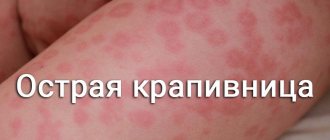
Chronic urticaria is the name of a skin disease that manifests itself as severely itchy blisters and lasts at least six months or is constantly recurring. The disease is most often allergic in origin.
Pharmacies offer many medications to combat dermatological diseases, but this disease cannot be defeated. This is due to the fact that in chronic urticaria the causes of development are so different that it is rarely possible to establish the exact one. Therefore, it is not possible to get rid of the factor that provoked the disease.
General information
Chronic urticaria is one of the complicated forms of ordinary urticaria, a skin disease that occurs under the influence of an allergic irritant. According to statistics, urticaria affects 15-25% of the population, and its protracted form affects at least 30%.
The disease is systematized depending on its symptoms. Despite the fact that its main manifestations are itching, redness, blisters, the pathology is nevertheless classified into various forms. Thus, the disease in question can be found in the following forms:
- immunological;
- physical;
- idiopathic.
Attention! Pathology negatively affects the patient’s quality of life, affecting all areas of his activity.
Skin rashes are typical for the onset of the disease.
Features of diagnosing the disease and identifying the cause
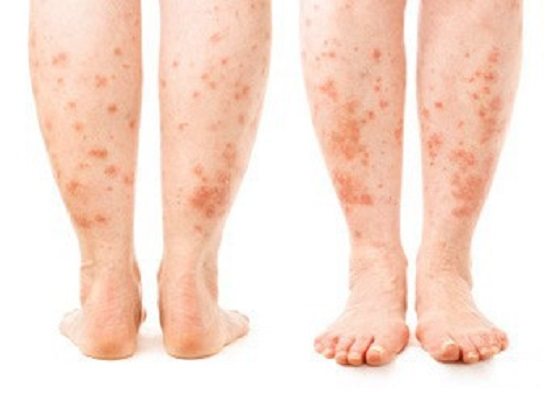
Without its definition, it is impossible to carry out accurate and effective treatment. The examination regimen is prescribed by an allergist and immunologist. Diagnosis of chronic urticaria includes the following examination methods:
- General blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula. With allergies, the level of eosinophils in the blood increases. When a bacterial infection is attached, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), the level of neutrophils increases, and the leukocyte formula shifts to the left.
- Analysis of stool for worm eggs.
- Blood tests for various allergens.
- Skin biopsy in the area of the rash. The biopsy is examined for the presence of immunoglobulins and specific antibodies.
- Examination of the body for the presence of a chronic source of infection. Consultations with an ENT specialist, infectious disease specialist, dentist, or dermatologist may be required.
Symptoms
Chronic urticaria in adults is presented in the form of rashes that appear for no apparent reason. According to many patients, provoking factors may be:
- ARVI,
- stress,
- climate change,
- taking medications.
The rash appears as flat, itchy, well-defined blisters protruding above the skin. The rashes can change their location depending on the degree of exacerbation of the disease. Sometimes they can be associated with angioedema. The most common rashes are:
- genitals,
- face,
- neck,
- language,
- lips.
In this case, the patient has difficulty swallowing and breathing. Involvement of the lining of the gastrointestinal tract in the disease process leads to:
- vomiting
- nausea,
- loose stool.
The rash may be accompanied by irritability and sleep disturbances.
Important. If the disease is not in the acute stage, then the blisters may disappear without a trace. In the chronic form, they will appear again, but in a different place.

The rash is localized in a variety of places and causes significant inconvenience to the patient
We recommend studying this topic:
Why does a baby develop hives and why is it dangerous?
3215
0
0
reading information
Preventive measures
Since treatment of chronic urticaria is a rather lengthy, labor-intensive, and uncomfortable process, it is worth taking the necessary measures to prevent the disease from occurring. People who are prone to allergic reactions should pay special attention to their health and daily routine. Prevention of chronic urticaria consists of the following steps:
These measures will not help a person completely insure himself against this allergic disease, but if it does appear, you should immediately go to the doctor. Timely treatment of a milder form of the disease will not allow it to become chronic, and illiterate self-medication will precisely contribute to this.
It will be quite difficult to completely get rid of chronic urticaria, but an experienced medical specialist will prescribe a comprehensive treatment that will, over time, achieve the desired result.
The chronic form of the disease manifests itself more sharply than during its normal course. If the problem has an internal basis, the patient should consult an immunologist, while allergies caused by external factors require treatment in an allergist’s office.
