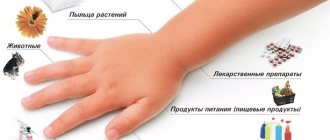
Encounters with insects do not pose any great dangers for most people.
However, in the presence of such a serious disease as an insect allergic reaction, contact with them can have serious consequences and become a threat to life.
It is important to be able to recognize this disease in time and be able to provide first aid to yourself and your loved ones, preventing serious complications.
This disease, unlike ordinary allergies, can be fatal. According to statistics, twice as many people die from insect reactions than from snake bites.
The body's insect response is a pronounced, hypersensitive immune reaction that occurs as a result of various contacts with insects, as well as with their metabolites (excrement). For example, with ant bites or bee stings. The name "insect" comes from the Latin "Insecta" (insects).
Place in the international classification
Insect allergy has its own unique code according to ICD 10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision), depending on the nature and location of the allergic reaction.
In order to establish the cause of the disease, auxiliary code W57 “Bite or sting by non-venomous insects and other non-venomous arthropods” is used. This classification was developed by the World Health Organization to organize medical diagnoses.
Additional facts
Allergic cough in children is one of the symptoms of allergies that occurs against the background of inflammation and swelling of the tissues of the bronchi, trachea and larynx. It has a non-productive paroxysmal character. It is formed during both acute and chronic course of the inflammatory reaction. It accompanies diseases such as allergic laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis, bronchial asthma and others. Currently, throughout the world there is an increase in the frequency of allergic pathologies in children. Approximately 10 to 12% of the infant population suffers from some type of atopy, with initial recognition of the disease occurring between 5 and 12 years of age. Children under three years of age practically do not suffer from the above pathologies.
Allergic cough in children
Why does such a serious reaction develop?
Penetrating into the body, the poison causes a hypersensitive reaction of the immune system. This is caused by a violation of the mechanism of the immune response. As a result of this disorder, the immune system reacts to antigens that are not harmful to health. In contrast to the body's normal reaction, hypersensitivity causes excessive secretion of IgE by plasma cells (cells that produce antibodies).
The risk group includes people with a hereditary predisposition to allergic reactions, as well as constant contact with allergens during work, for example, working in an apiary.
The mechanism of development of this disease includes the phases of early and late immune response.
During the early response phase, histamine is released, as well as other inflammatory mediators. A runny nose, itching, shortness of breath, and anaphylactic shock appear. In the zone of penetration of the allergen, a focus of inflammation is formed.
The late response phase develops after the cessation of the action of inflammatory mediators. Occurs 4-6 hours after the initial reaction.
There are several ways the allergen can enter the body:
- Stinging by Hymenoptera . Such insects include bees, wasps, hornets, bumblebees, ants, etc. Reactions to hymenoptera venom are the most severe and can be fatal.
- Penetration of venom from dipteran bites . For example, mosquitoes, horseflies, tsetse flies, etc.
- Touching insects, their parts, metabolites.
- Inhalation of insect parts or their metabolites.
Such allergies occur in 0.4-0.8% of people.
Symptoms
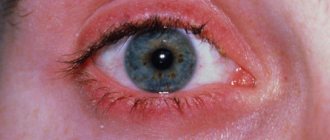
An allergic cough is usually unproductive, paroxysmal, barking, rough, and does not go away within several weeks or months. Sometimes sputum is released - transparent, not viscous, without a mixture of pus or blood. There are no signs of intoxication, body temperature does not rise, chills are not bothersome. A cough can be the only manifestation of an allergy or be combined with symptoms such as runny nose, sneezing and itching of the mucous membranes. With a prolonged and prolonged cough, pain in the chest area is possible due to overstrain of the skeletal muscles; at rest, they go away on their own. With the addition of allergic conjunctivitis, the clinic is complemented by redness, swelling of the eye tissues and watery eyes. The nature of an allergic cough depends on the type of underlying disease. In the case of bronchial asthma, it develops in the context of bronchospasm, is accompanied by difficulty in exhaling, and mainly causes anxiety at night or when the child wakes up. Coughing attacks may occur during exercise, laughing, crying, or exposure to tobacco smoke. During an attack, the patient breathes through his mouth and tries to sit with his hands on a table or chair seat, because breathing is facilitated by the use of additional skeletal muscles. At the end of a paroxysmal cough, a small amount of clear mucus may be released from the sputum. With allergic laryngitis, the cough is superficial, barking, combined with sore throat and hoarseness. If the disease progresses, the clinical picture is supplemented by shortness of breath, painful swallowing or a feeling of swelling in the throat, cyanosis of the lips and nasolabial triangle, and weakness due to tissue hypoxia. In chronic allergic alveolitis, a cough appears with the release of a small amount of mucous sputum, which occurs regardless of the time of day. A coughing attack may cause headaches, blood pressure, or palpitations. Obstructive bronchitis is characteristic of toxocaritis, giardiasis, accompanied by unproductive cough, wheezing and wheezing. Due to sensitization of the body, a rash, redness and itching of the skin appears. In the case of ascariasis, if left untreated, eosinophilic pneumonia may form. In this case, the cough is accompanied by fever, weakness and malaise. Deep dry cough. Difficulty in exhaling. Cough. Barking cough. Malaise. Dyspnea. Chills. Superficial cough. Cramps. Eosinophilia.
