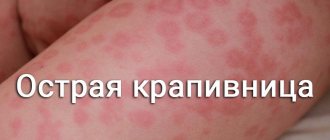
Cold urticaria (allergy to cold) manifests itself in the form of red, scaly spots when human skin interacts with certain atmospheric phenomena. Most often, such a disease occurs in winter or in windy weather. The disease can be either hereditary or acquired. Usually, the main symptoms of cold urticaria go away on their own after the cessation of adverse factors, but in some cases, without drug treatment it is impossible to get rid of the painful symptoms.
Classification of cold urticaria
Cold allergies have the following classification:
- Cold urticaria in acute or chronic form. Symptoms: itching of the epidermis. Locations are the face and upper limbs, less often the whole body. After some time, soft tissue swelling in the form of a blister is observed in the areas where itching occurs. Then rashes appear that look like a mosquito bite. They are accompanied by redness and itching. Symptoms in severe forms of the pathology are a general deterioration in health, chills, tachycardia, weakness and pain in the joints. This reaction may not occur throughout the entire cold period;
- Reflex pathology. Represents a local or general reaction to cold. Symptoms: the appearance of a rash on the epidermis around the site of hypothermia. No rashes appear on the area of the skin in contact with the cold;
- Recurrent pathology. The reaction occurs during the cold season - spring, winter and autumn. Rashes on the epidermis can also appear in the summer due to hypothermia;
- Family illness. Cold allergies are passed down from generation to generation at the genetic level. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of spots and papules on the epidermis when exposed to allergens. The rash is accompanied by burning and itching. The reaction appears 30 minutes or 3 hours after hypothermia of the skin. Associated symptoms are chills, fever, joint pain. Pathology can occur in another form. It is rare, but cases of such a disease have been recorded. The reaction occurs 20-30 hours after contact of the epidermis with the allergen. Rashes in this form are accompanied by discomfort;
- Cold rhinitis. A runny nose in this case appears only when the body is hypothermic. When warmed up, rhinitis goes away;
- Cold dermatitis. When going out into the cold, the epidermis itches and flakes. If the pathology occurs in a severe form, then swelling of the soft tissues appears, but not in individual areas, but in the entire body;
- Cold conjunctivitis. When going out into the cold, lacrimation and pain in the eyes begin;
- Cold erythema. Symptoms are redness of the epidermis and pain in the affected area.
How to take Zodak for hives
Dermatoses of allergic origin, complicated by itching;
If you take Zodak drops according to the instructions, one tablet per day, then cetirizine does not accumulate. After about 30 minutes, the maximum concentration in the blood accumulates.
During this period of time, about 300 ngml of the main active substance is concentrated in the blood, of which about 93% is bound by proteins. At the same time, an active process of biotransformation does not occur in the liver.
As a rule, drug excretion is ensured by the ureters in unchanged form.
Clinical studies have found that the accumulation of the maximum amount of the main active substance in the blood plasma does not depend on the race of the patient. In addition, there is no discrepancy in information about the absorption and impact of Zodak drops on the patient’s body in different forms of release.
What are the composition and release forms of Zodak
At the moment, the drug is sold in pharmacies in three main forms
Tablets are packaged in blister packs of 5 or 90 pcs.
To purchase Zodak in a pharmacy chain, you do not need a prescription. The drug has a shelf life of up to 3 years according to the instructions; it does not require special storage conditions.
ZODAK
Drug: ZODAK
Active substance: cetirizine
Excipients: methylparaben, propylparaben, glycerol, propylene glycol, liquid sorbitol, sodium saccharin, sodium acetate, glacial acetic acid, banana flavor, purified water.
100 ml - dark glass bottles (1) complete with a measuring spoon - cardboard packs.
The description of the drug is based on the officially approved instructions for use.
PHARMACHOLOGIC EFFECT
Antiallergic drug, histamine H1 receptor blocker. Cetirizine belongs to the group of competitive histamine antagonists. It has a pronounced antiallergic effect, prevents the development and facilitates the course of allergic reactions. Has antipruritic and antiexudative effect.
Affects the early stage of allergic reactions, and also reduces the migration of inflammatory cells; inhibits the release of mediators involved in a late allergic reaction. Reduces capillary permeability, prevents the development of tissue edema, relieves spasm of smooth muscles.
Eliminates skin reactions to the introduction of histamine, specific allergens, as well as to cooling (with cold urticaria).
It has virtually no anticholinergic and antiserotonin effects.
In therapeutic doses it has virtually no sedative effect. During the course of treatment, tolerance does not develop.
The effect of the drug begins after 20 minutes (in 50% of patients) or after 1 hour (in 95% of patients) and lasts for 24 hours.
PHARMACOKINETICS
After oral administration, cetirizine is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Cmax in blood plasma is determined after approximately 30-60 minutes. Food intake does not have a significant effect on the amount of absorption, but in this case the rate of absorption is slightly reduced.
The binding of cetirizine to plasma proteins is about 93%. The Vd value is low – 0.5 l/kg. Cetirizine does not penetrate into the cell. Does not penetrate the BBB.
Cetirizine is poorly metabolized in the liver to form an inactive metabolite.
With 10-day use at a dose of 10 mg, no accumulation is observed.
After a single dose, T1/2 is about 10 hours. About 70% is excreted by the kidneys, mainly unchanged. The systemic clearance is about 54 ml/min.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In children aged 2 to 12 years, T1/2 decreases to 5-6 hours.
