The role of proper nutrition
Since eczema is a skin disease, often of allergic origin, people suffering from this disease are advised to adhere to a diet that excludes foods that cause an allergic reaction. During periods of exacerbation of eczema, proper dietary nutrition helps to get rid of such an unpleasant symptom as itching. During the period of remission, the diet acts as a preventive measure for the recurrence of the disease.
A hypoallergenic diet for eczema includes a variety of foods, which does not cause much discomfort to the patient. Some foods can even be fried a little, with a little oil and, preferably without salt, but only if it is pre-cooked.
Dishes during a diet are best absorbed and digested in pureed or finely chopped form. Vegetables recommended for consumption during the diet (except cabbage) can be eaten in absolutely any form, raw, boiled, baked. The exception is vegetables that can be fried.
Dangerous products
In most cases, exacerbation of eczema is caused by protein foods, dishes high in starch and sugar, as well as vegetables, berries and fruits of red, black, yellow and orange. However, since the diet must be balanced and complete, you cannot blindly give up all types of protein foods and sweets in order to completely switch to safe plant-based foods. That is why it is not recommended to create your own diet: this should be done by a qualified allergist, dermatologist or nutritionist. At the same time, the patient himself must be sufficiently familiar with permitted and prohibited products in order to find an appropriate replacement for potentially dangerous dishes.
At the stage of exacerbation of eczema, it is necessary to completely exclude from the diet of adults:
- tomatoes, strawberries, red apples, sweets, fatty foods, baked goods;
- canned foods that provoke acute eczema
- semi-finished products;
- eliminate or minimize the consumption of potatoes;
- foods that cause increased itching are chocolate, jam, honey;
- mayonnaise, pickles, marinades.
Proper nutrition for different types of eczema
For eczema of any type, you can follow general recommendations, but each type has its own specific rules to avoid exacerbation.
For hand eczema
The diet should help relieve symptoms and put the disease into remission. Regular proper nutrition helps reduce the likelihood of relapse. With such eczema, you need to avoid sweet, spicy and fried foods. Semi-finished products, marinades, pickles and canned foods are also prohibited.
carriers of vitamins PP and B
Diet for eczema on the hands allows the consumption of lean meat (preferably turkey and rabbit) and fish. But during an exacerbation, it is advisable to adhere to a vegetarian diet. Vegetables will benefit the body, the amount of potatoes is reduced, and it is advisable to avoid pasta altogether.
To restore the deficiency of vitamins PP and B, you need to eat more lettuce, turnips, carrots, rutabaga and fresh cucumbers. Greens will also be useful: parsley and dill. There are usually no restrictions on the amount of liquid, but it is better to exclude coffee, store-bought juices, alcohol and carbonated drinks.
In some cases, eczema causes weepy patches on the hands. They occur when the water-salt balance and the inflammatory process are disturbed. With this pathology, the diet for eczema excludes foods rich in carbohydrates. You can include lean meat, dairy, and vegetables in your diet. You cannot eat cabbage and legumes, and salt is also not used when cooking.
For eczema on the legs
The diet for eczema on the legs excludes foods with difficult-to-digest fats. These include:
- fat;
- sweets;
- flour;
- pork;
- pates;
- lamb;
- meat dishes with butter.
During an exacerbation, you need to include fermented milk, porridge with water, and vegetable soups in your diet. In the first few days of illness, diluted vegetable and fruit juices are needed to cleanse the body.
For meat products, you should give preference to boiled or stewed turkey and rabbit, boiled fresh fish and lean beef. In this case, you need to steam, boil or bake.
Fermented milk products and plant foods should be present in the diet every day. Cabbage, peas, cucumbers, zucchini, carrots, beets and other vegetables have a beneficial effect on the body. Leaf and watercress contain vitamin C, iron, iodine and carotene, therefore they are useful for the patient.
During the period of remission, it is useful to add berries (raspberries, blueberries, rowan, gooseberries, currants), nuts, and melons to the diet. But during an exacerbation, these products are contraindicated. The diet must include porridge, especially oatmeal, buckwheat and wheat. It is strictly forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, coffee and strong tea.
Diet for dyshidrotic eczema
Diet for dyshidrotic eczema is an important component of treatment. Dyshidrotic skin lesions are a chronic disorder. Patients suffer from periodic rashes in the form of serous blisters on the skin of the soles and palms. A properly formulated diet prevents allergic reactions, and therefore the manifestations of the disease.
First of all, it is necessary to exclude red vegetables and fruits, as well as citrus fruits, from the diet. Any sweets and flour products are prohibited; sugar can be replaced with fructose. For meat products, low-fat dietary varieties of meat and fish are suitable. At the same time, many allergens are contained in smoked meats, pork and duck meat.
Spicy, fried, peppered and salty foods should also be removed from the diet, since such foods not only cause worsening of rashes and itching, but also negatively affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The basis of the diet is fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and dairy products. Cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir and cheese contain lactobacilli, which are essential for the intestines and local immunity. Their regular use prevents relapses of dyshidrotic skin lesions.
