What is herpetic vesicular dermatitis and how to treat it
Herpetic dermatitis is a disease of a permanent, that is, chronic nature, which develops due to exposure to the herpes virus on the body.
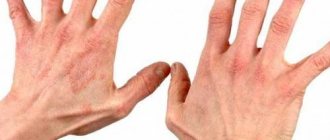
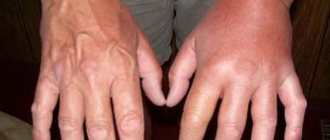
Its carriers today are about 90% of the world's population. And only 1 in 10 people have never encountered an infection. Recognizing vesicular herpetic dermatitis is quite simple. Its main symptom is the appearance of blisters. The infection most often appears on the arms, legs, face - wings of the nose, lips, mucous membranes.
Less often it can be observed on the ears and genitals.
Herpes simplex dermatitis develops due to exposure to the herpes simplex virus. After entering the blood, and this happens through contact or endogenous (airborne) routes, the virus tends to the nerve fibers of the spinal cord. There he remains in a dormant state. Unfortunately, once the herpes virus enters the human body, it will never leave it.
Only one factor can become an impetus for its awakening - weakening of the immune system. The body's defenses stop working for several reasons:
- constant nervous excitement, stressful conditions;
- improper, irrational nutrition;
- lack of vitamins;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- the presence of oncological pathologies, diabetes mellitus;
- frequent exposure to ARVI;
- hormonal disbalance;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- hypothermia, overheating;
- reluctance to move or play sports;
- physical and mental exhaustion of the body.
All these factors provoke a decline in immunity. As soon as this happens, the virus is activated, begins to multiply and moves closer to the skin.
Herpes simplex virus
Symptoms
The symptoms of the disease are as follows. After activation of the virus, an infected person experiences general malaise, manifested in weakness and fatigue. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. At the site of the lesion, the skin itches and tingles.
Then, on about 2-3 days, small blisters appear on the skin - vesicles, outlined by a red rim. It contains a clear liquid that becomes cloudy over time. There can be many such formations.
There is a possibility of their unification.
Then the blisters burst, and in their place there remain ulcerated areas, which are subsequently covered with crusts. After this, they disappear, and in their place dark spots remain, which disappear after a while.
Normally, external manifestations of herpes should disappear within 5-10 days. If the affected areas of the skin do not heal for a long time, then there is a high probability of a secondary bacterial or fungal infection. In addition, there is a high risk of scarring.
Features of the course of the disease in a child are that the baby refuses to eat and drink, is very capricious, and has problems sleeping.
Most often in children, vesicular herpetic dermatitis manifests itself in the form of stomatitis, that is, the rash is localized on the oral mucosa.
The process is necessarily accompanied by an increase in body temperature to high levels. In rare cases, diarrhea and weight loss are observed.
Dermatitis appears on the legs, arms, face, genitals, buttocks, shoulders, and mucous membranes. Can affect any part of the body. The exception is the palms and feet.
What does it look like
As already mentioned, the herpes virus can appear on different parts of the body. Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, the disease may look different.
- Eyes – herpes of the conjunctiva, cornea, corneal ulcer, vascular damage, damage to the deep layers.
- Mucous membranes of the mouth - stomatitis, gingivitis, tonsillitis.
- Mucous membranes of the genital organs - damage to the vagina, urethral canal, glans penis, vulva, etc.
- Skin – eczema, dermatitis.
Herpetic dermatitis
Diagnostics
Research activities are based on external examination of the rash and laboratory tests. The main diagnostic method is to take a scraping from the lesion. Next, the biological material is examined under a microscope.
Diagnosis of the disease is also carried out using blood sampling. In this case, antibodies to the herpes virus are detected.
If rashes occur, you should consult a dermatologist. If relapses occur frequently, you need to visit an immunologist.
Treatment
In case of illness, complex therapy is necessarily prescribed. You can't get by with drugs alone. It is important to completely reconsider your lifestyle. It is necessary to maintain immunity, provide adequate nutrition, etc.
As for drug treatment, it is prescribed depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease, the frequency of relapses, the general condition of the infected person and is based on the intake and application of antiviral drugs, immunomodulating agents, etc. to the skin.
