Physical therapy (physical therapy) for bronchial asthma involves various types of gymnastics and some restrictions. When compiling a list of recommendations, one should take into account not only the specifics of the disease, but also the patient’s condition. Some exercises should not be done during an exacerbation, some should be strengthened during remission. In general, all activities should make breathing easier, since bronchospasm, characteristic of bronchial asthma, causes suffocation and does not allow the patient to breathe freely.
Therapeutic exercise for bronchial asthma
Author: Victoria Vladimirovna Kazarinova
Victoria Vladimirovna Kazarinova
“Therapeutic exercise for bronchial asthma”
The main symptoms of bronchial asthma are episodes of shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing and chest congestion. The onset of symptoms after exposure to the allergen, seasonal variability of symptoms and the presence of relatives with bronchial asthma or other atopic diseases are essential. When combined with rhinitis, asthma symptoms may either appear only at certain times of the year or be present constantly with seasonal worsening. In some patients, seasonal increases in the level of certain aeroallergens in the air (for example, Alternaria pollen, birch, grass and ragweed) cause exacerbations.
Objectives of exercise therapy for bronchial asthma
The main objectives of therapeutic physical culture are:
· restoring the balance of excitation and inhibition processes in the cerebral cortex, extinguishing pathological reflexes and restoring the normal pattern of regulation of the respiratory apparatus;
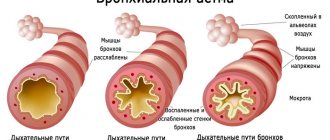
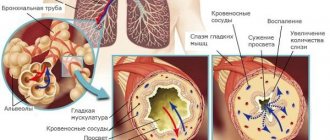
· reduction of spasm of the bronchi and bronchioles; improvement of pulmonary ventilation;
· activation of trophic processes in tissues;
· teaching the patient how to control his or her breathing apparatus during an asthmatic attack in order to alleviate it;
· training in extended exhalation.
Contraindications for physical exercise with bronchial asthma:
1. Any overload is contraindicated.
2. Exercises should be stopped if the first signs of an attack of suffocation are noticed: uneven breathing, spasm, cough.
3. Intense running and performing exercises without a break to establish calm breathing are not allowed.
4. In the room where the physical therapy session is being held, wet cleaning and ventilation must be carried out in advance.
5. It is contraindicated to exercise outside in unfavorable weather conditions (too cold weather, rain, wind), since any hypothermia can cause an attack of suffocation.
A mistake is the generally accepted opinion that patients with bronchial asthma should be limited in physical activity, since physical activity is considered one of the factors that provokes attacks of bronchospasm (bronchial asthma).
However, according to the literature, training in optimal conditions (temperature and humidity), on the contrary, reduces the frequency and severity of attacks. This load should be present in all patients with bronchial asthma.
Gymnastic exercises can help a patient with bronchial asthma cope with the first signs of an attack of suffocation and learn to dose physical exercises to maintain muscle activity without harming their health.
Therapeutic exercises for patients with bronchial asthma should include the simplest, easy-to-do exercises. Between breathing exercises with pronunciation of sounds, it is necessary to include a rest pause to relax the muscles. The dosage of exercises is 4-12, the pace is slow and medium.
Massage technique for bronchial asthma
Massage, as a rule, is carried out in the affected area and symmetrically to the lesion, in case of swelling and severe pain - above the affected area.
The massage course can be divided into three parts: 1) introductory – 1–3 procedures that are carried out to determine the body’s reaction to massage; 2) main – about 20 procedures, which are carried out taking into account the physiological state of the person being massaged and the characteristics of his disease; 3) final – 1–2 procedures.
As a rule, a massage course includes from 5 to 25 procedures, depending on the severity of the disease and the condition of the person being massaged.
Between courses you can take breaks from 10 days to 2-3 months. The number of procedures and the duration of the break between them are selected individually and can be either reduced or increased.
Massage and self-massage procedures also consist of three stages: 1) introductory – 1–3 minutes, during which the person being massaged is prepared for the main part using gentle techniques; 2) main – from 5 to 20 minutes; 3) final – 1–3 minutes, during which the intensity of exposure is reduced, normalizing body functions, and breathing exercises are performed.
The duration of the session can be from 3 minutes. up to an hour depending on indications. Massage is done daily or every other day, sometimes it is performed 2-3 times a week, combined with other types of complex treatment.
Approximate set of exercises
Physical exercises are used in the period between asthma attacks to improve well-being and improve performance, strengthen the respiratory muscles and improve ventilation, learn to control the breathing apparatus and develop full breathing, which makes it easier to endure asthmatic attacks.