So, therapy is based on following a strict diet. It is necessary to adhere to such a diet for 1-2 months, and to achieve lasting results - throughout life.
Diet for microbial eczema
The microbial diet is a vegetable-dairy diet. With this disease, the skin is covered with flat crusts, when removed, weeping areas appear. Most often, rashes appear on the legs, the back of the hands, and sometimes on the head. As a rule, a doctor compiles a list of permitted and prohibited foods. Coffee, chocolate, spices, pickles, soda, cheese, and alcohol are prohibited. The exception is plant allergens; the patient is allowed to eat nuts, corn, red vegetables, peas, and garlic. But if the disease worsens, these products are also prohibited.
The main diet consists of vegetable soups, unleavened porridges in water, river fish, steamed cutlets and meatballs, and dairy products. Restrictions also apply to the amount of spices in food. It is recommended to reduce or completely eliminate the use of salt and pepper. Don’t forget about maintaining water balance; you need to drink up to two liters of still mineral water every day.
Diet for allergic eczema
The diet for allergic eczema is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. Not only food products, but also dust, animal hair, pollen, cosmetics and much more can stimulate the appearance of skin rashes. Regardless of the pathogen, therapeutic nutrition can minimize the manifestations of the disease. It is necessary to adhere to a healthy regimen not only during the period of exacerbation to unload the body, but also during the period of remission.
This is interesting: Red spots on the body of an adult - red spots appeared on the face
Smoked meats, sausages, fried, fatty foods, and foods with spices are prohibited. As well as seafood, canned food, eggs, nuts, citrus fruits, mushrooms, grapes, carbonated drinks, confectionery.
It is necessary to limit the consumption of pasta, semolina, butter, full-fat sour cream and whole milk.
The diet should be based on fermented milk products, lean meat, light fruits (plums, currants, pears, apples), vegetables and herbs. You can eat grain breads and products made from second-grade flour, ghee and refined butter.
Diet for dry eczema
The diet for dry eczema involves a vegetarian diet. The menu is based on protein and plant foods. During the period of remission, you can add weak meat broths, lean meats and steamed meat dishes to your diet. You should definitely eat porridge, but without oil and salt, vegetable casseroles and stews with a minimum content of potatoes. As for fish, it is best to eat river fish, baked or boiled.
Dairy products such as cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk, yogurt and kefir help the body recover faster and accelerate skin regeneration processes. Plant foods are very useful, for example, peas and cabbage. Peas contain a lot of protein, so it is better to eat them during the summer period of exacerbation of the disease. Your daily diet should include carrots or carrot juice, as they contain a lot of B vitamins and carotene. The content of precisely these beneficial substances in patients with eczema is significantly underestimated.
If hypertension appears along with skin rashes and itching, then you should eat beans and beets, watercress and lettuce, as they are rich in vitamin C, iron, iodine and carotene. Dill helps with gastrointestinal disorders. Greens can be added to salads or made into smoothies based on kefir and dill.
Features of therapeutic nutrition
A hypoallergenic diet for eczema, especially during periods of exacerbation, should be based on the following principles:
- forced exclusion from your diet of foods that cause allergic reactions;
- refusal of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- drinking enough water (at least 1.5-2 liters per day);
- proper, fractional nutrition;
- taking a complex of multivitamins and minerals.
Hypoallergenic diet for eczema
On a note! Products that cause allergies can be of both plant and animal origin. Each person, of course, has his own reaction to the use of one or another component, but there are common allergens that provoke an exacerbation of the pathology.
Common allergens include:
- whole milk;
- chicken and quail egg whites;
- citrus fruits (oranges, limes, tangerines, bergamot, lemons, pomelo, grapefruits);
- some types of seafood (black and red caviar, crayfish, shrimp, mussels, brine, oysters);
- chocolate and cocoa;
- peanut;
- honey;
- spices and seasonings (cumin, mustard, barberry, turmeric);
- fruits and berries (grapes, figs, persimmons, strawberries, blueberries, blueberries, pomegranate, melon);
- some vegetables (red and orange bell peppers, tomatoes, radishes, eggplants);
- legumes (peas, lentils).
Food pyramid for psoriasis
Products from this list should be excluded for eczema, especially during periods of exacerbation of the disease. It is also undesirable to consume sweet carbonated drinks and industrially produced juices ; it is better to cook unsweetened compotes from dried fruits or seasonal fruits with a low level of allergenicity. But it is worth remembering that raisins, dried apricots, and dates can cause severe itching and rashes.
Prohibited Products
Proper nutrition for true eczema (see Is eczema contagious or not) is the exclusion of all fried, smoked, salted and dried foods from the diet. You should avoid kebabs, smoked sausages, balyk, herring, pickled mackerel, cakes, pastries, and chocolates. It is better to stew or steam meat, boil vegetables, bake apples.

Prohibited foods for eczema
Berries that can cause allergies in their raw form will become absolutely hypoallergenic in compotes. Avoid fast foods and delicatessen altogether - their products may contain emulsifiers, flavorings, preservatives and other harmful additives.
