Why is my tongue swollen and painful?
Swelling under the tongue is characterized by swelling of its root or frenulum, as a result of which part of the organ increases in size, and the person experiences difficulty eating and speaking. There can be many reasons that cause this condition - from minor injuries and burns to malignant tumors of the oral cavity.
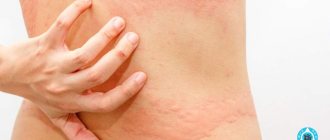
Allergy
Allergies are one of the most common reasons that cause swelling of the soft tissues of the face and mouth.
Allergens can be food or medications; sometimes a pathological reaction of the body is caused by cosmetics, personal care products, household chemicals, pollen, etc.
Swelling of the tongue, which appears when exposed to irritating factors, is called Quincke's edema.
It occurs on one side and develops quickly, sometimes literally in a few minutes (it seems that the organ is inflating like a balloon) and poses a serious threat to human life - it can cause suffocation and death. The patient needs to be given first aid immediately: give any antihistamine, and then take him to the hospital as soon as possible.
Mechanical injury to the frenulum
It is quite difficult to injure the frenulum, but if such a problem does occur, the root of the tongue may swell and hurt.
Swelling of the root of the tongue is often observed when burns from too hot food or drinks, as well as consumption of large amounts of sour, spicy or salty foods that irritate the salivary glands and taste buds.
Another common cause of pathology is piercing, which causes swelling and pain even if the piercing was done by an experienced master.
With minor injuries, unpleasant manifestations go away on their own after a few days, but sometimes an infection gets into the wound, resulting in an inflammatory or purulent-septic process that requires medical intervention.
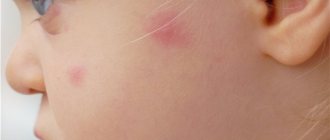
Inflammation of the lymph nodes and tonsils
Usually the lymph nodes and tonsils become inflamed during respiratory diseases (sore throat, flu, laryngitis, etc.), but in some cases similar symptoms are observed in people with disorders of the thyroid gland and upper digestive tract, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, carious processes in wisdom teeth . Extensive inflammation can spread to nearby tissues, including the root and frenulum of the tongue, and cause serious discomfort even in the absence of pain.
Thyroid diseases
Thyrotoxicosis, thyroiditis, hypothyroidism and other diseases associated with dysfunction of the thyroid gland are sometimes accompanied by swelling of the tonsils, throat and root of the tongue.
This is due to an increase in the size of the organ, impaired blood circulation and metabolic processes in the soft tissues, resulting in swelling.
Associated symptoms of thyroid disease include constant fatigue, psycho-emotional disorders (irritability, depression), unexplained weight loss or gain, and hair loss.
Cancer
Malignant neoplasms of the tongue are dangerous diseases that can lead to serious consequences.
In the initial stages they often go unnoticed, but as the pathological process develops, characteristic manifestations arise, including swelling and discomfort.
Typically, cancer looks like a small ulcer, growth or ball that gradually increases in size, and the list of symptoms is accompanied by severe pain that is not relieved by conventional painkillers.
Other reasons
There can be many reasons that cause swelling under the tongue - they include the following pathological conditions and diseases:
- advanced caries and gingivitis;
- HIV and syphilis;
- neurofibromatosis;
- anemia associated with vitamin B deficiency;
- dysfunction of the pituitary gland;
- tumor processes of the hematopoietic system (leukemia, myeloma);
- pathologies of muscle tissue - for example, rhabdomyolysis;
- genetic diseases (Down syndrome, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome);
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- diseases of the salivary glands;
- dehydration or fluid stagnation in the body;
- operations to remove teeth, trim the frenulum, etc.
Causes
There are many possible reasons for the appearance of lumps under the tongue. Here are some of the most common:
Ulcers on the mucous membrane
Canker sores, also known as canker sores, are open lesions that can develop anywhere in the mouth, including under the tongue.
Ulcers appear suddenly. They have no known cause, but are not contagious. Some researchers believe that ulcers are a type of immune system reaction ().
Here are other factors that can also cause ulcers:
- injury or damage to the tissue under the tongue
- exposure to spicy, sour or dairy foods
- hormonal changes, such as during menstruation, pregnancy or menopause
- gastrointestinal diseases such as celiac disease
- nutritional deficiencies such as low iron, folate, and vitamin B12
- physical or emotional stress
- genetics
- infections
Most ulcers are minor and go away on their own within 4–14 days ().
