In case of an allergic reaction, treatment must be started immediately to get rid of the pathological signs. Doctors prescribe various remedies, but not all of them are highly effective. Recently, experts have been of the opinion that calcium gluconate should be used for allergies. This remedy helps well in the fight against the disease, so it must be included in the therapeutic regimen. You should first figure out whether calcium gluconate needs to be administered intramuscularly or whether you can take tablets if you have allergies.
Mechanism of action
Calcium is an essential macronutrient necessary for the full functioning of living organisms. A person should receive it with food, but in case of allergies, additional intake of such a substance into the body is necessary. This medicine:
- Helps restore metabolism.
- Directly affects the permeability of blood vessels. Calcium helps to add strength and elasticity to blood vessels, making it difficult for irritants to penetrate through them, and accordingly, the severity of swelling, irritation, rashes and other signs of allergies decreases.
- Has a diuretic effect. This reduces swelling and removes allergens and toxins from the body.
- Enhances the effectiveness of antihistamines - classic allergy medications.
Calcium gluconate for allergies does not provide a quick therapeutic effect. It cannot be used as a replacement for the classical treatment regimen, but only complements it.
Calcium gluconate for allergies in children
Calcium is an essential substance for humans, and calcium gluconate is an indispensable medicine for allergies.
This common disease occurs due to a lack of calcium in the blood, which leads to a weakening of the body's immune system. Alone, the drug is not able to cure allergies, but the severity of the disease decreases during the course.
Indications for use
Gluconate should be taken for diseases that occur against the background of hypocalcemia. Calcium gluconate replenishes its reserves and helps in the fight against such ailments as:
- Allergy;
- Dermatitis and all skin irritations: urticaria, itching, burning, redness.
- Vitamin D deficiency;
- Liver diseases;
- Edema;
- Tuberculosis.
The ability of calcium gluconate to restore calcium balance in the body is used in cases of calcium deficiency during pregnancy, chronic diarrhea and metabolic disorders.
Can be prescribed to children during active growth and formation of the bone skeleton.
Recommended Calcium Allowances
Pharmacological action
The effect on the body is very similar to calcium chloride, but unlike it, gluconate acts more gently and does not provoke strong adverse reactions, the risk of their occurrence is much lower.
The mechanism of action affects:
- Permeability of vessel walls. Due to their compaction, it prevents the allergen from re-entering the blood and causing the formation of antibodies and subsequent allergies.
- Activity of the cardiac muscles. Ensures normal contraction of the heart muscles.
- Water balance. Relieves swelling by removing excess fluid.
- Connective tissue. Helps in the restoration and growth of new cells.
- Properties of blood. Improves coagulability, which prevents heavy bleeding.
- toxins. The diuretic effect ensures cleansing of the body from dangerous and toxic substances.
Dosage
Before use, it is necessary to consult with a specialist who will give precise recommendations based on the characteristics of each organism and the course of the allergy.
The table shows the average dosage values for the treatment of allergies with gluconate tablets.
The maximum dose of the drug per day is 10 grams.
| Age | The amount of calcium gluconate per day for allergies |
| Children 3-4 years old | 1 gram |
| Children 4-6 years old | 1.5 grams |
| Children 6-9 years old | 2 grams |
| Children from 10 years old and adults | 4-6 grams in two times |
| Elderly people after 55 years | No more than 2 grams |
Admission rules
When undergoing a course of treatment, it is necessary to monitor the attending physician and regularly donate blood for analysis. If you do not follow the rules presented in the instructions for use of the drug, you should not expect an effect.
Before consuming calcium gluconate tablets, they should be crushed into powder. Take plenty of liquid, most often water, although milk is not excluded if you are not allergic to it.
Calcium is highly dependent on vitamin D and vice versa, so it is better to take courses of treatment with these drugs in parallel.
The release form allows calcium gluconate to be administered intravenously or intramuscularly; the drug is often found in the form of a solution.
Prescribed only in the most serious cases of allergies under observation in a hospital.
The drug must be administered by injection slowly, no more than 1 ml per minute, and preheated. When a cold agent is administered, bruises form as quickly as possible; due to slow tissue restoration, the development of necrosis is possible.
A high rate of administration leads to the development of arrhythmia, a sharp decrease in pressure, a feeling of heat and severe weakness in the patient, and loss of consciousness may occur.
The course of taking gluconate for allergies lasts at least a week and no more than 14-16 days.
