Doctors often prescribe Prednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis, especially when severe symptoms and aggressive inflammation develop. With the development of additional autoimmune effects, the medicine becomes the No. 1 assistant, which can significantly make the patient’s life easier.
In most cases, patients take the drug in tablet form, but in particularly severe situations, doctors prescribe injections. The drug Prednisolone is widely used in the treatment of various arthritis, but it has some limitations and side effects that can become critical for certain groups of people. The medicine is especially dangerous for those who suffer from liver and kidney pathologies.
Description of substances and actions
The composition of Prednisolone contains synthetic hormones - replicas of cortisone and its derivative. In the human body, with rheumatoid arthritis, there is no significant change in the production of hormones, but increased dosages help relieve all the symptoms of the pathology.
The correct doses of Prednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis help relieve inflammation, remove harmful substances, and prevent shock and allergic reactions. However, with long-term use, disruption of the kidneys, liver and other massive side effects is possible.
Unpleasant symptoms appear after taking the medicine, even if the doctor prescribes a limited dosage.
Tablets and injections are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis during exacerbation, as well as in cases of severe forms of the disease. The drug is used to eliminate complicated types of pathology (vasculitis, for example).
A doctor should prescribe Prednisolone injections or tablets, since despite all its effectiveness, this substance often leads to severe side effects.
pharmachologic effect
The medicine Prednisolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid, a dehydrogenated analogue of hydrocortisone. It has anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, desensitizing, antishock, antitoxic and immunosuppressive, antipruritic and antiexudative effects.
Interacting with specific cytoplasmic receptors, prednisolone forms a complex that penetrates the cell nucleus, stimulates the synthesis of messenger RNA (ribonucleic acid), inducing the biosynthesis of proteins (including lipocortin) that mediate cellular effects.
By inhibiting the enzyme phospholipase A2, lipocortin suppresses the release of arachidonic acid, as well as the synthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which contribute to inflammatory, allergic and other pathological processes.
Prednisolone inhibits the release of β-lipotropin by the pituitary gland, but does not reduce the concentration of circulating β-endorphin, suppresses the secretion of THT (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), increases the excitability of the central nervous system (central nervous system), reduces the number of lymphocytes, eosinophils, increases the number of blood cells , stimulating the production of erythropoietins.
Prednisolone ointment, when applied externally, has an anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antipruritic and antiexudative effect; inhibits the formation of arachidonic acid, the formation and release of inflammatory mediators (prostaglandins, histamine, lysosomal enzymes, leukotrienes, etc.); suppresses inflammatory skin reactions, reduces vasodilation and increased vascular permeability at the site of inflammation.
The effect of Prednisolone on arthritis
The glucocorticosteroid drug has several powerful effects, which is why it is prescribed for the treatment of arthritis:
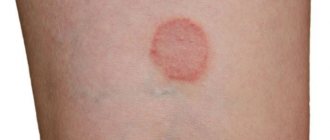
- almost completely eliminates swelling and inflammation during periods of exacerbation , prevents their progression for a long time;
- slows down the development of the disease , with early treatment it promotes regression of the disease (complete cure of arthritis is impossible);
- normalizes joint mobility - temporarily, for up to 6 months after the course;
- completely blocks or significantly limits autoimmune processes caused by arthritis;
- almost completely eliminates pain in the joints;
- increases the effectiveness of other anti-inflammatory drugs , including traditional recipes;
- slows down the process of joint destruction.
The effectiveness of therapy is maximum if the patient does not abuse the drug. Incorrect use “when necessary”, violation of courses lead to the formation of insensitivity of the body to therapy.
This medicine has a persistent effect, is chemically synthesized and is prescribed only by the attending physician. In this case, self-medication is not acceptable.
Prednisolone dosage regimen: dose
A particularly important role in treatment with Prednisolone is played by strict adherence to doses and the number of tablets per day. Doses are determined purely individually based on the weight and age of the patient, as well as the course of the disease and general health. Based on the fact that the release of glucocorticosteroid substances occurs cyclically, Prednisolone is recommended to be taken during the period of active wakefulness - from 6 am to 8 pm.
Read: Eufillin for bronchial asthma during exacerbation of bronchial asthma can be taken in a dose of up to 6 tablets per day. However, this dose of medication should not be taken for too long (the maximum period of administration is 10 days). It is necessary to gradually reduce the dose to 2 tablets per day. At the same time, American medical experts believe that greater results from the use of Prednisolone will be obtained if taken in the middle of the day (13:00 - 15:00), when bronchopulmonary lavage fluid is more effectively suppressed.