Breathing exercises and exercises accompanied by the pronunciation of certain sounds and their combinations as you exhale (sound gymnastics) help reduce spasm of the smooth muscles of the bronchi and bronchioles. Sound gymnastics acts on their walls like a vibration massage, relaxing the bronchial muscles. Relaxation of the muscles of the shoulder girdle also gives this effect.
Before starting the exercises and after doing them, walk at a fast pace for 5 minutes. It is better to do gymnastics in the morning, an hour after eating. The total walking and exercise time is 15–20 minutes. At the end - raising and relaxing lowering of the arms at the pace of calm breathing.
Recommended set of gymnastic exercises for bronchial asthma:
1. Sitting on a chair, hands on your knees. Hands behind your head, bend over - inhale; return to the starting position - exhale (4-6 times).
2. Sitting on a chair, hands on your belt. After inhaling, pull your knee to your chest with your hands - exhale (alternately, 3-6 times).
3. Sitting on a chair, feet shoulder-width apart, hands below. Tilt to the left, try to touch the floor with your left hand, exhale with your right hand to your shoulder; return to the starting position - inhale. The same with a tilt in the other direction.
4. Sitting on a chair. Hands to the sides - inhale; cross your arms over your ribs, standing up and leaning forward - exhale (4-8 times).
5. Sitting on a chair, hands on your knees. Moving your head back, bend over - inhale; return to the starting position - exhale extendedly through the mouth, pronounce the sound “w-w-w” (4-6 times).
6. Normal walking - 1-2 minutes. Walking with arms raised to the sides as you inhale and lowered as you exhale - 1-2 minutes. Walking with a slower pace and lengthening the exhalation (30-60 s).
7. Standing, legs apart, hands down. Bend over, joining straight arms behind your back - inhale; tilt your head forward, join your straight arms below in front of you - exhale for an extended period, pronouncing the sound “oo-oo-oo” (3-5 times).
8. Standing, legs apart, hands on your belt. Moving your left leg back onto your toes, slightly turn your torso to the right, right hand to the side (look at it) - inhale; return to the starting position - exhale; the same in the other direction (3-4 times).
9. Legs apart, hands down. Tilt to the right, right hand on the belt, left up - inhale; return to the starting position - exhale; the same in the other direction (3-4 times).
Gymnastics activates the release of the adrenal hormone - adrenaline, which in turn causes the expansion of the bronchi. Regularly performed exercises of the complex increase the ventilation effect of breathing with less energy consumption.
No less significant is the fact that chest breathing, characteristic of most people suffering from bronchial asthma, is replaced by the more physiologically appropriate - abdominal breathing, as a result of which the ventilation of the lower parts of the lungs significantly improves.
Emphysema
This is a chronic disease that results from chronic obstructive bronchitis. The elastic connective tissue of the lungs is replaced by fibrous tissue, pneumosclerosis develops, the lungs expand, the residual volume of the lungs increases, shallow breathing, rigidity and immobility of the chest develop.
Objectives of exercise therapy and massage
Strengthen local ventilation of the lungs, reduce hypoxemia and shortness of breath, increase metabolism in all tissues, especially in the heart muscle and nervous system, improve the function of the respiratory muscles.
Features of the exercise therapy technique
Expiratory gymnastics are used, that is, exercises that promote full exhalation, strengthen the muscles of the torso and abdominals, which are involved in breathing and maintain the mobility of the chest and spine - static and dynamic breathing exercises in combination with general strengthening exercises. IP in bed and semi-bed rest - lying and sitting with support on the back of a chair, and in general mode - standing, so as not to impede the function of the diaphragm. Exhale slowly through pursed lips, and inhale through the nose. This promotes better mobility of the diaphragm and deepening of breathing. Avoid exhaling quickly and forcefully, as this will stretch the alveoli even more. Perform exercises at a slow and medium pace (due to the presence of hypoxemia), 2-4 times. After exercise, rest breaks are required. It is recommended to independently perform breathing exercises 2-3 times a day, measured walking, and swimming.
Special exercises are recommended:
- walking in rhythm with breathing: inhale for 2 counts, exhale for 4-6 counts;
- standing, hands on the lower chest. Rise on your toes – inhale, lower yourself onto your full foot, squeezing your chest with your hands – exhale;
- standing facing the gymnastic wall, holding the bar at chest level with your hands. Do a full squat - exhale; return to the starting position - inhale;
- sitting astride a gymnastic bench, arms to the sides. Turn the body alternately in both directions independently or with help;
- sitting, leaning on the back of a chair, hands on your stomach. Exhale deeply while drawing in the abdomen and pressing on it with your hands;
- sitting, hands on stomach. Pulling your elbows back – inhale; bringing the elbows together with fingers pressing on the wall of the abdomen - deep exhalation;
- lying on your back. Deep diaphragmatic breathing with increasing duration of exhalation;
- IP - the same. Bend your legs, clasping them with your hands, press them to your chest - exhale; return to the starting position - inhale;
- IP - the same. Sit down, bend forward, trying to touch your toes with your hands - exhale; return to the starting position - inhale;
- lying on your stomach. Bend at the waist while simultaneously lifting your legs and head up – inhale; return to the starting position, relaxing the muscles - exhale.
