Negative immune reactions in children and adults with hypersensitivity of the body develop against the background of the influence of natural factors, drugs, food, and household irritants. When the immune response is abnormal, ordinary substances act as “aggressors.”
It is important to know the types of allergens. Classification is carried out according to several parameters. If you are prone to allergic reactions, knowledge will be useful to adult patients and parents who regularly encounter manifestations of urticaria, itchy dermatoses, and atopic dermatitis in children. For convenience, many data are presented in the form of tables and lists.
Individual allergens and their classification
Allergens are usually called things that cause an excessive reaction in our body. The list of allergens is very diverse, but it can still be classified into two main groups - exogenous and endogenous.
Exogenous are those allergens that enter the body from the external environment. They can be infectious (fungi, viruses, bacteria, waste products of microorganisms) and non-infectious (house dust, pollen, animal hair, food, certain medications, various chemical compounds).
Endogenous allergens (another name for them are autoallergens) include those that are produced directly by the human body.
Another classification involves dividing allergens into the following types:
- Biological.
Such individual allergens are essentially products of decay or metabolism of biological organisms - bacteria, viruses, helminths, insect poisons, fungi. Allergies can also be caused by vaccines that contain live or weakened microorganisms.
- Food.
Currently, chemical additives are widely added to food products, because of this, the group of food allergens is becoming more diverse and extensive. Foods that most often cause allergies include strawberries, citrus fruits, cow's milk, chocolate, nuts, wheat flour, eggs, seafood and fish. A person suffering from one type of allergy becomes more sensitive to other allergens and has a high risk of developing so-called cross-allergy.
- Industrial.
This type includes allergens that are produced industrially - household chemicals, dyes, reagents, mineral oils, various metals, fertilizers, insect killers. Laundry detergent, perfume, dye or hairspray are highly likely to cause allergies.
- Pollenaceae.
The name of this type of plant allergens speaks for itself. Often allergies are caused by pollen from weeds (ragweed, wormwood, quinoa, nettle), as well as trees during the flowering period (such as birch, hazel, alder, pine, willow, spruce).
- Household.
The most common household individual allergen that can attack a person all year round is house dust, which contains various fungi, waste products and remains of dust mites, hair, dandruff, pet fur, etc.
- Medicinal.
Allergic reactions are often caused by medications. About 18–20% of such cases are associated with the use of novocaine, as well as antibiotics (the most allergic are penicillins of the 1st and 2nd generation). In 7–9% of cases, allergies occur after consuming sulfonamides, vitamins (especially group B), and aspirin.
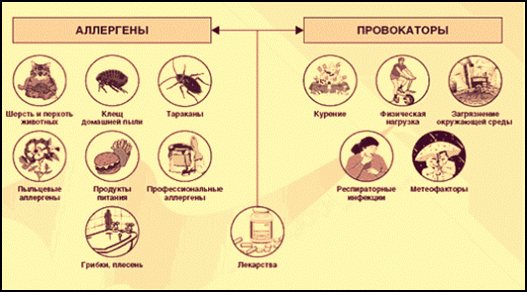
It is worth considering that, in addition to the allergens themselves, there are also provoking factors, which are illustrated in the figure:
The mechanisms of development of allergic reactions can be classified into the following types:
Type 1 - anaphylactic, immediate, reagin - is associated with the fact that reagin antibodies are formed in the body, which are associated with the presence of IgE . Reactions of this type, which are characteristic, for example, of non-infectious atopic allergies, are most common among children. On the surface of the cells, the allergen and reagin react, causing the release of biologically active substances - the slow-acting substance of anaphylaxis, histamine, etc. The nature of the allergic disease is determined precisely by how these substances affect tissues and organs.
Type 2 – cytotoxic, cytolytic – is observed in immune forms of blood diseases. Reactions of this type take place with the participation of IgE and IgM , as well as cell membranes. The cause of cell destruction is the interaction of antibodies and allergens.
Type 3 - immunocomplex, semi-delayed - is associated primarily with the formation of precipitating antibodies, which belong to the IgG class (IgG4) . Such reactions lead to the formation of immune complexes that cause damage to blood vessels.