It is necessary to take into account the incompatibility of the product with drugs based on tetracycline, fluorine and iron, as well as glycosides, carbonates and sulfates. There is no compatibility with alcohol; its use is strictly prohibited.
Adverse reactions
In most cases of taking calcium gluconate for allergies, no negative reactions are observed, but in some cases the following may appear:
- Irritation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Stool disorders;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Weakness.
If symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. You can cope with them by reducing the dosage or eliminating calcium gluconate.
Overdose
If the dose of glucanate is exceeded, calcium salts or toxins are deposited in the blood. Hypercalcemia often develops. In case of overdose, calcitonin or gastric lavage with a baking soda solution is prescribed.
Hypercalcemia
Contraindications
To prevent negative reactions, you should pay attention to a number of contraindications to the use of calcium gluconate:
- Diseases of the thyroid and parathyroid glands, in which calcium absorption is impaired.
- Liver pathologies, renal failure, inflammatory reactions.
- Hypercalcemia.
- Tendency to form blood clots.
- Individual intolerance.
- Poisoning with magnesium salts, fluoric or oxalic acid.
- Age up to 3 years.
Conclusion
Calcium gluconate has many advantages over other drugs in the fight against allergies. The drug is absolutely safe, it is prescribed even during pregnancy, and the price is an order of magnitude lower than analogues on the market.
The main advantage is the absence of drowsiness, which occurs when using most medications intended to treat allergies.
Based on patient reviews and the time during which the drug is produced and actively used, only successes in the fight against allergies can be noted.
The best evidence of the effectiveness of any drug is reviews from living people. To be sure, below are several points of view on the effects of calcium gluconate.
Reviews
A real necessity for the body, especially during pregnancy or growing up. During pregnancy, a woman’s body gives it some of the calcium, and the child’s body needs a large amount of “building material” to form bones. Gluconate tablets have a chalky taste; during pregnancy this was the only way I ate them. No side effects.
The child is 6 months old and began to notice blisters on the skin and redness. On the doctor’s advice, I purchased calcium gluconate without any additives, for which I have to pay extra. Helped with allergies with a bang! Mom immediately remembered that she saved me when I was a year old with the same remedy. Time-tested allergy medicine!
In the summer I was stung by a bee, and I have a terrible allergy to stings. The doctor prescribed calcium gluconate injections, and I, of course, thought that I would be wasting my money. But the price is ridiculous, so I decided to try it. And it helped! She also strengthened her nails and hair.
Source: https://zdorovo66.ru/allergiya-u-detej/kaltsij-glyukonat-pri-allergii-u-detej
How to take in tablets?
In order for the drug to be well absorbed by the body, it is very important to take it correctly:
- Before using the drug, it is important to crush the tablet to a powder state.
- The tablets should be taken approximately 1 hour before meals with water.
- It is important to check with your doctor about the need to take vitamin D in parallel, because if it is deficient, calcium may not be absorbed.
The classic single dosage for adults is 2–6 g of the drug. Reception should be carried out 2-3 times. per day. Elderly patients should take no more than 2 g of the drug per day.
The exact dosage and duration of therapy with calcium gluconate is determined individually by the attending physician. Most often, the duration of allergy treatment is limited to two weeks.
Instructions for use in children
The drug can also be used in the treatment of allergic diseases in children. But the dosage of this medication in this age group is different:
- A single dose for children from 3 to 4 years old is no more than 1 g.
- A single dose for children from 5 to 6 years old is 1–1.5 g.
- A single dose for children from 7 to 9 years old is 1.5–2 g.
- Children over 10 years of age are most often advised to take 2–3 g of the drug at a time.
It is worth considering that the intake of calcium gluconate by children should be strictly controlled by parents. An overdose of such a macronutrient can be very harmful to health.
Application and dosage of calcium gluconate
How to take calcium gluconate for allergies?
It is necessary to drink calcium gluconate in tablets before eating. The drug can be dissolved in clean cold water.
- Dosage for adults: 1-3 g (3-6 tablets) two or three times a day.
- Children from 2 to 10 years old should be given 1 gram (3 tablets) also two or three times a day. After 10 years, a single dosage is 2 g (4 tablets).
- People of retirement age are not recommended to take more than 2 grams of the drug per day.
Before using the medicine, you must consult your doctor to determine the exact dosage and time of administration.
The course of treatment is usually two or three weeks.
