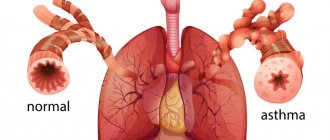
One of the most dangerous diseases of the respiratory system, which is characterized by spasms in the bronchi, is bronchial asthma. This chronic disease, which is of an allergic nature, during periods of development is manifested by attacks of suffocation, coughing and copious sputum production.
If, at the time of the attack, the patient is not provided with emergency assistance for bronchial asthma, status asthmaticus will begin to appear, which is much more difficult to eliminate. Moreover, its manifestations are fraught with multiple complications that lead to human death.
What are the causes of the disease, what are its symptoms, as well as how to provide first aid for bronchial asthma - you will find the answer to all these important questions in our article.
B2-agonists
Salbutamol and fenoterol are suitable not only for relieving acute symptoms, but also for preventive purposes arising from physical stress. Short-acting drugs are used up to 4 times a day. For mild cases, occasional oral administration of salbutamol and ventolin is acceptable. With forced frequent use, progression of bronchial activity is observed. It is necessary to review the basic therapy and adjust the treatment regimen. Popular aerosols:
- astalin;
- salbutamol with different names: AB, MHPP, Teva, Eco.
For inhalation the following are provided: ventolin nebula, salamol steri-neb. In their absence, formaterol is used in different forms: foradil, formoterol-native. For additional therapy, Oxis Turbuhaler is prescribed
Corticosteroid hormone therapy
Relieving an attack of exogenous, endogenous and mixed bronchial asthma is possible with the help of hormones - hydrocortisone, polcortolone, prednisone, desamethasone. There are several indications here:
- critical condition of the patient;
- immunity to other means.
The injection is given intravenously and subcutaneously. It is possible to relieve inflammation and relax muscles.
It is possible to take hormones once or complete a whole course (3-7 days). Once remission occurs, you can begin to reduce the dose.
Attention! It is forbidden to abruptly cancel hormones. This will contribute to the development of asphyxial syndrome.
Preventive actions
After a person has been given first aid as part of the formation of an acute attack, there is a possibility of its recurrence, especially with the obvious development of a chronic form of the underlying disease. Preventive measures include:
- Avoiding contact with allergens. It is performed in case of precise identification of a specific pathological agent that provokes an acute form of an attack. The latter can be dust, animal hair, certain types of food, detergents, exhaust gases, medications, etc.;
- Lifestyle correction. It is recommended to completely quit smoking, moderate physical cardio exercises as part of exercise therapy, regular walks in the fresh air, increase the length of stay in environmentally friendly and safe external conditions, and other actions as necessary;
- Preventive drug therapy. You should be sure to take the medications prescribed by your doctor, and always have an inhaler with a bronchodilator with you to quickly relieve an attack if necessary.
Folk remedies for relieving an attack
In some cases, you can use folk remedies for coughs at home. The following recipes are most often used to relieve cough and choking:
- A proven way to relieve an asthmatic attack is potato inhalation while drinking hot lingonberry tea. The procedure is carried out as follows: if suffocation occurs, you should unbutton tight clothes and, covering your head with a towel, inhale the vapors of potatoes boiling in a pan. Hot vapors dilate the bronchi, providing maximum assistance to the patient. At the same time, it is recommended to take a hot decoction of lingonberry leaves or berries, using them to relieve bronchospasm;

- during the acute development of an attack, you can swallow several pieces of ice, sniff cotton wool soaked in ammonia, and also take mustard plasters and apply them to the calf area;
- a good expectorant and softening effect of treatment with folk remedies is observed when inhaling smoke while burning the leaves of dry coltsfoot. Their smoke helps avoid further complications;
- in case of an acute attack, to thin the sputum, it is recommended to take a little baking soda (on the tip of a teaspoon) or drink 20 ml. sour dry wine;

- You can often find folk recipes with valerian tincture that relieve cough. To do this, you need to dilute 20 drops of tincture in a glass of water and drink during an attack.
