An allergic reaction affecting the eyes is one of the most unpleasant. In addition to general discomfort, the manifestation of allergies on the eyelids can be very noticeable and greatly spoil the appearance. In addition, significant swelling of the eyes can narrow the incision, which will to some extent affect a person’s performance and can reduce their quality of life. If you have an allergy to the eyelids, the reasons may be different. At the same time, it is important to know not only how to treat such a syndrome, but also how to return the eyes to their normal appearance as soon as possible.
Cosmetic procedures that cause severe swelling in women
Mild swelling or extensive swelling is a common phenomenon observed in women after certain cosmetic procedures, including eyelid tattooing, Botox injections, and eyelash extensions.
There can be several causes of swelling, and the most harmless of them is a natural reaction to mechanical trauma to the skin. Most manipulations involve the introduction of chemicals under the skin in the eye area, to which the tissue responds accordingly. Such swelling disappears within a few days without treatment or health consequences.
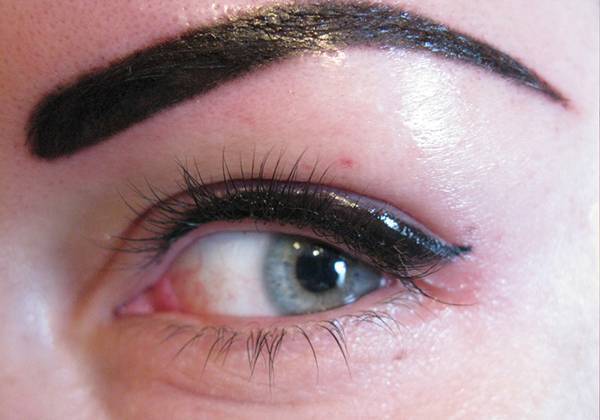

Photo 2. The procedure for tattooing on the eyelids in women often causes redness and the eyes become swollen.
The results of mistakes made by cosmetologists are of great danger - injections that are too deep, violation of procedure technology, the use of low-quality dyes and preparations, as well as individual reactions of the body.
Swelling caused by such factors does not go away for a long time and is accompanied by itching, inflammation and discomfort. To avoid the unpleasant consequences of cosmetic procedures, you must contact only experienced specialists and follow all recommendations for facial care after procedures.
Traditional methods for relieving allergic swelling
In addition to the main therapy, which should be prescribed by an allergist, you can use folk remedies. To improve the general well-being of the patient, you need to wash your eyes more often and apply compresses. It is not recommended to start self-medication without first consulting an ophthalmologist. Not every medicinal collection helps relieve puffiness or eliminate other manifestations of allergies in the eyes. If you don't know the allergen that provoked a strong reaction, you can only make the situation worse.
You can reduce pituitary discharge by using a regular compress. The procedure consists of applying a cotton swab moistened with water for ten minutes. Compresses can be done several times a day.
We advise you to read: Hydrocortisone or dexamethasone, which is better against edema
In addition to compresses, other water procedures can be used:
- Washing with water.
- Rinse with chamomile decoction, which is infused for about an hour beforehand.
- Applying a tea bag as a compress.
- Rinse with baking soda solution. This procedure helps relieve inflammation.
In addition to water procedures, you can use other methods to relieve swelling on the eyelids:
- lotions from potatoes (raw);
- lotions from apples, cucumbers.
- Lotions with medicinal herbs. To soothe the inflamed dermis, use sage, chamomile, and string.
To improve the patient's condition, it is necessary to follow the doctor's instructions.
source
Folk remedies for eyelid tumors
If swelling of the eyelid is caused not by illness, but by simple lack of sleep, consuming too much liquid or salty food, you can use folk recipes that will help reduce the intensity of the symptom and get rid of it altogether.
For example, you can make steam baths by adding a decoction of herbs: linden flowers, chamomile, birch leaves, etc. This procedure should be carried out several times a day until the eyelid returns to normal. In addition, a contrast shower for the face will help, when hot and cold water are used alternately. You can wash your face with decoctions of the herbs listed above.
Swollen eyelids can be removed in the following ways:
- parsley (two tablespoons of seeds need to be ground, pour a glass of hot water and leave for an hour; the finished product is taken one tablespoon four times a day orally);
- flaxseeds (pour four teaspoons into a liter of boiling water, then put on fire, boil for twenty minutes; the broth is filtered and taken orally three times a day, 100 milliliters each);
- Drink tea during the day, adding linden or mint.
A parsley mask applied to the eyelid has an anti-edematous effect: crushed greens are mixed in a 1:2 ratio with sour cream. Use the mass in the form of lotions on the area of swelling, hold for ten minutes. Black and green tea have proven themselves well, which is also used as a lotion (ten minutes at a time).
If you have a swollen eyelid for no apparent reason, there is no need to self-medicate. In this matter, it is best to trust your doctor.
When the eyelid above the eye is swollen, what to do is now clear.
How to remove swelling from the eyelids in the shortest possible time
If swelling caused by allergens occurs, immediate medical attention must be provided. The response is fleeting, it can instantly develop into angioedema - a condition leading to death.
The patient needs to be seen urgently by a doctor. The doctor will determine the cause of the swelling and select antihistamines for allergies.
Drugs
To suppress an allergic reaction, patients are prescribed:

- Antihistamine tablets. The development of the disease is suppressed by: Agistam, Suprastin, Zodak, Diazolin, Tavegil.
- Antihistamine drops. For treatment, Alomid, Ketotifen, Opatanol, Azelastine, Lecrolin drops are prescribed. After using the drugs, skin itching, burning and pain disappear.
- Vasoconstrictor drops. Medications Octilia and Visine relieve swelling and redness.
- Eye ointment with chloramphenicol. Levomycetin prevents the development of inflammatory processes.
- Glucocorticosteroid drops and ointments. Lotoprednol, Dexamethasone and other hormonal agents are used under strict medical supervision. After using ointments and drops, swelling subsides and inflammation subsides.
Traditional methods for relieving allergic swelling
Folk remedies are used as soon as the first signs of an allergic reaction appear. They are necessary to quickly relieve inflammation, swelling, itching and burning.
The eyes are a delicate paired organ; treating them yourself is dangerous. The choice of traditional methods of treatment should be entrusted to a doctor. The ophthalmologist, based on the cause of the swelling, will prescribe effective remedies.
The following methods effectively suppress irritation:
- Cold compresses on the eye area. Ice cubes are wrapped in a napkin and placed on swollen eyelids. Leave for 2 minutes. After a break, the procedure is repeated.

- Applications with freshly brewed green or black tea. The extract relieves irritation, burning, itching, and inflammation.
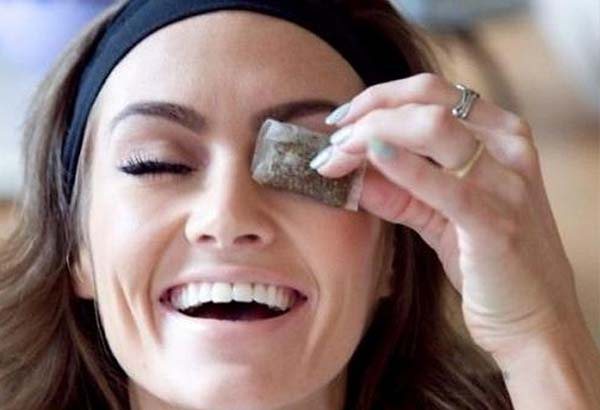

- Lotions with herbal decoctions. The procedure must be carried out following a certain algorithm. Brew 1 teaspoon of chamomile, sage or string in 200 ml of boiling water. Cool to a comfortable temperature and filter. Soak tampons in the extract and squeeze out. Apply on swelling. Session duration is 15 minutes.

