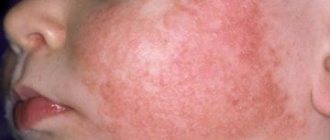
What is dermatitis? According to the medical definition, this is the name for any inflammatory processes occurring in the epidermis. Most often, dermatitis appears on the skin of the hands, which are constantly exposed to negative environmental influences. The disease does not pose an immediate threat to human life, however, it can cause many unpleasant moments. According to experts, treatment of dermatitis on the hands is possible only by eliminating the irritants that provoked the development of the pathology. Therefore, we will consider the causes, symptoms and effective methods of combating this disease.
What is dermatitis on the hands?
Dermatitis is a skin disease of inflammatory-allergic origin. It occurs mainly due to the impact of various environmental factors on human skin, and is manifested by all sorts of changes on the skin: from dryness and peeling to the appearance of ulcers and erosions.
According to experts, more than 75% of people have ever suffered from manifestations of dermatitis, and about 6-10% face this problem regularly, i.e. they have a chronic form of the disease. Dermatitis is, first of all, a disease, and not a cosmetic defect, so this condition requires not only timely diagnosis, but also comprehensive treatment prescribed by a specialist.
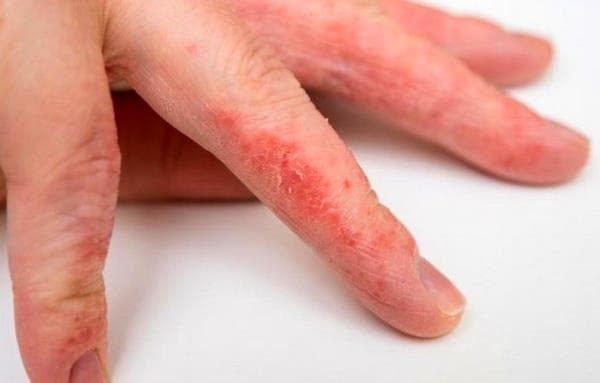
Dermatitis on the hands: what factors provoke this disease?
Scientists believe that the immediate causes of this condition are unfavorable factors acting on the skin, as well as all kinds of allergens - antigen substances that cause a number of allergic diseases (including dermatitis) in sensitized (sensitive) people. The reasons that provoke the occurrence of dermatitis include:
- chemical agents. This group includes various dyes, alkalis, detergents, cosmetics and household chemicals, metals used for the production of jewelry (for example, nickel). Dermatitis can also be caused by food allergens and medications.
- biological agents. Factors such as plant pollen, feathers, fluff, dust and mites living in it, as well as pet hair can contribute to the appearance of dermatitis on the hands. physical agents. The skin can be affected by a number of physical factors that lead to the appearance of the disease: cold or heat exposure, low or high humidity, wind, ultraviolet and infrared radiation, radiation, friction, compression and other mechanical influences.
In addition to provoking factors, contact with which directly leads to acute manifestations of the disease, there are a number of reasons that predispose to the occurrence of dermatitis. These include the following:
- hereditary predisposition to hyperreactivity reactions (allergic diseases). Scientists have established a connection between the occurrence of dermatitis and allergic diseases in the families of patients. It has been proven that parents can pass on to their children certain features of the immune system, which later lead to the development of dermatitis.
- stress. Psycho-emotional stress negatively affects all organs, but the immune system suffers the most. As a result of chronic stress, the immune system begins to perceive harmless agents that surround the human body as “antigens,” that is, foreign substances. As a result, a number of immune reactions occur in the body, which manifest themselves on the skin in the form of inflammation.
- concomitant chronic diseases. Disturbances in the immune, endocrine, nervous and digestive systems can also contribute to the development of the disease.
In most cases, the occurrence of dermatitis is triggered by one allergen and many additional causes, which often affect the body for years.
