The serious chronic disease psoriasis remains poorly understood. Risk groups, causes of relapse, its occurrence and the effectiveness of treatment methods continue to interest scientists and doctors. It has not yet been reliably proven whether psoriasis is inherited, but there is no scientific refutation either. Based on each specific case, specialists try to determine the causes of the disease and relapses.
Theories of the disease
There are several theories of pathology transmission. Although none of them has received mass recognition, when prescribing treatment, specialists tend to rely on more popular options that have a right to exist. Common transmission theories:
- allergic - pathology occurs as a result of chronic infectious diseases, in the presence of their foci;
- metabolic - can be observed when metabolic processes in the body are disrupted;
- hereditary - psoriasis is inherited from parents or close relatives to children;
- endocrine - dysfunction and pathologies of the endocrine glands;
- neurogenic - detected after serious injuries and disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system;
- viral is the most likely. Infection occurs through viruses during household contacts or with a congenital retrovirus;
- parasitic-infectious - associated with disruption of the immune system and changes in the endocrine system.
Regardless of which theory the specialist adheres to during treatment, it has been proven that psoriasis is not a contagious disease: it is not transmitted through sexual intercourse or contact with a patient.
Why is psoriasis dangerous?
If you do not treat scaly lichen, then in addition to severe physical and psychological discomfort, it can lead to very serious negative consequences. Is psoriasis dangerous and why exactly? The main results of advanced inflammatory disease are:
- The occurrence of psoriatic arthritis. This nuisance is characterized by the fact that the areas of the body affected by the disease are much deeper than the skin and lead to joint diseases. Failures in metabolic processes affect not only the stratum corneum: they go inside the body and affect cartilage tissue. Psoriasis of the nails, rashes on the hands or feet, affect the joints, which leads to a limitation of physical activity in a person.
- The mucous membrane can also suffer from lichen. If you do not start treating an autoimmune disease in a timely manner, it will move from the cornea to the mucous membranes. As a result, doctors diagnose a variety of ailments that are directly related to inflammation of the mucous membrane (visual impairment, conjunctivitis, and others).
- Psoriasis of the head or other parts of the body “acts out” on the liver. Problems in the functioning of this organ appear regardless of the location of the plaques and other external signs of the disease.
- During exacerbation of lichen planus, the endocrine system suffers, and this causes enlargement of the lymph nodes.
- At the second stage of psoriasis, disorders of the cardiovascular and central nervous systems are observed.
- Another dangerous complication is muscle atrophy. It appears in the final stages of the disease in the complete absence of therapy or when psoriasis affects the deep tissues of the body.
- How to salt salmon tasty and quickly
- How to play Battleship: rules
- Poses for a photo shoot in nature
Pathology risk groups
There are possible risk groups that have been identified using distribution statistics. According to its results, heredity became the main risk group. Of 100% of parents suffering from the disease, in 35−50% the diagnosis was confirmed in the child. In this case, the appearance of pathology is expected at approximately the same age as in relatives. Therefore, we can say for sure that the appearance of psoriasis in a child can be hereditary. Several possible risk groups:
- Heredity - a group of patients who have relatives with a history of psoriasis.
- Age category 15−35 years, both men and women.
- Climatic conditions - psoriasis most often occurs in cold climates.
- People with serious disorders of the central nervous system and metabolic processes, with exacerbations of focal infections, with diabetes mellitus and problems in the endocrine system.
- Patient taking drugs such as interferon, aminoquinoline drugs, systemic corticosteroids, adrenergic blockers.
It is worth noting that no matter what risk group a person suffering from psoriasis belongs to, the disease begins to progress and affect new areas of the skin in the presence of mechanical damage to the epidermis, cuts and various skin injuries. To find out more reliably whether psoriasis is inherited, you should learn about the mechanism of development of the pathology.
Preventive measures for unfavorable heredity
Since psoriasis is inherited by children, it is necessary to protect their body as much as possible from external negative influences. In order not to provoke the occurrence of pathology, preventive measures should be observed.
Rules for skin protection and care:
- Personal hygiene. Water procedures must be carried out daily. The use of hard washcloths is not allowed (to avoid mechanical damage to the epidermis). Do not use soap, gel or other hygiene products that have a drying effect.
- Cosmetic procedures . Dry skin is susceptible to the development of disease, so after washing it is recommended to use moisturizing creams, lotions, and softening oils. To care for your hair and scalp, you should use special anti-psoriatic shampoos. Nails require special care, since there is a special form of the disease - nail psoriasis.
- Injury to the skin . Any mechanical damage to the skin can transform into a psorizic defect. Rough contact with the skin, abrasions, cuts, etc. should be avoided.

Diet:
- Eliminate foods with a high allergenic index. Hyperallergenic are: strawberries, citrus fruits, chocolate sweets, eggs, nuts. Allergic reactions contribute to the activation of hereditary psoriasis.
- Limit as much as possible food prepared by frying, fatty meat, lard, butter. Such a diet significantly complicates the functioning of the digestive system.
