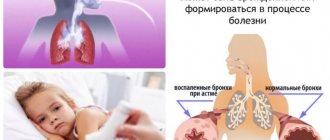
With bronchial asthma, the lungs and bronchi are actually clogged with mucus. This leads to disruption of physiological breathing and many problems. It is difficult for an asthmatic to both inhale and exhale. In addition, attacks of suffocation occur from time to time. During such a period, a person cannot breathe normally, there is a lack of oxygen, he coughs heavily, and the skin becomes bluish. Shortness of breath in bronchial asthma is the most pronounced symptom of the disease . At the very beginning of the disease, shortness of breath is not very pronounced, and it goes away in a matter of minutes. But as the disease progresses, shortness of breath becomes intense and frequent.
Classification and nature of shortness of breath
The severity of shortness of breath directly depends on the severity of the symptoms and the extent of the process.
There are 2 forms of shortness of breath:
Inspiratory
In this case, the nature of shortness of breath is expressed by difficulty in inhaling and develops with reflex spasms of the glottis, penetration of a foreign body into the respiratory tract, edema and tumor-like neoplasms of the trachea and larynx. In this form of the disease, breathing is called stridorous (noisy).
Expiratory
This symptom occurs as a result of narrowing of the bronchial lumens and most often occurs with bronchial asthma. In the case when the disease takes a chronic course, expiratory dyspnea is classified into several subtypes:
temporary - this type of shortness of breath most often occurs in patients suffering from acute lobar pneumonia, in which the inflammatory process spreads over a large area of the lung. This leads to the exclusion of a significant part of the lung from the respiratory process and poses a serious threat to the patient;
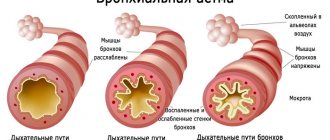
constant - this type of disease is observed in the presence of chronic processes in the lungs (emphysema, etc.); obstructive - the nature of the violation of this type of shortness of breath is closely related to the ventilation function of the lungs, when increased resistance to air movement causes a disturbance in the conductivity of the bronchi. The obstructive type of shortness of breath can appear at complete rest, characterized by slow and difficult exhalation.

If swelling of the mucous membranes of the trachea and larynx is associated, shortness of breath may be accompanied by a barking cough and a hoarse voice. If the nature and type of shortness of breath changes dramatically, resulting in cyanosis (blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle), urgent treatment should be started due to the likelihood of developing obstruction in the airways.
What it is
Shortness of breath is a purely subjective sensation of a person, but the complaints of patients are approximately the same: not enough air, a feeling of tightness in the chest and the inability to breathe in with full lungs.
According to clinical symptoms, shortness of breath is defined as an increase in the number of respiratory movements over 18 per minute (with the norm being 16-20) with a mandatory increase in the depth of inspiration.
A healthy person usually does not pay attention to how he breathes, thinking about this process only when breathing becomes difficult in some way.
At the same time, shortness of breath can be present in healthy people normally if they perform any physical activity.
If we are talking about performing standard actions (getting out of bed, walking slowly, self-care) or a state of rest, which is accompanied by shortness of breath, then we are talking about pathological processes in the human body.
Mechanism of development of shortness of breath
The type of asthmatic disease and symptoms depend on its nature. The cardiac form of asthma is expressed by insufficient activity of the cardiac system and appears as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the pulmonary artery. The result of these manifestations is inspiratory dyspnea.
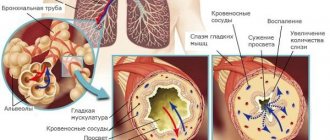
Bronchial asthma occurs as a result of narrowing of the lumens in the bronchi. The nature of the narrowing depends on the swelling of the mucous membrane in the lower respiratory tract, due to which the secretion of sputum increases. It acquires increased viscosity and is difficult to remove. The result of this is expiratory dyspnea.
