- How does therapy work?
- Contraindications for PUVA therapy
- Features of carrying out at home
- Types of therapy
- Advantages of PUVA
- Possible complications and side effects
PUVA therapy for psoriasis is a modern, effective way to get rid of plaques and papules on various parts of the patient’s body. This method involves the use of artificial ultraviolet rays to enhance the skin's natural ability to regenerate, as well as slow down the excessive growth of dermal cells.
A special feature of the technique is the combination of light treatment with substances of plant origin. Such components are called psoralens in medical practice. This type of treatment can be carried out both in a hospital setting and at home.
The principle of treating psoriasis using PUVA therapy
The name PUVA comes from two words Psoralens (psoralen) and UltraViolet A (ultraviolet A). That is, this method of therapy is based on the use of special psoralen preparations and exposure of the skin to long-wave ultraviolet A.
Psoralens are photosensitizers - they are activated after irradiation of the skin with ultraviolet light. As a result, cell division is suppressed, their oxygen saturation is stimulated, the secretion of arachidonic acid is improved and the processes leading to excessive keratinization of the epidermis are suppressed.
In turn, UV light also has a positive effect on the skin - it destroys bacteria, normalizes blood circulation, strengthens local immunity and activates the secretion of melanin. Thus, skin regeneration processes are launched. Ultraviolet rays normalize the production of vitamin D, have a positive effect on the nervous system, and improve metabolic processes.
PUVA therapy, that is, the simultaneous use of psoralen medications and ultraviolet radiation, increases the effectiveness of both principles of treatment.
Side effects of the method
Psoralens, regardless of their use, will not provide any therapeutic effect on their own. Their action is activated only after ultraviolet light hits the dermis.
After binding to the DNA of the epidermis, psoralens inhibit the active activity of certain molecules.
It is worth noting that this does not in any way affect the natural functions of skin cells and does not have a negative effect on them.
An hour and a half after irradiation, reactions will be launched in the epidermis, which will result in the creation of cross-connections. Such reactions have the following effects on the body:
- Stimulate the process of production of active oxygen.
- They have a detrimental effect on pathologically active lymphocytes and keratocytes.
- They act to reduce the level of DNA synthesis in the epidermis, but do not affect natural functions in any way.
- They become a preventing mechanism for the occurrence of pathological processes of keratinization of the skin.
- Activate the metabolic processes of arachidonic acid.
Ultraviolet irradiation is often used to treat psoriasis. It has immunomodulatory, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
The main advantages of photochemotherapy for psoriasis:
- High efficiency. The process of complete cleansing of the skin is observed in 85% of patients, and the severity of psoriasis is mitigated.
- Quickly achieve the desired result. Regression of skin manifestations usually occurs after 3-5 procedures.
- High efficiency is achieved even after repeating the course, which is explained by the lack of addiction.
- Outpatient therapy.
- Good tolerance. After the course of treatment received, there is a lengthening of the period between relapses, and there is also a stable remission, which ranges from 6 months to several years.
- Possibility of preventive treatment.
For more effective exposure to UV rays, it is necessary to apply psoralens to the skin.
Without exposure to UV radiation, photosensitizers do not affect the skin; they begin to have an active effect already in the body after irradiation. Then cell division is suppressed at the genetic level, their saturation with oxygen is stimulated, the growth of skin cells stops, and excessive keratinization of the skin slows down.
UV light has a bactericidal effect, it improves blood supply, activates the production of melanin, thereby regulating the processes of rejuvenation and cell restoration. Psoralen increases the photosensitivity of the skin.
Low doses of radiation will increase the local immunity of the skin, most of the unpleasant symptoms of psoriasis and other dermatological diseases will disappear after PUVA therapy, vitamin D is produced, which is responsible for the absorption of calcium, normalization of weight, and restful sleep.
The mutual effectiveness of drugs based on psoralen and UV irradiation increases when they are used simultaneously.