Features of the massage technique
The massage is similar to massage for bronchial asthma (see massage for bronchial asthma).
Exercise therapy for bronchial asthma
Bronchial asthma is a chronic pathology of inflammatory nature. The disease is characterized by attacks of suffocation, which without providing the necessary assistance can cause the death of the patient.
Exercise therapy for bronchial asthma is part of a complex of therapeutic measures aimed at reducing acute periods and generally improving the condition of the respiratory system.
Regular gymnastics, subject to all recommendations of the attending physician, promotes long-term remission.

Exercise therapy for asthma
What does exercise therapy consist of?
The main component is breathing and sound exercises. It can be performed in combination or separately. Both types are aimed at strengthening the respiratory tract. Only a doctor can tell which gymnastics is more effective, based on the individual characteristics of the course of the disease.
Today, the three most effective methods are known - exercises according to Strelnikova, according to Buteyko and Frolov’s innovation.
The first method of exercise therapy is a paradoxical method of breathing, where the emphasis is on exhalation rather than on entry. The second method is based on volitional relief from attacks, the manifestation of strength and desire. The third is to start endogenous breathing with a special simulator, when the work of all cells of the body is activated. All three methods received both positive and negative reviews, which indicates the purely individual properties of the human body.
Objectives of exercise therapy for asthma
The main tasks of exercise therapy, directly for bronchial asthma, are aimed at improving physical condition through therapeutic exercises:
- Improved blood circulation. The better the blood circulation, the more actively the organ cells are saturated with oxygen.
- Increases endurance and lung performance. Therapeutic physical activity will make the body more resilient in order to avoid suffocation attacks in the future at the slightest physical activity.
- Normalization of breathing. Correct breathing technique will ease asthmatic attacks.
- Improving the drainage function of the bronchi. The phlegm leaves more intensively after the exercises.
- Improving the patient's psychological mood. Therapeutic exercises for asthmatics give a positive charge of emotions, which is very important for this disease.

Exercise therapy for bronchial asthma - objectives
Why do you need exercise therapy?
The complex of exercise therapy for bronchial asthma is justified by the same goal as the main drug therapy - to alleviate the course of a chronic disease by suppressing symptoms. If respiratory pathology is really present, then it will not be possible to completely cure it. In this case, it is only possible to make the disease as invisible to the patient as possible.
Exercise therapy for asthma trains the respiratory system, strengthening the patient’s body. Even if it is not possible to completely suppress suffocation, if an attack occurs, it will be much easier for a person to cope with it. Let's look at what physical therapy gymnastics is aimed at.

Objectives of the therapeutic course of exercise therapy
What are the objectives of exercise therapy for bronchial asthma:
- Circulation. Gymnastics improves blood circulation. This indicates an increase in the level of oxygen saturation in the body, which is a necessary condition for asthmatics;
- Endurance. Proper physical activity will strengthen the respiratory system and increase performance. This means that asthmatic attacks will rarely occur;
- Breath. Exercises restore an even breathing rhythm. Lack of control of air flow and lung function during suffocation is a major problem for an asthmatic. Gymnastics is aimed at normalizing this process;
- Bronchi. This means drainage work. Choking and coughing are caused by increased secretion of secretions by the asthmatic’s body. The gymnastic complex will help the phlegm to clear away faster;
- Nervous system. A stable emotional state is the main condition in the treatment of asthma. Sports exercises increase the level of the happiness hormone in the body, due to which the patient is charged with positive emotions.
However, before performing breathing exercises for bronchial asthma, obtain your doctor’s permission. There are contraindications here. We'll look at which ones below. Let's talk about whether it is possible to play sports with asthma.
Contraindications
Like any type of physical activity, performing therapeutic exercises for bronchial asthma has a number of contraindications:
- Danger of hemorrhage.
- Severe form of the disease.
- Acute period of illness.
- Malignant formations in the respiratory organs.
- The occurrence of pain during physical activity.
- Presence of a disease (viral or infectious) at the time of classes.