In case of impaired renal function (creatinine clearance from 11 to 31 ml/min) and in patients on hemodialysis (creatinine clearance less than 7 ml/min), T1/2 increases by 3 times, clearance decreases by 70%.
Against the background of chronic diseases and in elderly patients, there is an increase in T1/2 by 50% and a decrease in clearance by 40%.
Cetirizine is not excreted by hemodialysis.
— seasonal and year-round allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis;
- itchy allergic dermatoses;
- hay fever (hay fever);
- urticaria (including chronic idiopathic);
DOSING REGIME
The drug is prescribed orally, regardless of food intake. Before taking, dissolve the drops in water.
Adults and children over 12 years old - 10 mg of cetirizine (20 drops or 2 scoops of syrup) 1 time / day, daily, preferably in the evening.
Children from 6 to 12 years old - 10 mg of cetirizine (20 drops or 2 measuring spoons of syrup) once a day or 5 mg of cetirizine (10 drops or 1 measuring spoon) 2 times a day - morning and evening.
Children from 2 to 6 years old - 5 mg of cetirizine (10 drops or 1 measuring spoon of syrup) 1 time / day or 2.5 mg of cetirizine (5 drops or 1/2 measuring spoon of syrup) 2 times / day - morning and evening.
Children from 1 to 2 years old - 2.5 mg (5 drops) 2 times a day.
In case of renal failure, the recommended dose should be reduced by 2 times.
In case of liver dysfunction , the dose should be selected individually, reducing it to 5 mg/day or less, with special caution in case of simultaneous renal failure .
Elderly patients with normal renal function do not require dose adjustment.
Rules for using a bottle with a safety cap
The bottle is closed with a cap with a safety device that prevents children from opening it. The bottle opens by pressing the cap firmly down and then unscrewing it counterclockwise. After use, the bottle cap must be screwed on tightly again.
SIDE EFFECT
From the digestive system: dry mouth, dyspepsia.
From the central nervous system: headache, drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, agitation, migraine.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, angioedema, urticaria, itching.
The drug is usually well tolerated. Side effects occur rarely and are transient.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- children under 1 year of age (drops for oral administration);
- children under 2 years of age (syrup);
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Use with caution in chronic renal failure of moderate and severe severity (adjustment of the dosage regimen is required), in elderly patients (glomerular filtration may decrease).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS
The simultaneous use of drugs that have a depressant effect on the central nervous system and alcohol consumption are not recommended.
Instructions for patients with diabetes mellitus
Drops for oral administration do not contain sugar (saccharin is used as a sweetener), so this dosage form can be prescribed to patients with diabetes.
10 ml of syrup (2 scoops) contains 3 g of sorbitol, which corresponds to 0.25 XE.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
OVERDOSE
Symptoms: possible drowsiness, lethargy, weakness, headache, tachycardia, increased irritability, urinary retention, fatigue (more often when taking cetirizine at a dose of 50 mg/day).
Treatment. gastric lavage, administration of activated carbon, symptomatic therapy. A specific antidote has not been identified. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
No clinically significant interactions of cetirizine with other drugs have been established.
Combined use with theophylline (400 mg/day) leads to a decrease in the overall clearance of cetirizine (theophylline kinetics does not change).
CONDITIONS OF VACATION FROM PHARMACIES
The drug is approved for use as a means of OTC.
Source: https://geraklionmed.ru/kak-prinimat-zodak-pri-krapivnitse/
Pathogenesis
What is the mechanism of development of cold urticaria? Under the influence of a provoking factor - cold - the granules present in mast cells are destroyed. As a result, certain active substances are released that contribute to the development of urticaria. The main substance in this case is histamine.
An excessive amount leads to increased vascular permeability, increased blood flow, resulting in a negative reaction on the skin.
When reacting to cold, other active substances may be released that affect the condition of the skin. In such cases, the use of antihistamines does not give the desired result.
The histopathology of urticaria consists of impaired superficial vascular response and soft tissue edema. Exposure to low temperatures leads to degranulation of mast cells, triggering the release of various mediators and histamine. It follows that mast cells are a kind of target for cold, because when exposed to it, the sensitivity threshold of the above-mentioned cells is significantly reduced.
Causes
What factors can trigger cold urticaria? The disease occurs as a result of increased sensitivity of epidermal cells to cold.
Factors:
- Infectious diseases,
- Chronic diseases of internal organs,
- Oncological diseases,
- Weak immune system
- Many toxins in the body,
- Hormonal imbalance
- Parasitic diseases,
- Lack of vitamins
- Heredity, genetic predisposition,
- Disorders of the stomach and intestines,
- Blood diseases
- Frequent nervous shocks and stress.
The presence of one or more of these factors leads to the development of urticaria.
The appearance of Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock can cause death. In addition, nettle fever from the cold disrupts the normal course of life.
The causes of the pathology are not fully understood. Experts come to the conclusion that rashes on cooled areas of the epidermis appear as concomitant symptoms of other ailments.
Cold allergies appear for the following reasons:
- weakening of the body's defenses;
- long-term drug therapy;
- chronic pathologies;
- unstable emotional background;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- genetic predisposition - in this case, cold urticaria occurs in children and accompanies the child throughout his life;
- infectious diseases, which include measles, rubella, mumps and other similar pathologies;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- ailments of the gastrointestinal tract.