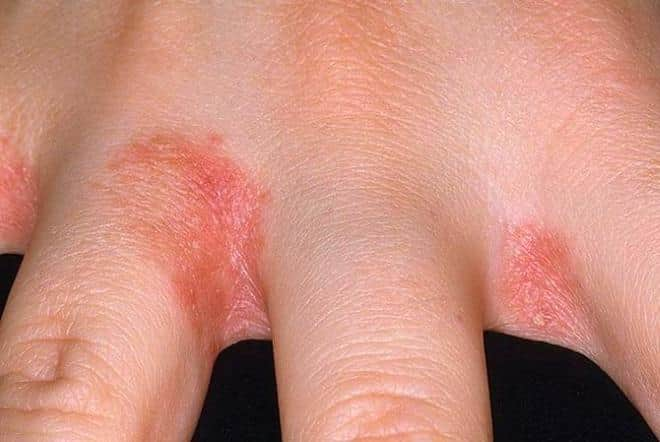
Classification
Depending on the etiology and symptoms, the following types of dermatitis are distinguished.
- Allergic: develops on the hands over several weeks of constant contact with an irritant (household chemicals, creams, lotions, animal hair, bird feathers). It becomes recurrent and complications are possible. Localized on the hands and wrists.
- Solar dermatitis: occurs when exposed to ultraviolet radiation after prolonged exposure to a solarium or on the beach. Often the first symptoms of photodermatitis appear in early spring, during the greatest solar activity, and subside in mid-summer. A characteristic feature is the accumulation of age spots on the hands. The hands and the area of the elbow bend are affected.
- Actinic: associated with occupational skills and related to acquired diseases. Symptoms usually disappear after changing occupation. Risk group: welders, metallurgists, radiologists, agricultural workers.
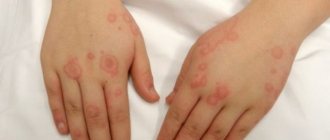
- Atopic dermatitis: the tendency to develop is transmitted genetically. Possible allergens: plant pollen, animal hair, dust. Characterized by the formation of red spots on the hands. Symptoms disappear after eliminating contact with the irritant. The disease is not completely cured.
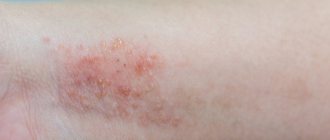
- Contact dermatitis: occurs upon contact with caustic chemicals (alkali, acid, concentrated saline solutions, cleaning products). Red spots appear only on those areas of the skin that were in contact with the irritant.
- Eczematous dermatitis: the cause of development is the addition of a bacterial infection. Characterized by the formation of ulcerations on the hands. Localized on the fingers and palms.
According to the nature of the course of dermatitis, acute, subacute and chronic forms are distinguished. In the first case, the symptoms are very pronounced: swelling, redness, burning, itching occur, and a characteristic rash forms. The disease lasts up to 10 days. After eliminating the allergen, the symptoms disappear.
The acute stage is replaced by the subacute stage. Develops 1–1.5 weeks after the first signs of the disease appear. The skin on the hands becomes covered with hard scales or crusts, which is accompanied by severe itching.
The chronic course is characterized by the occurrence of swelling of the affected area. Inflammation persists for a long time. The skin takes on a bluish tint, and the covering of the affected area thickens.
Symptoms of the disease
Although there are many forms of dermatitis, they all present with a range of symptoms. Most often, patients complain of dry skin (sometimes the skin may even crack), itching, burning, redness, swelling, peeling, rash (bubbles, spots, nodules). At later stages, crusts and scars appear on the skin, and the skin pattern becomes stronger. You can learn about dry dermatitis in this article.
Various parts of the upper limb can be affected: the back of the hand, palm, interdigital space, finger, wrist, elbow. In atopic dermatitis, the affected areas are usually symmetrical and appear on both limbs. Contact dermatitis manifests itself directly in the place where the damaging factor acted. With dry dermatitis, signs of inflammation appear on the elbows and hands (due to the effects of cold).
