Hay fever is a common allergic disease, occurring in the population with a frequency of 1.5 to 24%. The pathology is seasonal and is provoked by plant pollen.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Fortune teller Baba Nina: “There will always be plenty of money if you put it under your pillow...” Read more >>
Scientists have found that hay fever is a disease caused by genetic predisposition. If both parents have allergic manifestations, their children get sick in half the cases. If one of the adults is sick, there is a 25% chance that the child will develop hay fever. In children of healthy parents, the disease develops in 12.5% of cases.
Causes of hay fever
The etiological factor that causes an allergic reaction is pollen from flowering plants - these can be flowers, herbs, shrubs and trees.
The main reason for the development is increased sensitivity (sensitization) of the body to the irritating agent.
The pathogenesis of hay fever is based on repeated contact of a sensitized organism with an allergen.
During initial contact, allergen-specific Ig E antibodies are produced, which bind to the receptors of basophils and mast cells, and when the allergen is reintroduced into the body, they bind to antibodies fixed on the cells and trigger an allergic reaction.
An important role is also played by provoking factors, which in themselves do not cause the disease, but if there is a cause, they increase the risk of its occurrence and the speed of development of the response.
These include:
- burdened hereditary history: if at least one of the parents has a tendency to allergies, then the risk of developing an allergic disease in the child increases by 25%, but if both parents are allergic - by 50%, respectively;
- bad habits;
- frequent infectious diseases (mainly of viral origin) in young children, especially those that affect the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract;
- birth injury;
- dry, windy weather – there is a significant increase in pollen in the air;
- female;
- urban place of residence;
- occupational hazards;
- living in a certain geographical area.
Hay fever: how to deal with pollen allergies
For some, spring is a time of watery eyes, endless sneezing and sniffles, coughing, debilitating headaches and a sore throat. And there are not so few such people. According to the calculations of American colleagues, up to 20 million people suffer from this scourge every year. In our country the situation is no better.
So what causes these unpleasant, and sometimes completely unsettling, symptoms that last for weeks, or even months? It is at this time that the air is filled with billions of pollen particles - trees begin to bloom - in April these are birch, alder, willow, aspen and poplar, in May maple, oak, pine, bird cherry. Then there will be a respite for a couple of months, and in August everything will happen again with renewed vigor - wormwood and ragweed will bloom.
The ubiquitous pollen, being a strong allergen, activates mast cells in sensitive people, which begin to release histamine and other biologically active substances that trigger an allergic reaction.
Heredity plays a significant role in a person's predisposition to allergies. If one of the parents has spring allergies or so-called “hay fever,” one or more children will certainly inherit it. And if both are allergic, then in such a house they will definitely not love spring.
Symptoms of seasonal fever
Hay fever is manifested not only by symptoms of rhinitis and conjunctivitis, but also by dermatological diseases, respiratory tract lesions, and asthmatic attacks, which require emergency treatment. Allergy sufferers are rarely exposed to a complex of symptoms - the clinical picture depends on the allergen, and usually one of the signs of hay pathology predominates.
Nasal symptoms of seasonal allergies are as follows:
- bouts of sneezing;
- clear, mucous, odorless nasal discharge;
- dry congestion with loss of smell;
- itching, tickling, burning in the nasal cavity.
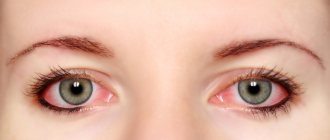
In most cases, rhinitis is accompanied by conjunctivitis with eye symptoms such as:
- itching, burning, tingling, sensation of a foreign body in the eyes;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- bilateral inflammatory eye damage;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- lacrimation;
- Photophobia is intolerance to bright light.
People suffering from symptoms of hay sickness are often diagnosed with underlying diseases of the nasal mucosa - adenoids, nasal polyps, sinusitis, the treatment of which is often ignored.