- An application with parsley is an excellent solution for swelling and redness of the eyes. Chopped greens are placed in a linen bag, immersed in boiling water for 2 minutes, and cooled. Apply on swelling. Remove the application after 15 minutes.

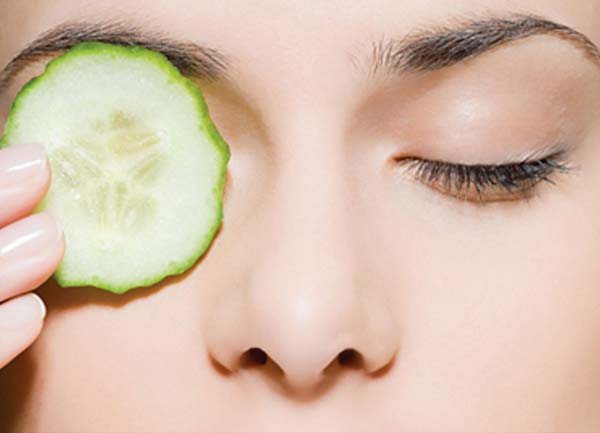
- Cucumber applications. When swelling of the eyelids is caused by an allergic reaction, cucumber gruel is used for treatment. This mask effectively fights swelling. The mass is distributed over a gauze napkin, applied to the eyes, and left for 20 minutes.

We recommend further reading: Causes and treatment of swelling above the eyes
Preventive measures
To prevent the formation of edema in the eyelid area, you need:
- control the amount of fluid entering the body, especially in the evening;
- moderate the amount of salted and smoked foods and marinades consumed;
- sleep on your back, with your head slightly elevated so that the fluid is better redistributed;
- protect eyes from direct contact with ultraviolet radiation;
- avoid overwork, sleep 7-8 hours a day;
- stop drinking alcohol;
- take a responsible approach to the choice of cosmetics, remove the remains of decorative products before going to bed.
You can also prevent the appearance of eyelid edema if you undergo a timely medical examination, monitor your health, and consult a doctor at the first alarming symptoms. This phenomenon is not always associated with pathological causes, but if it occurs systematically, then you need to consult a specialist and undergo diagnostic tests.
Treatment of allergic edema on the eyelid
When swelling in the eyelid is caused by an allergic reaction, which is characterized by itchy and red eyes, it is first advisable to determine the source and immediately eliminate it.
If a person has an allergic reaction to a food or medicine, you need to drink any absorbent, for example, activated carbon. You also need to increase the amount of fluid consumed (more specifically, water) in order to remove the allergen from the body as quickly as possible.
If a symptom is triggered by any cosmetic product, it should be thrown away and during treatment, do not use cosmetics at all. When a person has an allergic reaction to animal hair, mold or household dust, the only way is good ventilation of the room and constant wet cleaning.
During the treatment of allergic manifestations, it is necessary to observe standards of personal hygiene of the visual organs in order to prevent the penetration of infectious agents into them. If there is a predisposition to the appearance of such a reaction to a specific pathogen, you need to adhere to preventive rules, especially avoid contact with it.
If the above methods do not help eliminate the symptom, you need to go to an ophthalmologist who will prescribe medications. These are primarily antiallergic drugs in the form of tablets (Diazolin, Suprastin, Zodak, etc.) or in the form of eye drops (Opatanol, Lecrolin). To eliminate swelling, you need to use vasoconstrictor drops (Octilia or Visin). If swelling develops rapidly, you need to call an ambulance.
Symptoms
An allergic reaction that occurs before the eyes is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. The main symptoms of the disease include:
- burning;
- itching;
- pain syndrome;
- redness;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- edema;
- presence of a foreign body.
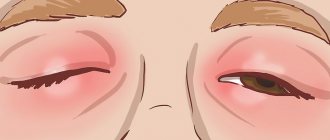
Redness
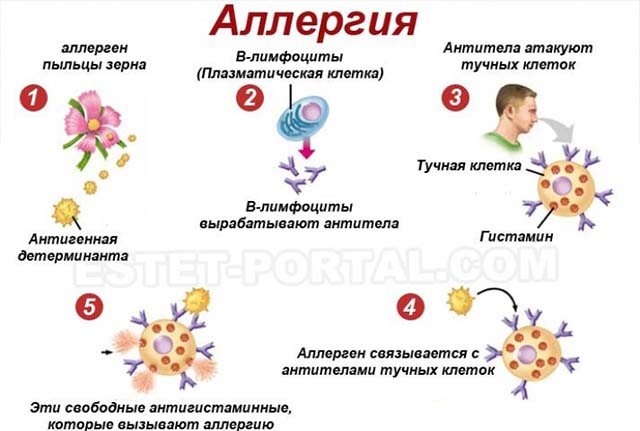
The conjunctiva of the eyelids turns red under the influence of allergic mediators. Histamine is released from mast cells in response to irritation. This connection narrows large vessels and dilates small ones.
The eyes are penetrated by a network of capillaries. When allergic edema appears, small vessels become filled with blood. Therefore, upon visual examination, redness of the conjunctiva is clearly visible.
Edema
Swollen eyelids and conjunctiva are key symptoms of allergic swelling. Severely swollen eyes due to exposure to an irritant are considered a natural phenomenon. The thin skin of the eyelids is very vulnerable and stretches easily. Large volumes of exudate accumulate in the loosened subcutaneous fat.
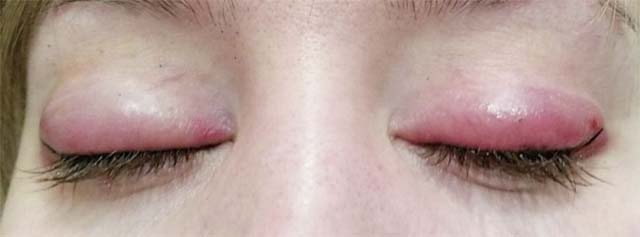
Fluid seeps into the interstitial space from vessels carrying blood and lymph. The skin stretches under the pressure of the leaked exudate. Swelling forms on the eyelids.
Irritation and pain
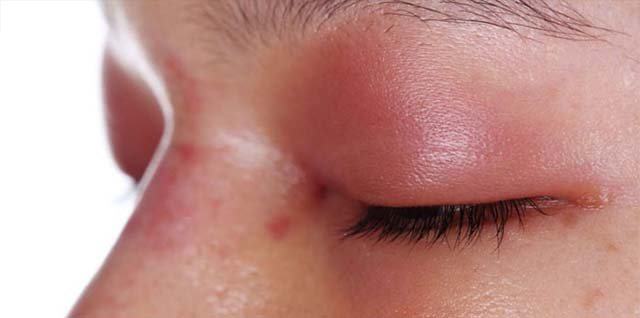
When the nerve roots that pass through the mucous membranes of the eyes are irritated, discomfort occurs. The skin is inflamed, painful, and burns. The affected areas are very itchy.
Tearing
An allergen that interacts with the mucous layer irritates the eye tissue. The lacrimal glands intensively produce the fluid necessary to wash away the irritant.
We recommend further reading: Why does a woman develop facial swelling, causes and treatment?
