A significant achievement in modern medicine is hot injections.
This advanced injection method is widely used in therapy to prevent many diseases that are associated with calcium deficiency. When the doctor injects the medicine, the blood vessels dilate and the person feels a pleasant warmth throughout the body, but the body temperature itself does not change. Organic and inorganic salts are used as active ingredients for injection.
BeautyHack figured out the pros and cons of hot injections.
The concept of "hot shot"
For most people who do not go into too much detail about the treatment, it becomes unclear why they are injected with a “hot” drug.
It seems that before the medicine is drawn into the syringe, it is heated. But this is not so - the very concept of “hot injection” means something else - it is the administration of a medicine that contains salts (inorganic and organic). How do salts affect the human body? As soon as the medicine is administered, the blood vessels dilate, so the person feels warmth throughout the body, which spreads or “slides” gradually down from the upper part of the body.
Description of medications
Allergy injections are divided into 3 groups. 1st and 2nd generation injections (Tavegil and Diphenhydramine) slow down the reaction, producing a hypnotic effect. 3rd generation drugs are strong drugs that are prescribed to patients to provide a quick but long-lasting effect.
This effect is necessary to instantly eliminate the signs of the disease. For allergies, an injection can be non-hormonal or hormonal. The latter drug has side effects and a large number of contraindications. The hormonal drug can cause a number of complications, so it is administered as prescribed by a doctor.
More often, such medications are used for no more than 5 days. Injections with hormones have a dramatic effect, instantly relieving swelling and increasing blood pressure. Antiallergic injections are prescribed if you need to quickly eliminate allergy symptoms. There are hot injections, which are characterized by a strong anti-shock effect.
Such injections should be given if the patient has anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema.
The hot injection consists of inorganic and organic salts, so during its administration the patient feels feverish. At the same time, blood vessels enlarge, and heat spreads throughout the body from top to bottom. A hot injection has a temperature that does not exceed that of the human body. Some injections can treat not only allergies, but also dermatitis, urticaria, and seasonal exacerbation.
If the injection contains long-acting hormones, then it is administered in two cases:
- for quick relief of severe allergies;
- for long-term interruption of the onset of intolerance.
Corticosteroids have significant side effects, so their use is strictly justified. More often, one of these injections is given to help with Quincke's edema. Stopping choking is the goal of prescribing corticosteroids.
Non-hormonal allergy injections are antihistamine injections used to desensitize the body.
Such solutions are effective for quickly relieving allergies. Such compositions include Suprastin, Tavegil. These injections are prescribed for 5 days. The desensitization technique involves introducing a minimum dosage of allergens into the body. Against the background of their influence, the immune system stabilizes. In this case, manifestations of intolerance are lost.
“Hot injection” or injection of calcium gluconate
There is no need to be afraid of this injection; the patient’s temperature remains the same and does not increase. The injection is prescribed to patients in case of allergic reactions, treatment of skin diseases, as well as inflammatory diseases.
The medicine is administered in the following ways:
- Into a vein - by intravenous administration.
- Into the muscle - intramuscular injection.
- The injection is intracardiac, when the drug enters a clearly designated place (ventricular space).
Injections with this drug are prescribed for the treatment of allergic diseases, inflammatory processes, the treatment of heart and vascular diseases, as well as to combat skin rashes and ailments. Injections are also prescribed if a person does not have enough calcium in the body to compensate for the deficiency of this substance.
Who can be prescribed “hot injections”? The list of diseases is impressive: calcium deficiency, rickets, kidney failure (a chronic form of the disease), when a person moves little or stays in bed for a long time, with chronic diarrhea, bleeding, allergic reactions of the body in the acute stage, respiratory diseases (tuberculosis, asthma), with hepatitis and during breastfeeding, menopause.
Contraindications for treatment with this drug are:
- excess calcium in the body;
- period of bearing a baby;
- severe kidney and heart diseases, as well as atherosclerosis.
Calcium gluconate is administered intravenously very, very slowly. Sometimes it takes 3 to 5 minutes to administer 1 ampoule of the drug. If the medicine is administered very quickly, the person may feel very hot and even faint.
Immediately after the first seconds of administration of the drug, a person feels a pleasant warmth in the mouth, which gradually, like a wave, covers the whole body. If the drug is administered in compliance with all the rules, then the person does not feel anything except warmth or mild fever. A few minutes after the injection, the sensation goes away.
By the way, this medicine is not prescribed to children to avoid the development of soft tissue necrosis.
Review of solutions for adults
What injections are prescribed for allergies? There are a significant number of different manufacturers of antiallergic injections on the pharmaceutical market. Among the foreign ones there are Alcon, Nycomed, Pliva, and among the domestic ones - Organika, Farmak, Veropharm. The most common hormonal injections for allergies of the new generation:
- Diprosan is prescribed in severe cases and when drug therapy is ineffective.
- Prednisolone is an injection with hormones that effectively helps relieve angioedema. It is used to restore airway patency in asthma. In case of severe allergic reaction, use for several days.
- Suprastin is an effective remedy for itching and swelling. With the help of its active substance, skin redness is removed. Side effects include drowsiness and lethargy.