Type 4 – cellular, delayed – is most often observed in infectious allergies. During the reactions, sensitized lymphocytes are formed, which, like antibodies, selectively damage tissue.
IgE is a dependent reaction that forms within minutes of contact with an allergen. IgG (IgG4) is a dependent reaction that manifests itself several hours, and sometimes even days after contact with an allergen, and is most characteristic of food allergies.
Recommended articles on the topic:
- Thermal detoxification: lightness of the body and clear skin
- Lipolytic therapy: indications, contraindications, stages of the procedure
- Weight correction: everything you need to know about the procedure
Types of irritants for cross allergies
With increased sensitization of the body, it is important to know what foods cannot be eaten if you are intolerant to citrus fruits or milk protein. A table of cross allergens will help you eliminate dangerous items from your diet and create a healthy and safe menu.
| Confirmed allergy to a certain type of irritant (leading allergen) | High risk of developing allergies to the following items |
| Wheat | Barley, rye, oats |
| Peach | Cherry, plum, apple |
| Walnuts | Hazelnuts, cashews, peanuts |
| Cow's milk | Goat milk, beef, veal, enzyme preparations using products from the pancreas of cattle |
| Latex | Avocado, bananas, kiwi |
| Shrimps | Lobster, crab, octopus, lobster |
| Kefir or kefir yeast | Blue cheese, natural kvass, mold mushrooms, yeast dough, penicillins, various types of mushrooms |
| Pollen of wormwood, birch | Peaches, melons, apples, cherries, potatoes, birch sap |
| Ambrosia pollen | Sunflower seeds, halva, refined and unrefined sunflower oil, bananas |
| Sea and river fish | Dry food for fish, any seafood |
| Potato | All plants from the nightshade family: peppers, eggplants, tomatoes |
Diagnosis of individual allergens
Today, using a comprehensive assessment of IgG-dependent food allergies, you can evaluate your own body’s reaction to 88, 90 and 190 foods and identify which of them are your individual allergens. The answer in the study results can be low, medium or high.
Having become the owner of a document confirming the presence of specific antibodies to certain food allergens, the patient should completely stop consuming them for a long period of time (from 3 months to six months). Subject to strict adherence to the diet, the concentration of allergen-specific immunoglobulins decreases, as a result of which the test gradually becomes negative.
In 70% of cases, eliminating individual allergens from the diet allows you to achieve a positive clinical effect, significantly improve the patient’s condition, or completely recover from the disease.
For many patients who have suffered from unexplained pain for a long time, testing for an individual IgG-dependent allergen becomes a real salvation. To achieve lasting improvement, it is necessary to exclude individual allergens from the diet for 3-6 months. After this, thanks to the elimination of toxic immune complexes, most patients consume foods that were previously dangerous every 3-4 days without any harm to health.
An elimination diet can also help you lose excess weight. Reviews from many patients indicate not only weight correction, but also an improvement in the condition of the body as a whole.
The level of identification of food allergens by determining specific IgG and IgE is 90% higher than by provocative testing. Conversely, if information on specific immunoglobulins and skin test results are combined, the number of identified allergens will not increase. To confidently talk about the presence of an allergy, it is necessary to conduct a series of tests for immediate and delayed hypersensitivity.
But there are also special cases of a severe reaction of the body to the influence of an individual allergen, when the patient should adhere to a diet even with negative results of repeated tests.
Allergy tests:
- A skin test performed on the back or forearm. The analysis is inexpensive, quick and painless, which makes it popular among patients. At the same time, in parallel with the skin test, due to its insufficient information content, a blood test is often performed. Having marked the required areas of the skin, the medical professional applies the allergen to them using injections, test strips or micro-scratches.
- A blood test for antibodies (immunoglobulins), which not only detects allergies, but also identifies the allergen. This test is expensive, but at the same time highly informative. A special panel of individual allergens includes a huge variety of probable allergy triggers.