Intravenous calcium gluconate is administered very slowly. The dosage is about 500 mg and depends on the age and weight of the patient. It is better to entrust injections to a highly qualified nurse. The injection method of administration is used only in emergency cases.
It is better for children to take this drug in tablets.
Intravenous administration
In some situations, doctors prescribe intravenous injections of calcium gluconate. The drug in ampoules can be bought at any pharmacy without a prescription, but it can only be administered by a specialist - a nurse in accordance with the doctor's instructions. The dosage for intravenous infusion is determined by the nature of the disease, the condition and age of the patient:
- Adults are usually administered 5–10 ml of the drug.
- Children under 6 months - 0.1–1 ml.
- Children from six months to one year - 1–1.5 ml.
- Children from one year to 3 - 1.5–2 ml.
- Children from 4 to 6 years old - 2–2.5 ml.
- Children from 7 to 14 years old - 3–5 ml.
When administering intravenous calcium, it is extremely important to warm the drug until it reaches body temperature. The administration is carried out slowly - over about 3 minutes, otherwise the patient may develop arrhythmia and hypotension, a feeling of heat and loss of consciousness are also possible.
Calcium gluconate for allergies in children – Health Prosto Medical Center in Yekaterinburg
“ Calcium gluconate ” is a domestic drug, well known to many generations. To this day, it remains the most prescribed calcium supplement of all the available options. After reading this article, you will learn when and why a child may need this medicine, how to use it to treat children, and what to consider.
At the chemical level, calcium gluconate is a salt that is formed by the interaction of calcium and gluconic acid. The result is a white, tasteless powder that easily dissolves in water, but cannot dissolve at all in alcohol or ether.
In medicine, it is considered a valuable mineral supplement that has an excellent therapeutic effect for patients in a state of hypocalcemia. This term refers to calcium deficiency in the body.
Calcium is very important for children, because it provides protection to bone tissue, strength of teeth, and also participates in the process of hematopoiesis (responsible for blood clotting), plays an important role in the normal functioning of the muscular skeleton, as well as the cardiovascular and nervous systems. Without calcium in sufficient quantities, the pancreas and thyroid glands will not function normally.
It should be noted that calcium successfully performs all these functions only if it interacts with magnesium, phosphorus and vitamin D. Therefore, a sufficient amount of them is very important so that calcium can be fully absorbed and have a positive effect.
In children during periods of intensive growth, the need for calcium is high. But this does not mean that everyone, without exception, should take Calcium Gluconate for prevention. This drug is prescribed by a doctor only to those children who really need it. Otherwise, an excess of calcium occurs, and this condition (as well as deficiency) is quite dangerous for the health and life of the baby.
You can find out whether your child needs this drug by visiting a doctor and taking blood tests for biochemistry. He will tell you in what concentration calcium is available (this parameter is determined in mmol per liter), whether this level is sufficient. Typically, the drug is recommended for the following conditions and diseases:
- hypocalcemia caused by insufficient or poor nutrition;
- hypocalcemia, accompanying various pathological changes in hematopoiesis, with low blood clotting;
- osteoporosis - a disease in which the bone skeleton softens and loses strength;
- imbalance of nutrients, metabolic disorders - vitamin D deficiency;
- with established and confirmed rickets;
- when there is an urgent need to obtain a mineral (during very rapid growth of a child or the eruption of several teeth at once);
- with large losses of calcium associated with taking diuretics, a prolonged illness during which the child was forced to lie in bed for a long time, with prolonged diarrhea, as well as during treatment with antiepileptic pharmaceuticals;
- for allergies - both acute and chronic, expressed in skin manifestations (urticaria, dermatoses) and respiratory (allergic rhinitis, angioedema, bronchial asthma);
- for various bleedings;
- with muscle weakness (myoplegia);
- for liver pathologies caused by exposure to certain toxins;
- for colds, frequent and severe acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections - to increase vascular permeability, which may be impaired due to the effects of the inflammatory infectious process;
- with some nephritis.
The drug exists in two pharmacological forms - tablet and solution for injections. Tablets (250 mg and 500 mg dosages) come in both hard and chewable forms. The solution was created specifically for intramuscular and intravenous administration.
For children's home use, only calcium salts in tablets are suitable.
Solutions are used for adult patients, they are often used by emergency doctors (in situations requiring an urgent response - with severe blood loss, allergic edema or shock, for this purpose the drug is administered intravenously or used in droppers).
