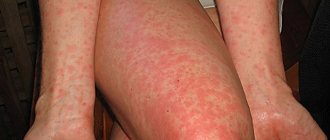
The causes of dermatitis can be different. Outwardly, it does not look very aesthetically pleasing, so people try to get rid of this disease as quickly as possible. Unlike psoriasis, dermatitis can be cured completely. Many people wonder whether dermatitis is contagious or not. Since the external manifestations of this disease are extremely unpleasant, intuitively some try to move away from people with this problem, experiencing hostility and fears about the contagiousness of the disease.
Neurodermatitis (atopic dermatitis) - what is this disease and how to treat it?
Neurodermatitis (atopic dermatitis) is a recurrent disease, the main symptoms of which are skin inflammation and severe itching.
This disease is chronic: having appeared in early childhood, as a rule, accompanies a person throughout his entire life. At the same time, life is not easy for people with neurodermatitis: they have to always be on alert and be ready to withstand unpleasant symptoms. Therefore, the main goal of treatment is to prolong the periods of rest of the skin without relapses and improve the quality of life of patients. The exact causes of the disease have not yet been established. It is believed that it is caused by genetic factors, as well as individual characteristics of the skin structure. Medical science also knows factors that can provoke the onset of the disease or its exacerbation. Let's look at these points in more detail.
Characteristics and causes of atopic dermatitis in humans
The term "atopy" first appeared in 1923. It refers to an increased (abnormal) reaction of the body's immune system to various allergens. Even earlier, at the end of the 19th century, the disease was given the name “neurodermatitis,” which indicated a clear connection with the nervous system. Today, the term "neurodermatitis" is synonymous with atopic dermatitis in adults. Modern research has proven that the impetus for the development of neurodermatitis in adults can be stress or a viral infection. However, atopic dermatitis most often occurs in childhood - in 90% of cases the disease is diagnosed between the ages of 6 months and 7 years. In children, the main factor provoking the occurrence of atopic dermatitis is allergies.
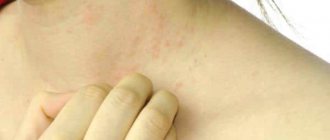
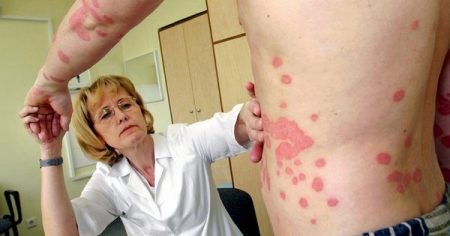
Symptoms of neurodermatitis are usually pronounced. This is severe itching, peeling, redness and damage to the skin in those places where it is thinnest: on the knees and elbows, in skin folds, on the neck. Pustular formations and rashes may also appear on the face. Often the listed symptoms are combined with allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, and hay fever.
Among the factors that can cause the occurrence of neurodermatitis or influence its exacerbation, the following can be noted:
- Constant contact with allergens: house dust, animal hair, plant pollen, fungal mold, food allergens.
- Strong emotional shocks, stress.
- Malfunctions of the hormonal system.
- Gastrointestinal problems.
- Vaccination performed without taking into account clinical and immunological status and previous prevention.
- Incorrect or uncontrolled use of medications.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules, use of low-quality household chemicals.
Depending on the location, there are several forms of neurodermatitis:
- linear;
- follicular;
- hypertrophic;
- psoriasis-like.
However, the most common division of neurodermatitis is focal and diffuse. In the first case, the affected skin is concentrated in a limited area. If the lesions are scattered over two or more areas, they speak of the diffuse nature of the disease. Often in patients, almost the entire surface of the skin is affected, with the exception of the nasolabial triangle and palms. And this is the most severe form of the disease.
Manifestations of neurodermatitis at various stages
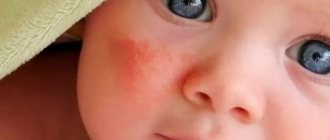
The first symptoms of neurodermatitis (atopic dermatitis) usually appear in the first months of life. This is redness on the face with slight swelling of the skin and peeling. Light-colored scales may form around the fontanelle, behind the ears and in the eyebrow area and come off when scraped. On the cheeks there are yellowish-brown crusts, the so-called milk scab. As the child grows, lesions may appear on the mucous membranes of the genitals, eyes, and nose. Papules and vesicles become crusty and the skin becomes rough. This is already a chronic course of the disease. In the autumn-winter period, exacerbations occur. In summer the condition improves.
The most characteristic sign of atopic dermatitis of the skin, starting from the first days of the disease, is itching. As a rule, it is pathological, painful in nature with frequent attacks.
During remission, symptoms decrease or disappear completely. The duration of the remission period ranges from several weeks to 5 years or more. In severe cases, this stage is absent; recurrent atopic dermatitis accompanies the patient constantly.
If symptoms do not return for 7 years or longer, we can talk about clinical recovery. However, there is no single point of view in the medical community on this matter. The nature of atopic dermatitis, as well as the causes, are not fully understood, and accordingly, there is no clear understanding of whether final recovery is possible. As numerous observations show, during puberty in a teenager, atopic dermatitis can disappear forever. If this does not happen, there is a high probability that relapses will recur periodically throughout the life of an adult.
Diagnosis of the disease
To diagnose atopic dermatitis, the patient must consult a dermatologist or allergist-immunologist. To make a diagnosis in medical practice, mandatory and additional criteria are used. The doctor will suspect neurodermatitis if the patient has at least three criteria from the main group and three from the additional group.
- skin itching;
- typical location and type of skin lesions;
- hereditary factor;
- presence of relapses.
- exacerbation of the disease due to stress and food allergies;
- first relapse at an early age;
- frequent skin infections (fungus, herpes, staphylococcus);
- dark circles around the eyes;
- seasonality of exacerbations;
- dry skin;
- the appearance of additional folds on the lower eyelids;
- white dermographism - change in skin color due to mechanical irritation.
The collected anamnesis and study of clinical manifestations will allow a preliminary diagnosis to be made. To confirm it, laboratory diagnostics are used. The patient is prescribed a general and biochemical blood test, urine and stool tests, as well as allergy tests.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis: attack on all fronts
Therapy for atopic dermatitis has two goals: to eliminate existing disturbances in the functioning of body systems and to reduce the frequency and duration of repeated relapses of the disease. Treatment is complex: from improving sanitary conditions to the use of antihistamines and hormonal drugs.
