Literature Main:
- Vanhanen, V.D. Guide to practical training in food hygiene / V.D. Vanhanen, E.A. Lebedeva. M.: Medicine, 1987.
- Martinchik, A.N. Human nutrition (basics of nutritionology) / A.N. Martinchik, I.V. Maev, A.B. Petukhov. M.: GOU VUNMC Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2002.
- Petrovsky, K.S. Food hygiene / K.S. Petrovsky, V.D. Vanhanen. M.: Medicine, 1982.
- Markova, N.N. Organization of therapeutic and preventive nutrition and control over it at industrial enterprises: Method. instructions for self work of students, subordinators / N.N. Markova. Yakutsk: Yakut. state University named after M.A. Amosova, 1992.
- Stozharov, A.A. Radiation medicine: textbook. allowance / A.A. Stozharov, L.A. Kvitkevich, A.R. Avetisov et al. – 2nd ed. reworked and additional – Mn: BSMU, 2002.
Tasks of the department
- Maintaining the highest level of squad combat readiness in daily activities and in the event of extreme peacetime situations;
- Carrying out therapeutic, diagnostic and rehabilitation measures for patients with allergies and acquired diseases of the bronchopulmonary apparatus;
- Conducting expert, advisory, methodological and scientific work.
The 46th allergy department has 28 beds and is intended for treatment and examination of patients with acute and acquired allergies, acquired respiratory diseases.
The priority nosological forms of the department are bronchial asthma, acute and acquired urticaria, acute toxicoallergic reactions, and atopic dermatitis. The department includes an allergology office, which is responsible for a large amount of advisory assistance and specific immunotherapy.
So what is an allergy?
An allergy is a specific (immune) reaction of the body to the most common substances, such as food, wool, dust, and household chemicals. For most people, these substances do not cause allergies or any body reactions.
Allergies do not occur immediately and not in everyone.
People who have a predisposition to allergies (heredity, characteristics of the immune system) may be exposed to a variety of substances over a long period of time, but this may not lead to the development of allergies, but depending on certain circumstances and criteria, which, in principle, have not been thoroughly studied, the immune system “remembers” the substance and produces an antibody to it, which, when the antigen subsequently enters the body, causes an allergic reaction. The prerequisite for the development of allergies is the body's immune response, which can be caused by a huge number of substances.
The main substances that cause allergies are:
• dust (street, home or book dust);
• pollen;
• fur of domestic animals or scales of their skin (cats, dogs);
• fungal or mold spores;
• food products (most often: eggs, milk, wheat, soy, seafood, nuts, fruits);
• bites (poison) of bees, wasps, bumblebees, ants;
• certain medications (penicillin);
• latex;
• household chemicals.
Allergy symptoms depend on the type of allergen, or more precisely, on the place where the allergen comes into contact with a part of your body.
So, depending on the location (respiratory tract, sinuses, skin, digestive system), different symptoms may appear:
• sneezing (usually loud and frequent);
• cough, chest tightness, feeling of shortness of breath, difficulty breathing or shortness of breath;
• itching in the nose and copious discharge of watery secretions from the nose;
• itching in the eyes, watery eyes, redness of the eyes and swelling of the eyelids;
• skin itching, redness of the skin, rashes on the skin, peeling of the skin;
• tingling in the mouth, tingling or numbness of the tongue;
• swelling of the lips, tongue, face, neck;
• nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
If you have any allergy symptoms for the first time, but you do not know what caused them, you need to contact your doctor to prescribe the correct treatment and find the cause of the allergy.
In addition to the examination and survey, a number of tests and studies that are specific to allergies will be needed.
Skin tests - this test is prescribed when there is a suspicion of an allergy.
The advantages of this study are ease of implementation, time to obtain results (15–20 minutes) and low cost. This study provides accurate information about the cause of the allergy, and more precisely, allows you to determine the allergen that caused the reaction. A skin test involves introducing an extremely small amount of various allergens into the skin, and depending on the body's reaction, allergens that can cause an allergic reaction in the person being tested are determined.
The study can be carried out on people of any age.
IgE blood test – measures the amount of IgE antibodies in the blood. The test requires a small amount of blood, which is taken from a vein. This study is carried out in cases where for some reason it is impossible to conduct skin tests or when the patient is forced to constantly take antiallergic drugs.