When taking psoralens orally, the following side effects are noted:
- nausea;
- epigastric discomfort;
- vomit;
- lowering blood pressure;
- dizziness;
- loss of appetite;
- allergy;
- itchy skin;
- headache;
- sleep disturbance;
- depression.
We suggest you read: How to get rid of excessive sweating?
note
Many side effects are the result of improper treatment. The most common of these are nausea, vomiting and epigastric pain, which occur in 12–19% of cases. Usually, they are short-lived and go away on their own.

PUVA therapy includes two components: medication and ultraviolet irradiation.
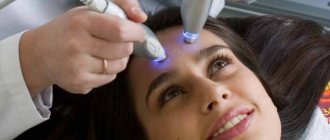
How does the session work?
PUVA therapy cabin
Before irradiating the spots, the patient is given a photosensitizer - a substance that increases the body's sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation. 1.5-2 hours after this, the skin is illuminated with ultraviolet light in a special cabin or using special devices for local irradiation.
Sessions are carried out 3 to 5 times a week. Ultraviolet light and photosensitizers do not act separately from each other.
Ammifurin is used in PUVA therapy
Medicines have a photosensitizing effect on the body: skin cells become more susceptible to ultraviolet radiation.
In Russia, PUVA therapy uses medications that cannot be taken independently (from pharmacies they are only available with a prescription). Available in the form of tablets, capsules, solutions for external use.

During PUVA therapy, several methods of taking photosensitizers are used:
- The tablets are taken 1.5-2 hours before ultraviolet irradiation so that they have time to act.
- PUVA baths. The photosensitizer is dissolved in water and a bath is taken.
- Local application. A solution with a photosensitizer is applied to the affected areas and then irradiated with ultraviolet light.
After the session, the patient's skin may be sensitive to ultraviolet radiation for 8 hours. Therefore, you need to take precautions: spend less time in the sun and wear protective glasses.
For photochemotherapy, therapeutic elements (lamps) with radiation with a wavelength of 315-400 nm are used, with a maximum effect at 365 nm.
Scientists believe that such ultraviolet radiation affects DNA synthesis in skin cells and inhibits the process of excessive cell division. Read the scientific confirmation in the publication: “Therapy of patients with psoriasis.”
Patients with all forms of psoriasis. However, for limited forms (up to 20%), using this method is inconvenient and useless. There is a risk of side effects.
If psoriasis covers less than 20%, it is convenient to use the 311 nm ultraviolet treatment method - it is suitable even for pregnant women and children over 3 years of age. In addition, you won’t have to take medications that cause all the side effects.
Treatment of psoriasis in Moscow using PUVA therapy takes place in clinics equipped with booths for this procedure.
Basically, these are private clinics. However, such treatment can be obtained, for example, at the state scientific center of dermatology and cosmetology. The cost of the procedure starts from 740 rubles.
- nausea, vomiting;
- decreased appetite;
- dizziness;
- skin itching, burns;
- skin hyperemia;
- nervousness, insomnia;
- depression;
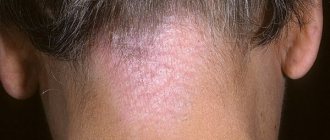
- symptoms of skin aging, skin cancer;
- cataract.
As a rule, no preparation is required before the procedure, but in order to avoid side effects, one of which is hyperpigmentation, patients are advised to avoid visiting the solarium and staying outside during hours of maximum sun activity at least 2-3 weeks before treatment. .

Before undergoing treatment, you should limit your exposure to the sun.
Systemic therapy
This is one of the most effective, but at the same time the most difficult PUVA methods. Its essence lies in the oral administration of dermatotropic drugs containing psoralen (“Methoxalen”, “Oxoralen”). These drugs have a photosensitizing effect, that is, they enhance the ability of the biological components of the epidermis to absorb light energy flow.
Taking tablets with psoralen is indicated for severe forms of psoriasis, mycosis, vitiligo, and lichen planus. Psoralen has high bioavailability and quickly binds to the plasma protein membrane, reaching its maximum concentration within 1-3 hours: this is exactly the interval that must be maintained between taking the drug and irradiation.