Treatment of chronic urticaria cannot be done without the patient following a special diet, which is also selected by the doctor. The course of taking medications is about 10 days, and if continuation of these procedures is required, the attending physician will notify his patient.
Causes
If the development of the disease is caused directly by an allergic reaction, then the causes of chronic urticaria are factors that are divided by their nature into two types . We are talking about:
1. Endogenous factors, that is, reasons that are associated with changes in organs:
- inflammatory processes in teeth, gums;
- liver problems;
- pancreatitis;
- gastritis;
- helminths.
2. Exogenous causes, when the appearance of blisters is caused by external factors:
- chemical reactions to various substances;
- temperature changes (overheating, cooling);
- mechanical - as a result of friction or vibration.
Inflammatory processes occurring in organs initiate bacterial infection. In response to this, the body responds with skin disease.
Note. When the process continues for no more than 6 months, we can assume an acute form of the disease, the essence of which is the body’s sensitivity to certain substances: dust, cosmetics, insect bites.
| Reason HC | Frequency of occurrence, % |
| 1. Infections, including Helicobacter pylori | 10-20 |
| 2. Autoimmune reactions (autoimmune urticaria associated with histamine-releasing and thyroid autoantibodies) | 40-60 |
| 3. Food and drug intolerance | <10 |
| 4. Physical factors (cold, heat, friction, skin compression, sunlight, vibration, etc.) | 20-30 |
| 5. Other causes of CU (hormonal disorders, tumors, autoinflammatory syndromes, etc.) | <10 |
| 6. The cause is not identified (idiopathic urticaria) | 40-90 |
The disease is provoked by a variety of reasons.
Providing first aid
The first group of medications should be taken in the evening.
Most often, experts recommend the use of Claritin, Tavegil, Suprastin.
When to see a doctor
In some cases, patients manage to eliminate the manifestations of chronic urticaria on their own. If the disease leads to the development of edema or anaphylactic shock, then the patient must urgently seek help from a doctor.
Principles of pathology treatment
Treatment of urticaria is carried out using medications. Most often, patients are recommended to use antihistamines, as well as leukotriene receptor antagonists.
The first group of medications eliminates itching and other symptoms of an allergic reaction. Medicines should be taken twice a day. The duration of use of the drugs is 3-12 months.
If the patient has rhinitis or bronchial spasms, then it is necessary to take a second group of drugs. Most often, patients are recommended to use Singulair.
If a person experiences pain with hives, he is recommended to use painkillers.
To avoid complications, the use of antimicrobial drugs is necessary. They are recommended for patients who have impaired stomach function. The most commonly used drugs are Dapsone or Colchicine.
If the patient’s body does not respond to antihistamines, then he is recommended to take Prednisolone. To combat the manifestations of the disease, the following is used:
- Prednisolone;
- Nezulina;
- Fenistila;
- Sinaflana, etc.
Medicines are produced in the form of an ointment and are intended for topical use. The dosage and frequency of use of the medicine should be determined by the doctor in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient.
This video will tell you what chronic urticaria is:
To combat the manifestations of recurrent urticaria, the use of traditional medicine is recommended. The most effective of them include:
It is quite a serious and responsible process. That is why it requires an integrated approach and constant monitoring by a doctor.
Diet therapy
To ensure the most effective treatment for urticaria, patients are advised to adhere to a diet. In this case, patients are strictly prohibited from eating spicy, salty and peppery foods.
Also, do not eat hard cheese, mustard, or mayonnaise. It is not recommended to use seafood, nuts and honey in cooking for urticaria. Drinking alcoholic beverages during treatment of the disease is strictly prohibited for patients.
The patient should avoid drinking hot sauce and coffee. Baked goods, chocolate and candies are not recommended for urticaria.
The diet should not include citrus fruits and strawberries.
When preparing a diet, preference is given to products whose action is aimed at increasing the concentration of histamine in the blood. It is recommended to prepare dishes using poultry.
The chronic form of urticaria is a rather unpleasant disease that can occur for various reasons. At the first manifestations of the disease, it is recommended to treat it.
For this purpose, drug therapy is used, as well as folk remedies. To ensure the highest possible effectiveness of treatment, the patient is recommended to adhere to a diet.
An allergic reaction of any type can become chronic if the problem does not go away within 6 weeks.
After such a transformation, the human body does not necessarily have direct contact with the provoking factor; the disease will periodically return for no apparent reason.
Chronic urticaria is often caused by external factors, but the presence of problems within the body can also cause this condition in a person.
The doctor will tell you what chronic urticaria is and how to treat it correctly in each individual case, but this does not relieve a person from the need to learn a little more facts about the allergic reaction.