Allergy symptoms coincide with signs of other pathologies that occur in the organs of vision. It is important to distinguish an allergic reaction to the eyes from other diseases.

Renal and cardiac edema are removed with diuretics. Diuretics do not relieve swelling caused by an allergic reaction. When swelling is caused by a bacterial infection, in addition to the main symptoms, specific symptoms arise - the discharge of pus.
Possible diseases
There are several eye diseases that often cause swelling of the upper eyelid. Often, a defect is formed as a result of an infection or virus entering the mucous membrane, which causes inflammation to develop and normal blood and fluid circulation to be disrupted. When exposed to all these factors, unilateral, less often bilateral, edema is formed.
Find out why your upper eyelids swell in the morning here.
Barley
Most often it causes swelling of one eye, which is caused by inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelashes. The main cause of stye is the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms onto the surface of the eyes, usually Staphylococcus aureus. The disease develops against the background of reduced immunity during colds or viral diseases, vitamin deficiency. In severe cases, swelling is accompanied by the release of pus, which is strictly not recommended to be squeezed out with your hands - this can lead to various complications (meningitis or orbital phlegmon).

Dacryocystitis
This disease is associated with inflammation in the lacrimal sac, which causes a number of side effects, including swelling of the eyelid. There is an acute and chronic form, which often develops against the background of prolonged blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. The disease has many side symptoms, for example, pain and inflammation of the affected areas, profuse lacrimation. Dacryocystitis responds well to drug therapy if the disease is diagnosed in the early stages. Massage also has a good effect on dacryocystitis.
Unilateral blepharitis
This is a severe inflammatory disease of the eyelid margin, which has many clinical forms (typical, ulcerative, scaly and others). In some cases, the cause of the disease is parasitic ticks. If left untreated, the disease may actively develop, which leads to defects in the cornea, conjunctiva, and can also lead to loss of visual acuity.
Conjunctivitis
In this case, swelling of the eyelid is caused by inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the eyeball. The disease is always accompanied by many side symptoms, for example, burning in the eye, discharge of pus, profuse redness of the eyelids
Timely treatment is extremely important due to the tendency of the disease to become chronic.
How to treat conjunctivitis in adults, read the material.
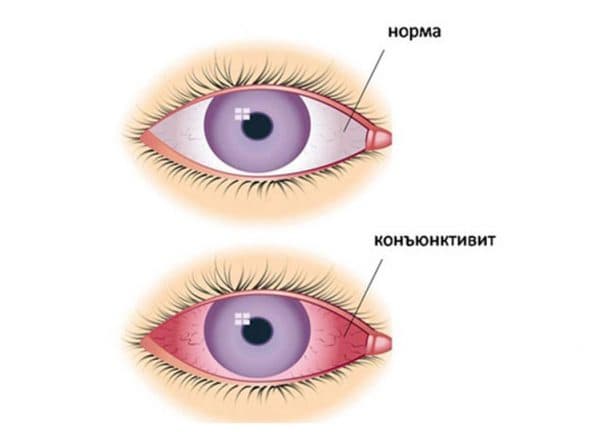
Allergic edema
Pathology of this type most often develops at lightning speed, but if first aid is provided in time, the symptoms begin to subside within 12 hours. Edema of this type appears due to an allergic reaction of a local or general nature. With Quincke's edema of large volume, the swelling can spread from the eyelids to the cheeks, right up to the corners of the lips. In severe cases, low-grade hyperthermia occurs, a general deterioration in health, as well as the discharge of pus. If left untreated, the disease can lead to chemosis of the conjunctiva, the development of glaucoma, and prolonged swelling of the eye area in rare cases results in the formation of exophthalmos and displacement of the eyeball.
What is an allergy
This is a symptom that represents an excessive accumulation of fluid in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the eyelids, resulting in their swelling. The common cause of this pathology is various diseases of a local or general nature. Swelling of the upper eyelid is most common, but sometimes it also occurs in the lower eyelid. The attack can be single or recurrent. Edema can develop at any age, but men and women over 30 are more prone to it.
In general, the eyelid is a fold of skin that protects the eyes from possible dangers, such as dust and bright flashes. It consists of two layers:
- Anterior, or superficial. This is the musculocutaneous layer that provides blinking. The muscle includes two parts: palpebral and orbital.
- Posterior, or deep. This is the conjunctival-cartilaginous layer. The cartilage of the eyelids consists of dense connective tissue located under the eye muscles.
Most of the human body is fluid. It occupies almost 70% of the total volume. Part of the fluid is located inside the cells, the rest is in the space between them. Swelling of the eyelid in one eye develops when the amount of water in the intercellular area becomes above a critical value of 1/3 of the total volume. Depending on the reason it happens:
- membranogenic - develops due to increased permeability of vascular walls to water and molecular substances;
- hydrostatic – associated with a decrease in the pressure of the same name inside the capillaries and tissues;
- hypoproteinemic - is a consequence of a decrease in colloid osmotic pressure.
Depending on the location, swelling is divided into bilateral and unilateral (on the right or left eye). These types are practically no different. Swelling of the lower eyelid is observed less frequently; swelling of the upper eyelid occurs more often. In the first case, cardiovascular diseases may be a serious cause. Taking into account the cause, edema is classified into:
- Inflammatory. Accompanied by pain, redness, and hyperemia of the skin. This type of inflammation is characteristic of eyelid swelling in one eye.
- Allergic. Also called angioedema. The eyelid doesn't hurt, it just itches. There are no other symptoms. When a child's upper eyelid is swollen, the most common cause is allergies.
- Non-inflammatory. The skin color remains normal or pale, there is no pain, as well as a local increase in temperature. Swelling of this type is often bilateral and occurs mainly in the morning.
- Traumatic. Characteristic of the condition after tattooing, in which pigment is driven under the skin to create a makeup effect. The cause can also be other trauma to the eyelids, for example, microtrauma when wearing contact lenses.
Inflammatory edema
This type of deviation is associated with infectious lesions of the eyes, and less often with other diseases, such as acute respiratory viral infections, sinusitis, sinusitis and other inflammations of the sinuses. Such pathologies are accompanied by:
- burning;
- itching;
- tingling;
- photophobia;
- tearfulness.
Similar symptoms in the case of colds develop more often in both eyes. If only one eyelid is swollen, then the likely cause is infectious pathologies of the organs of vision. The list of such diseases includes:
- Barley. It is formed after pathogenic bacteria, most often Staphylococcus aureus, enter the surface of the eyeball. The infection is an inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelashes. The eyelid turns red, swells, and hurts when pressed.
- Conjunctivitis. Inflammation develops in the mucous membrane of the eye. Redness appears. There is a feeling of a foreign body or sand in the eye. There is photophobia and discharge of pus or clear fluid.
- Blepharitis. This is a chronic disease accompanied by inflammation of the edge of the eyelids, which swells.
- Dacryocystitis. Characterized by inflammation of the lacrimal sac. Dacryocystitis is indicated by pain, redness, and swelling of the eyelids. Symptoms are localized closer to the inner edge of the eye.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases. These include abscess and phlegmon of the orbit, which develop as a result of bacteria entering the wound. In this case, the eyelid swells and hurts very much. In more severe cases, body temperature rises, general weakness and headache appear.
- Erysipelas lesions. This is a serious infectious disease that causes general intoxication of the body and inflammatory skin lesions. It can also cause swelling of the eyelid in one eye.