The cause of the development of an allergic reaction to hypothermia is also chronic cancer pathology. Here it is important to focus on the main symptoms and immediately seek medical help at the first signs of the disease. The disease in its final stages cannot be treated.
A weakened immune system can cause the development of allergies. It is obvious that cold urticaria occurs from the cold. Many years of work by researchers to identify the causes have yielded results, but the 100% source of the disease has not been identified. It is believed that this is not one irritant, but a combination. It is known that there are circumstances that provoke the development of the disease:
- presence of food allergies;
- weakened immune system. It may weaken as a result of previous illnesses, operations, or after taking potent drugs;
- helminthic infestations;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- genetic predisposition;
- chronic diseases;
- inflammatory processes.
Experts are sure: cold allergy is not an independent disease, but only a symptom that accompanies some kind of physical disease. The body, weakened by a long and latent course of the disease, gives such a response to cold, so the true reasons for the body’s non-standard reaction to cold have not yet been established.
A separate point is problems with the gastrointestinal tract: upon examination, it turns out that a person has chronic gastritis or cholecystitis, an ulcer... In principle, quite a few chronic ailments can provoke cold urticaria.
Cold allergies in children can also be a continuation of food allergies.
Therefore, all the attention is not on getting rid of symptoms, but on treating the underlying disease. The remaining measures can be considered temporary; they do not solve the problem, they only slightly alleviate the condition.
Is it possible to drink Zodak if you have hives?
Good afternoon Allergies are not uncommon today and they can literally arise out of nowhere. This happened with my child.
Sharp, fast, unexpected! Hives! From what, why? I have never been affected by this disease, I ate everything, flowers, cats at home.
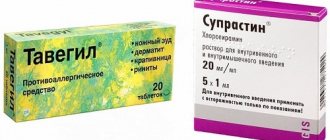
Fortunately, there is always suprastin in the medicine cabinet, but it is known to have side effects that are not always pleasant: drowsiness and lethargy. Therefore, it didn’t take long to turn to a more modern drug (naturally after visiting a doctor).
Zodak anti-allergy drops 10 mg/ml - this is exactly what this review is about.
Country of origin: Germany
Volume: 20 ml
Release form: drops, tablets
Active substance: cetirizine dihydrochloride
Package. Drops in a box, information on each side. The fact that they are for allergies is clearly visible. The box indicates the dosage according to the age group, the active composition, information about storage and the manufacturer. Inside there are huge instructions for use.
The drops themselves are in a glass bottle.
The push-open lid format is very convenient, as it serves one purpose: to prevent a child from accidentally unscrewing it.
For ease of removal, the bottle is equipped with a special dispenser that controls the amount of medicine.
So, I’ll continue about relieving the symptoms of urticaria. Suprastin removed them quickly, but in the morning everything happened again. Fortunately, I was able to quickly make an appointment with a doctor. To remove the allergen from the body, treatment was prescribed for 10 days:
✅ 5 days on an empty stomach, activated charcoal in the morning
✅ take Zodak 10 drops in the morning after breakfast and in the evening after dinner for 10 days.
Plus to all the recommendations ✅ Elimination diet
a nutritional program designed to rid your body of foods and chemicals to which you may be allergic or sensitive.
Result of application. In our case, urticaria looked like this.
Zodak drops taste sweet (I had to try it). The child drank them without any problems, sometimes even without drinking them.
The drops began to act within approximately 20-25 minutes. At first, the symptoms of itching subsided, and later the red spots began to disappear.
Zodak did not cause any side effects: there was no drowsiness or lethargy, and no headaches.
Within two days of taking the regimen, it was possible to completely relieve the symptoms of urticaria. We completed the course without any problems.
The identification of the allergen is ahead, but Zodak will now always be in my medicine cabinet as an effective and reliable remedy for combating allergies.
source
Urticaria: treatment, drugs
Treating allergies is not easy. If you take the wrong approach, you can have serious consequences.
Today in the article “Hives: Treatment, Drugs” we will talk about all existing methods of combating this disease, as well as consider the latest alternative approaches to the treatment of this disorder.
What kind of disease is this
We told you in detail about what the disease is, in what types and forms it occurs, as well as about the main reasons for the appearance of characteristic symptoms in the article “Skin allergies: urticaria.” Let us recall only the basic facts about urticaria.
- The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of itchy blisters on the skin, which resemble nettle burns.
- The disease has an acute form, which lasts no more than 6 weeks, and a chronic form, which exceeds this period and is more difficult to treat.
- The cause of the reaction can be any irritant that your immune system recognizes as a harmful antigen.
- For each antigen in the blood, a specific protein agent is produced - an antibody, which, with each repeated encounter with the allergen, causes the appearance of a rash and other signs.
- The symptoms of urticaria are essentially an inflammatory reaction, which occurs very powerfully and is provided by a special mediator substance - histamine.
- Urticaria always threatens to develop a condition that can be life-threatening. Quincke's edema is a risk of asphyxia due to obstruction of the airway, anaphylactic shock is vascular collapse and cardiac arrest.
- In addition to histamine, other mediators (intermediaries) influence the development of the reaction - serotonin, acetylcholine, leukotrienes. Therefore, there are forms of the disease that are not associated with excessive immune activity: dermatographic, cold, neurogenic urticaria.
- The reaction may occur on its own.
