Causes of swelling
If a child has swollen eyes in the morning for several days, this can be caused by a variety of reasons, so it is better to visit a pediatrician, get examined, find out the diagnosis, and start treatment.
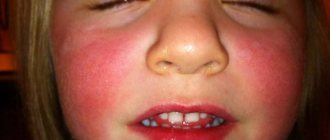
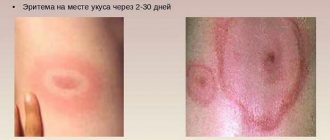
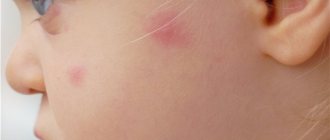
The cause of swollen eyes in a child can be a banal bite that irritates the delicate skin around the eyes. And, if the baby is prone to allergies, then a bite can provoke an allergic reaction in the body with unpredictable consequences.
In addition to allergies, the reason that a child’s eyes are swollen may be conjunctivitis, an inflammatory process accompanied by fever and purulent discharge from the eyes. Puffy eyes and puffy upper eyelids may indicate kidney disease or heart problems in children. In this case, it is recommended to undergo a full examination.
Herpes that has settled in a child’s body can also cause the child’s eyes to become very swollen and red. Puffiness and redness are accompanied by blisters on the skin where eyelashes grow. What to do if a child has swollen eyes due to herpes? If the doctor has identified this particular cause, local treatment with Acyclovir, for example, will be prescribed.
In three to four days, the herpes swelling of the eye will disappear.
During the examination, the ophthalmologist will assess how much the child’s eyes are swollen and red and will analyze whether this could be the result of bee stings, midges, injuries, or foreign body penetration. That is, there can be many reasons for swelling of the eyes, the doctor will figure it out, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
For example, minor swelling of the eyes of a child under one year old can be observed if he has been crying for some time. An infant swells after sleep due to poor nutrition, as well as a violation of the daily routine.
Puffy eyes in an older child may occur if he visited the pool, or perhaps he was bitten by some kind of midge or mosquito. Also, if a child wears contact lenses that do not clean well, the child’s eyes (lower and upper eyelids) may well become swollen.
One of the reasons for eye swelling is visiting the pool.
The main part of these causes, which causes red, swollen eyes in a child, are not considered serious, and can easily be cured on their own, at home, with warm or cold.
But there are more serious causes of swelling that appears in the morning under both eyes in children, or only under one.
Painless swelling of the eyes in a child is possible due to an allergic reaction of the body that blocks the sebaceous glands in the eyelids. To summarize, if a child has red and swollen eyes, he may have:
- conjunctivitis, in which the mucous membrane of the eye becomes inflamed, the child’s eye swells, itches, and pus is released;
- blepharitis, in which the eyes swell due to inflammation of the edges of the eyelids (lower and upper), they turn red, burn, the eyes are dry, tears flow involuntarily;
- stye, in which the sebaceous gland at the root of the eyelashes becomes inflamed, the child's eye swells and swells, and the temperature often rises;
- orbital cellulitis (phlegmon of the eyelids), which is an acute infectious inflammation of the eyes themselves, as well as the eyelids, eyebrows, and cheeks. It often occurs as a result of an insect bite or injury, and then swelling can be observed under one or both eyes;
- chalazion, which causes swelling of the eyelids and swollen eyes in a child due to blockage of the sebaceous gland and fluid accumulating in it;
- dacryocystitis, or obstruction of the tear ducts. As a result, after sleep, the child’s eyes become swollen, purulent, and watery.
- an allergic reaction that occurs to food, plant pollen, insect bites, medications, and is expressed by swelling of the eyes in a child;
- erysipelas, which is an infectious-allergic disease of the skin of the eyelids, leading to swollen eyes in a child;
- furunculosis (boil), which is a purulent disease of the hair follicle, leading to the child’s eyes becoming swollen, itchy, red, and purulent;
- trauma (thermal, chemical, physical). What to do if a child’s eye is swollen as a result of an injury; most often, such swelling will go away on its own and does not need to be treated. If the swelling thickens and becomes very painful, you should visit an ophthalmologist.
- entry of a foreign body.
If in the morning it turns out that a child’s eyes are swollen, it is possible that he was bitten by a midge, and poison entered the body, although a small amount, but sufficient to cause swelling. In this case, the temperature may even rise.
In addition to swelling localized in the child’s eye area, there may be:
- severe itching;
- slight swelling at the site of the bite;
- skin rash;
- signs of poisoning.
A bite to the eye area can be dangerous as the child unknowingly scratches the area around the eyes. If a child’s eye is swollen as a result of a bite, why is it dangerous, and what to do?
The danger is that an infection can penetrate through the wound, and the eye begins to fester. In addition, a very itchy, swollen and watery eye causes discomfort.
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to give the child any antiallergic drug to relieve swelling and itching, and apply a cold compress to the eye.
It is recommended to lubricate the area of puffiness under the child’s eyes with Tetracycline ointment. In case of suppuration, you should consult a doctor; you may need to take antibiotics.
Swelling under the eyes of a child can occur due to foreign bodies entering them, which affect the cornea, conjunctiva, eyelid, and cause symptoms such as:
- discomfort;
- eye pain;
- involuntary lacrimation;
- itching and burning;
- constant desire to rub the eye;
- inability to open the eyelid;
- decreased vision;
- “veil”, “sand” in the eyes.
Foreign bodies entering the eyes can not only cause eye injury, but also cause:
- blepharitis;
- keratitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- hemorrhage;
- other complications.

It happens that a child’s eyes suddenly become swollen for no apparent reason, and it is not clear why this happened. In this case, you should try to reduce the swelling and visit a doctor.
Warm and cold compresses will help as a decongestant. If the skin of the eyelids is too dry, you can lubricate it with Vaseline, or rich baby cream, or sea buckthorn oil.
The child has itchy eyes around the eyes, redness, swelling, treatment - Mishutka
The body's reaction to external stimuli varies.