This study may also be prescribed as an additional study to prove the results of skin tests.
This study is carried out to determine the prerequisites for the development of allergic skin reactions, such as contact dermatitis or eczema. A special consistency is prepared from paraffin or petroleum jelly, which contains the allergen that presumably caused the allergic reaction. This consistency is then applied to iron plates (about 1cm in diameter), several plates containing the consistencies of various allergens are prepared, and then they are attached to the skin of the back.
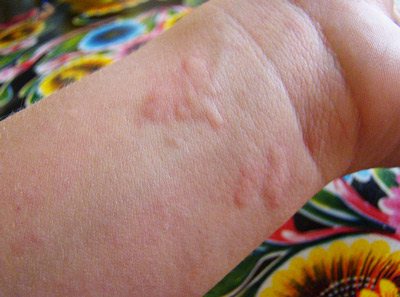
The patient is required to keep the skin dry for 48 hours. After this time, the plates are removed and the skin is examined for any reactions to the allergen. If there is no reaction, the patient is required to return for a repeat skin examination after 48 hours (without plates). During the re-examination, the presence of any changes is checked, the prerequisite for which may be a slow reaction of the body.
However, all the tests described above do not allow us to make a diagnosis of allergy with 100% certainty. The only way to 100% establish a diagnosis and detect the allergen is through a provocative test.
The essence of this study is to induce an allergic reaction in a patient through the consumption of goods or allergens, which presumably became a prerequisite for the occurrence of this reaction. It should be remembered that this study is carried out exclusively in a hospital under the supervision of specialists.
This study is traditionally carried out in 2 cases:
1) if skin tests and blood tests do not give the desired results;
2) if a patient (usually a child), with a history of allergies, loses the allergic reaction to a previously identified allergen after a long period of time.
The study is carried out in a specialized department in the presence and compliance with all security measures, as well as under the supervision of a group of specialists.
During the study, the allergen will be injected into your nasal cavity, under your tongue, into the bronchi, or into the digestive system, depending on the location of the previous allergic reaction. If an allergic reaction occurs, the study will be stopped and all necessary measures will be taken to eliminate allergy symptoms.
The most basic rule in treating allergies is avoiding contact with allergens. If you are allergic and you understand the allergens that can cause an allergic reaction in you, try to protect yourself very much from the slightest contact with them, since allergies have the property of provoking more and more severe reactions to repeated contact with the allergen.
Drug treatment is aimed at reducing the risk of developing an allergic reaction, as well as eliminating the symptoms caused by the allergic reaction.
Antihistamines - Fexofenadine (Telfast), Loratadine (Claritin), Cetirizine (Zyrtec), Chlorpyramin (Suprastin), Clemastine (Tavegil) - these drugs are products of the first group, they are one of the first prescribed during the treatment of allergic reactions.
When an allergen enters the body, your immune system produces a special substance called histamine. Histamine causes most of the symptoms consistent with an allergic reaction. This group of drugs allows you to reduce the amount of histamine released or completely block its release. But they still cannot remove all allergy symptoms.
Decongestants (Pseudoephedrine, Xylometazoline, Oxymetazoline) are a group of drugs that are used to relieve nasal congestion. Most often, these drugs are found in the form of sprays or drops.
They are prescribed for colds, hay fever (pollen allergy) or any allergic reaction, the symptoms of which are stuffy nose, flu and sinusitis.
The inner surface of the nose is covered with a large number of small vessels. When an allergen or antigen enters the nasal cavity, the vessels of the nasal mucosa dilate and blood flow increases - this is a typical defense system of the immune system.
A large influx of blood causes swelling of the mucous membrane and provokes copious mucus secretion. Decongestants act on the walls of the mucous vessels, causing them to narrow, which reduces blood flow and reduces swelling.
These drugs are not recommended for children under 12 years of age, as well as for nursing mothers and people with hypertension. It is also not recommended to use these drugs for more than 5-7 days, since with prolonged use they can cause a backlash and increase swelling of the nasal mucosa.
Leukotriene inhibitors (Montelukast (Singulair)) are chemicals that block reactions caused by leukotrienes (leukotrienes are substances released by the body during an allergic reaction and cause inflammation and swelling of the airways).
They are used in the treatment of bronchial asthma. Leukotriene inhibitors can be used in conjunction with other medications.