- Avoid canned foods: pickled and salted vegetables, mushrooms, canned fish and meat.
- Do not use hot spices and seasonings, as well as sauces that contain them. Essential oils can provoke allergies, and the warming effect increases subcutaneous blood circulation.
- Introduce fresh vegetables and fermented milk products into your daily diet, which help the gastrointestinal tract function and preserve the body's microflora.
- Maintain a drinking regime (at least two liters of water daily).
Auxiliary methods:
- course intake of vitamin and mineral complexes to maintain immunity;
- mandatory medical consultation before using any medications;
- timely treatment of infectious, viral, parasitic and other diseases.
Adults should categorically give up bad habits. Nicotine and alcohol addiction with a hereditary predisposition to psoriasis can become an impetus for its development.
An equally important factor in prevention is maintaining psychological stability. If necessary, you should seek help from a psychotherapist.
The main task is to maintain immunity and maintain stress resistance.
Development mechanism
The disease occurs for various reasons, which can be divided into 2 main groups. There are also rare cases that do not fit into this classification. There are 2 types of development mechanism:
- Psoriasis is associated with a violation of the gene level of leukocyte antigen: this type includes 65% of all cases of the disease. It is observed in families where family members or relatives have psoriasis. Occurs around the age of 25.
- Not associated with gene disorders: there is no family history of psoriasis. It is observed after the age of 50 years.
The result of long genetic studies of pathology has confirmed that psoriasis as an independent disease is not inherited: a child may be predisposed to its occurrence with altered genes.
Mother and child

Psoriasis is a non-congenital disease. It occurs against the backdrop of the baby’s development and his interaction with environmental factors. 15–20% of disease transmission occurs through the maternal line.
During pregnancy, the activity of psoriasis in a pregnant woman decreases. This is explained by hormonal changes in the body, the release of a large amount of biologically active substances.
They have the following effects on the patient:
- weakening of the local inflammatory process of the skin;
- eliminating itching;
- improving the condition of the skin.
In women who complained of excessive dryness of the epidermis, it is moistened and the visual manifestations of plaques are reduced. At the birth of a child, the pathology again enters the active phase.
This is also noticeable at the beginning of the menopausal period. Then the effect of hormones drops sharply, and psoriasis progresses.
Women planning a pregnancy often ask doctors whether psoriasis can be inherited. There is such a possibility. To determine the potential risk, before conceiving a child, you should consult a geneticist or dermatologist.
It is difficult to prevent such developments. Doctors teach future parents how to behave if a disease occurs. Whether it can be avoided or not is determined by the individual characteristics of each organism.
Hereditary predisposition

It has been established that predisposition to the disease occurs even during conception. It is then that the child can receive it with genes at the cellular level. At this stage, it is difficult to say whether he will be susceptible to pathology. It is likely that this problem will not affect him at all and the child will not suffer from skin diseases.
At the same time, there is a large percentage of the occurrence of pathology in children with a genetic predisposition under various unfavorable conditions. Adverse conditions need to be considered holistically. With a high quality of life, they can avoid problems completely or partially.
By parental line
It is possible to assume that psoriasis is inherited from the father or mother, but this happens extremely rarely. The probability increases by 50% if the pathology develops in both parents.
There are cases when a child receives a gene change from close relatives, while his parents do not suffer from skin diseases. The question of whether psoriasis is transmitted from father to child can be answered with percentages based on the results of genetic studies on hereditary factors:
- 40−70% - psoriasis genes were passed from father or mother to child;
- 16−30% - close relatives are susceptible to the disease.
During observations and studies, it was discovered that absolutely all patients had a gene that caused massive damage to epidermal cells, which provoked the symptoms of psoriasis.
You should know that the disease can occur over a generation, so when planning a pregnancy it is necessary to take these factors into account. A child born in such a family is considered to have a genetic predisposition. To avoid pathology, it is necessary to take into account some factors that can increase the risk of its occurrence.
What is psoriasis and does it spread to humans?
It may happen that people with psoriasis must reduce their social circle because they do not know whether psoriasis is transmitted from person to person. The instinct of self-preservation pushes people away from the disease, since they do not know exactly how psoriasis is transmitted. Their uncertainty is generated by various speculations, one of which is whether psoriasis will be transmitted or not.

This disease is considered not contagious, and the cause of psoriasis is in no way caused by pathogenic microorganisms. The disease is classified as scaly lichen, but it is impossible to say on this basis whether psoriasis is transmitted or not. Doctors say that it is impossible to contract psoriasis through blood. Also in everyday life: when answering the question that worries everyone, whether psoriasis is transmitted, they unequivocally state that there is no danger of infection.
The disease is caused by non-pathogenic microorganisms and is therefore not considered contagious. But there are cases of the disease in a family of several people in turn. Naturally, questions arise: how is psoriasis transmitted? However, the physical cause is not the route of transmission - this is explained by hereditary predisposition. But if we take into account the theory of origin - streptococci, tissue reaction, retroviruses, then how exactly psoriasis is transmitted cannot be stated with complete confidence. Scientists' assumptions do not provide a complete guarantee of the safety of a little-studied disease.

