Good afternoon, many will be interested in understanding their health and their loved ones, and I will tell you my experience, and we will talk about Acute urticaria: photos with a description of the symptoms, treatment and causes. Most likely, some details may differ, as was the case with you. Please note that you should always consult with highly specialized specialists and not self-medicate. Naturally, you can quickly find the answer to the simplest questions and diagnose yourself. Write your questions/suggestions in the comments, and together we will improve and supplement the quality of the material provided.
Acute urticaria. Causes
In acute urticaria, the causes of the disease in adults and children are the same:
- intolerance to drugs (antibiotics, especially penicillin type, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, sulfonamides, B-class vitamins, radiocontrast medications, anticonvulsants);
- allergies to food products (dairy, wheat, chicken, nuts and fruits, bee products, pollen, seafood, smoked meats, food additives);
- response to bee, wasp or ant venom;
- viruses (hepatitis B and C, herpes type 1, CMV, Coxsackie A and B);
- bacteria (microplasma, chlamydia, yersinia);
- parasitic creatures (such as helminths or protozoa);
- cosmetics and household powder and liquid products;
- environmental factors (overheating, solar radiation, low temperatures, wind);
- overstrain: prolonged stress, nervous breakdowns, depression.
The sooner you go to the doctor, the better. Otherwise, acute urticaria will be replaced by chronic urticaria.
Diet for acute urticaria
The menu should include:
- light-colored fruits and vegetables (for example, pears and cucumbers, cabbage and zucchini);
- lean meat (except chicken);
- fermented milk;
- coarse bread.
It is advisable to exclude (potential provocateurs):
- honey;
- anything chocolate, baked goods and sodas;
- eggs, mushrooms;
- smoked and fried;
- spices.
Traditional therapy only works as an additional measure. The acute form of urticaria does not respond to them. But the symptoms can be alleviated. A few recipes from experience:
- Swamp duckweed. The grass is dried and crushed. Mix with honey. Reception - 4 times a day. Important: honey is a strong allergen, so you should consult a doctor.
- Herbal infusion. Has a sedative effect. Suitable herbs include mint, motherwort and valerian.
- Collection of herbs. Take fresh or dried parts of the following plants: St. John's wort (3 parts), immortelle flowers (4 parts), triphol leaves and tansy flowers (2 parts each), mint leaves (1 part). Pour boiling water over and let it brew. Boiling water - a glass for 1 tablespoon of the composition. Take 3 times a day before meals.
- Hepaprotective plants. To support liver function. Examples: calendula or milk thistle. Instructions for use are indicated on the package.
The quantity and dosage of drugs is prescribed by the doctor. You should also be careful with herbs - they can cause an increased reaction. You should not self-medicate.
Acute urticaria in adults
Treatment of acute urticaria in adults is generally similar. However, in adulthood, the range of medications that can be taken orally expands.
The acute form mostly occurs in people over 45-50 years of age. Before this age, the chronic type of the disease predominates.
Despite the fact that older people have a mature body, they have a stronger and more severe course of acute urticaria (photos of symptoms and treatment are proof of this). However, even in this case, all manifestations may go away within a few hours.
Acute urticaria in children
For acute urticaria in children, treatment depends on age.
It is not recommended to take medications until 2-3 years of age. However, at any age, you can use a special menu - an elimination diet, in which certain foods are excluded.
The child should not be given:
- chocolate products;
- citruses;
- eggs;
- fish;
- canned food;
- preservatives.
Pharmacotherapy consists of prescribing antihistamines. Children's dosages are prescribed in the instructions. The medicine is prescribed by the doctor.
Note to parents:
- At the age of up to 2 years, it is acute urticaria that predominates (photos of children that can be viewed online clearly demonstrate this).
- In patients aged 2-12 years, chronic and acute forms occur, with a predominance of the latter.
- In adolescents over 12 years of age, chronic forms predominate.
- Usually the illness lasts no more than 6 weeks.
- Inpatient therapy is recommended for children from one month to three years of age.
- The acute form overwhelmingly affects children with atopic pathologies.
In children with acute urticaria, the cause of the disease in 74% of cases is food provocateurs.
For more serious and severe pathologies, the symptoms are:
Causes
The mechanism of development of allergic urticaria in adults and children is associated with massive degranulation of mast cells. These structures include histamine, heparin, leukotrienes and other biologically active compounds that shift metabolic processes in tissues. At the same time, the blood vessels expand, their walls become more permeable, tissue fluids accumulate, and pain receptors in the affected area are activated, which is felt as itching. As a result, a rash appears in a limited or large area. In severe cases, hives cover the entire body, and this can trigger a general reaction such as anaphylactic shock and angioedema.
Allergic urticaria can occur at any age, but is more common in children. Experts attribute this to the immaturity of the immune system.
The triggering factors are house dust, plant pollen, insect bites, UV exposure, contact with household chemicals, cold, tobacco smoke, animal hair, and cosmetics. Often occurs when consuming food allergens - tomatoes, citrus fruits, chocolate and chocolate products, honey and bee products, eggs, strawberries, seafood, nuts.
A skin reaction is often a symptom of another pathology: chronic stress, helminthic and parasitic infestations, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, diabetes, hormonal imbalance, endocrine disorders. Urticaria can accompany systemic lupus erythematosus, gout, and malignant tumors, regardless of location. It appears in case of drug overdose, as well as in various infectious diseases. Sometimes the reasons remain unclear.
We recommend reading: MRI of the lungs and bronchi: what it shows, features, indications and advantages
Allergic urticaria can be acute or chronic, although the boundaries between them are arbitrary. In the acute form, rashes and itching last no more than 6 weeks; in case of a longer course, the chronic form is diagnosed. In 20% of cases, symptoms persist for 5 years.
With urticaria, the organs of the immune system take part in the inflammatory process, antibodies are formed, and histamine levels increase. This disease should be distinguished from pseudoallergy, in which mast cells are activated without the participation of immune mechanisms. The following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- Cold and heat urticaria: the first is observed when the skin is exposed to cold, as well as consuming cold foods and drinks, the second is observed when exposed to high temperatures.