Cyst of the oral mucosa
Oral cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in the tissues of the mouth. An oral mucosal cyst develops near one of the openings of the salivary glands under the tongue, on the lips, cheeks, or floor of the mouth.
Oral cysts appear as soft, swollen bumps that range in color from flesh-colored to dark blue. These cysts typically disappear periodically when they rupture and reappear when they are irritated by saliva.
Although a person can develop oral cysts at any age, they usually appear between the ages of 10 and 30 ().
Human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus, or HPV, is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Scientists have identified more than 180 subtypes of HPV (,).
HPV infections lead to lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. According to the CDC, about 40 subtypes of HPV can infect the mouth and throat ().
People with minor oral HPV infections do not develop symptoms. However, those who experience them may notice:
- small, hard bumps under the tongue or on the lining of the mouth
- bumps that are white, pink, red, or flesh-colored
- painless, smooth and slightly rising bumps above the surface
- single irregularity or group of irregularities
The body can clear an HPV infection within 2 years without treatment. However, HPV is the leading cause of oropharyngeal cancer (,).
Lymphoepithelial cyst
Lymphoepithelial cysts are slow-growing benign formations that develop in the salivary glands.
These small, hard nodules are located just under the lining of the mouth. Lymphoepithelial cysts usually appear as flesh-colored, white or yellow bumps under the tongue or on the floor of the mouth.
Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis, also known as salivary stones, is a condition in which stones from crystallized minerals form in the ducts of the salivary glands. Sialolithiasis is the most common cause of swelling of the salivary glands ().
A stone that forms in the sublingual salivary gland, located under the tongue, can result in a painful lump.
Here are other symptoms of sialolithiasis:
- pain or discomfort in the mouth that gets worse while eating
- pain or swelling under the jaw
- infection in or near the affected gland
- dry mouth
Salivary gland tumor
A salivary gland tumor that forms in the sublingual salivary gland can cause a lump or tumor to form under the tongue or near the jaw.
Typically, if a tumor develops in a smaller salivary gland, it is more likely to be cancerous.
For example, although less than 1% of salivary gland tumors develop in the sublingual salivary gland, 70–90% of sublingual gland tumors are malignant. The malignant tumor grows quickly and can spread to other parts of the body ().
Tumors of the salivary glands can cause the following symptoms:
- lump or painful swelling under the tongue, jaw, ear, or neck
- numbness or muscle weakness in part of the face
- difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
- fluid leaks from ear
Symptoms accompanying a tumor under the tongue in humans
The most common symptom that occurs along with a tumor under the tongue is pain.
It can have varying intensity, be localized in one place, spread to the entire surface of the tongue and throat, or radiate to the neck, jaw or back of the head.
In infectious and inflammatory diseases, symptoms include high fever, cough, deterioration in general health and intoxication of the body.
If the cause of swelling is dental diseases, allergic reactions, vitamin deficiencies and thyroid disorders, the surface of the tongue changes color, becomes too bright or pale, becomes covered with cracks, white or yellow coating.
Treatment methods
Treatment for tongue swelling depends on the cause of the pathology - the most common of them is an allergic reaction, which can be relieved with antihistamines.
Often a similar symptom is observed during inflammatory and infectious processes, which are treated with antibiotics and symptomatic agents. In case of dental diseases, it is additionally necessary to sanitation the oral cavity and remove tartar.
Disorders of the thyroid gland require treatment with special medications that activate or block the activity of the organ, and for malignant neoplasms, surgical intervention is used.
At home, swelling and pain under the tongue can be removed with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, rinsing the mouth with solutions of soda, salt and propolis, and infusions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, oak bark, calendula, sage). In addition, you need to reduce the amount of salty, spicy and sour foods in your diet, eat grated and warm foods, and increase the amount of vitamins and microelements in your diet.
The tongue is a sensitive organ that is one of the first to react to problems in the body with swelling, pain and other symptoms. To avoid unpleasant health consequences, if any of its parts are swollen, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Source: zubki2.ru
What could be the cause of the problem?