Permission to exercise therapy for bronchial asthma can only be given by a doctor, after a complete diagnosis of the patient. An individual loading method is developed for each patient. Performing gymnastics without a doctor's recommendation can lead to a worsening of the condition.

Exercise therapy for asthma contraindications
Additional restrictions on exercise therapy
Playing sports with bronchial asthma is prohibited in case of an infectious or viral disease. During the course of the flu, sore throat or common cold, exercise therapy is contraindicated.
The periods of respiratory pathology itself are also important. Restrictions are present at the time of exacerbation. The need for permission from the attending physician has already been mentioned above. After consultation and testing, the doctor will tell you what sports you can do and whether you can do it at all.
Ignoring this recommendation threatens to worsen the patient’s condition. Now let’s move on to consider the complex of therapeutic exercises for bronchial asthma.
Numerous studies confirm that nervous mechanisms play a major role in the respiratory process. Exercise therapy is designed to improve the functioning of not only the lungs, but also other body systems.
Mechanism of action of exercise therapy
Physical exercises for asthma stabilize the functioning of the brain, normalize respiratory reflexes, which ensures rhythmic breathing, and restores vascular tone. This improves lung ventilation and prevents bronchospasms.
Exercise strengthens and tones the muscles, activates blood flow in the respiratory organs. The lungs become more elastic, their vital capacity increases.
In patients with bronchial asthma, exercise improves the patency of the bronchi, restoring their ability to remove mucus. Normalization of pulmonary gas exchange promotes complete saturation of tissues with oxygen, activates cardiac activity, and relieves swelling of the mucous membranes.
All this reduces the dependence of breathing on external factors. The risk of an attack due to exposure to allergens is reduced.
Performing gymnastics for asthma is calming and a person’s psychological state improves. The processes of inhibition/excitation of the nervous system are normalized, and the vulnerability of the respiratory process to stressful conditions is reduced.
Exercise therapy is not an independent treatment. Physical education must be combined with taking medications prescribed by a doctor.
Respiratory dysfunction triggers compensation processes in the body. If you start performing a set of properly selected exercises in the early stages of the disease, you can optimize compensation mechanisms.
Lung tissues and respiratory muscles that have undergone minor atrophic or degenerative changes can partially recover. This effect allows you to achieve sustainable remission.
A set of physical therapy exercises
Exercise therapy can only be performed between attacks. Its objectives are to normalize nervous processes, neutralize bronchospasm and establish normal breathing.
Introductory complex
The first days of training begin with an introductory course. All exercise therapy classes for bronchial asthma are carried out strictly in rhythm 1, 2...:
- Performed while sitting. On the count of 1, 2, take a deep breath (through your nose), 3,4 exhale (through your mouth, slightly open). Repeat 3 to 6 times.
- 1, 2 – inhale, simultaneously raising your arm up, 3, 4 – exhale while lowering your arm. 5-6 – breath holding (no more than 7 seconds). Perform with each hand 3 times.
- Sitting confidently on the edge of a chair, place your hands on top of your knees, palms facing up. Simultaneously bend your foot and hand, then straighten it. Then repeat again and so on 10 times.
- Perform while leaning on the back of a chair. 1-2 slow inhalation, 3,4,5,6 - slow exhalation, 7 - short-term breath holding. Do 6 reps.
- Press your hands to your chest and cough a few times.
- Standing position. Rest your hands on your knees, tilt your body slightly forward. 1, 2 inhale through the nose, 3, 4 exhale through the mouth, lips folded into a tube.
- Position: Sitting confidently on the edge of a chair. Place your hands directly on top of your shoulders, point your elbows forward as you inhale, and back as you exhale. Carry out 6-7 times.
- While inhaling, raise your shoulders up, and as you exhale, return to the starting position. Do this at least 4 times.
- Inhaling, raise your hands up, lower them, pronounce a drawn out “sh-sh-sh.”
- Starting position: hands are on your knees. Inhaling for 1, exhaling for 2,3,4,5,6, fold your hands into a lock at chest level and say a drawn out “w-w-w.”
- Raise your arms up at the count of 1, and lower your arms along the body on counts 2,3,4, saying “pfft.”
- Lean on the back of a chair, relax at a free pace of breathing.
Special exercises for bronchial asthma during exacerbation
The period of exacerbation of bronchial asthma occurs with an increase in the intensity of the symptoms of the pathology and an increase in the occurrence of asthmatic attacks. However, exacerbation of asthma does not always mean abandoning physical therapy. In most cases, reducing the load level will be sufficient. The following exercises will help alleviate the condition during an exacerbation:
- Take a lying position. Place a high pillow or cushion under your head. Take a calm breath through your nose, while raising your stomach. Then exhale through your mouth, lower your stomach. Perform the exercise 3 sets of 15-20 times.