General events
Considering that dermatitis is almost always allergic in nature, it is necessary to exclude the patient’s contact with potential allergens as much as possible. A strict diet is recommended, eliminating smoked and spicy foods, citrus fruits, chocolate, eggs, whole milk and cocoa from the diet. Daily wet cleaning is required. Carpets, soft toys and feather pillows should be removed from the patient’s room, and pets should be separated. In order to reduce the risk of re-infection, it is important to sanitize foci of chronic inflammation (gastritis, otitis media, tonsillitis, etc.).
Systemic treatment
Drug therapy begins with taking antihistamines. The most effective are the drugs of the 2nd and 3rd generations, created on the basis of substances such as loratadine (Claritin), ebastine (Kestin), cetirizine (Zyrtec, Zodak), terfenadine (Bronal) ) etc. They have a prolonged effect, do not have side effects on the central nervous system, and do not cause drowsiness or lethargy. The doctor selects the dosage based on the individual course of the disease.
In the acute phase of the disease, intravenous injections are prescribed. For example, a 30% solution of sodium thiosulfate or a 10% solution of calcium gluconate. Also, for severe atopic dermatitis and large areas of skin damage, corticosteroid drugs are used as treatment for a short period of time. They simultaneously have an antipruritic, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic effect, which, however, is short-lived. The most famous of the group are: prednisolone, dexamethasone, triamsinolone, silanar.
General principles of treatment
Treatment of neurodermatitis, as well as its diagnosis, must be comprehensive. Taking this into account, doctors prescribe the following groups of medications:
- Antihistamines that relieve itching, burning and flaking of the skin, as well as tissue swelling.
- Antipruritic medications. Prescribed along with antiallergic drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory agents for external use.
- Enterosorbents for getting rid of intoxication of the body and removing toxins.
These drugs have the greatest effect in the treatment of mild, limited neurodermatitis, but can also be used for diffuse or other forms of the disease. In parallel with drug therapy, alternative treatment methods are prescribed:
- PUVA therapy;
- acupuncture sessions;
- plasmapheresis;
- laser therapy;
- diet therapy, etc.
It is very important to know and understand how to treat neurodermatitis, therefore the use of certain drugs at your own discretion is unacceptable. All necessary recommendations can only be given by the attending physician, and although it is impossible to cure the disease completely, it is quite possible to transfer it into a phase of long-term remission.

Is dermatitis transmitted from person to person and is it contagious?
The causes of dermatitis can be different. Outwardly, it does not look very aesthetically pleasing, so people try to get rid of this disease as quickly as possible. Unlike psoriasis, dermatitis can be cured completely. Many people wonder whether dermatitis is contagious or not. Since the external manifestations of this disease are extremely unpleasant, intuitively some try to move away from people with this problem, experiencing hostility and fears about the contagiousness of the disease.
Why does dermatitis occur?
The causes of pathology may be different. One of the most popular is skin contact with household chemicals. People whose work involves chemicals are more likely to suffer from dermatitis than others. In addition, when washing dishes or floors with a special liquid, you need to take care of your skin so as not to get such a problem.
Dermatitis occurs if there is an allergy to any product. Food allergies very often manifest themselves as skin rashes, itching, and redness. Dermatitis is often confused with other diseases, including infectious ones. However, the symptoms of dermatitis are very different from the symptoms of other pathologies. These include:
Manifestations of pathology are possible simultaneously, or only one of them. In any case, only a dermatologist can make an accurate diagnosis. To make sure what kind of disease it is, dermatologists usually prescribe a series of tests that are necessary to confirm or refute the diagnosis.
Symptoms of dermatitis
To understand whether dermatitis is contagious, let's repeat what the main symptoms of this pathology are:
- rash;
- peeling;
- swelling;
- redness;
- itching and burning.
Skin manifestations can occur all at once or appear separately.
Probably everyone knows that dermatitis manifests itself in the form of redness on the skin. But there are many allergic diseases that have similar symptoms. How to distinguish dermatitis from urticaria or eczema?
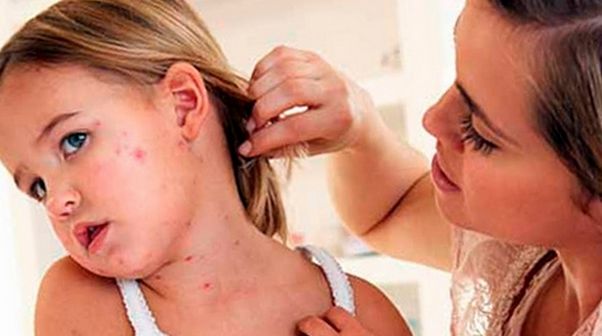
Manifestations of dermatitis depend on factors such as:
- Type of stimulus;
- Skin Features;
- The duration of the negative impact of a specific stimulus.
Main symptoms:
- Itching;
- Peeling;
- Intertrigo;
- Attrition;
- Allergic reactions;
- Chills;
- Ulcerative lesions;
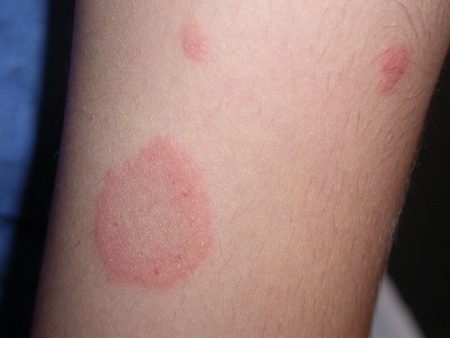
- Red spots;
- Loss of sensitivity in damaged areas of the skin.
Symptoms of the disease may vary depending on the type, area of distribution or stage of dermatitis.
Stages of development:
- Spicy. This period is characterized by the formation of bubbles on the skin, of different sizes and filled with liquid inside.
- Subacute. At this stage, dermatitis is accompanied by the formation of crusts and scales on the affected areas.
- Chronic. During this period, the disease has already become advanced, so the skin thickens, and areas with redness become darker (sometimes even purple).
Development mechanism
Dermatitis often develops as an immune response to an irritant. This may be a product to which you are allergic, or external effects on the skin from household chemicals or medications. In addition, it appears in cases of hereditary predisposition.