Psoriasis, as psoriasis is called, reduces the life of cells. Exfoliated scales cause caution among people who are afraid of contracting the disease and do not know whether psoriasis is transmitted from person to person by these dead cells. In addition, psoriasis of the fingernails causes concern, because the patient touches everything. Psoriasis is just a cosmetic defect. The formation of psoriasis occurs due to a failure of the endocrine system, nerves, weakened immunity, which means that the answer to whether psoriasis is transmitted from person to person in dermatology can definitely be negative.
Scientists have discovered the fact that the closest relatives of a patient with psoriasis have identical signs of the disease. The topic naturally suggests itself: how is psoriasis transmitted from person to person? Research has shown that psoriasis is transmitted at the cellular level. The manifestation of the disease does not always occur from the immediate environment. Quite often, this disease could be observed in ancestors and appear after exposure to provoking factors. Whether psoriasis is transmitted or not between relatives must be considered at the genetic level, and strangers cannot become infected with psoriasis through contact.

The answer lies in the genes, because psoriasis is inherited. The illness of one of the parents will not necessarily affect the child, and there is no point in saying that psoriasis is contagious or not. When both are sick, the risk of psoriasis is very high, but it is not necessary that the disease will manifest itself. Many factors are involved in the formation of psoriasis, and inheritance is only a potential opportunity for the disease to develop. The length of the disease is not at all important, the presence of clinical manifestations in relatives - due to the lack of knowledge of the disease, it is impossible to say with certainty whether psoriasis is inherited.
There is no clear answer. A larger number of doctors are inclined to argue that only a hereditary factor plays a role, so a direct statement that psoriasis is transmitted through contact is incorrect. Neither sharing utensils, nor shaking hands, nor skin contact poses a danger. Psoriasis is transmitted only by genetic factors. And living with or caring for a sick person is completely safe. Unpleasant communication is usually caused by ordinary hygienic or aesthetic reasons.
Partners can continue their relationship with complete peace of mind, since talk that psoriasis is sexually transmitted is a complete fabrication based on speculation. The only thing that psoriasis is dangerous about in intimate relationships is a terrible inferiority complex. Is psoriasis transmitted through sexual intercourse? No, this is unrealistic. There are enough examples of creating happy families where one of the spouses has psoriasis. Real feelings will push all prejudices into the background.
Based on materials from www.psoriazo.ru
Psoriasis is one of the most common chronic skin diseases. About 5% of the world's population suffers from this type of dermatosis in one form or another. Unpleasant peeling of the skin, red spots, and a lot of discomfort are all characteristics of this disease. Psoriasis - is it contagious, how does it manifest itself and how does it progress, is there a way to cure this disease? Let's look at it in order.
There is no clear answer to this question, although most doctors are inclined to think that the disease is transmitted only by inheritance and is triggered by infectious, viral and other factors.
Is psoriasis of the scalp and other skin contagious, including damage to deep tissues? No. Psoriasis, the transmission routes of which are limited by genetic factors, is NOT transmitted :
- Sexually.
- With saliva and due to sharing dishes, towels and other household items with the patient.
- Through a handshake and close skin contact.
Of course, close contact with a person with psoriasis may be unpleasant for purely aesthetic and hygienic reasons, but it is impossible to become infected from such a person.
Why is this so, and how is this data confirmed? Why can’t you get psoriasis through touch and close contact? To get answers to these questions, let's look at the disease in more detail.

The characteristics of the immune system, health status and susceptibility to certain infections are individual for each person, so it is impossible to derive a universal pattern for the development of the disease. In addition, psoriasis is inherited. However, there are a number of features by which a developing disease can be identified.
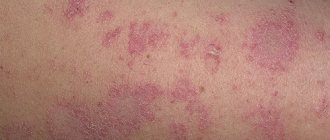
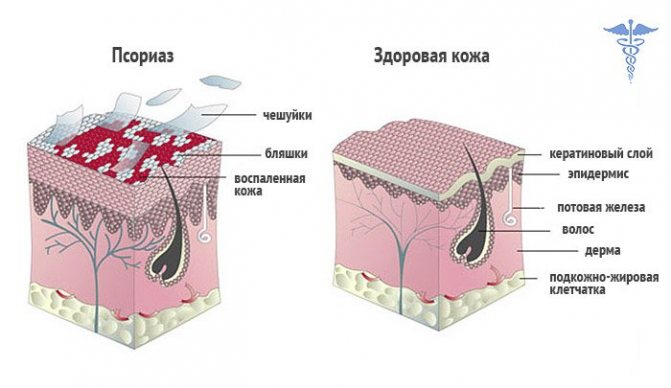
Red, dried-out spots form on the skin, on which the stratum corneum begins to peel off. These areas seem to be raised above the entire surface of the skin and can cause discomfort. Their appearance begins when the body begins to itch and redness forms. They collect an excess number of lymphocytes and other microparticles. Over time, they turn into dry, reddened plaques.