Swelling of the mucous membrane of the sinuses and nasal passages, the formation of excess mucus with obstructed outflow, and the addition of a bacterial infection contribute to the weakening of the immune system and the development of allergy symptoms in the form of seasonal fever.
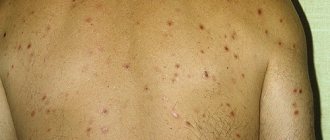
Sometimes hay fever manifests itself as urticaria with severe skin itching, Quincke's edema, eczema, atopic or contact dermatitis.
Hay fever rarely affects just one organ; a combination of nasal, eye, and skin symptoms is usually noticeable. Moreover, during the period of plant dusting, respiratory manifestations and pollen intoxication with symptoms are noticeable:
- headache;
- an increase in body temperature that can persist for a long time;
- increased fatigue;
- excessive irritability;
- loss of appetite;
- weight loss;
- sleep problems;
- increased sweating.
OR PARTIAL IMPROVEMENT OF WELL-BEING
It is often possible to get rid of hay fever almost completely by cleansing the body.
I once heard the story of a man who, before the upcoming flowering period, went on a hunger strike. It is nothing more than cleansing the body of accumulated toxins.
Another option may be antiparasitic cleansing of the body. You just need to take antiparasitic drugs regularly. Or carry out such cleaning before flowering begins. The result is exactly the same as with fasting.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you suspect hay fever, you should contact an allergist for diagnosis and treatment. The patient is prescribed tests of blood, nasal discharge, conjunctiva, and sputum; if the disease is allergic, an increased accumulation of eosinophils will be detected in the material. A blood test is also performed to detect specific antibodies produced in response to an allergen entering the body.
Then it is necessary to determine the plants whose pollen has become an allergen for the patient; for this purpose, allergological skin tests are performed. They are performed only during the period of remission of the disease (preferably in winter), and not earlier than 2-3 weeks after discontinuation of antihistamines. At the same time, skin tests with 5-10 or more allergens can be performed, depending on the age, well-being and individual characteristics of the patient. Typically, this diagnostic method allows you to identify the allergen.
If skin tests are negative, but the history, clinical picture and laboratory tests indicate hay fever, the patient may undergo provocative tests (nasal or conjunctival). They are carried out only in a hospital under the supervision of an allergist.
A CARDINAL SOLUTION TO THE PROBLEM
So many restrictions! What a horror to live such a life!
It turns out there is a way, if not to get rid of the problem completely, then at least to alleviate your condition, to alleviate your suffering. This method is called the method of multidimensional medicine.
You already know that the subconscious mind guards the body. It is designed to protect its wearer. But sometimes he needs to be prompted, since it does not involve pointless waste of energy. It is necessary to order the necessary part of the energy to be sent to the right place. The method of multidimensional medicine provides such an opportunity.
But first, to solve the problem, you need to find out from your subconscious the underlying cause of the body’s problems. Perhaps she won't be alone. And then eliminate them using vibration rows. Or in any other way that your subconscious indicates.
Treatment of polynosis
Hay fever can be treated in several ways. The first is to prevent contact with the allergen, the second is to take medications, and the third is to carry out immunotherapy.
In most cases, treatment occurs comprehensively using all possible methods. Sometimes, depending on the severity of the symptoms encountered, therapy may be minimal.
- Corticosteroid nasal sprays (aerosols)
(eg beclomethasone, triamcinolone and fluticasone.
Aerosols are effective in the majority of cases, and due to local application and a very small dose, they are free of side effects characteristic of corticosteroid preparations used orally or parenterally.
- Does not cause drowsiness.
- Eliminates itching, swelling of the mucous membrane, and nasal congestion.
- They require daily use and can sometimes take several days to achieve lasting effects.
- They are not classified as steroid drugs used to improve athletic performance and are not prohibited by the Anti-Doping Committee.