Types of disease
In some cases, it is not possible to identify the exact cause of the disease. In such cases, the disease is defined as “chronic idiopathic urticaria.” This form is the most common.
Depending on the degree of prevalence of the forms, the following are distinguished:
- Idiopathic (occurs with a frequency of 75-80%).
- A disease that appears due to physical causes (15-20%).
- A disease caused by contact with an allergen (5% of cases).
What is it - chronic idiopathic urticaria? This disease is characterized by a persistent course. The symptoms do not go away for quite a long time, more than six months. Purple rashes in the form of blisters are caused by:
- swelling of the skin;
- malaise;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- neurotic disorders.
Other forms are relatively rare. They are easily diagnosed and treated.
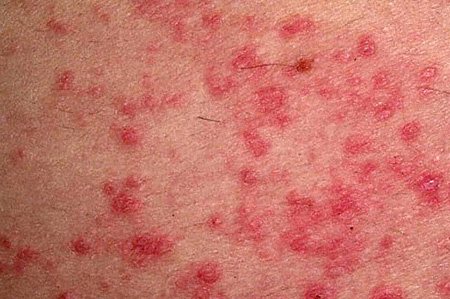
Most often, the cause of chronic urticaria remains unknown.
Chronic urticaria in children
Particular attention must be paid to the appearance of symptoms in children. It is in them that local lesions can quickly progress and take on a generalized form (spread throughout the body). At the same time, in 90-95% of cases it is almost impossible to identify the cause of the disease.
In children, chronic urticaria can last for years. At the same time, periods of remission tend to increase with age:
- in 50% remission occurs after 6 months;
- in 40% within 8 years;
- Just under 2% of all patients will suffer from recurrent manifestations of the disease for 25 years or more.
If your child has been diagnosed with chronic urticaria, hidden areas of the body should be examined periodically, because rashes most often appear in the armpits and groin.
With primary manifestations of urticaria in children, you should not rely on chance. You should undergo a full examination with him and identify the allergen2,3,5.
Diagnostics
The first thing a doctor should do to identify chronic allergic urticaria is listen to the patient and review the medical history. In some cases, it is already possible to make a correct diagnosis at this stage. For a more complete picture, additional examinations are carried out.
To do this, procedures are prescribed, during which it is necessary to find the provoking agent that caused the pathology. For this purpose, a number of tests are carried out, such as provocative tests, which make it possible to distinguish one pathology from another. Thus, a provocative test demonstrates the result of the effect on the body:
- water;
- cold;
- Sveta.
To exclude a secondary disease, such as chronic recurrent urticaria, an examination of the body must be carried out in order to identify the presence of infection in it.
Important. One of the most dangerous complications is Quincke's edema, which is characterized by attacks of suffocation that can be fatal.

The doctor can find out the cause of the disease during the examination of the patient, during a conversation with him
What complications may arise?
Negative consequences with chronic urticaria occur less frequently than with its acute course. In most cases, they develop against the background of secondary infection of the skin in the area with the rash.
Increased skin pigmentation
The most common complications include:
- Bacterial or fungal infection of the skin.
This can happen when scratching the dermis while itching occurs. Fungal infection often occurs after treatment with antibacterial drugs. - Increased skin pigmentation.
This can happen due to prolonged exposure to the sun or solarium. Sunbathing is contraindicated for patients with chronic urticaria.
Treatment of the consequences mentioned above is carried out by a dermatologist. To exclude the development of complications, it is important to contact a specialist at the first warning symptoms.
For quotation:
Cheburkin A.A. Chronic recurrent urticaria: syndrome or disease? // RMJ. 2011. No. 22. S. 1342
Urticaria develops as a result of the release and synthesis, mainly by mast cells located in the skin, of various inflammatory mediators. Causes of mast cell degranulation include immune, nonimmune, and idiopathic (currently unknown). In cases where the pathophysiological mechanism of chronic urticaria is not precisely known, a diagnosis of chronic idiopathic urticaria (CIU) is made. However, according to the results of recent studies, 25-45% of patients with CIC have IgG antibodies to the high-affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E (IgE) (FcεRI) or against IgE itself: it is believed that these antibodies are “responsible” for degranulation of mast cells and activation of inflammation. The main method of treating chronic urticaria, if its cause is identified, is therapy of the underlying disease. At the same time, urticaria is only its component - the syndrome and disappears against the background of its remission. In case of CIC, histamine H1 receptor antagonists come to the fore in treatment, among which desloratadine (Erius) stands out due to its specific properties: in addition to the antihistamine effect, its anti-inflammatory effect has been established.