Note! It is better to buy fresh meat at farmers' fairs or markets. Supermarkets very often use various antibiotics and formaldehydes (to extend the shelf life of hermetically sealed meat). They very often contribute to the development of eczema.
Authorized Products
For eczema, it is very useful to eat dishes such as vegetable soups, milk porridges (not made from whole milk, but diluted with water in equal proportions), heat-treated fruits and vegetables. The meat should not be very fatty (rabbit, chicken, quail, veal, young beef).

What can you eat if you have eczema?
Healthy vegetables include cauliflower, green beans, as well as zucchini, zucchini, potatoes, turnips, and cucumbers.
Nutrition for eczema
For eczema of the lips, face, groin, ears, scalp, dyshidrotic, it is very important to follow a diet, since some foods tend to worsen the well-being of patients. For example, sweets, citrus fruits, spicy and smoked foods increase itching.
Note: How the food is prepared is also important. For patients with eczema, it should be boiled or steamed.
It is especially important to adhere to a diet during the stage of exacerbation and remission of the disease: both in adults and in children and nursing mothers. It is not recommended to consume foods that cannot be stored for a long time. It is necessary to limit your diet by removing fatty foods, potatoes, tomatoes, and red apples. Strawberries are prohibited for eczema. It is advisable to give preference to soups made with vegetables and fermented milk products. You can eat porridge with water, lean meat (no more than 150 g per day) and fish (with the exception of sturgeon). It is allowed to drink light-colored juices.
Important! At the acute stage, it is better to refuse meat, giving preference to vegetarian dishes. When the condition improves, you can gradually introduce weak meat broths into the diet.
You need to eat fermented milk products every day. These include cottage cheese, yogurt, fermented baked milk, and kefir. A diet designed for eczema involves consuming large amounts of plant-based foods. It is recommended to choose peas, cabbage, carrots, beets, beans, etc. When the exacerbation stage is over, you can add nuts, pumpkin, raspberries, black currants, apricots to your diet.
Diet for eczema on hands and feet
Skin disease on the legs is often caused by a violation of water and salt balance. The skin becomes very dry. Thus, in addition to diet, it is important to adhere to the drinking regime. To do this, you need to use mineral water “Narzan”, “Arkhyz”, “Borjomi”. You should drink at least 2 liters of liquid per day, adding to this amount fresh juices, green tea and other permitted drinks.
As for the diet for hand disease, you need to include protein foods, as well as foods that contain a predominance of iron and iodine. These are parsley, cucumbers, carrots and others. You should definitely add folic and ascorbic acid, vitamins B, E, A to your diet, which promote rapid healing and restoration of the skin.
Drinking regime for eczema
You should pay attention not only to food intake, but also to drinking regime. Prohibited:
- freshly squeezed juices and factory-produced nectars;
- any alcoholic drinks;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- coffee drinks, chicory, natural coffee;
- Jelly, fruit drinks, compotes, etc.
It is acceptable to drink weak tea, mineral water with or without carbonation, and blackcurrant compote. Individual reactions to various types of drinks should be monitored and included in the diet according to the relief of the condition.

Diet for hand eczema: menu
With lesions of the hands and fingers, in addition to pain, there are also aesthetic inconveniences. Often the signs are weeping areas of the skin resulting from inflammatory processes, as well as disturbances in water and salt metabolism. In this case, the diet involves avoiding foods high in carbohydrates. It is necessary to include lean meat, milk, and vegetables in your diet. It is advisable to add as little salt as possible during cooking. It is important to stick to fractional meals. The liquid must be present in unlimited volume.
For breakfast you should cook porridge or eat cottage cheese with sour cream. Vegetable salads or fruits are suitable for a snack. For lunch, you can treat yourself to meat dishes (meatballs, steamed cutlets, etc.), not forgetting about soups. For dinner you can cook fish and make a vegetable salad.
Detailed menu for the week (table)
The nutrition plan should be drawn up by a nutritionist or attending physician, taking into account personal data and tests, but below is a sample menu that you can rely on. Deviation from the course of nutrition can provoke an increase in symptoms, as well as food restrictions. Diet menu for eczema for a week:
| Day of the week | Breakfast | Dinner | Afternoon snack | Dinner |
| Monday | Pear, homemade yogurt with raisins, juice. | Chicken broth soup, vegetable salad, compote. | Baked apple. | Vegetable salad, baked potatoes, bread. |
| Tuesday | Cottage cheese, any fruit, green tea. | Steamed fish, rice, stewed vegetables. | A glass of fermented baked milk and cookies. | Vegetable casserole, bread, tea. |
| Wednesday | Yogurt, allowed fruit and tea. | Boiled or steamed turkey, boiled vegetables, compote. | Cottage cheese and natural juice. | Barley porridge, vegetable salad, tea. |
| Thursday | Corn porridge, compote. | Baked fish, mashed potatoes, vegetables. | Cottage cheese with berries, green tea. | Boiled chicken, salad, tea. |
| Friday | Oatmeal, compote. | Borsch, steamed cutlet, vegetable salad. | Baked apples, a glass of fermented baked milk. | Stewed turkey with vegetables, dried fruit compote. |
| Saturday | Oatmeal, bread, a handful of berries (cranberries, lingonberries). | Vegetable puree, steamed cutlets, tea. | Green tea, cottage cheese. | Stewed mushrooms, mashed potatoes, cabbage salad. |
| Sunday | Wheat porridge, bread. | Fish cutlet, buckwheat, salad and tea. | Fruit salad with yogurt. | Vegetable stew, chicken, compote. |
Hypoallergenic diet for eczema
If patients are prone to allergic reactions, with eczema they simply need to follow a hypoallergenic diet. Its principle is to exclude from the diet foods that cause rash, irritation, itching and other similar manifestations.
