An allergy is a pathology of the immune system in which the body perceives substances that are safe for most people as an irritant. Upon contact with an allergen, a pronounced skin, respiratory or other reaction occurs, which in some cases can be dangerous to health and life.
To avoid unpleasant symptoms of allergies, it is important to accurately identify the irritant and select supportive therapy. This can be done in the Diagnostic and Treatment Center with the help of an experienced allergist.
How does an allergic reaction occur?
The essence of allergies is pathological sensitivity to certain substances. This can be food, pollen, wool, dust, chemical compounds, etc.
In a simplified way, the mechanism of allergy occurrence can be described as follows. If a person has a genetic predisposition to allergic reactions, under certain conditions a substance is perceived by the body as an “aggressor”. There will be no immediate reaction to it, but the next time you come into contact with this irritant substance, the immune system will try to counteract it.
The body will release antibodies and launch a protective immune reaction - these are the unpleasant allergy symptoms that a person feels. With each new contact with an allergen, the strength of the reaction may increase.
Allergies can occur at any time of the year, but for many people, exacerbations regularly occur during the warm season - spring and summer. During this period, plants bloom and bear fruit, the street becomes dusty, poplar fluff flies - all this can cause an allergic reaction.
In addition, sometimes allergies become acutely felt in the autumn, because mold and cold can also act as allergens.
External manifestations
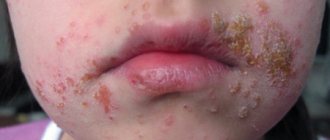
Spring exacerbation of allergies can manifest itself as failures of any body system. Most often the eyes, nasopharynx, lungs and gastrointestinal tract are affected.
Many allergy sufferers confuse the signs of pathology with a common runny nose. Indeed, rhinitis, sneezing, coughing are symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, but there are other causes. Often problems go away almost completely on a rainy, cloudy day, which indicates a high probability of a malfunction of the immune system.
Common symptoms of seasonal allergies include:
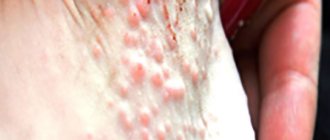
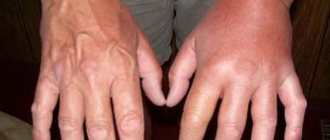
- skin lesions (rashes, redness, itching);
- chronic runny nose;
- breathing problems (asthmatic allergies);
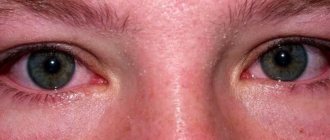
- conjunctivitis;
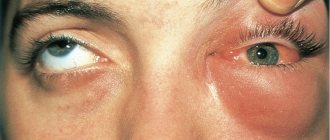
- swelling of the eyelids.
Often, spring exacerbation of allergies causes disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Pain, increased gas formation (flatulence), problems with bowel movements (frequent loose stools) occur.
Respiratory, skin and other allergic reactions
Each type of allergy has its own set of symptoms that occur upon contact with the allergen. All these symptoms are a reason to consult an allergist at the Kutuzovsky Children's Center. There are a lot of potential allergens, and only a specialist will be able to determine what exactly the body is reacting to inadequately.
The following groups of allergy symptoms are distinguished, depending on its origin:
- Respiratory (breathing): sneezing, watery discharge from the nose, severe cough, shortness of breath, bronchial asthma. This is how seasonal allergies usually manifest themselves during the flowering period of plants (its other name is hay fever).
- Signs of allergic conjunctivitis: redness and burning of the mucous membranes of the eyes, swelling, lacrimation.
- Skin: eczema, urticaria, atopic dermatitis, which are manifested by redness of the skin, peeling, itching.
- Symptoms from the digestive tract: colic, nausea, stool disorders and other manifestations. They are usually associated with food allergies.
- Quincke's edema is swelling of the subcutaneous tissue of the face and neck. The most dangerous thing is the development of edema of the laryngeal mucosa, which can lead to acute asphyxia (suffocation).