- In adults, if chronic urticaria occurs, then most often it is classified as idiopathic, that is, without an established factor in the development of the reaction (trigger).
- Pathology affects not only the condition of the skin, all organs and systems are involved. Therefore, additional symptoms can be quite varied.
- Urticaria can be either a separate disease or a consequence of some chronic disorder. It often accompanies autoimmune collagenoses: scleroderma, rheumatoid inflammation, systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Over the past decades, the frequency of diagnosis of the disease has increased significantly; this is associated with a violation of environmental well-being, a decrease in the quality of food consumed, and an increase in the number of nervous disorders.
Allergic urticaria is a disease that is under constant scrutiny by scientists around the world. New effective treatment regimens are constantly being developed. But until now, it remains one of the most dangerous diseases, the outcome of which is difficult to predict.
And anaphylactic shock, as a complication of urticaria, is often accompanied by death, even when observed in a hospital.
What does hives look like?
The main symptom of the disease is the rapid appearance of itchy lumps on any part of the skin. They are slightly hyperemic at the edges and paler in the center. Inflammatory formations merge and form patterns with different outlines on the skin.
The papular form of the disease is characterized by single blisters, with a small amount of exudate. The rash always rises above the surface of the skin. If deeper layers, for example, the hypodermis, are involved in the process, then visible tissue swelling is formed. Hives can be located anywhere in our body, including all mucous membranes.
Source: https://amalienau-haus.ru/mozhno-li-pit-zodak-pri-krapivnitse/
What are the symptoms of the disease in adults?
How does cold urticaria manifest? The symptoms of this type of urticaria are no different from those of other types.
The reaction to the stimulus appears within five to twenty minutes. In some cases, symptoms may occur within a few hours. What is characteristic of cold fever?
Symptoms:
- Red blisters on the epidermis, single or multiple, can merge into large spots,
- Severe itching, intense, sometimes unbearable,
- Poor health, weakness,
- Painful sensations in muscles, joints,
- Head pain, dizziness,
- Pre-fainting or fainting state,
- Swelling of tissues in contact with cold
- Difficulty breathing, runny nose, watery eyes,
- Nausea, in rare cases, gag reflex,
- Swelling of the mucous membranes, anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema.
Symptoms appear quite quickly. disappear gradually upon returning to a warm environment. Cold urticaria is divided into several types.
- Spicy. It is characterized by a sharp manifestation of symptoms, in rare cases severe reactions occur. The signs also disappear quickly.
- Reflex. An allergic reaction is present only in areas of the epidermis that come into contact with cold.
- Recurrent. Characterized by a seasonal manifestation, urticaria may not appear for a long time, after which it again affects the skin.
You can see what urticaria looks like in the photo.
Preventive measures will help avoid the occurrence of signs of the disease.
General recommendations
Patients diagnosed with cold allergies should not be allowed to suffer from hypothermia. It is not recommended to take walks in windy and cold weather, swim in bodies of cold water, or consume cold food and drinks. The following preventive measures will also help to avoid the development of pathology:
- taking immunostimulants to increase the body's defenses;
- applying protective drugs to the epidermis before going outside;
- wearing warm clothes made from natural fabrics.
Hardening
Doctors do not agree on the question of whether it is necessary to harden for this form of reaction of the body or not. Experts are unanimous in only one aspect - children from birth to three years old should not be hardened, as this can lead to dire consequences.
As for adults, hardening is recommended to be carried out gradually. First, you should wipe your face and hands with water. If there is no reaction, proceed to washing and rinsing your hands with water, gradually reducing the temperature.
If no signs of illness appear, you can proceed to hardening the whole body, but also gradually. First, take a slightly cool shower for a couple of seconds. If the body has responded normally to the procedure, you can begin to reduce the temperature and increase the duration of hardening. When symptoms appear, all manipulations are stopped immediately.
Most often, urticaria occurs from cold. However, sometimes its symptoms can be confused with elementary fatigue, ARVI, acute respiratory infections and other diseases. For example, when going out into the cold, an adult may feel a headache and cramping of the neck and facial muscles. You may experience pain in the back of your head and forehead, nausea and slight dizziness.
Less often, peeling appears under the knee, inner thighs (this manifestation is typical for women who abuse wearing thin nylon tights in the cold season), and swelling of the legs, face and arms also occurs.
Preventive measures
To make sure that such a pathology as cold urticaria is a problem, photos of symptoms and treatment can be found on the Internet. So it’s better to prevent its development.
The best way to prevent this disease is to avoid cold weather. However, this is not always possible. For this reason, the following precautions should be kept in mind:
- Before going outside in the cold or frost, exposed skin areas should be treated with a special nourishing and protective cream against wind and low temperatures. It is better to purchase the product at a pharmacy. Apply 25-30 minutes before expected exit.
- You should always wear a hat and gloves. Tights and underwear will also come in handy. The latter should be made from natural materials like cotton; synthetic fabrics and wool will only intensify symptomatic manifestations. It is advisable to wear a hood and a thick thick scarf.
- Before going out, you should not wash your face with soap. It destroys the skin's barrier protection, weakening resistance to cold.
- You should minimize your time spent outside in winter. At the first allergic manifestations, enter the building as quickly as possible.
- It is advisable to monitor your diet. Meals should be taken regularly at the same time. It is worth eliminating from the menu all products that can potentially cause irritation of the gastrointestinal mucosa, especially smoked foods and anything fried. It is worth leaning on foods with a high content of vitamin F. For example, these include sea fish and high-quality vegetable oils.