- Calcium gluconate is used if complex treatment of allergies with injections is prescribed.
- Sodium thiosulfate - does not have antihistamine activity, but removes toxins well, relieving skin itching and redness. At the same time, it is one of the effective drugs that reduce food and drug intolerance. Enter 10 days.
- Ruzam is a non-hormonal drug with minor side effects. This remedy effectively eliminates the symptoms of the reaction, increasing the defenses.
- Solyu-Decortin is an analogue of Prednisolone purified from impurities.
- Diphenhydramine - used rarely and only in emergency cases.
- Medipred - it contains prednisolone. The drug is administered for anaphylactic shock.
The above non-hormonal and hormonal allergy medications are used as prescribed by a doctor. Self-administration can cause serious harm to the body.
Calcium chloride or the same “hot injection”
As you can see, there are many drugs for the treatment of many ailments that can have a warming effect immediately after administration of the medicine. A common medicinal substance is calcium chloride. It also well replenishes the lack of calcium in the body, especially during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Such injections can also be prescribed if the body’s absorption of calcium is impaired in a natural way (through the intestinal walls) and in case of vitamin deficiency.
In addition, indications for use are also diseases of the kidneys, intestines and liver, but here this drug acts as an auxiliary drug to reduce acute pain (intestinal, renal or hepatic colic).
Calcium chloride helps very well in the treatment of allergic diseases; inflammatory processes are stopped immediately, reducing vascular permeability. A “hot injection” with calcium chloride is also used in cases where resuscitation is carried out, as an anti-shock drug.
Calcium chloride can be drunk (solution and tablets) to get rid of allergic reactions, as well as to strengthen the body if there is a lack of calcium.
With intravenous administration, side effects may develop: nausea, sometimes even leading to a gag reflex, as well as bradycardia (decreased heart rate).
Contraindications are as follows: individual intolerance to the drug, renal, cardiac and respiratory failure, pregnancy, excess calcium.
Non-hormonal injections against allergies
Medicines are used to eliminate allergy symptoms, reduce the sensitivity of the immune system and remove toxins from the body. The effects of drugs are:
- Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Tavegil - provide assistance in crisis cases, ensure stopping an acute allergic attack. In addition, the drugs rapidly block histamines. A timely injection reduces the severity of symptoms. After completing the course, allergy treatment continues with tablet medications and aerosols throughout the year.
- Sodium bromide, sodium chloride and ascorbic acid belong to the category of desensitizing substances. The drugs are produced in ampoules, and the main purpose is to reduce the sensitivity of the immune system to histamines. Injections for an allergic reaction prevent the penetration of mediators into the circulatory system. The main criterion for prescribing such medications is the manifestation of eczema and other skin rashes.
The injection ensures the neutralization of toxins in allergies. Ampoules of diuretic drugs, saline solution, and glucose are used. Medicines have a positive effect on eliminating swelling and toxins that are created during a state of shock or inflammation.
Hormonal injections for allergies are not used for a long period. The mechanism of action reduces the severity of allergy symptoms and improves the patient’s well-being. If the hormonal drug Dexamethasone does not require long-term use, then non-hormonal drugs will cope with this case.
“Hot injection” or injection of magnesia
Expectant mothers who have undergone treatment with “hot” injections have their own opinion on this matter. Most women shared their feelings: as soon as magnesium is introduced, it seems that the lower part of the body has become so hot that it is unbearable to endure. And also, many expectant mothers said that they felt spontaneous urination. Actually this is not true.
Magnesia or magnesium sulfate is prescribed to many pregnant women to reduce the tone of the uterus and maintain pregnancy (if there is a threat of miscarriage or even premature birth).
What is very important for the correct administration of a drug?
MirSovetov draws the attention of readers to the following points:
- Magnesium is administered only intramuscularly and preferably into the upper gluteal quadrant. There is a lot of muscle tissue in this place.
- The drug is administered very, very slowly so that the medicine does not stagnate in the muscles.
- It is necessary immediately after inserting the needle into the muscle, make sure that it is not in a small artery or blood vessel (the syringe plunger must be pulled towards you).
Pregnant women tolerate magnesium injections well, but immediately after administering the medicine, you need to lie down for a while. You can’t get up and run suddenly, so as not to get dizzy. There were cases when women even lost consciousness if they suddenly got up from the couch after the injection.
In some cases, magnesia is prescribed together with novocaine.
In addition to maintaining pregnancy, magnesium injections are prescribed for the following diseases:
- late toxicosis in pregnant women (eclampsia);
- with a lack of magnesium in the body (not only in pregnant women);
- high blood pressure;
- epilepsy;
- stagnation of urine;
- severe poisoning (to remove lead, arsenic and mercury);
- disturbances of blood supply and oxygen starvation of the brain;
- tachycardia.
Characteristics of calcium chloride
Chlorinated calcium is an odorless substance and has a bitter-salty taste. The product has good solubility in water. When exposed to air, calcium crystals begin to blur. Melting occurs at a temperature of 34 degrees.
The drug is sold in the form of a powder, which is packaged in glass containers, the stopper is hermetically sealed so that the substance does not suffer from contact with air. For medical purposes, the medicine is sold in the form of a solution placed in ampoules, dosages of 5 and 10 milliliters. 1 milliliter of solution contains 0.1 grams of calcium.