- Dermographic urticaria is a rare form that is triggered by physical pressure on the skin.
- Solar urticaria is a photoallergy in which sunlight is the trigger.
- Vibration urticaria is a pseudo-allergy to mechanical vibration of tissues, observed more often in construction workers.
- Aquagenic urticaria: occurs as a reaction to the pressure of water jets.
- Nervous urticaria: can be a consequence of stress, nervous strain, fear.
Urticaria rash: 10 photos, types and differences, description in adults and children
Rash is the main symptomatic sign of urticaria. However, the hives rash can have different descriptions. After all, its appearance depends on the type and causes of the pathology.
Causes of hives rash
A rash is a mandatory attribute of urticaria. And its causes depend on the type of disease. There are two main types of pathology:
- Allergic. Upon first contact with a provoking substance, it is “remembered” by mast cells - through a mechanism involving immunoglobulin E. Upon repeated contact with the allergen, the body exhibits hypersensitivity and produces an immediate reaction. A large volume of histamines, interleukins and other substances is released into the blood. The immune system perceives it as a foreign and harmful organism.
- Pseudo-allergic. It is formed due to the influence of internal and external factors. Such as bacterial and viral infections, excessive physical activity, temperature changes. Immunoglobulin E and the immune system are not affected in this case.
The rashes for both types are different. Photos of hives rash are available online.
The chain of internal reaction can be described as follows: upon contact with a provoking substance, the permeability of the capillary walls increases.
This leads to an increase in the volume of tissue fluid, blood intensely rushes to the skin, the thinned walls of the capillaries cannot cope and itching, redness, and rashes appear.
List of possible allergens leading to rash:
- food products (sea and bee products, legumes and nuts, fruits);
- medications (usually antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs);
- household products (contain aggressive substances);
- perfumes and cosmetics;
- dust;
- animal hair and fluff;
- insect poison (released when bitten by bees, ants, bumblebees, etc.).
These are the most common cases. However, there are specific allergens such as solar radiation and vibration of household appliances. What exactly caused the rash is determined in the doctor's office.
Find out more
Symptoms
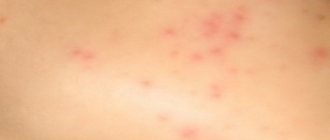
Urticaria is characterized by a rash in the form of pinkish-red blisters that rise slightly above the skin surface.
In the allergic form, the rashes have the following characteristics:
- intense itching a few minutes before the rash appears;
- bright red undertone of the formations (after pressing they become whitish);
- the size of individual formations is from 2-3 mm to 10-15 cm;
- smooth and clearly defined edges of the blisters;
- the area around the blister is also reddish.
Pseudoallergic urticaria has several types of rashes depending on the subtype. However, in general they are the same as for allergies.
So, what is the rash associated with hives:
- Solar urticaria. Small rash with blistering formations up to 1-2 mm in diameter. The color is pink, with a red edging around it. Appears a few minutes after sun exposure.
- Cold. The rash appears unevenly: either immediately after exposure to cold, or after 10 hours. The size of the blisters ranges from very small dots to large spots. Localization - at the site of cold exposure.
- Aquagenic. Rashes form on the most tender areas and resemble burns. They often progress. The skin becomes very dry. Sometimes there may be no rash - just itching.
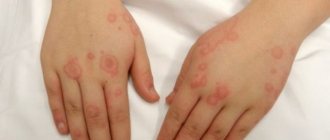
- Mechanical. It can appear in two ways. The first is scratch-like blisters that rise above the skin and are very itchy. At night the itching is more intense. The second option is round, light-colored blisters with a dark red edge.
- Stressful. The formations are large and round, and can merge into one or several spots. The shade is pinkish and pale. Sometimes the center may be white and the border may be pink.
- Cholinergic. The rash is small. Sometimes so much so that it is unnoticeable. It usually appears in the upper part of the body - on the forearms, chest, back, neck.
Thus, it is necessary to distinguish between rashes based on the type of urticaria. In chronic urticaria, the formations have a regular shape and clearly defined edges. Localization is variable and spontaneous. The color is less red than in acute cases.
Rashes in children
Children's rashes are practically no different from the clinical picture in adults. However, they are smaller and can appear faster and more abundantly - due to the incomplete formation of immunity. In addition, rashes can appear on the mucous membranes - this happens more often than in adults.
The hives-like rash may develop into pinkish-brown nodules. They resemble small bubbles. It is important not to comb them. Otherwise, erosions and crusts will form.
If the rash persists for a long time, the symptoms may become more complicated. The following will appear:
- restlessness and irritability;
- problems with appetite;
- vomit;
- constipation or diarrhea.
Most often, pathology occurs due to food products. Especially with exudative diathesis, which often affects children on artificial formula.
The next most common causes are progression of infection, allergies, gastrointestinal pathologies and sensitivity to household or cosmetic products.
As a rule, urticaria goes away without a trace by about 3-7 years. However, in rare cases, it can remain for life or develop into another disease - diffuse neurodermatitis.
Rash in adults
Education is no different from children's education. You can verify this by looking at photos of urticaria rashes in adults - they are available in large quantities on the Internet.
In an adult, the disease can manifest itself unexpectedly. Even if such cases have not happened before.
In most cases, the manifestation of urticaria and rashes is preceded by some disease or change in climatic conditions that lead to a malfunction of the immune system.
As a result, the body becomes more susceptible to certain biologically active substances. Histamines are produced more intensely and a rash appears.
It is worth remembering that adults are at greater risk of the pathology becoming chronic. Therefore, therapy should not be delayed.
Treatment of rash due to urticaria
For urticaria rash, the causes and treatment are determined by the doctor. He will investigate the pathogenesis and prescribe appropriate measures. However, in any case, the first priority is to eliminate provoking factors from the patient’s life.
Treatment options may include:
- Internal medications. They are divided into two types - immediate aid and course therapy drugs. The former are used once in difficult cases when the symptoms are complicated. As a rule, in the form of adrenaline injections and other means. The latter are prescribed by a doctor and often include sorbents, antihistamines, immunostimulants and corticosteroids. It is advisable to use the latest generation of medicines.