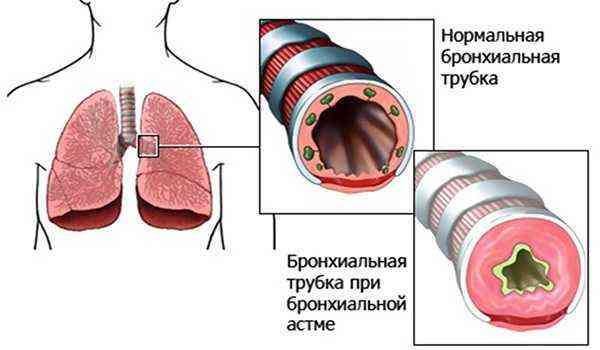
In asthmatic bronchial disease, the type of shortness of breath is characterized by a short, easy inhalation and a noisy, difficult exhalation. However, with drug therapy aimed at dilating the bronchi, respiratory activity quickly normalizes.
An attack of suffocation may occur after contact with allergens. In severe cases of the disease, the attack cannot be stopped with the help of bronchomimetics, resulting in loss of consciousness. The allergic type of asthma is the most dangerous for the patient and requires emergency treatment.
Treatment
Treatment of shortness of breath is primarily aimed at eliminating or relieving attacks of bronchial asthma. There are many methods of using medications, health procedures and physiotherapy. Only the doctor decides which technique to use for each patient , taking into account the diagnosis, causes and symptoms. The use of traditional medicine should also be carried out under the supervision of a physician.

To avoid exacerbations and to reduce shortness of breath, the patient should:
- exclude any contact with allergens;
- carry out wet cleaning of the room up to 2 times;
- stop smoking;
- do gymnastics, swimming, walk as much as possible;
- treat colds in a timely manner;
- Regularly observe personal hygiene rules.
Shortness of breath is a manifestation of bronchial asthma. It can occur in an acute form or increase gradually. To avoid complications and not put your health at risk, every patient should consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Symptoms of the disease
Shortness of breath, as an independent symptom, may be accompanied by other manifestations, among which the most common are:
subfebrile (38°C - 38.5°C) body temperature, which can rise sharply to high levels;
increased fatigue; the patient's appearance is apathetic; fatigue and weakness;

increased sweat production; dry cough or, conversely, with copious sputum; tingling pain in the chest area.
In addition, general symptoms of intoxication are characteristic.
Danger of shortness of breath
Dyspnea, as an independent phenomenon, cannot threaten the patient’s body, since it refers to the external manifestations of bronchial obstruction. Moreover, its treatment requires the use of special anti-asthma drugs, which quickly relieve both shortness of breath and bronchial symptoms caused by the disease.
It is much worse when the nature and type of shortness of breath intensifies during treatment, causing severe suffocation. Such symptoms indicate the transition of an asthma attack to status asthmaticus. As a rule, with the normal development of an attack, treatment of obstructive phenomena is stopped as quickly as possible with short-acting drugs (Salbutamol, Fenoterol, etc.).
As a result of status asthmaticus, a short-term improvement in the patient’s condition is determined, but shortness of breath, despite treatment with inhalers, cannot be completely neutralized. After a few hours, the attack may recur and be more severe.
Status asthmaticus is a life-threatening condition that can occur as a result of contact with allergens, with the sudden withdrawal of glucocorticosteroid anti-asthmatic drugs. The nature of status asthmaticus may change as a result of an overdose of an inhaled adrenergic agonist.
With the development of an asthma attack, increased blockage of the bronchial ducts occurs, the nature of respiratory disorders can be expressed by cyanosis of the skin, especially the nasolabial triangle. In addition, the face becomes pasty, the heartbeat quickens and there is a sharp rise in blood pressure. Subsequently, shortness of breath turns into shallow breathing, which is not able to saturate the body with oxygen fully. Blood pressure drops sharply and there may be a loss of consciousness to a complete coma, which leads to disruption of body functions and, as a result, to death.
In order to effectively treat shortness of breath, it is necessary to understand what causes this type of symptomatology. It is important to find out exactly what disease provoked its occurrence. Without finding out the reasons, quality treatment is impossible. In addition, incorrectly performed treatment measures as a result of an undetected cause of shortness of breath can cause irreparable harm to the patient.
Therapeutic measures
Drug therapy should be prescribed only by highly qualified specialists (therapist, pulmonologist, infectious disease specialist, cardiologist, etc.). In addition, treatment with traditional methods is not recommended, as they may be ineffective.
