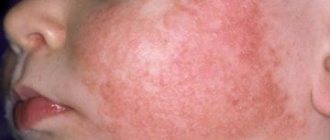
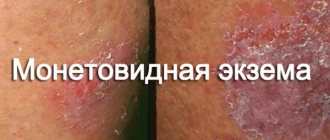
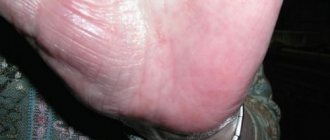
Drug treatment of eczema is based not only on the use of drugs intended for local therapy - ointments, creams and antiseptic solutions. Injections are also prescribed to stop the progression of skin pathology in difficult clinical cases. We invite you to find out what injections for eczema exist and how effective they are.
When and by whom are they appointed?
Injections for any form of eczema are administered intravenously or intramuscularly, which is suitable for patients of any age. Injectable drugs are prescribed by a dermatologist or allergist - a specialist who monitors the patient, if there are the following indications:
- The patient experiences progression of the disease despite local drug therapy measures.
- Eczema has a complex course and does not respond well to systemic therapy in the form of taking drugs in tablet form (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.).
- The patient has a generalized form of dermatosis and an increased risk of systemic complications.
- The patient suffers from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which limits his intake of various drugs intended for oral administration.
- The need to unload the digestive organs, provided that the patient takes at least 3-4 tablets or capsules per day due to the complex course of eczema or the presence of other chronic pathologies.
A specialist may also prescribe injection therapy for eczema in order to avoid increased stress on the liver, kidneys and digestive tract.
Folk remedies for itchy skin
Itching appears for various reasons, but if it is not associated with serious diseases, then folk remedies can help.
Herbal collection
You need to mix 1 tbsp. l. chamomile, lemon balm, mint and linden. Pour boiling water (1 l), leave for 20 minutes. Next, add 50 ml of honey to the solution and strain the finished tincture through cheesecloth. You need to take 50 ml 10 minutes before meals for 20 days.
Juniper
Pour crushed juniper with alcohol, leave in a dark place for 7 days and add 5 ml to the bath. These soothing baths should be taken every week and should not be used during pregnancy.
Series
2 tbsp. l string pour 100 ml of boiling water and brew for 15 minutes. Pour half the solution into the bath and sit in it for 10 minutes. Next, wipe the affected areas on the skin with a cotton swab and do not wipe.
Calendula and chamomile
1 tbsp. l. Boil these herbs in a water bath for 5 minutes. Cool the solution, pour it into the bath and sit in it for 30 minutes.
To prepare a bath with soda, you need to fill the bath with water and pour 1 tbsp into it. baking soda. Lie in such a bath for 30 minutes and let the skin dry without wiping.
Celandine
In the form of a decoction or tincture, celandine is an effective remedy against itching. It will take 1 tsp. celandine pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 15 minutes and strain. The resulting infusion should be used to wipe the affected areas of the skin and make compresses. A thick decoction of celandine is used for bathing.
Take 10 grams. plants and 100 ml of boiling water. You should take a bath for 15 minutes. You can also prepare an alcohol tincture from celandine. You will need 1 part herb and 5 parts vodka. Soak gauze in the solution and apply it to the itchy area for 15 minutes. To prevent skin irritation, the tincture is diluted with boiled water.
Honey has an antibacterial and wound-healing effect. For itching on the skin, apply a thin layer of honey, leave for 25 minutes and rinse with warm water.
Oatmeal and barley
2 tbsp. l. barley needs to be boiled in 1 liter of water, cooled, strained and used to irrigate the skin. Oatmeal should be diluted in water to a paste, mixed and applied to the affected areas. Itchy skin in adults and children interferes with enjoying life. Ointments prescribed by the doctor and folk remedies will help you quickly forget about this illness.
