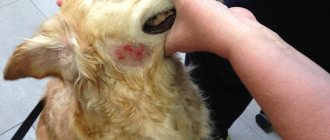
Itching is a signal from the body that forces you to pay attention to a particular organ. It is difficult to ignore this unpleasant sensation, especially if the scalp, for example, the parotid area, is itchy. Why does it itch behind the ears? This feeling is based on irritation of nerve endings under the influence of various mediators, primarily histamine.
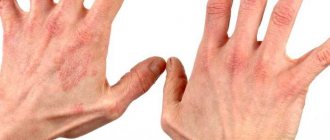
Allergy sufferers are well aware of this phenomenon, since histamine plays an important role in the development of an allergic reaction. But not only allergies cause itching - it can occur as a result of infection, insect bites, contact with irritating chemicals, etc. Itching is characterized by an irresistible desire to rub or scratch the irritated area. Scratching can damage the outer layer of skin. Damage to the skin only increases itching and leads to secondary problems, such as infection, purulent inflammation, scarring, etc. This is why it is very important to treat itching behind the ears while the integrity of the epidermis is not compromised.
Possible reasons
Why do people itch behind their ears? The reasons for this phenomenon are very diverse. Thus, itching of the parotid area of the skin occurs under the following conditions:
- seborrheic dermatitis - inflammation of the skin associated with hyperactivity of opportunistic fungal microflora of the skin; accompanied by peeling, itching, and dandruff;
- allergic reaction to dust mites, jewelry, cosmetics (for example, if a woman itches behind her ears after dyeing her hair, the possibility of an allergy to the dye should be considered);
- psoriasis is a multifactorial disease; its main symptom is a rash covered with dense keratinized skin scales; in many cases, psoriasis primarily affects the area behind the ears and the scalp;
- with otomycosis - a fungal infection of the outer ear - itching behind the ears, in the auricles and in the ear canal is disturbing;
- with atopic dermatitis, the skin behind the ears itches, becomes wet, and turns red; At the same time, other areas of the body where the skin is thin and dry are usually affected.
It is not always easy to independently determine why your ears itch behind your ears - it all depends on the severity of the accompanying symptoms. To identify the true cause of the disease, an examination and consultation with a dermatologist will be required. In some cases, tests are necessary to clarify the diagnosis.
The skin behind a child’s ear is peeling: what to do, how to treat
Scrofula is familiar to everyone from the well-known proverb - when they are plagued by failures, they say: “Then diarrhea, then scrofula.” However, few parents imagine the symptoms of scrofula in children and know how to deal with it. Although many babies after birth have yellowish crusts, peeling and weeping on their heads, which are scrofula. Such symptoms are often attributed to diathesis.
At first glance, it seems that the disease is not serious and will go away on its own, but this is not at all the case. Scrofula needs to be treated, and the sooner the better.
Scrofula is most common in infants
What is scrofula, and for what reasons does it occur?
Scrofula is a skin disease caused by the tubercle bacillus. It most often affects children under 10 years of age. Very rare in adults.
Scrofula's symptoms are similar to allergies and diathesis, so it is important to carry out a differential diagnosis. The danger of scrofula is that the pathogen is associated with Koch's bacillus, which causes tuberculosis.
Some experts believe that the advanced stage of the disease can develop into this dangerous disease. However, scrofula is not contagious, and sick children are not isolated.
They can safely play with their peers and attend kindergarten.
Why does this disease occur? Experts have conflicting opinions on this matter. Some believe that scrofula is associated with disorders of the circulatory system, others - with metabolic disorders.
Possible causes of scrofula:
- unhealthy lifestyle of the mother during pregnancy;
- intrauterine infection in combination with poor baby hygiene;
- late pregnancy;
- lack of vitamin D;
- excessive sweating;
- decreased immunity;
- violation of sanitary standards, lack of bathing;
- eating large amounts of sweets;
- feeding infants with non-adapted formulas;
- malnutrition, deficiency of vitamins, minerals and microelements;
- illness of syphilis or tuberculosis in close relatives.
Symptoms of skin disease
- the appearance of red diaper rash behind the ears and under the hair, after some time they become yellow, but the hair does not fall out or break (we recommend reading: reasons why hair falls out in a 6-year-old child);
- as the disease develops, the area of the lesion increases, it spreads to the neck, face, arms and legs;
- the skin becomes cracked, becomes wet and peels (we recommend reading: what to do if the skin on the head of a 5-year-old child is peeling?);
- severe itching;
- peeling of the earlobes;
- bloating, digestive system disorders;
- inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes (we recommend reading: what causes inflammation of the lymph nodes in a child’s neck?);
- joint pain, swelling;
- redness of the eyes.
An adult’s health deteriorates significantly, the temperature rises, sometimes to critical levels. In this case, a diagnosis of skin tuberculosis may be made.
The disease is also severe in newborns. The fact is that the baby’s immune system is still completely immature; it is not able to resist other diseases with scrofula. In addition to the symptoms described above, frequent colic, cramps, increased muscle tone, and discharge from the nose and ears are added. You can see what scrofula looks like in a child in the photo above (using the example of weeping wounds).
Features of treatment for children of different ages
As a rule, therapy for this disease does not depend on the patient’s age. If you suspect scrofula or diathesis, the skin is dry, cracking, or wet wounds appear behind the ears, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible (see also: dry skin on the legs and arms of a child). He will refer you for consultation to a pediatric dermatologist and allergist.
The next stage is the prescription of medications to relieve itching and remove crusts. If left untreated, a secondary infection may develop due to constant trauma to the skin when scratching; the wound behind the ears rots and enlarges. With timely treatment, scrofula can be cured in a short time.
It is important to strengthen the child's immunity. The defenses of a healthy baby’s body are able to cope with scrofula on their own.
Drug therapy
- Ointments. For the treatment of scrofula, Sudocrem, Tsindol, zinc ointment, Topicrem, Drapolene are used. They dry the wet crusts well, which then come off easily. Typically, these products are applied 2-4 times a day to clean skin, without washing off for several hours.
- To moisturize the skin with cracks and dryness, Bepanten is used.
- Cauterization with Fukortsin. This is a crimson-colored drug that effectively disinfects and cauterizes disease-affected skin. The child may complain of a burning sensation in the areas treated with Fukortsin. It is used if there is no improvement after 3-4 days of treatment with ointments.
- Enterosgel and other sorbents are used to remove toxins and cleanse the body. They also remove allergens.
Special diet
Strong allergens must be excluded from the diet of a child or nursing mother: sweets, chocolate, citrus fruits, nuts, milk, etc.
For scrofula, a food diary is kept where parents write down everything their child ate. This will allow you to track which products the reaction occurs to.
You are allowed to eat low-fat broths and meat, hypoallergenic vegetables and fruits, and water-based porridge. Subsequently, other foods are gradually and carefully introduced.
Newborns and bottle-fed infants must be given only adapted formulas. It is unacceptable to feed your child goat or cow milk, as it causes very severe allergies.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers an extensive list of recipes against scrofula. Before using them, you should consult your doctor.
For scrofula in a child, baths with:
- chamomile decoction;
- oak bark;
- walnut leaves;
- decoction of currant leaves;
- tea tree essential oil.
An infusion of string is used internally and externally. It dries the skin perfectly and has an antiseptic effect.
Disease prevention
To prevent scrofula it is necessary:
- observe the rules of hygiene - bathe and wipe all folds of a newborn baby on time;
- keep the home and children's room clean, do wet cleaning;
- spend more time outdoors, sunbathe according to the season;
- get enough sleep; children must have a quiet hour during the day;
- eat properly and balanced, take vitamin complexes (VitaMishki, Pikovit);
- up to 3 years of age, completely limit the consumption of sweets - sweets, chocolate, marshmallows, etc.;
- maintain immunity (harden yourself, play sports, walk in the fresh air).
The most important preventive measure to prevent the development of the disease is to monitor the child’s hygiene
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Experienced and respected pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky believes that the appearance of any skin rash occurs in three ways:
- due to non-compliance with the diet;
- through infection from a sick person through touch;
- by airborne droplets.