When a bronchial attack begins, you should follow the recommended actions:
Before the medical team arrives, the patient should be provided with fresh air by opening or opening the window. You can loosen tight clothing and give the patient the most comfortable position;

Treatment of bronchial asthma requires lifelong medication. Sometimes hormonal drugs containing glucocorticosteroids may be prescribed; if the bronchial attack is of the asthmatic type, in the absence of inhalers, etc. intravenous administration of 2.4% Eufillin solution is prescribed. The drug should be administered very slowly.
It is recommended to begin treatment of asthmatic disease with the introduction of dosed inhalations of selective beta-agonists with the shortest possible effect (Salbutamol, Berotec, etc.).
This requires compliance with certain rules:
It is not recommended to do more than two “injections” in a row. It is necessary to take at least a 20-minute break between inhalations. More frequent use of aerosols will not lead to a positive effect, and side effects may increase, such as rapid heartbeat, changes in blood pressure, etc. If the nature of shortness of breath changes, you should not wait for the onset of a severe attack and the associated risk. Appropriate measures must be taken immediately.

It is not recommended to exceed the daily dosage of the inhaler. Continuous use should not exceed 6-8 breaths. More frequent use of an inhaler during prolonged suffocation can be dangerous. This condition can develop into status asthmaticus, which is quite difficult to control even with the help of intensive therapy.
The main condition is timely prevention of various complications. To do this, it is recommended to seek help from highly qualified specialists and not to self-medicate, wasting valuable time. Only an integrated approach and regular medical examinations help to maximize the preservation of health and prevent disability of the patient.
Bronchial asthma (BA) is a chronic inflammatory process that occurs in the respiratory tract (mainly in the bronchi) and is manifested by attacks of suffocation. Patients with asthma are characterized by increased bronchial reactivity in response to various irritants, which in most people do not cause such reversible bronchospasm. The specific type of shortness of breath in bronchial asthma and its nature are one of the main criteria for suspecting the development of a chronic pathological process.
Why is it important to ask for help?
Asthma has a chronic course and its danger lies in complications that develop as the condition worsens. With the help of modern pharmacological agents, it is possible to successfully control the pathology and achieve stable remission. If no measures are taken to treat and control the disease, the patient will eventually be hospitalized in a serious condition called status asthmaticus.

Modern medicine has an impressive list of all kinds of inhalers. However, they are not suitable for permanent use. Otherwise, a person will get used to a certain medication, and the respiratory organs will simply no longer respond to it. The patient will eventually relapse into status asthmaticus.
Causes of the disease
There are many factors that can trigger the development of the disease. Conventionally, they are divided into two large groups:
Exogenous Widespread and sometimes irrational use of antibiotics, serums, vaccines, etc. Features of the climatic zone (abundance of flowering plants, damp climate, etc.). Environmental pollution. Widespread use of household chemicals, synthetic food additives, etc. Endogenous Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system (bronchitis, pneumonia, etc.). Hormonal imbalance. Malfunctions of the immune system. Genetic predisposition and much more.
Main forms of the disease
There are several variants of AD based on origin:
Allergic asthma, which occurs in patients with a history of allergic reactions, usually appears in childhood and adolescence. It is characterized by positive tests for allergens, as well as a history of other allergic diseases (urticaria, atopic dermatitis, etc.). Non-allergic asthma begins in adulthood. The causative allergen cannot be determined, and the triggering factor is a previous infectious disease. Mixed asthma combines the manifestations of the two above options.
Taking into account all the clinical symptoms of asthma, the severity of the disease is distinguished:
MildEpisodicPersistentModerateSevere
Clinical signs and symptoms of the pathological process
The picture of the disease is varied: from episodic mild symptoms to severe attacks of suffocation. The key manifestations of the disease are:
Shortness of breath is a change in the depth, rhythm, and frequency of breathing, which is felt as a lack of air. The nature of shortness of breath in bronchial asthma is expiratory, i.e. it is difficult for the patient to exhale.
