelling.

The cost varies from 10 to 40 rubles.
You should also consult your doctor before using cheap medications.
In addition to classical drugs, you can find a large number of analogues on the pharmacological market. They often have a lower cost but demonstrate high performance. The table shows inexpensive sprays for the treatment of allergic rhinitis.
| Spray name | Action | Price |
| Aquirin Rino | Hygienic product with anti-inflammatory and moisturizing effect. | 110 |
| Nazol Aqua | Saline-based spray to moisturize and irrigate the nose. | 97 |
| Aqua-Rinosol | Moisturizes the mucous membrane, thins secretions. Contains sodium chloride. | 66 |
| AquaMaster | Facilitates nasal breathing, moisturizes mucous membranes. The composition contains a saline solution. | 240 |
| Rinotaiss | Nasal spray based on sea water. Moisturizes, cleanses and normalizes the functioning of the mucous membrane. | 249 |
| Rhinorus | Vasoconstrictor spray based on xylometazoline. | 78 |
| Rinonorm-Teva | Vasoconstrictor drug. | 92 |
| Xylometazoline | A classic anticongestive (vasoconstrictor) agent. | 102 |
| Avamis | Hormonal drug, active substance – fluticasone. | 642 |
| Nazarel | Anti-inflammatory, decongestant spray from the GCS group based on fluticasone. | 397 |
Vasoconstrictor medications
Vasoconstrictor agents are indeed the most effective in relieving nasal congestion, but they should be used with caution in allergic rhinitis: long-term use of vasoconstrictor drops can not only be addictive, but also increase sensitivity to histamine.
Standing apart is the drug Xymelin Extra, which contains not only a vasoconstrictor component (xylometazoline), but also iptratropium bromide, a substance that reliably stops nasal discharge. It can only be used in adults and children over 6 years of age to reduce the amount of nasal discharge and only occasionally, not regularly.
To quickly ease nasal breathing, vasoconstrictor medications are often used. Here is a list of effective medications:
- Xymelin;
- Meralis;
- Nazivin;
- Knoxprey;
- Sanorin;
- Rhinostop;
- For nose;
- Farmazolin;
- Galazolin.
All drugs with vasoconstrictor properties are divided according to the active substance, which determines the duration of the therapeutic effect, contraindications, and adverse reactions.
Let's highlight groups of drugs with:
- short-acting (up to 4 hours) - with naphazoline;
- medium duration (up to 8 hours) - based on xymetazoline;
- long-term effect (up to 12 hours) - with oxymetazoline.
Among the contraindications it is worth highlighting:
- pheochromocytoma;
- uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
- glaucoma;
- cardiac rhythm disturbance;
- taking antidepressants;
- increase in prostate volume;
- diabetes;
- renal failure;
- epilepsy;
- increased production of thyroid hormones;
- severe atherosclerotic vascular damage.
Medicinal solutions are produced with different concentrations of the active substance, which makes it possible to prescribe drugs in childhood.
Side effects include:
- increased blood pressure;
- cardiac rhythm failure;
- tremor;
- urinary retention;
- dryness, irritation of the nasal mucosa;
- frequent sneezing;
- excitation.
If the recommended doses and duration of the treatment course are not observed, the sensitivity of blood vessels to the action of vasoconstrictors may decrease. As a result, the vessels remain dilated both under the influence of endogenous hormones (adrenaline) and after instillation of vasoconstrictors into the nose. Thus, addiction develops.
To avoid complications, you should read the instructions before using any drug.
Vasoconstrictor drops for allergies
Vasoconstrictor nasal drops are usually prescribed during the acute stage of the disease. Their use allows you to quickly remove swelling, thereby reducing the amount of mucous discharge and relieving nasal congestion.
Nasal vasoconstrictors are used only as an emergency option; they are not recommended for use for more than five days, otherwise the symptoms of a runny nose may worsen and it will be more difficult for the sick person to completely get rid of the disease.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Fenistil drops instructions for use, reviews
With the constant use of drops with vasoconstrictor components, the normal functioning of the walls of blood vessels is disrupted, as a result of which their expansion is removed only by selected drugs.