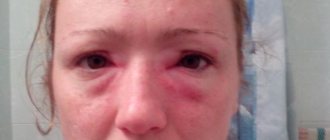
One of the most unpleasant manifestations of allergies is swelling and redness of the eyes. Allergic eye swelling is especially difficult for children. They become restless, whiny, eat poorly and often wake up at night. Parents try their best to alleviate the child’s suffering. However, allergy treatments depend on many factors.
Causes of eye allergies
Before starting treatment for the disease, it is necessary to find out what causes the allergic reaction. There are various reasons for eye allergies. Most often, swelling and swelling of the eyes and eyelids occur in children during the flowering of various plants. However, it is not uncommon for eye problems to occur during the winter. Causes of an allergic reaction:
- plant pollen;
- household dust;
- chemical components of cosmetics, washing powders and cleaning components;
- food colorings;
- fur, feathers and excretions of pets;
- Food;
- cigarette smoke;
- contact lenses;
- cold;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- topical medications;
- a foreign body on the eyelid or near the eyeball.
The reaction occurs after the root cause of the disease comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the eye. Children with reduced immunity and those whose loved ones suffer from various allergic manifestations are predisposed to allergies.
READ ALSO: what to do if a child’s eye is festering?
Forms and symptoms of the disease
Allergies to the eyes have different forms and types depending on the manifestations and source. The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. The first manifests itself when local immunity decreases and there is a high concentration of the pathogen (for example, seasonal allergies). With the second, a small amount of the allergen is enough to cause a reaction.
Allergic manifestations in the eyes have the following types:
- conjunctivitis;
- eyelid dermatitis;
- disease of the vascular part of the eye;
- corneal disease;
- inflammation of the retina;
- deterioration of the optic nerve.
In children, allergies manifest themselves in the form of conjunctivitis and dermatitis of the eyelids. The last four types of allergic reaction in a child can occur if the first two types of allergies were not treated in a timely manner. Symptoms and descriptions of the forms of conjunctivitis and dermatitis are presented in the table.
| Form of the disease | Description | Symptoms | |
| Allergic dermatitis | Occurs due to the use of cosmetics and topical medications. | Redness and swelling of the eyelids, rashes on the skin around the eyes. | |
| Conjunctivitis | allergic | It appears upon contact with a chemical, plant, or animal allergen. | Red eyes, watery eyes, sneezing, runny nose, swelling of the mucous membrane. |
| hay fever | Appears during the flowering of vegetation and has a strong seasonal character. | Swelling of the eyelids, redness of the eyes, tearing, photophobia, sneezing. | |
| spring | Occurs when there is bright sunlight. | Discharge of mucus and fluid from the eyes, fear of light, small growths on the inside of the eyelid. | |
| drug | Appears after prolonged use of medications or application of drugs to the surface of the eye. | Redness, swelling of the eyelids, tears. | |
| infectious | Consequence of bacterial infection. | Purulent discharge from the eyes, swelling and redness of the eyelids. | |
| papillary | Develops after entry of a foreign body. | Red eyeball, brightly highlighted vessels. |
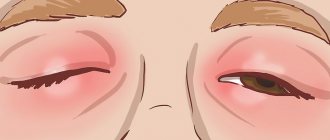
In the photo you can see the symptoms of various types of eye allergies. Almost all types of allergies are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- itching;
- redness of the eyeball;
- discharge from the eyes;
- swelling;
- burning;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye;
- sensitivity to light;
- deterioration of vision.
How are allergies diagnosed?
The process of diagnosing the disease takes place in several stages:
- examination of the patient;
- survey to identify concomitant diseases and hereditary predisposition;
- conducting clinical tests.
To determine the type of allergy, the following is carried out:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- blood biochemistry;
- examination of eye discharge;
- testing to identify allergens (skin, nasal, sublingual).
Drug treatment of eye allergies
The choice of medications depends on the causes of eye allergies and accompanying symptoms. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of an allergic reaction and increasing the body's resistance to the disease. Treatment involves a combination of local medications (drops, ointments) and internal medications.
Popular medications that are used to relieve severe swelling on and around the eyelids are Dexamethasone drops and Hydrocortisone ointment (we recommend reading: dosage and instructions for using Dexamethasone for children). The frequency and duration of use of the drugs is prescribed by the doctor depending on the type of allergy. The table below lists medications used to treat eye allergies in children.
| Direction of action | Name of the drug | Release form | Minimum patient age, years |
| Relieving redness of the eyelids, eliminating discharge from the eyes, itching, photophobia, burning | Albucid | Eye drops | From birth |
| Tobrex (we recommend reading: how to apply Tobrex eye drops for children?) | |||
| Floxal (we recommend reading: how to use the drug “Floxal” for children?) | |||
| Tavegil | 2 | ||
| Allergodil | 4 | ||
| Opatanol | 3 | ||
| To get rid of infection during complications, treatment of allergic infectious conjunctivitis | Erythromycin ointment 1% | Ointment | At the discretion of the doctor |
| Tetracycline ointment (we recommend reading: how to use Tetracycline eye ointment for children?) | Ointment | Not recommended up to 12 months | |
| Antihistamines | Suprastin | Tablets, injection solution | From 3 years, tablets, from 1 month, injections |
| Fenistil | Drops for oral administration | From 1 month | |
| Telfast | Pills | 6 | |
| Relieving itching and irritation of the eyelids | Naphthyzin | Vasoconstrictor drops | |
| Visine | |||
| Elimination of dry mucous membranes | Vidisik | Liquid | According to the doctor's decision |
| Boosting immunity | Multi-Tabs | Capsules | 3 |
| Fish fat | Capsules | 2 | |
| Vitrum | Chewable lozenges | 3 |
Folk remedies
The following traditional medicines exist:
- Compress from a tea bag. It is necessary to soak a bag of black tea without additives in hot water. Warm tea should be placed on the inflamed eye for 5 minutes. The compress helps when the eyes are swollen and red (we recommend reading: what to do if a child has a swollen eye?).