The reason for the development of this type of shortness of breath is reversible bronchial obstruction. When the reagent enters the respiratory tract, the mucous membrane swells and a spasm of the smooth muscles of the bronchi occurs, so inhalation is easy, but exhalation, due to the narrowing of the bronchi, is difficult. After some time, the spasm goes away and breathing is restored. With the long-term existence of the disease, irreversible changes occur in the walls of the bronchial tree, which are manifested by constant specific shortness of breath, expressed to a greater or lesser extent.
Attacks of suffocation. During an attack, the patient takes a characteristic position: sitting with his arms raised up. The auxiliary muscles of the abs and shoulder girdle begin to participate in the breathing process. Wheezing. As asthma attacks develop, wheezing is heard, which occurs due to spasm of the smooth muscles of the bronchi. In case of severe obstruction of air passage through the respiratory tract, wheezing may be absent. Dry, hysterical cough. At the end of a coughing attack, a small amount of viscous sputum is sometimes released, in which specific mucus and casts of small bronchi can be seen.
There is a variant of asthma, the key symptom of which is cough. This type of disease is more common in childhood; symptoms manifest themselves at night with bouts of coughing with a scanty amount of sputum.
Pain and discomfort in the chest area occur during prolonged, severe attacks.
Modern drugs: how to treat the disease in adults
To treat the disease, medications are used that can be divided into two groups: emergency medications to relieve bronchial spasm, and medications to control the course of the disease and the frequency of exacerbations.
To relieve an attack
Bronchodilator therapy in the treatment of asthma is symptomatic and does not affect the course of the disease and the number of exacerbations, but effectively relieves the symptoms of asthma attacks .
The frequency of use of bronchodilators ranges from 2-3 times a day to 1 time every few weeks (as needed) depending on the severity of the pathology and is an indicator of the effectiveness of basic treatment . To quickly achieve the desired effect, these medications are used in the form of inhalations.
REFERENCE! When choosing how and what to treat the disease in adults, it is worth considering that some drugs have properties that treat shortness of breath that worsens at night.
The following groups of drugs are used to relieve bronchospasm:
- Short-acting and long-acting beta-2 agonists . The therapeutic effect of compounds of this group is due to the interaction of the active substance with beta-2-adrenergic receptors located in the walls of the bronchial tree, as a result of which smooth muscle fibers relax, the lumen of the bronchi expands and air conduction improves. They also slightly increase the vital capacity of the lungs.
- Theophyllines . Rapid-acting theophyllines are used to relieve an asthmatic attack. Due to the connection with adenosine receptors, relaxation of the smooth muscle fibers of the walls of internal organs, including the bronchi, increases the tone of the respiratory muscles and dilation of blood vessels in the lungs, which increases the oxygen content in the blood. Theophyllines also prevent the release of active proteins from mast cells, which prevents further swelling and spasm of the bronchi.
- Anticholinergics. The principle of action of these drugs is based on the connection of the active substance of the drug with m-cholinergic receptors, their blockade and the cessation of the passage of nerve impulses, due to which the tone of the muscular component of the bronchial wall decreases, it relaxes and the reflex contraction is suppressed. Anticholinergics also have a positive effect on mucociliary clearance, which facilitates sputum discharge after relief of spasm.
Salbutamol

Available in inhalation form and is an effective remedy for relieving acute spasms, since the therapeutic response develops within 3-5 minutes after use .
The duration of action of Salbutamol is 4-6 hours (short-acting bronchodilator).
Used to relieve an attack of suffocation, as well as to prevent its development associated with contact with an allergen or increased physical activity.
IMPORTANT! Contraindicated in early childhood (under 2 years) and in the presence of allergic reactions to any component included in the composition. It is prescribed with caution to persons suffering from decompensated cardiac, hepatic or renal failure, heart defects, pheochromocytoma and thyrotoxicosis.
Reference! Use during pregnancy and lactation is permitted if the benefit to the mother's body outweighs the possible risk to the child.
Directions for use in adults: 2 inhalation doses (200 mcg) up to 4 times a day. To prevent the development of bronchospasm associated with physical effort: 1-2 inhalations 15-20 minutes before exercise.
Berotek
Included in the list of drugs is an inhaled short-acting beta-2 agonist produced by a German pharmaceutical company. The effect is observed 2-3 minutes after inhalation and lasts up to 6 hours. Used for the symptomatic treatment of bronchial asthma and to prevent the development of asthma associated with increased physical effort.