Methods for treating dermatitis on the hands
Hand dermatitis is diagnosed and treated by a dermatologist. Also, sometimes the patient requires consultation with other specialists: an immunologist, an allergist, a gastroenterologist, a neurologist, an endocrinologist and a nutritionist.
Therapy for all types of dermatitis should begin with identifying the factor that caused this condition. Only if contact with the irritating substance is avoided is a complete recovery possible.
Creams and ointments used to treat dermatitis
Local treatment for dermatitis on the hands is quite effective if prescribed by an experienced dermatologist. All drugs for local treatment of the disease are divided into 2 groups: non-hormonal and hormonal drugs. Non-hormonal ointments and creams are aimed at reducing inflammation, healing skin damage, relieving burning and itching, eliminating dryness and flaking. From the group of non-hormonal drugs for local treatment, the following drugs are most often prescribed:
- emollients (moisturize the skin): Bepanten, D-Panthenol, Pantestin;
- drying ointments (for symptoms of weeping): Skin-Cap, ointment with propolis;
- relieving itching: Fenistil, Losterin;
- enhancing regeneration: Radevit, Atopra;
- ointments with antibiotics (if a bacterial infection is attached): erythromycin ointment, Levomekol;
- antimycotic agents (if a fungal infection is attached): Exoderil, Triderm.
Complex preparations, which include components that have wound-healing, drying and antibacterial properties, are used to treat many forms of the disease. For example, ointments for contact dermatitis (Eplan, Elidel, La-Cri, Vundehil, Protopic) are also used in the treatment of other forms of the disease.
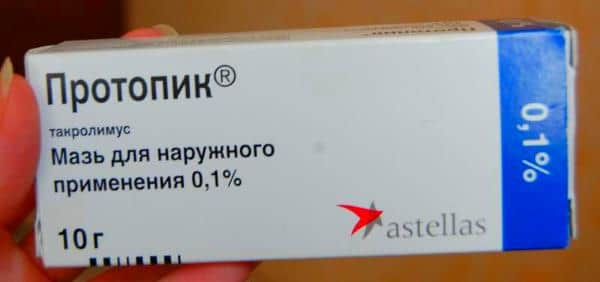
Hormonal creams and ointments are prescribed for prolonged, severe dermatitis. They are highly effective, but have many side effects and contraindications, so in no case should they be used uncontrolled. Today, pharmaceutical companies offer a wide range of hormonal drugs for topical treatment of dermatitis:
- Triamcinolone and drugs that contain it: Fluorocort, Ftoderm, Triacort, Polcortolone;
- Flumethasone and its analogues: Sinaflan, Flucinar, Flucort, Lorinden, Lokasalen, Ultralan;
- Mometasone and its derivatives: Elokom, Momat, Uniderm, Skinlight, Gistan N, Monovo, Momederm;
- Hydracortisone and products containing it: Hydracortisone ointment, Lokoid, Cortef, Sulfodecortem, Sopolcort, Fucidin, Gioxyzon;
- Clobetasol and analogues: Dermovate, Powercourt;
- Betamethasone and the products it includes: Betasalik, Fucicort, Celestoderm, Diprogent, Kuterid, Vipsogal.
It is important to use hormonal ointments and creams with extreme caution, take breaks between courses, and gradually reduce the number of applications. If you do not follow these recommendations, you may develop side effects such as atrophic changes in the skin, disorders of the excretory, endocrine, cardiovascular and digestive systems.
Other drugs for the treatment of dermatitis on the hands
In addition to local treatment, systemic drugs are also used in clinical practice. These include:
- antihistamines in tablets: Tavegil, Suprastin, Alerzin, Erius, Eden. They relieve swelling, redness, itching and burning, and reduce the intensity of the allergic reaction.
