pharmachologic effect
Loratadine (which is why it is popular) has antiallergic, antiexudative (eliminates increased vascular permeability and the release of fluid into tissues) and antipruritic properties.
Loratadine is able to block histamine receptors, which determines its antiallergic effect, aimed at reducing capillary permeability, preventing the development of tissue edema, and relieving smooth muscle spasms.
Loratadine, reviews confirm, does not produce a calming effect, and also does not have carcinogenic (does not contribute to the development of cancer), mutagenic (does not cause changes in the genetic apparatus) and teratogenic (does not cause malformations in the embryo) effects.
The therapeutic effect of the drug can be observed within 30-60 minutes after using Loratadine, after 4-12 hours the maximum effect develops, which lasts throughout the day.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
Psoriasis is a serious disease that is currently considered difficult to cure. From the moment of its occurrence, it gradually progresses, moving into the chronic stage. This does not mean that the disease cannot be treated at all - it can be kept in check for decades by approaching treatment comprehensively and systematically.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the following factors:
- systematic use of drugs that block the uncontrolled growth of immune cells in skin tissues;
- carrying out health and physical procedures aimed at reducing areas of affected skin;
- during periods of exacerbation, taking antihistamines;
- exclusion of factors that can lead to progression of the disease: smoking, drinking alcohol, stress;
- keeping the skin clean.
The complexity of the disease is clearly visible even if the last point is observed. Doctors know that frequent use of soap can trigger the start of another exacerbation and the appearance of itching. But the skin, especially with this disease, must be clean and breathe well. Therefore, to avoid harm and solve the problem, hygiene issues are carefully discussed with your doctor.
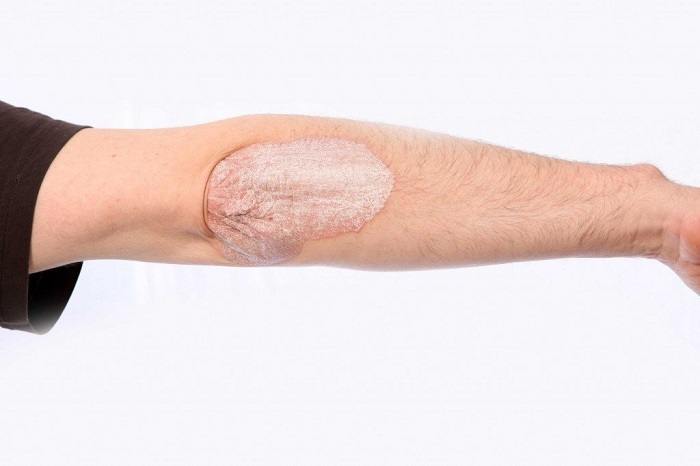
Psoriatic disease (“psoriasis”, “scaly lichen”) is an inflammatory non-infectious disease that has characteristic signs and features - poorly tolerated and controlled itching, burning on the skin, swelling with the formation of papules or intensive growth of red plaques with suppuration or sulfur coating .
More information about lichen can be found in the section of the same name. Both small children and adults are exposed to this misfortune - age characteristics do not play a role here. Finding the causes and their elimination is now at the stage of study, analysis and experimentation. Therefore, the use of one or another method of neutralizing psoriasis on the body will always occur in a comprehensive manner.
In 90% of cases, psoriasis develops quite rapidly. The first clinical manifestations are expressed in the appearance of pink or red papules on the skin. Foci of the disease are located mainly on the scalp, on the elbows and knees, in the lumbar region; in 25% of patients, papules also form on the legs. There is always severe itching of the skin at this stage.
Patients, as a rule, perceive the first signs as the beginning of the onset of lichen; they often make attempts at self-medication, which do not bring any results. As the number of papules on the body increases and their size increases, a thin whitish-gray scale appears on the surface of each plaque.