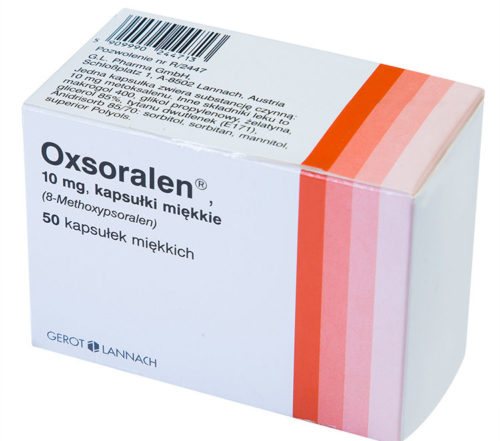
Capsules "Oxoralen"
Features of systemic PUVA therapy:
- Duration of the procedure is about 45-60 minutes;
- the required length of the light flux is 320-400 nm;
- absence of painful sensations during operation of the device (the patient may feel strong warmth at the site of exposure);
- the interval between taking the medicine and ultraviolet irradiation should be 2-3 hours;
- Only areas with affected tissue are treated.
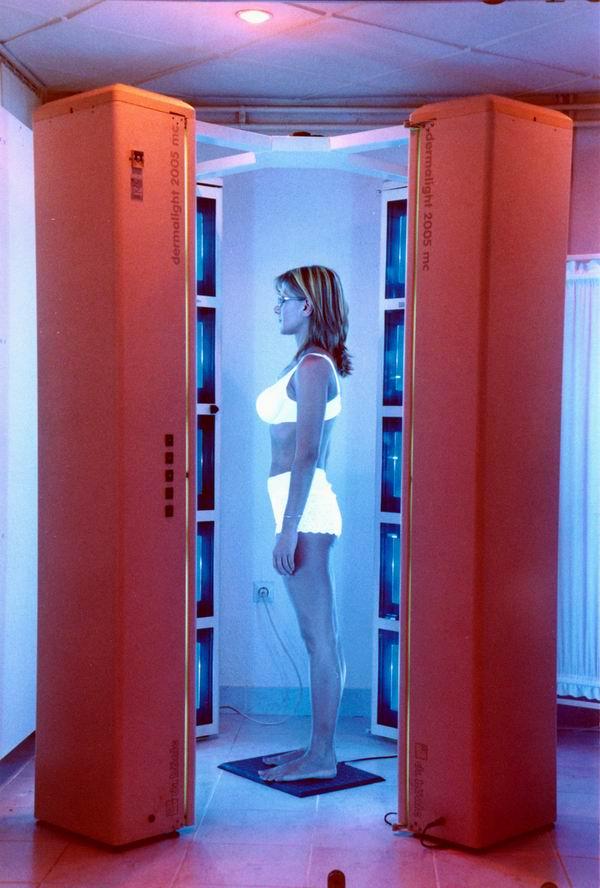
Irradiation takes place in a special booth, along the perimeter of which ultraviolet lamps of a given range and frequency are installed. The patient must wear protective glasses over his eyes to prevent thermal damage to the cornea. After the procedure is completed, the patient can immediately go home, since the PUVA method does not require recovery or rehabilitation.