- It is important to avoid temperature changes and strong winds.
One of the methods to prevent the development of pathology is hardening through dousing. The best time to start is summer. The temperature is reduced gradually over and over again.
source
Diagnostics
Cold allergies are diagnosed by a doctor. It is almost impossible to independently determine the pathology, since the disease has similar symptoms to other diseases. The main difference between allergies to cold and other ailments is that the reaction occurs only when the body is hypothermic.
The disease is diagnosed using a provocative test. To do this, take a piece of ice and apply it to the epidermis. After 10-15 minutes, the result is assessed. If the skin turns red, begins to itch, rashes, swelling of soft tissues and other discomfort appear, then cold urticaria is diagnosed.
The first symptoms of the disease usually appear within a few minutes after testing, but may appear several hours later. The disease is also characterized by stages of development, and external manifestations appear only at the third stage. For these reasons, the doctor also orders a blood test for the patient to confirm the diagnosis.
The presence of the disease can be detected independently, at home. The study is called the Duncan Test. To carry it out you will need an ice cube and 15 minutes of free time. Ice should be applied to the place where the skin is most sensitive (for example, the inner bend of the elbow or wrist) and hold for 10-15 minutes.
You can detect the presence of a cold allergy at home using a piece of ice.
In a medical institution, laboratory tests are carried out to confirm the presence of the disease. An important evaluation criterion is increased cryoglobulin protein. When an exacerbation occurs, the amount of this protein increases sharply; during remission, it decreases, but still exceeds the permissible norm.
To have an idea of the patient’s health status and possible causes of the disease, the following examinations are prescribed:
- blood test (biochemical, clinical);
- stool analysis for helminthic infestations;
- carry out urine collection;
- rheumatic tests;
- ECG;
- Ultrasound of the peritoneum;
- skin biopsy;
- X-ray;
- screening for antithyroid antibodies (for women and those with a family history of autoimmune diseases).
Note! The above is a complete list of possible tests, but the doctor may only order some of them if there is a specific idea about the possible cause.
A blood test is mandatory when determining the presence of a cold allergy
The diagnosis is made in specialized institutions. To detect a reaction, they do a test for the skin's perception of cold - a piece of ice is passed along the epidermis at the bend of the elbow. If a rash occurs, we can talk about the presence of urticaria.

If necessary, a variety of studies are used.
Methods:
- Blood and urine tests
- Allergen tests
- Immunological studies,
- Tests for the presence of parasites,
- The use of radiography and computed tomography,
- Research of the thyroid gland.
There are typical and atypical forms of cold urticaria. In the first case, urticaria is acquired; to diagnose it, a skin biopsy is performed.
The atypical form is a hereditary disease and is diagnosed using a blood test. Once an accurate diagnosis is made, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Causes of cold allergies
Therefore, it is very important for both the doctor and the patient to determine the nature of the allergic reaction in time. For this, along with complex studies using special equipment, there are quite simple methods. You can check whether you have a cold allergy at home: place a piece of ice on the crook of your elbow for 10-15 minutes, and if hives appear, then we can assume that you are predisposed to a cold allergy.
But if in doubt, you should consult a doctor; allergic diseases require laboratory blood tests.
So, how to recognize it, because cold allergies skillfully “disguise” as dermatitis, colds, acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections.
As soon as you stepped out into the cold, your head immediately began to hurt. The facial and neck muscles contract, pressing pain begins in the back of the head and forehead, and a feeling of nausea appears from the intensifying headache. It's time to go into a warm room: 10-15 minutes are usually enough to say goodbye to a headache attack. This symptom can be provoked not only by sub-zero air temperatures, but also, for example, by ice-cold drinks or a cold bed.
Reddish rashes, peeling and itching on the skin of the hands and face, sometimes under the knee and on the inner thighs.
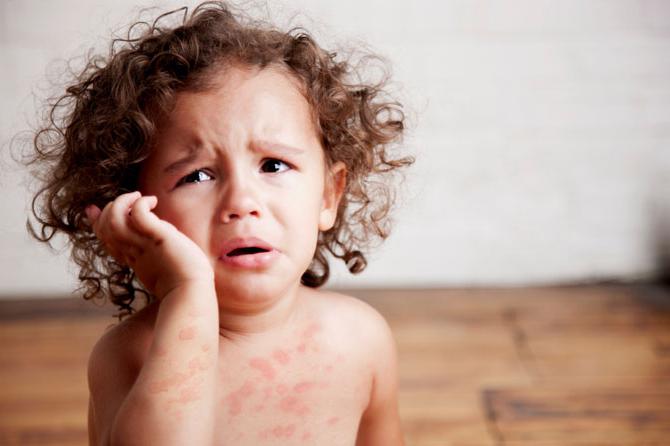
In adults, it all starts with cold allergies in the hands. At first, the skin of the hands simply itches, then becomes dry, rough, covered with cracks and even rashes such as hives. In the skin form of cold allergy in a child, the favorite place for rashes is the face. The cheeks, chin, and nasolabial area turn red.
Following urticaria, swelling of the face, legs, and arms appears.
Unexplained long-term runny nose, nasal congestion, itching in the nasal passages, sore throat and even conjunctivitis with lacrimation and itching of the mucous membranes of the eyes.