- Take a sitting position. Lean your back straight against the back of a chair or chair (wall). Inhale through your nose, while bending your arms at the elbow joints and touching your shoulder. While exhaling, cross your arms in the chest area. Perform the exercise 25-30 times.
- Take a position while sitting on a low trampoline. While taking a deep breath, spread your arms straight to the sides. As you exhale, bend forward and touch the floor with your palms. The exercise must be performed in 3 sets, 10-15 repetitions each.
Recommendations for exercise therapy
Before treating asthma with exercise therapy and massage, a number of measures are required to determine the patient’s condition. The doctor will allow the complex to be performed if the respiratory pathology is in remission. The doctor strictly controls the process for the first month, since the slightest incorrect actions will aggravate the condition.
Rules for performing exercise therapy for bronchial asthma:
- Do exercises in the morning (2 hours after breakfast, around 10 am)
- Do gymnastics mainly in the fresh air (street, loggia, open window)
- Ventilate the room before performing indoor exercise therapy during the cold season
Measure your breathing rate and make sure it does not exceed 20-25 times. There are cases when exercise therapy was approved by a doctor, but during the process the patient’s condition worsened. If this happens, stop exercising. It is also useful to combine the complex with additional walking or swimming training, or with light sports.
But! Avoid strenuous physical activity.
What is the best time to study?
It is recommended to conduct classes before lunchtime. The best option is 1.5 – 2 hours after breakfast. Physical activity immediately after eating is prohibited. In the morning, as a rule, there is the highest peak of activity, which has a good effect on exercise performance. Share the article on your social networks. Dissemination of this information will help alleviate the condition of respiratory system diseases. Surely there will be people on your list of friends or subscribers who will find this article useful.

The main symptom of asthma is suffocation caused by external or psychological stimuli. Drug therapy is aimed at suppressing the manifestations of respiratory pathology. Doctors recommend comprehensive treatment, including physical exercise. What is breathing exercises for asthma, we will consider below.
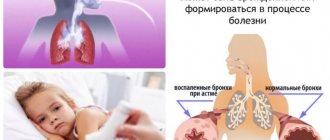
Features of classes for children
Exercise therapy for bronchial asthma in children differs slightly from exercises for adults, but has some nuances. The main thing is the duration of physical education: one lesson should not take more than 30 minutes. Breathing training is allowed from the age of three.
Breathing exercises exercise therapy for asthma
The exercises are similar to those performed by older people, but are carried out in a playful way. It is important to teach your child to breathe through his nose and hold his breath.
Attention: classes must take place in the presence of parents or an instructor!
There is no need to rush: as practice shows, it takes about a month and a half to master the full set of exercises. You can’t scold or irritate your child if something doesn’t work out the first time.
A positive attitude and enjoyment of training are of great importance. Therefore, children's therapeutic exercises for asthma involve group exercises with peers. At home, you can supplement your workouts with a contrast shower and rubbing your body with a dry towel.
If your child is diagnosed with asthma at an early age, exercise increases the chances that the disease will go away during adolescence. The main thing is to do them correctly, in compliance with all medical recommendations.
What is suitable for children?
Since many medications are contraindicated in childhood (especially under 3 years), emphasis should be placed on exercise therapy. Also, for bronchial asthma in children, it is recommended to do the following:
- Physiotherapy.
- Hardening with a contrast shower.
- Rubbing with a hard dry towel.
- Monitoring the cleanliness of the house (absence of dust and harmful household substances).
- Avoid contact with allergens.
- Proper nutrition.
- Massages.
- Maintain optimal air humidity and temperature.
General recommendations
Exercise therapy for asthma gives positive results when treating patients of different ages, regardless of the stage of the disease. Even with severe disease, exercise is allowed, but before physical exercise it is recommended to take a bronchodilator (medicine that dilates the bronchi).
- train only in the absence of exacerbations;
- start with a light warm-up: first warm up the limbs, then the muscles of the body;
- change exercises weekly;
- do gymnastics regularly: daily from 2 to 5 sessions;
- increase the load gradually - from easy tasks to complex ones;
- master breathing techniques under the supervision of a doctor;
- exhalation should be at least twice as long as inhalation;
- It’s better to practice in nature. When weather conditions do not allow this, the room must be well ventilated;
- Do not exercise if you have bronchial asthma immediately after eating.
Sharp pain, general deterioration of the condition is a reason to immediately interrupt classes and contact an instructor to adjust the load. It is good to combine exercise therapy with swimming, walking, and cycling.