Treatment of dermatitis is based on taking antiviral drugs to reduce the frequency of exacerbations and reduce the intensity of symptoms. For this purpose they prescribe:
- "Acyclovir".
- "Famvir."
- "Valacyclovir."
- "Valtrex".
Valtrex and Famvir
The duration of drug treatment is 5-7 days.
Immunosubstitution therapy is mandatory. The duration of therapy will directly depend on the patient’s condition and the intensity of the disease manifestations. The best immunomodulatory drugs are: Cycloferon, Lykopid, Ridostin.
Local treatment is also used for herpetic vesicular dermatitis. The following are considered effective antiviral ointments:
- "Acyclovir".
- "Pentsivir".
- "Fenistil".
- "Zovirax".
Acyclovir and Zovirax
To dry out the rash and quickly heal the affected areas of the skin, local sulfur-based products are prescribed. For large lesions, the use of corticosteroids is recommended.
There are many treatment methods for herpetic dermatitis. Thus, to prevent the development of secondary infection, it is recommended to use antiseptic drugs. In addition, physiotherapeutic and hardware methods - ultraviolet irradiation, infrared irradiation, laser therapy - are effective in combating the disease.
Traditional therapy
Effective folk remedies against herpetic dermatitis are:
- a decoction of celandine, string, sea buckthorn, knotweed, calendula and wormwood - applied to the affected skin;
- aloe juice, celandine, garlic, sea buckthorn oil;
- to maintain immunity - tincture based on echinacea, nut peels (green), tea with lemon, honey, rose hips, black currant leaves;
- a mixture of lard and dried, crushed belladonna leaves (2:1);
- Corvalol lotions, rinsing the mouth with hydrogen peroxide (for stomatitis);
- lotions made from laundry soap, toothpaste, sulfur, raw chicken protein.
Prevention
To resist infection with the herpes virus, you should avoid any contact with an infected person and do not use his personal belongings.
Relapses can be avoided by maintaining immunity.
Strengthening the body's protective functions is based on proper nutrition, exercise, avoidance of stress, hypothermia, overheating, and timely treatment of chronic diseases.
Women who are preparing to become mothers should also take care of prevention. The fact is that herpetic dermatitis is very dangerous for the fetus and newborn baby. Therefore, tests to detect infections and their timely treatment are very important even at the stage of planning a child.
Herpes simplex virus - home treatment
Prevention
There are no specific preventive measures in the fight against a disease such as herpetic dermatitis. The main thing is to follow certain rules that will help prevent relapses.
It is important to constantly monitor the state of the immune system. To maintain it in proper shape, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle.
During the period of bearing a child, during menopause or in the presence of pathologies of a viral or infectious nature, which can provoke a decrease in the body's protective functions, it is recommended to take multivitamin complexes and immunostimulating drugs.
On this topic
- Dermatitis
Everything you need to know about atopic dermatitis
- Irina Nasredinovna Nachoeva
- September 3, 2020
People with hypersensitivity to certain chemicals should adhere to a proper diet that excludes the consumption of foods containing iodine.
It is important not to forget that any disease is easier to prevent than to treat, and therapy in the early stages of the pathology is much simpler. You should be more attentive to all changes in your body and at the first signs of a disorder, immediately seek help from highly qualified specialists.
Herpetic dermatitis, regardless of the form in which it manifests itself and what degree of severity it has, requires special treatment measures.
Folk remedies: what will help?
Herpes dermatitis is a problem whose treatment requires an integrated approach. And in some cases, traditional medicine based on plant materials can also help.
- Decoctions of sea buckthorn, knotweed, juniper, licorice, and calendula are considered beneficial. It can be taken orally or added to bathing water. These herbs have pronounced anti-inflammatory properties and act as antihistamines.
- Periodically you need to take tinctures and decoctions of ginseng, echinacea, eleutherococcus, and rose hips. These products can be purchased at the pharmacy or prepared yourself. Medicines have a positive effect on the functioning of the immune system, strengthen the body, thereby preventing the activation of the herpes virus.
- At home, you can prepare an ointment to treat affected areas of the skin. For this purpose, you need to mix dry belladonna herb with pork fat in a 2:1 ratio. The mixture is prepared at a temperature of 90 degrees for six hours.
Of course, before using any home remedies, you should talk to your doctor and test for an allergic reaction.
