Currently, the number of patients with allergic diseases is increasing day by day. By taking antihistamines, many people only eliminate the allergy symptom in this way. Almost every person has a hypersensitivity to certain substances, so even in the absence of symptoms of the disease, prevention is not superfluous. A blood test for allergies allows you to identify what exactly led (or may subsequently lead) to a specific reaction of the immune system, and determine which allergens the patient has.
Allergen tests
An allergic reaction occurs when the immune system reacts to certain substances in the environment that are generally harmless to most people.
To protect the body from a perceived threat or antigen, the human immune system produces antibodies called immunoglobulin E (IgE).
IgE antibodies bind to the surface of mast cells (cells involved in the body's immune response) to release chemicals, including histamine, into the bloodstream.
It is histamine that causes various symptoms that affect the mucous membranes (eyes, nose, throat, lungs, gastrointestinal tract) and human skin.
Allergen blood tests are ordered when a person has symptoms of an allergic disease, such as hives, itchy eyes or nose, sneezing, nasal congestion, or breathing problems.
Symptoms can be seasonal (for example, in reactions to pollen) or year-round (for example, in the epidermis of animals).
What kind of analysis is done for allergens - let's look at it in more detail.
Clinical blood test
By taking a general blood test for allergies, you can evaluate the level of eosinophils. Eosinophilia (increased number of eosinophils) may indicate the presence of an allergic disease. It occurs in bronchial asthma, urticaria, etc.
Total immunoglobulin E
Total IgE measures the overall amount of immunoglobulin E. It is used to detect an allergic reaction in the body, rather than to detect an allergy to a specific substance. That is, it complements the information provided by studies of allergen-specific IgE.
Elevated antibody levels indicate that a person may have an allergy or parasitic infection.
If a person has a reaction to a seasonal allergen, such as pollen, then both specific and total IgE levels can be expected to increase during the time of year when flowering occurs.
If a person has a reaction to a persistent environmental irritant, such as mold in the house or cat dander, then the total level of immunoglobulin E may be constantly increased.
A normal IgE level does not exclude the presence of allergies, since in the intervals between allergic reactions, the level of total IgE may decrease.
Specific immunoglobulin E
IgE is unique to each allergen. That is, the antibodies produced to plant pollen differ from the antibodies produced, for example, to dust mites.
Tests for specific immunoglobulin E are carried out to identify the body's reaction to certain allergens, for example:
- pollen;
- mold;
- animal dander;
- dust mites;
- food products;
- medications;
- insect poison;
- latex.
A blood test to determine the level of antibodies, in contrast to skin testing, can be prescribed to those people who have already encountered life-threatening allergic reactions and testing would be too dangerous for them.
Allergy skin tests
Skin testing is carried out in a medical institution under the supervision of an allergist. This method has a number of limitations, one of them is age. Allergy testing is not carried out in children under 5 years of age.
Kinds
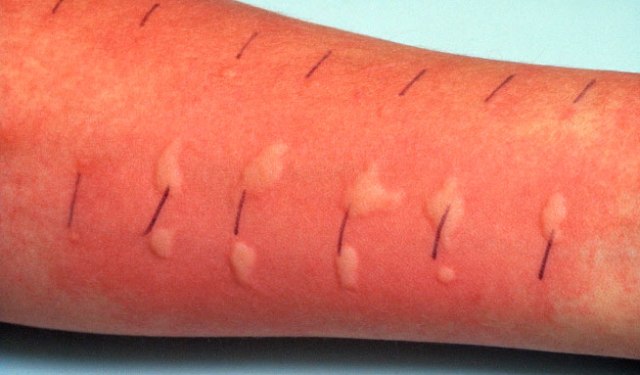
Prick test. It is carried out by applying allergens to the forearm and then puncturing them with a special lancet. It is possible to assess the body's response after 15-20 minutes.