It also happens that it appears in case of airborne infection. When allergens are inhaled in the air and symptoms of the disease appear on the skin after a while.
Depending on the type of dermatitis, they manifest themselves in different ways. Treatment is also based primarily on the type of disease.
Types of dermatitis
There are different types of dermatitis:
- seborrheic;
- allergic;
- atopic;
- contact.
They all have similar external features, however, they also have their own characteristics.
Atopic dermatitis occurs due to exposure of the body to certain types of allergens. However, it very often occurs in infants. It is a common disease in children under 1 year of age. It is quite unpleasant for a small organism, so it requires prompt treatment. Atopic dermatitis is not contagious to others, but it causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient.
To treat a child or adult for this type of dermatitis, a special hypoallergenic diet is required, as well as the use of antihistamines, both local and internal.
Contact dermatitis most often occurs when the skin comes into contact with external irritants. They can be household chemicals, some medications, herbs and plants, as well as some types of fabrics to which a person is allergic.
The causes of this pathology are the presence of allergens in the body and external irritants. This is what causes the skin reaction.
Seborrheic dermatitis appears on the scalp, face, and neck. It occurs as a result of exposure to a special fungus on the skin. It is not contagious, although it is transmitted through a fungus. The fungus that contributes to the development of this type of pathology is present on the skin of all people, but not everyone manifests it in the form of seborrhea.
So, in the event of exposure to certain factors, this fungus begins to multiply and seborrhea appears. The sebaceous glands, which work very actively, promote the proliferation of bacteria, which create a favorable environment for the development of the disease. Despite its unaesthetic appearance, the disease is not contagious. Occurs more often in people with oily skin type.
Allergic dermatitis occurs as a skin reaction to an allergen. It manifests itself as a rash, itching, and irritation on the body. Allergens include foods, cosmetics and some medications. This type is also not contagious to others. To completely get rid of it, you need to follow a special diet and take antihistamines.
If you want to know the causes of atopic dermatitis in adults, we recommend reading our publication.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious?
It is safe for others, but brings a lot of inconvenience to the patient. Seborrheic dermatitis is not contagious. Whether it is contagious or not is a question that many people ask, because it does not look very pleasant in appearance. Manifestations of the disease in the form of rash, redness and peeling can be confused with other pathologies, so you should always get the correct diagnosis, undergo an examination and consult a dermatologist to be sure of the diagnosis.
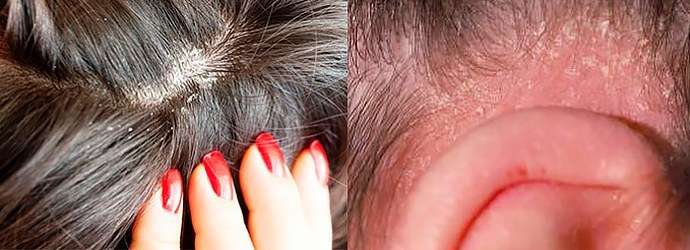
Seborrheic dermatitis is not inherited, but people with a family history of this disease need to be especially careful about their hygiene. Bedding should be washed more often than usual, especially pillowcases. All clothing should be steamed, especially hats. Hygiene should be daily.
Particular attention should be paid to the scalp and face to avoid the spread of the disease. What causes seborrheic dermatitis:
- stress;
- wrong lifestyle;
- lack of hygiene;
- hormonal imbalance.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis appears as rashes and redness on various parts of the body. Occurs where the body comes into contact with an irritant. They can be low-quality types of fabrics, household chemicals, cosmetics to which you are allergic.
This disease is not at all contagious and can be easily eliminated. It often appears as a result of exposure to alkali, acid, or chemical compounds. It also happens after frequent, regular friction in some places on the body. Occurs in people of different ages. However, the disease is not contagious.
Is atopic dermatitis contagious or not?
This type of disease appears mainly in young children, especially under one year of age. Babies are susceptible to various irritants; they often have allergies to any components of food or children's cosmetics. Atopic dermatitis is not contagious, although many mothers, seeing a child with such a problem, get scared and keep their child away so as not to get infected.
The atopic form of the disease can be inherited, or rather, a predisposition to pathology. However, it is not at all contagious to others. The disease is treated with diet and taking antihistamine medications.
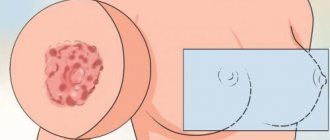
Is eczema transmitted from person to person?
The causes of the pathology may be internal disorders of the thyroid gland, the functioning of the adrenal glands, as well as disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system. Hand eczema is not transmitted by contact. Appears as a result of contact with irritants. They are allergens.
Eczema is popularly considered a contagious disease. Many who see its manifestations fear that they can become infected with eczema. But it is not transmitted from person to person . To determine how eczema is transmitted, it is necessary to find out the roots of the pathology.
Even with close contact it is impossible to become infected with this problem . If only the form of eczema becomes weeping, acquires a purulent character, then infection is possible, but the other person must have too weak an immune system and have open wounds for infection to occur. In this case, it will most likely not be about infection with eczema, but about the transmission of bacteria and infections into the blood.
Is neurodermatitis contagious?
Neurodermatitis occurs as a result of repeated irritation of an area of the body. It affects the neck, arms, and outer legs. Neurodermatitis is not contagious and has a neurological origin.
If you are interested in how to treat seborrheic dermatitis on the body, read our article.
How to smear weeping dermatitis can be found in the following publication.
How to properly use shampoo for seborrhea of the scalp, read here: https://psoriazweb.ru/dermatity/shampun-ot-seborei.html
Infectious allergic dermatitis
This disease is difficult to treat and make a correct diagnosis, since its symptoms are often similar to those of other ailments. Infectious allergic dermatitis is formed as a result of the appearance of infectious manifestations. These include chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever, and typhus. In case of illnesses, a rash, bumps, redness and other rashes appear on the body, depending on the nature of the disease.
Common Misconception
One of the myths is the misconception that neurodermatitis is contagious. The basis for this is the external symptoms of the disease. Amateurs are frightened by their similarity to certain types of lichen. Neurodermatitis is a non-microbial disease of exclusively internal immune dysfunction. There is no reason to fear that the disease is contagious. A sick child does not pose a threat to other children.
However, you should know that neurodermatitis provokes intense scratching, which damages the skin. This serves as the basis for the addition of a secondary biogenic infection.
