Good afternoon, many will be interested in understanding their health and their loved ones, and I will tell you my experience, and we will talk about Sputum in bronchial asthma. Most likely, some details may differ, as was the case with you. Please note that you should always consult with highly specialized specialists and not self-medicate. Naturally, you can quickly find the answer to the simplest questions and diagnose yourself. Write your questions/suggestions in the comments, and together we will improve and supplement the quality of the material provided.
Peculiarities
The characteristics of mucus always indicate a certain sign of disease. That is why it is advisable to conduct laboratory research.
Coughing up mucus may differ in several ways:
- Color (yellow, greenish-yellow, colorless, brown).
- Smell (normal, putrid).
- Consistency (viscous, liquid, thick).
Depending on the color and smell, the course of the disease (or concomitant infections) can be determined. For example, mucus that you cough up may turn green if your body has a respiratory tract infection. A putrid odor also indicates an inflammatory process in the bronchi or lungs. During an exacerbation of the disease, the secreted sputum has the appearance of molten glass, and therefore is called vitreous. However, it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis only by appearance; research is used for this.
Microscopy
For analysis, the sample is dried and placed on special laboratory glasses. After this, it is stained and the composition is analyzed for the presence of the following indicators:
- Bacteria indicate an infection in the body, which leads to complications of bronchial asthma.
- Alveolar macrophages – in obstructive asthma, macrophages with lipid droplets can be identified.
- Neutrophils - their increased number is characteristic of purulent sputum; in the endogenous form of the disease, neutrophils predominate.
- Fibrin - present during inflammatory processes, gives it viscosity.
- Eosinophils - present in sputum in exogenous (5-15%) and endogenous (5-20%) forms of the disease. This indicator decreases with treatment with corticosteroids, which makes it possible to analyze the effect of drug use on the course of the disease.
- Epithelial cells - the presence of columnar epithelium is normal as it lines the bronchi. If squamous epithelial cells are detected, it can be concluded that a small amount of saliva has entered the sputum.
In addition, the test sample may contain mucus, blood clots and nonspecific inclusions. The study involves the analysis of all indicators that are necessary to determine the form and course of the disease. If microscopy reveals that an inflammatory process is occurring in the body, the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostics to make an accurate diagnosis.
A patient with asthma is characterized by coughing up mucus, which fills the bronchi and is released there in large quantities. Sputum in bronchial asthma is usually difficult to cough up, this happens after an attack. To monitor the course of the disease, assess the effectiveness of medications taken and determine the severity of the disease, a sputum analysis is performed.

Diagnostics
If yellow sputum is present, the patient requires the help of a general practitioner or pulmonologist. During a physical examination of the patient, attention is paid to the participation of the chest in breathing, retraction of the intercostal spaces, and local areas of pain on palpation. Auscultation of the lungs provides valuable information - a preliminary diagnosis is made based on the presence of wheezing, harsh or amphoric breathing. The diagnostic scheme includes the following methods:
- X-ray studies.
On a survey X-ray of the chest in two projections, you can see areas of infiltration in the lungs, a round shadow with a horizontal fluid level, and local compaction. To diagnose tumors, a CT scan of the chest is performed. To confirm chronic bronchitis, bronchography is performed. - Endoscopy of the bronchial tree.
Bronchoscopy with visual examination of large and medium-sized bronchi is an informative method for diagnosing chronic inflammatory and fibrotic processes and detecting malignant tumors. During the examination, biopsies of suspicious tissue areas are taken for examination under a microscope. - Functional techniques.
In chronic diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, external respiration is impaired. To detect pathology, spirometry is prescribed, with the help of which the forced expiratory volume, vital capacity of the lungs, and other indicators are assessed. For express research, peak flowmetry is indicated. - Sputum tests.
The cytological method is aimed at identifying eosinophils and neutrophils, specific crystals and spirals of mucin in the tracheobronchial secretion. Culture with an antibiogram is used to determine the type of bacterial pathogen that caused the disease.
Additional diagnostic methods include a hemogram, which determines leukocytosis with an increase in ESR, eosinophilia, lymphopenia, as well as a biochemical blood test, which determines acute phase indicators and the ratio of plasma proteins. In chronic bronchopulmonary processes, heart function is often disrupted, so the examination plan includes an ECG and EchoCG.