Causes
To date, the exact causes of herpetic dermatitis are not known to medicine. There are some assumptions, including:
- heredity;
- autoimmune reactions;
- oncological diseases;
- infectious diseases;
- viral diseases (herpes, flu);
The herpes virus can infect the integument of a person suffering from other diseases, such as cancer, worms, ARVI and others.
- gluten intolerance;
- increased sensitivity to iodine;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vaccinations;
- hypothermia;
- emotional or physical exhaustion of the body;
- helminthic infestation;
- dysfunction of the immune system.
If herpes disease in children is not hereditary, it occurs against the background of viral infections. These usually occur through toys and household items. Often the source of infection is close people or children in kindergarten or school. Manifestations usually occur in carriers of herpes.
Dermatitis herpetiformis - symptoms, treatment and diet
The treatment regimen is drawn up individually for each patient, since much depends on the presence of concomitant diseases and the condition of the body. As a rule, some standard groups of drugs are used:
- Antiviral drugs that suppress the proliferation of viral particles. Acyclovir, Famciclovir and Viferon are considered effective. They are available in the form of tablets and gels for treating affected areas of the skin.
- Sometimes medications from the sulfone group - Dapsone, Sulfapyridine - are used to combat rashes.
- Antihistamine tablets and ointments help relieve skin swelling and get rid of itching.
- In case of severe inflammation, the use of glucocorticosteroids is necessary.
- Sometimes patients are prescribed Fukortsin to treat vesicles - they dry out the skin well.
- Since the disease is associated with a weakened immune system, patients need to take vitamins and immunomodulators.
- If there is a generalized rash, doctors recommend taking baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Herpetic dermatitis is a chronic disease. It is worth understanding that therapy can only relieve symptoms. It is almost impossible to completely cleanse the body of a viral infection.
Important! The course of therapeutic therapy is based on the use of traditional medicine methods, while folk remedies can only be used as additional ones and after consultation with a specialist.
Traditional methods involve the use of:
- medications of the sulfonic group, in particular Dapsone, Diucifon, Avlosulfone (in the initial stages of the development of pathology);
- corticosteroids for severe forms of the disease (Prednisolone and Dexamethasone);
- antihistamines to relieve burning and itching (Claritin);
- external agents (ointments, aerosols, creams, brilliant green);
- warm baths based on potassium permanganate. This method helps prevent the development of infection and relieves inflammation.
It is recommended to take vitamin-containing complexes as a fixative.
Traditional recipes:
- ointment based on internal pork fat (2/3) and medicinal herb belladonna (1/3). The fat should be melted and mixed with grass pre-cut into small pieces. The resulting mixture is simmered in the oven and then filtered. The ointment should be applied to the affected areas every day;
- herbal infusion of calendula, juniper, nettle, millennial and tansy. The base of the infusion is vodka (half a liter); It is recommended to infuse the healing composition for 10 days, after which you should wipe the affected areas with it.
Advice from a nutritionist, list of foods not recommended for consumption
To prevent herpetic dermatitis in children and adults, you should follow a therapeutic diet. To do this, you need to exclude the following foods from your diet:
- flour, as well as dishes containing malt, in particular beer and kvass;
- beans;
- cabbage;
- sweets such as ice cream and chocolate products;
- coffee substitutes;
- some sausages containing bread components.
Herpetic dermatitis is a skin disease that develops against the background of damage to the epidermis by the herpes virus of the first or second type. This is a chronic disease, accompanied by relapses and requiring complex treatment. It manifests itself as rashes on the shoulders, arms, thighs and buttocks, less often on other parts of the body, accompanied by itching and burning.
The culprit of herpetic dermatitis is the herpes virus type 1 or 2, which is called “fever”. It is accompanied by a characteristic rash on the lips.
First, vesicular rashes appear on the face - vesicles affect the nose, ears, then spread to the arms, lower back and groin, sometimes to the mucous membrane of the genital organs, affecting internal organs and the central nervous system. 90% of the population have had herpes at least once in their lives and remain hidden carriers of the virus.
However, the disease only spreads under certain conditions and is not dangerous for people with normal immunity. In ordinary people, herpes goes away in one to two weeks; if the disease develops into dermatitis, exacerbations can occur periodically for many years.