Steroid sprays (Beclomethasone (Beconas, Beclazon), Flucatisone (Nazarel, Flixonase, Avamis), Mometasone (Momat, Nasonex, Asmanex)) - these drugs are essentially hormonal products. Their action is to reduce inflammation in the nasal passages, thereby reducing the symptoms of allergic reactions, and specifically nasal congestion. Before using these drugs, it is better to consult your doctor.
Hyposensitization (immunotherapy) - in addition to avoiding contact with allergens and drug treatment, there is a method of treatment called immunotherapy.
This method involves the gradual, long-term introduction of increasing amounts of allergens into your body, which will lead to a decrease in your body's sensitivity to a given allergen.
The procedure involves the administration of small doses of the allergen in the form of a subcutaneous injection. At first, you will be given injections at intervals of a week or less, while the dose of the allergen will constantly increase, this regimen will be followed until a “maintenance dose” is reached - this is a dose, when administered, there will be a pronounced the effect of reducing a common allergic reaction.
However, once this “maintenance dose” is reached, it will need to be administered every few weeks for at least another 2–2.5 years. This healing method is usually prescribed when a person has a severe form of allergy that is difficult to respond to ordinary healing, as well as for certain types of allergies, such as allergies to bee and wasp stings. This type of healing is carried out only in a specialized medical institution under the supervision of a group.
Additional:
- Dunaevsky, G.A. Organization of dietary nutrition at industrial enterprises / G.A. Dunaevsky. M.: Medicine, 1980.
- Dotsenko, V.A. Organization of therapeutic and preventive nutrition / V.A. Dotsenko, G.I. Bondarev, A.N. Martinchik. L.: Medicine, 1987.
- Lebedeva, E.A. Nutrition in preventive medicine / E.A. Lebedeva. L., 1986.
- Stolmakova, A.I. Organization of therapeutic and preventive nutrition at industrial enterprises / A.I. Stolmakova, R.I. Ladanievsky, A.G. Kiselevich. Kyiv, 1984.
- Hygienic classification of working conditions No. 11-6-2002 RB // Sat. official documents on occupational medicine and industrial sanitation / Ed. ed. V.P. Filonova. Mn., 2003.
- Dotsenko, V.A.. Modern problems of therapeutic and preventive nutrition for industrial workers / V.A. Dotsenko, A.S. Buldakov // Med. labor and industrial ecol. No. 9, 1998.
- Kosyachenko, G.E. Scientific and methodological justification for the provision of therapeutic and preventive nutrition to those working in particularly hazardous working conditions: Instruction 2.2.10-13-26-2005 was approved and put into effect by the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Republic of Belarus No. 104 dated 08/09/2005 / G.E. Kosyachenko, I.P. Shcherbinskaya, Kh.Kh. Lavinsky, G.I. Tishkevich. Mn., 2005.
Annex 1
Principles for classifying working conditions
- Based on hygienic criteria, working conditions are divided into 4 classes: optimal, acceptable, harmful and dangerous.
Optimal working conditions (class 1) are conditions under which the health of workers is maintained and the prerequisites are created for maintaining a high level of performance. Optimal standards for production factors have been established for microclimatic parameters and labor process factors. For other factors, working conditions in which there are no unfavorable factors or do not exceed levels accepted as safe for the population are conditionally accepted as optimal.
- Acceptable working conditions (class 2) are characterized by such levels of environmental factors and the labor process that do not exceed established hygienic standards for workplaces, and possible changes in the functional state of the body that arise under their influence are restored during regulated rest or by the beginning of the next shift and not must have an adverse effect in the short and long term on the health of workers and their offspring. Acceptable working conditions are conditionally classified as safe.
- Harmful working conditions (class 3) are characterized by the presence of harmful production factors that exceed hygienic standards and have an adverse effect on the worker’s body and/or his offspring.
