Skin tests
- This is a diagnostic method that allows you to identify which allergen the patient’s body gives an allergic reaction to. Samples carried out specifically for this purpose are called qualitative. Quantitative skin tests are also carried out, which provide an idea of the degree of sensitivity of the body to a given allergen.
Many types of allergies can be diagnosed using skin tests. The most reliable results are obtained for allergens that enter the body through the respiratory system or skin (for example, hay fever - pollen allergy). In the case of food allergies or drug allergies, the reliability of this method is lower.
Allergy tests for a child
When a baby develops hay fever, skin tests are prescribed to determine the allergen.
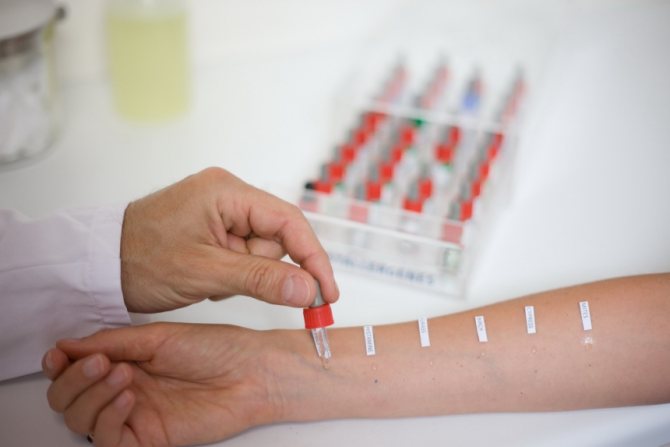
A study is performed by applying a solution containing the allergen to slightly damaged skin, after which the developing reaction to contact with the provoking agent is assessed.
The main indications for conducting such a test may be such differences as:
- Allergic dermatitis.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Bronchospasm.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Hay fever.
In addition to these conditions, tests are indicated in the presence of food allergies, after the onset of anaphylactic shock or angioedema.
Children are also often prescribed allergy tests for anesthetics.
They are advisable if the baby exhibits subsequent symptoms that are not justified by other reasons for development:
- Skin and other reactions that develop after an animal or insect bite, the introduction of pharmaceuticals, or the use of household chemicals.
- Diarrhea, pain in the stomach.
- Swelling of the skin.
- Burning, itchy feeling in the eyes.
- Severe lacrimation, inflammation of the tissues that form the organs of vision.
- Nasal congestion.
- The appearance of a rash.
- Seasonal, acquired rhinitis.
Skin tests for allergic responses can be carried out only after a month has passed after the development of primary allergy symptoms.
This is due to the fact that conducting the study as early as possible may yield unreliable results. In addition, skin testing is prohibited during periods of exacerbation of allergies.
Skin tests should only be carried out by an allergist and only in a room specially equipped for this purpose. Compliance with this rule allows you to guarantee not only obtaining a reliable result, but also minimizes the possible dangers of developing complications that require immediate medical attention.
Selecting a method
The most reliable method for identifying allergens is a comprehensive allergy diagnosis using a blood test. It allows you to simultaneously determine the body's sensitivity to 40 of the most common allergens of various types. This method may be the only possible one if there are contraindications to skin testing, but it is very expensive and inoperative.
Faster and more accessible are skin and provocative tests, with which you can check the immune system's reaction to a maximum of 20 allergens.
Skin allergy tests are classified according to several criteria.
According to the final result:
- qualitative – confirm or refute the presence of an allergy to a specific substance;
- quantitative - determine the strength of the allergen and its critical amount that can cause a negative reaction of the immune system.
According to the composition of the provoking substance used:
- direct - carried out by applying or introducing pure allergen into the skin;
- indirect (Praustnitz-Küstner reaction) - the subject is first injected with the blood serum of a person suffering from allergies, and a day later - the allergen.
By method of allergen administration:
- application (patch tests) - to determine the majority of existing allergens;
- scarification or needle tests (prick tests) - for seasonal allergies to plants, Quincke's edema, atopic dermatitis;
- intradermal (injection) - to identify fungi or bacteria that have become the causative agent of allergies.