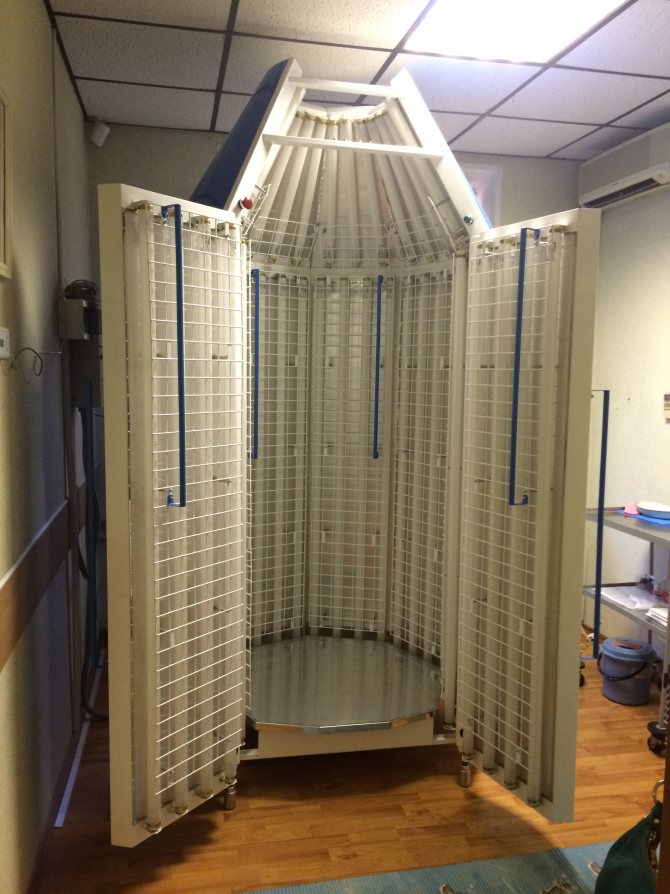

Cabin for the procedure
Fragmented (local) treatment is carried out according to the same principles as systemic PUVA therapy. The difference lies in the dosage form of the psoralens used and the method of their administration. With this method of exposure, the drug is applied to damaged skin areas in the form of a concentrated solution, after which the skin is treated with ultraviolet light.
This method is also quite effective for treating visible manifestations of neurodermatitis, vitiligo and other inflammatory skin diseases. Psoriatic plaques in patients with psoriasis smooth out and become lighter after 4-6 procedures.

The fragmentary method allows you to act only on the affected areas of the skin
PUVA baths (some call them surfactant baths) are a fairly young method of phototherapy, which has already established itself as one of the most effective methods of treating psoriasis, especially the palmoplantar form. The essence of the method lies in its name: the patient is immersed (entirely or individual parts of the body) in a bath to which a psoralen solution is added (most often “Ammifurin 0.3%”). The duration of such a bath is about 20 minutes.
After the bath, the patient also undergoes dosed ultraviolet irradiation. The sensations during the procedure are the same as when using other PUVA methods: a feeling of warmth at the site of treatment, possibly a slight tingling sensation.
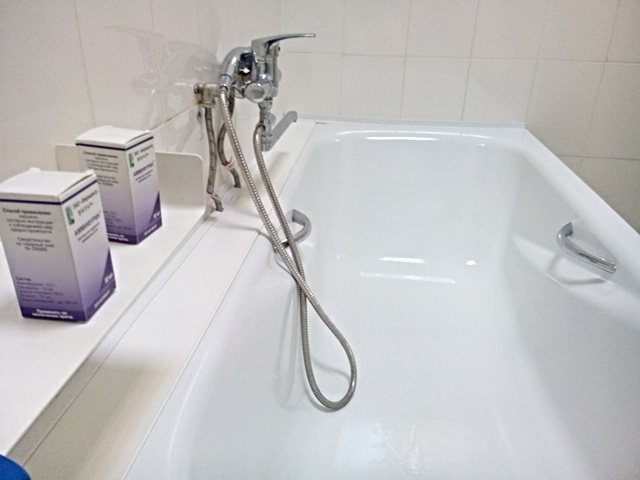

Before irradiation, the patient is prescribed a therapeutic bath with ammifurin
Side effects with the use of PUVA occur mainly with systemic therapy associated with oral administration of psoralens and their derivatives. The most common of these is nausea, which may be accompanied by severe headache and vomiting. In some patients, this side effect of phototherapy persists for 4-8 hours after the procedure, but more often such symptoms go away on their own within 1-2 hours.

Headache is one of the most common side effects of PUVA therapy.