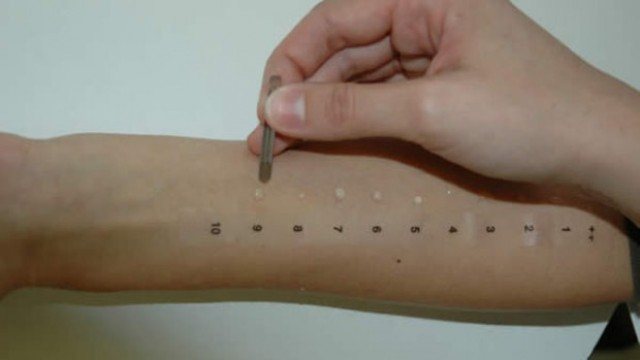
Carrying out a skin prick test
Scarification tests have the only difference from a prick test - this is a violation of the integrity of the skin. Instead of a puncture, a shallow scratch is made.
Patch tests involve wearing allergen-treated patches on the back skin for 24 hours or more.
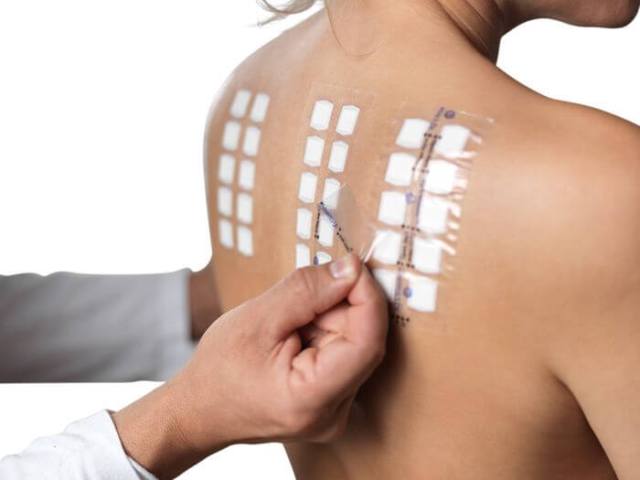
Carrying out application tests
Intradermal tests. In this case, the name speaks for itself: the suspected substance is injected under the patient’s skin.
You can read more about preparation, contraindications and interpretation of results in this article.
Basic methods for diagnosing allergies
To determine whether there is an allergy and what exactly provokes it, the doctor prescribes several types of diagnostics, including a blood test. And since some children really do not like such manipulations, they should be mentally prepared. Main types of research:
- Allergens are determined using special skin tests. This is done by prick testing (prick) or scarification test (scratch). Both methods are completely painless, but doctors believe that the injection method is safer. To carry out such a test, the child rubs his hand in the forearm area with an alcohol solution, then allergens are applied to this area in the form of drops. Then, using a scarifier, shallow scratches are made. During a skin prick test, instead of a scratch, small pricks are made with sterile needles. There is no need to worry about bleeding, as both methods are completely bloodless as the blood vessels are not damaged. During one session of the procedure, no more than 15 samples are made. If after a while swelling appears or the skin turns red, then most likely it causes an allergic reaction. To confirm or refute this information, several other types of diagnostics should be performed.
- To find out using IgE antibodies, you should get tested. To do this, the patient needs to donate blood from a vein. The information obtained from this test is similar to the information from skin testing, only the effect of the first is completely different.
- They are usually prescribed if the doctor, using the above methods, is unable to determine what the child is allergic to. These provocative tests are carried out by introducing a small amount of allergen under the tongue or into the respiratory tract. Sometimes the allergic reaction is so severe that immediate attention from a medical professional may be required.
- The simplicity of this method lies in the fact that the allergen is excluded. This is especially popular with a certain diet. The suspected pathogen is removed from the diet for 1 - 2 weeks. If allergic signs have disappeared, then the allergen has been identified.

Which diagnostic method is better?
Benefits of laboratory testing
- An allergen detection test measures the exact amount of circulating levels of IgE antibodies in the blood.