How to identify danger in time
Symptoms of this disease include local and systemic manifestations.
Local and systemic manifestations
Local manifestations are reactions that occur in the area of allergen penetration. Characterized by the presence of:
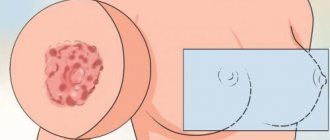
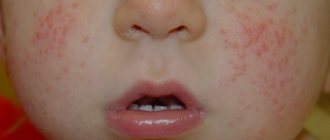
- urticaria (urticaria), manifested in the form of itchy blisters on the skin that disappear after a few hours (severe swelling in the affected area is possible if urticaria occurs on the eyes or lips);
- hyperemia (redness caused by an excess of blood in the vessels of the organ or affected area);
- white small bubbles with transparent contents;
- erythema (redness on the skin caused by dilated capillaries);
- hemorrhagic syndrome (spontaneous bleeding);
- severe skin itching.
Systemic manifestations are reactions involving a large number of organs. Characterized by the presence of:
- generalized (covering the entire skin surface) rash;
- generalized skin itching;
- necrosis (i.e. tissue death) of the skin;
- Quincke's edema, which may cause swelling of the face or limbs;
- bronchospasm (i.e. narrowing of the bronchi, which causes difficulty breathing).
The severity of the current
The severity of the disease can be divided into four types:
- General mild reactions . Urticaria is observed with a frequency of 33%. There is chills, fever, apathy, general weakness, or vice versa, general agitation,
- General symptoms are moderate . In 38% of cases, urticaria, nausea, dizziness, rapid and difficult breathing are present.
- General signs of severe severity . Added to the above symptoms are confusion, suffocation, and a feeling of doom. This condition is observed in 20% of cases.
- Development of a state of shock . Blood pressure decreases. Swelling of the larynx begins, bronchospasm appears. Breathing becomes noisy, hoarse and rapid. Hypoxia (oxygen starvation) develops. Loss of consciousness and fainting are possible. The incidence of this condition is 11%.
Unsafe insect allergies in children can develop more clearly. Parents should remember the necessary safety measures for a child at high risk of developing anaphylactic shock.
It is worth informing the child’s environment, including teachers, about the presence of the disease. The patient should have a bracelet with information about the disease, as well as recommendations for emergency care.
Allergic rash, unspecified, ICD code 10
Diagnostics • Careful collection of allergy and food history allows us to identify the relationship between the appearance of symptoms and the consumption of a particular food product • Performing skin tests with food allergens - to confirm the diagnosis of IgE - an mediated immediate hypersensitivity reaction • Radioallergosorbent test is designed to identify specific antibodies (IgE) to Ag of certain products • The most reliable way to confirm a food allergy is to keep a “food diary”, as well as conducting elimination and provocative tests •• The presence of symptoms and their relationship with the consumption of certain products (food diary) are recorded daily •• Elimination test: the food product is removed from the diet for 1–2 weeks •• If symptoms disappear due to dietary restriction or a noticeable improvement occurs, an oral food challenge test is performed under the supervision of a physician. Most allergic reactions occur within 0.5–2 hours after provocation, although reactions occurring after 12–24 hours are possible.
Causes and types of urticaria
An allergic reaction such as urticaria can occur to: food and additives, cosmetics, medications, insect bites, infections, physical impact on the skin, etc.
In response to these irritants, the immune system produces a chemical called histamine, which causes itching and inflammation of the skin.
Acute allergic urticaria
This is the most common type of hives that occurs when exposed to an allergen. Let's look at the causes of urticaria rash.
Allergies in the form of urticaria occur to the following types of products:
→ Causing the release of histamine: chicken eggs, chocolate, strawberries, pineapple, tropical fruits, fresh seafood (shellfish), fish, alcohol, tomatoes, etc.
→ High in histamine: beer, fermented cheeses (Roquefort, Brie), fish, sauerkraut, canned foods, etc.