In the second type of psoriasis, the nail plates are also affected; this phenomenon at the initial stage can be mistaken for a fungal infection. But the symptoms of these diseases cannot be confused; psoriasis is characterized by:
- Increasing the thickness of the nail, acquiring a yellow color;
- The nail plate becomes covered with microcracks.
In advanced stages, psoriasis even spreads to the joints; this disease is called psoriatic arthritis. The most common locations are the hands and feet. At the first stage, clinical manifestations are as follows:
- Severe pain when moving, swelling in the affected joints;
- Deformation of joints sometimes to significant stages of destruction.
It is important to start fighting the disease as early as possible, preventing further spread and progression of the pathology. The main treatment methods prescribed by doctors are local treatment of papules with creams and ointments. Let's take a closer look at their types, treatment periods, results and patient reviews.
Indications
The list of allergic reactions for which the drug is prescribed is very extensive - this includes almost all known allergy symptoms.
The drug helps with the following symptoms and reactions:
- urticaria, including with hyperemic rash and itching,
- rhinitis of an allergic nature, seasonal rhinitis, accompanied by profuse nasal discharge and interfering with the normal respiratory process,
- seasonal hay fever with or without sneezing,
- Quincke's swelling,
- itchy dermatitis,
- conjunctivitis with lacrimation, fear of light and pain in the eye area,
- bronchial asthma of allergic form (non-infectious),
- allergic reactions to medications,
- used for insect bites,
- food allergy,
- serum sickness,
- chronic eczema,
- pseudoallergic reactions.
It is used to relieve the results of allergic reactions: extensive swelling and anaphylactic shock, which pose a serious danger to the patient.
Antihistamines for psoriasis
Antihistamines are an important part of complex therapy for psoriasis. Antipruritic medications are extremely important because patients with psoriasis experience symptoms such as swelling, redness, peeling and itching of the skin.
Overcoming them is a big test for the patient, so doctors include antihistamines in the treatment of psoriasis in advance.
The purpose of antipruritic medications is to eliminate irritation and protect the patient from scratching the psoriatic rash, since there is a high risk of infection. Also, anti-inflammatory drugs actively remove toxic substances that accumulate in the body of patients suffering from psoriasis. Antihistamines will help with psoriasis of the scalp and eliminate unaesthetic dandruff from psoriatic plaques.
Antiallergic drugs have gone through several generations in their production. Doctors prescribe names from all three generations. The most popular are still effective drugs - representatives of the latest, third generation of drugs. In this case, patients are prescribed injections, tablet medications, and external agents.
Sedatives for relieving itching and irritation are represented by two large groups of drugs - hormonal and non-hormonal drugs. Treatment with hormonal drugs is more productive - they allow you to achieve the effect faster and eliminate the exacerbation of psoriasis. Non-hormonal drugs have a weak effect and are used at the initial stage or as a preventive measure for remission, but their undeniable advantage is their less toxic effect on the body.
Today, the well-known Diphenhydramine is practically not used - this medicine belongs to the first generation and today shows a weak effect. The list of new generation drugs is headed by Erius, Zyrtec, Telfast, Claritin, Semprex.
Monoclonal (biological) drugs for psoriasis
Developments by pharmacists in the field of psoriasis treatment have led to the creation of a fundamentally new drug group - monoclonal antibodies. These are drugs of biological origin. They selectively affect the mechanism of psoriasis, but monoclonal drugs for psoriasis do not have a negative effect on the patient’s immunity.
New drugs for the treatment of psoriasis are expensive and not all patients can afford them. At the pharmacy they cost more than 100 thousand rubles. However, reviews of patients who have already been treated with these drugs confirm their high effectiveness against psoriasis. At the same time, medications can cope even with generalized psoriasis, one of the most severe forms of the disease. The names of the drugs from the new group are Remicade, Flammegis, Humira, Adalimumab, Ustekinumab, Stelara, Infliximab.