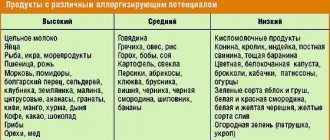
The list of highly allergenic products is supplemented by:
- egg white;
- fish of the sturgeon family;
- milk;
- beet;
- chocolate, honey and many other sweets;
- coffee.
Below are products with average allergenic activity:
- peas, rice, corn;
- potatoes, bell pepper;
- cranberry, apricot;
- rabbit, turkey, lean pork.
Low allergenic activity is distinguished by:
- green apples;
- pumpkin;
- horse meat and lamb;
- gooseberry;
- prunes;
- watermelon;
- leaf salad.
If the patient has an acute stage of illness, it is necessary to include in the diet a list of products from the last group. In other cases, it is allowed to use ingredients from the second group. As for highly allergenic foods, it is advisable to avoid them until complete recovery.
Proper nutrition for eczema (psoriasis, dermatitis, allergies) plays a big role. Some experts indicate that you can get rid of the disease only with the help of diet, without resorting to drug treatment.
Diet for eczema, useful advice from nutritionists
Eczema is a dermatological disease that occurs against the background of general dysfunction of the endocrine and nervous systems of the body. The disease is chronic, recurrent, and is not transmitted by contact. One of the reasons for the manifestation of pathology is genetic predisposition, so children whose parents suffered/suffer from dermatoses automatically fall into the risk group. Since the disease is neuro-allergic in nature, nutrition for eczema is very important. Following the advice of nutritionists, which involves eliminating certain foods from the diet, helps reduce the symptoms of the disease and achieve significant remission.
The article provides information about the clinical picture of the disease, its main symptoms, and also describes in detail what the diet should be for eczema in adults and children, and what foods should not be eaten with eczema. In addition, the material contains a table of foods that you can eat if you have eczema.
This is interesting: Castor oil for parasites (worms): how to take for adults and children, reviews
Additional Information! According to statistics, every 15 children and every 30 adults on the planet are affected by eczema. The disease is considered relatively young, however, despite this, it has a number of cardinal features that distinguish it from other skin pathologies.
Dermatologists began to identify eczema as a separate disease relatively recently, so at the moment there are a number of issues that require additional research. So, the exact cause of eczema has not yet been established; this area is quite relevant.
Eczema Food Chart
All foods in a special diet for the treatment of eczema can be divided into three groups: those that are strictly prohibited because they contain a large number of allergens, foods with a small content of allergenic substances (allowed to eat once every three days) and foods without allergens in composition that can be consumed in any quantity. This table includes products that are recommended for general use. Many people have individual intolerances to foods and are also prohibited from consuming them.
In adults, a diet for eczema causes mistrust that they will have to starve for a lot. But no, there are a lot of approved products. But what can and cannot be eaten if you have eczema?
| Prohibited | Allowed once every three days | Fully permitted |
| Fried food. | For a couple. You can also bake and boil. | |
| Fatty meats. It is poorly digested and does not nourish the body sufficiently. | Lean meats such as turkey, duck and rabbit | Lamb, horse meat. |
| Sea fish, seafood. | Fatty fish. | |
| Tomatoes, pomegranate, beets. | Apricots and peaches, potatoes, sweet peppers, berries. Cereals such as buckwheat, rice, as well as peas, corn, rye. | Greens, plums, pumpkin, apples, bananas, cucumbers, beans, cabbage. |
| Sweet food, buns, bread. | Bread. | |
| Sugar, everything sweet, including honey. | Sugar can be replaced with fructose. | |
| Sausage, as it contains low quality minced meat and food additives that contain allergens. | Replaced with baked meat. | |
| Yoghurts in stores. | Homemade yogurt. | |
| Mayonnaise in stores. | Homemade mayonnaise consisting of sour cream, mustard and lemon juice. | |
| Coffee. | Natural juices without additives or dyes. | |
| Whole milk. | Fermented milk products are especially recommended for children. | |
| Citrus fruits (orange, lime, lemon, grapefruit and others). | ||
| Eggs | ||
| Nuts. | ||
| Spicy foods (pepper, garlic, other spices) | ||
| Smoked products. | ||
| Alcohol products. |
Find out more
Clinical picture of eczema, how the disease manifests itself
Eczema belongs to a number of dermatological diseases, manifests itself in the form of rashes on the skin, which, if left untreated, can grow. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of vesicles filled with clear liquid, which over time begin to peel off, then become crusty and burst. At the site of the cracks, weeps form, causing particular discomfort to the patient and requiring immediate treatment. Advanced forms of pathology can lead to the development of complications in the form of a bacterial infection.