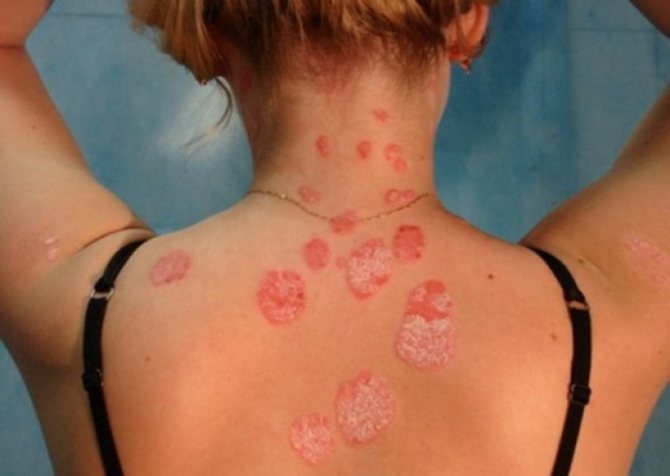
The places where redness and plaques appear are, as a rule, various curves of the body (elbows, knees, shoulders), as well as places with hair (head). Signs of psoriasis often appear on the back.
Why does this happen? Psoriasis, or, as it is also called, scaly lichen, significantly reduces the life cycle of cells located in the affected areas. Hence the peeling, white coating, and scales that constantly peel off from the skin, which is why the whole body begins to itch very much. Instead of 30-35 days, the stratum corneum cell lives only 4-5 days, after which it dies and disappears.
Modern medicine has proven the relationship between psoriatic disease and deep disorders in the body's systems. With scaly lichen, disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine, immune and even nervous systems are observed. Therefore, to the question of whether psoriasis is contagious or not, the answer must be sought much deeper than purely dermatological disorders suggest.
Most people suffering from this disease worry not only about their health and appearance, but also care about the health of loved ones, so they are interested in whether psoriasis is contagious. The answer to this question is given by theories of the origin of the disease that take into account many factors.
- Genetics. One of the most substantiated theories that is generally accepted today turns to genetics. Heredity is called the main factor in the tendency to develop psoriasis. The ways of transmitting psoriasis by inheritance are one of the most obvious. Three quarters of children whose parents suffered from psoriasis sooner or later also develop this disease. If only one of the parents showed a tendency to the disease, then the risk decreases to 25%. But this, unfortunately, does not eliminate the chances of further transmission of the disease by inheritance.
- The infectious theory states that psoriasis can develop as a complication after certain types of infectious diseases. Including due to damage to the human skin by harmful microorganisms, including various types of fungus. However, laboratory studies have shown a low likelihood of such a connection. On the other hand, doctors note that infection can serve as a kind of trigger for the disease. That is, if a predisposition to psoriasis already exists, then diseases transmitted by a person can accelerate its manifestation.
- The allergic theory justifies the surprisingly strong relationship between exacerbations of psoriasis in the spring and autumn, when there is also an increase in cases of allergies. Psoriasis is believed to be a type of allergic reaction to viruses or certain foods. The theory is also confirmed by the fact that psoriasis, like allergies, is not contagious.
- The theory of viruses is developed by scientists mainly in connection with genetics. A large number of people may be predisposed to psoriasis, but only those who are affected by certain viruses experience a surge in the activity of these factors and become ill as a result. If these studies are confirmed, it will be possible to say that psoriasis is a contagious disease, since it can be infected through the entry of viruses into the body.
- Violation of metabolic processes in the body, if not the cause, then certainly gives impetus to the development of the disease. Metabolic disorders in the blood lead to the accumulation of excess lymphocytes in different areas of the skin, which later lead to the first rashes and the appearance of reddened areas. But the patient almost always has a hereditary predisposition to the disease - not psoriasis itself, but the characteristic metabolic disorders that provoke it. Thanks to the same exchange theory, it was revealed that psoriasis occurs especially often in patients with diabetes. Their metabolic processes are a priori disrupted and there are problems with the immune and endocrine systems. Almost a third of diabetics suffer from lichen planus.
- The immune theory is akin to the exchange theory. If there are serious foci of infection in the body, this provokes disorders that are inherited as a predisposition to psoriasis. In addition, it is not necessary for the mother or father to have dermatological problems - chronic tonsillitis or sinusitis, incompletely cured sore throat or allergies can have such consequences. But in addition to immunity, one should remember about the presence of other factors.
- The endocrine theory describes psoriasis as a consequence of hormonal imbalances and the functioning of the endocrine gland, which, together with a number of other factors, affect the state of cell regeneration processes.
Psoriasis often appears in people who were not even aware of their predisposition to this disease, but who have suffered severe mental trauma, stress or a nervous breakdown. Probably, changes in the state of the nervous system and psychosomatics play a role: metabolic disorders are triggered, which, in turn, lead to an exacerbation of psoriasis.