The virus survives well in the environment and persists at temperatures from –70 to 60 degrees for almost a day. It enters the body through direct contact with the virus carrier, or infection occurs through contact - through the skin, during sexual intercourse, through bedding and personal hygiene items, and in children - through toys.
During pregnancy, the fetus is affected, and there is a risk of various pathologies and premature birth. The most dangerous stage is the opening of the blisters: the liquid they contain spreads the rash to other parts of the body. Penetrating through the upper layers of the epidermis, the virus remains in the body forever and manifests itself when resistance decreases.
Most often, the disease is diagnosed in people with reduced immunity and hereditary problems. Depending on the type of rash, herpetic dermatitis is divided into:
- Papular - papules.
- Bullous - blisters, like burns.
- Vesicular – vesicles.
- Urticariform - like nettle marks.
- Paraoncological – the body’s reaction to cancer.
- Strophuloid, trichophytoid, eczematoid are atypical forms.
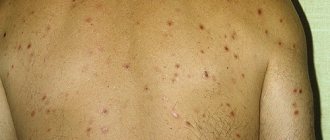
Photos of herpetic dermatitis are presented below.
Even before the rash appears, malaise and general weakness appear, and the temperature rises slightly. In certain areas of the body, tingling is felt, redness and slight swelling appear.
After this, a pink rash ranging in size from 5 mm to 2 cm with clear contours appears, the blisters are filled with purulent contents. A burning and itching sensation is felt in the areas of the rash; after a few days, the blisters burst, dry out and peel off.
If the body manages to cope with the virus, the rash disappears, and under certain conditions it appears again. In pregnant women, herpetic dermatitis occurs in the 1st-3rd trimester.
- Blistering rash.
- Itching and burning of the skin in areas of rash.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Low-grade fever.
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Fast fatiguability.
- General weakness.
The rash can appear on any part of the body, but more often on the face, neck and arms. The mucous membranes are affected only in 10% of cases.
Scientists have not yet established the exact causes of herpetic dermatitis, but there are factors that contribute to the development of the disease:
- Transmission by inheritance.
- The body's response to a primary disease.
- Oncology.
- Infections.
- Viruses.
- Allergy to gluten and iodine.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- The result of vaccinations.
- Hypothermia.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Emotional exhaustion.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Decreased immunity.
The herpes virus can remain in the human body for many years, under the influence of these factors it becomes active.
Herpes dermatitis in children is hereditary or develops against the background of other viruses. Routes of infection are through toys, hygiene items, bedding, and clothing.
The disease is most dangerous for children under 3 years of age; it does not occur in babies under 6 months of age - there are no IgG antibodies in the blood yet. But the mother must have them, otherwise a severe form of herpetic dermatitis may develop.
If the first signs of herpetic vesicular dermatitis occur, you can consult a dermatologist. He will examine the affected areas of the skin, prescribe examinations of purulent contents and scrapings.
The diagnosis can also be made using the Jadassohn test - a compress of potassium iodide and petroleum jelly. If after a day redness or papules appear in the place where it was applied, this will be confirmation of herpetic dermatitis.
Additionally, the doctor will prescribe a general blood test - an increased number of eosinophils will be indicative.
The most accurate method for diagnosing herpetic dermatitis is direct immunofluorescence.
The histology of the biomaterial makes it possible to verify the presence of antibodies and immunoglobulins and to detect the accumulation of eosinophils and neutrophils under the outer layer of the skin.
For older patients, X-rays, cardiograms, ultrasounds and other studies are prescribed, which make it possible to exclude oncological diseases.
With normal immunity, herpes goes away on its own and does not develop into herpetic vesicular dermatitis. In other cases, long-term treatment is required. Its regimen depends on the type of dermatitis, the age of the patient, the amount of rash and the location of the lesion.
Appointed:
- Sulfones or sulfonamides (“Diucifon”, “Sulfapyridine-2”). In order to eliminate the risk of anemia, they are supplemented with folic acid and vitamins B12.
- Corticosteroids (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone).
- Antihistamines (“Erius”, “Fenistil”, “Claritin”).
- Antiviral drugs (“Acyclovir”, “Viferon”).
- Antiseptics (diamond green, Fukortsin).
- Immunostimulants and multivitamins.
If the rash spreads slightly, it is treated with ointments, aerosols or creams; tablets are not prescribed.