In order to avoid the development of the disease, you need to follow simple rules:
- maintain hygiene;
- do not introduce complementary foods very early;
- do not give children exotic fruits and products, so as not to cause allergies;
- do not overfeed the baby;
- do not bathe your child in water that has been chlorinated;
- wash children's clothes with special hypoallergenic products;
- bathe the baby using soap and detergent no more than 2 times a week;
- Avoid contact of the baby with strong household allergens: pets, sprayers, aggressive household chemicals.
The skin behind the child's ears cracks and peels
Various factors can cause the skin behind a child's ears to crack.
If parents pay attention to such a symptom in a timely manner and seek help from a specialist, then there will be no special problems with treatment. The doctor will conduct an examination and prescribe therapy with appropriate medications.
Self-medication for pathologies with such a symptom is not recommended, as this can negatively affect the child.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a fungal disease that affects areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands. If a person suffers from itching specifically in the parotid area, the possibility of this disease should first be considered.
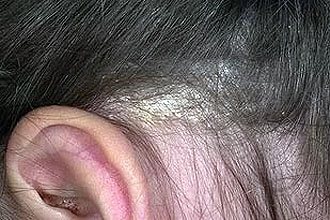
Seborrheic dermatitis develops as a result of an increase in the number of fungi of the genus Malassezia in the skin microflora. It is known that this disease affects people suffering from hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands (the fungus feeds on the lipids that make up the sebum). Malassezia is considered an opportunistic fungus, meaning it is present on the skin of most healthy people. When immune defense is reduced (for example, due to hormonal imbalance, sudden climate change, treatment with antibacterial drugs, etc.), the amount of fungal microflora increases significantly. As a result, the following violations develop:
- peeling skin behind the ears;
- dandruff;
- itching;
- oily skin and hair;
- the appearance of a rash (“irritation”) as a result of inflammation of the sebaceous glands;
- decreased skin resistance to infectious and chemical irritants.
Some symptoms are caused by the influence of fungal waste products on the skin, others by a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria (since fungi and bacteria constantly compete for the surface of the epithelium as a habitat).
Seborrheic dermatitis primarily affects the scalp - the scalp, the upper part of the forehead and the area behind the ears. In rare cases, inflammation spreads to the groin and armpits.
The affected areas of the skin behind the ears often crack and bleed. The situation is aggravated by the patient scratching the skin (this increases the risk of secondary infection). The fungus that causes seborrheic dermatitis can also affect the ear canals, in which case otitis externa occurs.
If left untreated, seborrheic dermatitis develops into seborrheic eczema.
The skin behind the ear peels and gets wet: causes, treatment methods for adults and children
Peeling of the skin behind the ear indicates the development of a pathological process in the body. Inflammation occurs under the influence of various provoking factors. Only a doctor can determine the exact reason why the skin behind the ear peels and gets wet, and prescribe the correct treatment.
Symptoms
If inflammation occurs behind the ears, a number of general symptoms appear on the epithelium:
- itching, discomfort, rash,
- the skin peels and gets wet,
- blisters appear on the irritated areas, after opening which yellow crusts form,
- humidity in the lesions progresses,
- cracks appear
- there is pain, redness, burning,
- the inflamed areas begin to itch unbearably,
- a foul odor emanates from wet skin,
- patients develop psychoemotional disorder.
If treatment is not started, the signs of the pathological process will increase:
- irritation appears
- sleep is disturbed
- performance decreases,
- a complication develops: in addition to the fact that the person’s skin behind the ears peels and gets wet, a secondary infection occurs in the areas of inflammation.
Causes
There are many factors that can cause peeling of the skin behind the ears. The main reasons include:
- allergic reactions,
- ignoring hygiene procedures,
- fungal infections,
- dermatological pathologies,
- scrofula and gneiss,
- eczema,
- dermatitis,
- purulent-inflammatory diseases (otitis).
The doctor carefully studies the features of the course and symptoms of the process. The signs and causes of inflammation are individual for each patient.
The appearance of weeping and flaky areas behind the ear is associated with the development of pathologies in the body. Foci of inflammation often appear against the background of infections, impaired digestion and imbalance of substances.
Scrofula, gneiss
With exudative diathesis, the skin in the parotid area peels and becomes wet in adults and children. Leads to scrofula:
- uncontrolled consumption of sweets,
- decreased immunity,
- genetic predisposition,
- lack of vitamins and minerals,
- unbalanced diet (monotonous, poor diet),
- complications after viral infections (flu, acute respiratory infections, measles).
When the skin becomes wet and itchy behind the ears of women, men or children, one should not take such a dermatological disorder carelessly. This is a pretty serious disorder. The development of inflammation leads to damage :
- circulatory system,
- joints,
- cartilage and bones.
In the parotid area, the skin begins to become wet due to gneiss caused by metabolic disorders. Areas of peeling with wet spots form near the ears and cover the scalp. Gneiss appears in the background:
- poor nutrition,
- hereditary predisposition,
- disrupted lifestyle,
- psychogenic disorders,
- nervous breakdowns, stress, depression.
Allergy
Epithelial tissues may peel and become wet when allergic reactions develop. Foci of inflammation appear on the skin that comes into contact with the irritant.
Allergies are provoked by:
- cosmetics (creams, shampoos),
- jewelry and accessories (earrings, glasses, headphones),
- aggressive chemicals from the environment (industrial gases, aerosols).
Allergens that penetrate inside the body lead to negative reactions:
- medicines,
- food products (citrus fruits, chocolate, honey, nuts).
Eczema and dermatitis
Dry skin with weeping areas and cracks appears behind the ears with eczema and dermatitis. The formation of inflammatory foci leads to:
- mechanical injuries,
- allergy.
The skin is damaged when the immune system is weakened and infectious diseases develop.
Eczema is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- blisters with exudate on the ears and skin adjacent to the shell,
- thickened epidermis in the affected area,
- formation of rashes,
- unbearable itching
- wet crusts.
Cracking, peeling and peeling of epithelial tissues are observed.
With dermatitis, the skin cracks. Papules with liquid form on the epithelium. After the blisters rupture, weeping areas appear, the surface of which is covered with yellow crusts.
In addition to the above reasons, diabetes, a viral or bacterial infection can cause weeping behind the ears.
Diagnostics
The doctor diagnoses the disease after a visual examination of the foci of inflammation and laboratory tests. The following methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- In case of purulent-inflammatory processes, the patient's ear is examined using an otoscope.
- If the disease is allergic, the patient is prescribed blood tests. Tests allow you to identify the irritant that led to a negative reaction.
- In case of eczema, damage to the epithelium is carefully examined.
- Patients suffering from diabetes undergo hormone tests.
The doctor selects diagnostic methods, taking into account the specifics of the disease.
Therapy
Treatment of the patient begins by determining the cause and type of disease. The treatment regimen includes the necessary medications and procedures.
If a man, woman or child has skin damage behind the ear caused by allergies, use the following algorithm:
- eliminate the irritant (jewelry, cosmetics, medicines),
- adhere to a hypoallergenic diet,
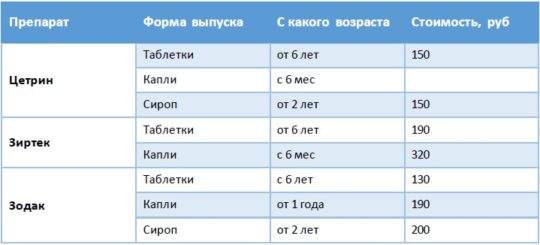
- Antihistamines are prescribed: Fenistil, Loratadine, Suprastin, Tavegil, Zyrtec.
For eczema or dermatitis, treatment is carried out as follows:
- They use drugs that can relieve inflammation and itching: Sofradex, Otipax.
- They use ointments and creams to eliminate swelling, dry out, soften the skin, and regenerate cells: Radevit, Dexpanthenol, Fenistil-gel, Ichthyol and Zinc ointment.
- In severe forms, the lesions should be smeared with external agents containing corticosteroids: Hydrocortisone, Pimafucort, Afloderm, Elokom.
- If a secondary infection occurs, antibiotics are used: Erythromycin, Doxycycline, Ciprofloxacin.
