Each of you, at least once in your life, heard the definition of “urticaria” and subconsciously drew a parallel with the plant of the same name. So they are really similar in some ways - they sting the same way, only the plant that grows along the fence is voluntarily used for the benefit of humans in many interpretations, but hives are clearly an undesirable problem on the skin.
Hives, unpleasant skin rashes
Call card: Allergic urticaria. Generalized form
Complaints
to multiple rashes all over the body, accompanied by itchy skin. The patient has no other complaints.
Anamnesis.
According to him, since yesterday evening he has noticed the appearance of isolated skin rashes, self-administration of suprastin without effect: over the course of 24 hours, the rashes increased, and the skin itching intensified.
He associates his condition with eating sauce with unknown spices. Previously, there were allergic reactions to animal fur, food (citrus fruits), medications (can’t remember the names).
Before arrival, the EMS denies taking medications.
Epidemiological history:
leaving Moscow for the last month, staying in tropical countries for the last 3 years, contact with infections - denies.
Objectively.
The general condition is moderate, consciousness is clear. Glasgow scale 15 points. Active position – within the apartment. The skin is dry and of normal color. Turgor is normal. Rash: see st. localis. Pharynx: mucous membranes are not hyperemic. Tonsils behind the arches, no plaque. Lymph nodes are not enlarged. There are no bedsores. There is no swelling. Temperature 36.5.
Respiratory system:
Respiratory rate is 18 per minute, there is no shortness of breath or pathological breathing. Auscultation: vesicular breathing can be heard in all parts of the lungs. No wheezing. There is no crepitus. Percussion sound is pulmonary over the entire surface. There is no cough or sputum production.
Circulatory organs:
Pulse 76 per minute, rhythmic. Filling is satisfactory, heart rate is 76 minutes, there is no pulse deficit. Blood pressure is 120/80 mm, usual – 120/80 mm, maximum – 130/80 mm. Heart sounds are muffled. There is no noise. There is no pericardial friction rub. An accent of 2 tones is heard on the aorta.
Digestive organs.
The tongue is wet and clean. The shape of the abdomen is correct, the abdomen is soft, not tense, painless in all areas upon palpation.
Symptoms of Obraztsov, Rovzing, Sitkovsky, Ortner, Murphy, Mayo-Robson, Shchetkin-Blumberg, Val are negative. Peristalsis is auscultated. The liver is not palpable. The spleen is not palpable. Vomits.
Regular bowel movements, once a day. Last bowel movement yesterday evening, stool formed, brown.
Nervous system.
Calm behavior. Contact. Sensitivity is not impaired. Speech is intelligible, without pathology. Pupils OD = OS, normal, photoreaction is positive, no nystagmus, no facial asymmetry. Meningeal symptoms are negative. There are no focal symptoms. No coordination tests were carried out.
Genitourinary system
There is no dysuria, urination is free, painless, urine is clear. The symptom of effleurage is negative.
Status localis.
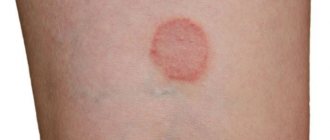
In the area of the face, neck, anterior surface of the chest, buttocks, and posterior surface of the thighs there are multiple small spots of urticarial hyperemia, in places confluent. When pressed, they turn pale and are not compacted. There are no signs of scratching on the body. The surrounding skin is not changed. Body weight approximately 80 kg.
D.S. _ Allergic urticaria, generalized form.
Help provided.
The patient no longer has contact with the suspected allergen.
Sol. Prednisoloni 60 mg + Sol. Natrii chloridi 0.9% – 10 ml IV
Sol.
Chloropyramini 20 mg + Sol. Natrii chloridi 0.9% – 10 ml i.v.
After 20 minutes, the condition improved, the skin itching disappeared, the rash decreased in size and turned pale. The patient does not present any new complaints.
The condition is satisfactory. Objectively: blood pressure 120/80 mm, pulse 80 per minute, respiratory rate 18 per minute. Moderate condition. The asset was left in the ONMP.