Additionally, you will need to consult with a nutritionist, the latter will help you create a diet for eczema (menu).
Symptoms of the disease
- the affected areas change color and become warmer compared to other areas of the skin;
- in places where the disease is localized, a rash appears, accompanied by burning and itching;
- vesicles filled with a transparent substance form on the skin;
- problem areas become covered with a crust, after a certain time it cracks, and weeping appears in place of the vesicles;
- The patient's general condition worsens, body temperature rises.
Types of disease
There are several types of disease. Eczema of the hands can be: true, dyshidrotic, microbial, mycotic, occupational, allergic, tylotic.
The form of manifestation of the disease can be wet and dry. With weeping eczema of the hands, the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves acutely, after which the disease gradually becomes chronic.
The skin of the hands swells and turns red, and small vesicles containing clear liquid form. From time to time, the blister bursts and forms a moist, painful, and then flaky erosive depression.
Clear liquid vesicles begin to flow onto the skin.
Dry eczema on the hands is eczematous dermatitis. In the dry form, there is excessive dryness of the skin, cracks and peeling of inflamed areas.
Species classification of eczema
When eczema is detected, a diet for eczema is prescribed depending on the symptoms, type and stage of the disease. External agents are especially popular, in particular ointments and creams, as well as antiseptics, antihistamines and corticosteroids. If a bacterial infection occurs, antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Before prescribing the drug, the dermatologist examines the patient and interviews him. This helps to make the correct diagnosis, determine the type of eczema and choose the appropriate course of treatment. A nutritionist will help you create a diet for eczema in a table.
Remember! Self-medication is not allowed when fighting eczema; you can take medications only after consulting a dermatologist. Self-treatment may lead to a deterioration in the patient’s overall health.
Types of eczema
- True eczema. The causes of the manifestation are usually associated with internal malfunctions, for example, such as disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid disease, vegetative-vascular dystonia, diabetes mellitus. In some cases, a predisposition to pathology is inherited;
- Atopic eczema occurs in patients suffering from food allergies. With this type of eczema, the patient’s daily diet is of particular importance; the patient is advised to adhere to the rules of a gentle diet and pay attention to what foods cannot be eaten with eczema, and to exclude allergens from the diet. The list of irritants that can cause such a reaction is determined by the doctor as a result of diagnostic measures;
- Microbial eczema. Accompanied by microbial and fungal infections of the epidermis. The pathology is characterized by constant burning and itching.
Difficulties in treating eczema
Why do so many people suffer from eczematous lesions for years? A question whose answer contains several points:
- As practice shows, and judging by the dialogues of patients on specialized forums, in the Russian Federation the level of medicine is not yet capable of providing a truly high-quality treatment program for eczematous lesions. And the world’s leading clinics have not yet fully resolved this issue either. The situation is aggravated not only by the complexity of the biochemical changes occurring at the cellular level, but also by their diversity. There are many scenarios for the development of eczema. Eczema is closely associated with two little-studied phenomena - allergic and autoimmune reactions. Allergies, i.e. an atypical immune reaction to some chemical or physical agent can provoke the formation of autoantibodies. Conversely, autoimmune diseases can also make the patient allergic. The key problem is that medicine is unable to answer exactly how abnormal immune responses occur. Are they absolutely dependent on the genotype? Or do they arise under the influence of exogenous factors?
- The consequence of the first point is that dermatologists prescribe treatment that is aimed at eliminating symptoms. As for the reasons, here doctors give only general recommendations regarding changing daily habits. While lifestyle adjustments are an exclusively individual program. And patients quickly become convinced of this, often discovering the ineffectiveness of following the general therapeutic regimen. Among non-drug treatment methods, most dermatologists put diet first, as the most powerful agent that regularly affects the body. Indeed, nutrition is a large set of different chemical compounds that regularly enter our body, changing the biochemistry and functioning of internal organs. First of all, the gastrointestinal tract. It is believed that the functioning of the digestive organs is most closely related to the condition of the dermis. There are two problems here - each patient is forced to choose a diet for himself, and that it does not always help.
- Another point is the types of eczema, of which there are about 10. But in fact, all types of eczema also come down to three phenomena: allergies, autoimmune processes, genetics. Even their drug and antisymptomatic therapy is similar. Accordingly, this also applies to a similar diet.