When treating with monoclonal drugs, the following effects can be achieved:
- simulate the body’s defense reaction, in which the immune system does not perceive the body’s own cells as foreign,
- suppress the production of C-reactive protein, which is responsible for the inflammatory response in the body,
- rapidly reduce the size of plaques and promote their rapid disappearance from the surface of the skin,
- suppress the infiltration reaction of the body - swelling, redness, itching, weeping,
- do not allow pathology to affect the joint elements.
Monoclonal antibodies are used to treat severe forms of the disease when other treatment methods do not help patients.
Taking monoclonal antibodies is prohibited in the following cases:
- with a severe infectious process in the body,
- in the presence of an abscess,
- if the patient suffers from AIDS.
Monoclonal antibodies for psoriasis are not recommended for patients with cardiovascular pathologies, during pregnancy and for use in young children. When using this group of drugs, doctors note that biological drugs for the treatment of psoriasis aggravate colds and provoke adverse reactions such as chills and fever. Patients have no appetite and spontaneous bleeding occurs.
In order to monitor therapy, doctors prefer to carry out treatment in the clinic. Inpatient treatment will help control the unwanted effects of medications.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=videoseries
Classification
Modern medicine uses the following groups of drugs, which are available in tablets, to combat psoriasis:
- Antihistamines. Their main task is to reduce the intensity of itching. Used by only half of psoriasis patients who report symptoms. Used at all stages of treatment.
- Cytostatics. They suppress the proliferation of keratinocytes. New plaques appear more slowly. Progression quickly stops. They are also used for complicated forms.
- Hepatoprotectors. A group of medications used to support the liver. Due to the use of aggressive drugs, hepatocytes are subjected to excessive stress. Hepatoprotectors improve their activity, but this is not a proven fact.
- Immunomodulators. Strengthen the body's defenses.
- Immunosuppressants. They block the factor of the autoimmune process in psoriasis.
- Hormonal medications. They are rarely used in tablet form. Helps reduce the severity of inflammation and have an antipruritic effect. Helps accelerate the process of the disease transitioning into remission.
- Antibiotics. These medications are relevant when pathogenic microflora are attached.
- NSAIDs. They are used primarily for psoriatic joint damage. Help suppress local inflammation, eliminate pain, reduce swelling.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes. Thanks to them, there is a general stabilization of metabolic reactions.

Side effects
The most common cause of side effects is excessive sensitivity to the ingredients. They disappear quickly after stopping treatment. Their appearance is associated with a reaction to drug metabolism products that penetrate the body’s tissues.
List of possible side effects (rare):
- nervous system: dizziness, headaches, decreased concentration, nervousness, agitation, anxiety, asthenia, insomnia, depression, tremor, numbness of extremities,
- respiratory system: various forms of cough, sneezing, nasal congestion, sinusitis, shortness of breath, pharyngitis, laryngitis. The active metabolite of the drug can cause irritation of the mucous membranes,
- musculoskeletal system: back pain, arthralgia, myalgia, calf cramps,
- cardiovascular system: palpitations, tachycardia,
- allergic phenomena, despite the fact that the drug itself treats them: urticaria, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock,
- genitourinary system: change in urine color, discomfort when urinating, mennorrhagia, vaginitis,
- digestive system: constipation, diarrhea, nausea, increased appetite, flatulence, jaundice, liver necrosis,
- others: sweating, dry skin, rash, chills, fever, blurred vision, ear pain.
Instructions for use of Loratadine
Loratadine is available in the form of tablets, syrup and suspension for oral administration.
Loratadine tablets, like other forms of the drug, are recommended to be taken before meals.
Loratadine for children over 12 years of age, weighing more than 30 kg, and adults should take 10 mg once a day, which corresponds to 1 tablet or two dosed spoons of syrup.
Loratadine for children 2-12 years of age whose body weight is less than 30 kg is prescribed at a dose of 5 mg once a day. The maximum daily dose of the drug should not exceed 40 mg. In case of renal or liver failure, dose adjustment is required: 5 mg daily or 10 mg every other day.
The duration of use of Loratadine is determined by the attending physician, assessing the clinical picture - from 1 day to 4 weeks.