Material taken from the website EMHelp.ru
ambulanceobstetrics and gynecologyallergosesrespiratory diseasesheart and vascular diseasesgastrointestinal diseasesjoint and bone diseaseshematologyeye diseasesinfectionsneurologyoncologyneonatologypediatricspsychiatryreanimationdentistrytoxicologytraumaurology and nephrologyear, throat, nosesurgeryendocrinologyhomeclinical examplesindividual symptomstestsapplicationsICD 10 for SMPSMP in tables ah▼ “,”author”:””,”date_published”:NULL,”lead_image_url”:NULL,” dek”:NULL,”next_page_url”:”//neotloga-ru.blogspot.com/?m=1″,”url”:”//neotloga-ru.blogspot.com/2018/05/blog-post_11.html ”,”domain”:”neotloga-ru.blogspot.com”,”excerpt”:”ЖаДобы на Ð¼Ð½Ð¾Ð¶ÐµÑ Ñ‚Ð²ÐµÐ½Ð½Ñ‹Ðµ Ð²Ñ‹Ñ Ñ‹Ð¿Ð° ‚теÐ‑ƒ ожным зудом. .. намнез. Со Ñ Ð»Ð¾Ð²…”,”word_count”:488,”direction”:”ltr”,”total_pages”:2,”pages_rendered”:2}
Source: //neotloga-ru.blogspot.com/2018/05/blog-post_11.html?m=1
Treatment for nettle fever
The first rescue operation comes down to the immediate elimination of the direct irritant causing the allergy. That is, any therapy will differ in the type of urticaria. Stress urticaria can be treated with specially prescribed ointments.
The main point of treatment is taking antihistamines, which block free histamine, preventing the formation of new reactions in tissues. In addition to the medications, the doctor prescribes a cold compress and the use of a product that relieves itching. In more severe cases, corticosteroids are added to general treatment; they have an anti-inflammatory effect.
If the swelling affects a large area of skin and spreads to the mucous membranes, thereby endangering the patient’s life, emergency therapy is prescribed. Active steroids and adrenaline are administered to the patient in large quantities. Chronic urticaria disease requires a more thorough study:
- the doctor draws up a detailed medical history,
- general tests are prescribed,
- X-ray examination.
In 50% of cases or more, it is almost impossible to establish an allergen in a chronic patient. The disease is difficult to cure and leads to a decrease in the patient’s ability to work.
Patients often confuse ordinary skin wounds with a rash in the form of urticaria, and use conventional cosmetic suspensions to moisturize and foundations to hide irritation. Such measures can aggravate the existing form of the disease.
Not only does urticaria itself cause pain, discomfort, and stress, but it also aggravates the overall functioning of the body and provokes complications. It is difficult to describe the entire list of possible problems; it is important to monitor the patient’s condition and record any changes in the course of the disease. The most severe consequences of urticaria can occur after a change from one form to another, or a worsening of the clinical picture.
X-ray examination is necessary for chronic disease
Treatment of urticaria and prevention of relapses
Prevention of urticaria consists of avoiding contact with already established allergens and factors that are potential sensitizers - allergenic foods and medications, chemicals, cold and excess heat, sunlight, mechanical stress, etc.
For these purposes, it is recommended to avoid visiting baths and saunas, wear loose clothing to avoid friction, do not engage in hardening without the advice of your doctor, apply photoprotective agents to exposed areas of the body before going outside, especially in spring and summer, and do not even use household vibrating construction tools .
Attending physicians should teach such patients the rules of behavior at work and in the home, explain the need and importance of following a hypoallergenic diet, and timely taking antihistamines when even mildly expressed symptoms of exacerbation appear.
In case of allergic reactions, the patient should be under constant medical care with an allergist at his place of residence.
To prevent further relapses in chronic urticaria after stopping the relapse for 3-6 months, regular use of second-order antihistamines is necessary, the preventive effectiveness of which is even higher than the therapeutic one, as well as strict adherence to an elimination diet for at least one month.
Idiopathic, unspecified and dermographic forms of the disease require mandatory examination by specialists of various profiles (gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, rheumatologist, otolaryngologist, oncologist) to identify foci of chronic infection and chronic diseases of internal organs, especially the gastrointestinal tract, and carry out appropriate treatment.
The cause-and-effect relationship of the disease with the identified concomitant pathology should only be determined by an allergist.
Indicators of the effectiveness of therapy and the prevention of relapses of urticaria are rapid relief of symptoms of the disease, success in achieving stable long-term remission and the absence of serious complications.
bellaestetica.ru
Classification and etiopathogenesis
The mechanisms of development of various forms are very complex and are still insufficiently studied.
How long does the illness last? In most clinical classifications, according to the duration of the pathological process, the following types of urticaria are distinguished:
- Acute, which can last from a few minutes to 6 weeks. It is much more common and is diagnosed on average in 75% of all cases of urticaria.
- Chronic. Its duration is more than 6 weeks. The chronic form with relapses occurs in 25%. In its natural course, this form of the disease can last mainly up to 10 years (in 20% of patients).