The drug has no analogues and has an economical price.
Lack of calcium
Insufficient calcium in the body leads to health problems. This substance affects the functioning of basic systems. Calcium ions improve performance:
- of cardio-vascular system;
- central and peripheral nervous system;
- circulatory systems;
- promote muscle contraction.
If the plasma contains an insufficient amount of calcium, this indicates pathological processes occurring in the body. An insufficient amount of calcium leads to severe tetany (tension, numbness, cramp). To cope with the malaise, you need to drink a medicine containing calcium.
In the blood, calcium is present in ionized form. When administered artificially, it is deposited in bone tissue. Excess substances are excreted by the kidneys or through the intestines.
Purpose of the drug
The main function of calcium chloride is to restore the supply of the substance in the body. This element is necessary for the successful functioning of the myocardium, it is involved in the formation of bone tissue, and also helps improve the process of blood clotting. The drug has the following positive effects on health:
- strengthens the walls of blood vessels and cells;
- protects against infections;
- strengthening the immune system;
- increases the production of epinephrine in the adrenal glands.
Calcium ions improve the conduction activity of nerve impulses, strengthen bone tissue and increase the contractility of the heart muscles.
Calcium chloride is produced in the form of a transparent liquid substance, which is packaged in ampoules. The remedy helps to cure the following:
- allergic reaction to medications;
- lack of calcium, causing osteoporosis, which is most pronounced during the growth period of the body;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- therapy of bronchial asthma;
- angina;
- insufficient activity of the parathyroid glands;
- tuberous sclerosis;
- hives;
- hay fever;
- pulmonary edema due to toxins;
- radiation sickness;
- serious kidney problems;
- psoriasis;
- lichen in humans (lichen lichen, ringworm, lichen planus, etc.);
- and other human skin diseases.
Calcium chloride has a mild diuretic effect. The medicine promotes blood clotting in the presence of bleeding. This drug is the best hemostatic agent at the moment. Using this drug you can relieve the symptoms of poisoning. The drug helps eliminate inflammatory and exudative phenomena accompanying:
In gynecology, this medicine is used to combat endometritis that occurs in the acute stage. Indications for use: uterine bleeding. The drug is also prescribed to stimulate labor.
Despite the fact that the medicine is given freely, without a doctor’s prescription, you cannot use the medicine yourself at home. Otherwise, very serious consequences may arise. But as a cosmetic product - masks and treasures prepared at home, the drug is quite suitable; it can also be added to shampoos and hair conditioners. The drug is suitable for cleansing the skin of dead cells. After the procedure, it is not recommended to be in direct sunlight for a couple of days to avoid skin burns.
For children, the drug is prescribed exclusively for oral administration. For a child, the injection option of administering the medicine is not suitable.
Mechanism of action of anti-allergy medications
People susceptible to allergic reactions should choose medications with extreme caution. Self-medication will cause anaphylaxis. Hormonal allergy injections using Diprospan require caution.
The drug has side effects that get worse with prolonged use. The action of Diprospan is aimed at overcoming acute symptoms of allergies. It is prescribed in situations where antihistamines have not shown effectiveness over six months.
Like other hormonal drugs, Diprospan includes a number of concomitant reactions that increase with frequent and prolonged use. Contraindications include pregnancy and lactation.
Prednisolone is produced in injectable form. The drug reduces swelling and removes the patient from a state of shock. Intravenous injections are performed. The action of the medication is aimed at raising blood pressure and preventing the formation of signs of suffocation during an asthmatic attack.
Prednisolone is included in the first aid kit. In case of an acute condition of an allergic patient, injections are administered for several days in a row. In the absence of Prednisolone, Diprospan is no less effective.
Injectable Suprastin reduces the severity of allergy symptoms. The drug eliminates swelling and skin rashes. Suprastin is prescribed to children and adults in various dosages. One of the side effects of the drug acts as a hypnotic effect.
Calcium gluconate belongs to the category of drugs used in conjunction with other drugs. The medication alone will not help get rid of the symptoms of irritation.
Hot injection or calcium chloride is used quite rarely. Injections are prescribed to urgently stop an allergic attack; they are administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The medication does not contain antihistamine properties, although it performs a detoxification function and removes toxins by enhancing intestinal motility.
Diphenhydramine is a drug with a pronounced antihistamine effect. When injections are administered, swelling decreases and itching disappears. Usually used in emergency situations, it has a hypnotic effect.
Instructions for use
The instructions for use state that the drug “Calcium Chloride” is intended for intravenous administration only. But there are other methods of taking the drug. Before being treated with the drug, you should read the instructions for oral use. The medicine can be used in the following ways:
- intravenously , jet injection, infuse up to 5 ml of the product over 5 minutes;
- drip injection - calcium chloride is diluted with a 5% glucose solution or saline to prevent bradycardia, the drug is administered slowly at a rate of 6 drops per minute, before use the solution is heated until it reaches body temperature;
- the solution is used for electrophoresis.