- Blood tests for allergens can be carried out regardless of the season - at any time of the year.
- There is no need to stop taking any medications.
- A blood test for allergies in children has no age restrictions.
- Diagnosis in infants is carried out only through blood sampling, since skin testing is contraindicated at this age.
- Blood sampling eliminates the occurrence of side effects in the form of allergic reactions, therefore it is considered a safe testing option.
- Laboratory tests are the preferred diagnostic method for people with skin conditions. For example, psoriasis, eczema, and dermatitis can make skin testing difficult.
Flaws
- Taking tests to determine allergens costs a person more than conducting tests.
- Waiting for the result of a test for identified allergens can take several days, unlike skin testing.
Only a doctor can determine the appropriate diagnostic method, taking into account the individual characteristics of each person’s body.
Serum immunoglobulins
For these studies, blood immunoglobulins IgE and IGg are used. Normally, a blood test for allergies is represented by the fact that the IgE immunoglobulin indicator is no more than 0.001% of the total volume of immunoglobulins in the blood serum.
In children under one year of age, the concentration of IgE is up to 15 kilounits, up to six years of age the concentration increases to 60 kilounits, in the primary school age period the numbers fluctuate to 90, during puberty the peak concentration corresponds to 200 kilounits, for the adult group of people the figure decreases to 100 kilo units
An increased level of IgE indicates the presence of allergic diseases in the human body. By examining blood using the IgG method, allergens associated with a delayed allergic reaction are identified. The interpretation of a blood test for allergies is carried out only by an allergist.
Continued adherence to the specialist’s recommendations will help restore health and avoid relapses.
Decoding the results
The interpretation of allergy tests should be carried out with an allergist, who will also take into account your medical history and your symptoms when diagnosing the disease.
A positive result is an indicator of an allergy in the test. He says that an increased level of specific antibodies was detected in the biological material being studied.
Different laboratories set their own reference values, as they use different types of equipment and research methods. Therefore, you should not compare the results of studies done in different laboratories.
A negative result means that the immune system is probably not responding to the substance being tested. However, in some cases it is possible to test negative and still be hypersensitive to a substance.
Advantages of a blood test over a skin test
If we look in more detail at what the difference is between these two tests, and why doctors recommend that children take a blood test, we can note the following:
- Skin tests are carried out strictly in the presence of a doctor.
- A nurse takes a blood test and then takes it to the laboratory.
- A single blood draw allows you to identify several causes and irritants of allergies.
- When donating blood, the child does not need to come into contact with the allergen, while in a skin test, the allergen is injected into the child's skin.
- For children who have dermatitis or eczema, the skin test will be difficult to perform.
- A blood test allows you to identify not only the irritant itself, but also determine the degree of sensitivity to it.
Seeing all the benefits for a child in taking blood, pediatricians and dermatologists refer the child for this particular test. It is informative and effective, allowing the doctor to prescribe effective treatment and save the child from the disease for many years. Therefore, it is advisable to identify the allergen through a blood test.
When are allergy tests prescribed?
It makes sense to take allergy tests if:
- Food allergies (manifests as a skin rash, itching).
- Hay fever (seasonal or year-round).
- Reactions to medications.
- Bronchial asthma.
- The presence of symptoms that together may indicate an allergy.
Important! An allergic reaction in adulthood can appear suddenly if the immune system has been weakened for a long time - after a long illness, in a state of immunodeficiency, after surgery, and also if a person encounters an allergen for the first time in his life. For example, living within the city, he may never encounter a plant that causes a reaction, but during a vacation in nature an allergic reaction may occur.

What are allergens
Before prescribing allergy tests, the doctor examines and interviews the patient to rule out an erroneous diagnosis. Viral rhinitis can be confused with the onset of hay fever; a skin rash is not necessarily allergic - it may indicate the presence of a skin disease.