Among children under 2 years of age, as a rule, only its acute form develops; after 2 years of age and up to 12 years of age, acute and chronic forms develop, but with a predominance of the first; after 12 years of age, urticaria with a chronic course is more common. Chronic urticaria is most common in people between 20 and 40 years of age.
A pattern has been noted - if a chronic process lasts for 3 months, then half of these people then suffer for at least another 3 years, and with a preliminary duration of more than six months, 40% of patients suffer from its symptoms for the next 10 years.
Remission in chronic urticaria can occur spontaneously, regardless of how this pathology is treated. In half of the patients it occurs within the first six months from the onset of the disease, in 20% - within 3 years, in another 20% - 5 years, and in 2% - 25 years.
In addition, at least 1 relapse develops in every 2nd patient suffering from a chronic course with spontaneous remission.
In addition, depending on the prevalence throughout the body, the disease is divided into options:
- localized - on a certain limited area of the body;
- generalized (spread of rash elements throughout the body), which is a life-threatening condition, especially when localized in the area of organs of vital importance.
Based on the cause and mechanism of formation of the reaction, the following forms of urticaria are distinguished:
- allergic, caused by various immunological (cytotoxic, reagin, immunocomplex) mechanisms of increased sensitivity (hypersensitivity);
- non-allergic.
Causes
The causes of hives are numerous. The most common of them include:
- Inhalation allergens, for example, household and industrial aerosols, epidermal antigens, pollen.
- Foods that promote the release of histamine contained in the body, or contain histamine themselves. These are eggs, cow's milk, pineapple, citrus fruits, honey, confectionery products with food additives in the form of salicylates and dyes, smoked products, many spices and mustard, fish products and seafood, tomatoes, legumes, eggplants, cheeses, extractives, alcoholic beverages etc. In addition, an acute form of urticaria in people suffering from hay fever can develop as a result of consuming food products that contain antigens that cross-pollinate. Thus, if there is a tendency to allergic reactions to pollen formed during the flowering of trees, urticaria may develop after eating nuts, berries and/or stone fruits, etc., sensitization to birch pollen can cause urticaria after eating carrots or apples, especially red ones .
- Viruses, bacteria and fungi.
- External, internal and injection medications. Urticaria is very common after antibiotics, sulfonamides, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs (salicylates, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), after taking anticonvulsants, vitamins, especially B vitamins and ascorbic acid, the use of antiseptics, iodine-containing drugs, including radiocontrast agents , drugs used for arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease and heart failure (captopril, enalapril, quinapril, Prestarium, Enam, etc.), insulin, blood and its protein substitutes, dental implants, etc. Very rarely, but all However, reactions occur even to antihistamines and glucocorticosteroids.
- Physical impact factors - pressure, friction, cold or high ambient temperature, vibration, sunlight, heavy physical activity, swimming.
- Poison from wasps, bees, hornets, mosquitoes, bedbug bites, fleas and even grasshoppers.
- Neuropsychic load under the influence of psychogenic factors.
- Tumor processes, thyroiditis, dysfunction of the thyroid gland and other endocrine organs, autoimmune connective tissue diseases, diseases of the digestive tract, etc.
READ MORE: Skin rash: causes, types, diseases (55 PHOTOS)
Also in the section: Cold urticaria
Among all chronic forms of urticaria, idiopathic (with an unknown cause) occurs on average in 75-80%, in 15% - caused by a physical factor, in 5% - caused by other factors, including allergic ones.
Development mechanisms
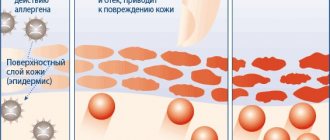
Under the influence of one or more causative factors, both immunological and non-immunological in nature, skin mast cells are activated with the destruction of their granules (degranulation), as a result of which mediators (biologically active substances) are released from them. They cause symptoms in the skin characteristic of acute local inflammatory processes.
In this case, the main biologically active substances are histamine and prostaglandins. Under the influence of histamine, local expansion of small skin vessels occurs with an increase in their permeability.
This results in limited redness of the skin (erythematous patch) and swelling of the hypodermal or submucosal layer with the formation of a blister or papule. In addition to hyperemia and edema, these mediators cause itching, sometimes significant.
Prostaglandin D2 and histamine are also activators of C-fibers that secrete neuropeptides. The latter cause additional vasodilation and degranulation processes in mast cells, which determines the duration (more than 12 hours) of the rash.
Most often, acute urticaria is associated with allergic, that is, with immunological reactions of activation of mast cells, on the surface of the membrane of which highly specific receptors for immunoglobulin “E” (IgE) antibodies are located, as well as receptors for cytokines, C3A, C5A receptors, etc.