Features of application
Injection therapy is selected individually for each patient. Its purpose helps to achieve the following goals and objectives:
- reduce the body's sensitivity to negative external factors;
- strengthen the immune system;
- stop clinical manifestations of allergic reactions;
- remove toxins and other harmful compounds from the body;
- reduce the severity of inflammatory manifestations.
As part of combination therapy, antihistamines, anti-inflammatory, sensitizing drugs, antibiotics, vitamins and diuretics are usually used. Injections for eczema last up to 6 hours. The time of therapeutic activity of injections, as a rule, is inferior to the work of tablets and capsules, but they have one undeniable advantage - a low risk of complications such as renal failure, irritation and stomach ulcers, pancreatitis compared to oral medication.
Side effects
During treatment, in very rare cases, negative side effects may occur, which manifest themselves as follows:
- sleep disorders, feeling of dizziness, irritability and excitability, pain in the head, impaired motor coordination;
- heart rhythm pathologies, decreased blood pressure;
- digestive dysfunctions;
- nausea and vomiting, indigestion, abdominal pain;
- increased pressure inside the eye, blurred vision;
- urinary dysfunction;
- development of allergic reactions (rash, itching, urticaria).
If the symptoms described above develop, as well as any other discomfort, it is necessary to interrupt therapy and seek advice from a specialist. It may be necessary to adjust the dose of Suprastin or replace it with an analogue.

Types of injections by action
Mild forms of eczema are treated with tablets and local medications, moderate and complicated forms are treated with injections. Let's look at what injections are used for eczema.
Antihistamine therapy
Antihistamine drugs block components that cause allergies and increased immune reactivity, reducing the severity of inflammation. With the help of antihistamine injections you can achieve the following results:
- reduce the severity of skin itching;
- create a sedative effect;
- eliminate swelling;
- prevent the risk of bronchospasms;
- improve the condition of the epidermis.
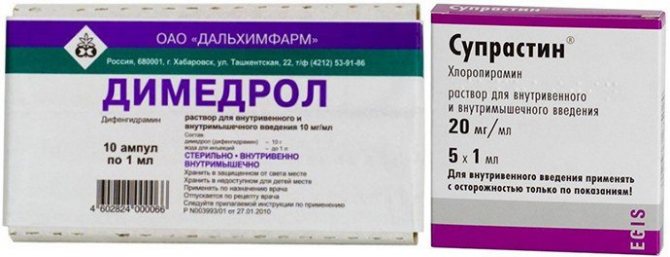
In case of advanced eczema and there are indications for antihistamine therapy, injections of Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Promethazine and Diphenhydramine are used.
Antibiotics
Prescribed for advanced forms of skin pathology complicated by bacterial infection. Antibacterial drugs quickly inhibit the vital activity of microorganisms, preventing their reproduction and spread, which makes it possible to successfully stop the inflammatory process.
Injection of antibiotics for eczema is indicated in the following cases:
- extensive lesions in the arms and legs;
- purulent complications, risk of sepsis;
- bacterial plaque in eczema lesions;
- weak immune system.
Often prescribed antibacterial injections for eczema are Gentamicin, Ampicillin, and Doxycycline. Injections, like tablet and local forms of antibiotics, do not cure eczema in isolation, but they accelerate the onset of remission and prevent possible complications of the disease.
Vitamins
For most skin pathologies - eczema, psoriasis, dermatoses of various origins, B vitamins are used. Positive results of therapy for eczema are observed when prescribing injections such as Milgamma, Cyanocobalamin and Combilipen. Their use almost doubles the effectiveness of complex treatment.
In combination with vitamin injections, it is recommended to use Omega-3, a product containing fatty acids that help valuable B components and retinol to be absorbed in the body. For complicated eczema, including the dry type, vitamins can achieve long-term remission, favorably influencing the general condition of the body.