Instructions for internal use:
Calcium gluconate in cosmetology (skin peeling)

Calcium gluconate has found wide application in cosmetology. It is used to exfoliate the skin. To cleanse the face of dead cells, the product is applied to the surface of the facial skin; the area around the eyes does not need to be treated. After the drug is distributed over the skin, you should wait until it dries. Then the procedure is carried out again and the product is removed with a damp cotton pad; dead cells will roll into balls and easily come off the skin. After the session, the face should be thoroughly rinsed with warm water.
Before you start peeling, you need to check for an allergic reaction. To do this, apply a few drops of the medicine to your hand in the place where the skin is thinner. After a few minutes the result is checked. If an allergic reaction occurs, the peeling procedure should be stopped.
Contraindications
Not everyone can use calcium chloride; there are contraindications for use. It is not prescribed if there is a diagnosis such as atherosclerosis. Also, you should not take this remedy if the calcium content in the body is exceeded. If a person has a tendency to form blood clots, then calcium chloride is contraindicated for use.
Concomitant use with the following substances is prohibited:
- phosphates;
- salicylates;
- salts of lead and silver;
- carbonates;
- sulfates.
During the therapeutic course, it should be taken into account that the medicine reduces the absorption of tetracyclines and drugs containing iron. Do not take it with digoxin. The medicine is not prescribed to children under one year of age.
What should children inject?
For skin allergies in children, injections are given, but only in emergency cases. The dosage of the solution depends on its name and the age of the patient. Since injections have a large number of contraindications, they are not prescribed to children under 3 years of age. Such therapy is contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women.
Any hormonal injection for allergies should not be administered for more than 10 days.
Follow-up therapy is carried out with tablets, antihistamines and ointments. Self-treatment of allergy sufferers is contraindicated.
Diprostan is an effective hormonal solution that is administered in two cases:
- severe reaction;
- lack of effect from antihistamines.
Adverse reactions of Diprostan intensify against the background of its long-term use. The drug is not administered during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Prednisolone is a hormonal injection that has a strong anti-shock and anti-edematous effect.
The last effect of the drug helps to increase blood pressure and relieve suffocation during Quincke's edema. Due to this mechanism of action, Prednisolone is included in the first aid kit. The injection may be given for several days if the patient has a severe reaction. Prednisolone can be replaced with Dexamethosone, which has a similar mechanism of action.
Injectable Suprastin is administered in case of severe intolerance reaction. It easily reduces swelling and itching. It can be used to cure hives. Since the injection provokes drowsiness, a slight inhibition of the neuropsychic reaction may be observed after its administration.
Side effects
When calcium chloride is taken orally, pain may appear primarily in the pancreas, but the pain can also be localized in another area. Once in the stomach, calcium chloride provokes heartburn.
Intravenous administration is accompanied by an abnormal heart rhythm. A chaotic heartbeat appears. This effect often occurs if the rate of drug administration has been exceeded.
Calcium chloride is a unique medicine. The drug helps to cope with various diseases. In order to prevent complications, you need to know how to take this medicine.
Calcium chloride is a medicine used to correct calcium deficiency. It has a wide range of effects. Often patients who have been prescribed calcium chloride injections do not know what they were prescribed for. At the same time, they have heard that these injections are painful and poorly tolerated, so they try to avoid this part of their treatment regimen.

This article will help you understand the purpose of injections with calcium chloride, how a person feels and how the drug affects him. Calcium chloride is not as scary a drug as it is portrayed to be.
Hormonal injections for allergies
Medicine practices the use of hormones only in emergency cases when there is a threat to the patient’s life. These include swelling of the respiratory system or the formation of anaphylaxis. Hormonal medications include:
- Dexamethasone;
- Diprospan;
- Prednisolone;
The doctor selects the necessary medication, but the patient should always be aware of the characteristics of the injections and the conditions for which they are effective.
Dexamethasone is used as a therapeutic measure for severe allergic manifestations. The drug is administered in intravenous and intramuscular forms. The action of the drug is anti-allergic and anti-edematous. The dosage is calculated individually. Rarely prescribed to pregnant women, due to the ability of the drug to negatively affect the fetus, causing a delay in its development.
Diprospan, like Dexamethasone, is a hormonal remedy against allergies. The use of the medication is intended to improve the condition of Quincke's edema and Anaphylactic shock. It is prescribed for cases where treatment with non-hormonal drugs has not brought the expected result. This occurs with hay fever, contact dermatitis and pathological processes.
Prednisolone is a decongestant and anti-shock drug. Intravenous administration of the drug causes an increase in blood pressure, the resumption of patency of the channels of the respiratory system during an asthmatic attack.
Pharmacological action and significance of calcium chloride
Calcium chloride is prescribed to patients whose laboratory tests reveal calcium deficiency or hypocalcemia.
Calcium is an essential trace element that performs structural and regulatory functions. It transmits nerve impulses, ensures contraction of skeletal and smooth muscles, supports myocardial function, and participates in the formation of bone tissue and blood clotting.
Thanks to calcium, cells and vessel walls become less permeable. It also works to prevent inflammatory processes, strengthens the immune system, helping the body fight infections.