- Medicines for external use. Soothing and anti-allergenic ointments, creams, gels. They are used at all stages of the disease. They are especially effective at the very beginning.
- Physiotherapy. Impact on diseased areas with ultrasound, ultraviolet training, skin treatment with the Darsonval apparatus. They may also prescribe radon and sulfide baths.
- Vitamins. Needed to improve immune function. B-vitamins, PP, C and A are often prescribed. Minerals such as magnesium will also be useful.
- Diet. The first priority is to avoid potential food provocateurs. Secondly, a proper and varied diet containing a large amount of greens, vegetables and proteins. In some cases, bifidobacteria are indicated.
It is important to start therapy as early as possible. Otherwise, the rash can cause complications, and under certain circumstances, become chronic.
Rash prevention and possible consequences
First of all, it is important to see a doctor regularly in order to correctly diagnose the pathology. A hives-like rash may be a symptom of rubella.
Other preventive measures:
- taking care of the immune system;
- regular use of soothing and moisturizing creams and gels;
- absence of overexertion and prolonged stress;
- avoiding being in a stuffy, unventilated room;
- wearing loose clothing and shoes made from natural materials;
- periodic use of sedatives (discussed individually with the doctor);
- regular light hardening;
- compliance with the indicated diet.
It is also possible to use traditional medicine, but you should first consult a hospital.
If the pathology is chronic, complications can develop in two ways:
- Development of infection. The patient may develop and progress a fungal or bacterial disease. The reason is the entry of the pathogen into damaged areas of the skin, which can be facilitated by scratching or long-term antibiotic therapy.
- Hyperpigmentation. Develops due to prolonged exposure to solar radiation. Persons with chronic urticaria are strictly contraindicated from being in direct sun for a long time, as well as using a solarium. A rash similar to urticaria
Also, in all cases of urticaria, in some patients the symptoms may be complicated by Quincke's edema. The swelling usually affects the face and larynx, causing breathing problems. If action is not taken in time, death is possible.
Source: //www.dermatit.net/krapivnica/syp-pri-krapivnitse/
Treatment
Acute forms of urticaria respond well to treatment with H1-histamine receptor blockers. Patients are prescribed antihistamines of the second and third generations (Loratadine, Cetirizine, Levocetirizine).
For chronic and recurrent allergic urticaria, the approach to treatment is different. In this case, basophil membrane stabilizers (ketotifen fumarate) and calcium antagonists (nifedipine) are indicated. These drugs prevent the activation of mast cells and slow down the development of skin reactions. If a decrease in the activity of the immune system is suspected, immunomodulators may be prescribed. If urticaria is a symptom of a systemic disease, treatment of the underlying disease is prescribed.
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of urticaria. The patient is prescribed a diet that reduces the allergenic background. After the patient's condition has stabilized, a provocative test can be performed to identify the nutritional or physical nature of the reaction, and then exclude this factor.
When allergic urticaria is extensive and combined with angioedema or leads to the development of anaphylactic shock, the patient is indicated for injections of adrenaline, steroids and intensive care in a hospital setting.
Hygiene in case of urticaria, especially in a child, plays an important role. On dirty skin, bacteria and germs multiply faster, and this can complicate the course of the disease. Therefore, regular bathing in warm water without hard washcloths is necessary so as not to damage the affected areas.
Allergic urticaria is a common disease, accounting for 20% of all cases of allergic skin reactions. It appears as a rash similar to a burn after contact with nettles. It can be an independent disease or a secondary pathology. More often it occurs as a reaction to food allergens, but in certain cases it acts as a symptom of a wide range of diseases.
Why does urticaria appear?
Children are the most susceptible to skin allergic manifestations; with age, the symptoms disappear completely or are characterized by a lesser degree of damage. Nocturnal manifestations of urticaria in a child:
- Exogenous factors Food that causes allergies in a child. During the day, manifestations of urticaria may not be observed, but after the child falls asleep, the body's reactivity decreases and a rash appears. Most often, children are sensitive to eggs, nuts, seafood and legumes.
- Medications. Children usually suffer after long-term treatment with antibiotics. In rare cases, antibiotics enter the body through low-quality dairy products.
- Chemical food additives. Eating low-quality foods can cause substances to enter the child's body that adults do not react to.
- Insects. In this case, the cause of urticaria can be not only the bites of mosquitoes, mosquitoes or fleas, but also direct skin contact with the insect. Ticks that are in the bed.
- Foreign microscopic particles. This includes pollen or plant parts, dust and fluff from pillows, and particles of washing powder.
- Damage by parasites. Most helminths are active at night.
READ ALSO: Rash around the eyes in a child: possible causes, symptoms, necessary diagnostics, treatment options, photos
Urticaria in children
Children are no less likely than adults to suffer from urticaria. Thus, from 5 to 7 percent of school-age children suffer from some form of urticaria. In early childhood ( up to 2–3 years
) predominantly acute urticaria predominates.
Both acute and chronic urticaria occur in children from 3 to 13 years of age. As for infants ( up to one year
), urticaria is a common cause of urgent
conditions
. For this reason, they are often hospitalized in the hospital.
As a rule, acute urticaria is observed in children with atopy ( predisposition to allergic reactions
). Studies have shown that one in five children admitted to hospital with acute urticaria also suffers from atopic dermatitis. More than half of hospitalized children have other allergic reactions.
Is hives contagious?
Symptoms of neurogenic urticaria
Psychogenic urticaria is characterized by large blisters that merge with each other, covering large areas of the body.
Individual elements of the rash have an oval or round shape, but when they are combined, the formations acquire smooth polygonal outlines. The color of the blisters can vary from white to pink, and in some cases the blisters can be two-colored ( white in the center and pink on the edges
). A mandatory symptom of neurogenic urticaria is intense itching.
Urticaria rash: what types and how to get rid of it?
The hives rash occurs suddenly. It is difficult to miss due to the blisters and severe itching. The disease can be acute or chronic. It is diagnosed in both infants and adults. Urticaria is classified as a multifactorial pathology.
Its treatment does not begin until the origin of the rash, which may be allergic or non-allergic in nature, is established. Urticaria comes in many varieties, and its symptoms are similar to those of other skin diseases.