1st degree, 3rd class (3.1) - working conditions are characterized by such deviations in the levels of harmful factors from hygienic standards that cause functional changes, which are restored, as a rule, with a longer interruption of contact with harmful factors (than at the beginning of the next shift) and increase the risk of damage to health ;
2 degree 3 class (3.2) - levels of harmful factors that cause persistent functional changes, leading in most cases to an increase in work-related morbidity (which is manifested by an increase in the level of morbidity with temporary disability and, first of all, those diseases that reflect the condition of the most vulnerable organs and systems for these harmful factors), the appearance of initial signs or mild (without loss of professional ability) forms of occupational diseases that arise after prolonged exposure (often after 15 years or more);
3rd degree 3rd class (3.3) - working conditions characterized by such levels of harmful factors, the impact of which leads to the development, as a rule, of occupational diseases of mild and moderate severity (with loss of professional ability to work) during the period of work, the growth of chronic (production-related) ) pathologies, including increased levels of morbidity with temporary disability (100–119 cases and 1000–1199 days of disability per 100 workers per year);
4 degree 3 class (3.4) - working conditions under which severe forms of occupational diseases can occur (with loss of general working capacity), there is a significant increase in the number of chronic diseases and high levels of morbidity with temporary disability (120–149 cases and 1200–1499 days disability per 100 workers per year).
- Hazardous (extreme) working conditions (class 4) are characterized by levels of production factors, the impact of which during a work shift (or part of it) creates a threat to life, a high risk of developing acute occupational injuries, including severe forms.
Appendix 2
How much histamine leads to intolerance and poisoning?
Histamine can cause allergy symptoms to appear despite no exposure to the allergen. The cause of this condition may be an increased concentration of this hormone in the body, which is a consequence of its excessive production.
However, the most common cause is a congenital or acquired deficiency of the enzyme diamine oxidase (DAO), which breaks down histamine in food. If there is not enough DAO or it is not working correctly, histamine is not broken down. Its excess enters the blood through the intestinal mucosa and causes symptoms reminiscent of allergies:
- headache and dizziness, migraine,
- irritation of the nasal mucosa,
- difficulty breathing,
- tachycardia, arterial hypertension,
- problems with the digestive system, such as bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea,
- skin rash, itching.
This condition is called histamine intolerance. In its treatment, a diet with limited consumption of foods rich in this hormone is recommended. Antihistamines can also be used.
Getting histamine from food in a dose of 5 to 10 mg can cause a pseudo-allergic reaction in sensitive people. In turn, the first symptoms of poisoning appear when the dose of histamine in food is above 50 mg/kg of product:
- headache,
- burning lips,
- hives,
- redness of the face and neck.
Exceeding 200 mg of histamine per 1 kg of product causes an increase in symptoms and they occur in an acute form with respiratory failure and a decrease in blood pressure.
It is worth knowing that the histamine content in fish and fish products above 1000 mg/kg leads to scombrotoxic poisoning (histamine poisoning), manifested in respiratory failure, and can even cause death in people with allergies.
The largest number of food poisonings caused by the presence of histamine in food is observed as a result of the consumption of fish products (mackerel, herring, tuna and sardines), as well as ripening cheeses.
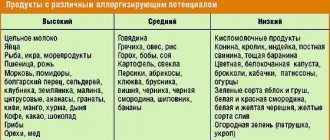
Histamine content in foods
What foods should you avoid if you have histamine intolerance?
Histamine-rich foods include: 1) Drinks.
- Fermented milk drinks: cabbage, vinegar, soy sauce, kefir, yogurt, kombucha, etc.
- Alcoholic drinks, especially wine, champagne and beer.
2) Products containing vinegar: pickles, mayonnaise, olives.
3) Sausages: bacon, pickles, pepperoni, cooked meats and sausages.
4) Dried fruits: apricots, prunes, dates, figs, raisins.
5) Most citrus fruits.
6) Cheeses, including goat cheese.
7) Nuts: walnuts, cashews and peanuts.
“8)” Vegetables: avocado, eggplant, spinach and tomatoes.
9) Smoked fish and some types of fish: mackerel, mahi-mahi, tuna, anchovies, sardines.
10) Sour cream, buttermilk.
11) Bread.
12) Fish and some types of fish: mackerel, mahi-mahi, tuna, anchovies, sardines.
1) Alcohol2) Bananas3) Chocolate4) Cow's milk5) Nuts6) Papaya7) Pineapple "8)" Shellfish9) Strawberries10) Tomatoes11) Wheat germ12) Many artificial preservatives and colors.
1) Alcohol.
2) Energy drinks.
3) Black tea.
4) Mate tea.
5) Green tea.
If you have histamine intolerance, it is helpful to eat and enjoy these foods.
But we must remember that freshness of food is the key to health when there is histamine intolerance.