Diet for various types of eczema: prohibited and permitted foods
For eczema (dry, weeping, tilotic, seborrheic, varicose, mycotic, idiopathic, occupational, microbial, pediatric), the doctor always selects an appropriate diet, because this is an integral part of successful treatment and long-term remission. The diet has to be changed completely, and during the period of exacerbation, nutrition is subject to even more strict correction. With constant implementation of the recommendations, it is possible to achieve a weakening of symptoms, as the body begins to function normally.
What foods should you avoid if you have eczema? What menu does the diet suggest for eczema in adults and children on the hands, feet and other parts of the body?
Seasonings and sauces that you can eat on a diet
A diet for eczema on the hands does not imply the use of factory-made sauces, ketchup, mayonnaise, or tomato paste. Patients who are accustomed to a diet supplemented with a lot of herbs and spices should reconsider their eating habits.
It is permissible to use low-fat sour cream. As food seasonings - dry or fresh dill, parsley, green onions, onions. You can, for example, prepare brine from sour cream, garlic, and a small amount of cheese. This sauce is much healthier than mayonnaise, and the taste can complement your favorite dishes much brighter.
Hypoallergenic diet for eczema on the hands and feet
There is eczema that develops after eating certain foods. Such an allergic reaction is not the most rare occurrence in sensitive people, so it is better to identify in advance what food intolerance is manifested.
It is convenient to do several tests to scientifically confirm or refute an allergy to a particular food. This recommendation is also useful because a hypoallergenic diet should always be individualized, adjusted to the characteristics of your illness and your own body.
A famous doctor in this video will talk about the features of a diet for eczema:
Product selection
Be sure to exclude from the diet foods that are allergens and can provoke an outbreak of the disease. These include:
- fat meat;
- coffee;
- spicy food;
- tomatoes;
- garlic;
- sweets;
- nuts;
- baking;
- smoked meats;
- citrus;
- whole milk;
- any fried food;
- strawberry;
- grenades;
- melon;
- wheat;
- beet;
- honey.
It is advisable to eat hypoallergenic foods, but the diet can be supplemented with foods that are moderately allergenic. You only need to exclude those names that provoke worsening of eczema symptoms. For convenience, use the eczema diet chart below.
Average allergenicity
Completely hypoallergenic
Substitutes for harmful products
Important Features
The total duration of the diet is determined by the doctor, but the standard period during which it is maintained is 3 weeks. Prohibiting certain types of foods does not mean that the patient must fast. On the contrary, an inadequate diet will also aggravate the manifestations of eczema. Therefore, you should adhere to reasonable limits without cutting back on the amount of nutrients and microelements.
- To avoid relapses of the disease, it is advisable in the future to consume as little food as possible that is included in the category of allergens. However, eating a small amount of them is still allowed, but only every 3 days.
- For eczema of the legs and arms, you should eat enough greens, carrots, rutabaga, cucumbers and other vegetables.
- It is imperative to choose other suitable dishes that increase hemoglobin and compensate for the lack of levels of vitamins PP and group B.
- In the most difficult cases, under the guidance of a doctor, products with moderate and low degrees of allergenicity are gradually abandoned.
- It is useful to additionally keep a food diary so that, together with the doctor, you can figure out what should be completely excluded. Supervision by a professional with such a strict diet is very important, otherwise there is a high risk of harm to health.
Next, we have selected nutritional (diet) tips for you in the treatment of various forms of eczema, which, according to reviews, are the most effective.
What not to eat if you have eczema
It is necessary to follow dietary recommendations for eczema as carefully as possible, since any allergen can provoke a relapse of the symptoms of the disease. The duration of the diet is on average 3 weeks, during which the following foods are prohibited:
- Fatty meats such as pork. It is difficult to chew and nutrients are poorly absorbed by the body.
- Butter.
- Nuts increase itching and rashes.
- Citrus fruits, that is, oranges, lemons, grapefruits.
- Sausage. It contains a minimum content of high-quality minced meat, as well as various additives that can increase symptoms.
- Coffee.
- Smoked, spicy.
- Sweets, including honey.
- Whole milk.
- Eggs.
- Alcohol products.
- Synthetic food additives.
Nutritional features for various forms of the disease
For microbial
For microbial eczema, the basis of the diet (nutrition) is vegetable and dairy products. The doctor determines everything that needs to be excluded. The following are almost always prohibited:
It’s better to build your menu around steamed and boiled food.
- Low-fat cutlets, fish and meatballs, dairy products, vegetarian soups and water-based porridges are allowed.
- All kinds of spices and salt will also need to be excluded, but if the food seems bland, then you can use various greens.
- Water is replaced with mineral water, but exclusively without gas. Maintaining water balance is very important, and this means that you will have to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water.
For allergic
Therapeutic nutrition allows you not to overload the body with other foods that aggravate the symptoms of the disease, so at the stage of exacerbation you should immediately switch to a diet. During remission, it is recommended to repeat it periodically for 1-2 weeks, which allows you to achieve a sustainable positive effect over a long period.
This is interesting: Pumpkin seeds for worms: how to take for children and adults? Reviews
Recommendations for allergic eczema are:
- The menu should include fermented milk products, grain breads, herbs, fruits (only light ones!). It is allowed to include refined oil, lean meat, and water-based porridge.