Children can also be given the drug intravenously - at a very low rate of administration. However, for this there must be very strong evidence. Under no circumstances should you do this on your own.
The tablets should be thoroughly crushed before use. Children are given the resulting powder with a small amount of water or breast milk. It is important to observe the age-appropriate dosage, because an excess of calcium leads to big problems. Doses for children:
- for infants up to 1 year and newborns – no more than 0.5 g;
- for children aged 2 to 5 years - 1 g (maximum daily dosage should not exceed 3 g);
- children from 5 to 7 years old - 1.0-1.5 g (no more than 4.5 g per day);
- children from 7 to 10 years old – 2 g (no more than 6 g per day);
- children from 10 to 13 years old - 2.0-2.5 g (no more than 8 g per day);
- adolescents over 13 years old - 3 g (no more than 9 g per day).
It is better to divide the daily dose of the drug into 2-3 doses. The child should be given the medicine before meals or an hour and a half after meals.
Crushed tablets should be washed down with water or milk. Regarding the use of milk when taking calcium supplements, doctors have not yet come to a consensus.
Many experts argue that it is better to use plain water, avoiding dairy products.
However, in the official instructions for the drug, the possibility of using milk is indicated as a completely acceptable alternative. If in doubt, it is better to ask your doctor this question.
During a severe allergic reaction (especially in the acute stage), children are prescribed “Calcium Gluconate” along with taking antihistamines, since calcium enhances their effect. In case of an inadequate reaction to any other medications, calcium can be recommended as a remedy that can eliminate other people’s “side effects.”
The course of therapy with calcium tablets is on average quite long - from 10 to 30 days. For some children, according to a doctor's indication, the course can be extended.
The so-called hot injection (10% calcium gluconate solution), preheated to body temperature, is administered in an amount of no more than 5 ml intravenously.
This should be done every two or three days - in case of severe blood loss and convulsions, which pose a certain danger to the child, in case of poisoning with magnesium salts and severe skin diseases.
Almost always - in case of acute and severe allergies that threaten the child’s life, which are associated with the occurrence of edema and difficulty breathing.
Children should not inject solutions into the muscle or subcutaneously; the risk of developing tissue necrosis is too great.
The drug should not be given to children with certain contraindications. These include:
- individual intolerance, sensitivity to calcium;
- hypercalciuria - a condition when mineral salts are excreted in excessively high concentrations in the urine;
- hypercalcemia - excess calcium;
- tendency to increased blood clotting and the formation of blood clots;
- atherosclerosis;
- with complex and severe types of renal failure;
- sarcoidosis
Usually, no associated unpleasant effects are observed when using this drug, unless the dosage and therapy schedule are violated. Only in a small percentage of cases the following phenomena may occur:
- heart rhythm disturbance (bradycardia type);
- oversaturation of the body with calcium;
- increased calcium levels in urine;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- swelling of the legs, frequent urination (with kidney disease);
- formation of stone-like deposits of mineral salts in the intestines (with long-term use of high doses of the drug);
- allergic reaction.
An excess of the mineral in a child is not immediately noticeable, but only some time after the start of taking increased or unreasonable doses. Hypercalcemia may manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- constipation or prolonged diarrhea;
- vomit;
- abdominal pain (in the stomach);
- muscle weakness;
- high blood pressure;
- formation of kidney stones;
- in especially severe cases - loss and confusion, hallucinations, coma.
- "Calcium glycerophosphate";
- "Calcium Sandoz";
- "Calcium D" - syrup;
- "Calcium D3 Nycomed";
- "Kaltsinova".
Quite often, this useful and necessary mineral is included in multivitamin complexes for children. However, such drugs cannot be considered therapeutic. They are intended to prevent deficiency of this useful substance, and not to treat conditions that occur due to a lack of calcium.
Many parents claim that their children tolerate taking Calcium gluconate tablets well, and this drug does not cause any side effects in their children.
From an economical point of view, this drug is very profitable and inexpensive. Some complex preparations with calcium are much more expensive. Experienced mothers who tried all the options did not feel much difference in the action and well-being of the child after treatment, and therefore there is no point in spending more.
The reviews say that some children, at first after starting treatment with the drug, experienced slight discomfort in the stomach and had problems with stool (constipation or diarrhea), but everything went away quite quickly.