This category of drugs includes Naphthyzin, Galazolin, Nazivin.
There is a certain term among health workers - “naphthyzine addiction” - this is a condition in which a person uses Naphthyzine every day for a number of years, sometimes the daily dosage in such patients reaches one bottle.

They are unable to stop the drug on their own - they develop a feeling of lack of air, severe headaches, and tinnitus.
In order not to become dependent on the dose of the drug when using vasoconstrictor drops, you must strictly follow the following rules:
- Treatment with vasoconstrictor drops should not exceed five days;
- The dosage indicated in the instructions or by the doctor must be strictly observed, especially for children;
- It is necessary to try to use drops only to relieve acute nasal breathing problems; to alleviate other manifestations of an allergic reaction, select another drug.
Homemade Kali
Homemade medications can be used to treat allergic rhinitis. To create such preparations, you will need a base (water, antiseptic or saline solution), an antihistamine component in the form of a solution and a vasoconstrictor component in the form of drops.
As an example, we can consider a drug obtained by mixing 30% Albucid (5 ml), 0.1% Tavegil (2 ml), 0.1% Xylometazoline (5 ml) and eucalyptus oil (3 ml).
Natural drops for the treatment of allergic rhinitis
Homeopathic nasal drops for allergies are also an effective addition to therapy. In acute allergic rhinitis, their use is aimed at achieving a wide range of results. Single-component use of homeopathic nasal preparations will most likely not bring obvious relief to an allergy sufferer. Meanwhile, the use of herbal-based drugs helps relieve swelling and inflammation, restore the mucous membrane, and strengthen local immunity.
There are practically no contraindications or side effects for drugs in this group, with the exception of individual intolerance. When treating allergic rhinitis in children, homeopathic drops are often prescribed. Unlike other nasal remedies, herbal formulations must be used frequently, every 1-2 hours throughout the day.

Antihistamine nasal drops for allergies produce the longest lasting effect
Experts prescribe the following medications to patients with allergic rhinitis as part of complex therapy:
- Euphorbium compositum;
- Edas-131;
- Delufen;
- Pinosol.
Local and general treatment of nasal congestion
Treatment of a stuffy nose can be divided into two groups of measures - treatment with local drugs and general treatment. Typically, the choice of a particular medicine is made by the attending physician based on the diagnosis.
Local treatment consists of local application of the product - specifically in the nose area. Thus, the maximum concentration of the substance is in the right place. The following drugs and techniques are used locally:
- nasal drops and sprays. Particularly effective in treating seasonal allergies;
- ointments and creams for the nasal mucosa;
- rinsing with pharmacy and home solutions;
- inhalation.
It is believed that hormonal sprays are by far the most effective remedy used for allergic rhinitis. They really do a good job of relieving nasal congestion, reducing nasal itching, sneezing and nasal discharge. Hormonal sprays have a somewhat less pronounced effect in conjunctivitis that occurs simultaneously with the symptoms of allergic rhinitis.
Modern drugs based on corticosteroids are not absorbed through the mucous membranes into the blood and remain on the mucous membranes for a long time after use.
However, with prolonged use of hormonal sprays, patients may develop nosebleeds. In addition, especially in children, hormonal sprays contribute to the development of infections on the mucous membranes, primarily fungal and viral.
Flixonase (a cheaper analogue, Nazarel) is the fastest-acting corticosteroid spray currently available. Its effect begins within 2-4 hours after the first application. Flixonase is usually prescribed to adults and children over 12 years of age. The drug is prescribed 1-2 doses in each nostril 2 times a day.
Avamis is a drug similar to flixonase, but differs primarily in its release form. One dose of Avamys when injected into the nose is 27.5 mg, as opposed to 50 mcg for flixonase. Because of this, Avamis can be used in children from 2 years of age.
