Types of parapsoriasis
There are several types of disease. Let's look at the main features.
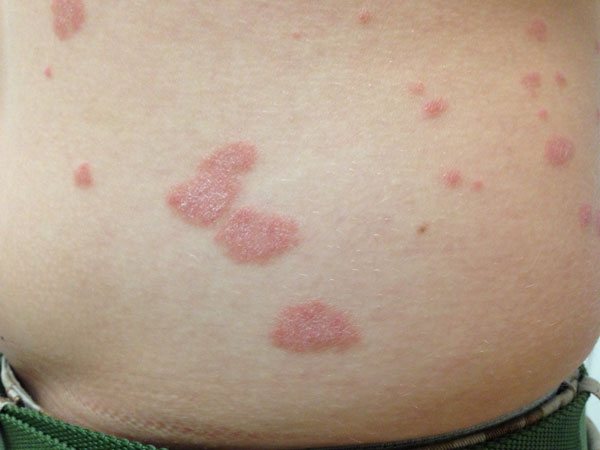
Guttate parapsoriasis
Unlike guttate psoriasis (a rash all over the body), it is localized mainly on the lateral surfaces of the body, on the arms and legs.
Nodular rashes have a round and oval shape, 2-5 cm in size. The color is light pink, darker - to brown-red.
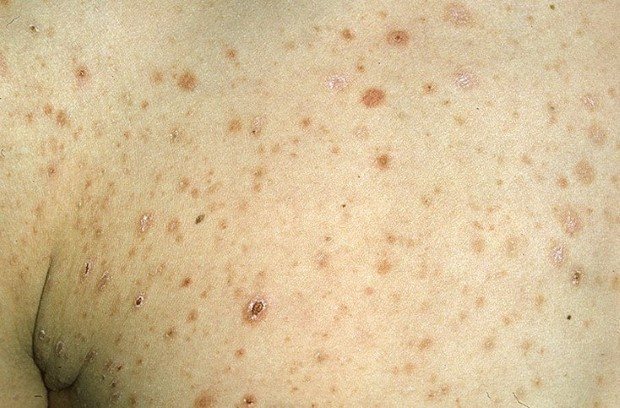
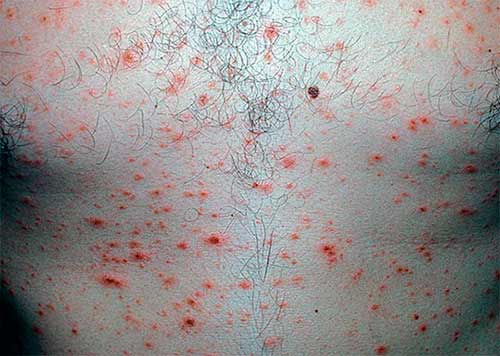
Rashes of guttate parapsoriasis
The rash is covered with characteristic scales: they fit tightly in the center of the spot, and lag behind at the edges. If you scrape it, it flies off without breaking. However, there may be spots without scales.
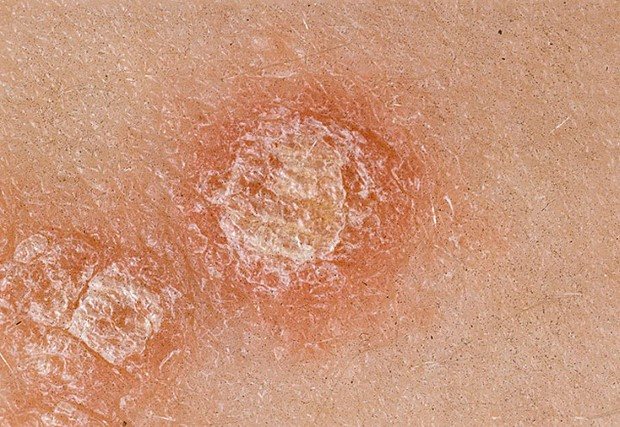
Guttate parapsoriasis spots
Guttate parapsoriasis differs from psoriasis in the nature of peeling and localization. When scratching spots without scales, a “hidden peeling phenomenon” appears; peeling appears from the inside.
Guttate parapsoriasis affects women 2 times more often than men, and is rare in children.
Acute parapsoriasis
A type of guttate parapsoriasis that occurs with exacerbation.
The disease often begins with elevated temperature and enlarged lymph nodes.