IMPORTANT! If bronchial asthma is accompanied by diseases associated with poor patency of the renal canals or inflammatory processes in the joints, then the dose of Prednisolone should be increased at the discretion of the attending physician.
Upon completion of the course of therapy, which can last from several weeks to several years, the dose should be reduced as much as possible. However, it is worth remembering that abruptly stopping taking the pills is fraught with exacerbation of bronchial asthma, as well as failure of the adrenal glands.
Treatment of bronchial asthma with this drug should be carried out under the supervision of an ophthalmologist. It is also necessary to constantly monitor blood pressure, the level of electrolytes in the blood and water in the body. Periodically it is necessary to take a sugar test. After all, Prednisolone tablets are not recommended for diabetics, and if they are used, then only under the supervision of a specialist.
To reduce side effects from taking it, doctors introduce medications that contain male hormones into the course of treatment. To avoid problems with the heart, taking the medication is often combined with taking pharmaceutical potassium and food that contains this trace element. It is worth noting that its use in conjunction with anticoagulants activates the effect of the latter on the body.
It is very important for a particular patient to adhere to the special instructions given to him by the doctor regarding the intake, process, dosages and completion of the course of treatment. Without this drug, treatment of bronchial asthma may not be as successful, but you should not resort to independent use. Even after a medical prescription, you must carefully study the instructions for use so as not to further harm your own health.
Indications for use of Prednisolone
Taking Prednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis is indicated if processes intensify or autoimmune reactions appear:
- painful sensations increase greatly, up to loss of performance;
- inflammatory processes accelerate, covering more tissues of the joint and muscles next to it;
- the risk of autoimmune reactions increases;
- the formation of complications with the threat of the formation of dangerous pathologies of a systemic nature (organ vasculitis);
- the process of joint destruction accelerates, or all the symptoms of the disease intensify;
- serious disabilities up to and including disability, partial or complete immobility of joints;
- long-term use of NSAIDs and the need to replace them with other medications.
For you: First aid for exacerbation of rheumatoid arthritis
But there are situations when taking Prednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis is completely contraindicated.
Prohibition on the use of the drug
Before taking Prednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis, you need to make sure there are no contraindications and also assess the possible risks. If contraindications are not observed, organ diseases that can be fatal may develop:
- the drug is prohibited for severe hypertension;
- You can’t take pills if you have diabetes;
- prohibited during pregnancy;
- do not take medicine for Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- inflammation of the kidneys and inner walls of the heart is a direct contraindication;
- You should not take pills for psychosis and mental disorders;
- Therapy is prohibited for circulatory deficiency of the 3rd degree;
- you cannot take pills over the age of 80;
- stomach and intestinal ulcers – a complete ban on taking the drug;
- syphilis and tuberculosis;
- internal operations.
It is prohibited to take Prednisolone if a person has increased aggressiveness and excitability.
Rules for the use of tablets and injections
The doctor prescribes a regimen for taking Prednisolone for rheumatoid arthritis:
- low doses - from 5 to 15 mg per day;
- average – from 20 to 40 mg per day;
- high – from 50 to 60 or more;
- pulse therapy – 1000 mg per day for a maximum of 3 days.
The very next day after the first use of the product, a sharp reduction in symptoms is observed. When injections are administered, relief from an acute attack occurs within 3-5 hours.
If the dosage is reduced quickly, withdrawal symptoms may occur.
With withdrawal syndrome, the symptoms of the pathology sometimes intensify, up to severe stiffness and arthralgia.
Taking low doses
An amount of up to 15 mg per day is prescribed to eliminate inflammation; therapy using non-steroidal drugs is comparable. Minimal toxicity protects against severe side effects. If you take the drug 7.5 mg per day, then within 2 years the rate of disease progression is noticeably reduced.
When starting treatment, the drug is taken 2-3 times a day, then you can take the tablets once in the morning. The duration of the course directly depends on the severity of symptoms, sometimes lasting several months.
If you take the drug at 1-2 am, then in the morning the painful sensation is reduced and the stiffness of the joints is reduced.