With any of these studies, some errors are possible due to external factors and characteristics of the body. To clarify the result if it does not coincide with the symptoms of the disease, provocative tests are additionally prescribed. They involve the direct impact of a provoking substance on the organ that has become the site of the allergic reaction.
The most commonly used tests are:
- conjunctival (for allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva);
- nasal (for similar inflammations of the nasal mucosa);
- inhalation (for diagnosing bronchial asthma).
Other provocative allergy tests can also be performed - exposure or elimination (for food allergies), heat or cold (for a corresponding thermal rash), etc.
There are several methods of skin analysis to identify allergens, their differences are insignificant. Their main advantage is the speed of obtaining results and the ability to detect a reaction to a large number of allergens at once.
This test allows you to detect an allergic reaction to 40 different allergens, and it is carried out by making small cuts in the upper layer of the epidermis.
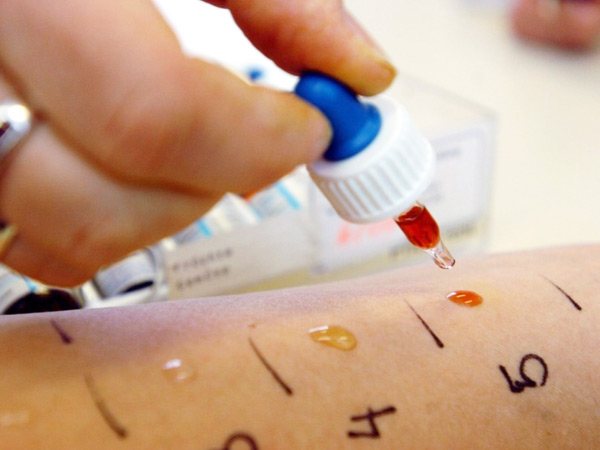
Several scratches are made in the area of the forearm or upper back at a short distance, after which a drop of allergen is applied to each cut. If there is an allergy, redness and a blister form at the site of the cut, and the more intense the reaction, the more pronounced the allergy.
Skin tests for allergens using the scarification method require the abolition of any antihistamines a week before undergoing this procedure, and the analysis should be carried out at the time of remission. This type of diagnosis is not suitable for children under 5 years of age.
Prick test
This research method is almost identical to the scarification method, the only difference is that during this test, punctures, rather than incisions, are made. This is the advantage of this method, since small punctures 1-1.5 mm deep do not injure the surface of the skin.
In addition, a false positive prick test reaction is excluded. Another advantage of this type of diagnosis is that it can reveal the body’s reaction to dairy products; it is enough to consume lactose (yogurt, cottage cheese) immediately before the analysis.
Intradermal tests
The main advantage of the intradermal test is the accuracy of its reaction, but this type of study is longer and more labor-intensive, and it also has a high risk of side effects. A small amount of solution with an allergen extract is injected under the skin with a syringe with a thin needle. The reaction can be observed after 15-20 minutes. after introduction.
The result of the study is visible by the condition of the skin at the site of injection of the allergic solution. The intensity of the reaction indicates the strength of the allergy to a particular product.
These studies are focused on contact reactions to allergens. It is better to perform this test on the upper back or forearm.
Patch testing is carried out by applying an allergen to the skin. The patient wears them for 2 days, only then can the result be interpreted. This diagnostic method is effective in detecting reactions to chemical allergens and medications.
Types of provoking substances
Provoking substances used to conduct skin allergy tests for a child are conventionally classified into several types:
- Direct.
In this case, the allergen used is in its pure form. - Indirect. In this case, the blood serum of a person who is suffering from an allergic reaction is used.
All allergenic substances are divided into types according to the methods of their application:
- Cold and thermo (thermal).
- Intradermal.
- Drip.
- Application.
- Scarification (prick tests).
It is important to find out in advance what allergy tests are done for children.
Reasons for inaccurate results
False negative and false positive results of allergy tests occur when:
- failure to comply with the correct research method or rules of analysis;
- the patient taking an antihistamine before the test or blood sampling;
- laboratory conditions for storing allergenic solutions used for analysis were violated;
- the specialist injects a too low or, on the contrary, too high dose of the solution under the skin or applies it to it, and the reaction is distorted.