Breathing in the cold becomes difficult and difficult; narrowing of the bronchi often causes shortness of breath.
And there are also signs of cold allergies such as feeling tired and mood swings.
Cold allergies can worsen and occur against the background of other diseases and be just their mask, for example, with a lack of vitamins (avitaminosis) and microelements, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.
If there is another allergic disease, for example atopic dermatitis, food allergies, allergic rhinitis, then cold allergies will be more severe. Often, cold allergies begin after suffering from acute respiratory viral infections or other infectious diseases.
Acute and chronic cold urticaria - this form of the disease is characterized by an acute onset, intense itching of exposed skin areas - the face, hands, and sometimes the entire surface of the body. Soon, swelling of the skin occurs at the itching sites, which manifests itself as a blister. Then rashes appear in the form of intense redness of individual areas of the skin, like a mosquito bite or a nettle sting.
A recurrent form of urticaria - it is characterized by seasonality: autumn, winter, early spring. Year-round exacerbations occur when the skin is exposed to cold water;
Reflex cold urticaria is a general or local reaction to cold, similar to cholinergic urticaria. Sometimes it occurs only when the whole body cools down. A local reaction to cold is manifested by a rash that appears around the chilled area of the skin, while the skin directly in contact with the cold is not affected;
Familial cold urticaria is a rare form of urticaria that is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Characterized by a maculopapular rash and burning sensation that occurs 0.5 to 3 hours after exposure to cold. Systemic manifestations of fever, chills, joint pain, and leukocytosis are possible. A rare form of the disease has been described in which urticaria occurs 20 to 30 hours after exposure to cold. Since the rash is accompanied by itching and burning, chronic idiopathic urticaria is often mistakenly diagnosed;
Cold erythema - manifested by redness of the skin (erythema). This form of the disease is characterized by severe pain in the affected areas of the skin;
Cold dermatitis - the skin is very itchy and flaky. If the disease has become quite severe, swelling of the entire body can be observed;
Cold rhinitis differs from a regular runny nose in that the feeling of nasal congestion occurs exclusively in the cold. As soon as a person suffering from a similar form of cold allergy enters a warm room, all symptoms immediately disappear;
Cold conjunctivitis - in the cold there is severe lacrimation, as well as pain in the eyes.
The described symptoms should not be confused with the body’s natural defense against cold and windy weather, which do not cause significant discomfort and quickly disappear in a warm environment.
The treatment method for cold allergies is similar to the treatment for true allergies. First of all, it is necessary to avoid contact with the provoking factor, in this case - cold. Winter allergy sufferers need to dress in clothes made from natural fabrics and not be exposed to cold. The degree of sensitivity is individual.
Medicines - antihistamines “Suprastin”, “Tavegil”, “Claritin”.
It must be borne in mind that some of them have a hypnotic effect and should not be used while performing work that requires concentration and reaction time, for example, driving a car. For bronchospasms, bronchodilators are used. In severe cases, doctors prescribe plasmapheresis, which clears the blood of cryoglobulins, glucocorticosteroids, and some immunosuppressants.
Most often, cold allergies appear in people who are not hardened and have foci of chronic infection (sore teeth, sinusitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, cholecystitis, pyelonephritis, etc.). Therefore, it is necessary to pay special attention to their treatment. Liver and intestinal dysfunctions and dysbacteriosis predispose to allergies, including cold allergies.
Before treatment with medications, be sure to consult your doctor!
Cold allergies can also be treated with folk remedies.
Raspberries. Pour 0.5 liters of water into 50 g of dry crushed raspberry roots. Simmer over low heat for 30-40 minutes. Then strain and cool. Drink 2 tbsp of the decoction before going out in the morning, after lunch and before bed. spoons. Treatment period is 2 months. If you do not skip taking folk remedies, medications will not be needed. Also drink the decoction for preventive purposes, starting 2 months before the winter cold. Then in winter, you will not feel any symptoms of the disease.
Sunflower seeds and regular red beets. Just eat more unsalted seeds and beets in all types in winter, and also drink half a glass three times a day of freshly squeezed beet juice.
Celery. For cold allergies, drink freshly squeezed celery root juice. It should be taken 0.5 teaspoon before meals, three times a day.
Mumiyo. For a medicinal solution, take 1 g of mummy per 1 liter of boiling water. High-quality raw materials dissolve without sediment. Take once a day in the morning, adults 100 ml. It is possible to treat cold allergies in children in this way, but a single dose for a child 1-3 years old is 50 ml, and for a primary school child - 70 ml.
For cold allergies on the hands and face, you can lubricate the skin with a solution of a higher concentration of 1 g per 100 ml of water.
Blueberries. Grind fresh blueberries and apply them as compresses to the affected areas of the skin.
Emulsion based on celandine, burdock, mint and calendula. If a cold allergy appears on the face, there is no better remedy. Grind and mix 10 g of celandine herb, mint leaves, burdock root and calendula flowers. 5 tbsp. Pour a tablespoon of the herbal mixture with sunflower oil, so that the oil level is 1 cm above the level of the raw material, leave for 24 hours. Sterilize in a water bath, stirring gently. Strain, cool and lubricate the skin. The emulsion perfectly relieves itching and dry skin.
Pine shoots in vegetable oil. In cases where a child’s allergy to cold is manifested by dryness, peeling and redness of the skin, the formation of small cracks and itching, an infusion of pine buds in vegetable oil is prepared. Young pine shoots are infused with vegetable oil in a 1:1 ratio in a dark place for about 5 months. The infusion is gently rubbed into the baby's skin.