- Anaphylactic shock: shortness of breath, convulsions, fainting, drop in blood pressure, bronchospasm, sometimes coma. These symptoms are especially dangerous, so immediate medical attention is required. They usually develop very quickly - within a few minutes after eating or contacting the allergen.
Diagnostics
To understand what an allergy may be in the fall, a comprehensive approach is required. A large number of laboratory tests are prescribed. They are carried out only in winter, when there is no active immune response. Be sure to check whether the person has an infectious-inflammatory process. Otherwise, the data may be false positive. To understand whether there is an allergy in the fall, research is carried out:
- Collection of data from the patient’s words (history). Find out if he has any allergies. Identify the presence of hypersensitivity in parents or other close relatives.
- General inspection. The doctor examines the condition of the patient’s skin, mucous membranes, and eyes. If he has signs of hypersensitivity, areas of redness, inflammation, rash, and peeling occur.
- General blood analysis. This is a general clinical test and does not provide definitive results about the cause of pathological symptoms. But with an allergy to leaves, pollen, dust in the blood, the level of leukocytes and ESR necessarily increases. The condition also occurs in other diseases; differential diagnosis is required.
- General urine analysis. In mild cases, clinical indicators do not change. If the patient has severe symptoms, the white blood cell count will increase. This is not specific for an allergic reaction, but is useful for identifying the condition of internal organs and the genitourinary system.
- Blood test for allergens (see “Blood test on a panel of allergens: types, indications for the study, preparation and interpretation of the results”). The test helps identify what you may be allergic to in September and other months in the fall. Determine the main types of antibodies for hypersensitivity. Most allergens cannot be identified; only the main types are detected. For example, allergies to animal hair, ragweed, house dust.
- Skin allergy test. Different types of allergens are applied to the patient's skin. Any type of antigen that causes sensitivity of the immune system is detected. Using the test, you can accurately determine which plants you may be allergic to in the fall. This is the most specific study.
Allergy skin testing is a very informative test for identifying an allergen.
It often happens that the symptoms are similar to other pathologies. Differential diagnosis is required. For example, the doctor prescribes bacteriological culture, PCR, ELISA, RIFA, smear with microscopy of the contents. If a person only has allergies, the data from these tests will show a negative result for the content of bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Most common allergens
The causes of allergies are not fully understood, and any, the most unpredictable substances can cause a reaction. However, there are a number of irritants that most often provoke an allergic reaction. People with a predisposition to allergies need to be more careful with them and deliberately try to avoid contact.
Among the most common allergens:
- Cat or dog hair;
- Street and house dust;
- Mold or mildew;
- Plant pollen;
- Bee or ant venom;
- Washing powder and other household chemicals;
- Latex;
- Penicillin and some other drugs;
- Nuts;
- Dairy products;
- Wheat (due to the gluten it contains).
An allergen is not always a substance. For example, there is a cold allergy, in which the skin reacts with redness and itching to lower air temperatures.
First generation of antihistamines
Such antihistamines must be taken frequently in fairly large doses. Among the main features is a decrease in the activity of mediators for up to 4-5 hours, sensitivity to alcohol intake with a simultaneous decrease in muscle activity, which leads to manifestations of a sedative and hypnotic effect. In some cases, psychomotor agitation may occur during administration. Due to their calming effects, they should not be taken in conditions requiring concentration. All sedatives multiply the effect of taking sedatives and hypnotics, narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics.

Due to their composition, such drugs can cause dry mouth and nasopharynx, urinary retention, constipation, blurred vision and tachycardia. This can negatively affect the course of glaucoma and aggravate the process in bronchial asthma and prostate adenoma. Allergy medications of this kind help against vomiting and motion sickness, and can also reduce the manifestations of Parkinson's disease.