Therefore, when making a diagnosis, dermatologists cannot do without conducting a differential analysis.
What is urticaria
Urticaria, or skin rash also called nettle fever, is a disease characterized by the sudden formation of itchy, flat, red or pink blisters.
The elements of the rash have a dense structure and different sizes, which can reach the size of the palm of an adult. The rash does not disappear from the skin until a couple of hours, after which it gradually goes away.
But in the absence of proper treatment, new blisters appear in place of old blisters.
Urticaria can be acute and (rarely) chronic, recurrent. The acute form of the pathology lasts 2-3 days. Chronic symptoms can torment a person for several months or even years. In complex cases, urticaria is accompanied by general malaise (fever, chills, headaches, drowsiness, etc.).
Doctors divide nettle fever into the following types:
- Sunny - its appearance is provoked by prolonged exposure to the sun (more than 20 minutes). The cause of sun rash is sometimes the components of skincare cosmetics, which, after application to the skin, increase its sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation (photosensitizers).
- Cold (reflex) - itchy rashes occur due to prolonged exposure to the cold or consumption of very cold foods/drinks. The rash occurs either immediately after exposure to a provoking factor, for example, after contact with water, or after 8-9 hours.
- Aquagenic is a rare form of the disease, which is an allergy to water or other liquid (a person’s own sweat), observed mainly in adults. Aquagenic urticaria is progressive in nature, that is, its symptoms become more pronounced every day. Doctors have clarified what causes urticaria in adults after contact with liquids. The provoking factor is not moisture, but its constituent components. For example, tap water contains chemical compounds that enter it from pipes and adapters, which means copper, lead or iron can become an irritating factor.
- Food - an allergic reaction of the body to certain foods. Usually observed in infants when complementary foods are introduced. In adults, food urticaria occurs against the background of diseases of the digestive tract. Nettle rash is accompanied by swelling of the larynx, cheeks and lips, more often than other types of urticaria it is complicated by Quincke's edema. The risk group includes adults with gastrointestinal dysfunction.
- Dermographic - nettle rash as a result of skin injury (friction by clothing, bruise). Occurs immediately during or after prolonged skin irritation. Dermographic urticaria is typical for people with a hereditary predisposition, ulcerative and endocrine diseases.
- Cholinergic - a rash is formed as a result of exposure of the skin to high temperatures, with increased sweating (prolonged stay in the sauna, physical activity). The development of pathology is based on the body’s high sensitivity to acetylcholine (an important mediator of the nervous system). When a mediator is suddenly released into the blood, itchy urticaria appears on the skin.
- Psychogenic (neurogenic) - this urticaria appears against the background of prolonged stress. Sometimes, a few hours after the rash, angioedema appears (affects the larynx and the mucous membrane of the digestive tract). If you do not get the help of a doctor, the swelling spreads to the internal organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The risk group includes hot-tempered, irritable people.
- Infectious - appears against the background of a viral infection (influenza, ARVI). It is characterized by a maculopapular rash, which can cause exanthema to be misdiagnosed.
- Hormonal - occurs in pregnant women and women in labor due to changes in hormonal levels. During this period, emotional stress and weak immunity contribute to the appearance of a rash. Without the necessary treatment, urticaria becomes chronic.
A common complication of acute urticaria is a bacterial infection (streptococci, staphylococci), which penetrates the skin when itchy blisters are scratched. As a result, the skin becomes covered with ulcers and boils.
What do skin rashes look like?
The nature of the rash with urticaria depends on the type of pathology. Here are some features and description of the rash:
Sunny - the blisters are small in size, approximately 1-2 mm, sometimes they increase to 1-2 cm. The color of the rash is pink, the edges of the elements are red. Cold - the sizes of the nettle spots are different (small, extensive). The color is whitish or pink. Aquagenic - elements of the rash appear in the form of painful red spots, reminiscent of burn injuries.
In some people, this type of urticaria develops without a rash, the only symptoms are dryness and itching. Food - manifests itself as pink-red small blisters that constantly itch. Dermographic - the elements of the rash are linear blisters, similar to scars. The blisters are swollen.
They have a pale color, and the surrounding areas range from pink to dark red. Cholinergic - characterized by the appearance of a small itchy maculopapular rash on the body. Psychogenic - represents large oval or round blisters that merge into one, which leads to extensive damage to the skin cover.
Elements of the rash are white or pink, some are white with a pink outline. Infectious - the characteristics of the rash are different, dense pink or red nodules, blisters with purulent bloody contents, erosions, dried crusts may appear on the skin. Hormonal - manifests itself as bright red blisters with severe itching .
In complex cases, urticaria is accompanied by a deterioration in general health (fever, chills, headache).
Where can a hives rash appear?
Urticaria rashes can affect any area of the skin:
- With the solar type of urticaria, blisters appear on exposed areas of the body (arms, face, neck).
- With urticaria, which occurs against the background of hormonal imbalance, the rash first appears on the stomach, and then spreads to the thighs and buttocks.
- Rash from exposure to cold most often occurs on the neck, face and arms, and can also appear on the thighs and calves.
- Aquagenic urticaria affects the skin of the knees and elbows, and the inner thighs.
- The rash of the dermographic type most often appears on the neck, hands, navel and inner thighs.
- During emotional and physical stress, a nettle rash usually affects the skin of the body, in particular the chest, abdomen, lower back, as well as the skin of the arms and neck.
Additional symptoms
The main symptom of nettle fever is a rash and severe itching.
But in advanced cases, for example, if urticaria is accompanied by an infection or the patient has Quincke's edema (usually in the food form of the pathology), itchy blisters not only appear on the skin.
Swelling develops, in particular, of the upper respiratory tract. Additionally, this condition may be accompanied by nausea, cough, redness of the sclera of the eyes, headache, severe abdominal discomfort, and stool disturbances.
How to distinguish an allergy rash from other diseases
Symptoms of urticaria are similar to those of the following pathologies:
- Lymphostasis (impaired lymph outflow) - the disease provokes swelling and a rash on the skin of the extremities, characteristic of urticaria.