Nasonex (a cheaper analogue - desrinit) is the most modern drug from this group. Due to the fact that it lingers longer on the nasal mucosa, it is recommended to use it not twice, like Flixonase or Avamys, but once a day. For allergic rhinitis, the effect of Nasonex usually appears on the 3-4th day of use.
Nasonex is often prescribed to children from 2 years of age, not only for allergic rhinitis, but also for other chronic rhinitis (for example, viral) and for enlarged adenoids. However, in approximately 70% of cases of infectious rhinitis, the use of Nasonex does not lead to the restoration of nasal breathing.
Steroid medications for allergic rhinitis can be used in tablet form or as a spray. Note that systemic corticosteroids have many side effects. They are prescribed as a last resort, to obtain a quick therapeutic effect.
Now we will look at hormonal drugs for allergic rhinitis for intranasal administration. Here is a list of commonly prescribed medications:
- Flixonase;
- Baconase;
- Nasonex;
- Avamis;
- Nasobek;
- Nazarel.
Flixonase has a powerful anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effect at the injection site. The medicine does not have a systemic effect. After opening the bottle, the healing properties of the solution remain for two months.
Contraindications include individual intolerance. The maximum duration of the course is 3 months. Before starting to use Flixonase, you should pay attention to the following contraindications:
- simultaneous use of systemic corticosteroids;
- the presence of infection in the paranasal cavities;
- presence of hyperthermia;
- ulcerative lesions of the nasal mucosa;
- recent injuries, surgical interventions in the nasopharyngeal area.
Flixonase is prescribed from the age of 18, two sprays once a day (preferably in the morning). For severe runny nose, two doses can be used twice a day. After the severity of symptoms decreases, you should return to the maintenance dose.
Adverse reactions include:
- headache;
- bad breath;
- change in taste sensations;
- nasal bleeding;
- dryness, irritation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
With prolonged use of a steroid spray, the risk of ulcerative defects, septal perforation, and the development of addiction increases.
Types of nasal drops for allergies
Each group of drugs is designed to eliminate a specific symptom or stop a pathological process.
Antihistamine drops
- Allergodil (substance - azelastine);
- Histimet, Reactin, Tizin Alergy (levocabastine).
One of the most commonly used drugs in allergology. The action is to block the effect of histamine on tissue. Thus, these are drops that relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa, itching, and sneezing.
Antihistamines are effective, non-addictive and do not dry out the mucous membranes.
Mast cell membrane stabilizers (MCMS)
- Cromohexal, Cromoglin (cromoglycic acid).
This type of drops affects the “source” of histamine – the basophil (in other words, the mast cell). As a result of strengthening, the membrane of the latter does not rupture when exposed to the allergen, and histamine is not released.
Among the disadvantages of SMTC are insufficient knowledge of its action, slow (up to two weeks) onset of effect, and the possibility of developing a large number of adverse reactions.
Vasoconstrictor drops
- Xymelin, Otrivin, Galazolin, ForNos (xylometazoline);
- Nazivin, Afrin, Nazol, Otrivin Oxy (oxymetazoline);
- Naphthyzin, Sanorin (naphazoline);
- Faryal (indanazoline).
Anticongestants - this is the correct medical name for this group of drugs - can help relieve nasal congestion by constricting blood vessels and stopping the process of exudation (secretion of mucus).
It is worth noting that such drops are addictive and cannot save the mucous membranes from dryness due to allergies.
Oil nasal drops should be highlighted as a separate group in this section :
- Pinovit;
- Pinosol.
Both of these products are made from plant components (pine oil, mint, eucalyptus) and have anti-edematous, anti-inflammatory and slight vasoconstrictor effects.
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that vasodilating nasal drops are not used. On the Internet you can find quite a few articles indicating this group of drugs in the title, but they are erroneous, and the material itself describes anticongestants.
The only drug that has a more or less similar effect is Rinofluimucil (only in the form of a spray), which is more of a combination drug. It contains acetylcysteine (as in the cough preparation “ACC”), which is capable of thinning mucus masses and facilitating their easier separation. However, this substance is an auxiliary, and the main active component - tuaminoheptane - belongs to the group of vasoconstrictors. This drug is actively used for sinusitis and asthma.