- Antihistamines
The most widely used short-acting drugs, available without a prescription in most countries, are diphenhydramine, clemastine, tripelennamine, and hydroxyzine. All of these antihistamines are inexpensive and relatively easily available, but their effects are short-lived, they also have a sedative effect and are contraindicated when operating dangerous machinery or any other activity that requires rapid response.
It should also be noted that with constant use, the sedative effect decreases over time, as does the anti-allergic effect; In addition, some of these drugs can become addictive, even to the point of becoming addicted.
Alternatively, long-acting drugs such as fexofenadine, loratadine and desloratadine may be used. These drugs are somewhat more expensive and are mostly available with a doctor's prescription, but their advantage is that they only need to be taken once (less often twice) a day and have virtually no sedative effects.
- Leukotriene inhibitors (another group of inflammatory mediators involved in the allergic reaction).
An example of a drug is montelukast, Singulair, which is FDA-approved for the treatment of hay fever and is available by prescription in the form of capsules, tablets, chewable lozenges, and granules and grains for sucking or adding to food (at room temperature), such as fruit puree.
Leukotriene inhibitors are especially effective when combined with antihistamines.
- Cromolyn sodium
Under the influence of the drug, the sensitivity of mucous membranes to allergens decreases. It turns out to be most effective as a preventive measure, that is, when taken in advance, even if you do not have allergy symptoms.
- Decongestants (decongestants or decongestants).
Decongestants are available in different forms - taken by mouth, such as pseudoephedrine, or in eye drops or aerosols, such as phenylephrine.
Eye drops are a fairly effective remedy for eliminating itching and redness of the eyes.
Nasal sprays are especially useful for relieving nasal congestion. However, drops can cause the so-called “ricochet” effect - the development of drug-induced rhinitis with prolonged and uncontrolled use of the drug.
Decongestants can lead to increased blood pressure, tachycardia, irritability, and nervousness, which also limits their use. There are cases of addiction and addiction, although relatively rare.
Any decongestants should be taken as directed, and usually for no more than three days in a row.

If you are taking any of these medications and you become pregnant or plan to become pregnant, be sure to tell your doctor.
Hay fever: how to deal with pollen allergies
For some, spring is a time of watery eyes, endless sneezing and sniffles, coughing, debilitating headaches and a sore throat.
And there are not so few such people. According to the calculations of American colleagues, up to 20 million people suffer from this scourge every year. In our country the situation is no better. So what causes these unpleasant, and sometimes completely unsettling, symptoms that last for weeks, or even months? It is at this time that the air is filled with billions of pollen particles - trees begin to bloom - in April these are birch, alder, willow, aspen and poplar, in May maple, oak, pine, bird cherry. Then there will be a respite for a couple of months, and in August everything will happen again with renewed vigor - wormwood and ragweed will bloom.
The ubiquitous pollen, being a strong allergen, activates mast cells in sensitive people, which begin to release histamine and other biologically active substances that trigger an allergic reaction.
Heredity plays a significant role in a person's predisposition to allergies. If one of the parents has spring allergies or so-called “hay fever,” one or more children will certainly inherit it. And if both are allergic, then in such a house they will definitely not love spring.
And here’s another interesting and alarming fact - global warming and climate change are leaving their mark on the flowering schedule of trees and significantly shifting the time of pollen appearance. Trees begin to bloom earlier and bloom longer, and consequently the duration and severity of hay fever in affected patients increases. According to experts, the pollen count may double from 2012 to 2040.
In addition to trees, herbs and mushrooms actively participate in the formation of allergens. The latter do not follow a seasonal schedule, but when favorable natural conditions coincide, such as precipitation, warm weather and an abundance of fog, they can grow abundantly on soil and plants and produce numerous spores.
Allergic conjunctivitis
Like the nasal mucosa, the mucous membrane of the eye reacts to contact with pollen by releasing histamine from mast cells, resulting in swelling, redness and itching. These symptoms can be prevented by mast cell stabilizing eye drops. They should be started at the first sign of hay fever and continued until the plant that triggers the allergy finishes flowering.