Urticaria is a pathological condition of the skin that occurs against the background of an allergic reaction. The disease is characterized by the presence of pronounced symptoms and requires timely treatment.
The chronic form of the disease lasts for a fairly long period. To avoid relapse of the disease, patients are advised to completely eliminate allergens.
Chronic urticaria is characterized by the presence of pronounced symptoms that do not go away within a month and a half. During the course of the disease, the following are observed on the patient’s skin:
- Papules;
- Rash;
- Scarring;
- Swelling;
- Plaques.
Most patients during the development of the pathological process complain of itching. The rash of the disease appears as pink or red blisters. Their location can be the neck, face, arms, legs, back.

The cause of scars on the skin is an allergic reaction. They are characterized by different sizes and shapes. Quite often, scars can disappear and appear again.
Some patients develop papular chronic urticaria. In this case, papules with a white center appear on the patient's skin. An inflammatory process on the skin is observed around them.
During the development of this disease, patients complain of itching, which intensifies in the evening. During the development of an allergic reaction, patients may experience swelling on the skin.
Quincke's edema is a fairly common symptom of the chronic form of the disease.
In places where edema appears, stretching and peeling of the skin is observed. The symptoms of the disease are not always pronounced.
In some cases, signs of the disease disappear, and after a certain time they appear again. That is why, when the first symptoms of the disease occur, patients are advised to immediately seek help from a doctor.
Causes of the disease
The main reason for the appearance of the pathological process is the effect on the body of a provoking factor. Against this background, the production of a special substance – histamine – is observed.
During the period of release of this protein, the capacity of the capillaries increases, which leads to the leakage of liquid through them. As a result, blisters and swelling of the skin develop.
The disease is autoimmune in nature. When exposed to an allergen, special antibodies are released and activated, which leads to an allergic reaction.
The causes of chronic urticaria and methods of treating it, see this video:
There are a huge number of provoking factors for the disease. Most often it is diagnosed against the background of impaired kidney function. With rheumatoid arthritis, the risk of pathology increases significantly.
Urticaria can be diagnosed in patients with malignant neoplasms.
If gallbladder diseases occur against the background of infectious processes, this may be the cause. The disease is often diagnosed in patients with Sjögren's syndrome.
With diabetes, a person is at risk of developing a chronic form of the disease. With lupus or lymphogranulomatosis, the development of the disease can be observed.
It is also diagnosed against the background of various diseases of the thyroid gland. The occurrence of pathology is diagnosed in patients with certain chronic diseases - caries, viral hepatitis, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism.
Pathology in the fairer sex may appear due to inflammation of the appendages. Urticaria in a certain group of patients develops against the background of caries.
Chronic urticaria can occur when exposed to a variety of provoking factors. That is why a patient with a tendency to allergic reactions needs to closely monitor their health.
How is chronic urticaria diagnosed?
To ensure an effective chronic form of the disease, it is necessary to diagnose it correctly. Initially, the doctor examines the patient and also collects anamnesis.
In order to confirm a preliminary diagnosis, appropriate tests must be performed. In this case, the patient's body is tested:
These factors are allergy triggers, with the help of which the type is established. To make a correct diagnosis, an instrumental examination is recommended.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, it is much easier to diagnose it. That is why patients are advised to seek help from a doctor when the first signs of the disease appear.
Treatment
Treatment should begin with eliminating the causes. The course is prescribed taking into account the severity of the disease. In any case, a diet should be followed that excludes the identified allergen and histamine-releasing products. Previously prescribed medications should be discontinued.
The practical experience of doctors in the treatment of chronic urticaria in adults and children has made it possible to identify effective methods that are used by specialists today. These include the use of:
- strict diets that make it possible to eliminate possible food allergic reactions;
- antihistamines that block the release and action of histamine;
- steroid tablets that prevent inflammation and relieve symptoms;
- itching-relieving creams and ointments;
- corticosteroid tablets to relieve symptoms.
Remember. Treatment of chronic idiopathic urticaria is a rather complex process. Its symptoms subside at times, but after a short period of relief, the disease makes itself felt again.

Tablets, ointments and antihistamines should be used in combination
Therapeutic diet
Diet for chronic urticaria is of particular importance, since the disease is part of a heterogeneous group of dermatoses that are the result of allergic reactions to various provoking agents. They are:
- household chemicals;
- insect bites;
- overheating and hypothermia;
- plant pollen.