Contraindications
Before prescribing PUVA sessions, it is necessary to ensure that patients have no contraindications to the procedure. The procedure is not prescribed if patients are diagnosed with:
- Hypersensitivity to photosensitizer drugs;
- Diseases that cause hypersensitivity to ultraviolet radiation;
- Severe damage to the liver and kidneys;
- Chronic diseases in the acute stage.
Temporary contraindications include pregnancy and lactation, a course of treatment with drugs containing tar, Anthralin, Grizeofulvin, Sulfonamides, Fluoroquinolones, that is, drugs with a photosensitizing effect. PUVA - treatment is prescribed only to adult patients; it is strictly prohibited to use it in the treatment of psoriasis in children under 12 years of age .
The most likely side effects of PUVA therapy are:
- Nausea, allergic reactions, dizziness, decreased blood pressure, headaches when taking psoralens orally;
- Increased skin dryness, itching, dermatitis with topical use of psoralens. If these symptoms are mild, then this is considered normal. If they intensify, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines and ointments with a calming effect to relieve irritation;
- Skin burns, hyperpigmented spots, premature aging of the skin, damage to the membranes of the eyes, formation of melanomas under the influence of UV light.
Correctly selected dosage of medications and dose of ultraviolet radiation help reduce the likelihood of adverse reactions during PUVA therapy. Patients are also required to strictly comply with all doctor’s recommendations throughout the entire course of phototherapy.
Security measures
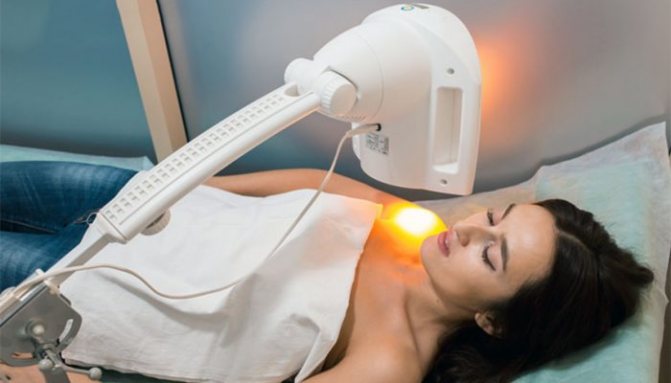
Before UV irradiation and during PUVA therapy, you should follow all doctor’s recommendations. Particular attention is paid to the following rules:
- Avoid cosmetics and products containing coal tar.
- Refrain from drinking alcohol.
- Avoid sun exposure before and after the procedure.
- Sunglasses and creams are used.
- The groin area in men is not irradiated.
In addition, you need to inform your doctor about all changes in your condition - both positive and negative. Regularly visiting a dermatologist and following his instructions will be the key to a successful recovery.
Types of PUVA therapy
Photochemotherapy for psoriasis is carried out in several ways:
- Systemic. The patient drinks one of the psoralens prescribed by the doctor and after 2-3 hours a session of ultraviolet irradiation of the body begins. The duration of the procedure is about one hour, the entire course consists of 5-14 procedures;
- Local or local. A photosensitizer in the form of a solution or gel is applied to psoriatic lesions, after which the installation that emits UV rays is turned on;
- PUVA baths. The psoralen solution is poured into a bath filled with water, after which the patient must lie in it for 10-15 minutes. The body is then exposed to ultraviolet light. The dosage of the drug solution is calculated by the doctor based on the severity of psoriasis.
What photosensitizers are used
Psoralens are divided into 2 groups:
- Natural. It is obtained by isolation from raw materials of plant origin, for example, citrus fruits, legumes and umbrella plants. These include Amminofurin (this is the only domestic psoralen) and Methoxalen (8-methoxypsoralen).
- Synthetic. For example, Trimethylpsoralen (more often used to treat vitiligo).
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what diseases psoriasis is similar to and what it can be confused with
These drugs are taken both internally and externally. In the case of internal administration, the dosage depends on the patient’s body weight: 0.6-0.8 mg per kilogram.