Preparing the child
Before the procedure, doctors usually advise following the following simple rules that do not require specific actions:
- You should stop using antihistamine medications.
- Avoid excessive physical and psycho-emotional activity.
- It is recommended to refrain from using fresh foods in food (especially if skin tests are prescribed to identify a food trigger).
- Children should be mentally prepared for skin allergy tests - it should be explained that the pain they will feel will be insignificant and they should not be afraid of it.
As a rule, such studies are well tolerated by children who are over 5 years old, since it is much easier for a child of this age to prepare for less painful injections and scarification of the skin.
Indications for allergy testing
Allergy testing is prescribed to make a correct diagnosis and determine further treatment, which includes limiting contact with the allergen, following a hypoallergenic diet, or replacing a medication that causes an increased reaction of the body.
As a rule, allergy tests are performed if a person has:
- allergic rhinitis (hay fever);
- allergic asthma;
- eczema, dermatitis of various etiologies;
- allergies to food, insect venom, mold, inhalation antigens, penicillin or other drugs.
Are there age restrictions
At what age can this study be carried out?
In general, blood can be taken for testing from birth.
In this way, specific immunoglobulin IG E can be detected. Its presence indicates an allergic reaction. A blood test is carried out both during the period of exacerbation and during the period of remission.
Skin tests are taken from children from an early age and only outside of acute manifestations of allergies.
Age restrictions may be lifted if:
- a prolonged runny nose (with no other signs of a cold);
- constant sore throat;
- itching and rashes on the skin that do not go away on their own;
- difficulty breathing;
- disappearance of symptoms due to the use of antihistamines.
Is it always possible to do allergy tests for a child?
What types of samples are there?
Having figured out how allergy tests are done in children, you should understand what tests can be done:
Instructions for use of Uniderm cream and ointment
- Blood test for antibodies. The first test done on the patient. This test does not increase the intolerance reaction and has no contraindications. Recommended for any form of intolerance.
- Direct skin tests. Allergens are introduced into microscratches on the skin, the number of samples is up to 20 units. The reaction is assessed after 1 or more days. The patient must be in a hospital setting under the supervision of the attending physician. A positive reaction is local or extensive redness (more than 2 mm), swelling of the point of application of the allergen.
- Indirect skin tests are administered by injection. In this case, the dose of the irritant is accompanied by a dose of blood serum that has increased sensitivity to the allergen. The reaction is also assessed after 1 or more days. The result is an assessment of the danger of this particular irritant for the patient’s body.
- Provocative tests are prescribed if the reaction signs do not coincide with the data on the development of allergies. There are conjunctive, nasal and inhalation tests. The latter should be taken from patients with bronchial asthma.
Contraindications for carrying out
Before prescribing the procedure, the allergist will certainly find out if the baby has any of the following contraindications:
- Presence of oncological processes.
- Presence in the anamnesis of information about the variants of the occurrence of convulsive seizures.
- The presence of an allergic reaction with a complicated course.
- The presence in the body of acute or acquired pathologies in a state of exacerbation.
If there is a need (for example, doubts arise regarding the exacerbation of acquired pathologies), the doctor may prescribe additional diagnostic tests or refer you for consultations with specialized specialists.
How are allergy tests done for children?
Blood tests to identify allergens in children
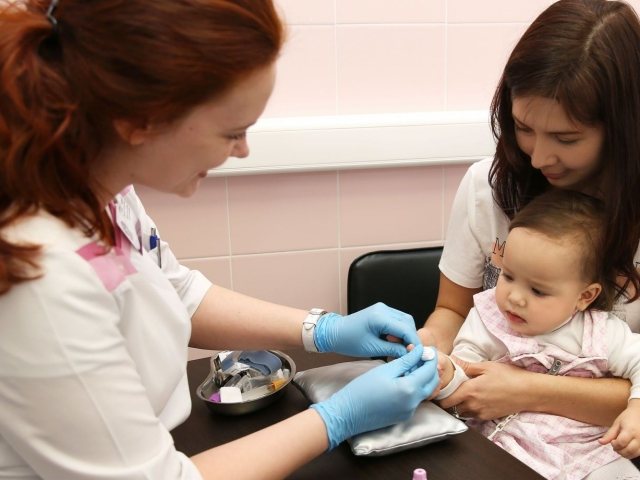
In a laboratory test for allergens, the immunological status is determined, but it can only be accurately determined in adults. In children, the immune defense system is at the stage of formation, so allergic intolerance may appear periodically or completely disappear on its own as immunity develops. Immunological tests are carried out when:
- frequent infectious diseases;
- protracted course of any infectious process;
- allergic type reactions;
- condition after surgery;
- suspected autoimmune disease;
- monitoring the level of immunoglobulins while taking certain drugs that affect the immune system.