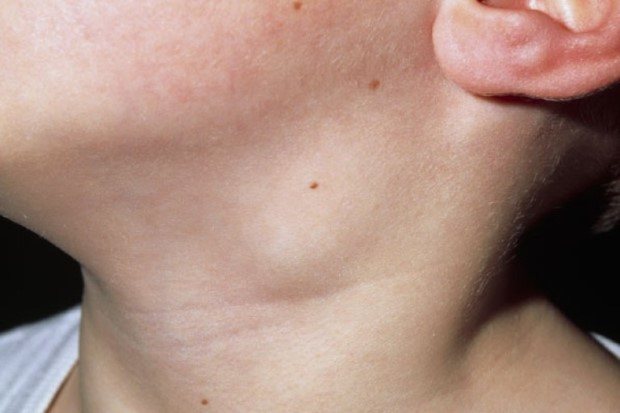
Enlarged lymph nodes
Rashes appear quickly and in large quantities. In addition to the usual spots for guttate parapsoriasis, papules with liquid bubbles appear, which quickly dry out and turn into brown-black crusts.
Guttate parapsoriasis
After some time, the crusts fall off and leave small scars.
Acute parapsoriasis lasts 5-6 weeks and can become chronic.
Overall, the disease looks more like chickenpox than psoriasis. But the manifestations of acute parapsoriasis are typical, so diagnosis by an experienced specialist does not cause difficulties.
Acute parapsoriasis occurs at any age, but more often in young men after infections. And in children, this form of parapsoriasis is rare.
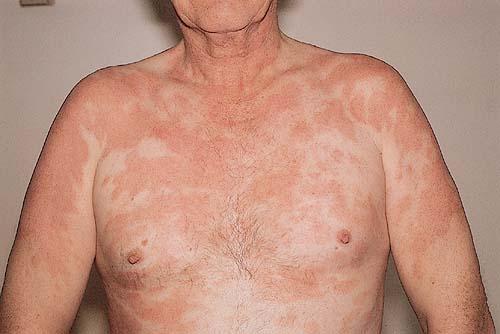
Plaque parapsoriasis
It appears as yellowish-brown or brown spots that have clear boundaries and sometimes irregular outlines.
The spots are strewn with small, almost imperceptible scales that fit tightly. Sometimes they are not noticeable at all, but when scraped they always appear (a symptom of hidden peeling).
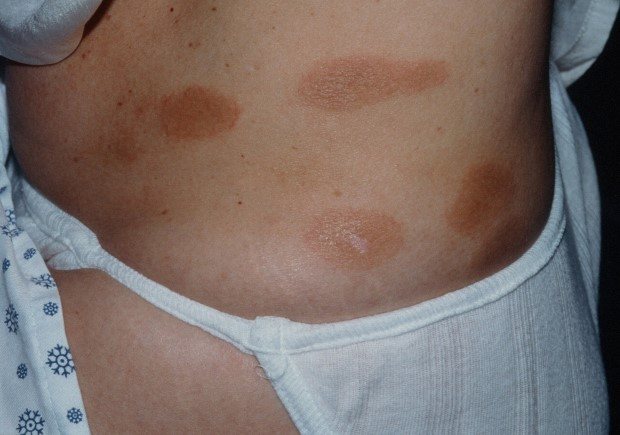
The size varies - from 5 mm to the size of the palm. Small elements merge into single foci with jagged edges.
Plaques most often appear on the body, on the legs, and rarely on the arms.
The difference with vulgar psoriasis (sometimes also called plaque psoriasis) is significant and these diseases are rarely confused:
With plaque parapsoriasis, there are no disturbances in general health, and there is no itching either. Often this type of parapsoriasis occurs in men aged 25 to 50 years.
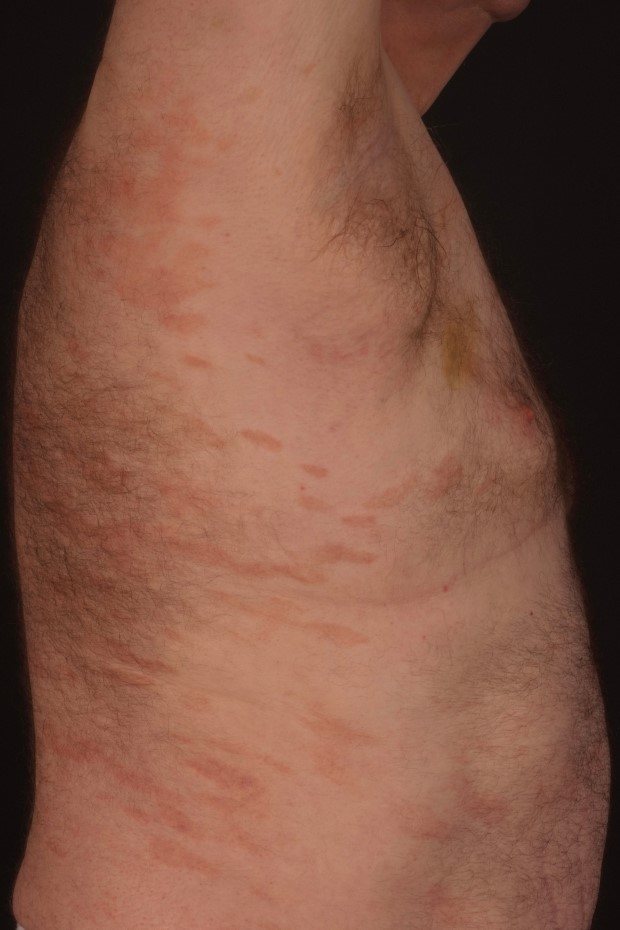
Lichenoid parapsoriasis
A rare type of parapsoriasis. The rash is the size of a pinhead, flat and shiny. The color is red-brown, and the surface is covered with small scales.