Application of pulse therapy
The maximum doses of Prednisolone are prescribed during exacerbation of the disease. They are administered intravenously when diluted in 150 ml of isotonic solution over 40 minutes. Such treatment guarantees active deposition of the drug in the organs and brain.
When using pulse therapy, even in such small courses, severe side effects may develop: hypertension, osteoporosis, problems with the adrenal glands. Reception is carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
The prescription of loading doses of the drug must be strictly justified, but it is impossible to regularly resort to therapy in this way.
Prednisolone analogues
pharmachologic effect
GKS. Suppresses the functions of leukocytes and tissue macrophages. Limits the migration of leukocytes to the area of inflammation. It disrupts the ability of macrophages to phagocytose, as well as to form interleukin-1. Helps stabilize lysosomal membranes, thereby reducing the concentration of proteolytic enzymes in the area of inflammation.
Reduces capillary permeability due to the release of histamine. Suppresses fibroblast activity and collagen formation. Inhibits the activity of phospholipase A2, which leads to suppression of the synthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Suppresses the release of COX (mainly COX-2), which also helps to reduce the production of prostaglandins.
Reduces the number of circulating lymphocytes (T- and B-cells), monocytes, eosinophils and basophils due to their movement from the vascular bed into the lymphoid tissue; suppresses the formation of antibodies. Prednisolone suppresses the release of ACTH and beta-lipotropin by the pituitary gland, but does not reduce the level of circulating beta-endorphin. Inhibits the secretion of TSH and FSH.
When directly applied to blood vessels, it has a vasoconstrictor effect. Prednisolone has a pronounced dose-dependent effect on the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Stimulates gluconeogenesis, promotes the uptake of amino acids by the liver and kidneys and increases the activity of gluconeogenesis enzymes.
In the liver, prednisolone enhances the deposition of glycogen, stimulating the activity of glycogen synthetase and the synthesis of glucose from protein metabolism products. An increase in blood glucose levels activates the release of insulin. Prednisolone inhibits the uptake of glucose into fat cells, which leads to activation of lipolysis.
However, due to increased insulin secretion, lipogenesis is stimulated, which promotes fat accumulation. It has a catabolic effect in lymphoid and connective tissue, muscles, adipose tissue, skin, bone tissue.
To a lesser extent than hydrocortisone, it affects the processes of water-electrolyte metabolism: it promotes the excretion of potassium and calcium ions, the retention of sodium and water ions in the body. Osteoporosis and Itsenko-Cushing syndrome are the main factors limiting long-term GCS therapy. As a result of the catabolic effect, growth suppression in children is possible.
In high doses, prednisolone can increase the excitability of brain tissue and help lower the seizure threshold. Stimulates excess production of hydrochloric acid and pepsin in the stomach, which leads to the development of peptic ulcers.
When used systemically, the therapeutic activity of prednisolone is due to its anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, immunosuppressive and antiproliferative effects. When applied externally and locally, the therapeutic activity of prednisolone is due to its anti-inflammatory, antiallergic and antiexudative (due to the vasoconstrictor effect) effect.
Compared with hydrocortisone, the anti-inflammatory activity of prednisolone is 4 times greater, mineralocorticoid activity is 0.6 times less.
Pharmacokinetics
When taken orally, it is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum plasma concentration is observed after 90 minutes. In plasma, most of the prednisolone is bound to transcortin (cortisol-binding globulin). Metabolized primarily in the liver. The half-life is approximately 200 minutes. Excreted unchanged by the kidneys - 20%.
Indications
For oral and intramuscular use: rheumatism; rheumatoid arthritis; dermatomyositis; periarteritis nodosa; scleroderma; Bekhterev's disease; bronchial asthma, status asthmaticus; acute and chronic allergic diseases; Addison's disease, acute adrenal insufficiency, adrenogenital syndrome; hepatitis, hepatic coma, hypoglycemic conditions, lipoid nephrosis; agranulocytosis, various forms of leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic anemia; chorea; pemphigus, eczema, itching, exfoliative dermatitis, psoriasis, prurigo, eczema, seborrheic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, erythroderma, psoriasis, alopecia. For use in ophthalmology: allergic, chronic and atypical conjunctivitis and blepharitis; inflammation of the cornea with intact mucosa; acute and chronic inflammation of the anterior segment of the choroid, sclera and episclera; sympathetic inflammation of the eyeball; after injuries and operations with prolonged irritation of the eyeballs. For intra-articular administration: chronic polyarthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, osteoarthritis of large joints, rheumatic lesions of individual joints, arthrosis.