- complexes of vitamins and minerals: Complivit, Multitabs, Vitrum, Triovit, Undevit. These preparations contain all the necessary vitamins and minerals that help improve the protective properties of the skin and improve its regeneration.
- systemic glucocorticosteroids: Betamethasone, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Triamcinolone, and stronger ones, for example, mometasone. These drugs are prescribed for severe forms of the disease (for example, atopic dermatitis in adults), as well as for the chronic course of the disease with frequent relapses.
Preparations for external use
Dermatitis on the hands is often accompanied by itching, which gets worse at night. Many patients complain of waking up in the middle of the night and being unable to fall back to sleep. In such cases, it is recommended to wear cotton gloves before going to bed and take a light herbal sleeping pill.
Acute inflammatory process is relieved with glucocorticoid ointments or creams. Depending on the severity of the lesion, the use of drugs of weak or moderate effect is prescribed. If skin lesions spread and affect not only the skin of the hands, but also other parts of the body, the use of strong hormonal drugs is necessary. Since dermatitis on the hands is accompanied by swelling and burning, patients are often prescribed creams. Due to their structure, they have a cooling effect, which helps reduce swelling, and a rapid antipruritic effect. Weak hormones include hydrocortisone, and moderate hormones include prednisolone, fluocortolone, and prednicarbate. Glucocorticoid creams are used for a limited amount of time, usually no longer than a week.
Relieving acute inflammation is only the first step of therapy. The chronic stage is also characterized by itching (albeit not as intense) and, most importantly, dry skin. Dryness provokes peeling and cracks that interfere with the healing of the skin. To normalize metabolic processes in the skin, including water balance, it is necessary to resort to additional hydration. The greatest effect comes from applying creams after hygiene procedures. Under the influence of warm (but not hot) water, the epidermis softens, and the crusts dissolve and come off.
However, it is worth noting that washing your hands with soap will most likely lead to a negative result, since alkali dries out the skin and, once it gets into the wounds, causes tingling and exudate. Delicate care is provided by special medicinal and cosmetic care products for inflamed skin. Thus, “Losterin” body gel, which can also be used as hand soap, does not contain surfactants, fragrances or dyes. And 4 types of vegetable oils in its composition, deresined naphthalan and Japanese sophora extract provide both cleansing, bactericidal effect, and moisturizing of the skin. In the acute period, it is recommended to cleanse the skin of the hands with micellar water and clean soft wipes.
The restoration of epithelial cells is facilitated by preparations with propolis. This natural remedy has desensitizing, anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties due to its composition. Propolis contains flavonoids, aromatic and fatty acids, free amino acids, proteins, alcohols, minerals, sugars, vitamins, steroids, and many microelements. However, ointments, sprays and creams with propolis can be prescribed only to those people who are not allergic to honey and pollen. In other cases, the product may cause a severe allergic reaction.
In most cases, chronic dermatitis on the hands can be treated with external herbal medicine. It can be combined with hygienic procedures. For example, after an evening shower, it is useful to take hand baths with extracts or infusions of pine needles, chamomile flowers, oak bark, calendula, birch buds, string, burdock root, plantain leaves, poplar buds, and lungwort. After a 10-minute bath, the skin of the hands is also dried with a towel and moisturizer is applied.
Unconventional methods for treating dermatitis on the hands
Alternative treatment methods will help improve the general condition of the patient, as well as get rid of unpleasant symptoms such as burning, itching, and pain. Below are folk remedies that are used to treat the disease.
Baths or lotions with chamomile infusion are considered a good way to relieve inflammation and burning. To prepare it, you need 5 tbsp. dried chamomile, which must be filled with 250-300 ml of boiling water. After 15-25 minutes, strain the infusion and let it cool. You can use this remedy 3-4 times a day. Compresses with lemon juice and vegetable oil reduce itching and speed up skin healing. To prepare such a compress you will need the juice of 2-3 lemons, 1-1.5 tsp. vegetable (or olive) oil and 500-600 ml of water. All ingredients need to be mixed, moistened with gauze and applied to the affected area of skin for 20-25 minutes.