The survey takes into account not only the patient’s complaints: it is important to know whether any close relatives suffer from allergies and under what conditions the reaction occurs. Also, before scheduling an examination, it would not hurt to take a general blood test: an increased level of eosinophils most likely indicates the presence of an allergy.
What can you find out from a general blood test?
A general blood test for allergies can only “hint”, since there are some signs that are characteristic of a very large group of diseases and conditions associated with allergies.
Typically this is:
- the number of leukocytes is normal, but not high, not “inflammatory”, without a shift of the formula to the left;
- red blood counts do not change, ESR is low;
- Very characteristic is an increase in eosinophils, over 5 in the leukoformula. In children, this is often associated with helminthic infestations. Moderate basophilia (more than 1 – 2 in the formula) may also occur.
Of course, only comprehensive, “targeted” allergy tests show the true picture, along with the results of clinical data, and necessarily anamnesis, and the connection between the deterioration of the condition and the identification of the allergen.
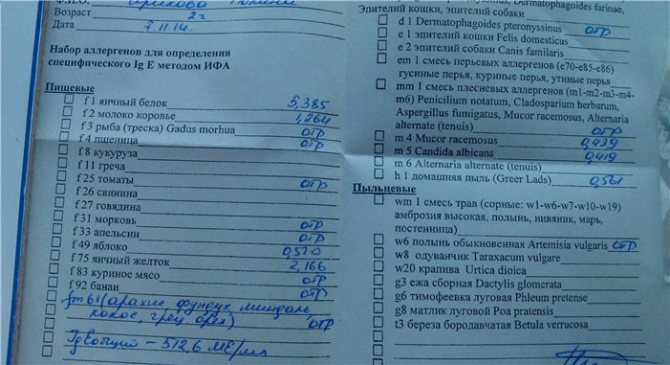
All patients should remember well that complete identification of all allergens for the patient’s body is a big step forward towards recovery. Even without medications, in most cases, elimination of the allergen can be achieved, and with treatment, a significant improvement in the quality of life and even complete recovery can be achieved.
Why specifically a blood test for allergens?
When diagnosing allergies, a blood test has advantages over skin (scarification) tests:
— there is no need for the patient’s skin to come into contact specifically with the allergen and, as a result, the possibility of an acute allergic reaction is excluded;
- a blood test can be done at any time, while skin tests are prohibited during periods of exacerbation of allergies;
— one blood draw is sufficient to test for an unlimited number of allergens;
— the result of a blood test for allergens contains both a quantitative and an objective indicator, which makes it possible to assess the degree of sensitivity to each allergen.
There are times when it is impossible to conduct skin tests, and then a blood test is indispensable.
Indications for which only a blood test for allergens is prescribed:
- significant damage to the skin (for example, the patient has eczema or atopic dermatitis);
- excessive allergic skin reaction - can give a false positive or false negative result (for example, with Quincke's edema, recurrent urticaria, mastocytosis);
- constant or frequent use of antiallergic drugs by the patient, as a result of which the sensitivity of the skin to allergens decreases;
- a history of an anaphylactic reaction or if there is a possibility of its development;
- the need to diagnose allergies in children or the elderly - a skin test in this category of patients for us may not be informative due to the modified degree of response to irritants.
What are the allergens being studied?
The rules for donating blood are very simple: no special preparation is required to identify a specific allergenic irritant; for this you just need to remember that you donate blood for allergens on an empty stomach on those days when the patient has manifestations of an allergic reaction.