With a lack of calcium, the functioning of the exocrine and endocrine glands is disrupted, there is increased excitability, heart rhythm disturbances, pain in the bones and muscles begins, memory deteriorates, neuroses and insomnia develop. Therefore, treatment of patients with calcium deficiency must begin, since the health status and quality of life with calcium deficiency sharply deteriorate.
At first, hypocalcemia is almost asymptomatic. Often its symptoms are also mistaken for signs of other diseases. It is important to undergo medical examination and take tests to determine the balance of microelements in the blood.
For mild calcium ion deficiency, the patient is prescribed calcium-containing oral medications with vitamin D for better absorption. With moderate and severe deficiency, injections are no longer necessary. Calcium chloride is used not only as a drug that replenishes missing trace elements, but also as an antidote, hemostatic agent, and antiallergic drug.
Its use in treatment protocols is justified and effective for:
- Magnesium intoxication;
- Hyperkalemia - excess potassium in the body;
- Poisoning with oxalic acid and its salts;
- Poisoning with fluoric acid and its salts;
- Serum sickness - a pathological immune reaction to the introduction of foreign proteins for preventive and therapeutic purposes;
- Angioedema, or as it is also called Quincke's edema, is a pathological swelling of the skin and mucous membranes;
- Hay fever;
- Hypersensitivity reactions to medications;
- Bleeding - uterine, pulmonary, gastric, intestinal, nasal.
With magnesium salts, oxalic and fluoric acids, calcium chloride forms insoluble compounds, which ensures their maximum removal from the body and prevents absorption into the blood until they are eliminated. This fact has been proven by clinical observations and many laboratory studies.
Indications for injection therapy
Allergies are the most common disease. There are many reasons for its occurrence. These can be flowering plants, fungal spores, animal hair, food - external sources. Hormonal allergies occur when there is a pathology in the functioning of the human body. Then the immune system begins to mistake the produced hormones for foreign cells and attacks them to destroy them. Allergy medications are used to treat symptoms.
Unconditional signs requiring allergy treatment with injections:
- an allergy crisis accompanied by a sharp narrowing of the bronchi;
- the occurrence of anaphylaxis or Quincke's edema;
- the appearance of irritation caused by insect bites in the facial area;
- a severe attack of urticaria that can cause pulmonary edema.
Injections are prescribed on a hormonal and non-hormonal basis; they make it possible to quickly stop an attack.
Methods of application of the solution and dosage
Calcium chloride is administered intramuscularly. The injection is usually placed in the upper outer lobe of the buttock. Less often - in the shoulder or thigh, which is generally undesirable, since painful lumps form in these places.
The sensations from the administration of calcium chloride are unusual, but almost painless. Those who have at least once been injected with calcium chloride described the feeling as unpleasant.
The patient feels as if the injection site is burned or poured with a very hot liquid, although it does not hurt him. Then the heat spreads to the pelvic area, causing a false sensation of involuntary urination. Afterwards, the hot wave extends the effect to the legs and arms, and after a while - to the neck, face and head. The injection site remains highly sensitive for some time and is very unpleasant to touch.
Intramuscular injections of calcium chloride with a 5% solution of calcium chloride and in a volume of up to 5 ml are allowed. A more concentrated solution has a destructive effect on the muscle, up to the destruction of its structure. This process is irreversible; it can only be stopped with antibiotic therapy and surgical removal of part of the dead muscle.
In many cases, calcium chloride injections are given intravenously. For example, this is necessary to stimulate the sympathetic parts of the nervous system, to enhance the release of adrenaline by the adrenal glands, and to stimulate diuresis.
Calcium chloride is used intravenously in inpatient settings when it is necessary to improve the patient's condition by quickly eliminating hypocalcemia and increasing the level of calcium in the blood plasma.
Drip method
If intravenous use of the drug is indicated, then the preferred form is slow drip rather than injection. The drops should be 6-8 drops per minute, for one application from 5 to 15 ml of a 10% solution of calcium chloride in 100-200 ml of saline or 5% glucose solution.
Faster intravenous administration is fraught with the development of cardiac ventricular fibrillation (tachycardia), which is undesirable for patients, especially the elderly, young, suffering from heart and vascular diseases.
Injections into a vein are carried out in treatment rooms. The patient should have the opportunity to sit under the supervision of a health care worker after the injection, to recover, since patients, especially young and old, may experience short-term weakness and dizziness in the first minutes after the drug is administered to them.
Injections of calcium chloride should be carried out by a medical professional, since if this drug is unsuccessfully administered by any method, tissue necrosis may rapidly develop, which is dangerous for the patient. This is especially true for rapid intravenous administration, intramuscular administration and accidental contact of the drug under the skin.
For these reasons, you should not inject calcium chloride yourself, even if you have experience in injecting yourself. Calcium chloride, despite its benefits, is quite insidious. Therefore, it is better to entrust your health to a professional and not try risky experiments on yourself.
Sometimes calcium chloride is administered orally, diluted with water or glucose solution (Vinpocetine also increases the flow of glucose). It is well absorbed in the intestines, which ensures the normal effect of the drug. You need to drink it after eating. A single dosage for an adult patient is 10-15 ml, for a child - 5-10 ml. The dosage regimen, frequency and duration are determined and adjusted by the doctor for a therapeutic effect.