- A blood test for eosinophils, which serve as indicators of an allergic reaction. In a healthy body that does not suffer from allergies, their level is 1–5% of all blood cells. If this figure exceeds 5%, there is a disorder of the immune system that provokes an allergic reaction. An additional analysis for immunoglobulins will allow us to make an unambiguous conclusion that it was allergies that caused the increase in the level of eosinophils in the blood.
- Provocative tests are used exclusively in cases where other tests have failed. The type of provocative test is determined by the allergic reaction that worries the patient. For conjunctivitis, an individual allergen is injected into the lacrimal gland, and for rhinitis - into the sinuses. The procedure is carried out only in the presence of a doctor in a hospital setting, because even a minimal amount of allergen can cause a severe reaction, which only medical workers can stop.
Read material on the topic: Lightening age spots
What types of allergy panels exist?
Respiratory allergies are a common disease in adults and children. Negative reactions are caused by various types of irritants. For successful therapy, it is important to know which substance is dangerous for a particular patient.
The respiratory allergen panel is a special set of volatile irritants, against the background of which signs of allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, hay fever, bronchial asthma, and urticaria most often appear. The result of testing using the immunoblotting method gives an accurate answer about the type and quantity of antibodies to a specific allergen.
Sources
- https://allergiinet.com/articles/vidy-allergenov.html
- https://allergiinet.com/articles/respiratornaya-panel-allergenov.html
- https://allergii.info/sovety/allergiya-panel-2.html
- https://KardioBit.ru/allergiya/vidy-allergenov-i-ih-klassifikatsiya
Interpretation of tests for individual allergens
Analysis for an individual allergen is an effective diagnostic method that allows you to identify the cause of the disease and begin treatment. It is important to correctly decipher the test results, so this work should be performed by a specialist. When performing skin tests, an allergy is indicated by swelling of the test site, as well as its redness within a radius of more than 3 mm.
With blood tests for individual allergens, not everything is so simple. To interpret the results, an allergen panel is used, in which classes (0, 1, 2, etc.) and groups (respiratory, food, pediatric, etc.) are identified. In each class, a separate result is provided for each indicator:
- there is no allergy - if less than 0.35 antibodies are detected in the blood (class 0);
- there is a possibility of an allergic reaction, but in most cases it is mild, - 0.35–0.7 antibodies in the blood (class 1);
- mild allergic reaction - up to 3.5 antibodies (class 2);
- allergy symptoms are clearly expressed - up to 17.5 antibodies (class 3);
- obvious allergy – up to 50 antibodies (class 4);
- severe manifestations of allergies, likelihood of asthma, shortness of breath, angioedema - up to 100 antibodies (class 5);
- an allergic reaction that is life-threatening without proper medical care - more than 100 antibodies (class 6).
There are four panels of individual allergens, each with different subgroups:
- Mixed (mites, egg whites, pollen, food products, animal hair) - it includes individual allergens that cause a strong reaction more often than others.
- Food. This panel includes foods that can cause an allergic reaction - rash, bloating, cough, etc. (nuts, egg whites, milk and dairy products, fish, vegetables and fruits, especially citrus fruits, as well as the individual food allergen coffee IgE).
- Respiratory – includes individual allergens, when inhaled, an allergic reaction may occur (swelling, shortness of breath, cough, runny nose). First of all, this is plant pollen, mites, animal hair (analysis for individual cat allergen is very popular today).
- Pediatric. This panel includes individual allergens that cause a reaction mainly in young children: mites, plants and their pollen, some foods, milk and lactose.
Of particular danger are allergic reactions that occur in a child and cause swelling of the larynx. If a reaction occurs periodically under the influence of individual allergens, you should consult an allergist and undergo the necessary tests.
Read the material on the topic: Body detoxification program
TESTS
The range of indicators for which tests are carried out depends on the form of release of the drugs (lyophilisates, solutions, suspensions, tablets).
Description
A description of the corresponding dosage form of the drug is provided. The test is carried out visually.
Authenticity
Specific allergenic components must be found in allergens and allergoids. Tests are carried out according to the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Determination of the authenticity of allergen preparations” or any suitable method set out in the regulatory documentation.