To moisturize the skin and enhance regeneration, you can use a mixture of St. John's wort juice and melted butter. These components should be mixed in a ratio of 1:5 and applied to the skin 2-3 times a day. Despite the fact that the variety of folk recipes that are used to treat dermatitis on the hands is very large, you should consult a doctor before using them. Since folk remedies do not have a sufficient evidence base, their use without first consulting a doctor can aggravate the patient’s condition and also cause a number of serious complications.
Traditional medicine recommendations
Cream, ointment, gel, solution can be made at home.
The following folk recipes allow you to fight the dermatitis agent:
- baths with a decoction of string, chamomile, which have an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect;
- juice of cucumber, potato, pumpkin, in which gauze bandages are soaked and then applied to the affected areas;
- homemade ointment with honey is prepared as follows: mix baby cream, golden mustache juice, honey, all this is applied to the skin twice or thrice a day;
- lotions based on cranberry juice, which is mixed in identical quantities with liquid honey (you can add a little propolis);

- Propolis oil is used to treat affected areas throughout the day.
Thanks to the considered compositions, it is possible to achieve an improvement in overall well-being and stabilization of the condition at the local level. In order to choose the optimal medication, as well as regarding the use of traditional recipes, consult your doctor.
Physiotherapy for dermatitis on hands
In addition to drug and alternative treatment, hardware therapy is used. This method is often used to treat atopic, seborrheic and contact dermatitis. Often, hardware therapy is used during the recovery period in order to speed up the regeneration processes. In order to remove keratinized epithelium, mechanical cleaning is used. Irradiation with UV lamps is also very effective, because... ultraviolet light has a bactericidal effect, which prevents the addition of a secondary infection.
For seborrheic dermatitis on the hands, a popular method of hardware treatment is the exposure of the skin to high-frequency, low-voltage currents. This procedure improves blood circulation and lymphatic drainage, as a result of which regenerative processes occur better.
Hardware therapy, like other treatment methods, should be used only after consulting a doctor. Otherwise, the use of such treatment methods may lead to a worsening of the patient's condition.
Symptoms
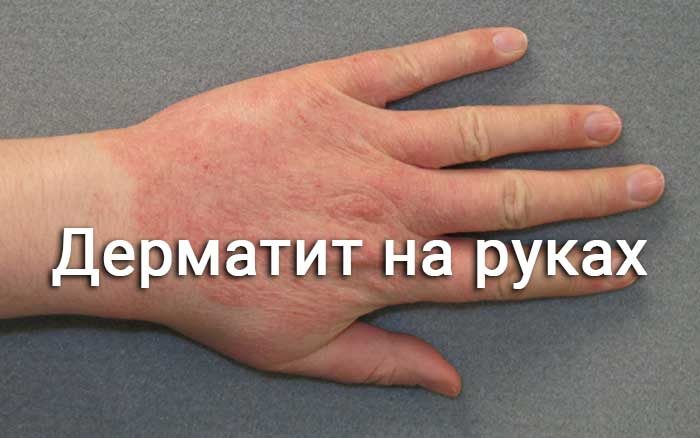
The disease manifests itself with a whole range of symptoms:
- pain in the skin, itching and burning;
- the skin turns red;
- erythematous edema of varying intensity develops;
- in severe cases, blisters appear that can be filled with clear or cloudy liquid;
- areas of necrosis also form;
- after the bubbles open, erosions form, which are subsequently covered with crusts and scales.
When the disease becomes chronic, the following symptoms may occur:
- thickening of individual layers of the dermis occurs;
- the skin becomes bluish in color;
- the skin may be very flaky;
- it becomes dry and covered with cracks;
- in the absence of adequate treatment, atrophy of the epidermis begins.