The skin is the body's protective barrier. Microbes (staphylococci, streptococci, etc.) are constantly present on it. Neurodermatitis reduces local skin immunity. Through the damaged surface, bacteria rush to places of least resistance. Strepto or staphyloderma is added to non-microbial inflammation. Purulent crusts form on the lesions. You can see what neurodermatitis complicated by a bacterial infection looks like in the photo.
Purulent skin lesions - pyoderma. This disease (not neurodermatitis) is contagious and is transmitted by contact. Causes in pathogenic bacteria. Neurodermatitis in the presence of pyoderma requires immediate antibiotic therapy.
Effective methods for treating dermatitis
Dermatitis is treated with different methods. Some prefer herbal medicine and medications, others prefer laser treatment. When treating affected surfaces with a laser, a quick recovery is achieved, since this technique is effective.
There are also special creams and ointments that can speed up the skin regeneration process. They act locally, thereby relieving inflammation and itching in the affected areas.
Depending on the type of dermatitis, dermatologists select an individual treatment regimen aimed at eliminating the symptoms and the root cause of the disease.
Treatment methods
You can treat seborrhea at home. But it is advisable to first confirm the diagnosis and differentiate the disease from systemic lupus erythematosus, rosacea, psoriasis, and dermatophytosis. Only a dermatologist can do this. Based on the initial examination and laboratory tests (microscopic examination of scale scrapings and bacteriological culture), he will accurately determine the patient’s health status. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment is selected taking into account the localization of the pathological process.
A set of measures for the treatment of the scalp:
- The patient is recommended to adhere to a restrictive diet and consume foods high in zinc, selenium, vitamin A, PP, B and C).
- Antifungal agents are prescribed: gels or shampoos (Dermazol, Nizoral, Cynovit, Danex).
- When washing your hair, it is advisable to use tar soap or tea tree oil.
- It is imperative to eliminate the provoking factors that gave impetus to the development of pathology.
Such treatment reduces the number of fungi and sebum produced, and removes scales. To achieve an effect, the duration of treatment should be two weeks.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the skin of the face and back begins with eliminating the provocateur factor. Then therapeutic tactics are applied that eliminate the main symptoms of skin pathology.
For oral administration the following are prescribed:
- antibacterial drugs (Doxycycline),
- antihistamines (Telfast, Loratadine),
- multivitamin complexes (Multitabs, Alphabet).
For external treatment the following is prescribed:
- antifungal ointments (Ketodine, Bifasam),
- hormonal creams (Elocom),
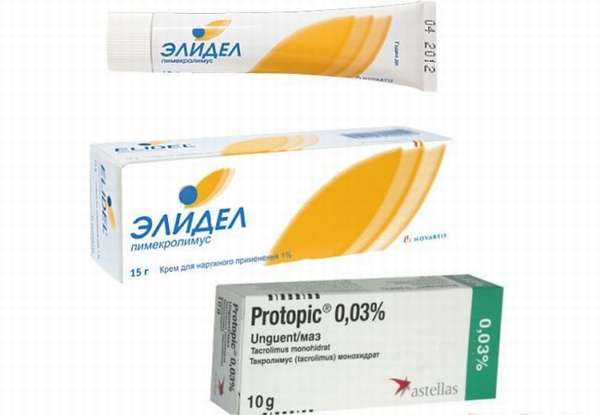
- immunomodulators (Protopic, Elidel).
If seborrheic dermatitis affects the skin of the eyelids, wash the eyes with antiseptic solutions and treat the affected areas with antibacterial ointments.
Preventing dermatitis
To prevent dermatitis, doctors prescribe a special hypoallergenic diet for those who are prone to manifestations. Those who are not prone to allergies can protect themselves by avoiding exposed areas of the body from touching chemicals, household chemicals, various acids and potential irritants. Despite the fact that the disease is not contagious, it causes inconvenience.
A diet for dermatitis involves the complete exclusion of red vegetables and fruits, berries, as well as baked goods and some cereals from the diet. Semolina is prohibited if you are ill. Cow's milk is also excluded. However, fermented milk products can be consumed. You can also eat all other cereals, except semolina, rye bread, nuts, fruits and vegetables that are not red in color.
If you suspect an allergy or dermatitis, you should contact a dermatologist to clarify the diagnosis. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the dermatologist will refer you for the necessary examinations and prescribe treatment that will relieve the disease in a short time.
Perioral dermatitis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, diet
Skin diseases are not only an aesthetic problem, but also seriously affect the patient’s quality of life. Among such ailments can be noted perioral dermatitis. The disease does not occur very often, but requires a special approach to treatment.
What is pathology
This disease has many names: perioral dermatitis, rosacea-like, flight attendant disease. Perioral dermatitis on the face is an inflammatory process that constantly recurs, which most often affects the area around the mouth.
A distinctive feature of the disease is the presence of an unaffected strip of skin adjacent to the lips. The disease was first diagnosed in the 50s of the twentieth century; now about 1% of the population is affected by this disease.
Types of dermatitis
Based on symptoms, doctors distinguish several forms of the disease:
- The first type appears as diffuse erythema around the mouth and small reddened areas of the skin.
- The second form is characterized not only by the formation of papules, but also by vesicles filled with liquid.
- The third form is accompanied by the formation of purulent blisters.
Reasons for the development of the disease
Doctors still cannot name the exact causes of perioral dermatitis. But there are some factors that can serve as provocative factors for the development of the disease. Among them, the following should be noted:
- Using low-quality or unsuitable cosmetics for your skin type. This initially leads to irritation, and gradually to the formation of dermatitis.
- Infectious skin diseases of bacterial nature. Various bacteria constantly live on the face; for unknown reasons, they can begin to multiply uncontrollably.
- Some types of perioral dermatitis develop due to the presence of parasites on the skin, such as Demodex folliculorum. They cause inflammation and irritation of the skin.
- Stressful situations can indirectly provoke the development of the disease. They negatively affect the entire body and the immune system, which is unable to resist bacteria.
- Constant exposure of the skin to cold temperatures, especially when combined with wind, dries out the skin and makes it more vulnerable to attack by pathogens.
- If you have problems with your immune system, some fungi, such as Candida albicans, can cause illness.
- Perioral dermatitis in an adult can be allergic in nature and appear after contact with an allergen.