Transparency
Transparency (for solutions). Transparent or slightly opalescent solution. The determination is carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Transparency and degree of turbidity of liquids” using comparison standards, as specified in the regulatory documentation.
pH
pH (for solutions and suspensions). The permissible pH value for allergens is from 6.5 to 7.3, allergoids - from 7.3 to 7.7, unless other requirements are specified in the regulatory documentation. The test is carried out using the potentiometric method in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Ionometry”.
Mechanical inclusions
Mechanical inclusions (for solutions and suspensions). Visible mechanical inclusions must comply with the requirements of the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Visible mechanical inclusions in dosage forms for parenteral use and ophthalmic dosage forms.”
Particle size
Particle size (for suspensions). Regulatory requirements are indicated in the pharmacopoeial monograph and regulatory documentation. Tests are carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Injectable dosage forms. Medicines for parenteral use."
Disintegration
Disintegration (for tablets). No more than 2 minutes. The determination is carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Disintegration of tablets and capsules.”
Sedimentation stability time
Sedimentation stability time (for suspensions). Regulatory requirements are specified in the pharmacopoeial monograph and regulatory documentation. Tests are carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Injectable dosage forms. Medicines for parenteral use."
Recoverable volume
Extractable volume (for solutions, suspensions). Must be no less than nominal. The determination is carried out according to the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Extractable volume of dosage forms for parenteral use.”
Water
Water (for lyophilisates and tablets). No more than 5%. Tests are carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Determination of Water” by the K. Fischer titration method or by the gravimetric method in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Determination of weight loss on drying”.
Total protein
Total protein (for drugs standardized in units of biological activity). Regulatory requirements are specified in the regulatory documentation. Tests are carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Determination of Protein”.
Protein nitrogen
Protein nitrogen (for drugs standardized in PNU units) – from 3000 to 12500 PNU. The determination is carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Determination of Protein” by the Kjeldahl method or the colorimetric method with Nessler’s reagent.
Sterility
Sterility (for injection forms) . Medicines must be sterile. The determination is carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Sterility” using direct seeding or membrane filtration methods.
Microbiological purity
Microbiological purity (for oral and sublingual forms) – category 3A. The determination is carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Microbiological Purity”.
Abnormal toxicity
Abnormal toxicity (injection solutions) . Medicines must be non-toxic . The determination is carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Abnormal toxicity”. Indicate test doses, method of administration and observation time for animals, their type and weight.
Specific/allergenic activity
Specific activity, residual allergenicity (in vivo tests). The determination is carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Determination of the specific activity of allergen preparations by skin testing”.
Allergenic activity (in vitro tests) – 50 – 150% of the specified amount. The allergenic activity of drugs is determined using CO using competitive immunoassay methods using specific sera containing IgE antibodies.
Phenol
(for allergens). From 2.0 to 4.0 mg/ml. The determination is carried out according to the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Quantitative determination of phenol by the spectrophotometric method in immunobiological medicinal products.”
Formaldehyde
(for allergoids). Not more than 0.14 mg/ml. The determination is carried out according to the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Quantitative determination of formaldehyde in immunobiological medicinal products.”
Glycerol
(for oral and sublingual drugs) – from 40 to 60%. The determination is carried out by the method set out in the pharmacopoeial monograph or regulatory documentation.
Aluminum
(for suspensions). From 80 to 120% of the specified amount. The determination is carried out in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Determination of aluminum ions in sorbed immunobiological medicinal products.”
Calcium
(for suspensions) From 80 to 120% of the specified amount. The determination is carried out by any suitable method specified in the pharmacopoeial monograph or regulatory documentation.
Specific and individual allergens IgE and IgG
The cause of allergic reactions is the impact on the human body and its defenses of individual allergens. Experts identify several types of allergens, for the determination of which appropriate conditions must be created.
Allergens IgG
Substances of this type are the cause of food intolerance, that is, a delayed allergic reaction, which about 20% of the world's population experiences from time to time. A reaction can occur several hours, and sometimes even days, after consuming a particular product. In this case, it becomes much more difficult to determine the substance that provoked the body’s negative response.