Antihistamines are also characterized by the property of local anesthesia. But such drugs must be changed every few weeks, since their antihistamine activity decreases during long-term use. The therapeutic effect of such drugs occurs soon, but does not last long. Some of the drugs in this group are included in cold medicines, sleeping pills and sedatives. Due to the wide range of side effects, first generation drugs for the treatment of allergic reactions were banned in many countries around the world.
A representative of this group is Diphenhydramine, or otherwise Diphenhydramine, which is characterized by antitussive and antiemetic effects. Due to the effect of local anesthesia, in some cases it is used as an alternative to Novocaine or Lidocaine if there is an individual intolerance to them. Diazolin, or otherwise Mebhydrolin, has a weaker sedative effect, but its use can even cause psychomotor agitation. There is information that Diazolin causes a toxic attack on nerve cells, especially in young bodies.
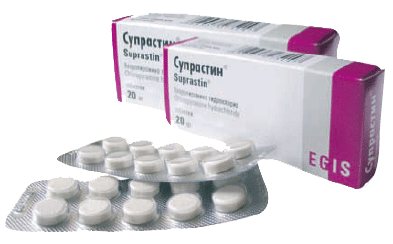
Suprastin, or otherwise Chloropyramine, is one of the most commonly used sedatives. Effectively fights the symptoms of seasonal and year-round conjunctivitis, dermatitis, Quincke's edema, eczema, urticaria, itching and various acute allergic manifestations. Long-term use does not cause an overdose. The effect of the drug Tavegil, or otherwise Clemastine, is similar to the effect of Diphenhydramine. The injection form can be used as an adjuvant for anaphylactic shock and angioedema, during the prevention and treatment of various allergic manifestations, but tavegil can itself cause allergies.
Diagnostics: what tests are used to determine the allergen?
In order to avoid irritating substances in everyday life and encounter allergic reactions as little as possible, it is important to know the cause of the allergy. The first diagnostic step is a conversation with a doctor, during which the specialist will collect anamnesis and suggest several possible irritants. It is important to talk in detail about allergy symptoms and the circumstances in which an allergic reaction typically occurs.
Next, various laboratory tests are carried out in the clinic:
- Skin tests. They allow you to quickly and safely monitor the body's reaction to several different allergens. For testing, samples of substances - potential irritants, selected in advance - are applied to the skin. A scarifier can be used to make micro-scratches. Skin testing is safe because it uses a negligible amount of each allergen. Such tests can be performed on both adults and children. Allergy test results can be ready within 20 minutes after the procedure.
- Application tests. Unlike the classic skin test, in this case the surface of the skin is not damaged. The potential allergen is applied to the skin and covered with a special bandage for a day or more, and then the reaction is assessed. In this way, it is possible to determine the cause of atopic dermatitis and other skin reactions that occur during tactile contact with an irritant.
- Blood test for antibodies. The laboratory measures the amount of specific antibodies that are produced during allergies - immunoglobulin E. These antibodies are unique for each allergen. An immunoglobulin test is performed instead of or in addition to skin tests to clarify the results. For the test, a small amount of blood is taken from a vein into a test tube.
- Provocative tests in a clinical setting. In this case, a certain amount of the allergen is introduced directly into the human body, the doctor records the reaction and helps to quickly stop it. This testing method is carried out only in a hospital under the supervision of doctors. The advantage of such an analysis is accuracy, because it allows you to determine 100% whether there is a reaction to a specific substance. A provocative test is carried out if other diagnostic methods are not informative enough.
Additionally, some general clinical tests may be required, for which the doctor will write a referral if necessary.
Possible adverse reactions
Therapeutic allergens undergo controlled studies and are released into production only with a small percentage of identified side effects.
But this does not guarantee that an individual intolerance reaction will not occur; it can be local and systemic.
POPULAR WITH READERS: How to choose an air purifier for allergy sufferers and asthmatics
Local manifestations of side effects of ASIT therapy include the appearance of changes at the injection site, these are:
- Swelling;
- Hyperemia;
- Itching.
The systemic reaction manifests itself:
- Quincke's edema;
- Anaphylactic shock;
- An attack of bronchial asthma.