For fungal infections, therapy includes:
- ointments, drops and solutions that can suppress the development of pathogenic microorganisms: Itraconazole, Terbinafine, Naftifine, Econazole, Clotrimazole, Fluconazole, Pimafucin,
- tablets: Flucostat, Pimafucin,
- medications to restore intestinal microflora: Bifiform, Acipol, Linex.
Skin lesions behind the ear with otitis media are treated with antibiotics:
Medicines and dosages are selected by the doctor depending on the pathology that has arisen. Self-medication without clarifying the diagnosis leads to the development of dangerous complications.
Prognosis and prevention
Patients who comply with the treatment regimen quickly get rid of the problem. Medicines relieve inflammation, relieve itching, eliminate flaking, and accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues. After treatment with appropriate medications, the skin behind the ear acquires a natural color and healthy appearance.
Dermatological disorders will not appear if you follow preventive measures:
- carry out hygiene procedures in a timely manner,
- eat rationally,
- consume sweets in limited quantities,
- do therapeutic exercises,
- do not be stressed.
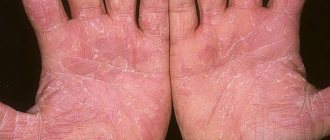
Healthy skin has an intact surface layer, there are no cracks, keratinized particles, rashes, or crusts. If the epithelial tissues in the parotid zone are flaky, wet and itchy, these are alarming signals. If these negative signs appear, you should immediately visit a doctor.
Assess your chances against coronavirus. Take our test
Attention!
The site administration advises you not to self-medicate, and in any controversial situations, consult a doctor.
Source: https://fr-dc.ru/kozhnye-zabolevaniya/pochemu-za-uhom-shelushitsya-cheshetsya-i-moknet-kozha
Diagnostics
Itching behind the ear - what could it be? It is not always possible to independently determine the exact cause of the disease.
A patient who is concerned about itching and flaking of the skin behind the ears should consult a dermatologist. Such symptoms often turn out to be harbingers of serious systemic pathologies - there is no need to waste time.
Some diseases can be diagnosed based on an in-person examination (for example, with psoriasis, the rash looks typical, and an experienced doctor is unlikely to confuse it with something else). For others, additional research will be required. Thus, the diagnosis of otomycosis is based on the results of bacteriological culture of a smear from the affected surface.
Diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis, in addition to culture of skin microflora, includes the following studies:
- blood chemistry;
- blood test for hormones (testosterone, cortisol, thyroid hormones);
- in some cases - ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- collecting anamnesis - the patient’s complaints, his feelings, history of the development of symptoms, family history.
If the presence of an allergic factor is suspected, the patient is asked to take a blood test for immunoglobulins E (markers of an allergic reaction).
Peeling skin in the ears: causes, treatment methods and effective methods of prevention
The appearance of dryness in the auricle, accompanied by itching and flaking, is evidence of pathological changes in the body, against the background of which accompanying symptoms appear: pain, partial hearing loss, etc.
Determining the source of the problem, making a final diagnosis and prescribing treatment should be carried out by a specialized specialist. With the first symptoms of peeling, you should contact an ENT specialist, who will conduct an initial examination.
If the doctor cannot determine the cause of dryness and itching within his competence, he will refer you to another specialist - a dermatologist, endocrinologist or surgeon.
The main causes of peeling ears
The detachment of keratinized skin particles in the ears can be caused by violation of hygiene rules by using inappropriate items to remove wax accumulations. Damaged skin is renewed during healing, and flakes similar to dandruff flake off easily.
Peeling in the ears can be a sign of:
- chronic liver pathologies;
- metabolic failures;
- diabetes mellitus;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- chemical burn;
- exhaustion of the nervous system due to frequent stress.
The skin in the ears can also peel under the influence of inflammatory processes, fungal infections or allergic reactions.
Inflammatory processes
Inflammatory processes of the internal and external auditory apparatus can stimulate tissue death. The inside of the ear begins to itch, and the skin begins to peel and itch.
Otitis
The disease is infectious and inflammatory in nature against the background of pronounced symptoms: acute pain, hearing loss, accompanied by the discharge of pus. Due to the high probability of complications, therapy aimed at eliminating the source of the disease and its symptoms can be prescribed by a doctor only after a comprehensive diagnosis.
Furuncle
Infection in open wounds of the injured epidermis of the ear can cause the formation of a boil, indicating an acute stage of the inflammatory process.
Swelling, hearing loss and redness of the skin accompanied by severe pain are the first symptoms of the disease.
Elimination of a boil is possible only surgically with supportive antibiotic therapy as prescribed by a doctor.
Allergic reactions
Excessive dryness, itching and flaking of the skin both in and behind the ears are often the result of allergies. The most common sources of this reaction in the body are:
- shampoo, hair conditioner, shower gel or cleanser;
- dye or solution for biochemical hair perm;
- jewelry (earrings, chains, pendants);
- food products (eggs, citrus fruits, etc.).
To determine the source of the allergic reaction, it is necessary to do allergy tests, and based on the result, exclude the irritating allergen and take a course of antihistamines as prescribed by the attending physician.
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is one of the forms of allergies with more severe symptoms:
- itching appears not only outside the ear, but also inside;
- the skin rapidly turns red;
- Small blisters form on the affected areas and collect fluid.
After spontaneous opening, a crust forms in place of the bubbles, which falls off over time. Treatment of dermatitis includes taking antihistamines and corticosteroids, which can be combined depending on the form and severity of the disease.
Eczema
An acute allergic reaction that can quickly develop into a chronic form (within 21 days). Burning and redness of compacted skin, followed by the appearance of a small rash that provokes the formation of dry crusts and cracks, are among the main symptoms of eczema.
Timely drug therapy using external medications in the form of anti-inflammatory ointments, wiping with alcohol or an oxycort-based aerosol guarantees recovery and the absence of relapses. In especially advanced cases, antibiotic therapy may be prescribed.
A hypoallergenic diet is a mandatory element of therapy until symptoms disappear completely.
Fungal infection
Most often, a fungal infection attacks a weakened body, in which it can quickly multiply. This process is facilitated by excessive ear hygiene and the use of other people's things (headphones, hearing aids, etc.). The main symptoms of fungal infection are:
- severe itching in which the skin peels off profusely;
- noise in ears;
- frequent headaches;
- sensation of a foreign object inside the ear;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Treatment for fungal infections involves prescribing antifungal agents in the form of gels, creams or capsules. Antihistamines can be used to eliminate itching, and special ointments can be used to restore the skin.
Dandruff
The appearance of dandruff in the ears can be the result of severe stress or an unhealthy diet. In this case, anti-stress medications are prescribed (herbal infusions, etc.) and the entire diet is reviewed.
An oily scalp and dysfunction of the sebaceous glands can aggravate the situation, regardless of what measures are taken to combat the source of flaking. To eliminate dead scales, medicated shampoos (Ketoconazole, Nizoral, etc.) are used.
Ignoring other symptoms along with flaking ears increases the likelihood of complications.
It is almost impossible to independently determine why peeling of the skin in the ears occurs, and therefore, as soon as redness appears in the ear, and the skin begins to dry and crack, it is better not to delay contacting an otolaryngologist.
Possible complications
Untimely and incorrect treatment of dry and cracked skin in the ears can lead to a number of complications:
- Sepsis is when an infection enters the blood and spreads throughout the body.
- Deep mycosis is a fungal infection of body systems: the oral mucosa, lymph nodes, liver, etc. It is impossible to completely get rid of the disease; relapses can be observed throughout life, and if the immune system is severely weakened, it can lead to death.
- Otoanthritis or pathology of infants is the flow of inflammation from the middle ear to the mastoid process.
- Destruction of the auditory ossicles and due to severe and protracted inflammatory processes.
- Perforation of the eardrum as a result of inflammatory processes, improper hygiene or other manipulations.
When your ears are peeling, and the cause of what is happening is not known for certain, you should not self-medicate, since instead of healing, you can harm the entire body.
Treatment
Depending on the primary source stimulating peeling in the ears, therapy may be prescribed, which includes:
- Medicines:
- Antibiotics in the form of ear drops ( Anauran, Otipax, etc.