Important! If the therapeutic dosage is exceeded or used more than 4 times a day, it affects the myocardium, slowing down the heart rate.
One inhalation dose contains 100 mcg of the active component fenoterol. To relieve bronchospasm, 1 dose is used; if the effect develops slowly, inhalation may be repeated after 5 minutes.
IMPORTANT! Contraindicated in cardiomyopathies, diseases accompanied by cardiac arrhythmias, decompensated diabetes mellitus, closed-angle glaucoma, threatened abortion, and the first weeks of pregnancy.
Atrovent
A noticeable effect occurs 10-15 minutes after use and lasts up to 6 hours.
Important! Atrovent is contraindicated in children under 6 years of age, in the first trimester of pregnancy, and in those who are allergic to the components of the drug.
The active ingredient is ipratropium bromide, per inhalation dose there is 0.021 mg of the compound. Use 2 inhalations as needed up to 6 times a day.
Theotard
It is a derivative of xanthine and belongs to the theophylline group, available in capsule form. It has a prolonged release and is therefore suitable for preventing bronchospasm at night and in the morning .
IMPORTANT! Prescription is prohibited during pregnancy and lactation, for epilepsy, acute myocardial infarction, ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract and in children under 3 years of age.
Since the bronchodilator effect occurs gradually, reaching a maximum 2-3 days after the start of taking the drug, Theotard is not used to relieve acute bronchospasm.
Approaches to diagnosing asthma
Reliable diagnosis of bronchial asthma occurs by excluding other diseases that give similar bronchospastic symptoms.
Sometimes the doctor makes a diagnosis only on the basis of the clinical picture, specifying what kind of shortness of breath with bronchial asthma worries the patient. Other points are also important:
Does the patient have a cough at night? Are there cases of wheezing? Does the patient’s condition worsen (cough, shortness of breath) when in contact with respiratory tract irritants? Does physical activity increase the severity of the condition? Is the attack controlled by taking anti-asthmatic drugs, etc.
One or more positive answers give the doctor reason to suspect the presence of a disease and conduct a more detailed diagnosis, which includes:
Typical patient complaints, a history of bronchial asthma in relatives, other allergic diseases (hay fever, atopic dermatitis, etc.). Allergy tests, determination of IgE levels. Microscopic examination of sputum. The presence of eosinophils, Kurshman spirals (areas of small bronchi), Charcot-Leyden crystals (decomposition products of eosinophils). Determination of changes in the values of the external respiration function. With the help of special equipment, the vital capacity of the lungs, the volume of forced inhalation and exhalation and other parameters characterizing the function of external respiration are determined, and the data obtained are compared with the norm. Clinical examination. Allows you to record typical expiratory shortness of breath, listen to wheezing and identify changes in the bronchi. If necessary, X-ray diagnostics or CT scan of the lungs are performed to exclude other pathological conditions accompanied by similar symptoms.
In the early stages, with scanty manifestations of the disease, tests are performed with bronchodilators, which make it possible to identify reversible bronchial obstruction. In case of an allergic form of the disease, skin tests can be performed to determine the causative allergen.
Aerosol – “helper” for shortness of breath
In case of shortness of breath or its more severe degree - an attack of suffocation, it is effective to use metered aerosols. Try not to succumb to panic attacks and then you will be able to restore your respiratory function.
The dosage of medicine in aerosols and their need during the day is individual and depends on the degree of the disease in bronchial asthma. Salbutamol or Berotec aerosol can be used 3 times a day to control the disease.
If you know about upcoming contact with asthma irritants: different types of allergens or physical activity, then use the aerosol for preventive purposes to prevent an attack or shortness of breath.