- Lotions with chamomile decoction relieve inflammation and burning around the eyes. It is necessary to make an infusion: 1 tbsp. spoon of dried flowers per 200 ml of boiling water. After 40 minutes, you need to moisten a piece of clean gauze in the solution and place it on your eyes. The procedure can be done up to 3 times a day for 10 minutes.
- Rinse with chamomile decoction.
- Washing with soda. To prepare the solution, you need to take 1 teaspoon of soda per 1 glass of water.
- A compress of grated raw potatoes relieves swelling around the eyelids.
- Lotions with dill. To prepare the infusion you need to take 1 tbsp. spoon of dry plant and pour 200 ml of boiling water. Apply to eyes for 7-10 minutes.
- Rinsing with aloe juice relieves inflammation of the mucous membrane. To prepare the solution, you need to take aloe juice and boiled water in proportions of 1:10.
Preventive measures to prevent allergic eye swelling
Preventive measures consist of reducing the duration of the child’s contact with the allergen or eliminating it altogether. Allergy prevention includes:
- reducing the child’s stay on the street during the flowering period of plants;
- protecting the eyes from active exposure to the sun if you are allergic to ultraviolet radiation (wearing glasses with dark lenses) (see also: symptoms of sun allergy in a child and description of treatment with photos);
- using natural products when washing clothes and cleaning the house;
- daily wet surface treatment;
- eliminating the pet that caused the disease;
- strengthening the immune system;
- exclusion of allergenic foods from food;
- contacting a specialist at the first symptoms of the disease.
Source:
A child’s eyes itch: treatment, causes, washing
Any discomfort or pain that occurs in a baby always worries his parents. If a child’s eyes itch, the reasons may be harmless, in which case they can be easily and quickly eliminated, or it may be a symptom of a serious pathology, in which case the young patient will need qualified medical help.
Main causes of discomfort
Itchy and red eyes in a child are a common symptom that can be caused by a variety of factors. Why children's eyes water and itch - the most common reasons are the following:
- Healing of small wounds . When wounds appear on a child’s body – even the smallest ones – the production of healing substances begins. A side effect of this process is itchy eyes;
- Obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculus . This pathology is congenital. Its signs are that the newborn’s eyes itch and redness appears. Children who suffer from this disease experience dry eyes because they are not moistened by tear fluid;
- Conjunctivitis . If a child’s eyes itch and there is redness and swelling, this may indicate allergic or viral conjunctivitis;
- Entry of a foreign body . The causes of itching and redness often lie in foreign objects (for example, grains of sand) getting under the baby's eyelid. Sometimes the particles that cause your eyes to itch are so small that they are almost impossible to see with the naked eye;
- Allergic reaction . In children under seven years of age, there is an increased susceptibility to the effects of aggressive environmental factors. If the eye is red, itchy, watery, or there is nasal congestion, then these signs indicate an allergy;
- Eye strain . If a child sits at the computer for a long time or spends a lot of time watching cartoons and TV shows, then red and itchy eyes simply need rest;
- Development of blepharitis . As this disease develops, the child's eyes itch, the eyelids become thickened, crusts may appear on them, and sometimes there is peeling of the skin around the eyes.
Treatment method
The question of what to do when a child nervously scratches his eyes arises for all parents who encounter this problem. Before starting therapy, you should determine what causes the child’s discomfort. The treatment strategy should be aimed not only at eliminating itching and redness, but also at combating the source of discomfort.
Entry of a foreign object
Necessary measures:
- rinse your eyelids with weak tea/boiled water;
- apply eye drops for children / place ointment under the eyelid.
Examples of medicines:
- Albucid solution
- Tetracycline eye ointment
You should not remove the speck with your hands, especially on the street, as this can cause infection. It is better to use a clean napkin or a damp stick.
Overvoltage
First of all, it is necessary to limit eye strain (reduce time playing on the computer or watching TV programs). Perform eye exercises with your child.
In the future, limiting eye strain should be constant.
Conjunctivitis
The course of therapy is prescribed by the doctor depending on the type and strength of the disease.
Examples of medications:
- Albucid solution 10% (permissible for use in the treatment of newborns)
- Colbiocin
- Eubetal
- Fucithalmic
- Vitabact
- Levomycetin
- Tetracycline ointment
- Erythromycin ointment
It is not recommended to use folk remedies when treating children.
Source: https://mishutka86.ru/drugoe/u-rebenka-cheshutsya-glaza-vokrug-glaz-krasnota-pripuhlost-lechenie.html
Causes of swelling in one eye
If only one eye is swollen, this may cause the following reasons:
- insect bite followed by an allergic reaction in a child;
- seasonal and periodic allergies to plant blooms, animal hair, bird feathers, house dust, food;
- bruises, cuts, abrasions on the skin around the eyes;
- development of an infectious inflammatory process on the eyelids, including blepharoconjunctivitis;
- viral diseases in which the organ of vision is involved in the pathological process, for example, influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, herpes;
- the formation of a wound on the skin around the eyes, followed by infection and suppuration;
- colds;
- entry of a foreign body under the eyelids with subsequent tissue infection;
- increased pressure inside the skull;
- pathologies of the renal system with the formation of edema;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- prolonged crying until hysteria occurs;
- state of teething.
Some of these causes can be determined visually by your doctor; others will require diagnostic tests.
Characteristic symptoms
The first thing children complain about with almost any eye problem is lacrimation and redness of the eyelid mucosa. Sometimes the onset of the development of a disease can be “caught” at this stage, react in time and eliminate the cause. For example, when examining a suddenly reddened eye, you can find a foreign body that has not been washed away with tears.
Eye swelling in a child is often accompanied by other symptoms that determine the origin of the problem. For example, if both eyes are red and swollen, and the child feels itchy and rubs them, an allergic reaction is likely occurring.
When a child's eye is swollen on one side or only one eyelid, this may be the result of a minor injury or a sign of the development of a stye. If the eyes and face swell after sleep, but there is no redness of the mucous membrane, the root of the problem lies in the functioning of the heart and kidneys. If purulent discharge is mixed with lacrimation, then most likely it is an infection.