) are used to fight bacterial infections. Their action is aimed at relieving itching, reducing pain and destroying pathogenic bacteria. If necessary, general antibiotics may be prescribed, for example, after opening a boil. - Antifungal agents for external use - against mold fungus Terbinafarin
, yeast -
Pimafucin
, etc., for oral administration -
Fluconazole
or its analogues. - Antihistamines ( Tavegil, Suprastin, Cetirizine
, etc.) are prescribed for allergies, eczema and dermatitis, depending on the source of the allergy and the form of the disease.
- Surgical intervention - to open the boils and clean the ear canal from pus.
Most drugs have a number of contraindications (for example, pregnancy) and side effects, which must be taken into account before starting therapy. The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the correct diagnosis.
A separate group includes folk remedies that help in cases where the ears are peeling.
The most effective are tampons soaked in sunflower or olive oil, which need to be inserted into the ear canal, held there for 20 minutes and removed. After this, the skin must be cleaned of residual oil and moisturizer applied. Some doctors advise repeating the procedure at least once within 7 days.
The oil can be replaced with decoctions of string, chamomile and other herbs that have an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect.
Prevention methods
The main methods that can prevent peeling of the skin in the ears are:
- Compliance with the rules for cleaning the ears - only the outer part of the ear canal is treated with a cotton swab, since wax comes out of the inner part on its own when chewing movements of the jaw are made.
- Regular treatment of hearing aids (if used) with special means, as well as the use of ear rinsing drops.
- Protecting ears from water, for example, in a swimming pool, which is important for adults and children. Infants (up to 1 year) must be bathed after closing the ear canals with special cotton swabs.
- Protect your ears from cold air and drafts.
- See a doctor and take prescribed medications for colds, acute respiratory viral infections, etc., which can stimulate the appearance of otitis media.
- To clean the ear canals, do not use improvised means that can injure the skin (hairpins, toothpicks, etc.).
Self-medication with the achievement of a visible cosmetic effect is not always evidence that the cause of peeling has been eliminated. Only a doctor can say exactly why the ears are peeling and how to eliminate this problem most effectively without harming other body systems. Timely therapy, selected taking into account the patient’s health characteristics, increases the chances of complete restoration of the skin in the ear area.
You can find even more useful articles about ENT diseases on the website https://lor-uhogorlonos.ru/
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/lor/shelushenie-koji-v-ushah-prichiny-sposoby-lecheniia-i-effektivnye-metody-profilaktiki-5afbe76f00b3dd6d5aede172
Treatment
There is no universal remedy that can cure itching behind the ears of any etiology. However, there are drugs that can improve the well-being of patients, regardless of what is causing the itching. For example, many topical preparations with cooling and moisturizing components may

time to relieve the discomfort. Ointments containing anesthetic components also relieve itching (as they reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings).
If the itching behind the ears is constant and very severe, the doctor may prescribe sedatives (sedatives, usually in the form of tablets). Antihistamines are also effective (they are usually prescribed for allergies). Their action is based on blocking the production of histamine, a neurotransmitter of inflammation. Thanks to this, the main symptoms of inflammation are suppressed - itching, pain, swelling, redness, etc. Antihistamines are also the drugs of choice for itching behind the ears caused by allergic dermatitis. In addition to taking antihistamines, the patient should limit contact with allergens.
It is important to understand that symptom relief is not a cure. To get rid of annoying itching behind the ears forever, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease.
Treatment should be based on what causes the unpleasant symptoms. This is why it is so important to make a correct diagnosis. When the main cause of the disease is eliminated, the unpleasant symptoms will go away on their own.
Why does a person itch behind the ears - itching in women and men 2020
If the skin behind the ears itches, the body sends a signal about disruptions in some vital processes. There are a huge number of reasons for the appearance of this symptom.
Some of them are completely harmless and over time the problem disappears on its own. However, itching can be a sign of a serious condition developing.
To clarify the situation, additional examinations may be needed: examination by a doctor, taking epithelial samples, blood tests, etc.
Treatment
Itching localized behind the ears is treated in accordance with the established diagnosis. That is why it is important to consult a doctor promptly to identify the underlying cause.
For dermatitis and derivative diseases, it is advisable to limit contact of the affected area with water during an exacerbation. You cannot peel off the crusts that have formed, as this will only worsen the situation.
If the peeling is dry, treatment is prescribed with anti-inflammatory ointments, which in addition have a vasoconstrictor and antifungal effect. Such products should also include antibacterial substances. The normal microflora can also be disrupted by excessive hygiene, when not only the ears are treated with water, but also the ear canals themselves.
Discharge of different character and color depending on the type of pathogen. Ears, as a rule, itch and flake as a result of infection with a fungus of the genus Aspergillus or Candida, sometimes an infection is added to them, for example, Staphylococcus aureus.
Apply them with a cotton swab to the sink and into the ear canal. First you need to establish the nature of their origin and only then begin treatment.
Before visiting the doctor, itching and flaking can be relieved for a while by cleansing the ears with an alcohol solution, Vaseline or vegetable oil.
Sebum also contains free and bound types of fatty acids, proteins, and nucleotides. As a result, a certain amount of free fatty acids is created, which have an irritating and comedogenic effect. In particular, it often signals seborrheic dermatitis. But there are fewer free fatty acids in such an epidermis, as well as squalene and paraffin esters.
In particular, where hair grows on the head, erythematous-squamous and follicular papular-squamous types of rashes grow. If the body has sufficiently activated local and general immunity, then the mushrooms remain in a spore state. It consists of using antifungal drugs, whose base is nizoral and miconazole.
Weeping skin behind the ears almost 100% indicates the presence of a certain skin disease. Such an unpleasant problem can affect both a baby or child and a completely adult person.
At first, the symptom may not be noticeable, but after several days, it worsens and is quite aggressive in nature. This affects a person's general condition, preventing him from concentrating and doing everyday activities.
Treatment is indicated by the doctor, based on the etiology of the disease and its stage. To eliminate allergic reactions, the doctor prescribes a strict diet and drug therapy to the patient. So, the diet should completely exclude sweet, starchy, spicy, salty and fatty foods.
Among medications, preference is given to antihistamines and ointments that have a drying and anti-inflammatory effect. Additional intake of vitamins is also indicated.
With gneiss and scrofula, baths and saunas are contraindicated. This may worsen the course of the disease. It is necessary to strictly adhere to the treatment regimen and, if possible, ensure maximum healing of the wounds. In case of diathesis in children, you should avoid a number of foods that can provoke a repeated negative reaction. You should also provide your child with frequent walks.
However, if the problem has become more widespread, then it must be eliminated after examination and doctor’s recommendations.
Peeling skin near the ears not only causes a lot of inconvenience, but is also quite a serious discomfort for the patient and others. In addition, significant problems accompanying the process include redness of local areas of the skin, rashes, and dryness of the epidermis.
Inflammatory processes are accompanied by numerous attacks of itching, characterized by the appearance of small blisters filled with liquid that regularly burst, after which the skin becomes constantly wet. When it gets wet behind the ears, the elements of the skin have an unpleasant odor. When drying occurs, areas are formed covered with dense, golden-colored crusts.
Treatment of weeping spots behind the ears is prescribed exclusively by a doctor after a full diagnosis. The complex of treatment for ear eczema includes the following measures:
- a strict diet that excludes sweet, starchy, spicy, salty and fatty foods;
- antihistamines;
- anti-inflammatory and drying ointments and gels for treating affected areas;
- restorative therapy, vitamins and dietary supplements.
An infusion of valerian, motherwort, and other sedative herbal remedies will help to obtain a good calming effect.
There is no universal remedy that can cure itching behind the ears of any etiology. However, there are drugs that can improve the well-being of patients, regardless of what is causing the itching.
For example, many topical preparations with cooling and moisturizing components can temporarily relieve discomfort.
Ointments containing anesthetic components also relieve itching (as they reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings).
Source: //xn--80ahsaqcbqq.xn--p1ai/simptomy/zud-za-ushami.html
Symptom manifestation
When it just itches behind the ear, a person may not pay attention to it if there is no severe itching. Typically, concern arises if the condition causes discomfort for a long time and other signs of developing pathology appear.