1) Meat and poultry are freshly prepared.
2) Freshly caught fish.
3) Cooked eggs.
4) Gluten-free grains*: rice, amaranth, quinoa, corn, millet.
5) Pure peanut butter*.
6) Fresh fruits: mango, pears, watermelon, apple, kiwi, melon, grapes.
7) Vegetables (except tomatoes, spinach, avocado and eggplant).
“8)” Milk substitutes: coconut milk, rice milk, hemp milk, almond milk*.
9) Cooking oil: olive oil, coconut oil.
10) Leafy herbs.
11) Herbal teas.
Note.
If you have autoimmune diseases, it is recommended to avoid foods marked with an * in the list.
Often such goods and products are stored for a long time, for example, alcoholic beverages. Sake or red wine is the alcohol with the highest histamine content. What else should allergy sufferers avoid?
- Smoked products of various types (meat or sausages)
- Cheese, including smoked
- Almost all seafood
- Fish that has very high levels of histamine
- Yeast is also prohibited
- No soy products or various marinades allowed.
- Coffee and cocoa are also not available.
You also need to be careful with fruits, because kiwi, pear, pineapple, strawberries and banana also contain a certain amount of histamine.
If you weigh everything, you can see that a very large number of products contain this additive. But don’t be afraid ahead of time, because this absolutely does not mean that your diet needs to be simplified to the minimum. You just need to know about the list of “foods containing histamine”, but those that can be eaten if you are incompatible or allergic to the product:
- Vegetable oil
- Bread or other baked goods, such as cookies
- Egg and milk
- Chicken or duck meat
- A plant like corn
- Cottage cheese
The main reason that incompatibility manifests itself in the body is an increased level of histamine in the body, that is, the body simply “fails” because it cannot cope with the load. And also when the production of certain enzymes is blocked or a person is exposed to ultraviolet radiation, or there are already pathogenic bacteria in the body, diseases of the stomach or intestines - these are also reasons for the body’s incompatibility with the histamine substance.
But in order to solve this problem, it is first of all important to find the source of this disease. And you shouldn’t try to cure yourself and recklessly “swallow” drugs that reduce histamine. It’s better to find an experienced doctor who will provide you with competent advice and determine the correct treatment method.
Antihistamine diet
Any antihistamine diet
pursues two good goals at the same time. First of all, this is a sharply limited diet, which reduces the food load on the body weakened by allergies, eliminating, in addition to the symptoms of the disease, excess weight.
And secondly, if possible, excludes allergens from the patient’s diet. Low calorie content does not mean nutritional deficiency. It is important to balance the diet by including fats, carbohydrates and proteins in the required quantities. Another necessary condition of the antihistamine diet
- drink plenty of fluids.
The liquid removes excess toxins from the body, which often provoke an exacerbation of allergies. Salt, or rather its absence, helps enhance the effect. If you are not used to eating somewhat tasteless food, then you should minimize the amount of salt in your diet to the minimum acceptable level.
Products completely excluded from the diet at the first stage of the antihistamine diet:
- milk;
- eggs;
- seafood;
- smoked meats;
- marinades and pickles;
- sauces, spices and seasonings, including vinegar, mayonnaise, soy sauce;
- red vegetables (red peppers, carrots, beets and tomatoes);
- other allergenic vegetables (celery, sorrel, sauerkraut and eggplant);
- almost all berries and fruits: pineapples and red apples, melon and raspberries, strawberries and strawberries, cherries and grapes, blueberries and pomegranates, persimmons and plums, and, of course, citrus fruits;
- nuts and dried fruits (prunes, dried pears and apples are not included in the list of restrictions);
- mushrooms, regardless of type and method of preparation;
- any products saturated with food additives, flavors and dyes: chewing gum, sweet yoghurts and factory-made curds, all kinds of snacks and fast food, carbonated drinks, chocolate, honey, caramel and marmalade;
- Coffee, cocoa and alcohol in any form are prohibited.
Some foods can be consumed in very limited quantities during the diet. This:
- cereals (buckwheat, rye, corn and wheat);
- stewed meat (pork, horse meat, turkey, rabbit, lamb);
- fruits and berries (peaches, currants, watermelon, bananas, lingonberries and apricots);
- vegetables (green peppers, potatoes, legumes). It is preferable to eat vegetables in the form of vegetable soups, purees, or stew with the addition of a small amount of vegetable oil.