In addition to swelling in one eye, a child may also experience additional symptoms:
- slight or excessive increase in body temperature;
- unpleasant sensation in the eye area: pain, itching, burning;
- suppuration on the skin or in the eye area;
- severe redness of the conjunctiva and cornea;
- increased production of tear fluid;
- severe crying;
- symptoms of illness: weakness, fatigue, lethargy, drowsiness, poor appetite;
- headache, dizziness;
- damage to the skin with the possibility of minor or significant bleeding;
- runny nose with clear or purulent discharge;
- mark on the skin from an insect bite;
- increased reaction of the eyes to bright light (photophobia);
- bruises around the eyes.
Based on the above symptoms, the doctor can offer a specific diagnosis, but it must be confirmed using laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
Edema in young children is easily noticeable, so an attentive and caring parent can hardly leave them unnoticed.
Symptoms that should prompt you to consult a doctor:
- increased body temperature;
- palpable compactions in the tissues of the eyelids;
- suppuration of the eyes;
- tearfulness.
ATTENTION: If you detect at least one of the above symptoms, do not rush to self-medicate. Using medications without a doctor's prescription can harm your child's health. Instead, immediately visit a pediatrician and ophthalmologist, who will determine the real cause of the swelling and prescribe the necessary treatment.

Swelling of the eyelids is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature, which can be either subtle or significant. Prolonged high body temperature with edema is fraught with increased intracranial pressure. The combination of a high temperature with tearfulness, headaches and problems with urination may indicate:
- diseases of the heart (swelling worsens in the evening) and thyroid gland;
- problems with the kidneys and liver;
- sinus diseases (sinusitis, rhinitis or sinusitis);
- diseases of veins and lymphatic vessels;
- allergies (including angioedema).
If swelling appears without any noticeable reason, accompanied by watery eyes, redness of the eyes, mucus from the nose and anxiety, this indicates the presence of an allergic reaction.
If edema is accompanied by a frequent urge to urinate, blood in the urine (determined by turbidity and a dark tint), pain in the head and back, and high fever, suspicions fall on diseases of the kidneys and urinary ducts.
If a child experiences fluid retention (the amount of moisture consumed does not correspond to the amount excreted), kidney disease, hormonal disorders, and cardiac decompensation may be present.
With nephrotic syndrome, severe anemia and heart failure, local swelling of the eyelids can develop into general swelling of all parts of the body (especially the lower extremities), which is accompanied by slow weight gain.
Expert opinion
Nosova Yulia Vladimirovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
It also matters which eyelid swells. Swelling of the upper eyelid may indicate problems with digestion, heart and kidney disease, allergies and oncology. Swelling of the lower eyelid may indicate pathologies of internal organs that are not inflammatory in nature. If the lower eyelid swells in the morning, diseases of the heart and blood vessels, thyroid gland and kidneys are possible.
A child’s eyes itch: why and what to do
15.02.2020
Good day, dear parents. You may be interested in this article if your child has itchy eyes. You will find out what can provoke this condition. Find out what accompanying signs may be present. You will find out what measures need to be taken in such a situation, what prevention methods can be.
Possible reasons
The eyes may itch due to the heavy strain placed on them by reading books or watching TV for a long time.
- Manifestation of an allergic reaction.
In such a situation, itchy eyes may be accompanied by a runny nose or sneezing, a rash or redness. If parents know about the baby’s tendency to allergies and assume contact with an allergen, then this is definitely an allergy.
- The result of overexertion or fatigue.
A situation where a baby spends a lot of time in front of a monitor, TV, tablet or phone screen may cause his eyes to get tired, which he will rub. The same situation can occur in a child who reads a lot. - The presence of obstruction of the lacrimal canal. This reason may occur in infants. This condition will be characterized by a lack of wetting of the mucous membrane of the eyes with tears and their drying out.
- Penetration of a foreign object into the organ of vision can also be characterized by a sensation of itching. Especially if it is a grain of sand or dust that has penetrated behind the eyelid. In this case, redness of the mucous membrane and burning in the eye area may also be observed.
- The eyes may itch as a result of increased eye pressure.
Only an ophthalmologist can indicate this condition by conducting a special diagnosis. - The presence of diseases of the organs of vision, in particular conjunctivitis. If a child's eye is red and itchy, he probably has this particular disease. Sight or blepharitis may also occur.
- Styes can cause itching in the eyes, especially around them. However, this phenomenon will be preceded by swelling of the eyelid, albeit minor, and painful sensations.
Treatment
Depending on the cause of itchy eyes, treatment for the condition may include the use of eye drops.
It is important, before starting to take any measures, to try to determine what exactly triggered the itching in the eyes. Ideally, you can seek help from a doctor, who will prescribe special treatment, including, for example, applying ointment or using eye drops.
- If you know that a speck has gotten into your toddler’s eye, you can rinse the eyelid with a weak solution of black tea or put eye drops intended for children on the eye.
- If you determine that redness and itching appeared as a result of prolonged viewing of TV or the computer, then you need to protect your child from this. Determine the permissible time per day that will not overload the baby’s vision.
- If your toddler has an obstruction of the tear duct, you should consult a doctor. Perhaps the problem can be solved with special massage sessions or the use of eye drops. Sometimes the doctor prescribes more radical measures.
- If you suspect conjunctivitis, then only a doctor should prescribe treatment, since this disease can be triggered by various pathogens (viruses, bacteria, fungi) or be a consequence of allergies. The specialist will prescribe a special ointment or drops. For example, he may prescribe Tetracycline ointment or Albucid.
- If an allergic reaction is to blame, then the child is prescribed antihistamines. The doctor may also prescribe eye rinsing, for example, with chamomile decoction.
- If the whole point is the presence of a pathology such as blepharitis, then the child will need complex, long-term treatment. The doctor may prescribe, for example, Tobrex.
Features of washing
If you are sure that the child does not have a pathological process, and you understand that it is necessary to wash the eye in order to improve the condition of the little one, then you need to remember to follow certain rules.
- The procedure is recommended to be carried out after taking a bath.