If the cause of herpetic dermatitis is a disruption of the gastrointestinal tract or a tendency to allergies, the doctor recommends a diet that excludes alcohol, chocolate, nuts, milk, and foods high in gluten and iodine. It is advisable to replace them with rice, buckwheat and corn. In addition, he can prescribe Exalb, Famciclovir, Viferon, Valacyclovir, Vectavir, etc.
Folk remedies are no less effective, but they are only good as an addition to the main treatment. When turning to traditional medicine, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Cauterize the affected areas, consume orally 2 times a day (2 teaspoons per 200 ml of water).
No less effective are tinctures of string, wormwood, oregano, celandine, used externally, and decoctions of ginseng, rosea radiola, rose hips, birch leaf, licorice root, used internally.
The herpes virus is not dangerous to a healthy person, so herpetic dermatitis does not develop and cannot cause complications. This disease is dangerous against the background of primary infections, immune and oncological diseases.
If left untreated, it becomes chronic and affects internal organs, causing the development of serious diseases.
Dermatitis is also dangerous during pregnancy - the fetus becomes infected, and there is a risk of pathologies and premature birth.
Diagnostics
To carry out basic diagnostic measures, you must consult a dermatologist. He visually examines the skin and mucous membranes. After this, the patient is sent for laboratory testing of material and biological fluid taken from the affected areas.
Additional measures are also prescribed:
- cytology of rashes;
- general blood analysis.
In some cases, especially if the patient is elderly, ultrasound, computed tomography and x-rays may be prescribed.
Dermatitis herpetiformis - symptoms, treatment and diet
Bullous, polymorphic or herpes dermatitis is otherwise called Dühring's disease. The term refers to a chronic skin disease with polymorphic rashes. It is rare, occurring in only 1% of people, and sometimes affects the mucous membranes (in 10% of cases). Herpetiform disease got its name from the professor who first described its symptoms and causes at the end of the 19th century.
Until now, doctors do not know exactly what causes herpetic dermatitis.
Modern research has established that a possible factor provoking Dühring's syndrome is an autoimmune reaction and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
The reasons are reduced immunity, increased sensitivity to gluten from cereals and halogens. Endocrine changes (pregnancy, menopause) also affect the occurrence of herpetiform disease.
It has been proven that women suffer from dermatitis herpetiformis less often than men. The disease can affect adults 25-55 years old; it rarely affects children and the elderly.
The causes of herpetiformis syndrome can be toxemia, vaccination, nervous, physical fatigue and lymphogranulomatosis.
Depending on the predominant type of rash that appears on the skin, the following forms of herpetiform disease are distinguished:
- herpetic vesicular dermatitis - the rash is represented by vesicles with serous transparent contents;
- papular - the rash resembles pimples in appearance with a red head, sometimes there may be pustules with a pronounced tip;
- bullous herpetiformis - rashes similar to vesicles, but larger in size;
- urticaria-like - the rash resembles a nettle burn in the form of spots.
Depending on the nature of the course of dermatitis, the following forms found in clinical medicine are distinguished:
- acute herpetiformis - characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms, a serious condition of the patient, fever, sleep disturbances, changes in blood counts;
- chronic herpetiformis - characterized by alternating periods of remission and exacerbation, remission is long - up to a year.
Dühring's dermatosis herpetiformis is characterized by a polyetiological syndrome - it develops against the background of other diseases (impaired functionality of the small intestine or the formation of allergic reactions).
The patient begins to feel itching, burning, tingling on the skin, and attacks of scratching.
Fever may begin, deterioration in health, and after a few hours vesicular or papular spots of large diameter with cavities inside may appear.
The rash herpetiformis is a combination of red, bloodshot spots and distended blisters. Swelling occurs, papules, vesicular and urticarial “burns” are visible.
The rashes are symmetrical - they can be found on the surfaces of the extremities involved in extension, buttocks, shoulders, and lower back. Spots on the face and scalp are common.
If the face is affected by dermatitis, the mucous membrane and epithelium of the mouth also suffer. At first they swell and turn red, then they become covered with blisters and vesicular bubbles.
The rashes are similar to herpes, which gives the name herpetiformis disease. After three days, the blisters open and form bright red erosions with jagged edges and mild pain.
The ulcers last in the mouth for about a crescent, are localized on the palate and cheeks, and leave crusts.