- Recurrent erysipelas is an infectious disease in which the skin is attacked by streptococci. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of red spots and an increase in temperature.
- Melkerson-Rosenthal syndrome is a neurological disorder accompanied by swelling of the face and lips.
- Infantile (nodular) prurigo - manifests itself as itchy nodules on the skin, observed in children under 5 years of age and in the elderly.
The differences between urticaria and the listed pathologies can only be identified by a doctor during differential diagnosis.
The main distinguishing signs of urticaria are the rapid appearance and disappearance of swelling, rash, and itching. Symptoms disappear if there is no physical or chemical effect on the skin for 24 hours.
Principles of treatment
Comprehensive treatment helps get rid of hives. If the rash is very severe, the person feels very unwell, is suffocating, emergency assistance must be provided.
First aid
Stages of first aid for nettle fever complicated by angioedema or anaphylactic shock (the person’s face turns red, breathing is difficult):
- Call an ambulance.
- Provide air access to the lungs through narrowed airways. The patient should be placed horizontally, the neck should be straightened, nothing should be placed under the head. Check the oral cavity for the presence of foreign objects (chewing gum, tablet, lollipop).
- Maintain blood pressure levels. The patient should lie horizontally, his legs bent at the knees.
- Inject 0.5% adrenaline intramuscularly into the upper thigh once, 1 milliliter; if there is no effect, repeat the injection after 10 minutes. Adrenaline eliminates spasms and relaxes the muscles of the respiratory tract. If there is no injection, then you should wait for the ambulance to arrive.
Treatment of urticaria
In order to begin to effectively treat hives, you should understand what causes blisters on the skin, and also try to eliminate them. Patients are prescribed cleansing enemas and an elimination diet for at least three days. It is necessary to exclude from the diet everything that can cause an allergic reaction - such foods can be citrus fruits, eggs, chicken, carbonated drinks, chocolate and others.
If you are diagnosed with urticaria, you should urgently start taking antihistamines.
(but be sure to consult your doctor!), such as:
- teridine
- telfast
- terfenadine
- bronal
- astelong
- Lomilan
- Zyrtec
- Claritin
- cetrin
- kestin
If the patient has a chronic form of the disease, then you can also take:
- belloid
- bellaspon
- bellataminal
#1 barcynya
Good afternoon. I am contacting you on behalf of my husband, we just don’t know how or what to treat. The situation is as follows. My husband is 27 years old. Weight 78, height 185, smokes, drinks moderately on holidays. Among the illnesses suffered are the annual acute respiratory viral infection (it goes away within a week) and bipolar affective disorder - the last episode was 4 years ago, now it is in stable remission, does not take any medications. Six months ago, severe hives began, always in the evening with large blisters, severe itching in the evening and at night. All red - the stomach, groin, legs, back, neck, the upper lip and left arm were swollen several times. By morning there was no trace. We drink Zodak and there is no hives at all. We just skip it in the morning and in the evening I’m covered in blisters again. We turned to a therapist, after tests and an in-person examination, he said that it was an allergy - drink Zodak if it helps. Goodbye.
Biochemistry General bilirubin 17.6 (normal up to 20.2) Direct bilirubin 5 (normal up to 5) Indirect bilirubin 12.6 (normal up to 15) a-amylase 30 (normal 16-32) ALT 0.4 (normal normal 0.1- 0.7) AST 0.29 (norm 0.1 - 0.7) Total protein 73 (norm 75-85) Cholestyrin 4.2
We recommend reading: Rice porridge for babies - how to cook it correctly. Frutonyanya and Nestle rice porridges.
We were surprised by eosinophils - 0. Shouldn't their increase be higher than normal in case of allergies? We took nemozol ourselves - once (for prevention a month ago, they suddenly thought it was parasites, they might cause a rash) The temperature is about 37 constantly. When palpated, the lymph nodes are clearly not enlarged (at least I didn’t notice). The tongue has a yellow coating. He has bowel movements every day - morning and evening at almost the same time, without constipation or diarrhea. I have never had any food allergies before, nor any allergies to medications.
Tell me, please, what could be the problem? Can I take any more tests? anything to pay attention to? We donated blood on our own initiative; the doctor did not prescribe it.
Signs and symptoms
Urticaria at night appears precisely acute, when a person wakes up from a high temperature and severe itching, but in the morning there may be no traces left, and upon examination and a thorough questioning, the doctor accurately diagnoses urticaria, prescribes a laxative, after taking which the disease does not recur in most cases. If you ignore contacting a doctor, a nighttime attack of urticaria may recur with greater force. When urticaria appears at night, the body temperature can rise to 39 degrees.
Chronic reductive is urticaria, which has many relapses. Appearing both during the day and at night, urticaria interferes with a person’s normal functioning and can lead to insomnia or other serious complications. Moreover, her treatment lasts a very long time and can drag on for months and years.
Chronic persistent papular urticaria affects a person for a long time, as it is caused by third-party, usually allergic, factors, when the rash disappears from the skin for one or more weeks, due to the fact that more and more new blisters constantly appear.
Reaction to certain foods
This is a common cause of urticaria in adults and children. Less common in adults than in children
. More often it is a pseudo-allergic reaction to the following products:
- Fish and other seafood.
- Chocolate.
- Citrus.
- Strawberry.
- Nuts (especially peanuts).
- Mushrooms.
- Alcohol.
- Eggs, dairy products.
In principle, anything can trigger the appearance of a rash, as an individual reaction of the body. Eating food can trigger the release of histamines.
If the product does not act as an allergen and does not trigger reactions characteristic of it, then the disease is pseudo-allergic. Surprisingly, hives can appear after ingesting a particular product, as well as upon contact with it.
Sometimes the body’s negative response may not appear immediately, but over the course of life or, on the contrary, disappear over time. It can be quite difficult for doctors to determine what causes hives, especially if there is a reaction to several foods at once. , excluding potentially dangerous foods from your diet will help you more accurately understand the reasons.