Of course, there are many restrictions, but the list of permitted products is quite impressive. They are limited only by their own intolerance or some reaction of the body.
So, during the antihistamine diet, you can eat the following foods, carefully monitoring your condition:
- fermented milk products (kefir, natural yogurt, cottage cheese, fermented baked milk);
- meat products (chicken, beef, lean pork, tongue, liver and kidneys);
- lean fish;
- cereals (rice, semolina, pearl barley and oatmeal);
- vegetables (white cabbage, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower, cucumbers, broccoli, zucchini, green salad, spinach, squash, turnips, rutabaga, dill and parsley);
- oil (sunflower, olive, butter);
- fruits and berries (gooseberries, white currants, green apples, white cherries, pears).
- you can, and even need to, eat some dried fruits: apples, prunes and pears, both raw and in the form of compotes;
- Among drinks, you should give preference to still mineral water, weak tea without flavorings, rosehip decoction and compotes from fruits allowed by the diet.
The antihistamine diet, or rather its main period, lasts from a week to ten days. After this time, you can begin to introduce foods excluded from the permitted list into your diet one by one. If there is no deterioration in the condition within three days, then gastronomic experiments can be continued. Before going on this diet, you should cleanse the body for two days, excluding everything except heavy drinking (weak tea, mineral and purified water) in a volume of at least one and a half liters per day, cereal or vegetable soups. The preparatory period sets the entire body in the right mood, which begins to actively fight against unfavorable environmental factors.
Sample menu for two days of an antihistamine diet
First day:
- Breakfast: buckwheat porridge (90 grams) with meat pate (60 grams) and a glass of tea.
- Snack: one large green apple.
- Lunch: vegetable soup (400 grams), meat and potatoes (150 grams) and dried fruit compote.
- Dinner: boiled fish (250 grams), cottage cheese and carrot zrazy (200 grams) and tea.
- At night: a glass of fermented milk drink.
- You can eat up to 300 grams of bread per day.
Second day:
- Breakfast: rice porridge with butter (150 grams) and boiled meat (80 grams), a glass of rosehip decoction.
- Snack: half a glass of apple juice.
- Lunch: cabbage soup made from fresh cabbage (400 grams), boiled or steamed fish with mashed potatoes (150 grams) and tea with a spoon of sugar.
- Afternoon snack: a glass of carrot juice.
- Dinner: stewed cabbage with vegetable oil (200 grams), low-fat cottage cheese with sugar (100 grams), and dried fruit compote.
- Before going to bed, it is good to drink a glass of low-fat kefir.
- You can eat 300 grams of bread per day (equal parts black and white). The permissible amount of sugar per day is 30 grams.
Therapeutic diet
not only cleanses the body of allergens and toxins, but also improves immunity, which is important for people weakened by any allergic disease. Diet has a therapeutic effect, but you should not rely on it alone.
Any allergic symptoms require monitoring by an allergist.
The doctor may also recommend that his patient adhere to dietary principles, while simultaneously keeping a food diary, which records what the patient ate and when, as well as how the dish was prepared.
This will allow you to more clearly outline the picture of the disease and prescribe the most productive treatment. For example, sometimes a patient with a negative reaction to fish has allergy symptoms only to uncooked or even raw fish, and adequate heat treatment may not cause harm to health.
Source: https://xn--80achd5ad.xn--p1ai/dietologiya/1900-antigistaminnaya-dieta.html
Specific reaction to histamine
Somewhere within one percent, maybe a little more, of the population of our planet are endowed with the property that they cannot tolerate histamine. That is, in fact, they should not eat foods containing histamines at all, especially if the percentage of this substance is very high. What does this mean?
- The minimum time after eating food with the presence of this remedy is when headaches begin to occur.
- Hives or some itching may occur
- Another unpleasant sensation is diarrhea
According to statistics, it is middle-aged females who most often experience rejection of this element. Not entirely rosy consequences are visible after frequent consumption of foods containing histamine. But it is also worth paying attention to the fact that the products defined in their composition do not have this substance, but if you take them, then as a result, natural synthesis of histamine occurs in the body. And people who are prone to allergies to such a substance should always adhere to a diet.
Apple vinegar.
