Swollen eyelids are a sign of various disorders in the body. The causes of this phenomenon may be allergic reactions, ophthalmological diseases and other factors. Swelling of the eyelids often occurs in children, especially preschoolers, as they are at risk for infectious eye pathologies. Let's look at the causes and methods of treating edema.
Inflammation of the upper or lower eyelid can be caused by various factors. Based on external signs, you can first guess what exactly caused the swelling. It depends on the degree of its severity, location, and whether it occurs in one or both eyes. Doctors also distinguish a separate type of edema, called reactive. It is named so because it develops literally in a matter of minutes. The location area can be any - both the upper and lower eyelids. This happens in some conditions. Let's look at the reasons why reactive swelling of the upper or lower eyelids may occur in a child.
Types of swelling under the eyes
To understand why your child has swelling under the eyes, you should consult a doctor. The doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations and find out the cause. There are several types of edema. Therefore, to determine the cause of their occurrence, an examination by a specialist is necessary. Swelling differs in location, density and color of the skin when pressed. The following types of “bags” under the eyes are distinguished:
- Physiological.
- Pathological.
- Hereditary.
Often, swelling is associated with the accumulation of excess fluid under the skin. They occur as a result of drinking water at night. Physiological edema also includes fatty “bags” under the eyes. They appear from the proliferation of subcutaneous tissue. A slight swelling and redness associated with lack of sleep can be mistaken for physiological swelling under the eyes in children.
Pathological “bags” are divided into mucous and protein. The first arise as a result of disruption of the thyroid gland. They have a soft consistency. Protein edema is associated with kidney disease. They are more pronounced in the morning and have a soft consistency.
Symptoms
Edema in young children is easily noticeable, so an attentive and caring parent can hardly leave them unnoticed.
When should you see a doctor?
Symptoms that should prompt you to consult a doctor:
- increased body temperature;
- palpable compactions in the tissues of the eyelids;
- suppuration of the eyes;
- tearfulness.
ATTENTION: If you detect at least one of the above symptoms, do not rush to self-medicate. Using medications without a doctor's prescription can harm your child's health.
. Instead, immediately visit a pediatrician and ophthalmologist, who will determine the real cause of the swelling and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Associated signs of diseases
Swelling of the eyelids is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature, which can be either subtle or significant. Prolonged high body temperature with edema is fraught with increased intracranial pressure
. The combination of a high temperature with tearfulness, headaches and problems with urination may indicate:
- diseases of the heart (swelling worsens in the evening) and thyroid gland;
- problems with the kidneys and liver;
- sinus diseases (sinusitis, rhinitis or sinusitis);
- diseases of veins and lymphatic vessels;
- allergies (including angioedema).
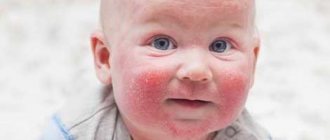
If swelling appears without any noticeable reason, accompanied by watery eyes, redness of the eyes, mucus from the nose and anxiety, this indicates the presence of an allergic reaction.
If edema is accompanied by a frequent urge to urinate, blood in the urine (determined by turbidity and a dark tint), pain in the head and back, and high fever, suspicions fall on diseases of the kidneys and urinary ducts.
If a child experiences fluid retention (the amount of moisture consumed does not correspond to the amount excreted), kidney disease, hormonal disorders, and cardiac decompensation may be present.
With nephrotic syndrome, severe anemia and heart failure, local swelling of the eyelids can develop into general swelling of all parts of the body (especially the lower extremities), which is accompanied by slow weight gain.
Expert opinion
Nosova Yulia Vladimirovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
It also matters which eyelid swells. Swelling of the upper eyelid may indicate problems with digestion, heart and kidney disease, allergies and oncology. Swelling of the lower eyelid may indicate pathologies of internal organs that are not inflammatory in nature
. If the lower eyelid swells in the morning, diseases of the heart and blood vessels, thyroid gland and kidneys are possible.