The disease is most often caused by shelf-stable foods
Hives on sweets deserve special mention
. For example, cocoa contained in chocolate, the remains of insect scales that ate these beans, and vegetable oils cause characteristic symptoms: redness and rashes on the skin of the face, swelling and itching. Similar symptoms appear when consuming honey, primarily due to the pollen and other components it contains.
Urticaria can also be caused by impurities contained in sugar. Accordingly, sweets that contain the above products should be excluded from the diet if a rash and itching appears.
Let’s also find out what causes the disease urticaria.
Treatment of urticaria in infants. Urticaria in infants rarely becomes chronic and, as a rule, goes away within 2 to 3 days. Treatment of this pathology involves eliminating the factor that initiates the appearance of the rash. Medications may also be prescribed to reduce itching and strengthen the child’s general condition.
Urticaria after sleep in a child
The main cause of so-called drug-induced urticaria, which accounts for approximately 60% of cases, is usually the use of antibiotics and other medications.
When such medications are re-prescribed, even in smaller doses, or substances with a similar chemical structure, the child’s allergy symptoms reappear. Sometimes symptoms of urticaria appear after sleep. Diagnosing the causes in this case is not an easy task. The child goes to bed healthy, and after sleep is covered in blisters and rashes. One reason may be the components of the laundry detergent used to wash bed linen and pajamas.
Food urticaria can be a consequence of eating known allergenic foods: chocolate, citrus fruits, honey, certain dairy products and others. This type of allergy occurs in 6-8% of children under 2 years of age, mainly in the first year of life. Subsequently, the number of manifestations of this disease decreases and in adults it is about 2%.
The risk of developing this form in children is influenced by allergic diseases, toxicosis, the use of medications and the mother’s diet during pregnancy, the characteristics of infant feeding (breastfeeding or artificial, the properties of products used for complementary feeding, the timing of introducing additional products into the child’s diet), the effect of allergens on a pregnant or nursing mother, in particular related to her professional activities, the presence of allergens in places where the child is.
Urticaria occurs in children who are especially sensitive to fungi, viruses and bacterial allergens. Often, the presence of sources of chronic infection in the child’s body, which are gastrointestinal diseases, in particular intestinal dysbiosis, as well as ENT pathology, also have an additional influence.
The causes of urticaria are often insect bites, the action of certain chemical compounds, iodine.
Cholinergic urticaria can occur due to stress of a mechanical and physical nature, nervous excitement, sudden temperature fluctuations, and the negative influence of the sun.
Tight and uncomfortable clothing of a child with pressure and rubbing of the skin, mechanical damage to the skin, as well as long trips, massage, jogging can cause urticaria (dermatographic or vibration, respectively).
Course of urticaria
Hives are characterized by itchy, inflamed rashes that can appear anywhere on the body.
The disease can occur in the following forms:
- chronic reducing;
- chronic papular;
- spicy;
- pseudo-allergic.
Chronic reducing course of urticaria is characterized by a constant rash throughout the body, which can appear at any time of the day. The disease can last for many months or even years, while the person feels itching, which does not allow him to live normally.
Papular chronic course is characterized by the fact that the patient experiences new rashes over a long period of time, while old manifestations of rashes quickly disappear and are replaced by new ones. This course may be associated with constant contact of the child with the allergen.
The sudden occurrence of urticaria at night is its acute course. In this case, the rash appears instantly, and after a short period of time completely disappears. The patient experiences a sudden awakening due to severe itching and scratching, and in the morning there is no trace of the rash.
The pseudoallergic course clinically differs little from the true one, but the etiology of its occurrence is related to the functioning of the digestive organs and liver.
Symptoms
Knowing the symptoms of urticaria in children, you can quickly identify an allergic reaction and take measures to eliminate it. Urticaria in a child manifests itself in the form of itchy rashes, mainly like blisters. They can occur not necessarily on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes of the eyes, lips and digestive organs.
Urticaria in a child requires a timely response and the adoption of appropriate measures, since it can cause Quincke's edema, or the so-called giant urticaria, when swelling of the airways occurs, breathing is impaired, and coughing attacks appear. In some cases, the child may exhibit symptoms such as swelling of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and vomiting, and in severe cases, the nervous system and membranes of the brain are affected.
Skin manifestations of nocturnal urticaria in children
If urticaria appears in a child, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor, since the disease can lead to the development of Quincke's edema.
Acute manifestation of urticaria in a child occurs between the ages of 1 and 5 years, and is characterized by:
- Waking up due to severe itching.
- Several blisters form on the skin, occupying a small or extensive part of the body.
- When large areas of skin are affected, an increase in body temperature may be observed.
- In the morning, the rash disappears completely; bloody crusts remain in the areas where the scratches were scratched.
- After a few days, the rash appears again.
Nature of the rash
Urticaria has a characteristic rash, which can be identified by a number of signs:
- They appear mainly on the back and stomach of the child.
- The body is covered with round pink spots, on which blisters with clear liquid can be distinguished.
- Several spots may merge together, forming large areas of damage.
- The child experiences severe itching in the area of the rash.
- When scratching, crusts may form.
If urticaria occurs at night, you should immediately seek help from a dermatologist or allergist; acute urticaria can be confused with other skin diseases, and incorrect treatment can cause complications.
The doctor examines the child, and if there is no rash on the body at the time of examination, special allergy tests are performed.
Parents need to pay attention to the child's food on the day of manifestation. You should pay attention to the surroundings and the condition of the bedding. Often allergens are not new products, but substances that the child has already encountered. It is necessary to note what events preceded the manifestation of nocturnal urticaria.
First aid for hives
When the first signs of hives appear, when you notice that the child is having difficulty breathing or is feeling nauseous, you should give him antihistamines and call an ambulance.
If the reasons that caused the acute allergic reaction are known, the fight against hives may be more effective. Before the doctors arrive, you should not give the child any food; only plenty of fluids are recommended, clean water is best.
Since hives most often appear after eating the “wrong foods,” you should rinse your stomach and take activated charcoal.
Gastric lavage for small children under one year old can cause certain difficulties. In this case, it is recommended to do a flushing enema. For this you can use regular heated boiled water.
For severe itching, cool compresses can help, which can be done using a decoction of medicinal chamomile.
Why does urticaria appear?