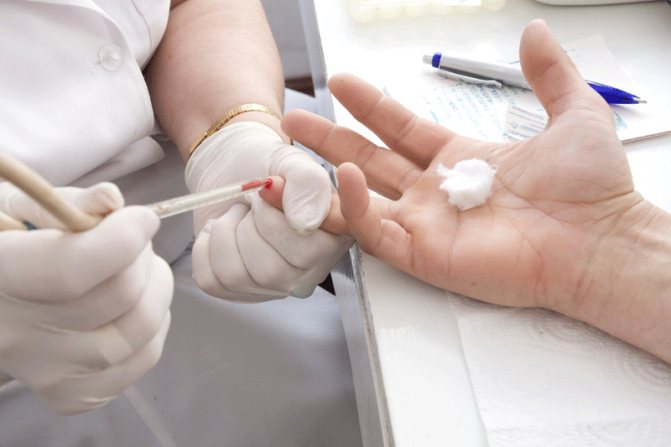
There are conditions, but they relate to restrictions. For example, a patient should stop taking antiallergic and antihistamine medications within a week, reduce stress levels within a few days, and not drink or smoke. Alcohol has an immunosuppressive and antihistamine effect. No other special preparations are required.
Basically, the following “targeted” analyzes are carried out in the laboratory:
You can test your blood for food allergens.
These are peanuts, crabs, cow's milk, shrimp, celery and soybeans, tomatoes and hazelnuts, chicken egg white and yolk. Even wheat flour can be an allergen, and quite a strong one. Regular wheat is sometimes a source of rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Patients with hay fever often experience cross-reactions - when the grasses are in bloom, they have a severe allergy to flour, a blood test shows an allergy when the grasses are in bloom - and they suffer all year round. In addition, food flour contains gluten, which may be a risk factor and contributes to the occurrence of multiple sclerosis;
There are many so-called household allergens.
These are animal hair and epithelium, various molds, and arthropods, for example, cockroaches. House dust testing is also being carried out. Thus, few people know that the determination of specific immunoglobulins to the allergen of dermatophagous mites often reveals the causes of allergies. This is the main household bed allergen. In house dust, in one gram of it from a sleeping mattress, up to 15,000 mites can be found.
These mites are tiny and not visible to the naked eye; their size does not exceed 0.3 mm. But the allergen of these mites is very strong. Their small body parts, the size of large bacteria, and their waste products, especially feces, are extremely strong allergens. As a result, in the morning after sleep, the patient develops Quincke's edema, allergic conjunctivitis, develops respiratory allergosis, and, ultimately, bronchial asthma. Therefore, a full examination of a patient with allergic reactions should include the identification of specific class E immunoglobulins for house dust, even if there have never been fish, hamsters, dogs or cats in the house;
Many pollen allergens are detected in the laboratory.
There are so many of them that there are entire sets of allergen panels, for example, for weed allergens. These are wormwood, dandelion, common ragweed, plantain. Some trees have highly allergenic pollen. This is birch, alder and willow, this is oak. From April to May, and a little later in Siberia, the pollen of these trees can also give strong and cross-reactions. Various meadow grasses, such as fescue, bluegrass, and Timothy grass, can significantly poison the patient’s life;
Also, in patients donating blood for allergens involves the detection of not only specific immunoglobulins E, but also class immunoglobulins G.
Immunoglobulins G and E are often found specifically for food allergens. And it is these antibodies that often determine increased sensitivity to food components when donating blood to allergens. This type of research has recently appeared because it was previously believed that immunoglobulins G were not related to allergies. But it turned out that this is not the case, and these compounds can be identified in the laboratory.
And if the patient is allergic to bananas or cheese, to pepper and parsley, to buckwheat and beer, to yogurt and coffee, to pumpkin, lemon, and even to black tea and millet, then this It is immunoglobulins G that are to blame.
You can read more about immunoglobulins of this class in the article “Immunoglobulin G: what is it? norm, reasons for increase and decrease.”
In addition, the laboratory conducts a blood test for allergens in adults and children, antibodies to gliadin, to identify intolerance to gluten and wheat.