Sputum analysis
Submission rules
To obtain material that is most suitable for analysis, the liquid for examination is collected in the morning immediately after waking up. At the beginning of an attack of bronchial asthma, sputum is collected in a special container. To get the most reliable sample you need:
- Collect sputum during an attack (this is the most comfortable way for the patient. If it is not possible to collect biomaterial in this way, inhalations are performed before the procedure, which facilitate coughing or percussion massage).
- The day before the test, you need to drink a lot of fluid (it thins the mucus and makes it easier to cough up during an attack of suffocation).
- Immediately before donation, it is necessary to rinse your mouth with an aqueous solution of soda (this is done in order to prevent microbes from entering the sputum from the mouth).
- Before starting the test, you need to take three as deep breaths as possible (this will allow the bronchi to open, which means it will be possible to collect more material for research).
Typically, the test requires three to five milliliters of sputum. It is also worth noting that the material for research is delivered to the laboratory no later than two hours after collection.
Sputum analysis for bronchial asthma is one of the diagnostic procedures. Examination of bronchial sputum allows the doctor to correctly select drug therapy for treatment. An analysis to determine how to derive a formula for competent treatment is also carried out during exacerbations to determine the reasons that caused the aggravation of the patient’s condition (bronchitis, pneumonia).
For a disease such as bronchial asthma, sputum is examined to determine the effectiveness of the therapy used.
Depending on the color and smell, the course of the disease (or concomitant infections) can be determined. For example, mucus that you cough up may turn green if your body has a respiratory tract infection. A putrid odor also indicates an inflammatory process in the bronchi or lungs. During an exacerbation of the disease, the secreted sputum has the appearance of molten glass, and therefore is called vitreous. However, it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis only by appearance; research is used for this.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Coughing up yellow sputum indicates serious damage to the respiratory system, so you should not delay a visit to the doctor. To relieve symptoms, the pus should drain unimpeded. To do this, it is recommended to take special drainage positions and massage the chest. It is forbidden to use antitussive drugs that contribute to the stagnation of pathological secretions in the bronchial tree.
Conservative therapy
In most cases, yellow sputum is purulent in nature, so patients need etiotropic antibacterial therapy. Medicines are selected empirically immediately after diagnosis of the disease, and after receiving the results of the antibiogram, the treatment plan is adjusted. Against the background of the destruction of pathogenic bacteria, purulent sputum ceases to be released. For pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment use:
- Expectorants
. They enhance the discharge of thick sputum and thin it, accelerating the sanitation of the bronchial tree. Thanks to the use of mucolytics and secretomotor drugs, recovery occurs faster. - Corticosteroids
. Hormone therapy is justified for eosinophilic lung disease. The drugs quickly stop the inflammatory reaction and reduce allergy symptoms. Glucocorticosteroids are used in the form of aerosols or parenterally. - Bronchodilators
. The production of yellow sputum in bronchiectasis or COPD requires the administration of beta-adrenergic agonists and anticholinergics. They are administered using nebulizers or spacers to ensure targeted delivery of the drug to the bronchi.
Surgery
In case of bronchiectasis and other chronic pathologies, when conservative measures are ineffective, they resort to therapeutic bronchoscopy and sanitation of the bronchial tree. After washing and removing the pus, the patients' condition improves. When lung diseases are complicated by pleurisy, a puncture is performed to remove exudate and targeted administration of medications.
Large abscesses, localized bronchiectasis, and areas of suppuration in the complicated course of Kartagener's syndrome are subject to surgical removal. If lung cancer is diagnosed early, radical surgery is performed in combination with radiation or chemotherapy. To alleviate the condition of cancer patients at stages 3-4, palliative interventions are indicated.
How to treat phlegm?
Any discharge of sputum is a pathology. It is necessary to clarify the exact cause of this symptom . Purulent and bloody sputum should cause particular concern. This is a situation when you need to see a doctor immediately. It is also necessary to see a doctor if you have been coughing up sputum for a long time - more than a month.