The clinical picture of allergic edema of the eyelid in one eye differs from inflammatory edema. Symptoms develop suddenly. Itching and swelling appear on the eyelid, it turns red. A person feels discomfort in the area of the affected eyeball. Skin rash, nasal congestion, and tearfulness also indicate the allergic nature of the disease. This reaction can be caused by:
- household chemicals;
- cosmetical tools;
- animal hair;
- plant pollen;
- insect vinegars;
- food products;
- hygiene products.
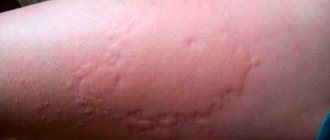
Allergic edema is classified into two types based on the symptoms and their severity. Based on these characteristics, the following are distinguished:
- Allergic dermatitis. Accompanied by not very strong swelling. Characteristic symptoms are itching and redness.
- Quincke's edema. Unlike the previous type, on the contrary, it causes severe swelling, which does not even allow a person to open his eyes. There are no other signs. This condition is dangerous because it can spread to the respiratory system.
Traumatic edema
Due to the soft and very delicate tissue, the eyelids are easily injured. Swelling may appear as a result of a burn, bruise or other mechanical stress. No specific treatment is required. Therapy is aimed at reducing symptoms and preventing purulent complications. This requires maintaining eye hygiene. There are other causes of traumatic swelling:
- Tattoo procedure. Involves driving pigment under the skin. Swelling develops due to too deep exposure. If the procedure is carried out correctly, the symptom disappears on its own after a day.
- Anatomical structure of the organs of vision. If the membrane between the fat layer and the skin is too thin, then it can swell under any negative influence.
This type of deviation is most often observed in the morning after waking up. In this case, swelling of the eyelids above the eyes is accompanied by severe pain, redness and hyperemia of the skin. At the same time, the external skin looks pale and cool. The cause of this complex of symptoms may be:
- oncological eye diseases;
- violation of lymph outflow or blood circulation;
- systemic diseases of the thyroid gland, vascular system, kidneys, digestive system;
- abuse of salty foods;
- smoking and drinking alcohol;
- lack of sleep;
- eye strain.
Swelling of the eyelids in the morning
At night, fluid gradually fills the space between the cells. This occurs due to prolonged exposure to a horizontal position. Then the swelling goes away throughout the day. The main causes of pronounced swelling after sleep, which occurs regularly, are:
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- abuse of pickles and alcohol the day before;
- first use of a new cosmetic product.
Allergy is a disease of modern society, since most people, for various reasons, have weak immunity. The body begins to be influenced by environmental factors that do not affect healthy people. A variety of substances can trigger allergies. An allergy manifests itself as an increased reaction of the body to certain compounds. The body forms an immune response to the presence of allergens and releases histamine, which causes allergic swelling.
If an allergen from the air immediately gets on the eye cornea, then the eyelids swell or turn red within 5-15 minutes, and if an allergic substance enters with food, the eyes swell after a longer time until the allergen reaches the mucous membranes of the eyelid through the bloodstream.
Infectious nature of edema
A tumor of the upper eyelid appears due to the formation of stye. This infection causes inflammation and redness of the eye membrane. Usually a stye appears in only one eye. Mostly children suffer from it due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.
At the beginning of the disease, the eyelid becomes red, swollen and painful. As the disease progresses, a white rod forms, which is not recommended to be squeezed out. Treatment of barley is carried out with anti-inflammatory drugs, and sometimes heating is prescribed.
Swelling of the upper eyelid during stye may be accompanied by temporary blurred vision, weakness, and irritability. Children during this period require special care. Do not allow your child to rub the eye, as this may cause it to swell further.
If a stye has formed inside the eyelid, then before going to bed it is recommended to apply a medicinal ointment under the eyelid. During the day, eye drops with an anti-inflammatory effect are instilled. Treatment of various eye diseases (glaucoma, cataracts) is carried out with several drugs.
Complication of stye
But eye medications, like all other medications, have side effects. If a problem occurs after using eye drops, ask your doctor why your eyes are swollen. It is possible that individual intolerance has arisen and you will need to select other means.
Almost always, at the initial stage of conjunctivitis, the upper eyelid of the affected eye swells. It is recommended to treat such an infection with medications. When instilling, use different wipes to avoid introducing infection into the healthy eye.
Eye surgery can also cause temporary swelling. Typically, during postoperative rehabilitation, such manifestations disappear.
Lotions or rinses to relieve swelling in the eyes can only be used with the permission of an ophthalmologist. If your healthy eye swells, you should tell your doctor.
First aid for acute allergic reaction
If the eye swells due to an acute allergic reaction, it is necessary to quickly remove allergic swelling from the eyes. Initially, it is necessary to eliminate contact with the allergen. Cold compresses help to reduce the feeling of burning, itching, and swelling. Place cotton pads moistened with cool (boiled) water over the eyes.
After eliminating the provoking factor, the patient should be given a tablet of antiallergic medication:
The doctor may prescribe the following creams:
If allergies are accompanied by allergic conjunctivitis, a specialist may prescribe one of the following eye drops:
After taking the medicine you need to call an ambulance.
After an allergic reaction, the patient can experience very dangerous consequences. Given this nuance, a patient with swollen eyelids needs to immediately pay attention to the disease. Swelling of the eyelids can provoke swelling of other organs (nasopharynx, throat, mucous membranes).
To speed up the removal of the allergen from the victim’s body, the patient should drink a lot of fluids (doctors give preference to water). You need to drink more water, the temperature of this drink should be between 18 - 20 degrees. It is useful to take activated carbon. In its absence, you can drink any adsorbent.
Calling an ambulance and visiting an allergist for swelling of the eyelids is a necessity . This pathology can provoke the development of Quincke's edema, which is dangerous to health. Sometimes a patient with eyelid swelling is hospitalized.
Clinical manifestations
The main symptom of swelling of the upper eyelid is swelling and increase in size. This is fluid accumulation. Swelling can be unilateral or bilateral. Most often the upper eyelids swell.
Based on the frequency of swelling, attacks are divided into single and recurrent. If swelling recurs frequently or is constantly present, then we are talking about some kind of pathology. Lack of timely treatment leads to complications and deterioration of general health.
Swelling of the eyelids can be determined visually by the following symptoms:
- Hyperemia, bluish or pale skin color, redness to varying degrees
- Skin tension and tension
- Thinning of the skin with a characteristic superficial shine
- The appearance of a visible pattern of blood vessels
- Pinpoint rash
- Reduction or complete tightening of the palpebral fissure
- Painful sensations when palpating
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes located near the auricle
- Tissue thickening around the eyes
- Presence of itching, burning, tingling, irritation in the eye area
Due to the nature of the disease, edema is considered to be a tissue-type disease. This is due to the accumulation of extravasation in the subcutaneous tissue.
Usually, with a one-time small accumulation of extravasation, a person does not experience severe discomfort, but if there is pain and a combination of symptoms, if we are talking about frequently recurring attacks, then consulting a doctor is necessary.
Common causes of edema
In the course of research, it was noticed that most often problems with eyelids occur in the summer months.
- As air temperatures rise, people drink more fluids, are exposed to the sun, and are exposed to insect bites, causing their eyelids to swell and their eyes to become tired and sore.
- Pollen from flowering plants is often a strong irritant. An allergic reaction to plants is accompanied by a runny nose, lacrimation, and swelling in the upper eyelids. In this case, treatment consists of taking antihistamines.
If during a morning jog or upon contact with plants you start coughing, sneezing, and your eyelids become very swollen, then there is only one reason - an allergy to plants. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to do allergy tests.