Allergens IgE
Acute IgE food allergy periodically affects 2–3% of the world's population. In this case, any food products can act as individual allergens. The reaction often develops very quickly - within 5-15 minutes from the moment the aggressive substance enters the body. The most dangerous manifestations of food allergies are anaphylaxis and choking.
Individual IgG allergens
Research to determine individual allergens must be comprehensive. If the test shows that the patient's IgE level is within the normal range, an IgG test should be performed. Factors that need to be taken into account are:
- seasonality of manifestations;
- region of residence;
- type of individual allergen;
- patient's age.
The cause of any chronic disease can be precisely the increased content of the IgG allergen. Do not forget that an allergic reaction to the smell of food often manifests itself in the form of a cough.
Read material on the topic: How to choose a diet: correctly and effectively
Causes
The causes of the disease are not fully understood to date.
Each person is individual, so allergens can be very different. True, there are several generally accepted reasons why the problem occurs. The main development factors include a person’s genetic predisposition. The most common causative agent for the development of pathology is dust mites.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
We are talking about the insects themselves, as well as the products of their vital activity. In addition, there are other causes, such as components of household cleaning chemicals and clothing, mold and its spores.
What is the difference between IgG and IgE allergens?
The main difference lies in the clinical picture of the disease, namely how quickly its symptoms appear after consuming an individual allergen. An increased level of IgG allergen is a sign of food intolerance, the manifestations of which become noticeable only after a certain period of time (from several hours to 2-3 days). The symptoms in this case are not acute and do not pose a threat to human life, including indigestion or stool disorder, rash.
If the content of an individual allergen is high, reactions of types 2, 3 and 4 may occur. Skin tests, unlike IgE allergen tests, indicate a negative result. An allergic reaction can be caused not only by consuming a product in large quantities, but also by mixing various substances.
The IgE allergen leads to the rapid occurrence of acute reactions that are life-threatening in the skin or respiratory system:
- hives;
- swelling of the mucous membranes of the mouth and larynx;
- asthma attacks;
- dyspnea;
- Quincke's edema;
- anaphylactic shock.
The reaction occurs after consuming a minimal amount of a dangerous product, and the results of skin tests are positive.
If you have a question about the need to conduct an analysis for individual allergens, the specialists of the Veronica Herba City Beauty and Health Center will help you in the shortest possible time.
At the Center, highly qualified professionals are at your service, ready to tell you everything you need to know about individual allergens. They will also help you create an algorithm for an individual course of combating allergic reactions.
There are two such centers in Moscow – near Timiryazevskaya metro station and Otradnoye metro station.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba Beauty and Health Center:
- This is a beauty center where you can diagnose your body for individual allergens at a reasonable cost, and you will be treated not by an ordinary specialist, but by one of the best dermatologists in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone 8 (495) 995-15-13
, and you will see for yourself!
Household chemicals

Cold allergy
Substances contained in laundry detergents, dish and bath detergents, paints and varnishes are fairly common allergens. Shampoos, soaps and even toothpastes can also cause an unpleasant reaction. In such cases, it is recommended to minimize the use of household chemicals, replacing them with simpler substances - baking soda, vinegar (allergies to them are very rare).
It is advisable to give preference to liquid products over powders; when cleaning and washing, use protection - face masks, rubber gloves. Allergies to cosmetics fall into this same area.
Latex
Natural latex, obtained from Hevea juice, quite often causes unpleasant reactions. The most dangerous items in this case are condoms and surgical gloves. There are cases when a person had an acute allergic reaction during an operation, as soon as the doctor touched the body with hands protected by gloves.
In medicine, many unique and, fortunately, rare forms of allergies have been recorded - to silver and gold jewelry, kisses (more precisely to the partner’s saliva) and sex (again, the reason is sweat, saliva and sperm), electromagnetic radiation from household appliances and mobile phones.
In most cases, exotic forms of allergies are associated not with physical, but with psychological factors, and not so much allergists as psychotherapists and neurologists help in their treatment.