If there is a lingering cough after suffering from an acute respiratory viral infection, this is most likely a manifestation of acute tracheitis or bronchitis. In this case, the doctor will probably prescribe expectorant medications.
It should be noted that coughing with sputum does not always require medication. If uncomplicated bronchitis without signs of bacterial inflammation and bronchospasm is detected, sometimes drinking plenty of warm drink is enough to somewhat facilitate the natural clearing of mucus from the airways.
A comparative study was conducted on the effect of popular cough syrups in children compared to regular drinking. It turned out that these actions are approximately equal in effectiveness.
We recommend reading: Cholera: causes, symptoms, treatment, diagnosis and prevention
Drinking plenty of fluids is necessary for any cough. It has been proven that drinking plenty of fluids, especially alkaline drinks, has an effect comparable to the effect of expectorants.
If the sputum is thick, viscous, difficult to cough up and causes significant inconvenience, measures are taken to facilitate its clearance.
There are several types of expectorants:
- Drugs that directly or indirectly stimulate the secretion of bronchial glands.
- Mucolytics - change the structure of the mucus itself.
Reflex-action drugs, when taken orally, irritate the stomach receptors. In large doses they can cause vomiting, and in small doses they indirectly stimulate the secretion of the bronchial glands and the movement of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium through reflex connections. As a result, the proportion of liquid secretion increases, sputum becomes thinner, making it easier to remove and cough up.
The drugs in this group include mainly herbal remedies:
- Thermopsis herb and preparations from it.
- Marshmallow root and products containing it.
- Liquorice root.
- Anise fruit.
Ready-made preparations containing one or more expectorant components include: dry cough medicine, cough tablets (thermopsis herb + soda), breast mixture No. 1, breast mixture No. 3, glycyram, marshmallow syrup, mucaltin, ammonia-anise drops, breast elixir.
Direct expectorants are taken orally, absorbed into the blood and secreted by the bronchial glands, as a result of which the sputum is diluted. These include solutions:
- Iodine salts (2-3% solution of sodium iodide or potassium iodide).
- Sodium bicarbonate.
- Essential oils (used inhalation).
Mucolytics act directly on bronchial secretions , changing the structure of mucus and making it less viscous. These are the drugs:
- Acetylcysteine (ACC, ACC-long, Fluimucil).
- Carbocisteine (Fluifort, Bronchobos).
- Ambroxol (Lazolvan, Ambrobene).
- Bromhexine (Solvin).
- Enzyme preparations. They act directly on sputum proteins, depolymerizing it. These include trypsin, chymotrypsin, ribonuclease.
Mucolytic drugs are taken both orally and, in severe cases, parenterally (there are injectable forms of acetylcysteine and bromhexine for intravenous administration). These products are also available in the form of solutions for inhalation (for use in nebulizers). Enzyme preparations are used only by inhalation.
Sputum discharge and provoking diseases
Bronchial asthma
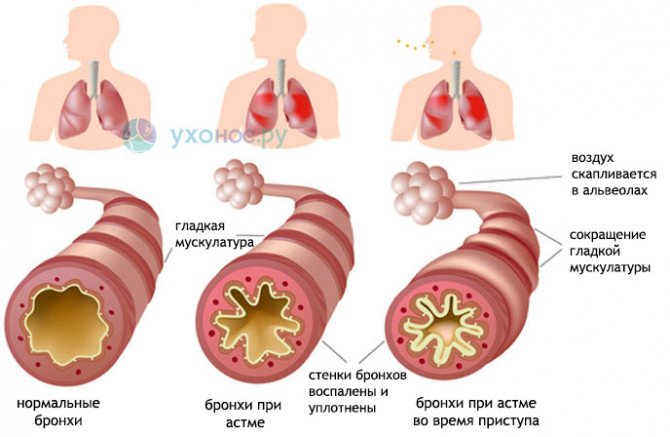
Sputum in bronchial asthma is a variable symptom. It is formed in the bronchi as a component of allergic inflammation and is an additional factor (in addition to bronchospasm and swelling of the mucous membrane) in the narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi during an attack of suffocation.