It is important to note that each stage of the disease requires appropriate therapy. It is prescribed by a doctor, providing basic and symptomatic therapy. And, of course, preventing the development of the disease plays a huge role. It is important to note that folk recipes, as well as medications, can only be used after prior consultation with a doctor, especially during pregnancy. This will avoid negative consequences.
Emergency care for an attack of bronchial asthma
Often, a person with asthma (asthmatic) helps himself using medications that relieve bronchospasm. These medications are available in the form of a pocket metered dose inhaler. In addition to the use of aerosol drugs, everyone should know how to properly provide assistance for bronchial asthma, which consists of several algorithms of action aimed at emergency expansion of the lumen of the bronchi.
- Reassure the patient, as panic only aggravates and intensifies the symptoms.
- Access to fresh air: open the window, unbutton your shirt.
- Eliminate contact with all allergens.
- When an attack occurs, the patient needs to take a comfortable position that will allow the diaphragm to relax and improve air flow to the bronchi. Most often, patients sit on the bed, keep their back straight, lean forward a little, leaning on their hands.
- Use an inhaler - Ventolin, Berodual, Salbutamol. During an attack, it is enough to take 2 inhalations. If the condition does not improve, repeat inhalation after 2–3 minutes. If there is no effect from the inhaler, you should not use it more than 3 times every 10 to 15 minutes, as there is a risk of developing side effects.
- Immerse your hands in hot water or breathe over hot steam. Warm air will help relax the smooth muscles of the bronchi, improve mucus discharge, thereby reducing the intensity of the attack.
All of the above measures will help stop a mild or moderate attack. In cases where the symptoms do not subside, there is no wet cough, shortness of breath and wheezing do not disappear, the patient’s condition worsens, you need to call an ambulance as soon as possible, since all signs may indicate status asthmaticus.
Symptoms of status asthmaticus need to be relieved in a hospital setting. Before the ambulance team arrives, the patient also needs help, but it must be provided with extreme caution, since it involves taking medications with a large number of contraindications.
First aid for an attack of bronchial asthma may include the administration of the following medications:
- Administration of Eufillin 10 ml of 2.4% solution intravenously.
- Taking an antihistamine at the beginning of an attack: Suprastin, Tavegil, Erius, Ketotifen.
- Oral administration of Prednisolone – 1 tablet or 90-120 mg intravenously.
- Administration of 8-16 mg of Dexamethasone intravenously or intramuscularly, 1 ampoule.
Any medication should be used with extreme caution, strictly following the recommended doses that are prescribed in the instructions or have been previously prescribed by a doctor. If you don’t have an inhaler or it doesn’t give the desired result, you can use hormonal medications: Dexamethasone or Prednisolone, which will also help reduce the symptoms of bronchial asthma. Upon arrival of the Ambulance, the doctor needs to tell in detail what measures were taken before their arrival.
If the attack is successfully stopped, its symptoms will disappear within 10 to 20 minutes. The person will develop a wet cough with sputum discharge, breathing will stabilize, shortness of breath and other signs of the disease will disappear. In severe cases, the attack can last several hours, but in this case the patient must be hospitalized.
First aid for bronchial asthma is very important, since the further dynamics of the disease and the prognosis for recovery depend on its quality.
Anticholinergic drugs
In this case, inhalations with oxytropium bromide and ipratropime are performed. They are indicated if the patient is diagnosed with hypertension or cardiovascular pathologies. Anticholinergic drugs are excellent for cases where the allergen is a viral infection. For children, the composition must be administered using a nebulizer.
It is possible to completely relieve the patient from suffocation. The effect occurs half an hour after injection. The volume of sputum and mucus decreases, muscles relax, and airway clearance increases.
Development mechanism
The mechanism of development of an asthmatic attack is characterized by delayed-type allergic reactions, when, as a result of the action of external and internal irritants, the inflammatory process of the bronchial system is triggered, which provokes an attack of suffocation.