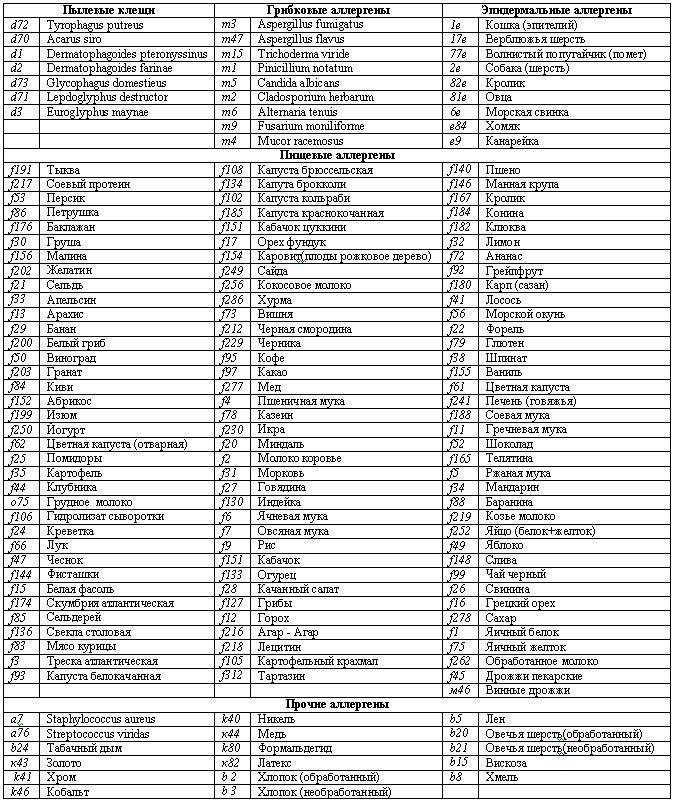
Allergens may include various chemical compounds, such as latex. The patient may develop contact dermatitis when wearing gloves or using condoms. For many people, various medications, most often antibiotics, can also cause allergy symptoms. When do you need to donate blood, and is there a difference between tests in adults and children?
Examination methods
If the body shows an allergy (demonstrates it), but independent diagnosis of the allergy - both its fact and its source, is impossible, then identification is carried out in the following ways:
- conducting a clinical blood test (taking into account nonspecific indicators);
- targeted blood testing to determine the level of immunoglobulins;
- assessment of skin tests (without the need to donate blood for allergens);
- immunoblotting technique (using allergy panels).
Research methods have age differences. So, if a blood test for allergies is a common method for children and adults, then children under 3 years of age are not checked with skin tests, and in less than six-month-old infants, the determination of immunoglobulins will give unreliable results (due to the level of the immune response that has not yet been fully formed).
General blood test for allergies
It answers the question of what is elevated in the blood during allergies, confirming the very fact of its existence.
Eosinophils - white blood cells with specific properties are always present in it, but their increased number (percentage in the total mass of cells and the ratio with the number of other white blood cells) indicates two conditions:
- selective (or general) allergization of the body;
- parasite carriage.
Thus, conducting a general clinical blood test is a method of only the most general allergy analysis.
Now, after confirming the assumption of the existence of a selective response to certain substances, the adult patient faces the question: what blood test should be taken to determine allergies?
If a child needs an examination, then parents are faced with two questions: where to donate blood for allergens closer to home (without driving a sick child around the city) and how much does a blood test for allergens cost, which the pediatrician must answer.
Immunoglobulins
This is one of the categories of proteins in the blood that have corresponding alphanumeric designations, depending on their structure and function.
To identify an excessive reaction to substances not only entering the body from the outside, but also those produced within the body, the content of total immunoglobulin class E (IgE) in the blood serum is assessed.
A blood test for allergens is carried out in adults and children only older than six months, because it makes sense to determine the IgE level only after the process of immunity formation is completed (in six-month-olds it is not complete).
Each age range has its own limits for the content of a chemical compound that performs in the body the function of recycling hazardous substances and cells foreign to it.
So, for children 2-14 years of age this indicator is from 0 to 150 mIU/ml, for adults under 60 years old - from 0 to 113, over 60 - from 0 to 114.