Method of performing PUVA therapy
When prescribing systemic photochemotherapy, the patient must take psoralen tablets prescribed by the doctor approximately two hours before the session. The most commonly used drugs from this group:
- Trimethylpsoralen. When using it, adverse reactions occur relatively rarely, but its cost is high;
- Amminofurin. Designed and produced in Russia. In budget clinics, when treating psoriasis with PUVA therapy, this particular psoralen is used;
- Methoxalen is a drug based on herbal ingredients.
The dosage for each patient is selected individually. The tablets should be taken half an hour before meals and washed down with milk or a fatty meal, this reduces the likelihood of nausea.
With local PUVA therapy, areas of change on the body are treated with photosensitizing solutions. After using psoralens, the patient must be exposed to ultraviolet irradiation. UV rays emit special installations, they can be of several types:
- Vertical. They are small booths with vertical fluorescent lamps;
- Horizontal. Unlike vertical ones, they allow you to act on the scalp;
- Installations intended for irradiation of individual areas of the body. They are used for insolation of the palms and feet, that is, with a limited spread of psoriatic changes;
- Portable lamps. The main feature is its compact size; these devices are convenient to use at home.
During the session, the patient must wear glasses that do not transmit ultraviolet rays. The first procedures are carried out within a few minutes, then the time of exposure to the body is extended and can reach up to one hour.

The duration of PUVA therapy for psoriasis is 10-30 sessions. They are carried out after 2-3 days. After completing the course, maintenance photochemotherapy is prescribed - for 2-3 months the patient must undergo treatment every 7-10 days.
PUVA treatment is prescribed both in the acute stage of psoriasis and after the inflammatory process has subsided. Different methods of photochemotherapy can be combined with each other. Usually the first sessions are systemic, then move on to local PUVA therapy.
Features of carrying out at home
Related articles:
Psoriasis and alcohol Ointment for psoriasis How to cure psoriasis quickly Psoriasis and sauna Psoriasis: contagious or not?
The modern market offers many lamps for home use. However, despite the free sale of devices, it is strictly not recommended to use them without consulting a doctor. In addition, it is almost impossible to independently calculate the dose of ultraviolet radiation at home. Success in treatment can only be achieved by observing the following precautions:
- Visit a specialist.
- Photosensitizers (means for increasing skin sensitivity) should also be selected exclusively by a doctor.
- Use only high-quality treatment devices.
- Strictly follow your doctor's recommendations regarding doses and timing of sessions.
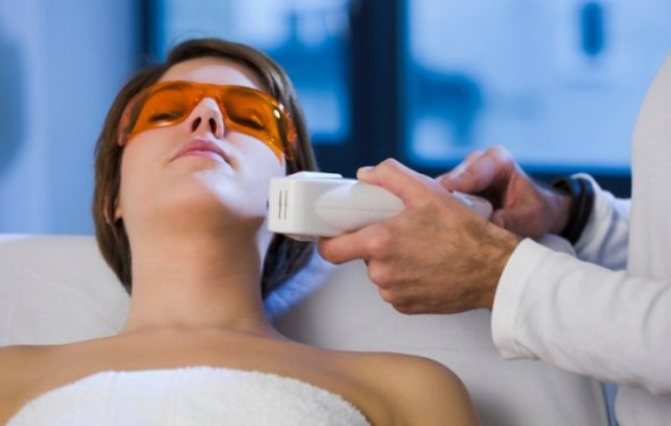
Post-procedure care
After each session, the patient must follow certain rules:
- Use sunglasses when walking outside. Their use reduces the risk of developing cataracts;
- Wear closed clothing, since after photochemotherapy the sensitivity of the skin to sunlight increases many times;
- Apply emollient and anti-inflammatory creams and ointments to the skin. They prevent the development of unwanted local reactions.
- If the itching worsens, take antihistamines.