Swelling under the eyes of a child: causes of occurrence
If edema appears in a child, you should not make hasty conclusions. It is better to observe the baby for several days and determine at what time the “bags” under the eyes appear and whether they are associated with fatigue. If swelling does not go away on its own, you should consult your pediatrician. The causes of physiological edema can be:
- Water retention in the body. The accumulation of excess fluid is not always a consequence of kidney problems. Water can be retained in a child's body due to poor nutrition. For example, when consuming salty foods or liquids in the evening.
- Tired eyes. Overexertion occurs as a result of prolonged watching TV, reading or sitting at the computer. As a result, not only vision deteriorates, but swelling also appears.
- Chronic lack of sleep. The correct regimen is very important, especially for children. Therefore, you should give your child at least 8 hours of sleep at night. Daytime naps are also important for preschool-aged children.
- Exposure to sunlight on facial skin. Due to ultraviolet radiation, the body's defense reaction is triggered, which provokes the accumulation of fluid.
In addition, swelling around the eyes is sometimes associated with the characteristics of the skin and fatty tissue. If the parents have slight edema that is not associated with the disease, this feature can be inherited by the child.
Treatment of the disease
If swelling appears systematically after sleep, a thorough examination by a pediatrician is necessary. The doctor will prescribe the necessary tests, the results of which will indicate the existing pathology. In this case, hospital treatment is necessary.
If the doctor does not detect any pathology or disease, then parents should completely reconsider the child’s lifestyle and nutrition. Most likely, the child does not get enough sleep, or does not spend enough time in the fresh air, and, perhaps, does not eat properly.
First of all, it is necessary to limit the child’s exposure to a computer or TV monitor and instill in him the need for an active lifestyle. It’s not without reason that the saying goes: “Life is in motion!”
Nutrition must be taken seriously:
- First, limit your consumption of salty foods.
- Secondly, introduce whole cereals, fresh fruits and vegetables into your diet.
- Thirdly, be sure to include vegetable and cereal soups and vegetable stews in your child’s menu.
Try to include more stewed and boiled vegetables in your diet. Consider the fact that a healthy child’s body needs about 1.5 liters of fluid per day.
In addition, teach your baby to go to bed at the same time, preferably before 10 p.m. It is the period of time before 12-00 midnight that is extremely important for maintaining health, since at this time the largest amount of the hormone melatonin is formed, without which the body cannot exist.
It is noteworthy that no period of time of the day can claim a similar intensity of production of such an important neurohormone, the deficiency of which leads to many diseases.
On topic: The best products for swelling
The appearance of pathological “bags” under the eyes
There are a large number of reasons why swelling under the eyes may occur in children. If all harmful effects have been excluded, it is necessary to get tested. One of the common causes is kidney pathologies. In some cases, swelling is the only manifestation of the disease. Due to kidney disease, water can remain in the body for a long time. Most often, fluid accumulates under the skin of the lower eyelids.
Another group of pathological causes are endocrine system disorders. Often, mucous swelling is associated with a lack of thyroid hormones. The main reason is hypothyroidism. In addition to pathologies of the thyroid gland, edema can occur due to impaired regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary system of the brain.
Another dangerous group of causes is heart disease. In this case, the swelling has a dense consistency and a bluish tint. The skin in the area of the “bags” is cold to the touch. In a child, severe swelling under the eyes may be a sign of a heart defect that forms in utero.
Other reasons include: liver pathologies, metabolic disorders and inflammatory diseases of the eyes and paranasal sinuses. In such cases, there are symptoms of intoxication, the child becomes restless, there is a runny nose or a violation of the outflow of tears.
Swelling of the eyelid due to stye
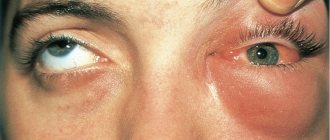
Redness and swelling are the first symptoms of stye (hordeolum). This is a purulent process in the hair follicle of the eyelash or in the sebaceous gland. In the internal form of the disease, inflammation affects the meibomian glands, which moisturize the conjunctiva and cornea. The eyelids swell with conjunctivitis, blepharitis, chalazion - diseases that have similar initial symptoms.
With barley, there is swelling in the area of the eyelid margin of one eye. The cause of inflammation is Staphylococcus aureus (bacterium). Treatment should begin at the first signs of local swelling on the eyelids. At the beginning of the inflammatory process, instillation of sodium sulfacyl solution helps. If the temperature rises, the child is given an antipyretic drug.