Typically discomfort is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the soft tissues near the auricle;
- peeling of the epidermis;
- spread of itching to other areas of the skin;
- the appearance of rashes, after which a crust may remain on the epidermis;
- headache;
- general deterioration of health;
- increase in body temperature;
- tearfulness;
- rhinitis.
The epidermis behind the ears can itch in both adults and children. Most often, this condition occurs in women and children.
In women, this is usually associated with the regular use of cosmetology products and household chemicals that cause allergies and irritation.
Itchy skin behind a child's ear most often indicates irritation. Any such condition that does not go away for a long time is a reason to visit a doctor.
General symptoms during the development of the disease
In the first stages of development, the symptoms do not cause any inconvenience, the signs are almost invisible. But three to four days pass, the exacerbation of symptoms cannot be ignored due to the rapid and aggressive increase in symptoms.
Both adults and children become restless, cannot concentrate on their usual activities, children refuse the most exciting games, they are not attracted to their favorite toys and entertainment.
Further development of the disease leads to the fact that it becomes difficult for the patient to focus on certain matters. In general, we can say that the patient's quality of life is significantly reduced. First of all, this is due to significant cosmetic defects in one of the most injury-prone areas of the body.
It is difficult not to notice the presence of red spots in the area of the earlobe or in the folds of skin behind the ears.
Sometimes the manifestations of the disease can be quite vague, which requires additional diagnostics and tests. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, as there is a risk of progression of the disease.
Based on the study and recording of symptoms, the main causes are identified, allowing for effective treatment of the underlying disease and associated complications.
Associated symptoms
Associated symptoms may vary, depending on the cause that led to the appearance of scabs. The color of the crusts is red, white and yellowish. Typically, before the onset of peeling, the following signs of illness appear:
- The skin becomes sensitive and inflamed. Blisters and bruising may occur.
- There is a feeling of skin tightness. The area behind the ears becomes darker in color and becomes rougher.
- The crust tightly covers the skin behind the auricle. After the crust falls off, bleeding occurs.
If itching behind the ears is accompanied by fever or symptoms of intoxication, you should see a doctor. The cause of this malaise can be serious illnesses.
Probable diseases
Itching behind the ears is a symptom of some diseases. To determine exactly why this condition occurs, it is recommended that you make an appointment with your doctor.
The causes of itching behind the ears in adults coincide with the causes of this condition in children. It may be a symptom of the following pathologies:
- Allergic reaction. This condition usually occurs due to an allergy to hair detergents or styling products, jewelry, or dust;
- Otitis externa is a pathology of the ears caused by inflammation. This disease can also cause discomfort;
- Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory disease of the epidermis. The main symptoms are itchy ears and head, itching is accompanied by flaking, dandruff appears;
- Psoriasis is a skin disease that causes rashes. During an exacerbation, the rash is accompanied by itching and peeling. The rash is localized throughout the body, and also appears in the area behind the ears and on the scalp;
- Atopic dermatitis is a disease of the epidermis in which red spots appear on the back of the head, which can become wet and itchy. The rash spreads throughout the body;
- Fungus. If this is the cause of the itching, then the ears themselves will also itch.
Independently determining the cause that led to this condition is not always accurate. For a more reliable diagnosis, it is recommended to consult a professional. You can find out about the causes of itchy ears in a child in this article.
Behind the ears itches and gets wet, what could it be?
Many of us in everyday life have encountered the problem of adults or children having itchy and wet ears behind their ears.
This is a very unpleasant phenomenon that brings a lot of unpleasant sensations to a person; in addition to this ailment, redness behind the ears, itching, various types of rashes, etc. can also be observed. Depending on the symptoms, the patient is given an appropriate diagnosis.
Often the disease manifests itself gradually; in any case, a number of additional tests will be required under the supervision of a specialist to exclude progression of the disease.
When we talk about humidity behind the ears or use the term “wetness” in the area behind the ears, an additional unpleasant symptom may be an unpleasant odor behind the ears. Some patients, embarrassed by this problem, do not immediately go to see a doctor; they often self-medicate, using folk lotions and compresses.
In some cases, this provides temporary improvement. However, the most important thing is to find the cause of this disease and eliminate it for a complete recovery. Weeping lesions behind the ears signal an inflammatory process in the body.
Sometimes they can form a crust; such formations can appear not only behind the ears, but also in the eyebrow area.
Many are faced with a situation when the base of the ear suddenly begins to hurt; what to do in such cases, we have described in the corresponding article.
Treatment options
Treatment of itching behind the ears is carried out based on the cause of this condition. If the discomfort is caused by an allergy, the patient is prescribed antihistamines for oral and external use.
When itching behind the ears occurs due to a fungus, the doctor prescribes antifungal drugs to the patient.
If the area behind the ears not only itches, but also gets wet, a specialist will also tell you how to treat it. In this case, complex therapy is prescribed. The treatment system includes:
- following a diet that is based on avoiding eating sweet, spicy, salty and starchy foods;
- taking antihistamines;
- ointments, gels and creams with anti-inflammatory properties;
- drying agents;
- the use of multivitamin complexes to increase the body's defenses.
For weeping rashes behind the ears that cause itching, water procedures are prohibited. You are not allowed to visit the swimming pool, sauna or bathhouse, or take a bath. Showering is allowed, but in such a way as to avoid getting water on the rash.
Traditional medicine will help speed up the healing process. For internal use and external use, it is recommended to use decoctions of chamomile, nettle, horsetail and blackcurrant leaves.
If itching occurs behind the ears, it is recommended to consult a doctor if this condition persists for several days. This will help to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner and begin therapy, which will reduce the risk of complications.
Article rating:
Loading…
Source
If the skin behind the ears itches, the body sends a signal about disruptions in some vital processes. There are a huge number of reasons for the appearance of this symptom. Some of them are completely harmless and over time the problem disappears on its own. However, itching can be a sign of a serious condition developing. To clarify the situation, additional examinations may be needed: examination by a doctor, taking epithelial samples, blood tests, etc.
What to do?
If such trouble befalls you, then you need to take immediate action, since any painful symptoms often signal serious illnesses. What should you do?
1. First, consult a dermatologist to find out the exact reasons. After examining the skin damage, he will make his assumptions and refer you for further examinations. Based on their results, appropriate treatment will be prescribed. 2. Try taking a course of the vitamin preparation “AEvit” or a full-fledged vitamin complex. This will not harm even a completely healthy person. 3. If itching behind the ear is accompanied by swelling of the eyes, watery eyes, sneezing and nasal congestion, then most likely you have an allergy. Try taking an antihistamine tablet - diazolin, suprastin, tavegil. If the symptoms decrease, then you have a direct path to an allergist. 4. If the skin is just peeling and not yet very irritated, then use moisturizing creams and oils for relief.
You can talk about the rest of the treatment only after visiting a doctor, and you should not engage in amateur activities until the reasons are clarified.
Symptom manifestation
Initially, the symptom may be unobtrusive, and therefore many people simply do not notice it. Over time, with continued exposure to the irritating factor, the itching intensifies and other accompanying signs may appear, indicating a possible source of the problem.
Most often, the skin behind the ears itches in children and women. Children's bodies are more susceptible to irritants, and women come into contact with chemical allergens, including those contained in cosmetics. Hormonal fluctuations also have an effect.
Scratch marks remain on the affected area, which, in turn, can lead to the spread of irritation and infection. If it is an allergy, redness and characteristic rashes are added. The following symptoms may also occur:
- peeling of the skin;
- formation of blisters and crusts;
- plaque on the skin;
- malaise;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- swelling;
- increased lacrimation;
- gradual spread of itching to neighboring areas;
Over time, itching not only behind the ears, but also the ears themselves, the scalp, face and neck. If the symptom activates and intensifies, you should not hesitate to visit the hospital.

Features of treatment for children of different ages
As a rule, therapy for this disease does not depend on the patient’s age. If you suspect scrofula or diathesis, the skin is dry, cracking, or wet wounds appear behind the ears, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible (see also: dry skin on the legs and arms of a child). He will refer you for consultation to a pediatric dermatologist and allergist.