In case of complications of dermatitis, the patient experiences body aches, fever, pain in joints and muscles.
The appearance of these symptoms can be triggered by exposure to a cold wind and hypothermia, which is another factor in the similarity of the disease to herpes.
The manifestation of herpetiform signs on the genitals and palms is extremely rare, but there may be no itching on the genitals.
Dermatitis herpetiformis is diagnosed based on typical manifestations. The diagnosis of Dühring is made after examining the patient based on the location of the blisters on the mucous membrane and face. The distinctive reactions of herpetiform disease are:
- negative Nikolsky symptom;
- disease cycles;
- polymorphism of rashes;
- absence of a certain type of cell (acantholytic);
- histological test according to Jadassohn.
Eosinophilia is present in the peripheral blood of a patient with dermatitis; dermatologists study the contents of the blisters for serousness and skin sensitivity to iodine.
In children, eosinophilia and sensitivity to iodine may be absent in the diagnosis of dermatitis.
The following forms of herpetiform disease are distinguished depending on the degree of differentiation of the blisters:
- true acantholytic pemphigus;
- nonacantholytic dermatitis;
- exudative erythema multiforme;
- bullous toxicoderma.
The treatment of Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis should be comprehensive. They use sulfone drugs, vitamins, antihistamines, and corticosteroids.
For severe persistent disease, antibiotics are prescribed.
To maintain the patient’s condition normally, a diet is prescribed that should prohibit gluten; traditional medicine is used as a preventive measure for herpetiform infection.
Treatment of Dühring's dermatitis, depending on the form, is carried out with the following medications:
- Mild herpetiform type - taking sulfonic drugs (Dapsone, DDS, Avlosulfone), Diucifon. Along with them, vitamins C, P, B, and antihistamines are taken.
- Severe herpetiformis type - corticosteroids are prescribed orally (Prednisolone, Dexamethasone solution), and in case of intolerance - sulfapyridines. To relieve itching due to dermatitis, antihistamine medications in the form of ointments and tablets are used, and complex vitamins are used to support the immune system. Experts give a positive prognosis for the cure of herpetiform disease.
ethnoscience
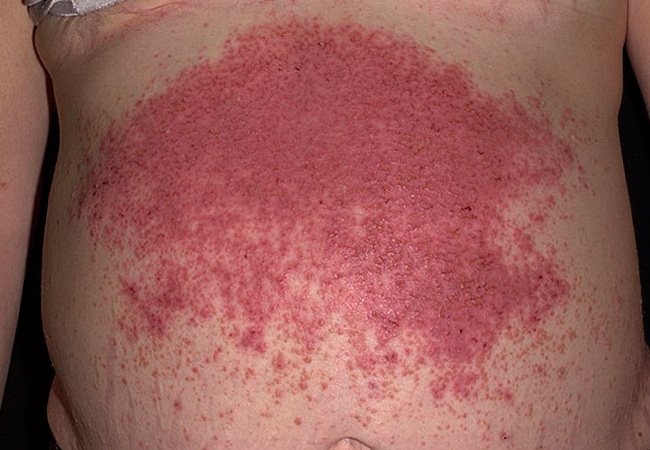
Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis can be treated with herbal medicine methods that have anti-inflammatory and antihistamine effects. Of the herbal components of decoctions, compresses or infusions, use:
- calendula;
- juniper;
- knotweed;
- mistletoe;
- licorice;
- sea buckthorn;
- Aralia;
- Leuzea.
| Product group | You can eat | Prohibited |
| Bread, cereals | Corn, rice flour, starch | Wheat, barley, rye flour |
| Squirrels | Meat, fish, poultry without fat, oven-cooked, milk, dairy products excluding yoghurts | Sausages, smoked meats, dumplings, pasties, meat pies |
| Vegetables | Any, except cereals, legumes, cabbage | Legumes, cabbage, cereals |
| Cereals | Rice, corn, buckwheat | Semolina, pearl barley, pasta, noodles |
| Soups | Vegetables, broths, purees | With peas, lentils, beans, vermicelli |
| Fruits | Any | No restrictions |
| Beverages | Still mineral water 1.5-2 liters per day, tea, coffee | Kvass, coffee, chicory, beer |
Forms
Depending on the type of rash on the skin, dermatitis is divided into the following types:
- papular - it is characterized by the formation of papules;
- vesicular – vesicles are formed;
- bullous - blisters appear that resemble a thermal burn;
- para-oncological – the cause of the rash is carcinogenic oncological neoplasms;
- urticaria-like - the rash is similar to the marks that appear upon contact with nettles;
- eczematoid;
- strophuloid;
- trichophytoid.
