Almost a third of the world's population suffers from hypersensitivity to certain foods. Due to the fact that the number of people with diagnosed symptoms increases every year, the fight against it is one of the priorities of medicine and science. It is becoming more and more serious. One of them is polyvalent allergy. What does it mean? How to treat? This article provides answers to these and other questions.
Causes of the disease
The mechanism of development of the immune response when a substance foreign to it penetrates into the body is quite complex and has not yet been fully studied.
But nevertheless, the ongoing research has made it possible to establish with greater accuracy how polyvalent allergies develop and what contributes to its appearance in each specific case.
Three stages of the immune system response have been identified, the last of which leads to clinical manifestations of the disease.
First stage.
At the first stage, the immune system reacts to the introduction of a new substance. An allergen that enters the body causes the formation of antibodies; this process is referred to as sensitization.

As a result of this reaction, the human body “remembers” the data about the allergen and subsequently launches special substances to fight it.
Second phase.
When the allergen is repeatedly exposed, a pathochemical reaction develops. Antibodies produced by the body cause the development of clinical manifestations of the disease.
And if at the first contacts with the irritant there is a small amount of histamine, then subsequently its production increases, and this in turn leads to an increase in the symptoms of the disease.
Third stage.
The third stage is the stage of clinical manifestations of allergies. The first symptoms can occur immediately or several hours or even days after contact with the allergen.
Polyvalent allergies are manifested by symptoms of damage to internal organs and rhinitis, conjunctivitis, and skin rashes.
There are several reasons for the development of polyvalent allergies; researchers put the following in first place:
- Genetic predisposition. The risk of developing intolerance to several allergens at once is several times higher in children whose parents both have one or another type of allergic reaction.
- Poor functioning of the immune system. Among patients, the majority of those who suffer from chronic diseases against a background of weakened immunity often develop polyvalent allergies after long-term treatment with antibiotics or other drugs that reduce the functioning of the immune system.
- In adults, allergies to several irritants are more often detected among smoking patients and among those who abuse alcohol.
In children, the development of a combined allergic reaction can be promoted by early introduction of complementary foods, abuse of adult and junk food.
The risk of developing the disease also increases in children with helminthiasis or a disorder of the intestinal microflora.
Typically, doctors identify several causes in one patient that contribute to the occurrence of various signs of intolerance.
What exactly is the reaction to?
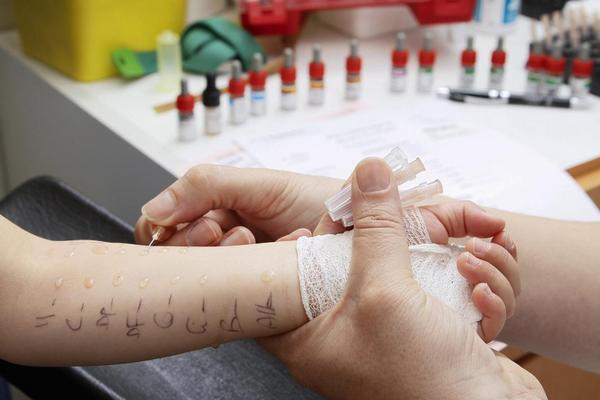
Given the variety of symptoms, it is quite difficult to immediately identify what a person is experiencing a pathological reaction to.
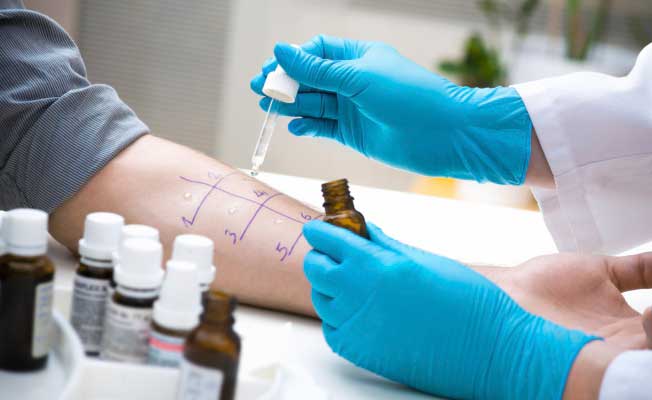
Several methods are used for diagnosis. The most common is skin testing. Small incisions are applied to the inside of the forearm, then a solution with an allergen is dripped onto them. This method has significant disadvantages:
- cannot be performed on children under 5 years of age;
- often the reaction appears several hours or a day after the introduction of the allergen;
- a person may develop a new allergy.