The next stage is the prescription of medications to relieve itching and remove crusts. If left untreated, a secondary infection may develop due to constant trauma to the skin when scratching; the wound behind the ears rots and enlarges. With timely treatment, scrofula can be cured in a short time.
It is important to strengthen the child's immunity. The defenses of a healthy baby’s body are able to cope with scrofula on their own.
- Ointments. For the treatment of scrofula, Sudocrem, Tsindol, zinc ointment, Topicrem, Drapolene are used. They dry the wet crusts well, which then come off easily. Typically, these products are applied 2-4 times a day to clean skin, without washing off for several hours.
- To moisturize the skin with cracks and dryness, Bepanten is used.
- Cauterization with Fukortsin. This is a crimson-colored drug that effectively disinfects and cauterizes disease-affected skin. The child may complain of a burning sensation in the areas treated with Fukortsin. It is used if there is no improvement after 3-4 days of treatment with ointments.
- Enterosgel and other sorbents are used to remove toxins and cleanse the body. They also remove allergens.
When scrofula does not cause symptoms other than crusts on the scalp and does not progress, it may not be treated. In this case, they get by by simply combing out the scab, that is, the crusts. Before this, the skin is generously lubricated with nourishing baby cream or Vaseline oil, and they are combed out with a regular comb. When removing crusts from a child under one year old, you need to be careful not to damage the fontanel.
When drug therapy is carried out, before using ointments it is important to thoroughly clean the skin and carry out other hygiene procedures. It is useful to take antiseptic baths with herbal decoctions.
Special diet
Strong allergens must be excluded from the diet of a child or nursing mother: candy, chocolate, citrus fruits, nuts, milk, etc. For scrofula, a food diary is kept, where parents write down everything that their child ate. This will allow you to track which products the reaction occurs to. You are allowed to eat low-fat broths and meat, hypoallergenic vegetables and fruits, and water-based porridge. Subsequently, other foods are gradually and carefully introduced.
Newborns and bottle-fed infants must be given only adapted formulas. It is unacceptable to feed your child goat or cow milk, as it causes very severe allergies.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine offers an extensive list of recipes against scrofula. Before using them, you should consult your doctor.

Due to its effectiveness, baths with chamomile decoction are in great demand in the treatment of scrofula.
For scrofula in a child, baths with:
- chamomile decoction;
- oak bark;
- walnut leaves;
- decoction of currant leaves;
- tea tree essential oil.
An infusion of string is used internally and externally. It dries the skin perfectly and has an antiseptic effect.
Probable diseases
The reason why the skin behind the ear itches and peels may be a specific disease. To make an accurate diagnosis, you may need to visit a dermatologist, ENT specialist, venereologist, allergist, endocrinologist and a number of other specialists.
Most often, itching is a symptom of the following diseases:
- Otitis externa. This is an inflammatory disease that can affect the ear and surrounding areas.
- Fungal infection. Itching is one of the main signs of a fungal infection. It is also indicated by specific formations on the skin.
- Dermatitis. Skin diseases are quite common. In some cases, you may need the help of a venereologist.
- Seborrheic eczema. It can be caused by a simple allergy. Subsequently, characteristic plaques appear. The disease is chronic.
- Psoriasis. A disease that is difficult to treat. The root cause may be an allergy. It is also called lichen planus.
Treatment methods
It is best to seek help from a specialist at the first signs of inflammation, but some measures and treatment can be taken at home on your own.
What can you do at home?
The first step at the first symptoms of inflammation and discomfort is to get rid of jewelry. After the earrings have been removed, the earlobe should be washed with warm water and soapy water.
If there are obvious signs of an inflammatory process, the affected area should be wiped with a disinfectant solution as often as possible. If redness and swelling do not go away, the solution must be changed and the procedure performed even more often. Hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin will definitely not make things worse, but it will help completely or at least partially wash out pathogenic bacteria.
When fluid collects at the site of the lesion, and pus is felt inside, then an antibacterial ointment must be added to the disinfectant, which will help draw the pus out and also suppress pathogenic bacteria.
All procedures must be carried out wearing gloves, or after washing your hands thoroughly, so as not to introduce any other infection.
If treatment does not even partially improve the condition, then you need to seek help from a doctor.
Surgical intervention
An advanced inflammatory process is usually treated with antibiotics, but if treatment is powerless and a formation is felt in the cavity of the epidermis, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
The doctor will perform an operation and remove the contents from the capsule. Afterwards, another operation will be needed to remove this capsule. If the inflammatory process causes suppuration, the exudate is pumped out, the wound is washed and, if necessary, drainage is installed. Surgical treatment is carried out under local anesthesia, pus and neoplasm are removed through a minor incision. Sutures are placed only in case of deep penetration; after surgery, in most cases, treatment is not necessary.
If the operation is performed in a timely manner, there will not even be any traces left on the earlobe.
Treatment options
Itching localized behind the ears is treated in accordance with the established diagnosis. That is why it is important to consult a doctor promptly to identify the underlying cause.
To reduce discomfort and at least temporarily eliminate itching, you can use sedatives and cooling sprays if there are no contraindications. Pain-relieving ointments are also used. For the treatment of adults, it is possible to use steroid drugs in accordance with the diagnosis. To get rid of the fungus, special antimycotic ointments are prescribed. To prevent allergies from complicating treatment, antihistamines are added to therapy. Only a doctor has the right to prescribe a specific list and course of medications after a thorough diagnosis.
For dermatitis and derivative diseases, it is advisable to limit contact of the affected area with water during an exacerbation. You cannot peel off the crusts that have formed, as this will only worsen the situation.
My child has a crack behind his ear
I am the mother of a five-year-old boy who suffers from a crack behind his ear. This phenomenon is popularly called scrofula, which used to be the official name of the disease.
Allergic rashes on the child's skin have appeared from time to time since birth. I bathed the boy in a bath with the addition of a decoction of string or chamomile, smeared the rashes with creams with D-Panthenol (Bepanten, D-Panthenol, Panthenol), limited the child in sweets and the rashes went away.
From about the age of four, small cracks began to appear behind the ear. They applied the same creams and they went away on their own. At five years and two months, a crack appeared again, covered with dry crusts, and the child was bothered by severe itching. The old remedies only slightly relieved the itching, but the crack did not go away.
I started applying Methyluracil ointment - the boy felt a little better, but the crack still did not heal. Even the kindergarten teachers began to tell me that the child was constantly scratching his ear. And indeed, there was already a feeling that a little more and the ear would come off completely.
All this lasted about a month.
We turned to doctors: a pediatrician and an allergist-immunologist. The pediatrician gave a referral for a blood test for sugar and prescribed treating the crack with hydrogen peroxide and syntomycin ointment (5%).
The allergist said that this is allergic dermatitis and it is necessary to exclude all sweets, including fruits, even such harmless ones as green apples and bananas, as well as everything fried and fatty. Also exclude juices and compotes. Do not buy any sweet dairy products with synthetics - cottage cheese, yoghurt, kefir. I allowed adding a little sugar to the tea.
The instructions actually say that the active ingredient is cetirizine. Allowed for children from 6 years of age. I decided that after all, my son is already a little older than 5, which means it’s okay to give it.
We were treated in accordance with the allergist’s recommendations for 7 days, the crusts began to disappear. There is still a fairly large combed spot under the ear. The itching still bothers me sometimes. I treat with chlorhexadyl and acry-derm in the morning and evening, if the itching bothers me during the day - with peroxide and syntomycin.
What advice can you give to other people facing the same disease? Prevention is always easier than cure, so never give your children sweets and fast food, no matter how tearfully they ask and no matter what eyes they look at.
Check your blood sugar level - elevated levels somewhat slow down the healing of cracks and scratches. Be careful with herbs - even the most harmless ones can sometimes cause allergic reactions.
The disease manifests itself, among other things, due to a lack of vitamin D, and it is produced under the influence of sunlight, so walk more, and take an additional vitamin D solution in winter.
Other causes of itching and their elimination
There are a number of other reasons why a person’s skin behind the ears itches. These factors include:
- Stress – frayed nerves can cause itching and various skin diseases in adults.