The drug Protargol, which is not inherently a vasoconstrictor, but has an astringent effect, can also be conditionally classified in this group. Its effects include relieving inflammation, antiseptic treatment of the nasal cavity, and reducing the intensity of mucus formation.
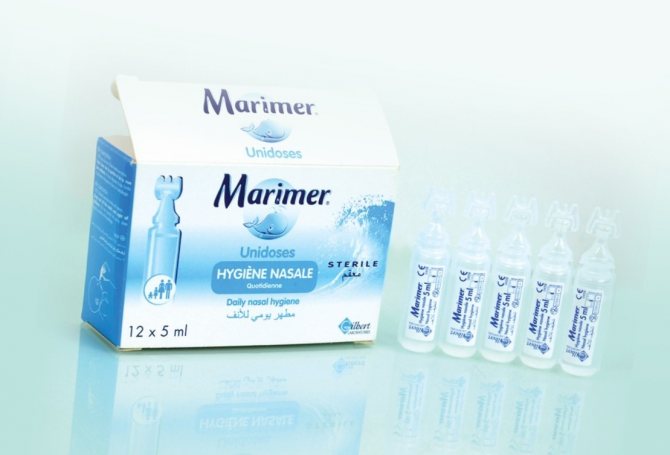
Saline solutions
- Humer;
- Aqua Lor;
- Marimer;
- Aqua Maris;
- Otrivin Sea;
- Dolphin (without herbs);
- Physiometer.
This group of nasal products is literally a “lifeline” not only for allergy sufferers, but also for people with a runny nose in general. The preparations are “non-specific”, do not contain medicinal substances - most of them contain purified sea water.
Their task is to use the salt in the composition to “pull” as much mucus as possible into the lumen of the nasal passages, and then mechanically clean them.
Hormonal drops
First of all, it is important to note: there are no hormonal drugs in the form of nasal drops; they are all available in the form of sprays. In this article it is appropriate to provide only a list of the most popular:
- Avamis;
- Nasonex;
- Desrinitis;
- Flixonase;
- Tafen.
The main effect of these drugs is to relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane.
What are the dangers of hormonal nasal drops for allergies?
Drugs based on glucocorticosteroids relieve inflammation by suppressing local immune reactions (which is why they are first-line drugs in the treatment of autoimmune diseases).
If an infection develops (and it is very easy to “catch” a runny nose, as you know), it will not be possible to notice it in time and quickly cure it; there is a risk of developing sinusitis, otitis, and upper respiratory tract diseases. In addition, uncontrolled use of hormones can lead to the development of a large number of side effects.
Combination drugs
- Vibrocil (dimetindene + phenylephrine);
- Grippocitron (the same);
- AlergoMax (same);
- Milt (same);
- Eden Reno (same);
- Adrianol (tramazoline + phenylephrine).
Combined nasal drops are a combination of a vasoconstrictor and an antihistamine. They are an optimal remedy for seasonal allergies and allergies to flowers, because... the combined decongestant effect of substances from two pharmacological groups is quite strong and copes with even a severe allergic reaction.
It cannot be said that these are non-addictive drops, but they can be used a little longer than pure decongestants.
Complex drops
Complex nasal drops are, in fact, the same combination drugs, but made independently. Is it worth making nasal drops yourself? Everyone must answer this question for themselves, remembering the lack of sterile conditions, high-precision measuring containers and instruments, as well as professional skills and knowledge.
In case the verdict is “homemade!”, here is an approximate recipe for complex nasal drops for allergies with diphenhydramine:
- Base or base: saline solution warmed to room temperature (NaCl 0.9% 5 ml;
- Antihistamine: diphenhydramine 1% 2 ml;
- Anticongestant: oxymetazoline 0.1% 5 ml.
Nasal filters
- Prevalin;
- Nazaval.