To compile an immunological status, a general blood test is performed or blood is taken from a vein to determine certain immunoglobulins.
Application allergy test
This type of skin test is performed using pieces of gauze or cotton pads that are small in size and pre-soaked in the allergen substance.
They are applied to the skin and secured with adhesive tape or cellophane film.
This action allows the provoking substance to enter the body with greater activity. Thus, you can get results much faster, and they will be more reliable.
Most common allergens
Allergens are foreign substances that, when they enter the body, cause a hypersensitivity reaction (allergies). Most of them contain specific proteins, which cause a super-strong immune response.
In young children, the disease usually occurs in response to substances contained in food (dairy products, fish, eggs, products with synthetic colors and flavors).
In adolescents and adults, other types of allergens come to the fore:
- Household.
- Pollen.
- Animal allergens.
- Fungal.
- Bacterial and viral.
- Household.
Ordinary house dust can cause allergies, and it can be quite difficult to determine the specific substance that caused the reaction. This is due to the large number of components in its composition. These include:
- Fungal spores.
- Particles of human and animal skin.
- Plant fibers.
- Insect excrement.
- Dust mites.
Especially often, dust mites and their waste products lead to the development of allergies. These microscopic insects live in especially large numbers in upholstered furniture, mattresses, carpets and pillows.
Pollen allergens
These include pollen released during the flowering of a wide variety of plants. Most often, the reaction occurs to pollen from weeds, such as ragweed, dandelion, and wormwood. Often, allergies occur to pollen from trees (poplar, birch, oak) and cereal plants (timothy, wheatgrass, rye).
Depending on the flowering period of various plants, several peaks of allergic reactions are observed:
- April May. During this period, trees bloom en masse.
- June July. Associated with the flowering of cereals.
- Aug. Sept. Occurs when weeds bloom.
Fungal allergens
Mold spores are ubiquitous; dozens of varieties of different fungi can be found in the air of any room. Therefore, determining the exact cause of allergies can be very difficult.
It is important to understand that the reaction can be caused not only by fungi, but by food that is produced through fermentation. For example, yeast dough, beer, fermented milk products.
Animal allergens
Typically, the disease occurs upon contact with the epidermis and particles of fur of domestic dogs and cats, and less often with bird feathers, which are used to fill feather beds and pillows. It is possible to develop reactions to urine, saliva, and other waste products of animals.
To find out which animal allergen led to the painful condition, you need to take an allergy test .
Scarification tests (prick tests)
This type of allergy test is performed on a child after mild irritation of the skin.

For this purpose, scarifying needles are used. Drops of an allergenic solution are applied to the acquired damage.
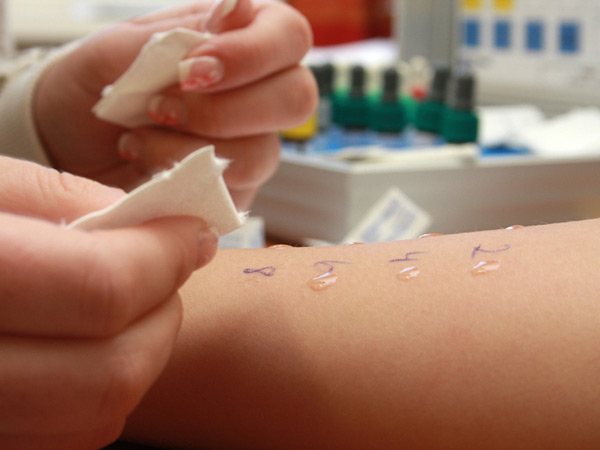
If the procedure is performed on children under 12 years of age, then only provoking substances can be used in one test. After 12 years, about 15 irritants can be used per function.