Calcium chloride cannot be administered subcutaneously in any volume or concentration due to the high risk of developing necrotic processes.
Bronchitis. Acute and chronic bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a diffuse acute inflammation of the tracheo-bronchial tree. Refers to common diseases.
Etiology, pathogenesis . The disease is caused by viruses (influenza viruses, parainfluenza viruses, adenoviruses, respiratory syncytial viruses, measles, pertussis, etc.
), bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, etc.); physical and chemical factors (dry, cold, hot air, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, etc.). Cooling, tobacco smoking, alcohol consumption, chronic focal infection in the nasopharyngeal area, impaired nasal breathing, and chest deformation predispose to the disease.
The damaging agent penetrates the trachea and bronchi with inhaled air, hematogenously or lymphogenously (uremic bronchitis). Acute inflammation of the bronchial tree may be accompanied by a violation of bronchial patency by an edematous-inflammatory or bronchospastic mechanism.
In severe forms, the inflammatory process affects not only the mucous membrane, but also the deep tissues of the bronchial wall.
Symptoms, course.
Bronchitis of infectious etiology often begins against the background of acute rhinitis and laryngitis.
With a mild course of the disease, rawness in the chest, a dry, less often wet cough, a feeling of weakness, and weakness occur.
There are no physical signs or severe breathing and dry wheezing are detected over the lungs. Body temperature is subfebrile or normal. The composition of peripheral blood does not change.
This course is observed more often with damage to the trachea and large bronchi.
In moderate cases , general malaise and weakness are significantly pronounced, and a severe dry cough with difficulty breathing and shortness of breath, pain in the lower parts of the chest and abdominal wall associated with muscle strain when coughing are characteristic.
The cough gradually becomes wet, the sputum becomes mucopurulent or purulent in nature. Hard breathing, dry and moist fine bubbling rales are heard above the surface of the lungs. The body temperature remains low-grade for several days.
There are no pronounced changes in the composition of peripheral blood.
A severe course of the disease is observed, as a rule, with predominant damage to the bronchioles (see Bronchiolitis). Acute symptoms of the disease subside by the 4th day and, with a favorable outcome, completely disappear by the 7th day.
Acute bronchitis with impaired bronchial obstruction tends to be protracted and develop into chronic bronchitis.
Acute bronchitis of toxic-chemical etiology is severe .
The disease begins with a painful cough with the release of mucous or bloody sputum, bronchospasm quickly develops (dry wheezing is heard against the background of prolonged exhalation) and shortness of breath progresses (up to suffocation), respiratory failure and hypoxemia increase. X-rays can reveal symptoms of acute pulmonary emphysema. Symptomatic erythrocytosis develops, hematocrit increases.
can also become severe . In addition to coughing (initially dry and then wet), severe shortness of breath and cyanosis of the mucous membranes are noted.
A boxy tint of percussion sound, harsh breathing, and dry wheezing are detected. Slight erythrositosis is possible.
X-ray reveals increased transparency of the lung fields and moderate expansion of the roots of the lungs.
TREATMENT OF ACUTE BRONCHITIS
Bed rest, plenty of warm drinks with honey, raspberries, linden blossom; heated alkaline mineral water;
- Acetylsalicylic acid 0.5 g 3 times a day, ascorbic acid up to 1 g per day, vitamin A 3 mg 3 times a day ; mustard plasters, jars on the chest.
- For severe dry cough, Codeine (0.015 g) with sodium bicarbonate (0.3 g) 2-3 times a day.
- The drug of choice may be Libexin , 2 tablets 3-4 times a day.
- The most effective expectorants are Thermopsis infusion (0.8 g per 200 ml, 1 tablespoon 6-8 times a day); 3% Potassium iodide solution (1 tablespoon 6 times a day), bromhexine 8 mg 3-4 times a day for 7 days, etc.
- Inhalation of expectorants, mucolytics, heated mineral alkaline water, 2% sodium bicarbonate solution, eucalyptus, anise oil using a steam or pocket inhaler is indicated Inhalations are carried out for 5 minutes 3-4 times a day for 3-5 days.
- Bronchospasm is relieved by prescribing Eufillin (0.15 g 3 times a day).
- Antihistamines are indicated
- If symptomatic therapy is ineffective for 2-3 days, as well as moderate and severe disease, antibiotics and sulfonamides in the same doses as for pneumonia.
Chronic bronchitis is a diffuse progressive inflammation of the bronchi, not associated with local or generalized lung damage and manifested by cough.
It is customary to speak of the chronic nature of the process if the cough continues for at least 3 months in 1 year for 2 years in a row.
Chronic bronchitis is the most common form of chronic nonspecific lung diseases (CNLD), which tends to become more frequent.
Etiology, pathogenesis.