As a rule, the situation is aggravated by the presence of other foci of infection in the human body. They are the transfer of severe infectious diseases (influenza, scarlet fever), the presence of chronic diseases (sinusitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis), exacerbation of existing infections in the body (caries, otitis media, chlamydia, and so on).
According to these theories, is skin psoriasis contagious? No, if the body does not have a clear predisposition to it and the foci of infection were eliminated in time. A good immune system and good metabolism will help protect against this unpleasant disease.
So, the factors that cause psoriasis include the following:
- Heredity.
- Disturbances in the immune, endocrine systems of the body and its metabolic processes.
- The presence of foci of inflammation and other infections in the body.
- Injuries occur in people who are at risk due to the factors listed above.
In addition to the quite obvious external factors that cause significant discomfort, psoriasis is also dangerous for its consequences, which manifest themselves in the later stages of the disease. Its consequences include:
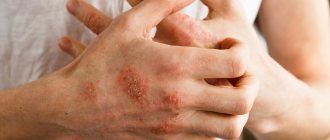
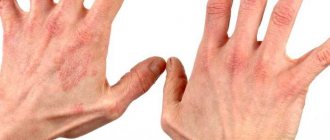
- Psoriatic arthritis is a phenomenon when the affected areas are much deeper than the skin and the disease affects the joints. The disruption of metabolic processes is reflected not only on the stratum corneum, but also goes inside the body, affecting the cartilaginous matter. Therefore, anyone who is worried about whether psoriasis on the hands is contagious should know that it is in the joints of the hands that it penetrates first. And if at the initial stage of the disease it can be simply unpleasant to shake hands and carry out the entire range of movements, then damage to the joints will mean a significant limitation of activity.
- Damage to mucous membranes. If measures are not taken in time to treat scaly lichen, it can spread further, from the horny to the mucous membranes. Delicate mucosal tissues do not tolerate metabolic disturbances and the presence of dying cells in their composition. As a result, constant conjunctivitis, problems with the eyes and vision, and other complications associated with inflammation of the mucous membranes.
- Impaired liver function, which is observed in all types of progressive psoriasis, can occur regardless of the location of the concentration of plaques and its other external signs. That is, while the patient is wondering whether scalp psoriasis is contagious and which shampoo to switch to due to constant dandruff, psoriasis is already affecting the internal organs. Therefore, it is necessary to treat the cause, not the symptoms.
- Muscle atrophy usually accompanies the stage of psoriasis when it moves from cartilage tissue (arthritis) to deeper tissues. It is observed only in the complete absence of treatment or in the final stages of the disease.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in psoriasis are associated with disturbances in the endocrine system.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous and cardiovascular systems are also observed at the second stage of the disease.
The following stages of psoriasis are distinguished:
- Progressive - the appearance of the first small rashes, mild itching in the places where they appear. If this is combined with other skin injuries (bites, burns), the development of the disease may accelerate.
- The stationary stage, at which the disease is treated, is characterized by the presence of many large red and white plaques with flaky skin scattered throughout the body.
- The regressive stage is the final stage, when after treatment the rash mostly goes away, leaving small marks on the skin. If the course of treatment is not resumed, they will return again.
Psoriasis is a severe, chronic disease that greatly affects the quality of life. However, with the use of modern treatment methods, the development of psoriasis can be slowed down and prolonged for many years, when the disease will not make itself felt even by the slightest discomfort. In addition to medicinal and physiological treatment, cosmetic products are also used, including as part of spa treatment - exfoliating mixtures, mud, wraps, baths and masks. Using the whole range of measures, you can get rid of unpleasant sensations and prevent illness from entering your life.
Based on materials from 1psoriaz.ru
Many people are interested in the question: is psoriasis contagious or not. This is natural, because this disease is quite common. The vast majority of people are afraid to come into contact with a person who has noticeable psoriatic papules on their skin. How justified this fear is, you can find out from this article.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! A product that will cleanse your skin and get rid of psoriasis forever. Doctors began secretly recommending it to their patients! Read more >>>
Communication with a person suffering from psoriasis can only cause aesthetic discomfort. Otherwise, such contact is completely safe for healthy people. The statement that psoriasis is contagious and dangerous to others is just a common myth.
It is impossible for a healthy person to contract psoriasis from a patient. Psoriasis is not transmitted:
- In case of contact with skin, through the use of the same household items with the patient (bed linen, towels, dishes).
- Through saliva, sweat.
- Sexually.
- When caring for the sick.
- Through blood.
And you can inherit a predisposition to the appearance of psoriasis.
The genetic factor plays a key role in the development of the disease. The likelihood that this disease will be transmitted from mother to child is high. It is 40-50%. If both parents are sick, the risk that their child will develop the disease reaches 75%. In patients with psoriasis, changes occur at the cellular level in the tissues of the skin. These pathogenic mutations are passed on to children at the genetic level. Their presence leads to changes in metabolic processes and the development of the disease.