- Allergies – to cosmetics, shampoo, hair dye, ingredients of a homemade cosmetic mask, jewelry, products and external irritants, including the material of the headdress. Allergies are treated with antihistamines and require limiting contact with the irritant.
- Climate change – a sudden change in environment weakens the body. In addition, unusual weather, for example, dryness and wind, can have an effect.
- Vitamin deficiency - a lack of vitamins is reflected primarily on the skin. Bad habits in adults increase this effect several times. You need to improve your diet and lifestyle.
- Dehydration – it is important to restore water balance. To do this, you need to drink more water and use humidifiers.
It is also important to maintain hygiene to avoid the accumulation of dirt and germs. If you notice itching behind the ears, you should definitely consult a doctor to find out its origin and only then begin treatment.
Source
Itching of the ears can be caused by factors such as exposure to bright sun, dust, hormonal changes, skin diseases, and pathologies of internal organs. And if the discomfort does not go away within 2-3 days, redness and peeling appear, you need to find out why the outside of the ear itches. The causes in adults and children in some cases differ due to physiological factors, and a doctor must make a diagnosis.

Itching behind the ear: causes of discomfort and methods of elimination
If the skin behind the ears itches, the body sends a signal about disruptions in some vital processes.
There are a huge number of reasons for the appearance of this symptom. Some of them are completely harmless and over time the problem disappears on its own. However, itching can be a sign of a serious condition developing.
To clarify the situation, additional examinations may be needed: examination by a doctor, taking epithelial samples, blood tests, etc.
Symptom manifestation
Initially, the symptom may be unobtrusive, and therefore many people simply do not notice it. Over time, with continued exposure to the irritating factor, the itching intensifies and other accompanying signs may appear, indicating a possible source of the problem.
Most often, the skin behind the ears itches in children and women. Children's bodies are more susceptible to irritants, and women come into contact with chemical allergens, including those contained in cosmetics. Hormonal fluctuations also have an effect.
Scratch marks remain on the affected area, which, in turn, can lead to the spread of irritation and infection. If it is an allergy, redness and characteristic rashes are added. The following symptoms may also occur:
- peeling of the skin;
- formation of blisters and crusts;
- plaque on the skin;
- malaise;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- swelling;
- increased lacrimation;
- gradual spread of itching to neighboring areas;
Over time, itching not only behind the ears, but also the ears themselves, the scalp, face and neck. If the symptom activates and intensifies, you should not hesitate to visit the hospital.
Probable diseases
The reason why the skin behind the ear itches and peels may be a specific disease. To make an accurate diagnosis, you may need to visit a dermatologist, ENT specialist, venereologist, allergist, endocrinologist and a number of other specialists.
Most often, itching is a symptom of the following diseases:
- Otitis externa. This is an inflammatory disease that can affect the ear and surrounding areas.
- Fungal infection. Itching is one of the main signs of a fungal infection. It is also indicated by specific formations on the skin.
- Dermatitis. Skin diseases are quite common. In some cases, you may need the help of a venereologist.
- Seborrheic eczema. It can be caused by a simple allergy. Subsequently, characteristic plaques appear. The disease is chronic.
- Psoriasis. A disease that is difficult to treat. The root cause may be an allergy. It is also called lichen planus.
Treatment options
Itching localized behind the ears is treated in accordance with the established diagnosis. That is why it is important to consult a doctor promptly to identify the underlying cause.
To reduce discomfort and at least temporarily eliminate itching, you can use sedatives and cooling sprays if there are no contraindications. Pain-relieving ointments are also used.
For the treatment of adults, it is possible to use steroid drugs in accordance with the diagnosis. To get rid of the fungus, special antimycotic ointments are prescribed. To prevent allergies from complicating treatment, antihistamines are added to therapy.
Only a doctor has the right to prescribe a specific list and course of medications after a thorough diagnosis.
For dermatitis and derivative diseases, it is advisable to limit contact of the affected area with water during an exacerbation. You cannot peel off the crusts that have formed, as this will only worsen the situation.
Other causes of itching and their elimination
There are a number of other reasons why a person’s skin behind the ears itches. These factors include:
- Stress – frayed nerves can cause itching and various skin diseases in adults.
- Allergies – to cosmetics, shampoo, hair dye, ingredients of a homemade cosmetic mask, jewelry, products and external irritants, including the material of the headdress. Allergies are treated with antihistamines and require limiting contact with the irritant.
- Climate change – a sudden change in environment weakens the body. In addition, unusual weather, for example, dryness and wind, can have an effect.
- Vitamin deficiency - a lack of vitamins is reflected primarily on the skin. Bad habits in adults increase this effect several times. You need to improve your diet and lifestyle.
- Dehydration – it is important to restore water balance. To do this, you need to drink more water and use humidifiers.
It is also important to maintain hygiene to avoid the accumulation of dirt and germs. If you notice itching behind the ears, you should definitely consult a doctor to find out its origin and only then begin treatment.
Source: //bezotita.ru/simptomy/cheshetsya-za-ushami.html
Why do my ears itch on the outside?
The degree of difficulty in eliminating the cause of discomfort depends on its nature. Sometimes it is enough to change hygiene products and forget about the itching.
Serious illnesses are fraught with the possibility of complications, because the bones of the skull and brain are in close proximity. Therefore, if a slight itching of the ears on the outside turns into pain, even minor, diagnosis and urgent treatment are necessary. After all, the reasons may be different.
- Otitis. Penetration of infection causes an inflammatory process. There are 3 forms of otitis: external, middle, internal. When external, the auricle and ear canal suffer. The patient hears worse than usual and suffers from itching.
- Damage to the middle ear is accompanied by fever, throbbing pain, hearing loss, and fever.
- The internal form is the most complex. First, itching appears and balance is disturbed, then the patient has a high temperature, the ear burns and hurts.
- diabetes,
liver and gallbladder diseases,
Periodic or constant itching is caused by vitamin deficiency and weak immunity. If the lack of useful components is not replenished, the condition can become the onset of dermatological pathologies, which are very difficult to completely cure.
Why does a person itch behind the ears - itching in women and men - ENT plus
If the skin behind the ears itches, the body sends a signal about disruptions in some vital processes. There are a huge number of reasons for the appearance of this symptom.
Some of them are completely harmless and over time the problem disappears on its own. However, itching can be a sign of a serious condition developing.
To clarify the situation, additional examinations may be needed: examination by a doctor, taking epithelial samples, blood tests, etc.
Itching behind the ear - allergy or dermatitis?
This is especially true for violations of a permanent or systematic nature.
If you experience itching, burning, pain and flaking behind the ears, you should consult a doctor and undergo an examination to find out what caused this problem.
Possible causes of itching behind the ears
Any negative phenomenon has reasons, and the sooner they are established, the easier it will be to cope with the problem. Therefore, it is very important not to ignore discomfort and unpleasant symptoms, but to seek help. It is not worth trying to eliminate the pathology on your own, since it is impossible to correctly assess the situation without special knowledge. Wrong actions will only make the situation worse.
It is also undesirable to expect that the discomfort will go away. Sometimes this happens, but more often the opposite situation occurs. To better understand the danger, you need to find out why children and adults sometimes itch behind the ears.
Allergic reaction
Peeling behind the ears can be a symptom of an allergy. Its occurrence is caused by a negative reaction of the body to the action of a certain substance, product or medicine.
This reaction is caused by sensitivity to the irritant, which is why the immune system, trying to protect the body from the threat, actively releases histamine. As a result, unfavorable symptoms appear, including the occurrence of itching in the ear area.
Depending on the characteristics of the body, allergies can manifest themselves in different ways. Sometimes it is just itching behind the ears, other times there are many symptoms.
These include:
- dry skin;
- rashes;
- pain;
- cough;
- sneezing;
- attacks of suffocation;
- nausea;
- abdominal pain, etc.
about diagnosing allergies:
Itching behind the ears is dangerous because it poses a risk of infection. Due to unpleasant sensations, the patient may scratch the skin, which leads to damage and the formation of wounds through which bacteria enter the body. If this problem is caused by an allergy, it is necessary to quickly treat it to prevent complications.