A reaction to an insect bite can also cause an unpleasant reaction. The consequence of this may be swelling of the eyes, itching, redness, nausea, and sometimes increased body temperature.
Tourists vacationing in exotic countries may be attacked by blood-sucking insects. Treatment in this case should be carried out by local doctors who know how to eliminate the consequences of such bites.
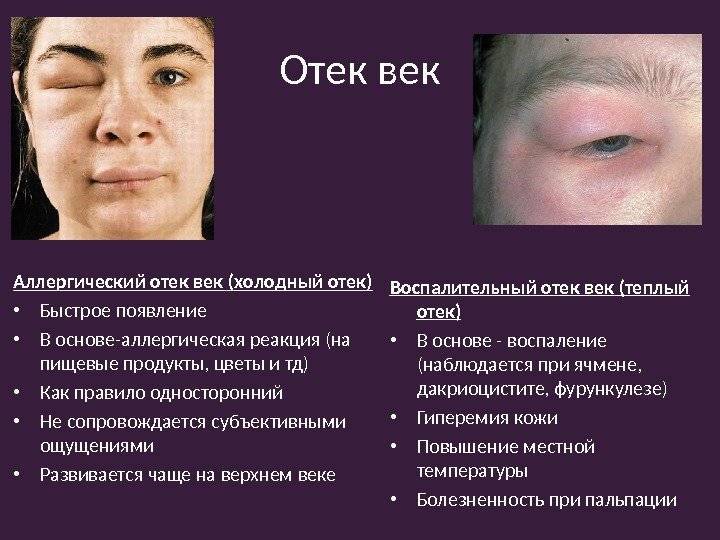
Causes of swelling of the eyelids
Swelling of the upper eyelid of one eye may be associated with working in a room where there is an air conditioner or fan.
Often, during hot periods, drafts are deliberately created to create comfortable conditions. However, a draft or a fan can cause eye inflammation, which is often accompanied by redness, swelling and burning in the eyes.
Another cause of swollen eyelids can be inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
Inflammation is accompanied by pain in the lower part of the face, uncontrolled lacrimation, and in the absence of timely treatment, the eyelids of one or both eyes may swell.
Depending on the severity of the inflammatory process, pain and redness do not decrease either after sleep or after taking painkillers. In case of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it is necessary to undergo a course of drug therapy and physical therapy. If the treatment is chosen correctly, the condition of the skin around the eyes returns to normal over time.
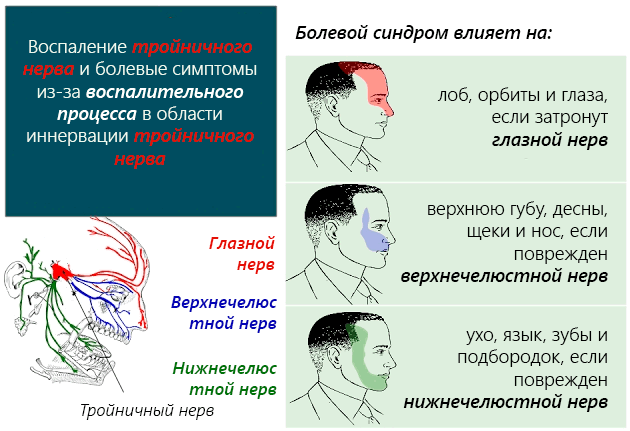
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Therapy methods
If itching occurs, you need to ensure that the child scratches his eyes as little as possible, as this can lead to such serious consequences as mechanical damage and infection.
Trying to eliminate symptoms such as allergies and swollen eyes on your own is highly discouraged.
If these signs appear in a child, you should consult a doctor. If, as a result of the examination, the diagnosis of “allergy” is confirmed, the specialist will prescribe appropriate therapy. Typically, in such cases, antiallergic drugs are prescribed (for example, Fenistil, Loratadine or Tavegil drops), as well as adsorbents - medications for removing harmful substances from the body.
It must be remembered that if swelling of a child’s eyes is not accompanied by lacrimation and itching, this is most likely a sign of kidney or heart pathology. In this situation, a comprehensive examination and treatment is necessary.
Sometimes irritation, swelling and itching are associated with eye injury. Then the child needs urgent medical attention, since mechanical damage can lead to decreased or even complete loss of vision. Depending on the situation, the doctor either removes the foreign body and disinfects the eye, or prescribes agents that speed up the healing process.
In the presence of an inflammatory process, ointments (erythromycin, tetracycline), as well as lotions with calendula and chamomile extract are prescribed.
Examination for swelling of the eyelids
Anamnesis. Collecting an anamnesis of the disease includes clarifying the following questions: when the edema developed, the unilateral or bilateral nature of the process, the presence or absence of previous injuries (including insect bites). Key symptoms: itching, pain, headache, changes in visual acuity, fever, presence of discharge from the eye.
When examining other systems, it is necessary to pay attention to the symptoms of possible causes of eyelid swelling: runny nose, itching, rash, shortness of breath (systemic allergic reactions); headache, nasal congestion, purulent discharge from the nose (sinusitis); toothache (oral infection); dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, heart failure); intolerance to low temperatures, skin changes (hypothyroidism); intolerance to high temperatures, anxiety, weight loss (hyperthyroidism). Collecting a life history includes clarifying the following questions: the presence of previous eye trauma, ophthalmological operations, the presence of diseases of the heart, liver, kidneys, thyroid gland, allergies, contact with possible allergens and the use of ACE inhibitors
Collecting a life history includes clarifying the following questions: the presence of previous eye trauma, ophthalmological operations, the presence of heart disease, liver, kidney, thyroid disease, allergies, contact with possible allergens and the use of ACE inhibitors.
Physical examination. Assessment of general condition indicators (fever, tachycardia).
During an ophthalmological examination, it is necessary to evaluate the following parameters: localization and extent of edema (unilateral or bilateral; upper and/or lower eyelid), the presence of hyperemia, local increase in temperature and pain. It is necessary to evaluate whether these symptoms are a sign of swelling of the eyelids, protrusion of the eyeball (exophthalmos), or a combination of these conditions
Particular attention should be paid to visual acuity and range of movement of the eyeballs (full or limited). In cases of severe edema, examination may be difficult, but it is necessary because
allows you to differentiate eyelid lesions from orbital or retro-orbital pathology; in some cases, the help of an assistant may be necessary. It is necessary to evaluate the conjunctival injection and the presence of discharge from the eyeball. The examination is performed using a slit lamp.
During a general examination, it is necessary to assess the presence of symptoms of intoxication, suggesting a systemic infection, as well as symptoms of the primary disease
It is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the skin: dryness, peeling (hypothyroidism); oily scales (seborrheic dermatitis). Swelling of the extremities or sacrococcygeal region indicates systemic disorders
Alarming symptoms. Warning symptoms include:
- fever;
- decreased visual acuity;
- difficulty moving the eyeballs;
- exophthalmos.
Interpretation of research results. Specialized studies help to make a differential diagnosis between different groups of diseases, for example, between inflammation, infection, allergic reaction, hypervolemia. Pain, redness, local hyperthermia, and tenderness suggest inflammation or infection, while absence of pain and pale skin are consistent with angioedema. The presence of itching suggests an allergic reaction, while in pathologies of the heart and kidneys no itching is observed.