Sensitizing drugs
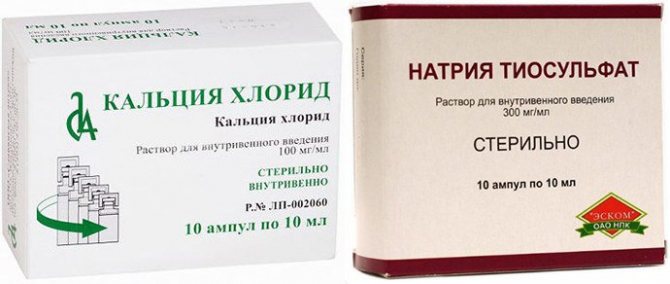
Hyposensitizing therapy for eczema is aimed at reducing the sensitivity of the epidermis to the negative influence of external factors. Preparations of this type are “Calcium gluconate”, “Calcium chloride” and “Sodium thiosulfate”.
Calcium is a valuable microelement that regulates the functioning of the cardiovascular and nervous systems and has a diuretic effect. Calcium preparations restore the activity of the central nervous system, disorders of which most often become a trigger for eczema.
“Calcium chloride” and “Calcium gluconate” are called hot injections; for eczema they are administered intravenously in a pre-diluted form (using saline or glucose). These drugs quickly stop the clinical manifestations of the disease, while simultaneously increasing the body's resistance.
“Sodium thiosulfate” is characterized not only by desensitizing, but also by antitoxic and anti-inflammatory properties. Its purpose is determined by the dynamics of the disease. Hyposensitizing therapy should be combined with the use of vitamin preparations.
Diuretic injections
Diuretic or diuretic drugs are prescribed if it is necessary to relieve swelling. They are used under mandatory blood pressure monitoring. Effective diuretics include Furosemide, a loop diuretic that inhibits the reabsorption of chlorine and sodium ions.
Lasix has similar pharmacological properties. The drug is similar to Furosemide, the only difference between them is the cost. Diuretic therapy for eczema is prescribed for a short period until the symptoms of the pathology are eliminated.
Anti-inflammatory injections
Advanced inflammatory processes in eczema can be controlled by injectable drugs such as Meloxicam, a drug from the oxicam group that has an analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect. The drug inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins, which are responsible for the appearance and progression of inflammatory processes.
Anti-inflammatory therapy in the form of injections is indicated for persons with gastrointestinal diseases, in particular ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum, for whom oral administration of such medications (NSAIDs) is contraindicated. In addition to Meloxicam, injections of Analgin and Diclofenac can be used.
Glucocorticosteroids
A doctor may prescribe a hormonal injection for eczema in severe cases of the disease, when complex conservative therapy does not give the expected therapeutic effect. Preparations with glucocorticosteroids, as a rule, have a quick positive result, but their use remains at high risk of developing adverse reactions, including the development of dependence on medications.
Therefore, experts prescribe hormonal injections in courses of up to 7 days. After acute symptoms are relieved, medications are immediately discontinued. For eczema, the following glucocorticosteroids are used:
- "Diprospan";
- "Dexamethasone";
- "Prednisolone."
With complex drug therapy for eczema, in particular, with the use of Dexamethasone injections, according to numerous reviews, it is possible to achieve remission, provided that the treatment process is carried out under medical supervision. Self-medication with hormonal drugs is excluded.
Principles of treatment
Itchy skin requires adequate treatment. The therapeutic course is usually based on a number of specific principles. If you follow them, you can get the desired result. Most antipruritic medications can help get rid of this particular symptom. But there are also those who fight the cause of the malaise.
Doctors call the following principles for treating skin itching:
- It is necessary to completely eliminate exposure to heat on the affected skin. It is best to stay in a cool room during treatment.
- You should avoid eating foods that dilate blood vessels. Alcoholic drinks and coffee are definitely excluded.
- It is necessary to at least temporarily abandon clothing made of wool or synthetic materials.
- After water procedures, it is necessary to moisturize the affected and healthy skin with special cosmetic and caring products.
- When bathing, it is advisable to limit the use of gels and soaps with a low acid-base balance.
If you follow these recommendations, you will be able to speed up the onset of the therapeutic effect after using pharmaceutical and home remedies.