The last three species are atypical and extremely rare.
Can it be cured?
Unfortunately, the symptoms of herpetic dermatitis, or herpetic vesicular dermatitis, can go away, but it is characterized by extremely frequent relapses.
This happens because at the final phase of the disease, in which the bubbles with their contents burst, flooding the skin, the virus penetrates the blood and captures the nerve endings, penetrates the cells and takes root in the infected person’s body forever. After this, there is no way to eliminate it, at least modern medicine admits its powerlessness.
Medicines
It is impossible to completely remove the virus from the body, but it is, of course, possible to eliminate the symptoms. To do this, it is recommended to take the following medications:
- Acyclovir
- Vectavir
- Valaciclovir
- Viferon.
Ointments with sulfur are also effective.
If antiviral drugs have no effect, then hormones - Prednisolone and Dexamethasone - are added to treatment. There are forms that come in the form of ointments.
To relieve itching and swelling, you should use antihistamines. Preparations based on medicinal herbs will also be effective.
Fukortsin and brilliant green solution will help dry out the skin.
Factors causing pathology
It is worth noting that it has still not been possible to identify the true causes of the appearance of skin pathological processes. Based on histological studies and examination of test results, a connection was established between the pathology and some provoking factors. It is believed that they can trigger the development of inflammatory mechanisms in the human body.
These factors include:
- Autoimmune disorders.
- Hypersensitivity to iodine compounds.
- Decreased immunity, as a result of which a person becomes susceptible to adverse external influences.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Past viral and infectious diseases (ARVI, human papillomavirus, herpetic infection, etc.).
- Malignant tumor of one of the internal organs.
- Intolerance to gluten (a protein compound found in some cereals - wheat, rye, oats).
- Problems with the intestines (impaired absorption due to the development of ascariasis).
- Gastrointestinal diseases (peptic ulcer, colitis, gastritis, etc.).
The manifestation of the pathology begins with an acute form, which over time becomes chronic.
Complications of Dühring's dermatitis photo
In the absence of timely and professional treatment, there is a possibility of developing complications, which usually have an infectious expression.
Dühring's dermatitis is not a complex disease, so if you follow the recommendations of a dermatologist and follow a diet, it is quite possible to get rid of its symptoms. This is facilitated by the consumption of foods of natural origin, fruits, vegetables, herbs, natural tea and mineral waters without iodine. These recommendations must be followed especially if a child is affected.
If the treatment is chosen incorrectly, the opposite effect may occur; many drugs can cause complications.
- Encephalitis. It develops during an exacerbation of the herpes simplex virus, more often in older people. The virus infects the brain, and when it reaches the meninges, meningitis develops.
- Genital herpes. It is caused by herpes type 2. Infection occurs through sexual contact, as soon as you touch the affected area of the skin. For a woman, the danger lies in further damage to the cervix, which can cause infertility. Genital herpes in men leads to urethritis, prostatitis, and can also cause herpetic cystitis.
- Shingles. Frequent exacerbations of type 3 herpes can cause it. It appears as small bubbles along the body along the costal nerves. This can lead to inflammation of the nerve ganglia - postherpetic neuralgia.
- If dermatitis was detected during pregnancy, then children are most likely to have the herpes simplex virus.
Symptoms of the disease
Often the disease begins to manifest itself with pronounced symptoms and proceeds in an aggravated form. The first symptoms precede the formation of a rash on the human skin.
Among the general signs of the onset of pathology are:
- general fatigue;
- weakness;
- sleep disturbance;
- discomfort;
- irritability;
- slight increase in temperature;
- tingling.
Initially, pigmented spots of a pinkish tint form on the skin, in place of which polymorphic elements of the rash then form. The above symptoms can be so pronounced that they cause significant discomfort to the person. The consequence of this may be nervous disorders and depressive mood.
The symptoms of herpetic dermatitis have their own peculiarities. For example, this is the absence of damage to the mucous membranes. Only in rare cases is it possible to form ulcers in the mouth, which then turn into erosions.