- Damage to the frenulum. This is a common cause of the problem. The mucous membrane is very vulnerable. There is a very delicate structure here that can be damaged during hygiene procedures or eating. If you have a shortened frenulum, then it can be injured while talking or eating. In childhood, stomatitis often occurs, which is accompanied by erosion throughout the entire oral cavity. This can also cause swelling in the mouth;
- Acute sore throat can cause inflammation of the area under the tongue;
- Teeth with caries are a source of infections. As a result, the mucous membrane may be affected; the area under the tongue is no exception;
- Formation of phlegmon or abscess. Swelling under the tongue is associated with purulent inflammation. This is a very dangerous disease that requires immediate specialist intervention. Cellulitis develops due to untreated periodontitis or periostitis;
- Inflammatory process of the salivary gland;
- Anomalies in the development of the hyoid bone or mechanical trauma that made its shape asymmetrical;
- Allergic reaction to irritants;
- Mechanical injury to muscle fibers, nerve endings, and blood vessels located in the oral cavity.
During treatment, you cannot do without consulting a doctor, as self-medication can lead to unpleasant consequences. It is necessary to choose medications taking into account the cause of the problem. Otherwise, it will be possible to remove only the consequence, which means that after a while it will make itself felt again.
At the first manifestations of negative sensations, you can independently check the oral cavity for the presence of ulcers, plaque, abscesses, pus and rashes. This way you will roughly understand what the problem is and how to solve it.
Diagnostics
A doctor can diagnose most causes of lumps under the tongue by performing a physical examination and asking the person to describe their current symptoms. He may also look at the person's and family's medical history to identify risk factors for certain diseases.
To confirm the diagnosis or rule out other possible causes, the doctor may use one or more diagnostic tests. These tests could be the following:
- a blood test that measures the number of white blood cells to check for infection
- smear culture test to detect infectious pathogens such as bacteria or fungi
- imaging tests, such as a CT scan or MRI, to look for structural abnormalities in the mouth
- biopsy to analyze tissue samples for cancer cells
Symptoms that indicate inflammation of the salivary gland:
- Inflammatory process in the tongue area;
- Pain that increases over time;
- The affected area has become bright red and shiny;
- Cloudy saliva accumulates under the tongue;
- The presence of purulent masses indicates an advanced condition that is dangerous to health;
- Increased body temperature to 39 degrees;
- Deterioration in health;
- It becomes painful to talk and eat.
This indicates prolonged absence of treatment and deterioration of the condition. It is important to choose the right comprehensive treatment, which will contain not only medications, but also nutritional correction. To stop the spread of the inflammatory process, it is enough to do good oral hygiene.
Saliva must be produced in the oral cavity constantly. If you notice that there is much less saliva, you need to consult a doctor to choose a remedy to activate its production. At home, cranberries, lemon and spices will help produce saliva.
Complications
The consequences of tissue inflammation in the sublingual area are as follows:
- neuritis;
- encephalitis;
- pancreatitis;
- nephritis;
- myocarditis;
- necrotic changes in biological fluid;
- inflammation of the membranes of the brain;
- the appearance of numerous purulent foci in the affected areas of soft tissue;
- sepsis.
On this topic
Complications occur due to blockage of the salivary ducts. Bacteria present in the oral cavity are excreted along with saliva. A closed duct causes germs to spread throughout the body and infect the salivary glands.
Another consequence of inflammation of the sublingual area is mumps or mumps. The disease affects the salivary glands located in the parotid space. In severe cases of the pathology, the salivary ducts and gonads are damaged.
Help at home
If you suffered a mechanical injury before your tongue became swollen or you visited a dentist, you can try to help yourself. However, this does not eliminate the need to visit a doctor.
- Rinsing the mouth with a solution of salt and soda, as well as antiseptic agents. If there is no improvement within two days, you should definitely see a doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment;
- Optimize your diet. If the pain under the tongue is not constant, then you should pay attention, after which they arise. Sour and bitter foods can cause allergic reactions;
- Avoid cigarettes, as they negatively affect the oral mucosa.
If the above recommendations do not help, then you should contact a specialist. He will determine the exact cause of the problem and prescribe effective treatment. Remember, only timely treatment guarantees recovery without health consequences.
