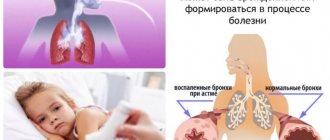
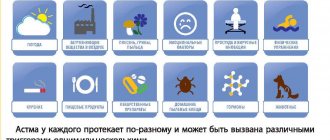
The statistics of childhood asthma are growing every year. More than 15% of children in Russia are registered with a chronic inflammatory disease of the respiratory system. Parents concerned about the severity of symptoms are increasingly learning how to apply for disability for a child with bronchial asthma. Incorrect diagnosis greatly complicates the treatment process, since asthmatic attacks are often confused with bronchitis. The disease develops slowly, which is why medical and social experts are in no hurry to assign disability to patients. The paroxysmal nature of the pathology is easily predictable:
- It is enough to identify the allergen or provoking factor;
- prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy;
- develop a plan to stop the attack.
For the first time, the child is examined by a general practitioner regarding the diagnosis, and at this stage the disease is most often overlooked. After all, to receive disability, it is necessary for the patient to be registered with an allergist or pulmonologist for six months. But it is not the duration of the disease, but the severity of the symptoms that affects the possibility of obtaining disability.
Asthma is assessed according to several criteria:
- severity of the disease;
- list of medications taken;
- the influence of symptoms on activity during the day and at night;
- changes in breathing.
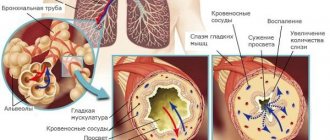
Asthma has an episodic or persistent course. A disease with periodic exacerbations no more than 2-3 times a year is not considered a basis for disability. An allergist identifies the allergen - the factor that causes attacks, and prescribes medications that prevent or quickly relieve exacerbations. Children are often recommended a special diet, but in general the disease does not affect activity.
A child with a persistent form is under medical supervision, as the disease tends to develop. Mild persistent asthma means that an attack can develop quickly and require immediate help. The disease easily becomes complicated and moves to the next stage.
Moderate asthma is characterized by prolonged attacks, the number of which exceeds 3 times a year. Some exacerbations are relieved quickly, others require hospitalization. The treatment plan is constantly adjusted as your health condition changes unpredictably.
Is there any disability for bronchial asthma?
You can receive a disability of any group, each of which has its own list of factors. Whether or not you are given disability for bronchial asthma depends on the signs of the disease.
After confirming the status of a disabled person, you will need to undergo re-examination in a year. It is necessary to change the status to current.
Which group can be given to an asthmatic?
For bronchial asthma, one of three disability groups is given.
To receive disability of the third group, you need the diagnosis of “asthma” and confirmation of the average severity of the disease. Prolonged attacks of suffocation are stopped quickly enough, but sometimes a person needs hospitalization to stabilize the condition and prevent a new exacerbation of the disease. For children, this group means limited ability to work and limited learning abilities. Physical activity is contraindicated for them. Adults can be transferred to reduced working hours or easier working conditions. They must work in well-ventilated areas, avoid dust, chemical fumes, and other unfavorable working conditions.
The second disability group is given to patients whose asthma is complicated by the lungs, endocrine, cardiovascular, and digestive systems of the body. Due to the constant deterioration of well-being and decreased physical activity, these people have a reduced level of self-care. Such patients require special working conditions, periodic inpatient and sanatorium treatment. An asthmatic child with disability group 2 often cannot attend kindergarten, and at school he is transferred to home schooling.
The first disability group can be registered in patients with asthma whose bodies have undergone irreversible changes due to this disease. Often the main diagnosis is accompanied by such as “pulmonary emphysema”, “coronary heart disease” and others. The patient has difficulty caring for himself and has difficulty moving. He also has shortness of breath at rest. He is not capable of work or learning at all. Patients with bronchial asthma often complain that it is almost impossible for them to receive disability. They consider their own condition to be unsatisfactory and even serious. Despite this, ITU experts come to the conclusion that such people are quite capable of caring for themselves, working and communicating in society, and on this basis they are denied the disability group. There is no need to blame the bureaucracy for everything. Registration of a group with asthma is a complex and sometimes lengthy procedure. If the ITU decision does not suit the patient, he can challenge it in court.