Laboratory analysis for allergies - ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent reaction). Specific immunoglobulins produced in response to a certain substance are detected in the patient’s blood. First, a general group of allergens is isolated, for example, analgesics, then a specific substance is examined.
If the allergy is mild and it is not possible to understand what exactly the immune system is reacting to inadequately, the allergist will advise keeping a patient diary. The patient should avoid contact with the suspected allergen and monitor his condition.
Respiratory system damage
The respiratory system most often produces an allergic reaction after contact with dust, pollen, animal protein, certain products, and chemicals.
Damage to the respiratory system is manifested by sneezing, itching of the mucous membrane of the nose and oral cavity, the release of copious mucous secretions, swelling of the tissues of the nasal passages, sometimes difficulty breathing, coughing and shortness of breath.
Nasal drops against allergies https://allergiik.ru/kapli-v-nos.html can partially save the situation.
Lesions from the gastrointestinal tract.
The digestive organs are most often affected when taking allergenic foods or medications. The patient is worried about colic, flatulence, loose stools, nausea and vomiting.
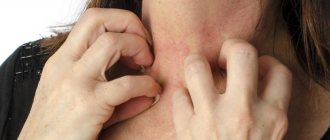
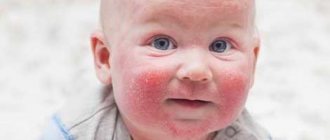
Skin symptoms.
Rash of different sizes and localization, urticaria occur both when the allergen gets inside and after its direct contact with the skin.
Rashes appear after consuming allergenic foods, medications, after contact with cosmetics, household chemicals, and after insect bites.
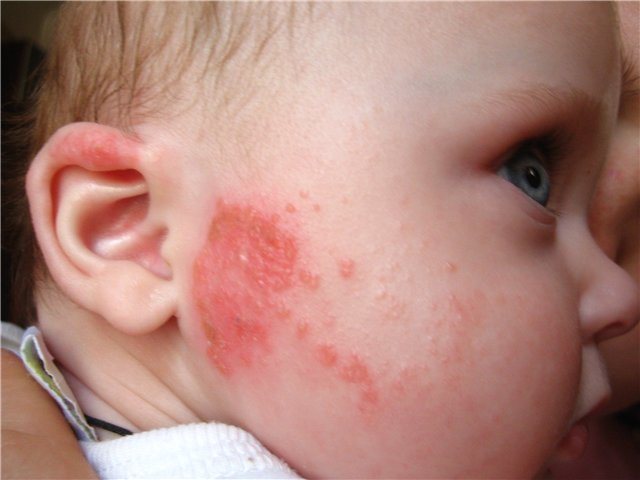
The appearance of pimples, blisters, spots is accompanied by itching, in some people redness and swelling of the skin, you need to immediately begin treating skin allergies.
POPULAR WITH READERS: What types of nasal filters for allergies are there, reviews
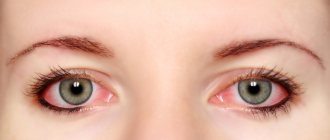
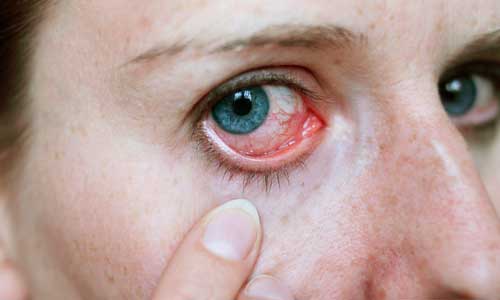
Conjunctivitis.