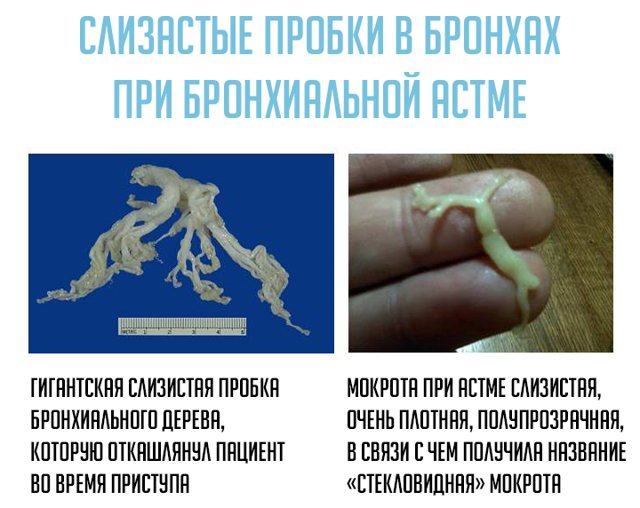
As a rule, after she clears her throat, the condition improves and the attack of suffocation passes. Sputum in bronchial asthma is thick, viscous, mucous in nature. May be yellow in color due to admixture of eosinophils.
Carrying out analysis
The exudate is submitted to the laboratory, where its detailed analysis is carried out: physicochemical properties are assessed, and the cellular composition is examined. Based on the data obtained, treatment is prescribed with mandatory consideration of the type of microflora detected.
The process of examining a sample of material for bronchial asthma usually lasts at least three days from the moment it is submitted to the laboratory. Among the peculiarities of assessing the material: the color of the discharge and impurities plays a huge role, among which, in severe cases, one can see fragments of tissue from the wall of the bronchial tree.
Decoding the results
In the result obtained, the laboratory assistant must indicate the cellular composition of the material, which determines the nature and nature of the disease:
- with an increased content of red blood cells, vascular damage can be assumed due to a destructive process in the tissues of the respiratory tract;
- a large number of eosinophils in the mucus is characteristic of bronchial asthma, they indicate its allergic nature;
- Charcot-Leyden crystals indicate the allergic process and its progression;
- the amount of ciliated epithelium increases with bronchial obstruction or inflammation of the bronchi;
- Kurshman spirals in the analysis are a pathognomonic sign of asthma, indicating bronchospasm and accumulation of thick secretion in the lumen;
- macrophages in the mucus discharge confirm the diagnosis of asthma.
Sputum analysis: conducting research
Sputum analysis is one of the main tests in clinical laboratory diagnostics. To collect it for analysis, use special plastic containers with a lid. It is advisable to collect sputum in the morning before eating, after thoroughly rinsing your mouth and throat with boiled water. The collected portion must be delivered to the laboratory as quickly as possible.
In addition to determining the color and nature of sputum, microscopy is also performed during general clinical analysis. Microscopy can reveal:
- Cells of the bronchial epithelium (cylindrical). Detected in bronchitis, tracheitis, bronchial asthma.
- Squamous epithelial cells. This is the epithelium of the oral cavity and has no diagnostic value.
- Leukocytes. There are small amounts of them in any sputum. During purulent processes, a large number of neutrophils are detected, and during allergic inflammations - eosinophils.
Red blood cells. Their number matters. Detection of more than two or three in a smear requires further examination.- Atypical cells in tumors.
- Kurshman spirals – for bronchospastic diseases.
- Pathogens: Mycobacterium tuberculosis, actinomycetes, echinococci.
To detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis, an analysis of at least three portions of sputum is required.
To identify these and other pathogens, bacteriological examination of sputum is also used: sowing it on special media, culturing it, followed by studying the resulting colonies of microorganisms. This analysis takes several days, but has great diagnostic value, and also determines the tactics of further treatment with antibacterial drugs.
- Iodine salts (2-3% solution of sodium iodide or potassium iodide).
- Sodium bicarbonate.
- Essential oils (used inhalation).
Submission rules
To obtain reliable results, the analysis of biological material from a patient with bronchial asthma must be carried out in strict compliance with certain rules. So, it is necessary to prepare the container and disinfect it. This should be done by a competent healthcare professional.