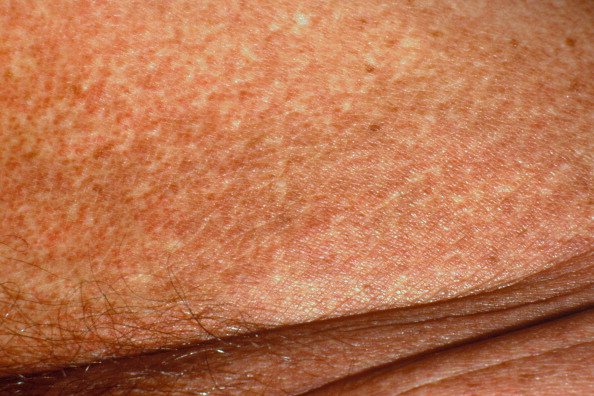
Lichenoid parapsoriasis
There is no itching with this type of psoriasis. Often appears together with plaque and guttate psoriasis. The disease affects people of both sexes between the ages of 20 and 40, rarely in children.
Prevention
Preventive measures come down to maintaining a healthy lifestyle:
- Timely and adequate treatment of foci of infection and chronic diseases of internal organs.
- Healthy eating.
- Hardening the body.
- Full sleep.
- Wearing clothes only from natural fabrics, washing them in warm water with laundry soap and rinsing them thoroughly.
- Taking general strengthening substances and vitamins in courses at least twice a year.
- Avoiding stress and severe nervous shock.
Treatment of parapsoriasis
In general, parapsoriasis is difficult to treat. Therapy depends on the form of the disease.
In the plaque form of parapsoriasis, an examination is carried out for infections and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and, first of all, these diseases are treated, if any.
Basically, treatment occurs using the following methods:
311 nm lamp
- Most often treated with complex therapy : vitamins B1, B6, B12, ascorbic and nicotinic acid.
- Ultraviolet irradiation gives lasting results. Photochemotherapy (PUVA therapy) is especially effective; good results are obtained using 311 nm ultraviolet light and 308 nm laser.
- A combination of salicylic ointments with 311 nm UV rays is often used.
- External treatment with ointments and creams rarely works.
- The chronic form of lichenoid parapsoriasis is treated with antibiotics, as well as potent substances: methotrexate, cyclosporine A.
Causes
It is impossible to identify the exact cause of the appearance of a group of dermatoses. Doctors assume that the main cause of skin inflammation is an infectious agent, but this cannot be proven. In addition, the causes of pathology include autoimmune disorders of the body, but this hypothesis has not been proven.
There are factors that affect human skin and can provoke the appearance of the disease:
- inflammatory and infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- flu;
- gastrointestinal diseases in the chronic stage of development;
- heavy tanning and prolonged exposure to the sun on the skin;
- endocrine system disorders - diabetes, obesity;
- allergic reactions that appear on the skin;
- helminthic infestations;
- exposure to adverse environmental factors;
- constant human tension, stressful situations.
Small plaque parapsoriasis can be inherited. It has been proven that people whose ancestors suffered from pathology are much more likely to suffer from this disease than others. Factors influencing the development of plaque parapsoriasis include a general decrease in immunity and intoxication of various etiologies.
Factors that can provoke lichenoid parapsoriasis include metabolic disorders, bad habits, and various skin disorders.
Conclusion: how does parapsoriasis differ from psoriasis?
Parapsoriasis is a group of diseases with similar symptoms. With parapsoriasis, the main symptom is spots:
- Light pink, brown-red color with guttate parapsoriasis.