The disease is associated with prolonged irritation of the bronchi by various harmful factors (smoking, inhalation of air contaminated with dust, smoke, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen and other chemical compounds) and recurrent respiratory infection (the main role belongs to respiratory viruses, Pfeiffer's bacillus, pneumococci), less commonly occurs in cystic fibrosis. Predisposing factors are chronic inflammatory and suppurative processes in the lungs, chronic foci of infection in the upper respiratory tract, decreased body reactivity, hereditary factors. The main pathogenetic mechanisms include hypertrophy and hyperfunction of the bronchial glands with increased mucus secretion, a relative decrease in serous secretion, a change in the composition of the secretion - a significant increase in acidic mucopolysaccharides in it, which increases the viscosity of sputum. Long-term hyperfunction leads to depletion of the mucociliary apparatus of the bronchi, dystrophy and atrophy of the epithelium. Inflammatory infiltration, superficial in large bronchi, in medium and small bronchi, as well as bronchioles, can be deep with the development of erosions, ulcerations and the formation of meso- and panbronchitis. The remission phase is characterized by a decrease in inflammation in general, a significant decrease in exudation, proliferation of connective tissue and epithelium, especially with ulceration of the mucous membrane. The outcome of the chronic inflammatory process of the bronchi is sclerosis of the bronchial wall, peribronchial sclerosis, atrophy of glands, muscles, elastic fibers, and cartilage. Possible stenosis of the lumen of the bronchus or its expansion with the formation of bronchiectasis.
Symptoms, course.
The beginning is gradual. The first symptom is a cough in the morning with mucous sputum. Gradually, the cough begins to occur both at night and during the day, worsening in cold weather, and becomes constant over the years. The amount of sputum increases, it becomes mucopurulent or purulent. Shortness of breath appears and progresses.
There are 4 forms of chronic bronchitis.
- In the Simple, Uncomplicated form, bronchitis occurs with the release of mucous sputum without bronchial obstruction.
- With Purulent Bronchitis, purulent sputum is constantly or periodically released, but bronchial obstruction is not expressed.
- Obstructive Chronic Bronchitis is characterized by persistent obstructive disorders.
- Purulent-obstructive Bronchitis occurs with the release of purulent sputum and obstructive ventilation disorders
During an exacerbation of any form of chronic bronchitis, Bronchospastic Syndrome .
Frequent exacerbations are typical, especially during periods of cold, damp weather: cough and shortness of breath intensify, the amount of sputum increases, malaise, night sweats, and fatigue appear.
Body temperature is normal or subfebrile, hard breathing and dry wheezing over the entire surface of the lungs can be detected.
The leukocyte count and ESR often remain normal; a slight leukocytosis with a band shift in the leukocyte formula is possible. Only with exacerbation of purulent bronchitis do the biochemical indicators of inflammation (C-reactive protein, sialic acids, seromucoid, fibrinogen, etc.) change slightly.
In diagnosing the activity of chronic bronchitis, sputum examination is of relatively great importance: macroscopic, cytological, biochemical. Broncho- and radiography are used in the diagnosis of chronic bronchitis. In the early stages of chronic bronchitis, there are no changes in bronchograms in most patients.
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC BRONCHITIS.
In the phase of exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, therapy should be aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the bronchi, improving bronchial patency, and restoring impaired general and local immunological reactivity.
- Antibiotics and sulfonamides are prescribed in courses sufficient to suppress the activity of the infection. The antibiotic is selected taking into account the sensitivity of the microflora of sputum (bronchial secretions), prescribed orally or parenterally, sometimes combined with intratracheal administration.
- Inhalation of phytoncides of garlic or onion is indicated (garlic and onion juice is prepared before inhalation, mixed with a 0.25% solution of novocaine or isotonic sodium chloride solution in a proportion of 1 part juice to 3 parts solvent). Inhalations are carried out 2 times a day; for a course of 20 inhalations.
Use: Expectorants, Mucolytic and Bronchospastic drugs , drink plenty of fluids.
- Potassium iodide, infusion of thermopsis, marshmallow root, coltsfoot leaves, plantain, as well as mucolytics and have an expectorant . Acetylcysteine (mucomist, mucosolvin, fluimucil, mistabrene) has the ability to break the disulfide bonds of mucus proteins and causes strong and rapid liquefaction of sputum. Apply as an aerosol 20% solution, 3-5 ml 2-3 times a day.
- Mucoregulators that affect both the secretion and synthesis of glycoproteins in the bronchial epithelium (bromhexine, or bisolvone) . Bromhexine (bisolvone) is prescribed 8 mg (2 tablets) 3-4 times a day for 7 days orally, 4 mg (2 ml) 2-3 times a day subcutaneously or inhaled (2 ml of bromhexine solution diluted with 2 ml distilled water) 2-3 times a day.
- Before inhalation of expectorants in aerosols, bronchodilators to prevent bronchospasm and enhance the effect of the drugs used. After inhalation, positional drainage is performed, which is mandatory for viscous sputum and inability to cough (2 times a day with a preliminary intake of expectorants and 400-600 ml of warm tea).
- If bronchial drainage is insufficient and there are symptoms of bronchial obstruction, the following are added to therapy: Bronchospasmolytics: aminophylline rectally (or intravenously) 2-3 times a day, anticholinergic blockers ( atropine, platiphylline orally, subcutaneously; atrovent in aerosols), adrenergic stimulants (ephedrine , isadrin, novodrin, euspiran, alupent, terbutaline, salbutamol, berotec) . The restoration of the drainage function of the bronchi is also facilitated by physical therapy, chest massage, and physiotherapy.