- It is important that the baby is calm at this moment.
- Rinsing should be done while the little one is lying on the bed or sitting on a chair.
- Place boiled water or tea leaves into a clean container.
- As a disinfectant, you can use a weak solution of potassium permanganate or chamomile decoction.
- Rinsing should be done with a lukewarm solution, but not cold.
- You need to use a gauze or cotton swab, which you soak in warm liquid, and blot the child’s closed eyelids.
- At the end of the procedure, you need to blot the little one’s eyes with a sterile napkin.
Precautionary measures
Remember your child's hand hygiene
There are certain steps that parents can follow to minimize the risk of itchy eyes in their child.
- It is important that the child maintains hand hygiene. You need to understand that children who are actively exploring the world around them constantly touch various objects and can even pick something up from the floor, including on the street. Therefore, it is extremely important to prevent the child from rubbing his eyes with dirty hands. Make sure he washes his hands. And if your little one touches something outside, immediately wipe his hands with antibacterial wipes.
- It is important to control how much time your child spends in front of a TV or computer screen. It is worth remembering that there are certain age restrictions regarding being in front of a blue screen. You also need to take into account the fact that children who study at school spend a lot of time doing homework, including in class, and their eyes are already overstrained.
- Try to strengthen your child's immunity. Equally important in this matter is having a daily routine, proper nutrition, and healthy sleep.
- It is important to understand that when the first manifestations of a disease occur, you should immediately consult a doctor, do not delay, and do not risk the development of complications.
Now you know why a child’s eyes may itch. It is important to understand that the culprit may be either ordinary fatigue or the presence of allergies or a pathological process in the organ of vision. Therefore, if you have any doubts, it is better not to delay and visit a doctor.
Source: https://zdorovyemalisha.ru/zdorovye/u-rebenka-cheshutsya-glaza.html
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of the patient’s condition consists of several stages:
- Anamnesis collection. These are complaints from the patient or his close relatives. Most often they complain of severe swelling of the eyes, increased lacrimation, and pain. In the presence of a viral or infectious disease, body temperature rises.
- General inspection. The doctor determines the presence of swelling on the face; often the patient cannot open the eyelids completely. The affected eye may have profuse redness.
- Bacteriological culture. The method determines the type of bacterial pathogen that caused the infectious process, as well as the antibiotic to which it is sensitive.
- PCR. Using the method, you can determine the type of virus that caused the disease.
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine, blood biochemistry. During inflammatory reactions in the body, ESR and leukocytes will increase. Based on the tests, the doctor can suggest pathology of the cardiovascular system and kidneys.
- Allergen test. To do this, various types of allergens are applied to the patient’s wrist in the fall and winter. If redness or itching occurs in any place, this means that the immune system overreacts to this product and the child has an allergy.
- Examination of ocular tissues using a slit lamp. The doctor may detect the presence of a foreign object that needs to be removed.
- If the condition occurs in an infant before the fontanelles have healed, an ultrasound of the brain can be done. The doctor will confirm or deny increased intracranial pressure and other pathologies.
- ECG, ultrasound of the heart.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
After receiving all the data, the doctor makes a reliable diagnosis, after which therapy begins.
Alarming symptoms that require urgent medical attention are:
- The swelling does not go away within 2-3 days.
- Eyelids swell too often.
- Other eye symptoms occur: redness, pain, itching, blurred vision, lacrimation.
- Symptoms from other organs appear: pain in the heart, kidneys, urination problems, and others.

If the baby has only swelling of the eyelids without signs of diseases of the internal organs, then an ophthalmologist begins the examination. The doctor examines swelling under the child’s eyes and asks about the suspected causes and other possible diseases. Next, he conducts a more detailed examination of the visual organ.
If ophthalmological causes are excluded, then the child is referred to a pediatrician. Mandatory examinations are:
- UAC;
- OAM;
- blood biochemistry;
- ECG.
To diagnose the cause of swelling, it is worth making an appointment with a doctor to determine what changes have occurred in the body, and accordingly, prescribe competent therapy.
Expert opinion
Nosova Yulia Vladimirovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
The eyes constantly water or have other discharge. All this causes discomfort and provokes changes in behavior. Such a reaction of the body may indicate angioedema. Changes can be observed in the area of the fontanel - it increases in size.
If the baby has problems with urination, he feels a nagging pain in the lumbar region, he is haunted by a migraine - these are problems with the kidneys. The swelling does not go away within a day. Not only the doctor is involved in diagnosing the disease; in addition to the traditional visit, he will prescribe a number of mandatory tests, such as:
- blood, stool and urine tests;
- analysis of the secretion or pus that is released from the eye;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
If a baby has a problem with eyelid swelling, you should immediately contact a specialist, because this may signal the development of a dangerous disease. In any case, in order to normalize the child’s health, the root cause must be correctly determined. Therefore, it is inappropriate to delay this issue.
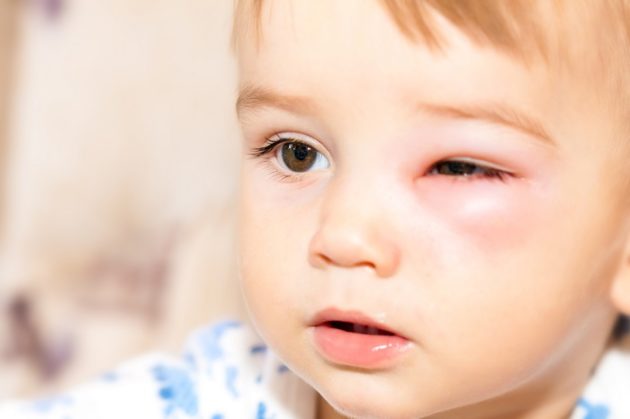
When symptoms of swelling of the eyelids are detected in a baby, it is forbidden to wait until everything “goes away on its own.” Depending on the location of the inflammation, one or another ailment is diagnosed. Initially, you should make an appointment with a pediatrician, who will prescribe treatment to relieve symptoms and write a referral to a specialist.