The described test allows you to identify the agent that provokes the allergy. Scarification tests are considered to be the most reliable compared to application and drip tests. In addition, the reliability of the test increases when performing a prick test, in which the skin is not scratched with a scarifier, but rather pierced.
Skin tests for allergens: types
Scarification test
A scarification allergy test consists of incisions on the skin of the forearm, through which the expected antigen, in the form of a solution, easily penetrates the human body.
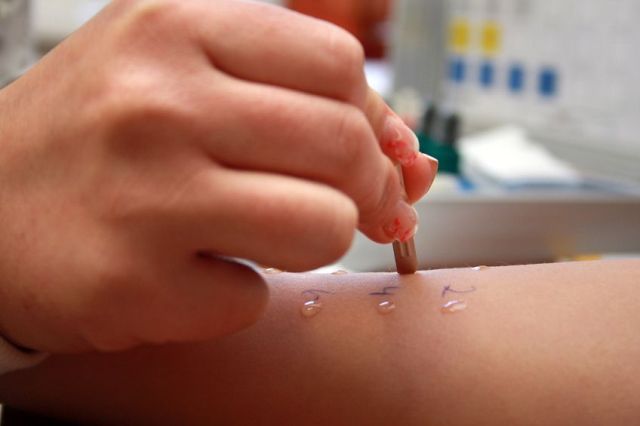
This type of study allows you to check for respiratory and household allergens.
Prick test for allergens
Prick allergy tests are performed by introducing an antigen under the patient’s skin, that is, they represent a kind of injection. A typical testing area is the skin of the forearm, less often the back.
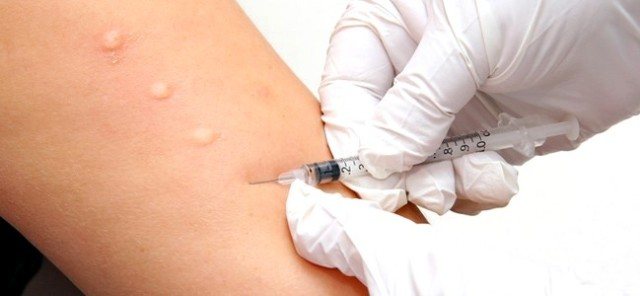
It is worth noting that intradermal tests are more sensitive than prick tests.
This allergy test allows you to identify sensitivity to insect venom, antibiotics and is not used to diagnose food allergies due to the high risks of false positive results and the risk of anaphylaxis.
Allergy patch tests (patch test)
This allergy test involves applying antigen-treated patches to the skin of the back for 48 hours. This examination is carried out to identify delayed-type allergies. That is, reactions are tested that occur after several hours or days after skin contact with the allergen, for example, contact dermatitis.
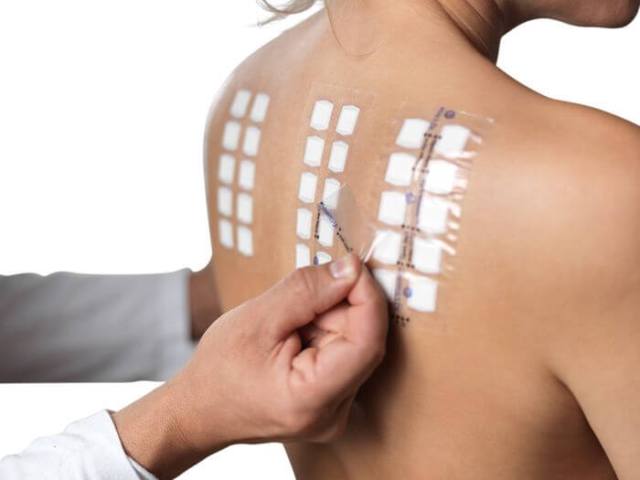
The patch test allows you to check your reaction to latex, metals, fragrances, medications, preservatives, resins, hair dyes, etc.