Birch sap to reduce allergic edema. Birch sap is an excellent tonic and regulating salt metabolism with a mild diuretic effect. Its consumption helps to quickly eliminate allergic swelling of the hands and face. You can consume it in unlimited quantities, but for an adult the daily dose should be at least 1 liter.
Walnut tincture. Walnut tincture, which has anti-inflammatory, bactericidal and anti-allergic effects, is prepared from fresh leaves and green pericarp of the walnut, at the rate of 50 g of crushed raw materials per 100 g of vodka or ethyl alcohol diluted to 40°C. Infuse in a tightly closed glass container for a week, shaking daily.
Treatment
Cold urticaria is treated in the same way as any other form of allergy, namely:
- taking antihistamines (Tavigil, Zirtek, Suprastin, Cetrin, etc.);
- treatment with traditional medicine (raspberries, seeds, beets, celery, mumiyo, blueberries);
- compliance with preventive measures.
Also, for this type of allergy, year-round intake of vitamins is indicated.
Symptoms
- Heavy breathing;
- Bronchospasm;
- Hoarseness.
These symptoms go away on their own if a person goes into a warm environment. When pathology appears, some patients complain of pain in the abdominal area. Cold urticaria is accompanied by arrhythmia.
Upon examination of the patient, he is diagnosed with increased heart rate. IMPORTANT! The first signs of cold urticaria are coughing attacks, as well as shortness of breath. During the development of the disease, nasal congestion appears.
A person experiences itching in the area of the nasal passages. With a strong cough, the patient may be diagnosed with bronchial asthma.
Cold urticaria has corresponding symptoms. That is why, when it appears, it is recommended to go to a medical center, where the doctor will prescribe rational treatment.
Causes
At the moment, experts have not been able to accurately determine the causes of this type of urticaria. But there are known factors, under the influence of which the risk of pathology increases significantly.
Under the influence of cold, amino acids stick together. The lump that results from them is perceived by the immune system as a foreign antigen. As the conflict develops, a corresponding skin reaction is observed.
Pathology develops against the background of an infectious process in the human body. The development of the pathological process can be observed against the background of chickenpox. In some patients, the disease is diagnosed with lymphosarcoma.
Cold urticaria is a serious condition that occurs for a variety of reasons. That is why people are advised to be as careful as possible about their health.
Cold urticaria in children manifests itself as redness in the cheeks, nasolabial folds and chin. After the appearance of spots with a size of 0.5-1.5 cm, babies experience burning and itching, as a result of which they try to rub and scratch the newly formed inflammations. In adults and children, the disease may be accompanied by a runny nose, sore throat and conjunctivitis.
Hives appear from cold and sudden changes in temperature. It can be complicated by other allergic reactions in the child. For example it could be:
- allergic rhinitis;
- food allergies;
- atopic dermatitis (especially difficult in infants);
- avitaminosis.
Often, urticaria can occur as a complication after a child has suffered from acute respiratory viral infections and other infectious diseases.
Any allergic reaction develops only under the influence of a certain irritating factor, in this case cold. It could be:
- cold or frosty air;
- cold drink;
- cold drinks;
- cold food;
- draft.
Symptoms of cold allergies vary in their diversity. The main features include:
- The rash is pink or red. It is usually localized in exposed areas of the skin as a result of the influence of low temperatures;
- Blisters or characteristic lumps;
- Redness;
- Itching;
- Peeling;
- Swelling of the lips;
- Seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- Dry lips;
- Tearing;
- Burning sensation;
- Swelling and pain in the eyes;
- Nasal congestion;
- Runny nose that goes away when entering a warm room;
- Dyspnea;
- Edema of the larynx;
- Allergic cough;
- Frequent sneezing;
- Feeling of suffocation;
- Headache.
All people notice a not entirely comfortable reaction of the body when returning from a cold street to a warm room. The most common phenomenon is redness of exposed skin. First of all, allergies to cold develop on the face and skin of the hands. Blood rushes to the vessels that contracted in the cold and then expanded in the warmth. Such negative reactions in a healthy person disappear within 30-40 minutes.
Sometimes a cold allergy resembles the onset of a cold or viral disease. The main difference is that with ARVI, the patient’s body temperature rises. Therefore, before starting treatment for cold allergies, it is necessary to carefully study all the symptoms. It is best to seek help from a qualified specialist who can accurately diagnose and also indicate how to properly treat cold urticaria, cold dermatitis and other types of pathology.
When an atypical reaction of the body to wind and cold occurs, the disease is determined by characteristic signs.
If a cold allergy appears, the following symptoms occur:
- discomfort in open areas of the epidermis - tingling, itching and pain;
- the appearance of various types of rashes on the skin - spots, blisters, papules and others on the skin of the face and hands;
- redness and peeling of the epidermis;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- hematomas in the affected areas of the skin.
Cold allergies are also accompanied by a rash and other symptoms that are not related to the skin:
- rhinitis;
- tearfulness;
- cough and sneezing;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- itching in the eyes and nose;
- sore throat.