However, to treat chronic urticaria, which may be caused by food intake, two types of special diets are prescribed:
- An elimination diet, during which those ingredients that could cause pathology are excluded from the diet. The body's reaction to a particular product can be recorded in a food diary.
- A provocative diet, on the contrary, involves introducing certain foods into the patient’s menu and monitoring the results.
Attention! Unfortunately, using similar methods it is not always possible to identify the provoking factor, and then the disease is recognized as idiopathic. She will require individual treatment.

By eliminating different foods, you can find the allergen
Folk remedies
Most skin diseases are treated with decoctions and infusions prepared according to traditional medicine recipes. Herbal decoctions are taken orally, compresses and lotions are made with them. Therapeutic baths with herbal infusions have a calming effect on the skin: they relieve inflammation and eliminate itching.
The main types of raw materials for infusions and decoctions are:
- chamomile;
- Oak bark;
- celandine;
- St. John's wort;
- sage.
One of the effective pain relievers is celery. To prepare the medicine you need the root. The juice squeezed out of it is taken 2 tsp. 3 times a day half an hour before meals. You can also apply a compress to the skin.
According to another recipe, a couple of tablespoons of crushed root are poured with distilled water (200 ml) and left for 2 hours. Drink a third of a glass during the day 30 minutes before meals.
Important. Folk remedies can be used only in cases where the cause of the disease has been identified and eliminated. Consultation with a doctor is required.

People have been treated with folk recipes for a long time. Many herbal decoctions can relieve unpleasant symptoms of chronic urticaria.
We recommend studying this topic:
How to quickly cure solar urticaria and protect your skin
4663
0
0
reading information
Complications in the absence of timely treatment
Sometimes patients ignore systematic treatment, not considering the skin reaction a serious disease. But if left untreated, urticaria can cause complications throughout the body and cause the development of diseases such as:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- celiac disease;
- type 1 diabetes mellitus;
- thyroid diseases;
- Sjögren's syndrome;
- lupus.
rheumatoid arthritis
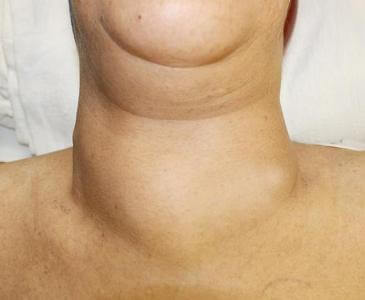
thyroid disease
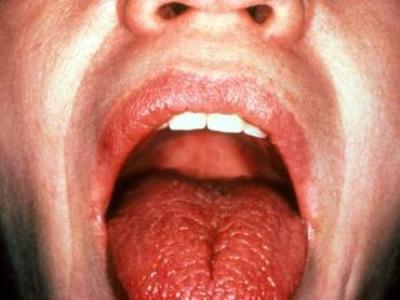
Sjögren's syndrome
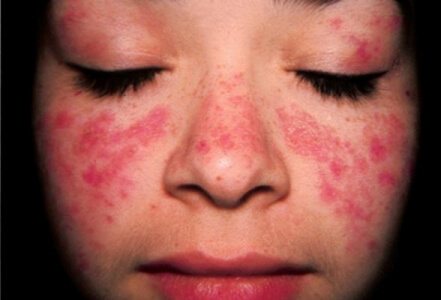
lupus
Exacerbations of urticaria in the form of anaphylactic shock also occur. This is an allergic reaction that is aimed at a malfunction of the respiratory system (narrowing of the bronchi, difficulty breathing) and a critical decrease in blood pressure. The victim suffocates, may experience dizziness, fainting, and, in the absence of first aid measures, death.
Prevention
Allergists believe that the disease in question is accompanied by various disorders of internal organs, for example, the gallbladder or stomach. In this regard, as a preventive measure, the amount of fat, salt and liquid prescribed in such situations is limited. Suitable foods for this diet are:
- Lean fish.
- Low-fat cottage cheese and low-fat sour cream.
- Butter (50 g per day).
- Porridge and vegetarian soups with vegetables.
- Vegetables.
- Fruits and berries.
During treatment, strict diets are prescribed
The key to health is the fulfillment of all prescriptions prescribed by doctors.
Etiological therapy
Etiological treatment is prescribed by the attending doctor after determining the cause of the disease. It is aimed at eliminating the primary cause.
When an allergen is identified, it is necessary to completely prevent possible contact with it. Until the rash disappears, the patient is advised to take antihistamines, and in severe cases, corticosteroids.
If the cause is an infection or helminthic infestation, therapy is carried out to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms.
For autoimmune pathology, cytostatics and corticosteroids are used.