Exceeding the upper limits of the age norm indicates the fact of allergization of the body.
Another method of identifying allergies is to conduct a RAST test (from the term radioallergosorbent) to detect excessive levels of not only IgE, but also IgG.
Blood for these studies is taken from the ulnar (cubital) vein. Preparation for the analysis includes the patient's condition on an empty stomach (with food intake 8 hours before the examination).
Before the study you must refrain from:
- from consuming a presumably allergenic product;
- from contact with animals.
It is necessary to refrain from smoking and taking antihistamines. The presence of pregnancy, fever, cold symptoms, exacerbation of chronic diseases, or undergoing a course of hormone therapy is the reason for postponing the analysis to a more favorable time.
Video from an expert:
This method also does not answer which specific agent caused the body’s hyperreaction. This request can be answered by performing skin tests or using their modification with the assessment of a narrower range of substances that can mobilize the body to protect itself from a falsely understood threat - allergy panels.
Skin tests
The method is based on the reaction of the skin when microdoses of substances with a presumed allergic effect get inside it through specially made shallow incisions. If changes in the state of the microwound occur after 20 minutes, the reaction is considered positive.
This may appear:
- redness;
- local edema;
- skin itching;
- the sum of all the above characteristics.
In addition to the advantage (ease of implementation), the technique has disadvantages such as the inability to test more than 10-15 substances per session, as well as the likelihood of false-negative or false-positive responses.
Allergy panels
The technique is based on the same principles as the skin test method, but differs by grouping the most common allergens into separate panels, including:
- exclusively food products;
- substances that enter the body through inhalation (entered with inhaled air);
- combinations of substances of the first and second categories (mixed panel);
- the most common substances that provoke children's hyperreaction.
The last composition (pediatric panel) is a selection of allergens that most often affect the child’s body:
- protein of milk, eggs;
- pet hair;
- pollen of the most common plants;
- house dust containing mites.
The panel of food provocateurs includes:
- peanut;
- milk protein;
- tomato;
- apple;
- orange and much more.
In addition to those listed, there are also other, less relevant, panels.
Skin testing techniques are divided into:
- scarification (with making cuts through a drop of the applied substance);
- application (with the application of a tampon moistened with a solution of the suspected irritant to the surface of the skin);
- prick tests (where, in contrast to using a scarifier, skin is damaged with disposable needles);
- intradermal administration of solutions of allergenic substances.
Preparation for skin testing and allergy panels includes the need to accurately recall the date of the last allergic episode (30 days or less), which must be reported to the laboratory physician.
Psychological preparation should be carried out, taking into account the need to stay in a medical facility for the entire period necessary to complete the analysis (due to the possibility of deterioration of the condition).
It is necessary to stop taking antihistamines (with the permission of your doctor) and avoid contact with provoking substances.
The time to evaluate skin tests depends on the properties of the substance used. The first results appear after the first 20 minutes from the start of the manipulation, the later ones are read after one or two days.
Its results are indicated in the form in the form of a record:
- negative;
- positive;
- weakly positive;
- doubtful.
Video from Dr. Malysheva:
Symptoms
Every person should know how to determine the presence of allergies.
To do this, there is a list of the first symptoms of the disease:
- rhinitis – stuffy nose;
- frequent coughing and sneezing;
- swelling in the area of soft tissues and mucous membranes;
- sensations of discomfort in the larynx area;
- inflammatory processes on the skin (redness, rashes of various sizes, etc.);
- itching in areas of inflammation;
- increased tearfulness;
- redness and swelling of the mucous membranes of the eyes;
- disruption of the respiratory system;
- general weakness of the body;
- urges of nausea and vomiting;
- uncontrolled process of urination and defecation.
If the above symptoms are present, you should immediately go to the nearest medical facility, where the doctor will take a blood test for allergies in the child, confirm the diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment method.