Diseases are diagnosed based on a visual examination of the patient and a series of examinations. The patient must undergo a general blood test, which can show the general condition of the body. If you suspect an allergy, it is recommended to take an allergy test.
The treatment regimen is selected individually in each case. For infectious diseases, the patient is prescribed a local and systemic antibiotic, as well as antiseptic solutions for washing the eyes. If the disease is caused by allergies, then antihistamines are indicated.
Since swelling of the eyelids can be caused by many different reasons, the most important measure for their prevention is medical examinations of the child. During the medical examination, it is important to identify hidden diseases and begin their treatment, as well as establish a predisposition to allergies. In addition, children need to follow the following recommendations:
- maintain an optimal daily routine (at least 8 hours of sleep, sleep during the day is desirable);
- sleep on a flat pillow, in a pre-ventilated area;
- take a walk in the fresh air every day;
- do not drink a lot of water at night.
Treatment
Puffiness of the eyes is only a symptom, and in order to relieve it, you must first eliminate the disease that caused this reaction of the body. If your baby’s eyes are swollen from lack of sleep or excess fluid, correcting the daily routine and reviewing the diet will help. It is recommended to adhere to several rules and tips.
- To reduce swelling, take a folded piece of gauze, soak it in warm water, and place it over your eyes. Do the procedure for 5 - 10 minutes several times a day.
- If there are lice on the baby's eyelashes (this happens), causing swelling, Vaseline, applied in a thin layer to the skin of the eyelids, can remove them.
- For a child with a genetic predisposition to puffiness, before going for a walk on a sunny day, it is advisable to apply a special cream to the eyelids that can protect against sun rays. Sunbathing is not recommended for such a baby. A cool compress will help relieve swelling that has already appeared.
- The child’s diet must contain all the vitamins and microelements necessary for the body (list of eye vitamins and their sources). Excessive drinking is also harmful, as is its lack. Pickles and marinades also have a significant impact.
- It is necessary to observe the sleep schedule and duration. The norm for children is 8 - 9 hours.
- The baby's eyes should be given time to rest. You should not allow too much strain on your vision created by modern gadgets. This is especially true for children aged 3-4 years, who can watch TV no more than half an hour a day.
For eye infectious diseases, such as conjunctivitis or blepharitis, drops (Levomycetin, Albucid) or ointment (Tetracycline 1%) are usually prescribed. But you can’t start treatment at home. A visit to a doctor is extremely important, since if treated incorrectly, the baby may experience complications.
Allergies and their consequences are usually eliminated by stopping contact with the irritant. A regular compress will help relieve swelling. In cases of a strong reaction, or if the child has been exposed to the allergen for a long time, antihistamines (for example, Diazolin) are indicated. Any serious ailments - high blood pressure, Quincke's edema or kidney disease - are treated exclusively according to the methods prescribed by the doctor.
Although puffiness of the eyes mainly appears in the morning, such a symptom can, in principle, occur at any time and not subside for quite a long time. You should not rely on the fact that it will pass sooner or later. The most effective help is the participation of a qualified specialist in solving the problem.
Complications
If therapy was not carried out in a timely manner or was completely absent, the child may experience the following complications:
- decreased visual acuity;
- hemorrhage in the cornea or inside the eyeball;
- transition of the infectious process to internal tissues or blood, which is dangerous to the health and life of the child;
- spread of the infectious and inflammatory process to neighboring tissues and organs, for example, the nasopharynx, sinuses;
- a critical rise in body temperature to 39 degrees or higher, when the child’s risk of seizures increases;
- systemic allergic reactions, for example, angioedema, which threatens the life and health of the child.
To avoid complications, you must consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease.
Treatment of a swollen eye in a child
The symptoms of all the above eye diseases are similar: swelling, puffiness, redness, itching, suppuration. The treatment of different pathologies is not very different; let’s look at some of them.
Barley on the eye quickly ripens and goes away with the use of eye drops and ointments with antibiotics, as well as due to warming up, for example, during physical procedures.
For conjunctivitis, tetracycline ointment, drops, herbal and manganese rinses relieve eye inflammation well.
If swelling caused by allergies appears under the eyes of children in the morning, the doctor will conduct tests to determine the causative allergen, and then prescribe treatment with antihistamines and avoid contact with the allergen.
Symptom treatment
Treatment is the main element of eliminating red eye symptoms as quickly as possible. If the situation is difficult, you need to give the child the opportunity to get a good night's sleep and also reduce visual stress during the day.
The following methods cannot be used during treatment:
- washing with saline solution or potassium permanganate;
- heating using a dry method (for example, using sand);
- instill half the dose of medicinal drops for prevention purposes.
Is it possible to solve the problem without medication?
First aid consists of washing the eyes with a neutral substance - clean water or miramistin. It is worth visiting a doctor in any case: this will eliminate the risk of possible complications. If the situation is acute, you must go to the hospital immediately. The doctor will decide whether to take medications.

Medicines
Medications are used for infectious and allergic processes that affect the mucous membrane of the organ of vision. Any medications are used strictly as prescribed by a pediatrician or ophthalmologist.
Drops
Most often, drops are prescribed for red eyes.
- "Albucid". Children are prescribed 20% drops. Their main component is sulfacetamide. It relieves redness. The drug can be instilled up to five times a day, 1-2 drops. If the dynamics are positive, the dosage is reduced.
- "Vitabact". Antimicrobial drops are often recommended for conjunctivitis. An antiseptic destroys pathogenic microorganisms. The product has a disinfectant effect.
- "Levomycetin" is used for inflammatory processes. Drops have an antibacterial effect. It is usually recommended to use no more than one drop at a time. Can be used from four months. The course of treatment can be carried out for up to two weeks.
Solutions
Among the ready-made pharmaceutical solutions for washing children's eyes, the following are used:
- "Furacilin". Dissolve one tablet in a glass of boiled water. Before use, carefully filter the composition through multilayer gauze.
- Miramistin is considered an effective antiseptic that can qualitatively clean the mucous membrane of the eye In ophthalmology, the lowest concentration of this active substance is used.