Most often, the drug is prescribed to children for allergies. If the child is already 3 years old, such tablets help independently (almost without the help of other medications) to relieve the baby from a minor allergic reaction.
Practical tips:
- Many mothers prefer to give their children calcium for prevention. However, these should not be tablets and syrups. Homemade cottage cheese with calcium gluconate is suitable for these purposes. You can prepare it according to a simple and accessible recipe.
Take 10 tablets of the drug per liter of milk. The milk is heated, but not brought to a boil. The tablets are crushed and added to milk. When the milk has curdled, the cottage cheese is placed on cheesecloth, the whey is allowed to drain, after which this product is given to the child.
- Neither medications nor homemade calcined curds will be of any use if the child has a lack of vitamin D in the body. In order for calcium to be sufficiently absorbed, the child must be outside more often, since the vitamin is formed in the skin under the influence of sunlight. If for some reason this is not possible, the child should also be prescribed medications containing vitamin D.
- Newborns do not particularly need the drug, since they receive the daily dose of the mineral they need through breast milk from their mother (or as part of adapted milk formulas if the child is bottle-fed). If a mother experiences a calcium deficiency after giving birth (hair becomes dull, nails break, problems with teeth appear), let her start taking the drug herself. Calcium gluconate passes into breast milk, and the baby receives it in this form.
Source: https://zdorovie-prosto.ru/beremennost/kaltsiya-glyukonat-pri-allergii-detyam-2.html
Advantages
The medicine has been used in the correction of allergic diseases for decades, so doctors can be confident in its benefits:
- Completely safe.
- It really gives a therapeutic effect for allergies.
- It's quite inexpensive.
- Can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding (after consultation with a doctor).
- Suitable for children (tablets are not prescribed to children under 3 years of age).
- It extremely rarely causes side effects.
- Combines well with other allergy medications.
Despite all the advantages of the drug, it cannot be used for self-medication.
Why is calcium gluconate prescribed for urticaria?
This is a very effective drug that requires proper use.
Medical studies have shown that allergies are often accompanied by a lack of calcium in the blood. Calcium gluconate is able to replenish reserves of useful substances, regulate metabolic processes, and this drug also has a positive effect on:
- permeability and strength of vascular walls;
- connective tissue cells.
Reviews about the presented product are quite different. Some argue that the drug is completely useless.
Others claim that after taking it they immediately noticed a positive result. It should be noted that this medicine, like any other, is not able to instantly eliminate hives.
It should be combined with antihistamines. Calcium gluconate for urticaria has a weak diuretic effect, which helps to quickly remove toxins and other harmful substances from the body.
Can it be used by children?
Urticaria appears in children for various reasons. Calcium gluconate is not only possible, but must be given to a child with this disease, which is due to the ability of the child’s body to absorb the above substance.
The fact is that children develop physically quite quickly. Their connective tissues and bones grow rapidly, which can be seen with the naked eye.
In this case, calcium deficiency often appears in the child’s body. Because of this, metabolic reactions worsen, which negatively affects the state of the immune system.
Sometimes a lack of calcium in a child is provoked by a deficiency of vitamin D. Therefore, it is often recommended to give this substance to children along with gluconate. Gluconate is especially effective in the treatment of acute urticaria.
What is urticaria? Types of urticaria
Urticaria is a common skin disease that most often has an allergic origin. It is characterized by the appearance of a specific rash in the form of itchy flat blisters. The blisters are similar to sting marks from nettles, which is how the disease got its name.
This is a fairly common allergic reaction. According to statistics, every third inhabitant of our planet has encountered unpleasant manifestations of urticaria at least once in their life.
There are acute and chronic forms of urticaria. In the acute form of urticaria, the rashes appear suddenly, last from one to two weeks (they can change their localization within the surface of the human body, as well as the mucous membrane), then gradually disappear.
In the chronic form, foci of urticaria appear and disappear, and relapses can continue for a year or more.
The rash characteristic of urticaria appears due to the accumulation of histamine in the tissues, a substance that increases vascular permeability and promotes tissue swelling.
Allergic reactions of the body to food, drugs, pollen, animal fur, physical factors (cold, heat, sun, etc.), cosmetics and even parasites living in the body lead to a massive release of histamine by mast cells.