- There is an increased predisposition to the formation of pathology in people who have problems in the digestive tract and suffer from gastritis.
- Perioral dermatitis in an infant can develop due to frequent and prolonged pacifier sucking.
- Exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun can cause skin irritation or worsen dermatitis.
- Regular use of fluoride toothpastes for dental care. This element is irritating to the skin.
- The use of cortisone-based creams and ointments in the first stages of therapy weakens the symptoms, and then causes a relapse of the disease.
- Among the causes of perioral dermatitis are hormonal imbalances, for example, during pregnancy and menopause.
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals, especially A and E.
- Neurological disorders.
- Eating certain foods may increase your chance of developing dermatitis, such as cinnamon.
The disease can occur with periodic exacerbations and remissions. Pathology activity can be maintained by:
- Frequent visits to the solarium or prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Taking oral contraceptives.
- Chronic foci of infection in the body: caries, sinusitis.
- The period of bearing a baby.
- Tuberculosis.
- Hormonal disorders.
When several provoking factors are combined, the likelihood of developing perioral dermatitis increases. At the slightest suspicion, you should consult a doctor.
Signs of the disease
The symptoms of perioral dermatitis are very similar to those of other diseases, such as eczema or rosacea, so a diagnosis must be made by a doctor and effective therapy prescribed.
But we can note the most striking manifestations of the disease:
- Redness and a burning sensation appear in the lip area.
- Small erythemas appear on the skin of the face, which can develop into vesicles and pustules.
- Itching of the affected areas.
- In pathological areas of the face, peeling and redness are observed.
- Single formations gradually increase in size and merge with each other, forming continuous spots.
- The rashes are usually localized symmetrically on both sides.
- The skin feels sore.
- Swelling appears.
- Gradually, the affected areas of the skin become covered with scales and crusts, which fall off over time. If you peel them off yourself, pigment spots remain that are difficult to remove.
The disease often leads to neurological disorders, especially in women due to its appearance. They become withdrawn, some even quit their jobs, and conflicts arise in the family.
Is perioral dermatitis contagious?
Pathogenic microorganisms that cause the development of the disease can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person. But with a strong immune system and the absence of other provoking factors, the pathology is unlikely to manifest itself.
But we must remember that when the disease develops under the influence of fungi and bacteria, infection is still possible.
Features of the disease in childhood
Manifestations of the disease in children have their own characteristics. Before puberty, most often the rashes differ little in color from the skin. They are usually flesh-colored, but may be slightly pink. There are almost no other symptoms; sometimes the child may complain of a burning sensation in the affected areas of the skin.
The rash can be single or form clusters in the form of spots. Not only the area around the mouth can be affected, but also near the ears, eyes, skin on the head, hands, and genital area.
With the onset of puberty, the manifestations of the disease are practically no different from those in an adult.
Diagnosis of the disease
Only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis; it is important to differentiate the disease from other similar pathologies. To recognize dermatitis, the following is prescribed:
- Examination of the patient by a dermatologist.
- Examination of the skin using dermatoscopy. The doctor examines pathological areas using a device that provides 10x magnification.
- The microflora from the affected areas of the skin is inoculated.
- A blood test may show a slight increase in ESR, which is explained by the presence of inflammation or infection in the body.
After the doctor has no doubt about the presence of perioral dermatitis, treatment is prescribed.
Main directions of treatment
Any skin pathology requires an integrated approach; it will not be possible to get rid of the disease using only external means. The treatment regimen for perioral dermatitis may look like this:
- Taking medications. Only a doctor prescribes them. The main remedy for perioral dermatitis is Metronidazole. If the pathology proceeds without complications, then the patient is prescribed 500 mg per day for 3-6 weeks. In severe cases, treatment begins with taking 1 gram of the drug for at least 3 weeks, and then, when a therapeutic effect is obtained, the dosage is reduced to 500 mg and taken for another 1-1.5 months.
- If you are allergic to Metronidazole, the drug can be replaced with Ornidazole. It can be taken in shorter courses.
- Severe forms of dermatitis have to be treated with drugs from the tetracycline group: Unidox, Solutab. If a woman is pregnant, then Tetracycline should not be used. It can be replaced with Erythromycin.
- A long-term antibacterial course of treatment negatively affects the state of the intestinal microflora, so it is advisable to take probiotics at the same time.
In addition to drugs for internal use, external agents must be prescribed; among them, the following ointments are effective for perioral dermatitis:
- Doxycycline ointment. Destroys many pathogenic microorganisms. Apply to affected areas 2 times a day.
- 1% cream "Metronidazole". Apply a thin layer to the affected skin twice a day for 2 months.
- "Metrogil gel". A drug based on metronidazole. It is well tolerated, quickly absorbed, and a good therapeutic effect is observed. But it is not recommended for pregnant women, as well as for renal failure.
- Pimecrolimus ointment is an immunosuppressant and is often prescribed if the disease is provoked by corticosteroids. The product removes inflammation well.
If the patient has intolerance to metronidazole, then use a cream or ointment with azelaic acid. The preparations must be applied to the skin twice a day. Among the external products containing this acid are: “Skinoren”, “Azix Derm”, “Azogel”.
If during the treatment of the disease the patient begins to be bothered by dry skin and irritation, the doctor prescribes Skin-cap cream. It softens the skin well, relieves inflammation, and has an antibacterial and antifungal effect. If there are purulent rashes, retinoic ointment will help; its components contribute to the rapid restoration of the skin. You can use "Bepanten".
The answer to the question of how long it takes to treat perioral dermatitis depends on the severity of the pathology. But usually it takes at least 3-6 weeks.
Other treatments
Doctors often prescribe laser therapy or pulsed light to patients, but there is no evidence that the procedures are 100% effective. The prescription is based on the therapeutic effect of such treatments for rosacea.
Traditional treatment of dermatitis
Therapy for skin diseases can be supplemented with the use of folk remedies. To reduce symptoms on the skin, traditional healers recommend using the following remedies:
- Compresses with linseed oil. To do this, you need to mix flax oil and honey in equal proportions and heat in a water bath. Then add onion juice. Moisten a cloth with the resulting mixture and apply to the affected area of the skin. Repeat 2-3 times a day.
- Prepare a puree from raw pumpkin pulp and apply it to the skin.
- Prepare a decoction from the string: pour a tablespoon of raw material with a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Wet the cloth and wipe the affected areas.