Source: dentalgu.ru
How to treat an abscess in children
To identify an abscess, a puncture is often performed. This will make it possible to find out which specific pathogen caused the abscess. Also, the doctor will immediately determine which antibiotic is most effective against it. Most often, treatment is surgical. The doctor opens the abscess, cleans it, treats it with antibacterial agents, prescribes antibiotics and other drugs.
As a result, we emphasize once again that it is easier to avoid such inflammation than to treat it later. Just don't forget about basic hygiene. Well, if symptoms of the disease appear, immediately go to the doctor.
More
- Cracks in the tongue
- Oral candidiasis
- Arthritis of the jaw joint
Location of the gland and the mouth of the excretory duct
The sublingual gland (in Latin sublingual glandem) is mixed and secretes a serous-mucosal secretion (saliva). This is a paired organ that is located at the bottom of the mouth on either side of the tongue. Its excretory duct opens on the sublingual vessel, forming the papilla.
Human digestion begins with the oral cavity, and saliva plays one of the main roles in this. It moistens and softens food, thereby facilitating the process of swallowing it, and is involved in the primary breakdown of carbohydrates. In addition, salivary enzymes have antibacterial and protective properties.
Therefore, if the gland has increased in size and painful sensations have appeared, then this is a reason to contact a dentist, since there are many pathologies of the salivary glands that need to be treated immediately. In medicine, inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue is called sublinguitis.
Treatment of frenulum and gland blockage
If alarming symptoms appear, consult a doctor who will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and determine the cause of the pathology. Treatment is prescribed only after the factors causing the disease have been identified.
For inflammations and injuries of the frenulum, rinses with antiseptics are prescribed, which remove pathogenic bacteria from the oral cavity and stop the inflammatory process. The simplest options are soda solution and furatsilin. You can use special medications:
- Stomatofit – dilute 10 ml of tincture in 50 ml of water;
- Romazulan is a concentrated infusion of pharmaceutical chamomile. For 1 liter of water, take 2 tablespoons. The drug is suitable for children;
- Chlorophyllipt is an alcoholic tincture of eucalyptus. To rinse, take a tablespoon of product per 300 ml of water. Children can use it. Note that Chlorophyllipt is often used against stomatitis;
- Calamus tincture – dilute 5 ml of alcohol tincture in 100 ml of water;
- Stomatidin, Hexoral are herbal medicines for hexidine. Strong antibacterial and antiseptic agents that do not require dilution. Efficiency is high;
- Iodinol or blue is a ready-to-use solution that is prescribed for wiping the oral mucosa. This drug is also often used in the treatment of stomatitis. Read more about how to use silka for stomatitis in this material.
You need to rinse your mouth every time after eating, since solutions can be toxic and should not be swallowed. You cannot eat or drink for half an hour after the procedure. You can replace pharmaceutical remedies with folk remedies - for example, a solution of salt and soda, cabbage juice (diluted with water 1:1), parsley juice (wipe the inflamed area).
If everything is fine with the frenulum, but there is pain or swelling, contact your dentist for a diagnosis. Possible causes of inflammation are problems with teeth, inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth, destructive processes in the salivary gland, lymph nodes, purulent processes. Do not self-medicate, because you can only make the situation worse and waste time.
You can also get rid of pathology using proven folk methods. They are used in combination with traditional treatment methods. Rinsing the mouth with a saline solution will help get rid of inflammation of the salivary gland. To prepare it, it is better to use sea salt. For a glass of warm water you need to take a teaspoon of salt. The oral cavity is treated with this solution after each meal.
If the inflammation in the mouth under the tongue has an infectious etiology, a weak solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) should be used. The substance has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties. You can also cleanse the oral cavity of pathogenic pathogens using baking soda. The solution is prepared at the rate of 1 teaspoon of soda per 200 ml of hot water. You should rinse your mouth after the solution has cooled to an acceptable temperature (30-35 °C).
The main task of the doctor in the treatment of blockage of the salivary glands is to restore the process of salivation.
Various techniques are used for this:
- Stones from the gland are removed manually by the dentist.
- In simple cases, it is enough to chew or suck something sour to stimulate salivation.
- In severe cases, surgical intervention is required, including removal of the salivary gland.
Inflammation in the hyoid frenulum can be caused by:
- periodontitis, stomatitis, gingivitis;

- allergies;
- low-quality hygiene products: brush, toothpaste, mouthwash.