Do not heat, squeeze or in any way open the stye on the eye.
What to do if a stye forms on the eye:
- instill eye drops with an antibiotic (Sulfacil);
- apply antibiotic ointments (Tetracycline, Erythromycin) behind the eyelid;
- give antihistamine drops or syrup to drink (Zodak, Erius);
- rinse the eyelids with furacillin solution (when pus comes out).
The ointment is applied in the part where the eyes are swollen and a bulge appears. Barley differs from chalazion in that it suppurates, ejects purulent contents and completely disappears within an average of a week. The chalazion hardens into a dome shape with a diameter of 0.5–1 cm and persists for weeks or months. Inside it is a dense capsule.
Edema in kidney diseases
Kidney disease is the main cause of the development of pathological edema. The pathogenesis of this syndrome is associated with damage to the glomerular nephron system. The inflammatory process developing in the kidney tissues leads to their swelling. As a result, compression of the blood vessels occurs. Due to a decrease in circulating blood volume, the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidneys is irritated. As a result, the secretion of renin and aldosterone increases. The consequence of this is sodium retention in the body. The level of antidiuretic hormone in the blood increases and osmoreceptors are irritated. As a result, the reabsorption of water by the renal tubules increases and fluid accumulates in the subcutaneous tissue. Most often, swelling under a child’s eyes in the morning is associated with this very reason. In such cases, you should pay attention to the baby’s urination and compare the amount of fluid drunk and excreted. To detect chronic kidney disease, special urine samples must be taken.
Why do babies' eyelids swell and what to do about it?
Swelling of the eyelids in children under one year of age occurs for the same reasons as in older children. At the same time, the cause of edema at this age is much less likely to be pathology. In infants, eyelid swelling is less often accompanied by other symptoms and is more often associated with less serious causes. Some parents mistake a thick network of capillaries visible through the thin skin of the eyelids for edema.

The causes of swelling of the eyelids in infancy can be:
- excess salty or fatty foods;
- drinking disorders;
- prolonged crying (swelling can persist for up to several hours after crying);
- eye fatigue from being in a dark or too brightly lit room for a long time.
If, simultaneously with swelling of the eyelids, swelling of the fontanelles, tearfulness and anxiety of the child are noticeable, this may indicate increased pressure inside the skull.
Edema due to heart pathologies
One of the causes of swelling under the eyes in children is heart failure. Unfortunately, such pathologies develop during the period of organ formation in the fetus and are not always diagnosed in time. Congenital diseases include heart defects. In some cases, the pathological condition develops as a result of viral and bacterial infections. Among them is myocarditis. Edema in heart disease has a complex pathogenesis. They appear due to impaired blood flow in the vessels of the kidneys, circulatory hypoxia and increased venous pressure. All these factors lead to an influx of plasma into the tissue. Cardiac edema is cold to the touch and has a bluish tint. Compared to the “bags” under the eyes that occur with kidney pathologies, they are denser in consistency. Such swelling can appear not only on the face, but also on the legs. In addition, heart disease in children is accompanied by cyanosis and shortness of breath.
Allergic conjunctivitis
This pathology is accompanied by the discharge of mucus from the nose and sneezing. It is often caused by a hereditary predisposition and manifests itself as a result of exposure to external stimuli. Ailments such as angioedema or rhinitis may be an explanation for why the eyes become very swollen after sleep. In this case, the child feels the presence of a foreign object in the area of the organs of vision, he is bothered by a feeling of itching, and copious secretion of tear fluid.
If symptoms occur, you should get tested. After the doctor finds out what provokes the development of an allergic reaction, you need to try to eliminate these things from the baby’s environment. As a rule, individual intolerance is caused by the following factors:
- Food (nuts, dairy products, fruits and berries, nut kernels, eggs).
- Household chemicals.
- Hygienic cosmetics.
- Chlorine, which is found in water.
- Medicines.
- Pollen.
- Pet fur.
- Arthropod bites (with this phenomenon, swelling is most often observed in the area of one eyelid, bridge of the nose, cheeks).