Dermatitis often causes swelling, abrasions, blisters and even calluses to appear on the hands. Cold dermatitis is manifested by severe itching, as well as the formation of reddish-blue swelling. Contact dermatitis on the hands is characterized by a limited affected area. When the irritant is eliminated, the skin quickly recovers.
Is diet therapy important for dermatitis?
Since the mechanisms of dermatitis are based on hypersensitivity reactions, the diet prescribed for this condition should also be aimed at reducing the intensity of allergic reactions. For these purposes, a hypoallergenic diet is used.
Since food allergens are among the most powerful, you need to avoid eating foods that may contain them. The following products are considered highly allergenic:
- citrus;
- seafood;
- chocolate;
- honey;
- chicken eggs;
- red berries and fruits;
- nuts;
- sauces;
- spices;
- alcohol.
You should also limit your intake of salt, smoked, fried, fatty foods, fast food and carbonated drinks. If we are talking about an acute form of the disease, then a hypoallergenic diet should be followed throughout the entire treatment, as well as 2-3 weeks after its completion. In chronic forms of dermatitis, it is necessary to permanently exclude highly allergenic foods - this will help avoid exacerbations of the disease.

Prognosis and complications
If you consider dermatitis just a cosmetic problem and do not treat it for a long time, the disease will become chronic, and a number of serious complications may also arise. These include:
- the addition of a secondary infection (fungal, viral, bacterial) - this complication is especially characteristic of childhood. If it develops, treatment with antibiotics and sometimes even hospitalization may be required. The most common developments are pyoderma, phlegmon, and abscesses.
- skin atrophy. This complication is caused by prolonged and uncontrolled use of hormonal ointments.
- with atopic dermatitis in childhood, there is a risk of developing allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis and bronchial asthma. Despite the fact that these complications can occur many years later, they are particularly severe.
Some of the conditions described above can be dangerous not only to health, but also to life. That is why, if the first symptoms of the disease appear, you must immediately contact a specialist.
How to avoid dermatitis on your hands
It is much easier to prevent dermatitis than to treat it. In order not to encounter manifestations of the disease, experts recommend following the following rules:
- care for the skin of your hands and protect it from the negative effects of temperature, wind and chemicals;
- eat a balanced and rational diet. This recommendation will help not only avoid dermatitis, but also improve the condition of the skin.
- avoid stress and overwork of the body;
- minimize contact with allergens (especially if there have already been cases of allergic reactions);
- use hypoallergenic household chemicals, cosmetics and personal hygiene products.
Dermatitis is a disease that can cause not only physical but also psychological discomfort. Doctors say that the sooner you go to a medical facility, the greater the chances of curing dermatitis and avoiding complications.
Diagnostics
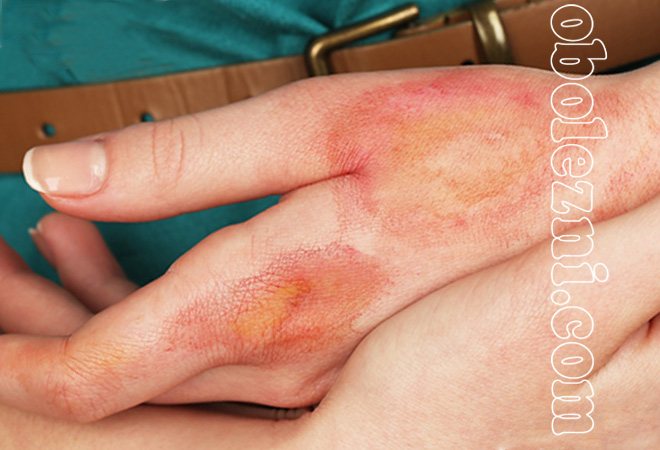
A photo of dermatitis on the hands of adults suggests that the specific manifestations of the disease usually do not cause difficulties in diagnosis. However, to clarify the diagnosis, allergy tests, blood tests, and PCR tests are necessary.