Consequences
If we talk about the serious consequences of using PUVA therapy, it is necessary to talk about the following dangers:

The effectiveness of photochemotherapy
PUVA therapy really helps to cope with psoriasis in cases where drug therapy is powerless. Positive changes are noted after 5-6 sessions - psoriatic spots turn pale, their size decreases, and inflammation goes away. In 80% of cases, photochemotherapy allows one to achieve stable remission, that is, the patient does not experience exacerbations for six months or more. Some people note that after PUVA therapy, remission lasts for 3-5 years or more. To prolong the relapse-free course of psoriasis, maintenance photochemotherapy courses should be carried out at least once a year.
Advantages
PUVA therapy has a number of advantages:
- the ability to provide supportive care;
- a pleasant addition to using the technique is an even tan;
- convenient treatment conditions;
- there is no need to take time off for treatment;
- repeated courses give more effective results;
- duration of remission from 6 months to several years;
- well tolerated by all patients;
- efficiency 80%;
- the procedures are not addictive;
- After just five sessions you can see noticeable results.

Advantages and disadvantages of PUVA therapy

The popularity of PUVA therapy is explained by the fact that such treatment has many advantages, the main ones being:
- High efficiency of the method. In most patients, after phototherapy, the skin clears completely; almost all patients, without exception, note positive dynamics during the course of the disease;
- Rapid appearance of positive changes - skin regeneration begins in the 3-5th session;
- Good tolerability of treatment, subject to all rules for the use of psoralents and UV rays;
- Achieving stable remission;
- Lack of addiction, which allows you to repeat courses as often as necessary;
- Possibility of undergoing procedures on an outpatient basis;
- A small number of contraindications;
- Preventive effect - PUVA therapy can be used during the remission stage as a way to prevent exacerbation of psoriasis.
Photochemotherapy also has disadvantages. Most patients include the need to frequently visit medical centers to undergo the procedure, the high cost of treatment, and an increased risk of developing adverse reactions, some of which (cataracts, malignant skin lesions) are difficult to reverse.
PUVA therapy is a treatment method for psoriasis that deserves attention. You cannot independently prescribe sessions of ultraviolet irradiation in combination with the use of photosensitizing drugs. When assessing the possible effect and harm to health from PUVA therapy, doctors take into account not only the severity of the pathology, but also the form of the disease, the severity of symptoms, the presence of contraindications and concomitant diseases. Therefore, PUVA therapy may not always be recommended.
What it is?
So, PUVA therapy – what is it? PUVA therapy is a method of physiotherapy using a photoactive drug. In other words, this is the irradiation of the affected skin areas with ultraviolet radiation.

This technique, as already mentioned, was developed in the middle of the last century, and was quite successfully used in America and Europe for the treatment of skin pathologies. According to statistics, the success rate of therapy is 85%.
Indications for use
At first, the technique was used only to treat patients with psoriasis. Over time, the list of indications has expanded. The therapy is widely used for dermatological pathologies such as atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides.
Sessions are effective for all forms of psoriasis:
- exudative;
- pustular;
- plaque;
- erythrodermic;
- teardrop-shaped;
- palmoplantar.
Procedures are prescribed if the area of the affected areas is more than 20%. Effective during periods of exacerbation of often recurrent pathology.
PUVA therapy for the treatment of psoriasis is prescribed if the use of drugs with hormonal components and phototherapy have not produced results. To treat the progressive form, detoxification therapy is first prescribed, local medications and sedatives are used.
When should the procedure not be performed?
There are certain contraindications to treatment with psoralens and ultraviolet irradiation. These include:
- pregnancy;
- absence of lens (aphakia);
- malignant neoplasms, including skin tumors;
- diseases in which sensitivity to ultraviolet rays increases (lupus erythematosus, albinism, etc.);
- individual hypersensitivity or intolerance to photosensitizers.
It is also necessary to be careful when prescribing such procedures to persons with light skin color, with reduced immunity, as well as in diseases accompanied by the impossibility of the patient staying in an ultraviolet installation for a long time.
If there are even relative contraindications, it is better to refuse this procedure, since the risk of side effects in this case increases significantly.