Skin psoriasis does not necessarily appear in the next generation. It may arise within a generation. The disease is often in a latent state. A person does not realize that he has a predisposition to its development.
There are situations when psoriatic papules first form in children, and after a while they appear in parents. This indicates the presence of the disease in the hereditary line.
Psoriasis is not a contagious disease. But it is important to identify it and not confuse it with other dermatological diseases that are transmitted through contact.
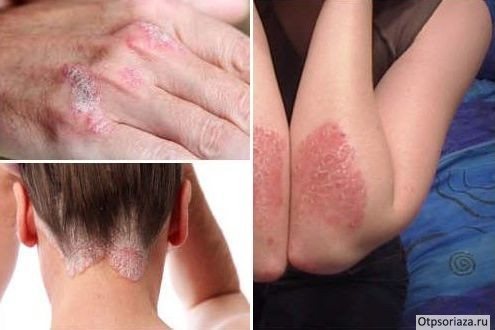
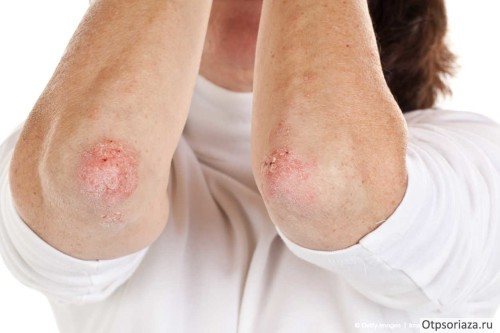
With the development of psoriasis, isolated red spots form on the surface of the skin. At first they are small in size. Formations are growing quite quickly. The stratum corneum of the rash peels off greatly and turns into plaques. These are papules. The places where they are located itch. The first rashes appear, as a rule, on the curves of the body (knees, elbows, shoulders), on the head, and back.
Even “advanced” psoriasis can be cured at home. Just remember to apply once a day.
Distinctive signs of psoriasis:
- Formation of a “stearin stain” ─ papule scales quickly peel off when their surface is lightly scraped.
- The appearance of a “terminal film” ─ after the scales peel off, the surface of the skin becomes thin and shiny, as if wet.
- “Blood dew” effect ─ if the terminal film is damaged, small drops of blood form on the surface, reminiscent of dew.
Although psoriasis cannot be contracted, it is a very dangerous disease. It should be treated when the first symptoms appear. This disease affects the skin as well as internal organs. This is where its danger lies. If you do not complete the course of treatment selected by your doctor in a timely manner, serious complications may develop:
- Damage to the nail plate.
- Joint damage, development of psoriatic arthritis. The disease can have a pathological effect on the spine, leading to disability.
- Eye diseases ─ lens sclerosis, conjunctivitis, episcleritis, uveitis.
- Damage to the mucous membranes ─ if plaques appear in the urethra, bladder, this threatens with urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis.
- Kidney and liver diseases.
- Enlargement of the inguinal and femoral lymph nodes.
- Muscle pain, weakening.
- Damage to the nervous system ─ there is a risk of developing epilepsy, encephalopathy, and polyneuritis.
Psoriasis is a systemic disease that affects all organs. Possible death in very advanced stages.
It is impossible to cure psoriasis completely. This is a chronic disease. However, modern medicine methods minimize the rate of its development and prolong the period of remission for a long time. It can last for years or even decades.

The main types of treatment for psoriasis:
1. Therapeutic methods:
- Photochemotherapy.
- Ultraviolet radiation.
- Laser therapy.
- PUVA therapy.
2. Medication methods:
- Hormonal drugs, in particular ointments.
- Use of flavored retinoids.
- Monoclonal antibodies.
- Antihistamines.
3. Special diet
An integrated approach to treatment demonstrates maximum effectiveness.
Rate this article
(
1 ratings, average 5.00 out of 5)
Based on materials from otpsoriaza.ru
An abnormality of the skin, which is one of the most common ailments - psoriasis. This type of dermatosis affects approximately 5-6% of men and women around the world. How does skin disease manifest itself and how dangerous is it?
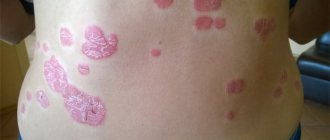
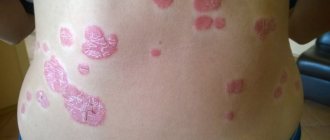
The skin disease psoriasis (or scaly lichen) is a chronic disorder characterized by excessive division of cells in the upper layers of the skin, a strong inflammatory process and damage to various organs and internal human systems. The non-infectious disease affects the skin and its appendages (nails, hair). The main symptoms of psoriasis are the appearance of pinkish spots, which over time begin to peel off and cause itching. The disease is characterized by alternating exacerbation and remission.