Recommendations for patients
Since psoriasis occurs in waves, the main goal of treatment is to increase the duration of remission. Antihistamines help with this. They should be taken as needed, especially at the first symptoms of relapse.
If you combine antipruritic drugs and other medications, you can stop the exacerbation and speed up the approach of remission. Each generation of antihistamines has its own indications and contraindications, so treatment is selected on an individual basis.
The use of antipruritic antihistamines for psoriatic rashes must be alternated, otherwise the patient will develop addiction and there will be no positive effect from therapy.
The bulk of medications against the symptoms of the disease are produced in tablets. This form is very convenient to use and can be used at any time. However, there are also products in the form of injections and ointments. They are recommended to be used only in rare cases and at the discretion of the doctor.
general characteristics
Loratadine is a drug that is one of the most commonly prescribed for allergies, relieving or relieving its symptoms. Belongs to the group of antiallergic, antihistamine drugs.
The drug has a complex effect on the body.
Relieving the pain and effects associated with allergies, the product has a complex effect:
- antiallergic,
- decongestant,
- antipruritic.
It is non-addictive and has a systemic and long-lasting effect.
The medicine begins to show its effect 20–30 minutes after use.
This is a second generation histamine drug and, accordingly, it is more effective than first generation drugs such as Diazolin, Suprastin, Clemastine. Unlike them, it does not have any effects on the nervous system.
Cytostatics
A group of medications that belong to the systemic basic therapy of psoriasis. They have an effect directly on cells. Causes them to divide more slowly. Methotrexate remains the most popular and accessible drug.
It is a folic acid antagonist. Affects primarily pathological cells, disrupting adequate synthesis of DNA and RNA. However, it can also affect healthy tissue. Because of this, its use is accompanied by a large number of side effects.
Methotrexate for psoriasis helps achieve several important results at once:
- Reducing the activity of disease progression;
- Reducing the number of plaques;
- Gradual cleansing of the skin.
Tablets have a negative impact on the general condition of patients in many ways. Because of this, they must be taken under the supervision of a doctor. He will be able to adjust the dose and suggest how to avoid certain adverse reactions.

Release form
Today this drug is presented on the market in three forms:
- Loratadine tablets are regular, round, flat-cylindrical, biconvex in shape with a dividing line on one side. The color is white or yellowish. One tablet contains loratadine in an amount of 10 mg,
- effervescent tablets. Color white or yellowish, round. loratadine in one piece - 10 mg,
- syrup with cherry or apricot flavor with a specific smell. It is transparent or colorless to light yellow, greenish yellow. Available in glass or plastic bottles with a capacity of 100 ml with a measuring spoon of 5 ml. There is 1 mg of loratadine in 1 ml of liquid.
Tablets are packaged in 7 or 10 pieces. in contour blisters made of polyvinyl chloride and foil. In a cardboard package - 1, 2, 3 blisters.
Features of application
For kidney and liver diseases, the daily dose is halved (half a tablet or 5 mg) or the medicine is taken every other day.
For children
Instructions for use in children: up to 2 years of age, taking the drug is not advisable and is carried out according to the doctor’s recommendations.
At the age of 2 to 12 years, the dose depends on body weight and is up to 30 kg - half a tablet or 5 mg. If the child weighs more than 30 kg, as well as children from 12 to 18 years old with this weight - 10 mg or a whole tablet.
Pregnant and lactating
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, Loratadine is prescribed, but with caution, taking into account the expected benefit for the pregnant woman, taking into account the possible risk to the fetus.
The drug is strictly contraindicated during breastfeeding, since the medicine can pass from the body into breast milk, and from there into the baby’s body, where it can lead to serious problems with the functioning of the heart, kidneys, liver, and respiratory organs.
If, however, it is impossible to do without taking the drug, breastfeeding is replaced by taking milk formulas.
For drivers
While taking the drug, it is not recommended to drive a car, similar equipment, or operate technical mechanisms with an increased level of danger.