- It is useful to wash your face with decoctions of birch buds, oak bark or diluted aloe juice, and then leave the skin to dry naturally.
- Beekeeping products will help cope with the manifestations of the disease. They have bactericidal properties. You can prepare propolis ointment: combine 1 part of the product with 4 parts of any oil and heat until dissolved in a water bath. Use to lubricate sore areas. But we must take into account that there is a possibility of developing an allergy, so initially try the product on a small area of skin.
Before using folk remedies, it is better to consult a doctor.
Diet during disease therapy
Diet is important for perioral dermatitis. It is important to remove from the diet all foods that can become potential provocateurs of the disease. We will have to exclude:
- Milk.
- Sweets.
- Limit fried and fatty foods.
- Do not eat exotic fruits.
- Reduce salt intake.
- Reduce the amount of fish in your diet.
- Limit consumption of caviar and mushrooms.
- Stay hydrated and drink enough fluids.
There is no need to starve yourself; nutrition should be balanced in terms of vitamins and minerals. It is better to prefer homemade dishes with a high fiber content.
Disease prevention
If there is a predisposition to skin diseases, then special attention should be paid to preventive measures. Among them are the following:
- Promptly treat any infectious diseases in the body and prevent them from becoming chronic.
- Do not use skin care ointments and creams containing corticosteroids without a doctor's prescription.
- Use only proven and safe products for skin care.
- Buy quality cosmetics.
- Do not constantly use fluoride toothpaste.
- Adjust your diet and adhere to the principle of healthy eating.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
Perioral dermatitis is not a dangerous pathology for health, but it causes a lot of trouble for patients.
Do not overdo it in skin care, do not expose it to excessive exposure to cold and wind, then you will not have to look for remedies to combat the disease.
If a diagnosis has already been made, then follow all the specialist’s recommendations. Self-medication using dubious means will only worsen the situation.
Source: //FB.ru/article/19414/uu-perioralnyiy-dermatit-prichinyi-simptomyi-diagnostika-lechenie-dieta
Is dermatitis transmitted from person to person and is it contagious?
Dermatitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the skin. The skin of a person with dermatitis looks scary. Seeing red, inflamed areas of skin, those around you shy away in horror, fearing infection. But is dermatitis contagious or are all fears in vain? Let's try to understand this issue.
Many people consider dermatoses to be a childhood disease. Indeed, this skin disease is often observed in children. But adults can also experience manifestations of this disease.
Not everyone knows whether dermatitis is transmitted from person to person. Moreover, most are confident that this disease is contagious, since it is often possible to see that members of the same family are sick. But the point here is not an infection, but a genetic predisposition.
Therapy for perioral dermatitis
Frequent inflammations on the surface of the skin near the mouth become chronic. Doctors make a diagnosis of perioral dermatitis. The disease is long-lasting and prone to recurrence. During an exacerbation, microbubbles (vesicles) or compactions (papules) form on the face.
The source of the disease is not known for certain. The disease is a medical and social problem at the same time. Patients are able to work, but undergo outpatient therapy for a long time.
General information
In the specialized literature you can find other names for this disease: photosensitive, steroid-induced or rosacea-like dermatitis.
Perioral dermatitis is a fairly common disease that occurs in one in a hundred adults. The main age category of suffering patients is from twenty to thirty years old, with women twelve times more likely to get sick than men. But the disease is diagnosed in both preschool children and the elderly.
Scientists believe that the roots for the development of the disease go back to allergies. Triggering is possible due to excessive use of moisturizing cosmetics, creams with glucocorticoids, and toothpaste with fluoride.
Provoking and maintaining cases of exacerbation:
- - prolonged exposure to sunlight, excessive visits to the solarium;
- - taking oral contraceptives;
- — foci of chronic infection in the body;
- - hormone imbalance;
- — tuberculosis and other severe infectious diseases;
- - expecting a child.
Sometimes it is possible to isolate bacteria from the genus Fusobacteria from the contents of the vesicles, which indicates the participation of infection in the evolution of perioral dermatitis. It is believed that in a certain percentage of patients the disease is associated with Demodex mites and Candida fungus.
Details
Regular use of cosmetics leads to the collection of fluid in the stratum corneum of the dermis, resulting in the formation of edema. The skin's protective properties weaken and bacteria colonize.
Infectious manifestations collect at the mouths of the follicles of the curls. Inflammatory processes of the dermis occur - dermatitis. Having noticed swelling and redness of the dermis, most patients try glucocorticoid ointments. These medications initially provide short-term positive dynamics, but later there is a strong and prolonged deterioration in the course of the disease.
Patients often use glucocorticoids with fluoride on the recommendation of a dermatologist.
Beneficial environment for perioral dermatitis:
- worsening of the natural bactericidal properties of the skin due to long-term use of external glucocorticoids;
- decreased immunity;
- allergy to bacterial antigens;
- hormonal disbalance;
- thinning of the skin under the influence of hormonal ointments.
The disease can also be treated at home
Following the dietary regimen and doctor's orders. Refusal of drugs with glucocorticoids. After three to four days, “withdrawal dermatitis” is noticeable - increased redness and swelling of the epidermis of the face, expressed by burning and itching.
Reducing the manifestations of “withdrawal dermatitis” will help to implement a hypoallergenic diet without meat, eggs, fish, sausages, citrus fruits, tea, coffee drinks and alcohol; virtual absence of salt and sugar.
Prescription of antiallergic drugs.
In case of aggravated course of the disease, the doctor prescribes sedatives. Reflexology and acupuncture can help correct the situation.
If the initial therapy does not work, then move on to the next step in therapy.
Externally - Metronidazole and Azelaic acid - monotherapy for mild to moderate severity of the disease.
Common medications that contain azelaic acid are Skinoren, Skinoklir, Azelik, Azix Derm, Aknestop, Azogel.
The third remedy that is used for external treatment of perioral dermatitis is one percent pimecrolimus cream. Elidel cream contains pimecrolimus.
The doctor also prescribes tetracycline or erythromycin ointments - the safest antibiotics.
The therapy is long and requires patience. Only one hundred percent adherence to the doctor’s recommendations can heal you!
Source: //iplastica.ru/kosmetologia/zarazen-li-perioralnyj-dermatit.html
Varieties
To figure out whether you can get infected with dermatitis or not, you first need to understand what types of diseases exist.