- During an exacerbation, do not eat seafood, fatty foods, sweets, mushrooms, red berries, grapes, nuts, or sausage.
- Full-fat milk and all kinds of products made from it, semolina and pasta are consumed, but in very small quantities.
You will learn further about what kind of diet suggests dry dyshidrotic eczema.
Experts will talk about a plant-based diet as a way to overcome eczema in the video below:
- If you have dry type of eczema, it is highly recommended to study the principles of vegetarian nutrition, since it is desirable that the main dishes on the menu be of plant origin.
- During remission, it is allowed to supplement it with protein dishes. Along with lean meat, they eat weak broths, casseroles, and soups.
- Porridge should be present in the daily diet, as they have a beneficial effect on the general condition and support the activity of the stomach.
- You should reduce your consumption of potatoes and seafood. But eating river fish is highly recommended, but, of course, not fried.
- Vegetable juices should be prepared daily. Carrot fruit has a particularly good effect on health. For variety, you can combine several vegetables or add permitted sweet fruits. It is the juice that contains a concentrated amount of vitamin substances, and most of all the body lacks B vitamins, so it is advisable to choose vegetables that contain them.
Dry eczema is sometimes accompanied by hypertension. A moderate diet does not overload the heart, but you should still inform your doctor about this phenomenon in order to prevent its progression.
For chronic
Any eczema is an exclusively chronic disease, only in some, under the influence of various irritants, it recurs much more often. It is required to adhere to the principles of hypoallergenic nutrition to prevent constant exacerbations. We talked above about which foods should be completely excluded.
It is best to avoid drinking alcohol throughout the diet. If the body is weakened by a long course of the disease, the doctor will not only recommend a certain diet, but also prescribe vitamin supplements.
Let's find out further what diet is required for weeping eczema.
When wet
This type of eczema is considered one of the most unpleasant, as wet areas require constant treatment. Bacteria can always get into constantly forming cracks and abrasions, which means that the disease will also be complicated by purulent inflammation. Because of this, the diet for weeping eczema is very strict, implying a categorical refusal of any food that can provoke an attack. Indeed, even a small portion of the prohibited product eaten can cause a strong surge in symptoms.
- Fruits and vegetables are almost always welcome in the diet, but in this case it is very important to exclude everything sour: kiwi, citrus fruits, apples. Watermelons and melons should also not be eaten.
- Food must be natural, preferably prepared independently, so dinner options made from semi-finished or instant products are strictly excluded.
- It is better to compensate for protein deficiency with plant components, cottage cheese. Lean meat is also allowed, but you should not eat more than 200 g of it daily. The diet is supplemented with river fish, cereals, and light soups.
- You can prepare recipes from vegetarian cuisine, but do not forget that the use of spices is kept to a minimum.
With any type of eczema, you can diversify your diet; you don’t have to eat exclusively bland food. Find suitable recipes, modernize them, use various herbs instead of salt and usual spices. This way your menu will be delicious, and the symptoms of the disease will gradually disappear.
The video below will tell you about the features of treatment and diet for facial eczema:
Causes of eczema
The following forms of the disease can be distinguished:
- True. This is primarily due to diseases of the intestines, stomach, diabetes, nervousness, problems with the thyroid gland, and VSD.
- Microbial. Red cells in the body cannot cope with introduced infections and microbes. Diet for microbial eczema requires a special approach.
- Atopic. This type of eczema occurs when a person is allergic to food. Most often, he does not know which one. And in order to figure out what caused such a reaction in the body, it is worth planning a special nutritional system and reviewing your diet. The hypoallergenic nutrition system is aimed at eliminating the allergen product.
Scientists have not clearly identified the occurrence of eczema on the hands and feet. There are some factors that influence the manifestation of this disease: infections, nervousness, allergies to food or medications, contact with chemicals, poor condition of internal organs. These and similar problems can cause eczema on the hands, palms, and feet. This is not exactly a childhood disease; adults are more often susceptible to it.
Science has proven that nutrition is the key to healthy skin and body, hair, teeth and nails. In most cases, eczema develops due to poor diet, allergies to certain foods, or poor metabolism. If this is about you, then you need to reconsider what you eat, rid yourself and your body of fatty, spicy, salty, sweet, carbonated drinks and the like. Such a diet for eczema of the hands and a diet for eczema on the legs will quickly remove the physical symptom.
Features of nutrition for eczema on the arms and legs ^
Most often, eczema appears on the arms and legs, and its symptoms depend on the specific type:
- Idiopathic: hyperemia, swelling at the site of the lesion, peeling;
- Microbial: inflammation, purulent crusts and erosions form around scratches and abrasions;
- Mycotic: its symptoms are combined with a fungal infection of the skin, and it is also characterized by weeping blisters, itching and rash;
- Seborrheic: Occurs mainly on the scalp, ears, face and chest. Manifests itself in the form of flaky yellow spots, which eventually form into plaques;
- Dyshidrotic: appears on the palms and soles in the form of blisters;
- Callosal: affects the palms and soles when blisters form on them that look like calluses;
- Varicose veins appear in the area of dilated veins in the form of an itchy rash.