When working requiring concentration
It is not recommended to engage in work that requires high concentration and requires quick reactions.
It is prohibited to engage in such work if loss of acuity is fraught with dangerous consequences.
Compound
The drug consists of an active substance of the same name – loratadine. This component is the main one in the drug; it is responsible for the long-term blocking of H1-histamine receptors
Different options for excipients do not affect the overall effectiveness of the drug and depend on the manufacturer and form of release of the product (regular or effervescent tablets, syrup):
- in the syrup, the auxiliary ingredients are replaced by glycerol, refined sugar, anhydrous citric acid, sodium benzoate, propylene glycol, food flavoring "Apricot 059" or cherry, purified water,
- in effervescent tablets - anhydrous sodium carbonate, anhydrous citric acid, povidone, anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, macrogol 6000, polysorbate 80,
- in tablets - lactose monohydrate, corn or potato starch, colloidal silicon dioxide anhydrous, povidone, polysorbate 80, microcrystalline, crospovidone, talc, magnesium stearate.
Hepatoprotectors
During psoriasis, the liver receives a strong blow. Also, many medications for this skin disease contain toxins, which causes even more damage to the liver. Therefore, to protect such an important gland in our body, it is necessary to use special means - hepatoprotectors.
Heptral
These tablets not only restore liver cells, but also have an antidepressant effect. The main active component is ademetionine 1,4-butane disulfonate.
The tablets should not be taken by pregnant women or those with individual intolerance to the components. The product very rarely causes side effects. Many people prefer other medications because of the high cost - one package of tablets costs at least 1000 rubles, the price reaches two thousand.
Karsil
The product is considered safe as it consists of herbal ingredients. The main active ingredient is spotted milk thistle. It contains a lot of vitamins and minerals.
Very rarely causes a laxative effect. The only contraindications are individual intolerance to milk thistle. The cost varies from 300 to 450 rubles.
Properties of antihistamines
The goal of treating psoriasis with antihistamines is to relieve the unpleasant symptoms of skin irritation. In this way, you can protect the patient from scratching the itchy rash, which usually leads not only to the appearance of scratches, but also to their infection. Taking antihistamines significantly improves the quality of life of a person suffering from psoriasis.
The effects of antihistamines on the human body
For psoriasis, antihistamines are prescribed that block H1 receptors located in the vascular endothelium, heart, central nervous system, smooth muscles of the bronchi and intestines. Thus, nerve endings of this type become insensitive to histamine, but these drugs still have virtually no effect on its release.
The main effect of antihistamines, regardless of their generation, is as follows:
- relaxation of smooth muscles,
- decreased permeability of blood vessel walls,
- elimination of itching, hyperemia and swelling.
In addition, first-generation drugs have a pronounced sedative effect. They help calm patients who are exhausted by unbearable itching.
How can antihistamines help?
Treatment of psoriasis gives positive dynamics only with an integrated approach.
You should not rely on any one drug, especially since a universal remedy still does not exist. When used together, medications selected individually ensure the elimination of symptoms of the disease and the achievement of long-term remission. A huge role in the treatment of psoriasis is assigned to antihistamines and antiproliferative drugs, without which normal restoration of the skin is impossible. These funds are mandatory.
How do antihistamines work? With psoriasis, mast cells appear in the skin tissues, which are the so-called histamine storage facility. When the immune system malfunctions, the body sends them for protection.
If a patient has psoriasis, he:
- causes the immune system to perceive its cells as an infection;
- mast cells begin to act on them, including histamine;
- as a result, capillary permeability increases, swelling, blood stagnation;
- The “infection” is blocked, but itching appears in the affected area.
Discomfort occurs when histamine binds them to special receptors. The essence of antihistamines is to disrupt the connection of free receptors with histamine.
The first antihistamines did not provide a long-term, sustainable effect. However, today pharmacology has more powerful and effective medications that are actively used to eliminate the signs of psoriasis.