→ High in tyramine: cheeses (Gruyere), smoked fish, sausages, cabbage, grapes, white wine, etc.
- E102 (tartrazine);
- E110 (sunset food coloring)
- E 124-125 (food coloring “Crimson”)
- E127 (food coloring Erythrosine)
- E200 (sorbic acid)
- E210 (benzoic acid)
- E 211-217 (benzoic acid derivatives)
→ Emulsifiers, thickeners and gelling agents.
Medicines are responsible for 30% of all cases of skin manifestations. A rash in the form of hives occurs within a few minutes or hours after taking the drug. The route of administration does not matter; it can be oral, rectal, parenteral, dermal, vaginal or inhalation.
Drugs that cause allergic rash:
Antibiotics: sulfonamides, penicillin and its derivatives, ampicillin, methicillin, cloxacillin, carbenicillin, cephalosporins.
Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs: aspirin, indomethacin, antipyrine, phenacetin, paracetamol, amidopyrine, etc.
Histamine-releasing drugs: polymyxin, atropine, beta-blockers, muscle relaxants, dextran, hydralazine, etc.
Cosmetics and household chemicals
Skin contact with certain substances causes localized urticaria in some people - for example, a reaction to washing powder, latex gloves, face cream, etc.
Allergic reactions to plant pollen, animal fur or saliva can also appear on the skin in the form of a rash.
Chronic allergic urticaria
Chronic skin urticaria usually lasts more than 6 weeks. Causes may be similar to acute urticaria and may also include immune system problems, chronic infections, hormonal imbalances and tumors.
The hallmark of chronic urticaria is a duration of more than 6 weeks.
Pseudoallergic urticaria
This type of urticaria is called the pseudoallergic form, since the rash in this case manifests itself for other reasons that are not related to allergies (i.e., the level of antibodies in the blood during urticaria remained unchanged).
Solar urticaria
It is impossible to determine the exact causes of the rash on your own based on the appearance of the rash; only a dermatologist or allergist can make an accurate diagnosis.
Urticaria in adults and children may appear for the following reasons:
- Physical effects: reaction to cold, sun, friction or sweating (for example, hives in children that appear on diapers).
- Parasites in the intestines or blood
- Disorders of the digestive system
- Infectious and viral diseases (flu, ARVI, urinary tract infections, etc.)
- Sepsis
- Hepatitis
What is an allergic reaction, what is the ICD-10 code
Source: https://blotos.ru/allergiceskaa-reakcia-kod-po-mkb-10-pisevaa-neutocnennaa-lekarstvennaa
What to do after an insect attack
Once the poison enters the body, it is necessary to stop its further intake. If there is a sting left, you must remove it (along with the sting, a bag of poison remains, which continues to inject poison under the skin for a couple of minutes). This can be done with tweezers, a pin, or even a plastic card. It is better to disinfect the “tool” before use. It is important to be careful not to leave parts of the sting under the skin.
After removal, you need to treat the wound with an antiseptic and apply ice (you can use a hypothermic bag purchased at a pharmacy), apply a tourniquet above the sting site (if possible), which will limit the spread of the poison for some time. Take antihistamines (for example, Suprastin).
Bibliography
1. Allergic diseases: textbook / Melnikov V.L., Mitrofanova N.E., Melnikov L.V. - 2020. 2. Hypersensitivity cough: pathophysiology, differential diagnosis, treatment/ Abrosimov V.N. // Attending physician. 3. How to treat cough in children / Samsygina G. A. //Attending physician. – 2003.
Source
Cough is a protective response of the body to incoming provoking factors. It is a severe cough that remains the most important symptom of allergic bronchitis. Moreover, in this case, the attacks are strong and tearing in nature.
Occurs due to penetration of an allergen into the respiratory tract. A very common pathological process among children. It is they who develop bronchitis due to allergies. This can be affected by plants during the flowering period, taking medications or eating food.
Emergency and conventional treatment
If an allergy appears for the first time, a consultation with an allergist is scheduled to carry out the necessary tests, after which the necessary therapy is carried out.
Emergency treatment is the relief or prevention of anaphylactic shock and anaphylatoxic reactions. Further actions depend on the measures taken immediately after contact with the insect. When anaphylaxis develops, the doctor administers a solution of adrenaline, as well as glucocorticosteroids (steroid hormones) and antihistamines. After the critical condition has been relieved, the doctor continues antihistamine therapy (perhaps the administration of steroid hormones will also be continued).
If the condition turns out to be non-critical and does not require hospitalization, then treatment of insect allergies may be limited to the administration of antihistamines and antihistamine gel, which is used to treat the site of contact with the allergen.