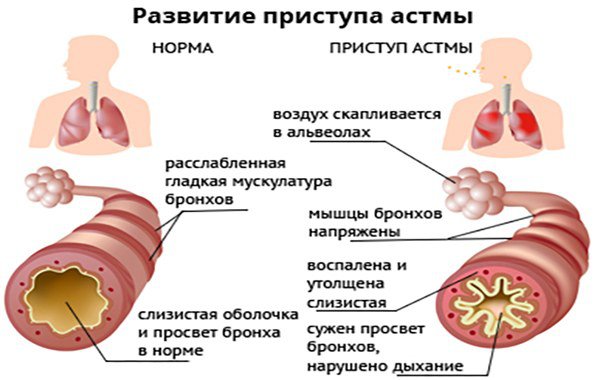
The triggering mechanism of external irritants (pollen, dust, foods, medications, painkillers, etc.) directly depends on the severity of asthma and the susceptibility of the patient’s immune system. In addition, some viruses and bacteria are external irritating factors, which, in combination with heredity, can trigger the mechanism of asthma and provoke a new attack.
The triggering mechanism for the attack may depend on the age category of the patient. As a rule, children suffering from bronchial asthma may experience stable remission by the age of puberty. If the initial mechanism of development of asthmatic diseases occurs in adulthood, a bronchial attack can proceed unpredictably. In some patients, asthma can progress with increasing severity, causing serious complications, such as status asthmaticus. For others, the attack can occur in waves, alternating between remissions and exacerbations.
Antihistamines
Relieving an attack of aspirin-induced, reflux-induced, occupational and other bronchial asthma is possible with the help of antihistamines. Most often used:
- arolin,
- allertek,
- suprastin,
- pipolfen.
Subcutaneous injections of no-shpa and papaverine also help stop the attack. When determining dosage, it is important to take into account the patient's current condition.
Using a nebulizer
First aid for acute asthma attacks, as well as as part of preventive therapy to prevent recurrent attacks, includes the use of a nebulizer. This device is a fairly popular portable medical device that operates on the basis of a compressor or ultrasound.
From suspensions or solutions, it forms extremely small droplets that look like fog or smoke. In this context, such a substance becomes an alternative to classic aerosol inhalations. Clear advantages of a nebulizer:
- Versatility. Such a device can be used not only to relieve an acute attack and provide emergency assistance, but also in everyday life to extract necessary medications into the bronchi and lungs;
- No foreign substances. The vapor from the nebulizer does not contain freon and other propellants, which are the working fluid in the vast majority of aerosol inhalers;
- Adjustable dosage and no need for coordination and breathing. Using the device, it is possible to conduct high-dose bronchodilator therapy. In addition, there is no need to coordinate inhalation with direct inhalation of drugs, since the therapy procedure is carried out as part of the natural respiratory process through the mouth and nose;
- Ease of use and other advantages. The device is easy to use for any category of patients. In addition, the nebulizer can be included in the oxygen supply circuit and used together with a ventilator, and an extremely small fraction of working medicinal fluids practically does not settle in the pharynx and oral cavity.
In modern domestic pharmacy chains, popular bronchodilators (berodual, salbutamol, etc.) are available, enclosed in nebulas or small containers - you can use them with a nebulizer as easily as with classic aerosol inhalers.
Rules for hypoallergenic living. Preventing asthma
Do wet cleaning daily and vacuum the room several times a week while your child is at school. Place a humidifier in the room where he sleeps.
Store textbooks, books and toys in a closet or locked drawers. Every month, wash soft hares, bears and other inhabitants of the nursery, do not leave them in sight.
No down or feather pillows or blankets - they accumulate a huge number of microscopic mites, causing severe household allergies. The reaction to animal fur cannot be compared with it! Buy bedding for your child made of wool or high-quality padding polyester.
Ventilate the apartment every 1-2 hours. If there are damp corners in which fungus grows in the form of a black coating (this is a strong allergen), dry them with a heater or electric fireplace. Thoroughly brush the grout lines between bathroom tiles.
No flowers in the nursery - they emit allergenic pollen, collect dust, and mold often grows in pots, to which the bronchi also react with spasms.