Swelling limited to one eyelid, in the absence of other symptoms, rarely indicates serious illness. An alarming symptom is pronounced swelling of both the upper and lower eyelids (unilateral or bilateral). Symptoms such as exophthalmos, decreased visual acuity, difficulty moving the eyeballs, and signs of inflammation indicate orbital diseases. These diseases may cause exophthalmos, damage to muscles and nerves.
Prevention
Prevention involves preventing contact with allergens. If this is not possible, interaction with hazardous substances must be minimized. Daily wet cleaning will help prevent allergies. Avoid carpets, soft toys and blankets. Replace feather pillows with hypoallergenic ones.
Expert opinion
Kim Oksana Alexandrovna
Head of the ophthalmology clinic. Ophthalmologist with more than 10 years of experience.
Two weeks before the plants bloom, start using antihistamines and drops. Do not visit forested areas during this period. Wear safety glasses when outdoors. After returning home, wash your hands thoroughly to prevent allergens from getting into your eyes. Limit your use of cosmetics. Remove allergenic foods from your diet. Pay attention to the composition. Preservatives and food colorings often provoke a reaction.
Allergies are incurable conditions. But a competent approach will help achieve stable, long-term remission. If symptoms appear, you should seek help from a specialist. Allergies cannot be treated on your own. Otherwise, the disease will develop into a more severe form, one of the manifestations of which is suffocation. All methods of therapy must be agreed with a doctor. To prevent allergies, attention should be paid to prevention.
Author of the article
Internet journalist, copywriter.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Source
Home » Symptoms »
Allergic eye swelling is considered one of the most common forms of an allergic reaction. Allergists explain the frequent manifestation of allergies in the eyes by the fact that the organs of vision are constantly exposed to the irritant. The upper eyelids swell most often; swelling of the lower eyelids also occurs in medical practice. Below you will find out why allergic swelling under the eyes occurs, what to do when such an unpleasant symptom appears, and the main methods of treatment.

Causes of the disease
Swelling of the eyelids often occurs due to inflammation. Types of inflammation of the eyelids are numerous; predominantly, they are manifested by swelling, redness, pain, lacrimation, etc. Inflammation can be caused by bacteria or viruses. A specific group consists of allergic inflammation.
Common triggers of the disease may include the following factors:
- fatigue, exhaustion and lack of sleep;
- continuous work on the computer;
- excessive consumption of alcohol and salt;
- overuse of certain medications;
- poor drainage and lymph accumulation;
- insufficient kidney function;
- weakening of heart function;
- liver diseases;
- sagging eyelids (hereditary factor).
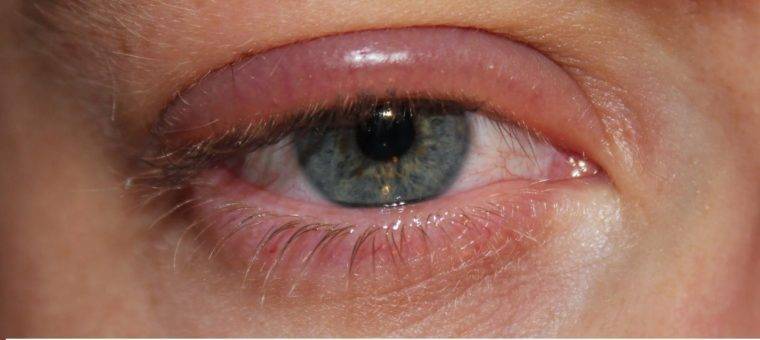
Swelling of the upper eyelids
- arise as a result of abuse of pharmacological drugs;
- the reason may be the accumulation of lymph (due to illness, lack or excess sleep);
- a common trigger is kidney failure or liver disease.
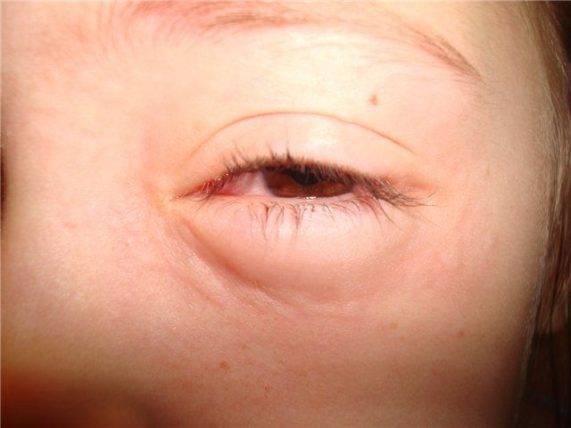
Swelling of the lower eyelids
- drug abuse;
- poor drainage and lymph accumulation;
- exhaustion of the body;
- improper use of lenses in glasses;
- weakened kidney or heart function.
Drooping upper eyelids
- the problem may be caused by a muscle disease (myasthenia gravis);
- exhaustion of the body;
- lack of sleep;
- depressive psychosis;
- sprain due to improper technique of applying and removing eye makeup.
What to do if your lower eyelid is swollen in one eye? Recommendations
Self-medication in the case of swelling of the lower eyelid is not recommended, since the root cause of the inflammatory process must be eliminated. However, you can make life easier with swelling, relieve redness, itching and burning temporarily with the help of home treatment. But here there are some nuances that you should be aware of. Ophthalmologists under no circumstances allow heating the site of swelling, since heat can provoke an exacerbation in the case of a malignant neoplasm or thrombosis in the eyeball. Do not rub or scratch the swollen eyelid, as you may cause additional infection and make the situation worse. It is not recommended to drink a lot of water, it only increases swelling, and also avoid stressful situations if possible. Try to get enough sleep - a full eight-hour sleep has never harmed anyone, but lack of sleep aggravates swelling, as the tone of the eye muscles decreases. Until the ophthalmologist has established the true cause of the disease and prescribed competent therapeutic treatment, you can resort to compresses. For example, make a compress from strong tea, cucumber, calendula or mint.
When do the upper and lower eyelids swell during inflammatory processes?
Inflammatory edema occurs due to pathogenic microorganisms entering the body. Most often, this symptom occurs during infectious processes in the tissues of the eyes, less often - during other diseases (ARVI, influenza, tonsillitis, etc.).
Viruses
In viral diseases, swelling of the eyelids develops as a result of rhinitis due to dilation of the blood vessels in the eyes. This condition is accompanied by copious secretion of mucus from the nasal passages, redness and inflammation of the eyes, and rarely – itching and discomfort when pressed.
Bacterial infection
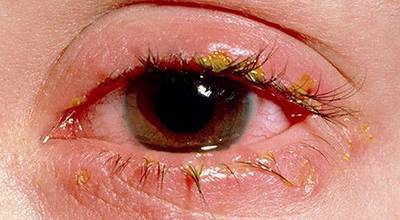
With bacterial infections, the clinical picture is usually more pronounced than with viral infections.
Patients experience severe swelling of the soft tissues of the upper and lower eyelids, itching, as well as mucous or purulent discharge from the eyes.
Ophthalmic diseases
Inflammatory eye diseases (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, abscesses, phlegmon) are caused by staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci and other microorganisms, in some cases fungi act as causative agents. With these pathologies, swelling of the eyelids, discomfort, itching and other symptoms are accompanied by visual disturbances, rapid eye fatigue and redness of the conjunctiva.
Reference! Inflammatory processes in the tissues of the eyes, caused by bacteria or viruses, most often begin on one side, after which they can spread to the other eye.
Eye diseases and injuries in children
Edema may be associated with the presence of pathological processes such as:
- Inflammation of the connective membrane of the eye (manifested by redness, lacrimation, purulent discharge).