- If allergic syndromes occur, calcium chloride orally and intravenously , and antihistamines; It is possible to carry out a short (until the allergic syndrome is relieved) course of glucocorticoids (the daily dose should not exceed 30 mg). The danger of infection activation does not allow us to recommend long-term use of glucocorticoids.
- If a patient with chronic bronchitis develops bronchial obstruction syndrome, the following can be prescribed: Etimizole (0.05-0.1 g 2 times a day orally for 1 month) and Heparin (5000 units 4 times a day subcutaneously for 3- 4 weeks) with gradual withdrawal of the drug.
- In patients with chronic bronchitis complicated by respiratory failure and chronic cor pulmonale, the use of Veroshpiron (up to 150-200 mg/day) is indicated.
- Prescribe ascorbic acid in a daily dose of 1 g, B vitamins, nicotinic acid; if necessary - levamisole, aloe, methyluracil .
- When the disease is complicated by pulmonary and pulmonary-heart failure, oxygen therapy and auxiliary artificial ventilation are used. Oxygen therapy includes inhalation of 30-40% oxygen mixed with air, it should be intermittent. Eliminating it by intense and prolonged inhalation of oxygen leads to a decrease in the function of the respiratory center, an increase in alveolar hypoventilation and hypercapnic coma.
- For stable pulmonary hypertension, long-acting nitrates and calcium ion antagonists (verapamil, phenigidine) .
- Cardiac glycosides and saluretics are prescribed for congestive heart failure.
Patients need systematic maintenance therapy, which is carried out in a hospital or by a local doctor. The goal of therapy is to combat the progression of pulmonary heart failure, amyloidosis and other possible complications of the disease. These patients are examined at least once a month. The diet of patients should be high-calorie and fortified.
Source: https://www.medglav.com/bolezni-organov-dixaniya/bronxity.html
Side effects of the solution
The use of the medicine is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, which should not become the main reason for discontinuing the drug.
In addition to the described feeling of heat from a “hot injection”, the patient may experience the following effects from the beginning of the injection of the drug into a vein or muscle and for some time after (usually up to half an hour):
- Dry mouth;
- False hyperemia (a feeling of increased body temperature to subfebrile levels);
- The taste of chalk on the tongue;
- Redness of the skin on the face;
- Increased heart rate;
- Weakness and tremors;
- Slight dizziness.
These side effects are caused by the medicine dilating blood vessels, reducing blood flow and dramatically lowering blood pressure. After a short time, the vessels become toned, the pressure returns to normal, and the patient’s condition is restored.
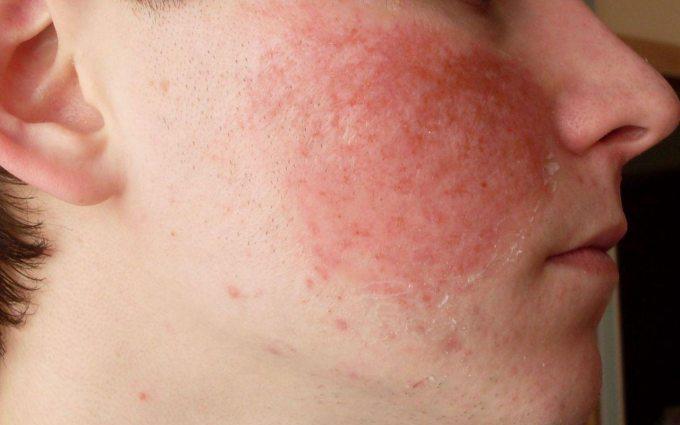
When taken orally, short-term severe and moderately severe pain in the stomach and/or intestines, so-called gastralgia, is possible. Patients also report heartburn. These sensations pass quickly. If they persist, then you should go to the doctor for a possible dosage adjustment or change in the method of using the drug. Not all patients are suitable for taking the drug orally.
Interaction of the dropper with other drugs
Calcium chloride slows down the absorption of tetracycline antibiotics, the cardiac glycoside digoxin, and iron supplements taken orally. When taken simultaneously with diuretics, hypercalcemia may develop. Calcium preparations reduce the bioavailability of the active ingredients of anticonvulsants. With complex vitamin therapy, the intake of calcium and iron supplements should be spaced out in time, and the interval between them should be at least two hours.
Calcium chloride is recognized as incompatible with the following elements and compounds:
- Lead salts;
- Silver salts;
- Sodium barbital;
- Monovalent mercury.
It is capable of forming heavy insoluble compounds that have toxic effects. In this case, the heart and kidneys are particularly affected, leading to the development of heart or kidney failure.
Side effects of “hot” injections
Many patients are afraid to take calcium chloride injections because they are not sure that it is safe. In fact, if you strictly follow the instructions and take into account contraindications, then no unwanted reactions will occur.
But side effects may still occur in some cases. These include not very pleasant sensations - burning in the mouth and throughout the body. Also, after the injection, blood pressure sometimes decreases. If the product gets into the muscle, it can lead to severe irritation and necrosis.
If the drug is administered too quickly or combined in one syringe with other medications, the heart rate may increase, and this sometimes leads to cardiac arrest.