Children are the most susceptible to skin allergic manifestations; with age, the symptoms disappear completely or are characterized by a lesser degree of damage. Nocturnal manifestations of urticaria in a child:
- Exogenous factors Food that causes allergies in a child. During the day, manifestations of urticaria may not be observed, but after the child falls asleep, the body's reactivity decreases and a rash appears. Most often, children are sensitive to eggs, nuts, seafood and legumes.
- Medications. Children usually suffer after long-term treatment with antibiotics. In rare cases, antibiotics enter the body through low-quality dairy products.
- Chemical food additives. Eating low-quality foods can cause substances to enter the child's body that adults do not react to.
- Insects. In this case, the cause of urticaria can be not only the bites of mosquitoes, mosquitoes or fleas, but also direct skin contact with the insect. Ticks that are in the bed.
- Foreign microscopic particles. This includes pollen or plant parts, dust and fluff from pillows, and particles of washing powder.
- Damage by parasites. Most helminths are active at night.
Forms of flow
As stated above, urticaria can be either acute or chronic. Moreover, its transition to a chronic form can take a fairly short period and amount to only a few hours.
- headaches; - nausea; - general weakness; - slight increase in temperature.
Treatment
For treatment of urticaria in children to be effective, parents need to consult a dermatologist immediately after the onset of symptoms. This is especially true for a child under one year old. Only a doctor will tell you how to treat urticaria in children and what needs to be done in your particular case so that it does not recur.
What medications to take and how long the doctor will prescribe after carrying out the necessary tests, of which there may be quite a lot. After which it is necessary to strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions so that relapses do not occur.
Taking medication may last for several days. Treatment should not be stopped, no matter how long it takes. An untreated disease can lead to complications.
It is also advisable to determine the type of allergen and prevent it from entering the body.
After visiting a doctor and starting to take medications, it is recommended to follow a diet, which consists of giving up certain types of foods. First of all, these are foods that cause an allergic reaction after consumption, as well as sweet and canned foods. Preference should be given to dairy products (the exception is the presence of lactase deficiency in the child).
Citrus fruits, some berries and fruits (usually red) are also excluded from the diet.
If the disease manifests itself after the child is in the cold or, conversely, in the heat and is caused by sudden changes in temperature, which is observed in the hereditary form, such situations should be prevented. You should also avoid eating too cold or hot food, which may cause swelling of the tongue and larynx.
If the disease manifests itself after sleep, first of all it is necessary to eliminate all possible factors that could cause it. It is recommended to change the washing powder, bed linen and pajamas first.
It is advisable to replace them with hypoallergenic ones. It will be useful to ventilate the bedroom. Children often sweat while sleeping and after sleep already have signs of illness - redness and blisters.
Therefore, creating a healthy sleep environment is very important.
How to treat nocturnal urticaria?
The treatment regimen for all manifestations of allergies is based on the removal of the allergen and the use of antihistamines. The treatment regimen for adults and children is approximately the same, differing only in the dosage of the drugs used.
- Determination of the nature of the allergen. To do this, allergy tests are carried out to determine the nature of the allergen affecting the child. In case of reactions to food or medications, they are excluded from the children's diet. It is necessary to use hypoallergenic mattresses, pillows and blankets to avoid reactions to them. In case of exposure to helminths, comprehensive treatment is carried out; in case of exposure to insects, disinfection of the room is necessary; when walking, it is necessary to treat the child with insect bite repellents.
- Drug therapy. There are a huge variety of antihistamines on the modern market; the doctor prescribes treatment based on the sensitivity and health status of the child.
- Diet. In the acute form of urticaria, a reaction may occur even to foods that did not previously cause allergies. They must be excluded until complete recovery.
The manifestation of urticaria at night indicates acute processes in the body; to improve the child’s condition, you should immediately seek help from a specialist in the early stages of manifestation. Lack of timely treatment can affect the child’s health.
Traditional methods
— To reduce itching, you can use a compress with propolis tincture. Dilute a teaspoon of tincture in half a glass of water. Gauze must be moistened with this solution and then applied to the affected area of the body for up to 10 minutes. - It is also good to use chamomile or calendula decoctions to reduce itching.
The method for preparing the decoction is indicated on the package. - Infusions of mint or nettle are good sedatives. They are brewed as tea and taken several times a day. You will need a tablespoon of one or another herb per 300 ml of boiling water. - For baths when bathing, you can use a decoction of string, chamomile, celandine, sage and valerian root.
All herbs are mixed in equal quantities. Then five spoons of the mixture are poured into a liter of boiling water and infused. The infusion is then brought to a boil. Bathing should be done for at least twenty minutes throughout the week. - A good infusion for baths can be prepared from ordinary nettle. It is recommended to take baths with this infusion for several days in a row.
Your experience in using these folk remedies will tell you how much and what to take.
Source: https://alfastroy-n.ru/krapivnitsa-posle-rebenka/
Symptoms of urticaria
Symptoms of urticaria can last from a few minutes to months or even years. They are clearly expressed and easily identified visually.
It is the initial symptom of urticaria, followed by rashes. Often worsens in the evening.
Pink or red blisters
Manifestation of urticaria in the form of blisters
They resemble marks from nettles or mosquito bites.
They can appear on any part of the body, change shape and location, disappear and appear within short periods of time. Their size ranges from 1 to 5 mm.
The blisters can be small and round, ring-shaped or large and random, the latter can reach a size of up to 20 cm. They are usually surrounded by a small area of red skin (cutaneous hyperemia).
- Decreased blood pressure.
- Swelling of the upper respiratory tract and tongue.
- Breathing problems.
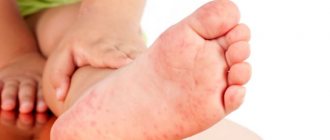
Urticaria in children: symptoms in photos
Tablets, ointments and other products
The following groups of drugs are used:
- Systemic steroids are the most powerful group that suppresses the immune response. Injectable and external forms are used (Diprospan, Advantan, Akriderm).