How to distinguish an allergic cough from a common cold?
ARI or acute respiratory viral infection rarely lasts longer than 7-10 days. If symptoms last longer or return on a regular basis, it may be a sign of an allergy. An allergy may also be suspected if symptoms appear at the same time every year.
Allergic rhinitis
This is the most common symptom of hay fever. But if not treated correctly, it can lead to a number of complications - chronic or acute sinusitis, otitis media, sleep disturbances, chronic fatigue, loss of smell and taste of food, headaches and chronic pharyngitis. It can also worsen asthma.
It is treated by washing the nose with sea water and local hormonal sprays. Vasoconstrictor drops can also be used to control the symptoms of allergic rhinitis, but it must be remembered that this group of drugs can themselves cause inflammation of the mucous membrane, bleeding and drug-induced rhinitis.
Antihistamines for hay fever
The mainstream here is the prescription of second-generation drugs, or so-called non-sedatives (although this group can still cause drowsiness in some patients). Many of these medications are available over-the-counter, taken once a day, and can make your life a lot easier.
Immunotherapy or desensitizing injections
Treatment begins with microdoses of the allergen, with their gradual increase. It is assumed that repeated doses provide a protective effect by increasing the levels of immunoglobulin G4 and regulatory T lymphocytes. This allows the immune system to quickly bind the allergen, interrupting the cascade of allergic reactions.
Immunotherapy can be carried out only after determining the provoking allergen using skin testing. The advantage of this method is the ability to significantly reduce the manifestations of allergies, or even get rid of them completely.
The downside is the risk of developing anaphylactic shock. The duration of treatment is from 10 months to 3 - 5 years. Medicines are not always available; they often have to be imported from abroad.
Prevention measures
Treatment of hay fever with medications can have certain consequences for the body of the sick person. That is why it is best to prevent the occurrence of this disease rather than treat it. For this purpose, certain rules have been created, the implementation of which minimizes the risk of the disease.
- Doctors also recommend following a diet. The most common food allergens should be excluded from your diet. This is due to the fact that a person with hay fever can develop a cross-allergy to food. Products such as eggs, hams, red fruits and vegetables, honey and bee products, etc. fall into the suspect zone. Preservatives and dyes also cause allergies. It is also worth reducing the amount of cereals you eat if you have hay fever. First of all, this applies to oatmeal, semolina and barley.
- The flowering period of plants that are allergens has a potential danger for a sick person. It is very important at this time to protect yourself as much as possible from places such as parks, squares, gardens, meadows, vegetable gardens and fields. That is, you should stay at a distance from accumulations of potentially dangerous grasses, bushes and trees.
- Growing home flowers or storing them in an apartment can be potentially dangerous. It is worth remembering that allergies can also be acquired. With constant contact with the pathogen, an adverse reaction of the body occurs.
- Pillows and carpets should be removed as much as possible from the room in which a sick person lives. They can accumulate pollen and are quite difficult to care for.
- Plant pollen can quite easily penetrate into rooms where people live. To prevent this from happening, you should cover the windows with tulle and curtains. It is also necessary to do a little wet cleaning in the evenings. It is best to ventilate rooms at night, when the amount of allergens in the air is minimal.
If you fully follow all the recommendations of doctors, you can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence of hay fever.
FLOWERING CALENDAR OF ALLERGENIC PLANTS
- March - April: hazel, alder, birch, poplar, oak.
- May: pine, willow, walnut, maple, elm, chestnut, birch, ash, aspen, spruce.
- June - July: intense dusting of herbs - plantain, nettle, cereals.
- August - September: wormwood, hemp, sunflower, asters, ragweed.
In different years, due to weather conditions, the flowering dates of plants may shift. The time of manifestation of hay fever symptoms also shifts: a deviation in one direction or the other is possible for 1-2 weeks.