In place of the pigmented spots, various elements of the rash begin to appear. There are true and false polymorphisms.
True polymorphism implies the spread of the original skin formations:
- spots;
- papules;
- blisters;
- vesicle.
During the healing of inflamed lesions, transformation of the elements of the rash occurs, resulting in the development of false polymorphism. It involves the formation of crusts at the site of rashes, as well as scars at the site of ulcers.
As a result of scratching the affected areas, foci of inflammation of various natures and shapes form in place of pigmented spots. Gradually they transform into formations that look like blisters. Their growth and fusion are observed, as a result of which a vesicular area of the inflammatory area of a bluish tint is formed. Then, in their place, papules may appear, representing juicy round blisters.
In some cases, vesicles (small blistering rashes) or bullae (large blisters) predominate among the elements of the rash. All these skin formations are filled with a clear liquid, which can become cloudy in color. This indicates a concomitant secondary infection. Treatment of Dühring's dermatitis in this case is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of primary and secondary pathology.
Why does the disease appear?
The principle of development and the reasons for the sudden appearance of the disease are unknown. But there are factors that indicate the relationship of a number of diseases and other phenomena with vesicular dermatitis. For example, there are people who are intolerant to the protein gluten, which is found in grains.
Scientists say that the development of the disease is facilitated by:
- ascariasis;
- gastrointestinal diseases, in particular ulcers and gastritis;
- hereditary factor;
- the body's sensitivity to iodine deficiency;
- viral infections.
Herpetic vesicular dermatitis can appear in people of different ages, but most often it affects 40-year-old men and women. Men are more affected by this disease. Often, Dühring's dermatitis is a consequence of malignant formations on internal organs, manifesting itself in the form of a skin rash (para-oncological dermatitis).
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of Dühring's dermatitis are varied. As a rule, polymorphic rashes appear first. This process can be further complicated by elevated body temperature, tingling sensation, weakness and painful itching. The rash can form on any part of the body except the palms and soles of the feet. However, most often, signs in the form of rashes and redness appear in the areas of flexion and extension of the arms and legs. The buttocks area, shoulders, shoulder blades and lower back are at risk. Herpetic vesicular dermatitis does not appear on mucous areas. It is very rare to notice the development of blisters in the mouth, which quickly turn into erosion. On the palms, ecchymosis and petechiae are rare occurrences - large intradermal hemorrhages in the form of 3-mm spots.
The rash makes a person feel uncomfortable and has symptoms such as burning at the site of the rash, severe itching and a tingling sensation. A distinctive feature of the disease is that blisters, papules, erythematous spots, and blisters immediately appear on the skin. After some time, false polymorphism is added to direct polymorphism: erosion, crusts and excoriation after strong scratching of the rash. When the rashes are completely healed, a person may be left with scars, hyper- and hypopigmentation.
In dermatitis herpetiformis, erythematous lesions are round in shape and have clear outlines. They are smooth to the touch, often covered with serous, bloody crusts and scratches. After a little time, the rashes form into blisters. The affected skin then turns pinkish-blue or pale red.
The rash itself with Dühring's dermatitis mainly consists of small elements (they are called vesicles). But there are elements of the rash larger than 20 mm: these are bullous lesions. They contain a clear liquid, and if there is an infection, it will be cloudy. These blisters burst and dry out, forming crusts. Then symptoms arise (dryness and itching), as a result of which the person begins to scratch the scabs. After this, erosion remains.
There are several types of dermatitis herpetiformis. It all depends on which type of rash predominates over others:
- bullous;
- papular;
- urticariform;
- vesicular.
There are other types of the disease:
- eczematoid;
- trichophytoid;
- strophuloid.
In the acute form of the disease, the symptoms are: insomnia, feeling tired and high fever. A person can suffer from Dühring's dermatitis for several years. This disease also occurs in children.
Causes
To date, the exact causes of the development of dermatitis duhring herpetiformis have not been established. It is assumed that the disease is autoimmune in nature. It is also believed that a hereditary factor is largely to blame.
In support of this, dermatologists have found that the majority of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis have a non-inflammatory disease of the intestinal system (gastritis). In addition, an important role in the development of the disease belongs to the body’s excessive sensitivity to iodine.