Allergic
From the name it is clear that allergic dermatitis is a disease caused by an inadequate reaction to contact with external irritants. The cause of an allergic reaction can be:
- plant factor – pollen;
- house dust;
- pet hair;
- selected food products;
- medicines;
- cosmetics;
- household chemicals.
Manifestations of allergic dermatitis appear only after contact with certain substances. Thus, a patient with allergic dermatitis is not dangerous to others, since allergic reactions are an individual thing.
Advice! But there is a genetic predisposition to the development of allergic diseases, so members of the same family (blood relatives) often get sick.
It is difficult to treat this skin disease; the only effective method is to eliminate the allergen. In this case, skin healing occurs within several days. Remission will continue until new contact with the allergen.
Contact
Contact dermatitis is very similar to allergic dermatitis. The difference between contact skin lesions is that the inflammatory reaction occurs when the allergen comes into direct contact with the skin. That is, the cause of contact dermatitis is synthetic clothing, underwear, as well as household chemicals and cosmetics.
It is impossible to become infected with contact dermatitis, because the disease is not infectious, so it cannot be transmitted even through close contact with the patient.
Atopic
Atopic dermatitis is often a complication of the allergic form of the disease if appropriate treatment is not carried out. However, the atopic variety of the disease can also be hereditary.
The first manifestations of hereditary atopic skin lesions are observed in infancy. But sometimes the disease proceeds secretly, without manifesting pronounced symptoms. The impetus for the development of an inflammatory reaction can be:
- hormonal fluctuations (during adolescence, pregnancy, etc.);
- long-term improper skin care;
- stress, nervous shock.
You should not assume that this is a contagious disease; it is not transmitted from person to person through communication and tactile contact. But dermatitis is inherited, so if parents have this disease, then there is a high probability that their child will develop it.
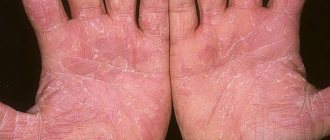
Seborrheic dermatitis is a disease that affects the sebaceous glands. Under the influence of saprophytic flora, the glands begin to work incorrectly, as pathogenic microorganisms change the composition of their secretions. There are dry and oily seborrhea, these forms differ in symptoms:
- Dry seborrhea is characterized by severe peeling and dry skin;
- oily seborrhea is manifested by increased secretion of sebum, which provokes the development of pustular rashes.
Since the disease is caused by pathogenic microflora, we can conclude that seborrheic dermatitis is contagious. However, it is not. Any specialist, when asked whether seborrheic dermatitis is contagious, will answer negatively.
The fact is that saprophytic flora is present on the skin of almost every person, but it does not cause negative changes. The skin and sebaceous glands begin to become inflamed only with uncontrolled proliferation of fungi, which can be triggered by stress, general illness, mechanical or chemical exposure.
Infectious
The types of dermatitis listed above are caused by internal causes, which means that the patient does not pose a threat to the people around him. The allergy will not be transmitted either through direct contact or through the use of shared things, so those around you do not have to worry about their health.
However, there are also infectious dermatitis, the cause of which is an infectious disease. To answer the question of how infectious dermatitis is transmitted, it is worth getting acquainted with its causes. The development of an inflammatory process on the skin can be provoked by:
- infectious diseases - measles, scarlet fever, chicken pox. The course of these diseases is accompanied by characteristic skin reactions. In this case, it is not the skin lesion that can be transmitted, but the infection that caused the disease;
- infection of wound surfaces with a secondary infection (most often staphylococcus or streptococcus). In this case, carbuncles, boils, and abscesses form on the surface of the skin. In this case, the disease can spread to another person through close contact only if the contactee has reduced immunity and has lesions on the skin;
- a disease caused by fungal microflora; the fungal infection itself is contagious, but the disease will develop only if a person has reduced immunity. In addition, a predisposing factor for the development of the disease is increased sweating and constant moisture of the skin.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious or not and how is it transmitted?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a harmless disease. It brings other problems, in particular, aesthetic and psychological ones. The rashes appear on the neck, face and scalp and are very noticeable.
People around perceive the external symptoms of seborrheic lesions with caution and often try to reduce contact with patients for fear of becoming infected.
Therefore, both the patient and the people around him are concerned about the question of whether seborrheic dermatitis is contagious or not.
Mechanism of development and symptoms
The disease is chronic and affects areas of the skin and scalp where the sebaceous glands actively work (usually the face and upper body). The exact mechanism of seborrheic type dermatitis has not yet been determined; existing assumptions require proof.
It is believed that the cause is the lipophilic (fat-eating) yeast-like fungus Malassezia, which is found on human skin and is not contagious. According to statistics, these fungi are found in the skin microflora of more than 78% of people. Settled around the sebaceous glands, they use the sebum secreted by the skin as food for their own development.
With normal skin condition and normal functioning of the sebaceous glands, the fungi are kept in an inactive state and do not cause harm to humans. But if the functioning of certain systems is disrupted, the lifestyle is incorrect, as well as some individual characteristics of the body, the fungi are activated, and the immune system ceases to limit their development.
As a result, increased work of the sebaceous gland begins, which is manifested by rashes, peeling, and dandruff (if it is the hairy part). When the microflora is disturbed, the vital activity of fungi is activated. By processing sebum, they release components that irritate the skin.
Internal factors leading to activation of fungi:
- frequent and severe stress;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems, the digestive tract;
- HIV;
- weakening of the immune system.
External factors:
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating);
- folds on the skin due to excess weight;
- increased sebum production (therefore, people with oily skin have a greater risk of developing the disease).
The disease can also develop under the influence of external irritants (acid, alkali from detergents), and alcohol consumption.
The human body can control the growth of fungi. However, due to weakened immune defenses, frequent stressful situations, endocrine disorders, and nervous diseases, this natural ability is lost. Yeast-like fungi begin to grow and multiply.
The symptoms are:
- Peeling of the skin and dandruff.
- Inflammation with itching.
- The rash is pink and noticeably different in color from normal skin. The lesions are usually large and merge with each other. If symptoms appear behind the ears, on the chest or between the shoulder blades, the spots may be separate, round in shape, and small in size.
- Formation of a greasy seborrheic crust, which is easily removed. In severe cases of dermatitis, pus may accumulate under the crust.