- In acute parapsoriasis, spots of the same color. Accompanied by increased temperature and enlarged lymph nodes.
- Plaque parapsoriasis is characterized by yellowish and brown rashes with clear edges.
- Rashes the size of a pinhead, shiny and smooth, are characteristic of lichenoid parapsoriasis.
In psoriasis, the main symptom is red, thickened patches with scales on top. Parapsoriasis does not always cause peeling, itching, or poor health.
Treatment of parapsoriasis is complex:
- vitamins B1, B6, B12, nicotinic and ascorbic acid;
- phototherapy methods: Puva therapy, excimer laser, ultraviolet 311 nm;
- in severe cases: methotrexate, cyclosporine A, antibiotics.
Treatment is in many ways similar to the treatment of psoriasis. Read more about psoriasis and its symptoms in the publication: “Psoriasis: photos, symptoms, treatment”
Forecast and consequences
In the case of guttate and acute parapsoriasis, the prognosis is favorable, since with timely and adequate treatment they end in recovery in 1–2 months. Small scars will most likely remain at the sites of the rash.
The prognosis is also favorable for small plaque parapsoriasis. Areas of depigmentation may remain, the tone of which will even out with healthy skin over time.
With large plaque and lichenoid parapsoriasis, the prognosis is not so certain. These dermatoses exist for a long time (usually several years), and they may degenerate into mycosis fungoides. There is evidence that X-ray irradiation of affected areas with parapsoriasis can also lead to mycosis fungoides.
Large plaque parapsoriasis can also transform into mycosis fungoides, but its transformation into T-cell lymphoma of the skin is more dangerous. You need to remember this, and if severe itching, swelling, or redness of plaques begins, immediately seek advice from a specialist.
A chronic process on the skin, especially in women, almost always means depression, physical and mental discomfort. People with long-term dermatoses have difficulty adapting to society.
Complications of the disease
There are two most important complications of parapsoriasis:
- Mycosis fungoides.
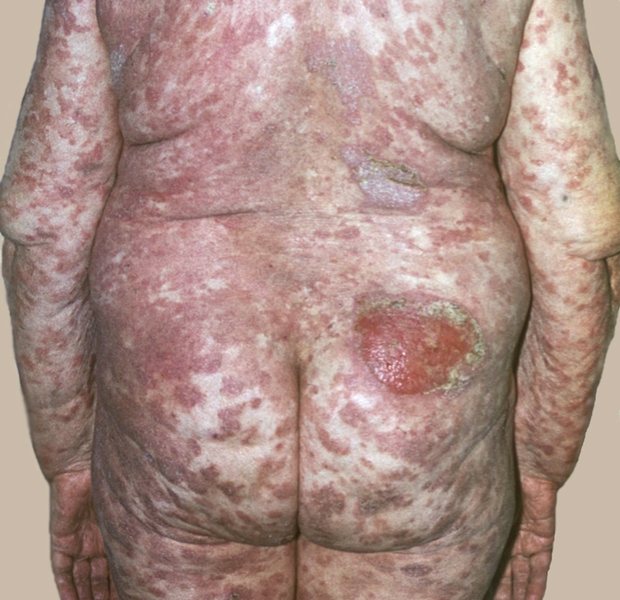
The plaque form of mycosis fungoides is a serious complication of parapsoriasis. - Malignant T-cell lymphoma of the skin.
In T-cell lymphoma of the skin, uncontrolled division of T cells and their movement into the epidermis is observed.
The best remedies for Psoriasis

Add to cart
Antipsoriasis cream 990 rub.

Add to cart
Magnipsor ointment RUB 1,490

Ultraviolet lamp Dermalight ® RUB 14,900.
Plaque type
This is the most common form of pathology. Externally, the disease resembles pityriasis rosea or mycosis fungoides.
Plaques can be large or small. The large plaque form can degenerate into lymphoma. The spots are pale pink in color and may be yellow or brown. The shape of the rash is usually oval, from 3 to 5 centimeters in diameter.
Plaques usually do not rise above the surface of the skin and can appear all over the body and on the legs. The rash rarely merges, but pityriasis-like scales may appear. The skin in areas affected by parapsoriasis resembles a crumpled sheet of paper. Dilated blood vessels may be visible near the plaques, the skin itself loses its natural pigment and becomes pale.