Key principles of disease therapy
Bronchial asthma is a disease whose treatment lasts a lifetime. General recommendations include:
Basic educational skills. The patient learns ways to prevent attacks, records important symptoms and manifestations of his illness, and monitors peak expiratory flow using a portable peak flow meter. These data will help the doctor in determining the severity of asthma and selecting a treatment regimen. Eliminating or limiting contact with causative irritants. Timely elimination of the allergen is very effective in controlling the disease. Selection of individual drug therapy, which is determined by the severity of the disease and the presence of concomitant diseases. Cromones, inhaled glucocorticosteroids, leukotriene receptor antagonists and other agents are used for treatment. The choice of drug, its dosage and method of administration is determined by the attending physician, taking into account all the nuances of the pathological process. Development of a plan of behavior in emergency conditions (attack of suffocation, status asthmaticus). The patient and his relatives should know how to stop an exacerbation of the disease and what medications to use before the ambulance arrives. Clinical observation. The patient must periodically visit a doctor to monitor the condition of the respiratory tract. Outside of an exacerbation, it is worth trying non-drug therapy methods: a hypoallergenic diet, spa treatment, massage, breathing exercises, etc.
Full existence and periods of long-term remission are possible only with constant monitoring of the patient’s condition. Adequate drug therapy and medical supervision will help avoid complications and improve the quality of life.
Dyspnea in bronchial asthma is the main symptom that helps identify this disease. Dyspnea is a violation of the depth and frequency of breathing. During its manifestation, the patient feels a lack of air.
Prevention
Primary preventive measures:
- favorable environmental conditions;
- frequent cleaning of premises, a minimum number of objects that accumulate dust;
- compliance with personal hygiene requirements;
- absence of pets (if there are any, then the animals must be kept clean);
- use of hypoallergenic household items;
- balanced diet;
- minimal use of air fresheners, perfumes and other aromatic products;
- quitting cigarettes;
- taking medications only after a doctor’s prescription;
- elimination of allergic manifestations in the shortest possible time, identification of the irritant;
- timely treatment of respiratory diseases;
- Healthy lifestyle (sports, hardening, race walking);
- sanatorium-resort holiday at sea or in the highlands.
Secondary prevention measures:
To give up smoking
- timely treatment of pathological conditions of the lungs and bronchi;
- complete cessation of tobacco products and alcohol;
- daily wet cleaning;
- preventing contact with animals, even aquarium fish (their food contains allergens);
- exercise caution when flowering plants;
- avoiding insect bites;
- exclusion of allergenic products from the menu;
- therapeutic massage procedures;
- breathing exercises, inhalations;
- acupuncture, herbal prevention, salt caves;
- sanatorium-resort holiday.
Primary and secondary prevention measures are closely intertwined and reduce the likelihood of asthma, and therefore shortness of breath.
Medical indications
Shortness of breath occurs due to insufficient enrichment of the body with oxygen, as a result of which the respiratory center of the brain is irritated. In asthma, this symptom allows you to determine the stage of the disease and identify the presence of respiratory failure in the patient. Shortness of breath in bronchial asthma does not manifest itself in the same way as during pneumonia or in the presence of a foreign body in the respiratory tract.
Experts identify the following types of shortness of breath:
Severity of shortness of breath. Inspiratory - complications when inhaling. Such symptoms indicate the presence of cardiovascular diseases. It worsens during sleep or rest. This is due to the fact that when a person is in a horizontal position, the vessels of the lungs become overfilled with blood. Difficulty occurs when inhaling. In such cases, it is necessary to take an upright position and facilitate the work of the heart and lungs. Expiratory - difficulty in exhaling. This type of shortness of breath is the opposite of inspiratory; such shortness of breath is in most cases caused by chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (bronchial asthma, polio, emphysema, tuberculosis, several types of bronchitis). Mixed - difficulty inhaling and exhaling. One of the manifestations of this type of shortness of breath is stridor breathing - noisy breathing and complications when inhaling and exhaling. Such shortness of breath can be caused by a mechanical obstruction in the respiratory system. An obstacle can be a foreign body - an enlarged thyroid gland, which puts pressure on the cartilage of the larynx or various types of neoplasms.
Classification of shortness of breath in bronchial asthma depending on the depth and frequency of breathing:
rapid - tachypnea; rare - bradypnea; rare and shallow - oligopnea; frequent and deep - hyperpnea and polypnea.
Clinical picture
Shortness of breath may appear suddenly or develop slowly over a long period (several months or years). Doctors call sudden shortness of breath “acute.” This symptom is observed with pneumonia or bronchial asthma. In the latter case, shortness of breath precedes attacks of the disease. This symptom may occur against the background of myocardial infarction, heart disease or angina. Acute shortness of breath in bronchial asthma can be caused by severe allergic reactions that provoke swelling of the larynx.