Since the patient scratches the itchy areas, dermatitis can be complemented by another infectious disease that penetrates through the scratched wounds.
Is seborrheic dermatitis contagious?
The main question for others is: is this disease transmitted from person to person? In short: no, it is not transferable. Most people have this fungus on their skin in a healthy state, that is, theoretically, almost all of us can get sick anyway.
The cause of dermatitis is abnormalities in the functioning of the immune system and the hormonal system, so the disease is not transmitted through contact from person to person through any transmission route (airborne, through touch, through clothing, sexual contact).
If your own health is in order, you will not become infected even if you touch the affected area of a sick person. If you have any disorders and your skin is prone to excessive oiliness, seborrheic dermatitis may develop, even if you have never seen anyone with this disease.
The only amendment: if the patient has some additional infectious disease, for example, a staphylococcal infection, others can become infected with it through blood from scratched wounds.
Similar but contagious diseases
Many dermatological diseases manifest themselves with symptoms that can easily be confused with seborrheic dermatitis. This is why people fear for their health if they see patients with problem skin (rashes, redness, peeling). An ordinary person cannot recognize at first glance whether a disease is contagious or not.
In terms of symptoms, the following infectious diseases are similar to seborrheic (oily and dry) dermatitis:
- Scabies. The skin becomes covered in rashes, peels, and is very itchy. The rashes look different in appearance - brighter in color, small and frequent.
- Tinea versicolor. Rashes are localized not only where the sebaceous glands are actively working. The rash comes in different shades and can spread over a large area.
- Dermatomycosis. The disease also occurs due to fungi, but is contagious. The rashes are round in shape and large in size, so they can be distinguished visually from the seborrheic type of dermatitis. The disease is highly contagious, so patients diagnosed with infectious dermatomycosis need to observe hygiene measures so as not to spread the infection.
Reasonable prevention measures
To prevent dermatitis, you need to properly and regularly take care of yourself. Rules and recommendations:
- Using products to care for oily skin. Skin prone to excessive sebum production requires special cosmetics. Not every remedy is suitable for it. They should be used on an ongoing basis (if sebum is secreted constantly, regardless of the weather) or during periods of heavy secretion (in summer, winter under warm clothes).
- Dieting. You should avoid foods with a lot of glucose (sweets, confectionery, baked goods), fatty foods, and fried foods. If there are any problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you need to follow a diet appropriate for your illness.
- Regular change of bed and underwear.
- Avoiding stress and moral overload.
- Timely treatment of problems with the immune system, gastrointestinal tract, central nervous system.
- Prevention of obesity, and if you are overweight, regular hygiene and careful care of the areas in the folds.
- If the scalp is oily, choose a suitable shampoo (it is recommended to seek the help of a trichologist or dermatologist) or a short haircut.
All people with oily skin and intensively working sebaceous glands need to adhere to preventive measures. Teenagers are most susceptible to the seborrheic type of skin inflammation. During adolescence, the sebaceous glands function more actively than in a healthy adult. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the number of hygiene procedures.
You may also like
Source: https://tden.ru/health/seborejnyj-zarazen-ili-net
Prevention measures
How can you prevent contracting an infectious variant of the disease? The main rule is careful personal hygiene. Necessary:
- use personal hygiene items, do not use other people’s combs, towels, etc.;
- Try to strengthen your immune system by leading the healthiest lifestyle possible.
An effective measure to prevent the development of infectious diseases accompanied by inflammatory processes in the skin (measles, chickenpox, etc.) is timely vaccination.
It is impossible to protect against the development of allergic or atopic dermatitis, but patients can take measures to prevent relapses of the disease. To do this, you need to avoid contact with allergens and strengthen the body. For allergic and seborrheic dermatitis, an important role in preventing relapse is played by a diet that excludes sweets, fatty foods, and foods that provoke allergic reactions.
Many people have to deal with a disease such as dermatitis: is this skin disease contagious or not? Patients with this skin disease, in most cases, are not dangerous to the people around them, since the disease develops due to an inadequate response of the immune system or other internal reasons.
Causes of dermatitis
Inflammation of the skin (or dermatitis) raises a natural question among others - whether it is contagious or not. Dermatitis is a term used to describe various skin disorders that cause inflammation and red, itchy rashes.
The condition is not life-threatening and is not transmitted from one person to another, although it may have a family history.

Are infectious agents found as the root cause of dermatitis? Let's look at this using the example of several forms of the disease. Theoretically, seborrheic dermatitis could be suspected of being contagious, because it actively multiplies the fungus Malassezia furfur.
But this fungus is not an infectious agent, as it is found on the skin of absolutely healthy people. Several reasons lead to its rapid growth.
This includes hormonal dysfunction of the body caused by improper functioning of the endocrine system, and problems and malfunctions in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
The development of the disease is also facilitated by a weakened immune system, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, stress and medication.
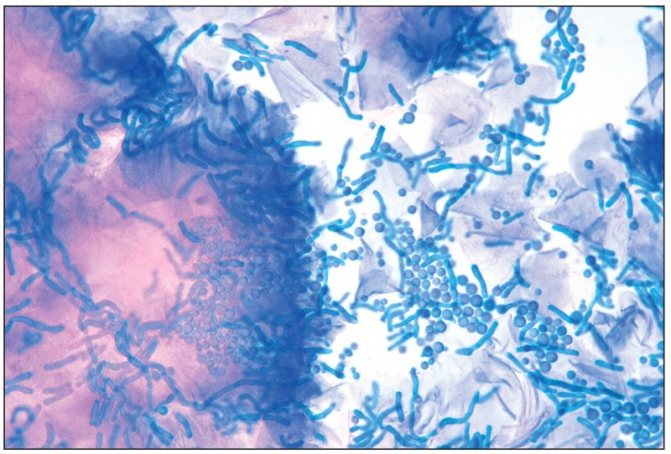
The fungus Malassezia furfur actively reproduces in seborrheic dermatitis, but is not contagious, because is present in absolutely all people
The allergic form of dermatitis is more common in people suffering from various forms of allergies. There is no bacterial or fungal nature of the pathogen here at all.
Allergen in the form of pollen, animal hair, etc. is the cause of this type of disease. And, yes, you can “get infected” with it through direct contact with the allergen.
But only if an allergic person comes into contact with the allergen. There is absolutely no chance of getting infected from another person.