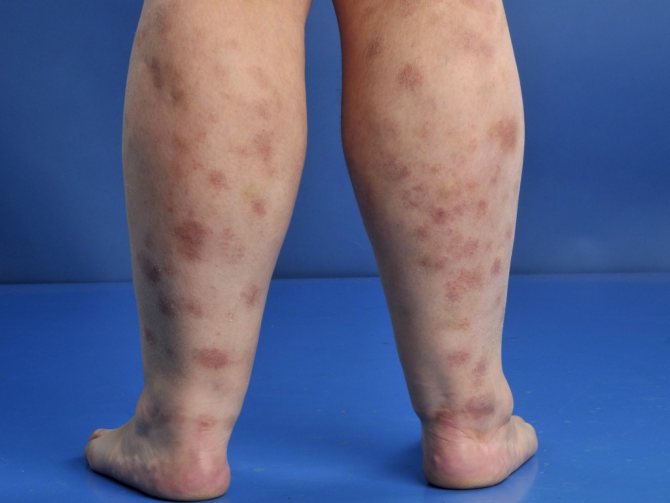
What does traditional medicine offer?
Along with conservative therapy, doctors recommend using traditional medicine recipes, especially if the form of the disease is simple and at an initial stage, as in the photo below. Treatment of parapsoriasis is carried out using herbal baths.
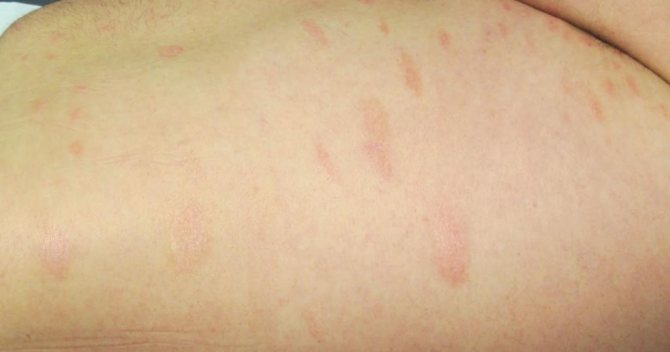
The simplest, but very effective recipe, for the preparation of which you will need:
- valerian;
- St. John's wort;
- celandine;
- sage;
- series.
All herbs are mixed in equal parts. They should be poured with boiling water and left for 8 hours. After this, you can strain the broth and add it to the bath for bathing. This recipe is also suitable for quickly relieving annoying itching. If the herbs have an unexpectedly negative effect and the patient has unpleasant sensations, then instead of herbal tea, you can make a decoction of birch leaves or pine needles.
To relieve itching, you can take baths with a decoction of juniper berries. To prepare, you need 200 grams of fresh berries, which are poured with boiling water and infused for 5 to 6 hours. Baths with medicinal herbs must be taken for 20 minutes. The course of treatment with any of the described decoctions should last from 15 to 20 procedures.
There are also recipes for preparing oral remedies that can eliminate symptoms. According to reviews, treatment of parapsoriasis can be carried out with an infusion of kombucha. First, brew black tea at the rate of 5 grams per 1.5 liters of water, you can add honey or sugar. After the tea has cooled, the kombucha is placed in the container with it. After 4 days the medicine is ready for use. Before drinking, it should be diluted with clean water. This remedy will strengthen your immune system in a short time.
To remove the external manifestations of parapsoriasis, doctors recommend using a decoction of birch leaves. Birch tar is suitable and is used to wipe the affected areas of the skin. The duration of the first session should not exceed 20 seconds, the time of subsequent procedures increases gradually.
There are many more folk remedies for treating parapsoriasis, but you can’t do it without adjusting your diet
Nutrition
If you have parapsoriasis, you should follow a diet. The principles of nutrition for this disease are:
- exclude from the diet foods that cause severe allergic reactions (seasonings, citrus fruits, chocolate, marinades);
- give up smoked meats, table salt, sugar, baked goods, fatty foods;
- eat dietary meats and fish;
- include green cereals, vegetables and fruits in your diet.
You should also eat more foods that contain a variety of vitamins.
Can it be cured forever?
Parapsoriasis is an incurable autoimmune disorder. Despite numerous studies, the nature of its origin is still unknown. The following possible causes of its occurrence are distinguished:
- stress, nervous tension;
- improper functioning of the digestive organs;
- frequent colds;
- hormonal system disorder;
- unsuitable climate zone;
- bad ecology;
- diseases of the vascular system;
- deterioration of the immune system.
One of the factors provoking this disease is poor ecology.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis cannot be called easy, since parapsoriasis is easily confused with other skin pathologies. Accurate laboratory tests to establish a 100% reliable diagnosis have not been created to date. The specialist is based on the general clinical picture, biopsy and blood test.
These data help to correctly diagnose the disease, identify its form and distinguish it from other skin diseases.