These are barrier drugs that form a film when they enter the nasal cavity and thereby prevent allergens from entering the mucous membrane and blood. And because there is no contact with the irritant, and there is no allergic reaction.
These drugs are indispensable for rhinitis from pollen allergies, i.e. when there is hay fever (for example, with an allergy to ragweed).
Homeopathic drops
- Cinnabsin;
- Delufen;
- Euphorbium Compositum.
There is no reliable data on the mechanism by which homeopathic drops act and the effects they provide.
How to put it in your nose
Before starting treatment for rhinitis, it is necessary to eliminate the allergen. Before instillation, the nasal sinuses must be washed with saline solution. The drugs are administered in a supine position. Medicines are injected deep into the nasal cavity.
After instillation, you need to turn your head in the same direction as the nostril into which the drug was injected and tilt your head back. You should remain in this position for 10 minutes.
Read how to properly treat allergic rhinitis with folk remedies here.
Nasal congestion: mechanism of occurrence and development
The occurrence of nasal congestion is a natural reaction of the mucous membrane to the penetration of a foreign object, allergen or pathological microorganism. In this case, two processes occur at once (in some cases only one):
- the nasal mucosa swells, resulting in problems with nasal breathing;
- after this, active secretion of mucus begins, the task of which is to wash away pathogenic microflora or allergen. In this case, the well-known runny nose occurs.
conclusions
- Allergic rhinitis or runny nose is a chronic disease that occurs in attacks. May be seasonal or year-round.
- A large number of nasal sprays, differing in composition and effect, are used for treatment.
- Therapy for allergic rhinitis comes down to eliminating symptoms. For this purpose, antihistamines, vasoconstrictors, moisturizers and hormonal agents, and antibiotics are used.
- With the help of medications, you can reduce the risk of exacerbation of rhinitis. For prevention, spray filters and mast cell stabilizers are prescribed.
- Nasal sprays are more convenient to use than drops with a similar composition. Thanks to the dispenser, the drug is consumed economically and can be used at any time.
- Allergic rhinitis develops due to the body's increased sensitivity to irritants (pollen, medications, and others).
- Treatment of the disease is carried out mainly with the help of drops, which remove the irritant from the nose and eliminate the symptoms of the pathology.
- In the treatment of the disease, vasoconstrictor drops, antihistamines and hormonal medications, and saline solutions are used.
- The drugs are administered in a supine position into the previously cleaned nasal cavity.
- The use of each medicine must be agreed with your doctor.
Causes of nasal congestion
There are several causes of nasal congestion:
- neoplasms in the nasal cavity;
- onset of ARI;
- polyps;
- chronic infection of the mucous membrane. This often happens in people who work in conditions that increase the risk of developing allergies;
- allergic reaction;
- adenoids;
- vasomotor rhinitis;
- reaction to taking certain medications;
- sinusitis;
- bacterial infection of the nose.
Nasal congestion due to allergies is fundamentally different from any other type of runny nose. Vasomotor allergic rhinitis can be determined by the following signs:
- swelling of the nasal mucosa may be accompanied by itching, frequent sneezing and even coughing;
- Gradually, the congestion is accompanied by the release of mucous contents (snot), which usually has a watery consistency and is colorless;
- a feeling of soreness in the nose may develop;
- An additional symptom is redness and itching of the eyes.
Allergies can be either seasonal (hay fever) or year-round. A variety of substances can trigger allergic rhinitis. There are many classifications of allergies.
Price-quality ratio
Are the best drops always expensive? Not always, but often. And this is understandable - the higher the price of the drug, the purer it is, the better the raw materials used for it. But sometimes buyers have to overpay solely for the brand.
Inexpensive drops that are worthy competitors of expensive ones:
- Naphthyzin;
- Galazolin;
- Xylene;
- Sanorin;
- ForNose;
- Adrianol.
Cheap drops, however, are more likely to cause side effects and allergic reactions.
Domestic nasal drops exist. Here are some of them:
- Xymelin;
- Rhinonorm;
- Rhinorus.