Mechanism of action
The antiallergic effect is manifested:
- suppression of the release of immediate allergy mediators;
- a decrease in the level of basophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes and an increase in platelets, red blood cells;
- weakening of allergies by removing from a state of shock, improving the functioning of the central nervous system, cleansing the body of toxins, reducing the release of hormones;
- by decreasing the permeability of capillaries (small blood vessels), decreasing the number of basophils, this helps reduce itching and swelling present in all allergies;
- suppresses excessive manifestation of the immune system, which leads to the development of allergic reactions.
Naturally, only a doctor should select the necessary anti-allergy injection.
Self-treatment for allergy sufferers is strictly contraindicated, as this can result in anaphylactic shock.
But you should always know which injections are used most often and for what conditions they are prescribed.
Diprospan.
This is a hormonal injectable drug.
This medicine is used in two cases - if a person develops a severe allergic reaction or if the use of other antihistamines does not work.
Diprospan has some side effects, which only increase with prolonged and frequent use.
The medicine is not prescribed during pregnancy; breastfeeding should also be stopped during treatment.
Prednisolone.
Hormonal injection drug.
The medicine has a pronounced anti-edematous and anti-shock effect.
When administered intravenously, blood pressure quickly increases, airway patency is restored during an attack of bronchial asthma, and suffocation during Quincke's edema is relieved.
Due to this mechanism of action, Prednisolone injections are included in the emergency first aid kit.
Prescribing the drug for several days in injections is used only in some severe cases of an allergic reaction.
In the absence of Prednisolone, it is replaced with Dexamethosone; their mechanisms of action are almost identical.
Injectable Suprastin.
It is also administered in cases of severe intolerance reactions.
Under the influence of the components of this drug, swelling, skin itching, and manifestations of urticaria are reduced.
Suprastin is prescribed to both adults and children, but only following a certain dosage.
The medicine has a hypnotic effect, so after it there is some inhibition of neuropsychic reactions. This limits the ability to control complex devices.
Calcium gluconate.
Refers to those allergy medications that are used only in complex treatment.
This drug increases calcium levels in the body, which reduces the severity of allergic reactions.
Only a doctor should prescribe calcium gluconate and using it alone in treatment will not help to completely get rid of the symptoms of an intolerance reaction.
Sodium thiosulfate.
This is a detoxification drug; in case of allergies, it is given intravenously in a course of 10 days.
The antiallergic effect of prednisolone injections develops as a result of a decrease in the formation and release of specific substances (allergy mediators), a decrease in the intensity of their release from specialized cells, and a decrease in the number of these cells circulating in the blood; inhibition of the development of lymphoid and connective tissue, reducing the sensitivity of cells to allergy mediators, reducing the intensity of the formation of specific antibodies, changing the nature of the body's immune response.
For respiratory diseases associated with impaired air entry into the bronchi, the effect of the drug inhibits inflammation, prevents or reduces swelling of the mucous membrane, eliminates deposits in the mucous and submucosal layer of the bronchial epithelium, eosinophils and circulating immune complexes, eliminates damage and desquamation of the mucosa.
Prednisolone increases the sensitivity of specific bronchial receptors to catecholamines produced by the body (adrenaline, etc.) and bronchial dilators, reduces the viscosity of mucus and reduces its production.
Main causes of allergies
The main cause of urticaria, like all allergic reactions, is hypersensitivity to irritants.
The most important reason for any allergic reaction is an increase in the body's sensitivity to an allergen or a group of them.
In certain circumstances, the human immune system begins to react to foreign proteins coming from outside or formed inside the body with an incorrect reaction, as a result of which special substances are formed.
These substances are usually referred to as inflammatory mediators; it is under their influence that all allergy symptoms develop, ranging from minor skin manifestations to severe anaphylactic shock.
Scientists explain the increase in the number of patients with various types of allergies for several reasons, the most important of which include:
Poor environmental conditions.
The air, water, and soil become more and more polluted every year, and many compounds dangerous to humans accumulate in them.
Once inside the body, these elements cause a malfunction of the immune system, which leads to an incorrect reaction to various proteins.
Heredity.
It has been proven that allergic reactions can also be transmitted through the genomic code. The risk of a possible allergy increases many times over if both parents pass on a mutated gene to their child.
Disruption of the digestive system.
The cause of the disease may be an allergen in the food product. In this case, antihistamines for urticaria are used once at the very beginning of its manifestation.
This is usually enough to get rid of hives. In the future, this product will be excluded from the menu forever.
It is not difficult to determine, because the allergy appears almost instantly after consumption.