The substance is taken in the morning. At this time, the bronchial tree is filled most completely. The collection can also be carried out during an attack. In any case, the day before the test the patient should drink a lot of clean water.
It is also important to follow these rules.
- If there are problems with the discharge of exudate, inhalation and percussion massage are required.
- In difficult situations, a catheter should be used.
- Immediately before the procedure, the patient should rinse his mouth with boiled water and soda.
Sputum collection
Mucus is collected during coughing. Collection containers must be sterile. It is better to buy a special plastic jar at the pharmacy. It is easier to do this in the morning, because the phlegm was not removed from the bronchi all night. In order to make a general analysis, you need to collect at least 3-5 ml of mucus.
Since sputum in asthma is weak, the following procedures are first performed:
- The day before the general test, drink a lot of fluids so that the mucus comes out more easily.
- Before the procedure, use an inhaler or perform a percussion massage.
- At the beginning of the collection, take three deep breaths.
Sputum analysis
The study of bronchial substances in asthma is a mandatory procedure. This way it is possible to determine the number of eosinophils. Thanks to this, it is possible to give an accurate assessment of the condition of the bronchi and determine whether there is an infection in the respiratory system.
The analysis involves bacterioscopic, cellular, microscopic and chemical examination of the components of sputum. If necessary, additional studies are prescribed.
In a healthy person, mucus is coughed up or swallowed without difficulty. In smokers, patients with pneumonia or bronchitis, biological material is coughed up. This condition is considered normal. No more than 100 ml should be released per day.
Kurshman spirals are important research criteria. This way it is possible to find out about spasm of a large bronchus due to increased viscosity of mucus and the progression of the allergic process.
What is sputum
Sputum is a biological mixture consisting of accumulated tracheobronchial secretions, saliva, mucous fluids of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Saliva and mucus formed in the nasal cavity have pronounced bactericidal properties, while the formation of bronchial and tracheal secretions is aimed at cleansing the body of cellular metabolic products.
The volume of tracheobronchial secretion produced varies from 10 to 100 ml per day. It is worth noting that with normal functioning of the respiratory system, all mucus produced is swallowed.
The appearance of mucus stagnation is associated with:
- increasing the amount of synthesized secretion;
- changes in the composition of mucus due to the development of inflammatory processes in the bronchi (allergies, infections);
- disruption of the mechanism of fluid release from tracheobronchial structures.
In the case of the development of an acute inflammatory process, a weakening of the ciliated epithelium is observed, leading to the formation of congestion in the bronchi.
Types of sputum in asthma and ways to remove it
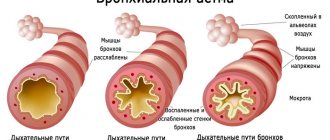
Bronchial asthma is a serious pathology of the respiratory system of an inflammatory nature.
With this disease, swelling of the nose and pharynx is observed, sputum accumulates in the lumen of the bronchi, which interferes with the normal passage of air.
This leads to difficulty breathing and shortness of breath, which worsens with physical exertion. Excessive accumulation of mucus causes attacks during which the patient coughs violently and feels suffocated.
Normally, the cells of the bronchial lining produce a small amount of mucus. A healthy person produces 100-150 ml of secretion per day. It is needed to protect the bronchi from the penetration of dust, germs and other toxic substances. The mucous membrane of the bronchi has small cilia that protrude into their lumen. They push excess mucus from the bronchial lumen into the pharynx.
Normally, this secretion is quietly swallowed by a person without causing discomfort. This happens day after day throughout life and is considered normal. Sputum in asthma is dangerous for humans, since when it accumulates, the lumen of the bronchi narrows and the passage of air becomes difficult.
We recommend reading: Detralex and alcohol: compatibility, consequences of interaction
Bronchial asthma is characterized by increased mucus production. In this case, the bronchial lining becomes inflamed. Asthmatic bronchitis develops. The patient complains of sputum discharge during coughing and a feeling of chest congestion. Mucus can be of different colors, smells and consistency.
The discharge looks different - it depends on the course of the disease. They are often viscous. Sputum in bronchial asthma may resemble ordinary mucus and contain pus or blood. The smell may also vary.