If you did not have pets before the first attack, you should not have them. Are they in the house where you go to visit? Give your child an allergy pill, don't allow pets to be petted (if this happens, wash your child's hands immediately), and don't stay in such a house for long. When a cat or dog lives in a family from the birth of a son or daughter, their presence in the first months acts as a vaccine against asthma and allergies - this fact was recently established by scientists. So you shouldn’t give your pets “in good hands,” since they are not dangerous to a child. However, it is recommended to bathe animals every week to remove epidermal scales and saliva residues from the fur - these are the ones that have allergenic properties.
Important An exercise to create positive pressure at the end of exhalation is useful. You will need a glass with a lid and a straw threaded into it. You need to take a deep breath through your nose, and then exhale slowly through a tube lowered into a glass a quarter filled with water.
Clinical picture of the pathological process
In general, modern medicine distinguishes several stages in the development of bronchial asthma. Stage zero or precursors are characterized by moderate tachycardia, dilated pupils, redness of the face, irregular nausea and vomiting. After some time, direct symptoms of an attack develop:
- At the initial stage. Weak and noisy breathing, increased tachycardia without the appearance of wheezing against the background of partial organic compensation of the pathological process;
- At the middle stage. Rapid development of a serious condition with the formation of respiratory failure, increased heart rate, and decreased blood pressure. In some cases, partial hypoxic coma is recorded;
- At a late stage . The most severe degree of an acute asthma attack is characterized by a high risk of death, extremely rapid progression of hypoxia, loss of consciousness, powerful tachycardia, shortness of breath, and partial or complete disappearance of a number of physiological reflexes.
After the attack ends on its own or stops using standard emergency methods, the person feels weak throughout the body, and his blood pressure is reduced. In this case, breathing is gradually restored and normalized.
Seizure development in children
The algorithm for the development of bronchial manifestations in children, as well as in adults, assumes the appearance of precursors before the onset of an attack. This condition can last from 2-3 hours to several days. At this time, the child is hyperexcitable, irritable, and has disturbed sleep.
The attack most often occurs at night. The reasons for this are the increased activity of biological substances that provoke narrowing of the bronchi, specifically at night. A severe night cough may occur that is almost impossible to stop. At the peak of the cough, vomiting with viscous mucous sputum and runny nasal discharge may occur. An increase in body temperature is often noted, making diagnosis difficult.

As a rule, at the developmental stage, an attack can be stopped with the help of inhaled medications (for better sputum discharge), after which the child becomes lethargic and lethargic. It must be taken into account that in children under 3 years of age, the typical development of an attack occurs very rarely. As a rule, there is the appearance of a persistent, painful cough that disrupts the child’s night sleep.
First aid
At the first signs, you can try to block the attack with non-drug means.
- A person sits in a comfortable position near an open window and inhales ammonia. Ammonium hydroxide vapor accelerates the outflow of blood from the chest area, which alleviates the condition.
- Hot foot baths relieve spasms. If there are contraindications to warming up, the patient sits in the bathroom next to pouring boiling water or breathes over a pan of hot water with a soda solution.
For difficulty breathing, coughing up thick sputum, drink: lingonberry tea from leaves and berries, hot milk with soda, alkaline mineral water. If the attack could not be prevented in time, you need to call a team of doctors.
Please follow and like us:
Development of an attack during pregnancy
Symptomatic manifestations of asthma during pregnancy in predisposed categories of patients are practically no different from the usual ones, and do not depend on the forms of the course.
Initially, pre-asthma appears in the form of chronic development of bronchial diseases or pneumonia in combination with bronchospasm, but without an attack of suffocation. At an early stage of development, an attack occurs quite rarely, manifesting itself as a dry cough. Further, the attack becomes more frequent at night, and is accompanied by a painful cough, rhinitis and lack of oxygen. The progression of an attack during pregnancy can be rapid and unpredictable. In addition to coughing, expiratory shortness of breath occurs, and then suffocation may occur.

The most dangerous complication (especially during pregnancy and childhood) is status asthmaticus. It occurs with increasing severity of symptoms and a prolonged attack of suffocation with copious sputum production, which can provoke an increase in blood pressure. During pregnancy, this can negatively affect the placenta, causing premature delivery. In addition, negative symptoms cause complications in the intrauterine development of the child. To avoid this, a woman should be regularly monitored by a doctor during pregnancy.