Source: https://zdorovo.live/kozha/dlya-chego-naznachayut-glyukonat-kaltsiya-pri-krapivnitse.html
Contraindications
In fact, calcium gluconate, like any medication, has certain contraindications for use. This medicine should not be used if:
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
- Hypercalcemia.
- Severe hypercalciuria.
- Excessive blood clotting.
- Tendency to form blood clots.
- Severe atherosclerosis.
- Calcium nephrourolithiasis.
- Serious renal failure.
- Sarcoidosis.
It is also worth noting that the medicine is absolutely incompatible with alcohol and some medications, including digitalis preparations, products with tetracycline, fluorine and iron, as well as cardiac glycosides, carbonates, salicylates and sulfates.
Side effects
As a rule, calcium gluconate is well tolerated by patients, but in some cases it can provoke:
- Bradycardia.
- Hypercalcemia or hypercalciuria.
- Disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, represented by nausea and vomiting, loose stools, discomfort and even pain in the epigastric region. Long-term use of the drug in high dosages is fraught with the formation of calcium stones in the intestines.
- Impaired kidney function, which can be manifested by frequent urination, as well as swelling of the lower extremities.
- A feeling of widespread heat (including in the oral cavity) during intravenous administration of the drug.
If undesirable effects occur after taking the drug, it is important to consult your doctor. As a rule, all side effects quickly disappear after stopping the medication.
A course of treatment
The course of treatment with the drug cannot be less than a week or more than 16 days. During treatment, you should also review other medications you are taking.
Incompatibility with other medications.
Calcium gluconate for allergies is prohibited during simultaneous treatment with iron supplements, cardiac glycosides, and tetracycline antibiotics.
Calcium neutralizes the active substances in these medications and may also cause unwanted effects.
The medicine is also incompatible with alcohol; simultaneous intake of ethanol and calcium reduces the absorption of the drug and leads to liver dysfunction.
Adverse reactions.
When taking calcium gluconate to treat allergies, some people develop various adverse reactions.
Most often they are expressed by dyspeptic disorders - epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, loose stools.
If these signs increase, the drug should be discontinued and you should consult a doctor.
The dosage of the medicine must be completely observed; exceeding it leads to the development of arrhythmia and problems with the digestive organs.
Before using calcium gluconate for allergies, it is advisable to determine the level of the trace element in the blood, this will help avoid unwanted reactions.
Contraindications.
Calcium gluconate for allergies is contraindicated in certain diseases, including:
- Inflammatory phenomena in the kidneys, especially causing renal failure;
- Poisoning with oxalic or fluoric acid, magnesium salts;
- Thyroid dysfunction. In this condition, calcium gluconate will not be absorbed, so there is no point in taking it;
- Hypercalcemia;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Blood clotting disorder;
- Severe liver damage.
Contraindications and side effects are considered sufficient grounds for calcium gluconate to be prescribed only by a qualified physician.
Failure to comply with the treatment regimen or exceeding the dosage can lead to poisoning, which will require the use of other medications.
Can it cause allergic reactions?

Calcium itself is a structural element of the body, so there can be no allergy to it. However, a small percentage of patients do experience allergic reactions after taking the pills. Unpleasant symptoms can be caused by the auxiliary components of the drug, because even the most common pharmaceutical tablets contain, in addition to calcium, also potato starch, talc, as well as magnesium stearate and anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide. And if tablets with a more complex composition are used, the risk of allergies increases.
If you cannot tolerate the tablets, your doctor may prescribe intravenous administration of pure calcium gluconate. In this case, no additional substances enter the body.
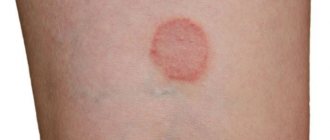
Allergic manifestations in children
During childhood, bones grow and teeth develop, so the body especially needs calcium. If there is a shortage of it, it is spent from the body’s reserves, which has a bad effect on the immune system.
A lack of calcium in the body in children occurs due to a lack of vitamin D, for this reason both microelements are prescribed. It is not advisable to treat infants under 3 years of age with this medicine.
For allergic conditions, taking chloride can help cure urticaria, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, eczema and hay fever, intolerance to certain medications, and serum sickness.
The child had intolerance to some drugs. And the doctor prescribed treatment for allergies with activated carbon and calcium gluconate. After the course we are doing well!
Victoria, 26 years old