This product is one of the most effective natural anti-allergic agents and does not cause side effects. Apple cider vinegar is a natural antibiotic and an effective antihistamine as it suppresses allergy symptoms. It is best used in combination with a tablespoon of honey and lemon juice.
Then take the mixture three times a day to effectively combat any signs of allergies. Apple cider vinegar strengthens the lungs, strengthens the immune system, improves blood circulation and helps improve the body's digestive functions.
Real reviews about Tyramine
- I read about Tyramine on the Internet; I have had problems with my thyroid gland for the last couple of years. I studied a lot of information and decided to try it. The first problem I was afraid of was counterfeits, so I bought from certified sellers. I took it for 2 weeks, felt relief, even my voice changed a little, the pills themselves are easy to take. I didn't notice any side effects. I think I’ll take another course in 2 months.
- I have had problems with the thyroid gland since childhood. I undergo treatment periodically and constantly monitor my iodine levels. For prevention, I often smear iodine on my heels, make tinctures from nut jumpers, and now I additionally drink Tyramine. I have already completed 3 courses over the past year, but I did not go to the doctor, since I know all the diagnoses. Overall, I can’t call it useless, I don’t feel any exacerbations. I’m thinking of going through an inspection and finding out what and how has changed there.
- When problems with hormones began, I learned about the drug from a friend, saying it was on a natural basis and all that. There is no pharmacies in my city, and many pharmacists have not even heard of Tyramine, so I went to the regional pharmacy and bought it there. The price of course shocked me, I didn’t think it was so expensive. I drank it, of course, hoping for better results for the money. In principle, the situation has really improved, judging by the tests, but I was also taking other drugs at the same time, so the purity of the experiment is in question.
Friends, leave your experience of using this drug in the comments and be healthy!
Migraines are accompanied by severe throbbing headaches. They can be caused by many reasons, one of which is poor nutrition.
There are a number of foods that need to be excluded from the diet to reduce the likelihood of an attack. In children, migraines can be triggered by allergic reactions to specific foods. Therefore, it is necessary to identify the source of the problem and adhere to a hypoallergenic diet.
Diseases and their treatments
Foods that reduce the inflammatory response caused by various agents
Products
Counteracts histamine
- Black currants, kiwi fruits, cherries and rose hips are very rich in vitamin C, a natural antihistamine. To improve the absorption of vitamin C, these products are best taken together with bioflavonoids.
- Quercetin protects white blood cells from reacting to excess histamine and also has a strong anti-inflammatory effect. Algae contain a lot of quercetin: blue-green (spirulina), brown (alaria), green magma.
- Ginger rhizome, another natural antihistamine, can be taken either raw or fried (see - 155).
- B vitamins such as biotin, choline and inositol support the liver, which detoxifies histamine circulating in the blood. Buckwheat, brown rice, veal liver, chicken, eggs, lentils, oats and sunflower seeds are rich in these vitamins.
- The essential acid methionine is necessary to maintain the detoxification function of the liver. A lot of methionine is found in eggs, fish, meat and poultry.
- Silymarin also supports liver function. Sea thistle is rich in it.
Fighting the kinins
- A diet rich in vegetables and fruits reduces kinin levels.
- Cranberry juice, which has an alkalizing effect, restores the acid-base balance of the body when the internal environment is acidified.
- High protein foods (chicken, nuts, tofu, fish and legumes) acidify the body's pH.
- Salt, soy sauce, vinegar and other seasonings are strong acidifying agents.
Counteracts prostaglandins
- Bromelain, found in pineapples, blocks prostaglandins that promote inflammation while increasing levels of anti-inflammatory prostaglandins.
- Ginger inhibits the activity of prostaglandins that promote inflammation.
- Enzymes that provide the formation of anti-inflammatory prostaglandins require vitamins C, B3 and biotin, as well as the trace elements magnesium and zinc.
Anti-leukotrienes
- Quercetin prevents the formation of leukotrienes. It is found in its most concentrated form in the outer layers of onions. Moreover, there is more of it in red onions than in other varieties.
- The spice turmeric contains the active substance curcumin, which reduces the formation of leukotrienes.
- All products of animal origin contain the amino acid arginine, which inhibits the activity of leukotrienes.