Provocative tests in allergology
Oral or nasal allergy provocation tests are performed when there is a suspicion that a person has an allergic reaction to food or medications.
The procedure is carried out as follows: the suspected allergen, starting with very small doses, is eaten or inhaled under the close supervision of an allergist. If there is no reaction, the dose is increased until the body shows a positive response to the antigen.
Rinse test
This procedure involves the diagnosis of food or drug intolerance, used for both true and false allergies.
After contact of the antigen with the oral mucosa, the number of leukocytes is assessed. Sensitivity to the substance causes inhibition of neutrophil emigration, which indicates the presence of an allergy.
Allergy tests at home
Do not attempt allergy tests at home. Self-administered food allergy testing can cause anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction. A drug allergy test should also be carried out only in a medical institution under the supervision of a highly qualified specialist who can provide emergency assistance in case of an unfavorable course of testing.
Intradermal allergy test
This type of skin test is performed by subcutaneous injection of an allergen solution using a narrow needle. A similar test is indicated to identify sensitivity to certain microorganisms (fungi, bacteria).
Modern doctors perform the following tests in a similar way:
- Pirke.
- Kasoni.
- Mantoux.
Thermal allergy tests. These tests can be either thermal or cold. They perform them using:
- Test tubes filled with ice or hot (42 degrees) water.
- Pieces of ice.
The outcome of an allergy test is assessed based on the appearance of a blister on the skin.
In similar embodiments, the skin test is considered positive for the influence of the applied thermal factor.
Allergy symptoms
The following manifestations indicate the occurrence of an allergic reaction:
- Prolonged, profuse runny nose.
- Excessive lacrimation, itching in the eye area.
- Sneezing attacks, itchy nose.
- Itchy skin rashes.
- Labored breathing.
If you experience one or more of the above symptoms, be sure to consult an allergist. Only a specialist will be able to prescribe the correct test to determine allergies and effective treatment of the disease.
Negative reactions after allergy tests
In some cases, a small patient may develop reactions of varying severity during a skin test:
- Itching, rashes all over the body.
- Severe irritation in the area of the allergy test.
- Compressive feeling in the sternum when breathing.
- Changes in blood pressure, manifested by fainting and dizziness.
- Discomfortable feelings in the intestinal tract, stomach.
These symptoms usually develop within a couple of hours after the test and can persist throughout the day.
Severe side effects can become a prerequisite for severe complications, in some cases leading to a fatal outcome.
In connection with this, the allergist notifies parents about possible negative reactions before the tests and advises them to stay in the hospital for several hours or days.
In fact, allergy tests can be done for a child in any city medical institution, where a specialist, an allergist, conducts the consultation. In addition, services for their implementation are provided by virtually all multidisciplinary personal clinics. You can check with your doctor about where to take allergy tests for your child.
How the body reacts
There are several types of reactions to drugs. There are immediate and delayed reactions. This can be an immediate reaction in the form of swelling, urticaria and anaphylactic reaction, or delayed skin reactions.
Article on the topic
Swelling, shock... How to provide first aid for allergies in a child Death when using a medication (most often an anesthetic) usually occurs from anaphylaxis. It develops within 5 minutes, leading to swelling of the larynx, inability to breathe and, as a result, death. For immediate assistance in treatment rooms and manipulation rooms, there is an anti-shock first aid kit with adrenaline. And here it is simply important to help the person in a timely manner.
Those people who have been diagnosed with anaphylaxis (for example, have already had a problem when administering a medication) are prescribed constant wearing of adrenaline and its use in an emergency in an age-specific (or weight) dosage. All over the world, such patients are recommended to constantly carry an anaphylaxis patient’s passport in their pocket. This allows doctors to respond more quickly in the event of an unexpected situation that can develop even with simple medical intervention.
Particular attention should be paid to predicting allergic reactions in children. After all, in children everything develops much faster, but it is often more difficult. You can predict the development of a problem in a baby by collecting the child’s medical history and identifying a hereditary predisposition to allergies. This is an indication for laboratory analysis (study of specific IgE).
If adverse reactions develop that threaten the child's life, adrenaline is also used. It is important to understand that any administration of drugs to a child should be carried out exclusively under the supervision of a doctor.