Red spots on the face and other exposed areas of the body after frost may go away immediately after being warm, or may last for several hours. If the symptoms of the disease do not disappear, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Cold urticaria has the following features:
- several signs of the disease occur simultaneously;
- an atypical reaction when a rash appears around a supercooled area of skin, and not on the affected area itself;
- symptoms disappear 30-60 minutes after onset, but with subsequent reactions they remain on the epidermis for a longer period;
- urticarial rashes that appear a few hours after contact with the allergen and last for several days.
Typically, dermatitis due to frost and wind manifests itself in the form of itchy spots on areas of the epidermis unprotected by clothing.
If such signs of an allergy to cold appear, this indicates the development of other pathologies in the body that can threaten the health and even the life of the patient. Such ailments require immediate diagnosis and treatment.
Severe course
Cold urticaria can be severe. Typically, this reaction occurs due to exposure to cold or cold reins for a long time. Symptoms of the disease:
- blisters cause discomfort, increase in size and merge with each other, affecting large areas of the epidermis;
- swelling of the soft tissues of the tongue and larynx, which leads to suffocation;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- severe headaches;
- temperature increase;
- pain in the joints;
- rhinitis.
The pathology may also be accompanied by an anaphylactic reaction if the epidermis is characterized by increased susceptibility to hypothermia. In this case, the following signs are observed:
- chills and elevated body temperature;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- problems with stool;
- pain in the abdomen;
- tachycardia, respiratory failure;
- shortness of breath and cough;
- weakness and headaches;
- dizziness and fainting;
- decrease in blood pressure.
Familial cold urticaria occurs in young children. Symptoms occur 1-3 hours after hypothermia:
- rashes on the epidermis with swelling of soft tissues;
- pain in the joints;
- increase in body temperature.
Such symptoms intensify within 7 hours. The symptoms disappear in about a day on their own without any therapy.
Associated symptoms:
- itching of the skin;
- tearing and redness of the eyes;
- drowsiness and lethargy even after a full night's sleep;
- headache;
- hypersweating;
- nausea;
- thirst.
A distinctive feature of the disease, which is inherited, is that symptoms after contact with the allergen appear only after a few hours. This makes diagnosis difficult, since the provoking test shows a negative result.
To correctly determine the disease in this case, it is recommended to carefully study the pathologies of relatives in the anamnesis and conduct appropriate blood tests.
This is a type of family illness. The symptoms in this case will be as follows:
- rash, itching, redness of the epidermis and swelling of soft tissues;
- angioedema, including laryngeal edema;
- fainting;
- nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- chills and fever;
- pain in the joints.
Symptoms of the disease occur due to wind, frost, water procedures in cold water, cold food and drinks.
With this form of pathology, the provoking test also shows a negative result.
Prevention methods
The development of cold urticaria on the legs, arms and other parts of the body can be prevented if certain preventive measures are followed.
Measures:
- Dress according to the weather, do not forget about warm underwear, hats and scarves.
- It is recommended to use special protective agents and apply them to exposed areas of the skin.
- If signs of hives occur, immediately go to a warm place.
- Particular attention is paid to proper nutrition; the diet should not contain foods that can cause an allergic reaction.
- If possible, try to avoid contact with the allergen.
- Treat all diseases in a timely manner - infectious, viral, fungal.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Rash in the groin in men: photos, possible diseases, removal
Cold urticaria is an unpleasant disease that disrupts a person’s normal lifestyle. It is not possible to cure the disease completely, but following the instructions will allow you to achieve stable remission.
Good day, dear visitors of the project “Good IS!” ", section " "!
I am pleased to present to your attention another article from the health section, namely, about cold allergies, or as it is often called, cold urticaria. So…
Cold allergy or
cold urticaria (lat.
"Urtica"
– nettle)
- an allergic reaction on exposed parts of the body in the form of rashes or red spots caused by cold (cold air or water).
Although it is called an allergy, in reality this response of the body has nothing to do with a true allergic reaction. Cold, dampness, frost are physical factors, and not a substance that causes sensitization - hypersensitivity. But in this article, we will not replace generally accepted definitions, so we will still call this reaction to cold a cold allergy.
Cold allergies manifest themselves literally within a few minutes after exposure to low temperatures in the form of rashes on open areas of the skin: on the face, hands, and often on the lips after drinking cold drinks. The rash is pink or whitish in color, dense, accompanied by itching, can last for several hours, and then disappear without a trace.
There are also other forms of cold allergies that occur in the presence of other diseases - dysfunction of the thyroid gland, lupus erythematosus, and are much more severe. Sometimes a rare form occurs - hereditary. It is accompanied by a burning sensation and is more the body's reaction to the wind than to the cold.
But even the most seemingly harmless form of cold allergy is not as safe as we think. It causes severe itching and a feeling of discomfort, and your health worsens: appear. And in general, more severe manifestations may appear - the so-called Quincke's edema. (Manifestation of Quincke's edema is an enlargement of the face or part of it, or a limb, but the color of the skin does not change.)
Complications
Complications of cold allergies:
- Injury to the epidermis due to itching. This leads to harmful microorganisms entering the body through damaged skin;
- Swelling of the larynx. This condition leads to suffocation, which can cause death;
- Anaphylactic shock. If this condition continues for more than 5 minutes, it can also lead to death of the patient;
- Bronchial spasm. At the same time, the person begins to choke, and the lack of timely assistance leads to death.
- Autoimmune urticaria photo
- Urticaria in pregnant women photo
- Aquagenic urticaria in adults and children 2019
- Urticaria photo in adults hands