What disability group can you count on for asthma?
Recognition of the status is carried out with moderate severity, which causes problems in the functioning of the respiratory system. Whether asthma is disabled depends on the severity of the disease. The reason for the possibility of disability is associated with a deterioration in the quality of life.
If suffocation goes away after taking basic medications, then there will be no reason.
First group
Individuals with a severe persistent form of the disease can receive it. The following factors will clearly indicate the presence of a form:
- attacks every day, regardless of the time of day;
- daily dosage of GCS more than 1,000 mcg;
- dependence on corticosteroids, lower dosages can lead to a worsening of the patient’s condition;
- exacerbations that can be relieved in the hospital occur from 5 times a year;
- OFS-1 <60%, readings vary by more than 30%;
- X-ray makes it clear that there is bronchial obstruction;
- there is respiratory and heart failure;
- shortness of breath according to MRC 2 or 3 degrees.
Second degree - at rest with shortness of breath, the frequency is 25-30 times per minute. Third degree – frequency more than 30 times per minute.
There must also be stage 2 restrictions on movement, and stage 2 or 3 restrictions on labor. A person may not control the disease at all or may be able to partially influence the disease.
Features that appear in extremely severe forms of the disease:
- the daily dose of medication to prevent seizures is more than 1,000 mcg;
- control is impossible, attacks happen at any time;
- glucocorticosteroid drugs are given in a daily dosage of >20 mcg;
- DHNZ;
- personal service or labor time is less than 4 hours;
- shortness of breath has a degree of 3 or 4, due to which any exertion leads to an attack;
- shortness of breath appears at rest;
- formation of complications.

Second group
To qualify, you must have moderate bronchial asthma. It can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
- inhalation dosage up to 1,000 mcg;
- during the week, attacks occur more often 3 times during the daytime, and 1 time at night;
- OFS-1 from 80% to 60%;
- physical activity entails a decrease in output power;
- exacerbations that can be relieved with glucocorticosteroid drugs, no more than 5 times a year;
- 2-agonists are prescribed for daily use for short-term effects;
- shortness of breath with a respiratory rate of 20-25 times, an increase noticeable with slight physical exertion.
Control of such a disease is partial. Bronchial asthma imposes 2-3 degree restrictions on activity and work.
Third group
In case of bronchial asthma, disability of the third group is recognized in case of minor disorders of the respiratory system. To determine severity, rely on the following signs:
- daytime attacks occur no more than once a week;
- exacerbation occurs no more than once a year;
- night attacks occur no more than twice a month;
- glucocorticosteroid drugs are not prescribed.
Such bronchial asthma can be controlled and successfully treated. X-rays show that there is no obstruction.
If the patient’s condition has worsened, then to change the disability group it is necessary to document this fact.
The quality of life deteriorates in cases where a person needs to seek help from medical professionals to eliminate the consequences of an exacerbation.
How to apply for disability?
A referral for a medical and social examination is given to a child by a local pediatrician or pulmonologist. Even if the degree of asthma is mild, the health worker does not have the right to refuse to issue a document. The referral indicates the exact diagnosis of the disease, as well as:
- degree of severity;
- frequency and severity of attacks;
- regularity of taking steroid drugs;
- the presence of complications from the lungs and heart.
It is necessary to have with you a completed bypass sheet from several specialists, in addition to the general practitioner: a cardiologist, a surgeon, a neurologist and an endocrinologist to obtain an objective picture of your health status.
Is it possible to acquire permanent disabled status?
To find out whether bronchial asthma in adults gives permanent disability, you need to determine the severity of the disease. A re-examination after some time will not be required if a person has persistent disorders of the cardiovascular system caused by bronchial asthma. Severe respiratory failure must also be present. In other cases, re-examination will be required.
Re-examination can not only change the disability group, but also completely remove such status from a person if the symptoms of the disease have become invisible.
If an indefinite status was issued to a child, he will still need re-examination, but only upon reaching adulthood.

The procedure for registering disability.