Other reasons
Symptoms such as dry skin behind the ears and itching in this area can be caused not only by allergies and seborrheic dermatitis. These diseases most often lead to similar problems, but there are other reasons.
Among them are:
- Wearing low-quality jewelry. Earrings made from cheap alloys can cause irritation of the earlobes. If you do not stop using them, the negative manifestations intensify and spread to neighboring areas.
- Air saturation with chemical components. This is detrimental to the whole body and to the skin. Accordingly, reactions may occur from different areas.
- High dust content in the air. Dust gets on the skin of exposed parts of the body, clogging the pores. In addition, dust may contain harmful particles: parasite eggs, fungus, etc. When they come into contact with the skin, itching, burning and pain occur.
- Increased sweating. The parotid zone contains a large number of sweat glands. When you sweat profusely, secretions accumulate, causing irritation.
- Using low-quality cosmetics for hair and face care. The components it contains can also cause a negative reaction.
- A bite of an insect. Such cases are often accompanied by swelling, redness and itching.
- Temperature changes. Frequent changes in temperature affect the condition of the skin, causing pathological symptoms.
These factors are not particularly dangerous. The adverse manifestations caused by them in most cases are eliminated on their own, after the traumatic effect has been neutralized. If this does not happen and the symptoms persist, then you need to seek help.
Why does your head itch and how to get rid of itching?
Perhaps you just didn't wash out the shampoo well, and this caused skin irritation.
Or maybe itching and a rash on the head are signs of allergic contact dermatitis. It is common among people who dye their hair.
You may also be allergic to shampoo, conditioner, or any other hair product. To check your suspicions, simply apply the substance to the crook of your elbow. If a rash appears there, then your fears are not in vain.
What to do
It is better to wash your hair so that shampoo does not remain on it. If it's an allergy, find and stop using the product that causes it.
If this doesn't help, go to the doctor. He will look into the causes and may prescribe an antihistamine to relieve the itching.
Hairstyle
An everyday ponytail or bun can also cause itching.
Hairstyles that are too tight damage the hair follicles and can cause an itchy scalp and hair loss.
Natalya Koporeva, dermatovenerologist, medical trichologist, work experience - 21 years
Which doctor should I contact: diagnosis
Itching under the influence of weather conditions, insufficient hygiene, and external irritants is easy to overcome. It is enough to analyze the circumstances and correct the situation. But if your ears itch on the outside due to dermatological problems or diseases of various etiologies, you cannot do without medical help.
- If the skin peels or yellow plaques appear, you should go to a dermatologist.
- Ear pain, fever, weakness indicate the need to visit an ENT doctor.
- If your ears are red and burning, you should make an appointment with an allergist.
If you have any symptoms, you can go to a therapist. After the examination, the doctor will refer you to the right specialist so that he can take a scraping for analysis or prescribe allergy tests. The doctor can determine the causes and prescribe treatment after the first examination, if he does not need additional research.
The skin behind the ears of a child cracks and peels: causes of formation in infants
Crusts behind the ears in infants are a fairly common phenomenon. Young mothers usually notice them when they carry out daily hygiene procedures. What worries young parents most is that this peeling has an unpleasant odor.
In this article we will understand the reason for their appearance and find out how dangerous this phenomenon is for the health of the child.
Crusts behind the ears of a baby are not only an aesthetic problem. They often cause itching, which is why the baby can be capricious, cry, and have difficulty sleeping.
The child may constantly rub his head and refuse to eat. This phenomenon does not seem serious, but it is necessary to find out the cause. Contact your therapist and he will determine the cause and prescribe the appropriate course of treatment.
Next, let's talk about what could provoke the appearance of crusts behind the ears of a baby.
Hygiene procedures
To get rid of this unpleasant phenomenon, the following manipulations should be carried out. How to bathe a baby to get rid of crusts?
- During hygiene procedures, immerse the child in water so that only the face remains on the surface. This way, the crusts will become softer and easier to separate from the skin.
- After bathing, dry the surface behind the ears. Take a small piece of gauze and wrap it around your finger. Soak it in sea buckthorn oil. Lubricate a clean and dry surface to relieve irritation. Be careful: sea buckthorn oil can stain clothes!
- After a couple of minutes, gently wipe the treated areas. Remove any remaining oil and any plaque along with it.
Now you know how to bathe a baby. By following these rules, you can combat the appearance of severe irritation. This kind of ear care is a prevention of the problem.
If you do not have the opportunity to bathe your child every day, then try to wipe the area behind the ears every day with a cotton pad dipped in warm water. After this, you can apply moisturizer or baby oil.
This will soften the tissue and help gently remove plaque.
Important! Particular attention should be paid to caring for your ears in hot weather. In summer, sweat accumulates especially quickly in this area, and the baby will suffer from diaper rash and irritation. Subsequently, the inflammatory process will begin and pathogenic microflora may join. If you notice that moisture constantly accumulates behind your ears in the heat, then use powder.
The appearance of crusts as a result of the action of staphylococcus
If you follow all the rules of hygiene, and the condition only worsens, then you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Perhaps the cause of the trouble lies in infection with Staphylococcus aureus. What is this? This is a bacterium that belongs to the opportunistic microflora. Most people are carriers of it. But with normal functioning of the immune system and compliance with hygiene rules, the bacterium is not dangerous.
If hygiene rules are not followed and immunity is weakened, bacteria begin to quickly multiply and spread to other parts of the body. They can cause a lot of trouble later. For example, purulent sore throat or meningitis.
In order to confirm that Staphylococcus aureus is the cause of the appearance of crusts behind the ears of a baby, you need to take a microflora culture.
If severe irritation is accompanied by a symptom such as a high temperature, then you need to urgently call a doctor! In this case, the doctor will prescribe antibiotic therapy to stop the infection.
Do not self-medicate with folk remedies. They won't help here, and you'll waste valuable time. Any lotions with herbal infusions can only aggravate the situation, since organic products create a breeding ground for bacteria.
Disease prevention
To prevent scrofula it is necessary:
- observe the rules of hygiene - bathe and wipe all folds of a newborn baby on time;
- keep the home and children's room clean, do wet cleaning;
- spend more time outdoors, sunbathe according to the season;
- get enough sleep; children must have a quiet hour during the day;
- eat properly and balanced, take vitamin complexes (VitaMishki, Pikovit);
- up to 3 years of age, completely limit the consumption of sweets - sweets, chocolate, marshmallows, etc.;
- maintain immunity (harden yourself, play sports, walk in the fresh air).
Potential allergens
Until the nursing mother figures this out, it is better to exclude potential allergens from the diet:
Source: https://MedLazaret.ru/krasnuha/korochki-za-ushami-u-grudnichka.html
What medications are used for itching behind the ears?
You cannot use or take medications on your own. They completely cure some patients, but in others they can cause serious consequences, including anaphylactic shock. Therefore, the review of drugs is for general information only:
- antihistamines: Suprastin, Loratadine, Tavegil, Cetirizine, Erius, Parlazin, Prednisolone,


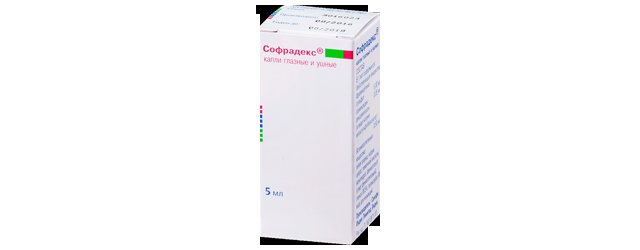

In most cases, the course of treatment includes physiotherapy. If there is a lack of useful components in the body, vitamin and mineral complexes are additionally prescribed.
Symptoms
If inflammation occurs behind the ears, a number of general symptoms appear on the epithelium:
- itching, discomfort, rash,
- the skin peels and gets wet,
- blisters appear on the irritated areas, after opening which yellow crusts form,
- humidity in the lesions progresses,
- cracks appear
- there is pain, redness, burning,
- the inflamed areas begin to itch unbearably,
- a foul odor emanates from wet skin,
- patients develop psychoemotional disorder.