- Saline solution. Sodium chloride is classified as an injection solution, but this does not prevent it from being used for other purposes. Saline solution is a sterile saline solution. It is as close as possible to the various fluids of our body (tears, blood). For children, it is necessary to use a less concentrated composition diluted with water. Suitable for babies.
Ointments
Eye ointment is prescribed less frequently than drops. Nevertheless, it has a number of advantages: the product is resistant to changes in climatic conditions, completely dissolves under the influence of body temperature and does not irritate the organs of vision.
Disadvantage: after bookmarking, you need to maintain a time interval of 30-40 minutes, and only then perform some actions that require concentration.
- Tetracycline ointment. The therapeutic role of the drug is undergoing some changes: it has become more limited in modern medicine. Nevertheless, the ointment successfully fights various types of bacteria and relieves the inflammatory process. Prohibited for the treatment of children under eight years of age. During treatment, other local remedies should not be used.
- Erythromycin ointment is considered a mild antibiotic. It does not contain toxins, so it can even be used in the treatment of newborns. Prevents the proliferation of bacteria and kills viruses. The procedure for applying the ointment is performed up to three times during the day.
- Tobrex ointment contains an antibiotic from the group of glycosides that can cope with many types of bacteria. It is prescribed for children over one year of age. During use, you may feel a burning sensation or the presence of a foreign object in the eye. In this situation, you will want to rub your eye, which you should not do.
Folk recipes
If you can’t get an appointment with a specialist in the first hours, you can use folk remedies:
- Lotions made from cotton pads soaked in a decoction of medicinal herbs: chamomile, linden, mint, cornflower. Tea is also suitable, but it should be without flavorings or additives.
- Water compresses alternating warm and cool water. The liquid relieves dry eyes, and the coolness soothes them.
- Apply cucumber slices to sore eyes for 15 minutes.
- Peel raw potatoes and grate them. Lightly squeeze out the excess juice, place the pulp in gauze bags and make a compress.
- Warm milk is beneficial. Soak a cotton pad in the drink and wipe your eyes. This procedure can be done daily.
- Mix a tablespoon of boiled water with a drop of honey. When the beekeeping product is completely dissolved, add 2 drops of liquid to the eyes.
Folk remedies help if red eyes are the result of fatigue or an external irritant. In case of a serious illness, this will not bring results, but will only lead to short-term relief.
Useful video
Causes of red eyes in children and how to treat the pathology?
Prevention of eye diseases
To protect your child from diseases, including eye diseases, the following preventive measures are necessary:
- Hygiene of the baby's face and hands. You need to wash your child at least twice a day; you can also wipe your eyes with cotton pads from the outer to the inner corner of the eye. Wash your baby's hands more often and trim his nails promptly.
- Cleanliness of parents' hands - perform any actions with the baby, especially infants, only with washed hands.
- Maintaining optimal temperature and humidity in the room, regular ventilation, wet cleaning.
- Prevention of colds and viral diseases, timely vaccinations, measures to strengthen the immune system.
You can prevent swollen eyes in a child if you follow these recommendations:
- Use only a personal towel.
- Avoid places where blood-sucking insects accumulate or use special ointments for protection.
- Make sure that the child does not rub his eyes with his hands.
- If the child is prone to allergies, then exclude all allergenic foods from the diet.
You should not self-medicate; any medications should be given to a child only as prescribed by a doctor.
A swollen eye in a child can be caused by conjunctivitis or allergies. In this condition, the baby should be shown to a doctor, he will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
To avoid the appearance of swelling under children's eyes, you need to normalize your daily routine. The child should have proper rest, sleep at least 8 hours. It is recommended to add more fruits and vegetables to the diet, as well as to give the child multivitamins 2 times a day in preventive courses. Daily walks in the fresh air are required.
The appearance of swelling under the eyes among children may indicate the presence of diseases. Therefore, it is recommended to consult a doctor for examination, even if it seems to you that the swelling is not serious. Only a specialist can accurately determine what is normal and what is pathology.
Share the article with your friends on social networks. Tell us in the comments if your child had swelling under the eyes and what caused them. Health to you and your baby.
To prevent a disease that causes swelling of the eyes, you should follow these rules:
- the use of chemical insect repellents while in natural conditions;
- timely use of antihistamines if the child has allergies;
- the use of antibacterial drugs for the formation of suppuration in the eye area;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases, especially in the head area (sore throat, sinusitis);
- providing first aid for wounds and bruises.
Swelling of one eye occurs only in the presence of any pathology. It is necessary to begin treatment immediately to prevent possible complications. If the child’s parents cannot cope on their own, they should immediately contact a pediatrician.
- You should not buy dubious creams or other hygiene and washing products that may contain dangerous chemicals that cause swelling.
- If a child wants to try a new fruit or vegetable, it is better to give him a small slice, thereby testing for allergies. If after 2-3 hours no redness or swelling is detected on the skin, the new fruit can be given whole.
- When applying the cream to the face and body, be sure to remove any residue that has not been absorbed.
- Three hours before bedtime, it is advisable to limit pickles, sweets and various drinks.
- Before going to bed, it is advisable to ventilate the room and ensure the optimal percentage of humidity.
- It is better to sleep without a pillow or make it as flat as possible.
Useful video
Symptoms of the phenomenon when a child’s eyes are swollen and red
The eyes turn red due to violations of the integrity of the vascular network , which permeates the body of the eyeball, as well as when the capillaries dilate , especially if they are located close to the surface of the eyes.
As a result of negative effects from external factors, the area around the eyes with such problems may swell and swell.
In this case, the patient feels discomfort, burning and itching in the eye area , and sometimes such a disorder may be accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity.
This disorder may be more common in newborns , but it is very rarely a cause for concern.
Since mainly redness and swelling of the eyes can be observed due to the postpartum outflow of fluid and blood in the eye area.
For your information! Another reason is spasms of facial vessels due to pressure on the skull from the walls of the birth canal. In such situations, the condition of the visual organs will return to normal within a week on average.