In addition, there is often a general deterioration in well-being, expressed by headache, aching muscles and joints, and discomfort throughout the body.
A systemic reaction is considered dangerous to the body, which is why it is so important to be under medical supervision for the first 60 minutes after administration of the drug.
If a health care worker records signs indicating hypersensitivity to therapeutic allergens, he will quickly provide the necessary medical assistance, which consists of:
- In applying a tourniquet above the injection site;
- By applying adrenaline directly to the area of the previous injection;
- When administering aminophylline into a vein for bronchospasm;
- In the intravenous administration of antishock and antihistamine drugs.
If symptoms of systemic intolerance develop outside the walls of a medical facility, then it is imperative to call an ambulance.
How are allergies treated?
The main principle during the treatment of allergies is to avoid contact with a substance that causes an undesirable reaction. It is important, if possible, not to provoke the immune system to produce antibodies, because each episode of exacerbation of allergies is stress for the body and the risk of a severe reaction. Your doctor will advise you, based on laboratory tests, on which substances to watch out for.
In parallel, the allergist may prescribe:
- Taking antihistamines - constantly or only when forced into contact with allergens. Such medications significantly alleviate most allergy symptoms.
- Additional medications to relieve symptoms. To reduce respiratory manifestations of allergies, shortness of breath and other specific manifestations of allergies, separate medications in the form of tablets, sprays, and inhalers may be required.
- Allergen-specific immunotherapy. This is a modern method of treating allergies, the goal of which is not just to relieve the symptoms of the disease, but to reduce the body’s sensitivity to a specific irritant. You can compare this method with preventive vaccinations. Its essence is that a small dose of the allergen is introduced into the body over a long period of time, which gradually increases. Immunotherapy is carried out according to a certain scheme over several years and requires patience from the patient: the intensity of the allergic reaction will decrease gradually. This treatment is prescribed in a situation where the allergen is precisely known.
Third generation of antihistamines
The new generation of products combine the positive qualities of the previous two generations, without exerting a cardiotoxic effect on the human body even when using high doses. They act due to the production of active metabolites in the blood. The latest generation of allergy medications are characterized by high antihistamine activity, the absence of sedative and cardiotoxic effects, and reduce the occurrence of bronchospasms.
Drugs of this group are successfully used in the treatment of allergic manifestations of a year-round and seasonal nature in the form of a runny nose or conjunctivitis, chronic urticaria, allergic contact and atopic dermatitis. The special composition of such drugs ensures a high degree of safety and effectiveness. Drugs of this level are the most promising in the development of pharmacology.
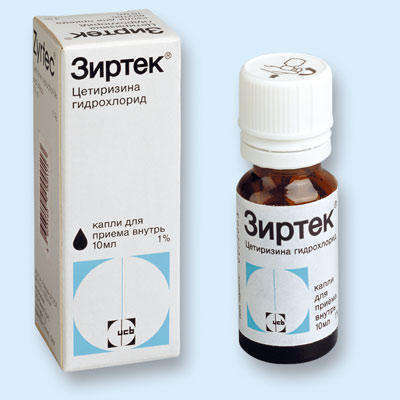
Zirtec, Cetrin (Cetirizine) have the ability to penetrate the skin well, which ensures their effectiveness in treating skin allergic manifestations. The effect becomes noticeable 2 hours after administration and lasts for 24 hours. Such drugs do not cause sedative and cardiotoxic effects if their use is strictly regulated by medical recommendations. In case of impaired renal function, they should be prescribed with caution.
Telfast, or otherwise Fexofenadine, does not interact with other medications. It does not have a sedative effect or influence on psychomotor skills. This remedy is effective and the safest among antihistamines. Trexyl has a fairly rapid action and is used to relieve the symptoms of allergic rhinitis, dermatological manifestations, asthma and acute allergic reactions to various irritants. Trexyl is safe for patients suffering from glaucoma and prostate diseases.