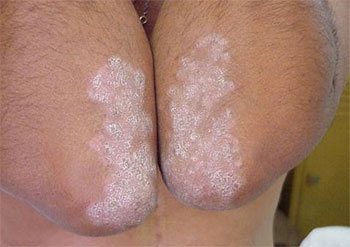
Often, lichen forms on the elbows, knees, and scalp. Often those areas of the integument that are constantly injured or subject to friction are affected. In the case of atypical forms of psoriasis, the disease affects other places on the human body. Doctors distinguish three stages of development of lichen with peeling:
- Progressive stage. It is characterized by the formation of new rashes and severe itching.
- Stationary stage. New lichen spots with peeling do not appear, and old ones gradually heal.
- Regression. The disease practically recedes, leaving strong pigmentation on the body (at the sites of plaques the skin is darker than in healthy areas).
Many people often ask their dermatologist whether it is possible to become infected with psoriasis. Scaly lichen is not an infectious disease. The psoriatic pathway develops according to completely different “laws”. Given this fact, a chronic disease cannot be transmitted as follows:
- Many people think that psoriasis is transmitted through contact. Direct contact and household transmission (airborne transmission, handshaking, hugging, using someone else's towel, etc.) is also excluded. Is psoriasis contagious? Naturally not.
- In the process of caring for a patient who has lichen, there is also no risk of infection. Changing clothes, washing the patient's dishes and similar actions will not affect the well-being of a healthy person. Skin psoriasis is not dangerous for others.
- Psoriasis and sex are two concepts that are in no way related. It is safe to have sex with a man or woman who suffers from lichen planus. Is psoriasis transmitted sexually? The answer to this question is: no.
- Through blood transfusion, lichen is also not transmitted from the patient. The presence of such a disorder will not affect health.
It is worth understanding how people get psoriasis and why this skin disease occurs. To date, the exact causes of damage to the body have not yet been identified. There are several theories that are close to the truth:
- Genetic predisposition. The hereditary factor is considered the main “culprit” in the transmission of the inflammatory non-contagious disease. When both parents have psoriasis, the chance of the child being affected by this disease is 75%. If only mom or dad are diagnosed with lichen, then the risk of inheriting it is reduced by a quarter.
- Allergic theory. Often, with exacerbation of psoriasis, there is an increase in allergy attacks. In this case, doctors say that scaly lichen is a reaction to viruses or allergenic products.
- Endocrine factor. The disease appears due to disruption of the thyroid gland and hormonal imbalance.
- Viral theory. It is believed that psoriasis can be transmitted by viruses. Most people are susceptible to developing non-contagious rashes, but only those whose bodies have been affected by viral organisms get sick.
- Infectious factor. This theory, which explains how lichen can be transmitted, has existed for a long time, but does not yet have modern scientific evidence. Doctors have repeatedly noticed that exacerbations occur during seasonal infections (flu, sore throat, bronchitis, etc.). Such diseases significantly suppress the immune system, which makes the body more vulnerable to psoriasis.
If you do not treat scaly lichen, then in addition to severe physical and psychological discomfort, it can lead to very serious negative consequences. Is psoriasis dangerous and why exactly? The main results of advanced inflammatory disease are:
- The occurrence of psoriatic arthritis. This nuisance is characterized by the fact that the areas of the body affected by the disease are much deeper than the skin and lead to joint diseases. Failures in metabolic processes affect not only the stratum corneum: they go inside the body and affect cartilage tissue. Psoriasis of the nails, rashes on the hands or feet, affect the joints, which leads to a limitation of physical activity in a person.
- The mucous membrane can also suffer from lichen. If you do not start treating an autoimmune disease in a timely manner, it will move from the cornea to the mucous membranes. As a result, doctors diagnose a variety of ailments that are directly related to inflammation of the mucous membrane (visual impairment, conjunctivitis, and others).
- Psoriasis of the head or other parts of the body “acts out” on the liver. Problems in the functioning of this organ appear regardless of the location of the plaques and other external signs of the disease.
- During exacerbation of lichen planus, the endocrine system suffers, and this causes enlargement of the lymph nodes.
- At the second stage of psoriasis, disorders of the cardiovascular and central nervous systems are observed.
- Another dangerous complication is muscle atrophy. It appears in the final stages of the disease in the complete absence of therapy or when psoriasis affects the deep tissues of the body.
Based on materials from sovets.net
Negative factors
To reduce the risk of psoriasis in a child, parents of such children need to know the negative factors that can affect the health of their children. When protecting the child from adverse factors, relatives are obliged to take the necessary measures and promptly eliminate their harmful effects. Main risk factors:

- chronic infections, their foci;
- family dysfunctional psycho-emotional situation, stress, emotional instability;
- weakened immunity, AIDS, HIV;
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- self-medication and use of medications without prescription from a specialist.
Parents need to pay special attention to having psychological conversations with their child. From early childhood, he needs to be told about the dangers of alcohol, which is also one of the main factors in the development of pathology. Girls need to be explained that skin problems can appear during pregnancy, so planning for conception must be taken very seriously.
What measures should be taken to mitigate the risks?