- Antihistamines - have a significant anti-inflammatory effect, especially 3rd generation antihistamines for urticaria (Desloratadine), 1st and 2nd generation antihistamines (Xizal, Suprastin, Tavegil, Fenistil, Erius);
- Leukotriene receptor antagonists (Zafirlukast).
- Immunomodulators - increase the body’s resistance (Galavit).
- Sorbents (Enterosgel, Polysrob).
- Desensitizing agents (calcium gluconate).
- Local anti-inflammatory agents (Zinc ointment).
It is worth highlighting plasmapheresis as a mechanical method of eliminating allergens from the body.
First aid for a child in the event of an acute form of urticaria should include the first three groups of drugs.
Lecture by P.V. Kolhir “New perspectives in the diagnosis and treatment of urticaria and angioedema”
By duration
- acute urticaria (rash lasts up to 6 weeks);
- chronic urticaria (the rash lasts more than 6 weeks, elements can occur almost daily or have a recurrent course, and rash-free periods range from several days to several weeks).
Note: sometimes urticaria may appear after completing a course of medication
Let's work together to make the unique material even better, and after reading it, we ask you to repost it on a social network convenient for you. net.
Urticaria worsens at night – Allergic skin lesions
An allergic reaction is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms, including hives.
It appears as a pink or red skin rash. Allergy sufferers may notice that their hives get worse at night. It is accompanied by severe itching, which does not allow you to relax before going to bed. As a result of this, a person becomes irritable, his performance decreases, and his biorhythm is disrupted. If urticaria worsens in a young child, all family members suffer, since children tolerate the symptoms of an allergic reaction more difficult. Parents have to control the child’s condition, sacrificing their sleep.
To get rid of annoying allergy symptoms, you need to visit a dermatologist or allergist.
Character traits
Nighttime urticaria is considered a common symptom of an allergic reaction. Its peak manifestation often occurs at night. This is due to the peculiarity of histamine production. It appears in response to the body's reaction upon contact with an allergen.
In this case, it is not at all necessary that a person come into contact with the irritant at night. The symptom can be triggered the day before by household dust, pollen, household chemicals, cosmetics, food, etc. Often, itching and rashes intensify at night with a mild form of allergy.
During the day, due to his busyness, a person simply does not pay attention to developing symptoms. Along with urticaria, allergic symptoms affecting the respiratory system may also appear at night.
In a lying position, stagnation of mucus and phlegm occurs, causing an allergic cough and discomfort in the nasal passages. In the morning, the symptoms of an allergic reaction become less pronounced.
Causes
If hives worsen late at night, the person wakes up in a broken state the next morning. This affects his quality of life. The chronic form of an allergic reaction is especially dangerous - it is distinguished by the frequency of relapses.
Rashes intensify during periods of depressed immune system: during pregnancy, with long-term drug treatment, vitamin deficiency, etc. Before treating a disease, it is necessary to discover the cause of its occurrence.
Allergens can be objects with which a person comes into close contact the day before or during sleep. These include:
- volatile substances contained in bed linen washing products;
- small insects (bugs, mosquitoes, midges, etc.);
- fillings that are used to make pillows or blankets (wool, feathers or down);
- dust particles on furniture and interior items;
- plant pollen entering the room from the street;
- Food.
The list is far from complete.
Treatment
Actions aimed at eliminating urticaria require an integrated approach. Therapy includes several aspects:
- Diagnostics . In order to search for an irritant, allergy tests are carried out. They allow us to understand the nature of the origin of the body’s negative reaction. A dermatologist gives a list of necessary tests.
- Drug therapy . It includes, first of all, taking antihistamines; auxiliary therapy is possible in the form of the use of immunomodulators, enterosorbents, antiseptics and other drugs. Drugs are selected individually.
- Diet for urticaria . In an acute form of an allergic reaction, all potential allergens are excluded from the diet.
When hives worsen at night, medications that block the release of histamine are prescribed. These include: Erius, Xizal, Tavegil, Desloratadine and Suprastin. Sorbents have a cleansing effect on the body. The most popular are Polysorb and Enterosgel.
Immunomodulators - Interferon, Lykopid, Viferon - help increase the body's resistance. Anti-inflammatory agents, such as zinc ointment, are applied directly to the area of the rash. In some severe cases, hormonal drugs such as Advantan, Diprospan or Akriderm may be prescribed.
Traditional medicine helps get rid of hives in a short time.
Sources used: allergick.com
SEE ALSO: Urticaria from the point of view of homeopathy Urticaria and badger fat
Hives at night
Perhaps long-term use of medications has caused you to develop a condition called AUTOALLERGY (erroneous production of protective antibodies to substances that are not dangerous to the body,
secreted by the body itself). But “antiallergic” drugs will not eliminate
allergies as such, but will only relieve flare-ups for a while. And against the background of an existing allergy, reactions will be caused even by those products that have never been allergens for you...
However, there is a chance (albeit small) to “convince” the body... Homeopathy can help here... To do this, you need to purchase 2 drugs from a homeopathic pharmacy: “Urtica Urens” C3 and “Sambucus nigra” C3 in lozenges (write this on a piece of paper and show in a public pharmacy). Take (dissolve) according to
5 balls 3 times a day before meals (at least six months).
Then there is a chance that the disease may disappear...
If you have any additional questions, please write to [email protected]
consultations by email mail, individual production of medicinal ointments and lotions
tel.
mob.
(call from 9.00 to 11.00 in the morning and from 18.00 to 20.00 in the evening
Website for reviews: //prodoctorov.ru/moskva/vrach/130209-chernyavskiy/#otzivi
Attention, I do not answer questions How to treat (write a prescription, prescribe treatment, etc.) Prescribing treatment in absentia can harm the patient and is legally illegal. What is this? Make a diagnosis from a photograph Only psychics, of which I am not one, can make a diagnosis from photographs.
In some cases, a high-quality photo can only suggest a diagnosis, which must be confirmed (clarified) at an in-person appointment with a doctor. I do not answer questions asked in personal messages. In exceptional cases, correspondence on a paid basis is possible. Reception in
Rostov-on-Don
344023, Rostov-on-Don, Lenin Ave., 251 Directions tel. +7,
My sites
Sources used: www.consmed.ru