Severe swelling under the eyes in a child under one year old
It is more difficult to understand the cause of edema in infants than in older children. After all, kids cannot say what exactly hurts them. Therefore, if “bags” appear under the eyes in a child under one year old, you should immediately consult a doctor. The reasons may vary. In rare cases, infants develop physiological swelling under the eyes. This is usually associated with sleep disturbance, which occurs due to insufficient nutrition, intestinal colic, teething, etc. Much more dangerous is pathological swelling under the eyes of a child. After its appearance, the baby should be examined. The most common causes of this syndrome include: hypothyroidism, heart defects and kidney disease.

Demodectic blepharitis
A common ophthalmological pathology, the causative agent of which is a mite of the genus Demodex. It measures 0.2-0.5 mm in size and is distributed in the ducts of the meibomian and sebaceous glands, at the base of the hair follicles of the eyelashes. Up to 25 individuals can live in one follicle, feeding on dead epithelial cells and gland secretions. This pathogenic microorganism is found in 90% of adults - they are simply asymptomatic carriers of it. However, when certain external factors arise, the mite becomes active, and then demodicosis begins to develop.

When demodicosis appears, the child begins to complain of burning and itching in the eye area, and these sensations intensify with heat (in the sun, in the bath), dryness and irritation. The edges of the eyelids are thickened and hyperemic. A characteristic initial sign of demodectic blepharitis is glued eyelashes, strewn with white particles at the base, as if frosted. Subsequently, pronounced swelling of the eyelids and ciliary edges occurs. With a long course of the disease, conjunctivitis, keratoconjunctivitis, trichiasis, and, as a result, dysfunction of the meibomian glands can develop. Elimination of demodectic blepharitis should be done in a timely manner so that it does not take an acute form.
Swelling due to inflammatory processes
The causes of red swelling under the eyes of a child include inflammatory diseases. Among them are sinusitis, rhinitis, conjunctivitis. All these diseases are associated with colds. The inflammatory process leads to the fact that vascular permeability increases and fluid enters the surrounding subcutaneous tissue. In addition, puffiness under the eyes can be caused by allergic reactions. It is not difficult to identify such reasons. All inflammatory diseases are accompanied by fever, tearfulness, and runny nose. With conjunctivitis, in addition to swelling, there is an accumulation of mucus or pus on the mucous membrane of the eyelids. “Bags” under the eyes go away on their own after the infection is eliminated.
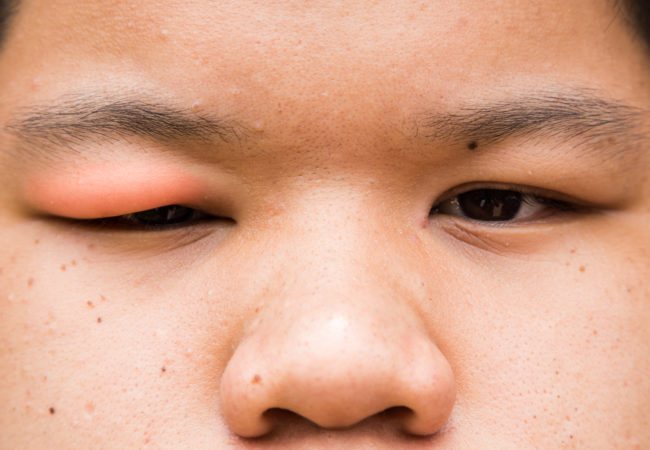

Treatment depending on the causes
The swelling itself can often be relieved using folk remedies or improvised means , but doing this without consulting a doctor is not recommended.
Firstly, if the root cause is not eliminated, such swelling will still appear again .
Secondly, in relation to children, traditional medicine methods are generally recommended to be used only in extreme cases, since unpredictable reactions of the body to some of the drugs used are possible.
You should know! According to statistics, eyelid swelling in children most often occurs as an allergic reaction, regardless of whether the allergen is food ingredients or plant pollen.
In such cases, antihistamines in the form of drops and ointments are prescribed individually: oratadine, lecrolin, opatanol and others.