The main causes of increasing shortness of breath are severe forms of bronchial asthma. The symptom in question is permanent. If the cause of shortness of breath is blockage of the bronchi, then anti-asthmatic drugs are used. The patient's life is at risk if shortness of breath increases during treatment. This indicates that the disease has progressed from an asthmatic attack to status asthmaticus. In an ordinary crisis, attacks can be easily combated with quick-acting drugs (Fenoterol). If the disease progresses to status, then shortness of breath can only be alleviated for a while.
Status asthmaticus is one of those conditions where the patient's life is at risk. As the disease progresses, the medications stop working. Status asthmaticus can occur with severe allergies, sudden suspension of anti-asthmatic drugs, or abuse of inhaled adrenergic agonists.
The main signs of status asthmaticus:
suffocation; pallor; cyanosis; lowering blood pressure; clouding of consciousness.
The above symptoms can put the patient into a coma or provoke death.
Useful tips
If you follow the principles of prevention, you can minimize the manifestations of attacks of shortness of breath:
- eliminate contact with people who smoke;
- if you yourself smoke, you must definitely quit the bad habit;
- carry out prevention of acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, infectious and viral diseases;
- do not contact animals and be careful when visiting people who have pets;
- regularly engage in physical therapy and do not neglect classes;
- do not be nervous and enjoy life, avoiding stress in every possible way;
- get vaccinated against allergic pathologies.
An attack of suffocation can take a person by surprise at any inopportune moment, and if measures are not taken to eliminate it, it will lead to serious complications, even death.
And most importantly, you need to keep in mind what harbinger led to suffocation. So, a strong dry cough, difficulty breathing, and runny nose indicate that a condition is approaching. All these symptoms are usually observed several days before the attack. The person becomes nervous, hot-tempered, and very tired for no reason.
Immediately before the attack itself, the person breaks into a sweat, the lips may acquire a bluish tint, and the skin becomes pale.
Typically, the condition occurs at night. First aid measures must be taken immediately.
Unquestioning adherence to all the specialist’s recommendations will easily and quickly help bring the pathology into a state of stable remission. However, remember that asthma should never be ignored.
Author of the publication: Anna Umerova
source
Therapy methods
When the first signs of shortness of breath appear, you should consult a specialist.
Bronchial asthma cannot be cured.
Patients suffer from this disease throughout their lives. Therapy for shortness of breath in bronchial asthma includes taking medications such as:
hormonal drugs; medications that dilate the bronchi (Salbutamol, Berotec).
If the inhaler does not have the desired effect after several presses, you should call a doctor. Don't wait for the situation to worsen.
During shortness of breath with asthma, the patient must be isolated from factors that can provoke this condition. Correctly selected and coordinated treatment will help the patient not to feel a lack of oxygen or shortness of breath during attacks. The use of β-adrenergic agonists can relieve all symptoms of asthma attacks.
Along with anti-asthmatic drugs, warming procedures have a positive effect. Drinking hot water improves mucus removal. In severe cases of bronchial asthma, it is more difficult to get rid of the feeling of lack of air. In this case, treatment is aimed at alleviating the patient's condition.
Helping the sick
Many who have experienced what asthma is advise against resorting to medications for relief. However, the nature of this disease and its course are different for everyone, so doctors advise: if simple correct actions do not help, be sure to turn to traditional treatment with drugs.
How to make breathing easier with asthma
- Open a window or door to make the room feel fresher;
- Be prepared for an attack, don't panic. It is this condition that will allow you to endure even a severe attack on your own. If your loved one is having an attack, instill maximum calm in them and move on;
- Proper breathing is important. Try to restore it yourself: try to breathe through your nose with abdominal breathing - when you inhale, all the air goes, as if into the stomach, and when you exhale, we release it from there;
- It is not necessary, but it is useful to give the patient a massage of the wings of the nose: to do this, hold the person’s chin with one hand, and massage with the other hand in quick circular movements for 1-2 minutes.
When the attack subsides, you can give the patient warm baths for his hands and feet and give him warm tea, milk, and clean water.