The decision to assign disability is made by the medical and social commission. It is carried out on the direction of a therapist, pulmonologist or pediatrician (if we are talking about children).
The attending physician also fills out an extract from the medical history, which indicates the severity of the disease and the frequency of attacks, dependence on hormonal drugs and the presence of complications. In addition, the patient undergoes the necessary diagnostic procedures (fluorography, ECG, spirogram), and also takes tests (general blood and urine tests, blood tests for hormones).
Experts evaluate not only the severity of the disease, but also the patient’s quality of life (specialty, job functions, working conditions). Taking into account all factors together, disability is assigned.
The commission is carried out by appointment. You must have with you: a passport or birth certificate for the child, a medical insurance policy, a referral and medical documents.
What are the benefits?
Disability due to bronchial asthma of the first group makes it possible to use the following benefits:
- free medicines;
- free visit to the sanatorium;
- free travel on public transport;
- priority right to purchase land;
- compensation for travel to the sanatorium;
- privileges for the purchase of housing.
The list of benefits directly depends on the level of disability. Thus, disabled people of group 3 will be able to count only on a 50% discount on travel around the city and medicines, a priority right to purchase land and privileges when purchasing real estate.
Disability due to asthma in adults and children is determined according to the same rules. The reason for the possibility of becoming disabled is the inability to move and work, which affects the quality of life.
Types of disability groups
Patients suffering from asthma may experience a variety of symptoms. The course of the disease can be unnoticed or with serious complications, so disability is classified into several groups. With a minor form of the disease, in rare cases it is possible to obtain the status of a third group disabled person when the patient complains of the following symptoms:
- Partial decrease in working capacity.
- Shortness of breath during exercise.
- Problems with self-care and mobility.
Disability groups and asthma symptoms
Depending on the frequency of attacks, symptoms of the disease and dependence on medications, one of three disability groups is assigned:
- The third group is assigned to children with a diagnosis of bronchial asthma confirmed to be of moderate severity. The attacks are prolonged, but are quickly relieved with medications. The patient requires hospitalization to normalize the condition and prevent exacerbations. Therefore, children with moderate asthma often miss school and experience breathing problems during physical activity.
- The second group is bronchial asthma with complications. There are changes in lung function, hormonal imbalances, diseases of the heart and blood vessels, and digestive tract - heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease. Children need a special education regime and visits to health resorts.
- The first group are patients with irreversible changes due to attacks. Children with emphysema or coronary heart disease suffer from constant shortness of breath and therefore cannot study.
List of documents for group registration
The main document submitted for medical and social examination (MSE) is a certificate from the attending physician, form o88u-o6. The following documents should also be prepared for submission:
- Application from your own or an authorized representative.
- Original and copy of birth certificate or passport.
- Medical certificates, extracts and x-rays from the patient’s outpatient card (original and copy).
- A copy of the work record book or certificate of education.
- Extracts with periods of incapacity for work on sick leave.
All patient extracts, diagnoses from treating specialists, as well as referrals must have the doctor’s seal, the signature of the head physician and the seal of the medical institution. If the document has not been certified by the seal of the health care facility, it will not be accepted until the necessary requirement is met. After the documents have been accepted, a time is set for the commission, where it is necessary to fully describe the problem based on the diagnosis and state of health of the patient at the moment.
You will also need a description of the course of bronchial asthma, statements of treatment measures and what medications were used. The procedure for assigning a disability group can be carried out at home or in absentia if the patient is seriously ill and is unable to independently appear at the commission. To do this, you need a certificate from a medical institution with medical protocols.
If a person believes that the refusal to receive a benefit is unreasonable, he has the right to ask experts for an explanation of the reasons for such a conclusion. Submission of documents for re-examination and appeal of the verdict is carried out to the Main Bureau of Medical and Social Expertise. However, such a procedure must be carried out no later than one month from the date of refusal. Acceptance and invitation for examination are also determined within a month.
If you were able to obtain disability due to asthma, then the registration date is counted from the date of submission of the referral and accompanying documents. However, pension accruals for benefits are processed only from the date of submission of the corresponding application to the Pension Fund. To ensure that they are carried out as early as possible, you should immediately contact the Pension Fund.