For infiltration administration into tissues: epicondylitis, tendovaginitis, bursitis, humeroscapular periarthritis, keloids, sciatica, Dupuytren's contracture, rheumatic and similar lesions of joints and various tissues.
Dosage regimen
When taken orally for replacement therapy in adults, the initial dose is 20-30 mg/day, the maintenance dose is 5-10 mg/day. If necessary, the initial dose can be 15-100 mg/day, maintenance - 5-15 mg/day. The daily dose should be reduced gradually.
For children, the initial dose is 1-2 mg/kg/day in 4-6 divided doses, maintenance dose is 300-600 mcg/kg/day. When administered intramuscularly, the dose, frequency and duration of use are determined individually.
When administered intra-articularly, a dose of 25-50 mg is used in large joints, for medium-sized joints - 10-25 mg, for small joints - 5-10 mg. For infiltration into tissue, depending on the severity of the disease and the size of the affected area, doses from 5 to 50 mg are used.
Used locally in ophthalmology 3 times a day, the course of treatment is no more than 14 days; in dermatology – 1-3 times/day.
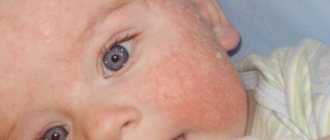
Side effect
From the endocrine system: Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, weight gain. Hyperglycemia up to the development of steroid diabetes, depletion (up to atrophy) of the function of the adrenal cortex. From the digestive system: increased acidity of gastric juice, ulcerogenic effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
Metabolism: increased excretion of potassium, sodium retention in the body with the formation of edema, negative nitrogen balance. From the cardiovascular system: arterial hypertension. From the blood coagulation system: increased blood clotting.
From the musculoskeletal system: osteoporosis, aseptic bone necrosis. From the organ of vision: steroid cataract, provoking latent glaucoma. From the central nervous system: mental disorders.
Effects due to immunosuppressive effects: decreased resistance to infections, delayed wound healing.
When used externally: possible appearance of steroid acne, purpura, telangiectasia, as well as burning, itching, irritation, dry skin; with prolonged use and/or when applied to large surfaces of the skin, a resorptive effect may develop.
When applied topically: a slight burning sensation is possible.
Contraindications
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, osteoporosis, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, tendency to thromboembolism, renal failure, severe arterial hypertension, systemic mycoses, viral infections, vaccination period, active form of tuberculosis, glaucoma, productive symptoms in mental illness. Hypersensitivity to prednisolone.
Infiltration injection into lesions of the skin and tissues during chickenpox, specific infections, mycoses, and local reactions to vaccination.
In ophthalmology – viral and bacterial eye diseases, primary glaucoma, diseases of the cornea with damage to the epithelium.
In dermatology - bacterial, viral, fungal skin lesions, tuberculosis, syphilis, skin tumors.
Pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy (especially in the first trimester) it is used only for health reasons. If it is necessary to use it during lactation, the expected benefits of treatment for the mother and the risk for the child should be carefully weighed.
special instructions
Not intended for intravenous administration. During the day, it is recommended to use it taking into account the circadian rhythm of endogenous secretion of GCS in the interval from 6 to 8 am. Use with caution in patients with a history of psychosis; nonspecific infections subject to simultaneous chemotherapy or antibiotic therapy.
In diabetes mellitus, use is possible only for absolute indications or to prevent suspected insulin resistance. For latent forms of tuberculosis, prednisolone can only be used in combination with anti-tuberculosis drugs.
During treatment (especially long-term), observation by an ophthalmologist, monitoring of blood pressure and water-electrolyte balance, as well as peripheral blood patterns and blood sugar levels are necessary; In order to reduce side effects, you can prescribe anabolic steroids, antibiotics, and also increase the intake of potassium in the body (diet, potassium supplements).
It is recommended to clarify the need for ACTH administration after a course of treatment with prednisone (after performing a skin test!). In Addison's disease, concomitant use with barbiturates should be avoided.
After stopping treatment, withdrawal syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, and exacerbation of the disease for which prednisolone was prescribed may occur.
It should not be used externally for more than 14 days. If used for acne vulgaris or rosacea, an exacerbation of the disease is possible.
Prednisolone in the form of tablets, solution for injection, dry substance for injection, eye drops, ointments is included in the List of Vital and Essential Drugs.