If conjunctivitis, rhinitis (runny nose) or bronchial asthma develops, appropriate treatment is carried out (administration of histamine blockers, taking bronchospasmodic drugs).
To treat urticaria, your doctor may prescribe medications that affect vascular permeability.
Diagnostics
At the first manifestations of an allergy, it is necessary to identify the food allergen, which will allow it to be eliminated from the diet as early as possible. Skin allergy tests are a series of pricks on a child's skin using a plastic applicator that contains a concentrated allergen. A food allergy is diagnosed if a child's skin reacts with a papule or redness. Skin allergy tests for foods (not for aeroallergens) have a high false-positive rate, that is, the test may be positive but the child is not truly allergic, or has no symptoms. This test is not used in children with severe anaphylactic reactions or widespread eczema. An allergist may also conduct an experiment to test for allergies. The child takes the suspected product in increasing quantities to see what reaction occurs. Allergists call one of the tests RAST (Radio-Allergo-Sorbent Test). It measures the amount of IgE antibodies in the blood that are produced to certain known food allergens. Like the allergy skin test, RAST and other antibody tests have a high false-positive rate. Doctors also recommend dietary restrictions. The main diet is a series of products that are not allergy triggers. This diet consists of foods such as lamb, poultry, rice, vegetables and all fruits except citrus fruits and berries. Every week one new product is introduced into the diet. The patient's response is recorded weekly. If the child does not have a reaction, the product is considered safe and can remain in the diet. If there is a reaction, this product is excluded from the diet.
Allergy skin test
How to protect yourself from the problem
To reduce sensitivity to an allergen, it is necessary to carry out allergen-specific therapy. If it is not possible, the doctor may prescribe courses of antihistamines during the period of expected contact with insects.
Prevention also includes avoiding encounters with insects and wearing closed clothing in places where they accumulate. During the warm season, you should not use cosmetics that have a strong odor. If bees attack, you should not kill them, as they emit a scent that attracts other bees.
A protective net should be installed on the windows in the house. Ultrasonic fumigators can be used to repel insects. When in the forest, it makes sense to use repellents (cosmetics that repel insects).
Allergy sufferers should always have antihistamines with them.
Possible complications
Allergic diseases caused by increased sensitivity and accompanied by coughing attacks, without proper treatment, can lead to serious complications: the transition from acute inflammation to a chronic form with the subsequent formation of foci of pneumosclerosis, the formation of pulmonary heart due to stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation, the development of respiratory failure, stenosing laryngitis, status asthmaticus. With the last three pathologies, urgent hospitalization of the child in the intensive care unit is necessary.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of bronchitis of allergic origin in adults and young patients is clearly expressive. The most important symptom remains cough. This is how bronchitis is sometimes diagnosed.
Don't delay treatment. The cough is so severe that it interferes with eating, sleeping and working normally. Most often it manifests itself at night, and you won’t be able to get a good night’s sleep either.
The following cough features are characteristic of bronchitis of allergic origin:
- coughing attacks are characterized by persistent and unobtrusive reflex spasms affecting the respiratory tract;
- the cough begins to bother you at night, although it is possible that it occurs during the day;
- at the initial stage of development of the pathological process, the cough takes on a non-productive type, with no mucus discharge;
- in the later stages of the development of the disease, sharp spastic exhalations are observed, which lead to the release of secretions;
- cough occurs very quickly after suffering stress, negative emotions and physical exercise.
The clinical picture of bronchitis of allergic origin is accompanied not only by cough.
The patient may also experience the following symptoms:
- dyspnea;
- labored breathing;
- dry wheezing (very rarely wet).
The peculiarity of the pathological process that occurs against the background of allergies is that the onset and end of the symptoms are sudden. When the coughing attacks have left the patient, he feels relief, which creates the illusion of relief. Cough affects the patient several times a day.
Bronchitis of allergic origin in children and adults can be diagnosed at any age. The pathology is accompanied by a relapsing course. The exacerbation phase occurs several times a month. Their duration can range from two days to 2 months.
Typical symptoms of the disease in question include a sore throat. At first, nasal congestion and rhinitis occur. In young patients, bronchitis develops against the background of other diseases that are allergic in origin.
What to do if a cough does not go away after bronchitis.
But this article will help you understand what to do when a child’s cough does not go away after bronchitis.
How is badger fat treated for cough and bronchitis and how effective is such a remedy? This information will help you understand: https://prolor.ru/g/lechenie/barsuchij-zhir-primenenie-pri-kashle.html
This article will help you understand which antibiotic is the most effective for bronchitis in children and what its name is.