- Inflammation of the eyelash bulbs (severe and painful swelling of the tissue, redness of the skin).

- Cellulitis (accompanied by pain and swelling of the eyelids, high fever).
- Insect bites (toxins entering the eye and skin of the eyelid, causing redness and tearing, as well as intense itching).
- Injuries (entry of foreign bodies: particles of earth, dust, lime, powder, and so on provokes eye irritation).
If unpleasant symptoms occur, the question arises: if an allergy occurs, the child’s eyes are swollen, what to do.
Preventive measures
Prevention of swelling of the upper eyelid is a healthy lifestyle, taking care of your body and the absence of chronic diseases.
Doctors recommend following the following rules to prevent edema:
- Don't drink a lot of fluids at night
- Periodically use diuretic herbal preparations
- Reduce salt intake in food
- Regularly take health-improving vitamin complexes
- Maintain personal hygiene
- Avoid stressful situations, overwork and lack of sleep
However, the best prevention of edema is timely treatment of any diseases and health care.
Good sleep, active rest, use of appropriate cosmetics, personal hygiene, treatment of diseases - this will help maintain the beauty and health of the eyes.
Oct 21, 2015
How to get rid of a tumor
In case of mechanical damage to the organ of vision, first aid must be provided to the patient. If foreign objects get into the eye, it must be immediately rinsed with water and the foreign body removed. If this is not possible, you should seek help from a doctor.

Why can’t you remove debris from your eyes yourself? Never remove a foreign object in the eye yourself if the following gets into the eye socket:
- a particle firmly attached to the eyeball;
- a piece of metal shavings;
- a particle that enters the iris of the eye.
Mechanism for removing other foreign objects from the eye:
- You need to close your eyes tightly several times, then the object will come out on its own with tears.
- If the foreign body is located behind the lower eyelid or on the visible part of the cornea, it can be removed with a clean paper tissue.
- If the particle is not visible, it means it has gone under the upper eyelid. In this case, it is necessary to lift the upper eyelid, pull it back and remove the foreign object.
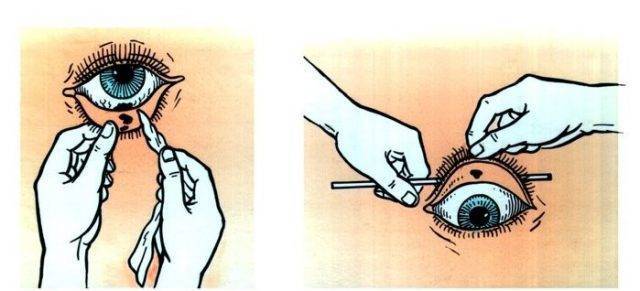
Scheme on how to remove a foreign body from the eye
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
If you notice a swollen and reddened eyelid, the best solution is to visit a specialist. The most common cause is allergies.
If the eyelids are regularly swollen, it is necessary to undergo a set of tests to determine the nature of the swollen and inflamed eyelid.
Furunculosis, popularly called barley, is on the list of one of the dangerous eye diseases. When it appears, you may experience high fever, malaise, and constant eye pain. If it is not possible to reduce the temperature for a long time, and the pain intensifies, urgent consultation with a doctor is required.
Swelling or caused by injury. These manifestations are easily diagnosed due to superficial signs (bruising). Recovery occurs within a week and no medical intervention is required. But if lumps, swelling, or pain occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Causes of eye allergies
Before starting treatment for the disease, it is necessary to find out what causes the allergic reaction. There are various reasons for eye allergies. Most often, swelling and swelling of the eyes and eyelids occur in children during the flowering of various plants. However, it is not uncommon for eye problems to occur during the winter. Causes of an allergic reaction:
- plant pollen;
- household dust;
- chemical components of cosmetics, washing powders and cleaning components;
- food colorings;
- fur, feathers and excretions of pets;
- Food;
- cigarette smoke;
- contact lenses;
- cold;
- ultraviolet radiation;
- topical medications;
- a foreign body on the eyelid or near the eyeball.
The reaction occurs after the root cause of the disease comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the eye. Children with reduced immunity and those whose loved ones suffer from various allergic manifestations are predisposed to allergies.
Causes of swelling of the upper eyelid
Two types of swelling:
- Inflammatory: the eyelid above the eye swells, turns red and quickly enlarges. Pain and itching may occur.
- Non-inflammatory: noticeable enlargement of the eyelid.
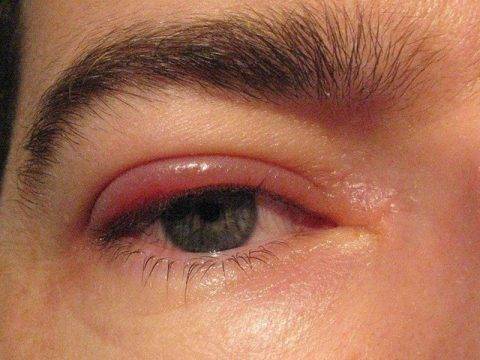
If you experience regular swelling of the eyelids, which is accompanied by pain, you should immediately contact a medical facility. If the eyelid above the eye is swollen, this may be preceded by:
- disturbance of sleep and rest patterns;
- overstrain of the organ of vision (long-term work at a computer monitor);
- drinking large amounts of fluid before bed;
- alcohol-containing drinks retain fluid in the body;
- dysfunction of internal organs.
Reasons why eyelids swell:
- The eyelids appear red and swollen if the eye is exposed to air, for example in a draft. In this case, the eyelid may become swollen and painful.
- Allergy. If the eyelid is sharply swollen and red, this indicates the presence of an allergen in the human body. To get rid of these symptoms, you need to take antihistamines (anti-allergy) medications and apply a cool compress. To avoid subsequent problems, you need to find the source of the allergens or contact a specialist and do a test.
- Conjunctivitis. If the eyelid is swollen and red, the symptoms are accompanied by an inflammatory process, this means signs of conjunctivitis. The disease is an inflammation that affects the mucous membrane. Eyelids can become swollen due to allergies, bacteria and viruses entering the eyes. Dryness, burning, and purulent discharge may appear. The main symptom of this disease is difficulty opening the eyelids in the morning. There is a gluing of dried tear secretions at the corners of the orbit. Methods and methods of treatment depend on the severity of the disease. Self-medication is unacceptable. We need to see a doctor.
- Barley is an acute inflammation of the meibomian gland with subsequent blockage. The cause of the disease is infection. With barley, the eyelid may swell, begin to hurt and turn red, and a small bump on the edge of the eyelid may become inflamed and swollen. The eye socket can become inflamed when infected from the outside. Inflamed stye occurs due to a weakened immune system. To combat swelling of the eyelid, it is better to use antiseptic drops or creams.
- Chalazion is a chronic condition in which the edges of the eyelid become inflamed. At the beginning, the symptoms are similar to barley, and after a few days a tissue compaction appears at the site of the pimple, which does not cause pain when palpated. If a lump appears, you should consult your doctor.
- Blepharitis is a wide group of diverse eye diseases. This is a chronic inflammation of the edges of the eyelid. Accompanied by itching and peeling of the skin. The cause is pathogenic bacteria that enter the eyes when personal hygiene rules are violated. It is difficult to treat.
- Ocular herpes occurs when the virus infects other organs and tissues. Symptoms include swelling of the eyelids, pain when blinking, and blurred vision. Treatment of herpes involves the use of antiviral medications. The symptoms of herpes on the eyelids can be easily treated. Antimicrobial ointment (Zovirax, Tetracycline) is applied to the affected area. Untimely treatment of the disease leads to glaucoma.