Many factors can contribute to the appearance of such a disease: hereditary predisposition to allergies, weak immunity, dermatological diseases, hormonal imbalances, skin lesions of a chemical, thermal or mechanical nature.
Regardless of the form of the disease, it is necessary not only to start treatment in a timely manner, but also to rebuild your diet, and the question of whether a diet is needed for eczema is quite relevant. It is needed at a minimum because a person’s health depends on what he eats, and he can only get all the necessary vitamins and microelements with food.
Therapeutic diet for eczema: recommended foods
The diet for patients with eczema should be based on the following principles:
- During remission, to prevent exacerbation, it is advisable to eat watermelons, pumpkin, zucchini, watermelons, currants, gooseberries, lingonberries, cranberries;
- During an exacerbation, the menu should be dominated by plant foods: fruits, vegetables, cereals, herbs, as well as fermented milk products. Smoked meats, salty and spicy foods, milk, sweets, citrus fruits, canned food, pork, eggs and processed foods should be excluded.
By following a therapeutic diet for eczema of the hands and other parts of the body, you can significantly prolong remission, and exacerbations will bother you much less often and you can forget about the disease even for years.
Classification and types of eczema
According to statistics, about 30% of the world's population suffers from eczema. The fact is that the disease worsens only from time to time - as a rule, under the influence of factors of an allergic nature or an inflammatory process in tissues and organs.
There are the following types of eczema:
- Dry eczema is typical for elderly patients. As a rule, the pathology worsens in the area of the hands in the autumn and spring. It differs from other types of eczema in that ulcers and ulcers do not form at all. The patient suffers from peeling and painful dry skin, which is accompanied by itching.
- Weeping eczema can appear in both adults and infants. The pathology is characterized by severe itching, as well as the appearance of vesicles. These are small pimples, inside of which fluid resembling pus accumulates. You cannot burst the vesicles on your own; if you follow a diet for eczema of the hands (of a weeping nature), the rashes and itching should go away on their own.
- Dyshidrotic eczema is characterized by the appearance of spontaneous discomfort. This form of eczema is also called acute. It can be located both in the area of the hands and in the area of the feet, shoulder blades, forearms, and face. The patient experiences severe itching, the skin turns red and peels.
- Microbial eczema (synonym - periwound) is characteristic of an inflammatory dermatological process that arose under the influence of streptococci, candidal fungus, staphylococcus, etc. Microbial eczema, in turn, is classified into coin-shaped, varicose, sycosiform.

Diet for eczema: menu and features of therapeutic nutrition ^
Does a diet for eczema help achieve stable remission of the disease: reviews from doctors
Diet rules for eczema:
- Since eczema is most often a chronic disease, to maintain remission the diet must be followed throughout your life;
- You should remove from your menu all foods that can cause aggravation.
Hypoallergenic diet for eczema
This diet option is suitable for all patients, and it is allowed to consume hypoallergenic foods in unlimited quantities, and limit food with more harmful allergenicity:
- Hypoallergenic: turnips, horse meat, lamb, gooseberries, squash, zucchini, prunes, bananas, plums, apples, watermelon, pumpkin, lettuce;
- Moderate allergenicity: green peppers, peas, broccoli, apricots, cranberries, peaches, rabbit, buckwheat, rice, potatoes.
Diet for dyshidrotic eczema
In general, with this form of the disease, it is enough for patients to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet and adhere to a protein-carbohydrate menu, but if there are weeping erosions on the skin, the following products should be excluded from it:
Dairy-plant diet for eczema
This diet option is suitable for everyone, but it is recommended to consult a doctor before using it. What you can use:
- Low-fat cottage cheese, sour cream, kefir, yogurt;
- Porridge, fruits, vegetables, herbs;
- Fruit and vegetable natural juices.
Diet for dry eczema
To avoid exacerbation of dry eczema, you need to avoid a number of foods:
- Citrus fruits, strawberries, bananas;
- Eggs;
- Red fruits, vegetables and berries;
- Sweet pastries and chocolate.
Dry eczema and the importance of proper nutrition
Dry eczema is more common in older people, while children and adolescents are characterized by an acute form of the disease. Dermatologists say that this pathology develops due to improper water regime, as well as a deficiency of vitamin A and healthy fatty acids.
Based on this information, we can conclude that the diet for dry eczema on the hands should contain an abundance of foods rich in these components. Therefore, older people with dry eczema can include fish and seafood in their diet, as well as add as many cold-pressed oils to porridge as possible (in particular, focus on flaxseed and olive oil).
But carrots, which are very rich in vitamin A, are not recommended for inclusion in the menu. This vegetable, in addition to vitamins, is also rich in natural dyes, which are often quite powerful allergens. Whether to add carrots to the diet for dry eczema should be decided by the patient himself, depending on the individual reaction of the body and skin to this vegetable.