Allergic reactions are mediated primarily by the participation of immunoglobulin “E”. Characteristics of urticaria, regardless of the cause, are increased permeability of microcirculatory vessels and the development of acute edema in the tissues located around these vessels, with various manifestations of an allergic reaction.
In cases of a chronic form of the disease, immunological mechanisms are not excluded, for example, in the presence of autoimmune pathology (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism, scleroderma, etc.). At the same time, in a chronic process, activation of mast cells more often occurs through nonspecific (non-immunological) stimuli (emotional stress, the influence of alcoholic beverages, the premenstrual period, physical factors, etc.).
In the last 10 years, the concept of the autoimmune nature of the chronic course of the pathological process has prevailed, according to which autoimmune urticaria is caused by the presence of autoantibodies to IgE receptors with high affinity and antibodies directed against IgE. This mechanism occurs in 30-50% of patients suffering from chronic urticaria.
READ MORE: Aquagenic urticaria - Allergies
Autoantibodies bind to the IgE receptor, resulting in activation of basophils or mast cells, which leads to histamine-like reactions with corresponding symptoms. This principle formed the basis of a relatively new theory, according to which in some patients the chronic form is an autoimmune disease.
The participation of other mediators, such as bradykinin, prostaglandins, neuropeptides, leukotrienes, and platelet activating factor, is also possible in maintaining the chronic course. During remission, mast cells are restored to their normal state.
Is hives contagious and can you get rid of it?
Treatment of the rash
Treatment of patients with an acute course or relapse of the disease is aimed at the fastest possible complete relief of all clinical manifestations, especially in cases of development of symptoms that threaten the patient’s life. In addition, the goal of treatment is to achieve a state of clinical remission as long as possible in the chronic form.
READ MORE: Nervous urticaria due to stress: treatment
Treating urticaria at home and diet
First, you need to accurately determine the allergen that triggered the urticaria rash. There is a group of highly allergenic foods that are excluded from the diet first, especially in case of digestive tract disorders.
It is worth noting that for most people, the cause of hives can be various allergens, which is dangerous for one, safe for another. To achieve a positive result, most products are excluded, after which new ones are periodically introduced into the menu.
Such actions help to analyze and establish the exact cause of allergic dermatitis. During treatment, it is recommended to follow a strict diet.
Treatment may include topical medications to relieve itching and reduce the external manifestations of the disease. Doctors note that such remedies do not provide much relief.
Antihistamines are prescribed to treat the rash. For complex forms, long-term drug treatment, blood transfusions, and histoglobulin injections are prescribed.
Important: Self-medication for urticaria rash is not recommended, since eliminating external symptoms does not eliminate the causes of skin changes. Continued contact with the allergen can lead to skin hypersensitivity and swelling.
PROGNOSIS FOR RECOVERY
With timely diagnosis, exclusion of the provoking factor and proper treatment, the prognosis is generally favorable. When complications develop, the prognosis is determined by the severity of the underlying condition.
In the case of chronic urticaria, the prognosis for recovery is less favorable and depends mainly on the completeness of elimination of the provoking factor.
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl Enter
pillsman.org
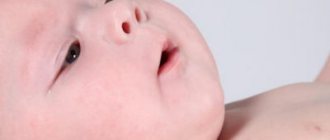
Diagnosis of rashes in children
Hives in a child appear at the site of contact with clothing, in skin folds. The rash is light pink in color and varies in shape.
Skin rashes cause discomfort and itching; children very often scratch the blisters, which then increase in volume, and it becomes very difficult to visualize a separate spot. When you press on the blister in the center, you can see small white dots.
A pediatrician or dermatologist can diagnose the disease in a child; for a more accurate diagnosis, skin sampling and a general blood test may be prescribed. Stool analysis and thyroid examinations are also often performed. Sometimes your doctor may order liver function tests.
Doctors distinguish four main stages of treatment for a child:
- Eliminating contact with the allergen - first of all, all products that can cause hives are removed. It is necessary to review all medications that have been taken recently.
- Diet - food can include the safest foods possible, vegetables and fruits, except red and orange ones; you should also not eat tropical fruits, including bananas. The consumption of fermented milk products and cereals is allowed. A strict diet is followed for 2-4 weeks, after which one product is added to the menu once a week; if there is no reaction, then it can be left.
- Drug therapy - depending on the form of the disease, the doctor prescribes pharmacological treatment at his discretion.
- Cleansing the body - sometimes gastric lavage or blood transfusion is required.
Important: During treatment, you should completely avoid the use of all cosmetics and detergents.