Why do children's eyes swell?
In children, allergic manifestations are practically no different from similar manifestations in adults.
The difference is that they occur more often due to unformed immunity and violation of personal hygiene rules. In children, allergies do not always go away without a trace; they usually occur with complications. Most often, one eye first becomes inflamed, and then a reaction occurs in the second. The intensity of symptoms may vary: in the form of one or several signs. It's connected:
- with the time of year (seasonal manifestations);
- with a specific pathogen;
- with the age of the child;
- with the characteristics of the body.
Treatment of allergic eye swelling
Before you begin treatment for allergic eye swelling, the allergen should be identified. This is why a thorough diagnosis is necessary. Only after this will the doctor prescribe medications
It is very important to exclude the patient from contact with the allergen in order to completely get rid of allergies.
Symptomatic drug treatment of allergic eye edema is based on the use of drugs that eliminate the disease:
- antihistamine eye drops to relieve swelling and itching;
- hormonal eye ointments to relieve inflammation and swelling;
- antihistamines to relieve symptoms associated with the disease;
- medications with a vasoconstrictor effect to eliminate red eyes.
Any medicine can be taken only as prescribed by an ophthalmologist. The doctor will create an individual program for you to treat and prevent the disease.
In case of deep and severe damage to the lower and/or upper eyelid, the doctor may prescribe local or general antimicrobial drugs. They prevent infection and relieve inflammation.
Only a doctor knows how to relieve allergic swelling of the eyelids. Strengthening the patient's immune system when an allergen is injected under the skin in small doses is today an effective treatment method. Over time, the patient’s immunity ceases to recognize the allergen as an irritant, and any negative reactions soon disappear from the body.
How to treat in children and adults
If an allergy in the eyes is not treated, then upon repeated contact with the allergen there is a high risk of it getting into the mucous membrane of the eye, followed by the development of severe consequences. Vision will gradually deteriorate, and if the outcome is unfavorable, blindness may occur.
Treatment is prescribed based on test results. Therapy includes several groups of drugs. The complex effect allows you to speed up recovery and recovery.
- Prescription of antiallergic eye drops – Opatanol, Allergodil. Improvement occurs after several uses.
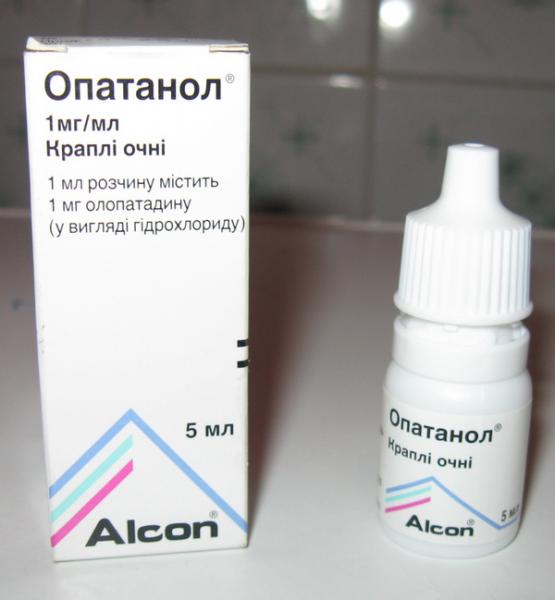
- Antihistamines for intramuscular injections or tablets - Suprastin, Cetrin, Tavegil.
- For life-threatening conditions, corticosteroid drugs in tablet form are prescribed - Prednisolone, Cortef. They effectively reduce inflammation and get rid of swelling.
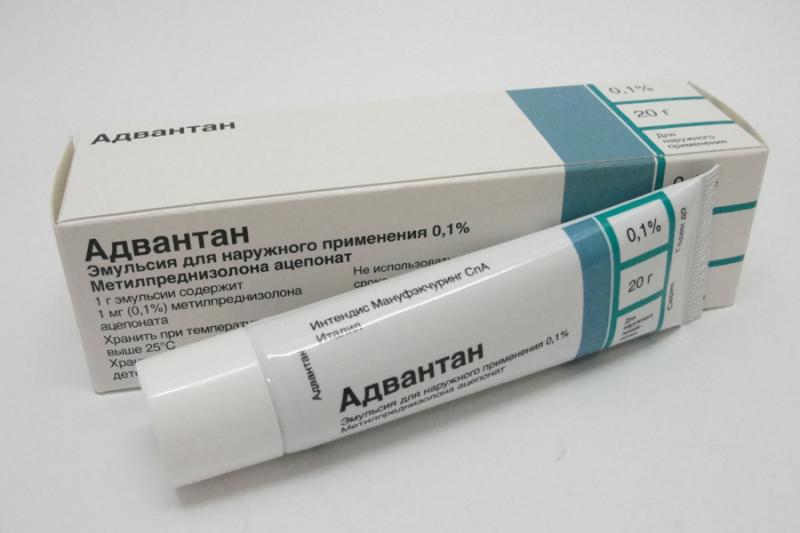
- For the treatment of chronic allergies, hormonal ointments are prescribed - Advantan. It is allowed even for babies from 4 months. The duration of therapy is determined individually by the doctor. The ointment relieves swelling well and reduces inflammation.
- To relieve redness of the eyes, Visin and Okumetil drops are prescribed.
- It is necessary to additionally moisturize the mucous membrane. Pure Tear drops and Systane cope with this task. They are an artificial tear substitute.
- Be sure to prescribe a sorbent. It accelerates the removal of allergens and accumulated toxins from the body. It is recommended to take Smecta and Enterosgel.
Treatment
- refractive error correction;
- removal of irritating factors;
- mechanical removal of scabs by wiping with a swab;
- wiping the edge of the eyelid with a 3% AgNO3 solution;
- massage with corticosteroid ointments in combination with antibiotics - sulfonamides;
- in severe forms of the disease - general treatment with antibiotics.
Viral
The situation changes if the swelling of the eyelids is viral, induced by viruses. Usually these are processes caused by herpes viruses, primarily herpes simplex palpabrae. First, swelling of the eyelids occurs, then typical vesicles begin to form on the eyelid. As a rule, the disease affects one eye and often recurs, especially with any other diseases, stress, etc.
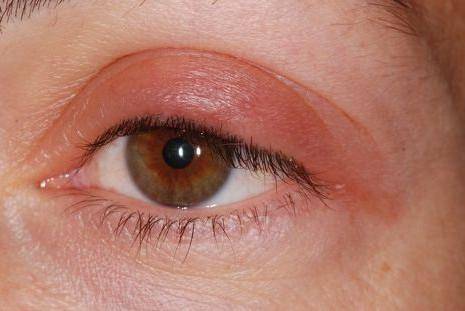
Often the disease resolves spontaneously, without treatment. The doctor intervenes only in case of frequent relapses: the medications Herpesin or Zovirax and other therapeutic methods are used. An increased intake of B vitamins and vitamin C may have a positive effect.
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus can also be the causative agent. We are talking about the ophthalmic form of herpes zoster (the first branch of the trigeminal nerve). The patient experiences a headache and blisters appear on the eyelid, forehead and scalp. Therapy is carried out with Acyclovir.
Treatment of edema caused by viruses:
- acyclovir;
- vitamins B and C;
- locally indifferent powders, liquid powders, gentian violet;
- analgesics as needed.