If swelling is caused by pathological inflammatory processes in the tissues of the eye, after examination, decongestant, antibacterial and soothing ointments and drops for topical use are prescribed.
also sometimes recommended to use vasoconstrictors .
In any other cases and in case of diseases of internal organs that provoke the development of swelling, you must first undergo an examination and determine the cause of the disorder.
Diagnostic measures for edema
To eliminate puffiness under the eyes, the cause of this symptom must be determined. First of all, you should pay attention to the child’s routine. If possible, you should avoid staying at the computer and normalize your sleep. If after this the swelling does not disappear, it is necessary to undergo a full examination. If you have soft bags under your eyes or redness in the morning, you should take a blood and urine test. If there are any deviations from the norm, an ultrasound of the kidneys is performed. If the doctor suspects the presence of cardiac edema, special diagnostics are required. The child should undergo echocardiography to exclude developmental defects. In case of mucous edema, it is necessary to donate blood for thyroid and pituitary hormones. In order for the “bags” under the eyes to disappear, etiological therapy is first required, that is, elimination of the cause of their appearance.
How to treat?
Albucid eye drops perfectly treat stye from the first days of life. The treatment regimen is prescribed by the doctor depending on the diagnosis. Eyelids swollen due to stye are treated with Albucid drops, which resolve from the first days of a newborn’s life. Analogs are “Tobrex” and “Levomycetin” drops. Ointments have a longer lasting effect; they do not sting or irritate the eyes. For example, "Floxal". With the permission of the pediatrician, you can also use traditional methods. The eyes are washed with agave juice, decoctions of birch leaves, plantain, and dill seeds.
Conjunctivitis is treated depending on the type. Viral - with compresses of salt and boiled water, interferons and antiviral ointments: Zovirax, Virolex, Oksolin, Tebrofen and others. For allergic conjunctivitis, you should get rid of the allergen, and then give the child antihistamines. For example, “Eden” or “Fenistil”. In case of bacterial infections, antibiotics are mandatory, as well as Tetracycline ointment 1% and drops of Levomycetin 0.25% are used. Suitable for rinsing are brewed tea, chamomile decoction, and calendula.
Treatment of dacryocystitis comes down to restoring the patency of the lacrimal canal. An ophthalmologist or pediatrician shows a set of massage actions (jerky pressure on the lacrimal sac), thanks to which the swelling symptoms will go away. Repeat at least 7 times a day. At the end, the conjunctiva is washed with antiseptic drugs and antibacterial drugs are instilled. If the eyes become even more swollen and do not go away, then probing is performed.
Treatment of edema in children
Treatment of edema depends on the provoking factor. In some cases, the use of antiviral drugs, such as Anaferon or Viferon suppositories, is sufficient. These medications will help you cope with colds and the redness under your eyes will disappear. For renal edema, hormonal therapy is required, and diuretics are also prescribed. Pathogenetic therapy includes drugs that improve blood circulation, for example the drug Dipyridamole. Heart defects require surgery. For hormonal deficiency, the drugs "Eutirox" and "Iodomarin" are prescribed.
What to do and what medications to use?
Drops will help relieve irritation. If the upper eyelid is red, the child should be shown to the pediatrician as soon as possible. After all, problems with the upper and lower eyelids indicate different diseases. If your eyelids are swollen and swollen in the morning, and the problem disappears within 24 hours, then you need to pay attention to the baby’s daily routine. Most likely, he does not eat properly and rarely moves, and does not get enough sleep. Such reasons need to be eliminated. With mechanical damage, the eyelid above the eye swells. During the treatment, the eye is cleaned and drops are prescribed. They are aimed at restoring the mucous membrane and relieve all symptoms by morning. “Balarpan”, “Defislez” and others are effective.
If allergic reactions are confirmed, you need to remove the source of irritation to the mucous membrane and take antihistamines. For example, “Fenistil”, “Eden”. If the eyelid is red, swollen and swollen due to infection, then antibacterial drugs are needed (Tobrex drops, Floxal, Erythromycin ointment, Tetracycline). During the treatment period, it is strictly forbidden to use cosmetics on the face and eyes, heat the site of inflammation, or open the stye yourself.