Drug interactions
With the simultaneous use of prednisolone with anticoagulants, the anticoagulant effect of the latter may be enhanced; with salicylates – the likelihood of bleeding increases; with diuretics – possible aggravation of electrolyte metabolism disorders; with antidiabetic drugs – the rate of decrease in blood sugar decreases; with cardiac glycosides – the risk of developing glycoside intoxication increases; with rifampicin – weakening of the therapeutic effect of rifampicin.
Source: https://analogi.info/prednizolon
Side effects from Prednisolone
Unpleasant reactions to taking the drug develop from almost all body systems. They can be combined or be an independent phenomenon:
- problems with the endocrine system , including menstrual irregularities and deterioration of adrenal function, diabetes, developmental delay in children;
- gastrointestinal problems: ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis, as well as many other pathologies;
- metabolism: low nitrogen balance, calcium excretion, weight gain, increased sweating;
- heart: arrhythmia, diseases of different parts of the heart, hypertension.
For you: Principles of therapeutic nutrition for rheumatoid arthritis
When taking Prednisolone, both the skeletal system and the central nervous system suffer, as well as the immune system, vision and other organs.
Prednisolone is very effective in eliminating severe symptoms of arthritis. But taking it is a big risk for other organs.
How to replace Prednisolone tablets?
Tyubik.Net » Tablets » Go back
In the presence of systemic diseases leading to an extensive inflammatory reaction or autoimmune pathologies, Prednisolone is prescribed. If patients have contraindications to the use of the product, the doctor will advise replacing it with analogues.
The problem with using Prednisolone
Prednisolone is used for systemic allergic reactions, inflammatory processes, and autoimmune pathologies. It suppresses the deviation quickly, but causes many side effects. If there are contraindications or complications of therapy, analogs (generics) are used. It is difficult to choose the right drug; most steroid substances negatively affect organ function.
Application of Decortina
Decortin is a systemic glucocorticosteroid used in tablet form. It has immunosuppressive, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory effects. Indications for use:
- inflammatory pathologies of joints;
- bronchial asthma;
- systemic allergy, serum sickness;
- androgenital syndrome;
- inflammation of the liver, kidneys;
- cancer of the blood, immune system, thrombocytopenic purpura;
- dermatological pathologies.
The drug has fewer contraindications in adults compared to prednisolone:
- gastrointestinal ulcers;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- high risk of thromboembolism, hypertension;
- minor age;
- infection by viruses, bacteria, fungi.
The medicine has much fewer side effects with constant use:
- immunosuppression with a high risk of infection;
- increased blood pressure with hypertensive crisis;
- osteoporosis;
- gastrointestinal ulcers;
- glucosuria, hypokalemia.
The drug, like Prednisolone, is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Inflanefran for injection
Inflanefran is a glucocorticosteroid based on prednisolone. Available in ampoules for injection, administered intravenously and intramuscularly. Provisions for use:
- intoxication, burn shock, surgery, trauma;
- systemic allergic reactions;
- swelling, tumors, brain injuries;
- radiation therapy;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- increased production of thyroid hormones with the formation of a crisis;
- liver inflammation;
- chemical burns with complicated formation of scar tissue.
Contraindications:
- infection by bacteria, viruses, fungi;
- vaccine administration;
- immunodeficiency;
- diabetes, thyrotoxicosis;
- osteoporosis;
- glaucoma.
The product has fewer side effects:
- diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis;
- menstrual irregularities;
- arrhythmia, increased thrombus formation;
- seizures, insomnia, mood swings;
- growth slowdown;
- infection;
- changes in mineral metabolism;
- increased intraocular pressure with the development of glaucoma.
Difference with Prednisolone: causes fewer side effects from the digestive tract. The drug penetrates directly into the blood by injection, so it rarely causes dyspeptic disorders or ulcers of the mucous membrane. Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract are possible only with an increased dosage, when the active substance is distributed throughout all tissues with the blood.