But if this does not happen, it makes sense to examine the child for the presence of dacryocystitis (inflammation and blockage of the tear ducts).
Advice for worried parents
So, there are many reasons why swelling of the lower eyelid can occur. If swelling suddenly appears, it is important to rule out bites and injuries, and only then make an appointment with an ophthalmologist. It is not recommended to self-medicate, since if the problem lies in any diseases, over time the situation may worsen and lead to a deterioration in both general well-being and the functioning of the visual organs due to severe swelling of the eyelid.
Parents should analyze what their child ate the day before. Quite often the cause of illness is the use of new foods. You should visually inspect the baby's eye to see if small debris or an eyelash has gotten into the mucous membrane.
You can wash your baby's eyes with strong tea leaves or chamomile decoction. A solution of Furacilin or Miramistin is suitable for washing.
If your baby's eye is very swollen and his general condition is rapidly deteriorating, he should be shown to a doctor. Only a specialist can correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
If a child's eye suddenly swells up (literally in a matter of minutes), parents need to call an ambulance. If a child wakes up with swollen eyelids for several days in a row, the main thing for parents is not to panic, but to try to reduce the swelling. But, if the cause of swollen eyes is not clear to parents, then it is worth going to the doctor.
Caring parents, in order to prevent swelling of the eyes of their son or daughter, must follow some rules:
- Create a complete, fortified diet for your child. Nothing fatty or too salty, which causes fluid retention in the body.
- Provide the child with a daily routine with games, walks in the fresh air, daytime rest and a full night's sleep (at least nine hours).
- Consider hardening activities and physical exercises to strengthen the child’s body and organism.
- To prevent allergies, exclude foods that cause allergic reactions from baby food.

May the children always be healthy!
The child’s eyes are swollen and itchy: what to do, causes of redness
Children's eyes may itch from dust during a walk or from water when visiting a swimming pool. In this case, it is easy to cope with unpleasant consequences. But not all causes are so harmless, and to eliminate them may require treatment at home or in a hospital.
If the discomfort does not go away, you need to visit an ophthalmologist and find out why the child is scratching his eyes and how to help him. This condition should not be ignored, because if left untreated, the baby’s health condition may worsen.
Itchy eyes of a child: reasons
You can determine the factors that caused redness and itching around the eyes or the corneas themselves. In some cases, it is enough to rinse the affected area once or twice, and the discomfort will go away.
You cannot rely on this, because the same visual symptoms may indicate that a speck has entered and a developing pathology.
If a child constantly scratches his eyes, it is very important to correctly determine the cause of the itching.
Overexertion and lack of sleep
A common cause is redness and swelling around the eyes. It is necessary to reconsider the child’s daily routine. First, exclude watching TV, games and computer activities, knitting, embroidery.
When the symptoms pass, such harsh measures are not necessary, and you can devote up to half an hour a day to exercise. It is also necessary to ensure adequate sleep time. Children of primary school age should sleep 10 hours.
Allergy
Children, especially under the age of 7, are sensitive to the environment: emissions into the atmosphere, animal hair, pollen, odors, and the material from which toys are made. The body reacts with redness and itching of the eyes, a runny or stuffy nose, and watery eyes.
Obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculus
A congenital pathology in which the conjunctiva is not lubricated by tear fluid. The baby's eyes are constantly itching and redness is noticeable. The problem may disappear on its own by the time the baby is one month old or require medical intervention.
Drug treatment: what to do
If a child’s eyes are swollen and itchy, and the condition does not go away within 24 hours, you should go to the doctor to prescribe therapy. Minor problems can be dealt with on your own.
- Entry of a foreign body. You cannot remove the speck with your hands. A 10% Albucid solution should be instilled. If the foreign body does not come out with the drops, use a cotton swab or napkin. At night, treat the eyelids with Tetracycline eye ointment.
- Conjunctivitis. The course of treatment depends on the type and degree of manifestation of the disease. The doctor prescribes one or more medications:
- Albucid eye drops 5-6 times a day for a month;
Eubetal 5 times a day for up to a month;
- Vitabact 2-6 times a day for up to 10 days;
- Levomycetin 3 times a day, 1 drop for no longer than a week;
- Tsipromed 1-2 drops up to 8 times up to two weeks;
- Colbiocin only for children over 8 years old, 1-2 drops 3 times a day for 5 days;
- Okoferon every 2 hours for the first day, then 4 times a day for a week;
- Ophthalmoferon 1 drop 8 times a day, after symptoms decrease 3 times a day;
- eye ointments Vitabact 3 times a day, Oxolinic, Tetracycline, Erythromycin - at night.
- Allergy. For topical use in children over 4 years of age, the doctor prescribes Lecrolin 1-2 drops 4 times a day, Octilia 1 drop 2 times a day for 4 days, no longer. Additionally, Ketotifen may be prescribed 2 times a day, 1 tablet for 2-3 months. Syrup is recommended for babies under one year of age. In case of secondary viral or bacterial infection, the doctor supplements or completely changes the course of therapy.
- Obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculus. Vitabact drops can moisten the eyes of a newborn; probing the canal helps to completely solve the problem.
- Blepharitis. As soon as the child’s lower eyelids are swollen, itchy, and redness appears, you can use one of the drugs: Albucid, Eubetal, Vitabact, 1-2 drops each, then you need to consult a doctor. For treatment, atibiotherapy, taking vitamins, physiotherapy, and the use of antiseborrheic shampoos are prescribed.
- Barley. Infants are prescribed Albucid or Tobrex 1 drop 3 times a day. From the age of one, you can use Ciprofloxan, 2 drops every 4 hours, from three years - Sofradex. Drops are effective for advanced stages of barley. Prescribe 1-2 drops every 4 hours. Hydrocortisone and Tetracycline ointments help to cope with barley. They are recommended to be placed under the eyelid 3 times a day if the patient can stay at home.
You cannot prescribe medications to children on your own. Depending on the individual characteristics of the body, the components can cause a burning sensation and deterioration of the child’s general condition. Many cannot be used at the same time.