Unfortunately, you won’t be able to completely protect yourself if the forecasts are unfavorable. But you can significantly reduce the risk of disease. To do this, you should give up bad habits (if any), reconsider your diet, giving preference to healthy foods. You should also be more attentive to your own health, because psoriasis often develops against the background of various endocrine diseases and ailments affecting the nervous system.
If psoriasis nevertheless passes to you as a hereditary disease, in addition to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, taking vitamins and undergoing physical procedures, pay attention to caring for the affected skin. During periods of remission, maintain optimal levels of hydration and lipid balance. “Losterin” products, developed by , are ideal for this. The “Losterin” line contains everything that is required for daily care of skin affected by psoriasis - shower gels and shampoos, cream and ointment.

Line of products Losterin
Designed for daily skin care in the complex treatment of chronic skin diseases - psoriasis, eczema, neurodermatitis, atopic dermatitis .
The preparations contain a balanced combination of active ingredients ( resin-free naphthalan, urea, salicylic acid, medicinal herbal extracts, natural oils ) selected for the most effective therapeutic effect on the skin for various skin diseases.
Recommendations for parents
Parents whose children are conditionally susceptible to a genetic predisposition cannot 100% protect their child from serious skin problems. But they may well provide comfortable conditions and a normal psycho-emotional mood in the family. These indicators are the main ones in the prevention of psoriasis.
From birth, such children should be treated with great care and love. In addition, several rules should be followed to improve the life support of a child who already has psoriasis. A few rules for parents:

- If areas of skin with signs of psoriasis appear, you need to monitor them. Affected areas should be ventilated and always dry.
- Eliminate from the child's diet all foods that have high allergenic properties.
- In hot weather, the child should wear a thin T-shirt with sleeves and a cap or scarf on his head.
- Strictly limit your hours in the sun.
In addition, it is necessary to take proper nutrition as a rule. You should give preference only to wholesome and healthy foods. By following these simple rules, parents can significantly reduce the risk of psoriasis.
Psoriasis is partly hereditary, but it should not be considered a death sentence. With the development of medicine, more and more new drugs and means appear that are effective in the fight against pathology. Only parents can protect a child with a genetic predisposition by constantly improving his quality of life. For health and improvement of psycho-emotional state, it is recommended to undergo sanatorium-resort treatment once a year.
Is psoriasis inherited?
The deterioration of the general and local ecology, an irrational approach to nutrition, low physical activity, and the emergence of new viruses have become the reason that a huge number of modern people suffer from a variety of diseases, the carriers of which only yesterday were few. One of these diseases is psoriasis.
Psoriasis is most often a hereditary chronic disease of a non-infectious nature that affects the human skin, and is most typical for people in the middle age group, however, cases of psoriasis are also becoming more frequent among very young children and adolescents. The disease manifests itself in different ways, depending on the form of its severity. The only thing that remains unchanged is the presence of plaques protruding above the surface of healthy skin. Scratching them leads to the appearance of blood.
But there is good news: psoriasis is a disease that occurs in waves. Exacerbations alternate with periods of remission, which can be extended by every sick person who takes a responsible approach to their health.
Symptoms of psoriasis - is it contagious or not?
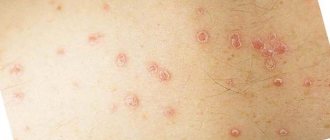
With the development of psoriasis, small reddish spots first form on the patient’s body, which can reach any size.
Over time, the spots turn into flaky itchy plaques with characteristic signs:
- After combing and peeling off the dry scales, the formation of a so-called “stearin stain” occurs;
- A “terminal” film appears, the skin becomes thin and smooth;
- If the film is damaged by combing, small droplets of blood appear, reminiscent of dew on the grass on a foggy morning, which in turn leads to infection by pathogenic microbes.
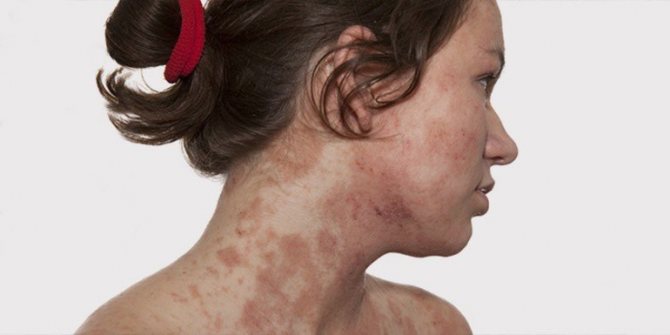
The localization of plaques, as a rule, first appears in the bends of the body: on the hands and knees. Subsequently, they clearly appear on the head, neck, back and abdomen. Particular inconvenience is caused by psoriasis of the scalp.
Unbearable itching, constant peeling and the appearance of repulsive plaques lead to the patient's psychological discomfort, depression, social isolation, and social phobia may even develop.
Related article:
How to recognize the initial stage of psoriasis on the hands? Signs, symptoms and treatment