Glucocorticosteroid Metipred
Metipred is a glucocorticosteroid based on methylprednisolone, it is an analogue of Prednisolone in tablets. Its negative effect on the body is reduced, since 1 tablet contains a lower concentration of the active substance (instead of 5 mg it contains 4 mg). Indications for use:
- systemic pathologies of connective tissue;
- inflammation of the joints in the acute stage;
- rheumatism, rheumatic carditis;
- bronchial asthma;
- systemic allergy in chronic and acute stages;
- inflammatory skin pathologies;
- cerebral edema;
- inflammation of the eyeball and tissues around it;
- adrenal insufficiency, nephritis;
- thyroiditis;
- anemia, cancer of the blood and immune system;
- liver inflammation;
- hypoglycemia, hypercalcemia;
- ulcerative colitis.
Side effects are identical. What is the difference between Prednisolone and methylprednisolone: the load on the digestive tract, endocrine organs, and cardiovascular system is significantly reduced, since the concentration of the hormone is reduced. The product is used not only for systemic allergic reactions, but also for hay fever. There are much fewer contraindications for use than Prednisolone:
- fungal infection of the body;
- drinking alcohol;
- vaccination;
- breast-feeding.
The drug is used during pregnancy, but only for health reasons.
Millipred as the most gentle drug
Millipred is a glucocorticosteroid based on prednisolone acetate, produced in the USA. It is used intravenously or intramuscularly. Causes pain at the injection site. Indications for use:
- allergy;
- dermatitis;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- inflammation of the eyeball and tissues around it;
- bronchial asthma;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukemia;
- shock.
Contraindications are similar to Prednisolone, but there are fewer side effects:
- neurological disorders, insomnia;
- blood pressure surges;
- edema, alkalosis, hypokalemia;
- menstrual irregularities;
- immunodeficiency;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
There are no side effects from the gastrointestinal tract. The drug in a reduced dosage enters directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive tract, so erosion and ulceration of the mucous membrane does not occur.
How to choose an analogue?
Generics of different generations according to dosage, active ingredients contained, and method of administration. The choice of product depends on the following factors.
- Main disease. If the patient has severe illness, a high dose of the drug is indicated. Decortin and Inflanefran are used. For pathologies of moderate severity, it is recommended to select more gentle agents with a reduced concentration of the hormone (Millipred, Metipred).
- Functionality of the adrenal glands. If there is insufficient production of glucocorticosteroids, strong drugs are used.
- Laboratory test indicators. The state of mineral metabolism, gluconeogenesis, and the endocrine system is taken into account.
- Determination of the state of the immune system, the presence of viruses, infections, fungi.
- Presence of chronic diseases. These include diabetes mellitus, abnormalities in the thyroid gland, kidney and liver pathology, and ulcerative formations in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Identification of contraindications.
Prednisolone is a serious drug that has a systemic effect on the body.
Assessing the correctness of such a tool
If the drug is chosen correctly, the patient’s well-being will stabilize. Inflammation gradually decreases, allergic reactions disappear. The functioning of the immune system decreases. Side effects may occur, but to a minor extent. To eliminate the risk of complications, laboratory and instrumental studies are periodically prescribed.
Prednisolone and its analogues are prescribed only for emergency indications. If treatment is completed, any of these remedies cannot be canceled immediately. The dosage is reduced gradually, bringing it to a minimum. If the steps are completed correctly, withdrawal symptoms will not occur.
Is it necessary to replace Prednisolone with analogues?
The need to replace Prednisolone is indicated by the following factors: the presence of contraindications for use and the occurrence of adverse reactions.
If you have inflammation or mild allergies, Prednisolone is not recommended; it is better to use dexamethasone-based medications.
The replacement product may contain the same hormonal substance, but the negative consequences will be reduced.
This depends on the dose of the active ingredient and the route of administration of the drugs. Under the influence of Prednisolone, ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum often develop. Especially in patients with a predisposition.
To avoid this, replace taking pills with administering a solution intravenously (injections, droppers) or intramuscularly (Prednisolone Bufus).
According to the instructions, dexamethasone suppresses the inflammatory reaction and the immune system response, but has significantly fewer side effects.
The product is not compatible with autoimmune pathologies, shock and other serious conditions.
Taking the drug does not always lead to a complete recovery; patients often require lifelong hormonal therapy to normalize their well-being and the functions of their internal organs.
With prolonged use, side effects will periodically appear, since Prednisolone negatively affects most organs and systems, accumulating in tissues.
This is especially true for patients who use large doses of the drug for autoimmune diseases and inflammatory joint pathologies.
i
Please rate the article, we tried:
Source: https://tyubik.net/tabletki/736-chem-zamenit-tabletki-prednizolon.html