Suppress complement activation
- Vitamins A, C and E, as well as the microelements selenium and zinc, are powerful antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals. Vegetables and fruits of yellow, red and orange colors (except tomatoes and peppers) are rich in vitamin A. Berries, sweet potatoes and kiwi are especially rich in vitamin C. Selenium is found in seafood and sesame seeds, and pumpkin seeds and oysters are especially rich in zinc.
| 06/10/2019 21:55:00 5 nutritional rules for burning belly fat A flat stomach without hunger, dieting, or grueling sports is the cherished dream of most women and men. With our scientifically proven tips and tricks suitable for everyday use, you can finally make this dream come true. Everyone can become slim! |
| 06/10/2019 21:30:00 These 7 principles of healthy eating turned out to be false It is impossible to live without food, so there is a lot of advice on nutrition. But not all of them are useful. Let's find out which principles of healthy eating are false from the point of view of endocrinologists and other medical specialists. |
| 09.06.2019 07:30:00 |
Maybe you didn’t know, but a very large number of people suffer from the fact that the body does not perceive histamine. Since the presence of such a remedy can create an unexpected immune reaction, in the form of any allergy. But, first of all, it is histamine that causes the blood vessels to dilate, and this can cause real anaphylactic shock. And here you can provide help only if you give an injection of adrenaline. And in this case, we urge people that they must have information about what foods are high in histamine. And if you abuse such food, then you need to immediately change your diet.
Sources
- Amino acid histidine. Included in some products, it is the basis for the synthesis of histamine in connective tissue. It is called endogenous; deposited in the form of granules in specialized cells (basophils or mast cells).
- Foods containing histamine. In this case it is exogenous.
- The accumulation of histamine can also be observed when the intestinal microflora is disrupted, for example, with dysbiosis.
Responses
In cells, histamine is contained in bound form. Under stress, tissue damage, the action of toxins, foreign agents, etc., it is released and goes into an active form, which is manifested by a number of reactions:
- smooth muscle spasms,
- increase in the amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach,
- lowering blood pressure,
- dilatation of peripheral vessels,
- mucus secretion,
- constriction of blood vessels in the pulmonary circulation,
- swelling of the skin, mucous membranes,
- hyperemia.
Histamine, which comes from food and accumulated as a result of improper functioning of the intestines, causes the same reactions in the body as the released endogenous one. Manifestations depend on which receptor the interaction occurs with.
There are 3 types of histamine receptors: H1, H2, H3.
The first are located in smooth muscles, the lining of blood vessels, and the central nervous system. When bound to H1, the bronchial muscles, intestinal muscles, and blood vessels contract, and the production of prostaglandins increases. Receptors of this type lead to the accumulation of fluid near the vessels, causing swelling and hives.
H2 receptors are found in the parietal cells of the stomach. Interacting with them, histamine causes increased activity of the stomach glands and the formation of mucus. Simultaneous stimulation of H1 and H2 leads to dilation of peripheral vessels and the occurrence of itching. H3 receptors, located in the central nervous system and peripheral parts of the nervous system, suppress the release of serotonin, norepinephrine and other neurotransmitters.
Free histamine can be bound to blood proteins or inactivated by the enzymes methylhistamine and histaminase. This process occurs in the liver, connective tissue, placenta, and kidneys. Inactivated, it is again stored in mast cells. A small amount is excreted in the urine.
Foods can directly cause the release of endogenous histamine, leading to the development of an allergic reaction, or they themselves are a source of increased amounts, causing food intolerance. In the latter case, histamine entering the body causes manifestations similar to true allergies.
The level of histamine in products is regulated by certain standards. Thus, according to Russian standards, its content in fish, for example, should not exceed 100 mg/kg.
The following foods activate your own histamine:
- strawberry,
- chocolate,
- alcohol,
- pig liver,
- egg white,
- wheat,
- shrimps,
- artificial additives (dyes, preservatives, etc.).
Products containing high levels of histamine include:
- sausages,
- beer,
- cheeses,
- sauerkraut,
- eggplants,
- tomatoes,
- canned foods.
The amount of histamine in products can increase significantly if they are stored improperly, if transportation conditions are violated, or if they are canned or frozen. After eating such food, even healthy people can have reactions to it.
Since histamine is quickly inactivated, mild single manifestations may go away on their own. However, in case of numerous and severe reactions, it is necessary to take antihistamines (according to the instructions for use). Histamine poisoning can lead to suffocation, seizures and death.