Profuse lacrimation, redness of the sclera and conjunctiva of the eyes, itching and swelling of tissues occur after contact with plant allergens, cosmetics and a number of other substances.
Conjunctivitis is accompanied by itching and goes away only after exposure to the allergen is eliminated.
In such a situation, as a rule, the doctor prescribes eye drops.
Quincke's edema.
This condition is serious and requires emergency care.
Quincke's edema is characterized by swelling of the face, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, and in severe cases, asphyxia occurs. Quincke's edema is caused by drugs and food.
Anaphylactic shock.
In anaphylactic shock, the patient’s serious condition with depression of respiratory and cardiac activity develops within a few minutes.
Blood pressure drops, pre-syncope and fainting occur, breathing becomes difficult, and convulsive syndrome may develop.
Anaphylactic shock is the result of drug and food intolerance.
Qualified medical care for anaphylactic shock, as well as for angioedema, should be provided within a few minutes, which allows saving a person’s life.
When a polyvalent allergy develops, a person is often bothered by several pronounced clinical signs at once.
Rhinitis and conjunctivitis can be combined with skin rashes, colic along the intestines, and general symptoms of intoxication of the body.
Also, shortness of breath and sneezing are often accompanied by hives and itching of the skin.
Often, with polyvalent allergies, it is difficult to identify several probable sources of an allergic reaction at once, so skin tests for allergies help to accurately diagnose them in most cases.
Classification of the disease
With polyvalent allergies, the body can react to the same type of allergens. However, an increased reaction to completely different substances, for example, pollen and cosmetics, is common. This allergy can develop throughout life. At first, a person cannot tolerate certain substances, then the reaction spreads to other allergens.
In medical practice, the most common types of polyvalent allergies are:
- Food type. For example, a person cannot tolerate bee products and milk protein.
- Medicinal type. The patient is diagnosed with hypersensitivity to drugs of different groups, for example, antipyretics and antibiotics.
- Pollen type. A person reacts inappropriately to pollen from various plants and some foods or animal hair.
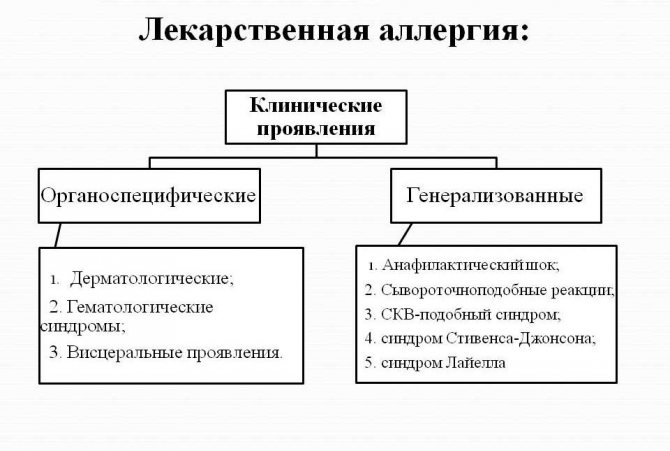
Polyvalent drug allergy
An allergy to several drugs from different groups can develop simultaneously or throughout a person’s life.
A presumptive theory of the development of polyvalent drug allergies has been put forward; according to it, the main cause of this disease can be considered long-term and sometimes uncontrolled use of pharmacological agents.
Poor environmental conditions, bad habits, and weakened functioning of the immune system also have a certain influence.
Previously, drug allergies were observed to some types of antibiotics; today, intolerance even to iodine occurs.
Polyvalent drug allergies pose a certain danger.
- Firstly, such a reaction often ends in angioedema or anaphylactic shock;
- Secondly, when emergency conditions that threaten health develop, it is difficult to choose the right medicine for first, emergency care.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out comprehensively.
A number of measures taken:
- Identification and exclusion of the allergen.
- Taking antihistamines. First generation drugs: suprastin or diphenhydramine will help quickly relieve acute symptoms.

For long-term use (for example, for allergies to pollen of flowering plants), drugs of the second and third generations are prescribed.