You need to take unpleasant-smelling discharge especially seriously. They may indicate the presence of other diseases of the respiratory system, such as tumors that are in the process of decay.
In addition, it may be purulent sputum formed as a result of a bacterial infection.
Bronchial asthma is characterized by a progressive course. As the disease progresses, the amount of sputum increases, leading to blockage first of the small bronchi - bronchioles, and later of the large bronchi. This leads to difficulty breathing in the patient. Often during an attack he begins to choke. This condition is life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
Yellow or yellow-green discharge indicates an infection. For colds and allergies, they are often transparent. The appearance of sputum streaked with blood indicates a rupture of a small vessel in the lung tissue.
Also, this type of discharge may appear with the development of complications, such as inflammation or pulmonary edema, tuberculosis.
- In this regard, if you have difficulty breathing and the discharge of such sputum, you should urgently consult a doctor and begin treatment.
- Transparent sputum that is released for a long time also requires determining the cause, since if it is ignored, other serious ailments may develop.
- Sometimes a large amount of liquid mucus and cough are observed in a person who smokes.
In this case, it is almost impossible to get rid of annoying symptoms, but often they do not increase and are not complicated by other diseases.
This is due to the characteristics of the body. During the night, a large amount of secretion accumulates in the lumen of the bronchi. To collect it at the pharmacy you need to buy a special container.
The resulting secretions are examined in the laboratory. The ease of mucus removal depends on its consistency. If the bronchi are filled with viscous mucus, it will be difficult to cough up. Poorly discharged secretions must be liquefied.
This can be done in various ways.
It is also important to follow these rules.
Information content of diagnostics
To collect sputum, you should prepare a container in advance by disinfecting it. The procedure is performed after waking up in the morning, when the filling of the bronchial tree with exudate is maximum.
Bronchial asthma is a complex disease of the respiratory system, which in most cases takes a chronic form. If treatment is not started in time, the disease can lead to disastrous results. Therefore, it is very important to take certain tests to control the process.
Sputum analysis is mandatory for diagnosis, with which the doctor can determine the number of eosinophils. Their indicator will allow you to give an accurate assessment of the condition of the bronchi and the presence of infection in the respiratory system.
The sputum itself will allow you to study the mucus to identify bacteria and the presence or absence of pus. In addition, if the patient has frequent and severe attacks of suffocation, there may be blood present. An increased number of neutrophils in the mucus also indicates the severity of the disease.
Sputum analysis
Using this diagnostic method, the doctor determines the presence of bronchial asthma in the patient. Laboratory studies of mucus include determination of its physical components, cytology and bacterial composition.
In a healthy person, sputum can be easily coughed up or swallowed. People who smoke, as well as those with bronchitis or pneumonia, expectorate sputum. This is a normal indicator and should not cause concern. If the amount of discharge does not exceed 100 ml per day, the condition of the large bronchi and trachea is normal.
Mucus is an important component for the body. It not only performs a protective function, but also helps remove small particles that a person inhales from the respiratory system, and also helps cleanse the bronchial system.
If pathologies are detected during laboratory tests, the patient has asthma attacks with a small amount of sputum, the doctor diagnoses asthma. Therefore, sputum analysis is one of the main indicators that indicates the presence or absence of the disease.
Analysis may be prescribed in the following cases:
- if the patient suffers from a prolonged cough with sputum production;
- if bronchitis, pneumonia and other diseases associated with the respiratory system are diagnosed;
- if a patient is suspected of having tuberculosis;
- if there is a suspicion of the presence of malignant tumors.
Important! A patient suspected of having asthma must undergo a sputum test.
What is sputum in bronchial asthma
In most cases, it has a viscous consistency with the presence of mucus, a small amount of pus or inclusions of blood. Most often, it has an unpleasant odor, which is associated with the decay or growth of malignant tumors.
In severe forms of the disease, there is quite a lot of mucus , as a result of which it causes blockage of the airways, provoking an attack. If in case of colds it has a transparent tint, in case of asthma it is yellow or greenish. In some cases, blood clots may be present.
Important! If the mucus has an odor, there is a high probability of malignancy.