Use in children, pregnant and lactating women, the elderly
CHILDREN. When prescribing injections for the treatment of eczema to a child, the doctor takes into account his constitutional characteristics and clinical picture of the disease, and the risk of possible complications. The fight against skin pathology, as a rule, begins with the use of anti-inflammatory, antihistamine and sensitizing injection agents, against the background of which the symptoms of the disease quickly stop and its acute phase subsides.
Calcium supplements in the form of injections are recommended for children over 5 years of age. Before reaching this age, it is advisable to use the microelement in the form of tablets and powders. “Sodium thiosulfate” is indicated at any age, since the drug has a mild anti-allergic effect and removes toxins and allergens from the body. The list of antihistamine injections approved for use in children includes Suprastin, Diphenhydramine and Tavegil. For the microbial form of eczema, Ampicillin injections are allowed.
PREGNANT. Eczema in expectant mothers also requires the use of the above range of medications, however, most of these medications are prohibited during pregnancy, so treatment tactics for the woman are selected individually. In uncomplicated clinical cases, the use of local medications based on panthenol and plant extracts is recommended. These drugs stop the inflammatory process, restore damaged layers of the dermis and eliminate itching.
With complicated eczema, more serious therapy is required, the choice of which depends on factors such as gestational age, severity of symptoms, and potential risk to the child. Injections during pregnancy are allowed from the third trimester - these can be antihistamines "Suprastin" and "Tavegil", sensitizing agents, diuretics "Furosemide", according to strict indications, anti-inflammatory injections "Diclofenac", "Movalis" and glucocorticosteroids in the form of creams "Lokoid" and "Afloderm".
NURSING. During breastfeeding, exacerbations of eczema require complex treatment. Most medications can pass into the baby's body through breast milk, which precludes their use, including in injection form.
For mild skin pathologies, it is recommended to use local relatively safe products based on zinc, panthenol, and birch tar. If complications develop, it is recommended to temporarily interrupt breastfeeding and undergo the necessary course of treatment, protecting the child from taking medications into the body.
ELDERLY. Injections in elderly patients with severe forms of eczema are not contraindicated, provided that the medications are individually tolerated and there are no restrictions on their use. Among antibiotics, it is recommended that elderly people be prescribed macrolides and semisynthetic penicillins. Gamma globulin injections have a good effect. If indicated, hormonal therapy with Prednisolone is performed.
Elimination of itching in diabetes mellitus
People who have been diagnosed with diabetes often experience itchy skin. With such a symptom, the doctor may recommend taking inexpensive but very effective medications.
Unpleasant itching in diabetes mellitus develops due to the fact that after sugar forms in the blood vessels, it has a negative effect on the skin. Because of this process, it becomes drier and rougher.
Diabetics need to start treating itching from the first day after its onset. They should not scratch the skin, as this leads to painful wounds that take a very long time to heal.
For diabetes mellitus, the following medications are recommended:
- " Dermozolon ". A combined drug that has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and antifungal effects. If a diabetic has itchy skin, this medicine will be a real savior for him. It copes well with signs of itching in different parts of the body.
- " Flucinar ". A hormonal agent that effectively fights severe inflammatory processes on the skin. In addition, it accelerates the healing of tissues affected by the disease. It is best to use the ointment for itching that is not caused by infection.
- " Fusiderm ". External ointment gives a pronounced antimicrobial effect. This quality is due to its composition. Therefore, it makes sense to use this pharmaceutical drug for skin lesions from pathogenic microflora.
Additionally, a suitable antifungal agent may be prescribed.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to certain components of injectable drugs is an important contraindication to their use. The introduction of additional allergens into the body will negatively affect both its condition as a whole and the course of the skin disease.
Injections are also refused if widespread inflammatory processes are observed in the area where the drug is administered or the patient needs to be administered several ampoules of different effects at once (for concomitant diseases) - it is forbidden to overload the veins and muscles.