- Use of enterosorbents. They will help get rid of toxins and alleviate the condition in the shortest possible time.

- Sometimes you can get by with local antihistamines: ointments or drops.
- Therapeutic baths help with skin allergies.

- Life-threatening conditions - Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock - are treated by doctors with the help of hormones from the group of corticosteroids.
Allergy treatment should be carried out only after consultation with a doctor! Self-prescribing medications can be life-threatening.
Polyvalent food allergy
Allergies to several foods at once are quite common. Both children and adults are susceptible to this allergic reaction.
The intolerance reaction is caused both by the food product itself and by the chemical components used in food production.
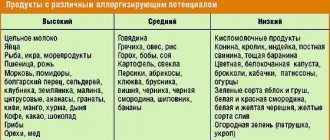
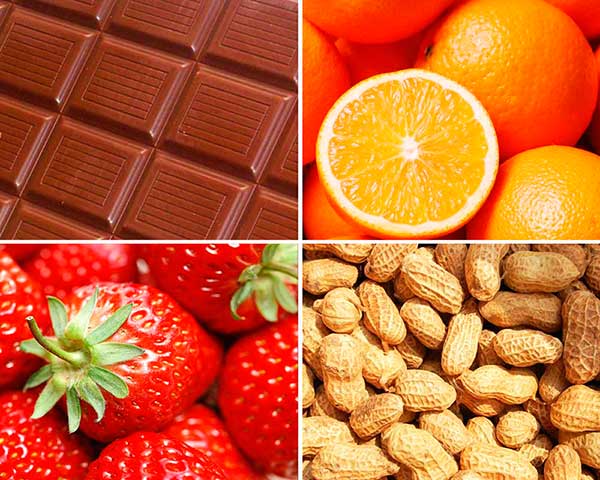
There are several groups of products, allergies to which develop in most cases, these include:
- Nuts - even when consuming a minimal amount, a severe allergy attack can occur, which often ends in anaphylactic shock. The most common culprit of intolerance is peanuts.
- Seafood is the largest group of allergens. Shrimp, mussels, exotic fish, caviar cause the development of food intolerance. Often what causes an allergy is not the product itself, but the dyes or preservatives used during its flavoring, freezing and other types of pre-treatment.
- Eggs and chicken meat. It has been noticed that if a person has intolerance to the white or yolk of eggs, then in most cases they will develop an allergy to chicken.
- Citrus fruits, as well as a group of some exotic fruits, contain special substances to which our body reacts as if they were a foreign protein.
- Cereals. Polyvalent food allergies also develop to gluten, a protein found in cereals. People may not tolerate semolina, barley, rice, or corn.
- Honey and other bee products are highly allergenic due to the pollen they contain.

Food allergies to several types of different foods manifest themselves with numerous symptoms.
This may include abdominal pain, indigestion, rashes all over the body, sneezing, itching of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Often, food intolerance and consumption of a large amount of an allergen product at once leads to the rapid development of Quincke's edema or anaphylactic shock.
The latter condition often develops a few seconds after swallowing food.
Polyvalent food allergies in children may subside by adolescence. Sometimes the allergy remains only to one type of product.
But in order to achieve this relief from intolerance reactions, parents need to wisely select the diet for the child.
Diagnostics
It is quite difficult to identify all types of allergens to which the body reacts in an unnecessary way.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Yeast allergy, causes of pathology, methods of treatment
Skin tests can help in diagnosis to reveal sensitivity to certain substances. The laboratory also does a blood test for antibodies.
But since it is impossible for one person to administer hundreds of samples at once, the patient first needs to keep a diary in which it is necessary to record all the symptoms that arise when consuming a new food product, using medications, cosmetics, and household detergents.
That is, identifying allergies is the task of not only the doctor, but also the patient himself.
At the first signs that resemble an allergic reaction, you should consult a doctor. Self-treatment does not always result in a positive result and, in addition, makes further diagnosis difficult.
When conducting allergy tests, the patient must stop taking antihistamines.