To relieve inflammation, the mouth is rinsed with the following solutions:
- based on chamomile and sage;
- stomatophyte;
- chlorophyllipt;
- based on soda diluted in boiled water.
But even after the inflammation is relieved, a visit to the dentist cannot be avoided. The doctor will examine the damage and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Of course, at the first symptoms of pain in the area under the tongue, you should seek qualified medical advice. He must quickly determine the cause of the pathology and prescribe the correct treatment. It will depend on what exactly provoked the appearance of pain in the tongue area. As practice shows, most often this happens due to an inflammatory process or injury to soft tissues. Quite often the frenulum becomes inflamed. This problem is especially relevant for those who have pathologically short periods. With a short bridle, it is easy to injure it, since it experiences more load than a normal-length bridle. If the doctor has determined that the main reason lies in the fact that the frenulum was injured or inflamed, then rinsing with antiseptic agents will help you. They will help eliminate pathogenic bacteria from the oral cavity and relieve inflammation. These are the simplest and most affordable drugs. For example, furatsilin, a soda solution, is suitable. There are also herbal-based preparations. They are perfect even for treating children. Let's take a closer look at these mouthwashes. Most often, doctors prescribe the following mouth rinses in this situation:
- Stomatophyte. You need to dilute 10 ml of this product in 50 ml of water.
- Romazulan. This is an infusion of pharmaceutical chamomile, just more concentrated than we usually brew. For a whole liter of water you will need only 2 tablespoons. This drug is safe even for children.
- Chlorophyllipt. This drug is an alcoholic infusion of eucalyptus. Dissolve a tablespoon of the product in 300 ml of water and rinse your mouth with the resulting solution. It is also suitable for children.
- Tincture of calamus (alcohol). 5 ml of the substance must be diluted in 100 ml of water.
- Hexoral and Stomatidin. These drugs are no longer herbal. These products are based on a synthesized substance – hexidine. It has proven itself to be an antibacterial and antiseptic agent. It doesn't get divorced. These drugs are often prescribed for stomatitis. And they do their job perfectly. Even severe forms of stomatitis are not scary for them.
- Iodinol. This drug also does not require dilution. It is initially ready for use. Doctors often prescribe it for wiping the delicate oral mucosa.
In order for all these solutions to work as efficiently and safely as possible, you should take into account simple rules:
- Rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Never swallow even a small amount of the solution.
- For the rinse to work. After it, you should not eat or drink for at least half an hour.
- Also rinse your mouth in the morning and before bed.
For pain under the tongue, not only pharmaceutical rinsing solutions help. Traditional medicine is no less effective.
- The most affordable of them is to use a solution of table salt and baking soda as an antibacterial rinse.
- Cabbage juice is also the most effective. It should be diluted in half with water.
- Wipe areas where there is inflammation with regular parsley juice.
- For the same purpose, you can use carrot or beet juice. It is diluted half and half with water.
All of these folk remedies have pronounced antiseptic properties, that is, they are able to destroy pathogens in the oral cavity.
purulent inflammation, dental problems, inflammation of the lymph nodes or salivary gland. With such a symptom, you need to rush to the doctor. He should quickly prescribe treatment and carefully monitor the general condition of the patient. It is unacceptable to self-medicate! Traditional medicine can only be a light addition to the main treatment. There are the most complex cases that even require hospitalization or urgent surgery.
In any case, contact your dentist at the first sign of pain under your tongue. Perhaps, thanks to the timely assistance of a specialist, you will avoid serious and dangerous complications.
Classification of inflammation
Inflammation of the salivary glands under the tongue is classified as follows:
| Signs of inflammation | Classification |
| By etiology |
|
| Inflammatory in nature |
|
| According to the form of the disease |
|
| By localization |
|
| According to the nature of the disease |
|
Below is an image - a photo of inflammation of the gland under the tongue
Causes of inflammation of the salivary gland duct
The ducts of the salivary gland in the sublingual area become inflamed, usually due to mechanical damage when:
- preparation of lower teeth for crowns;
- wounds;
- during operations in the area of the tongue;
- removal of concretions - stones.
A stone in the duct (calculus) most often forms in the submandibular and sublingual glands. The main reasons for its formation:
- slow flow of saliva;
- insufficient saliva production;
- deformation of the salivary ducts;
- consequences of treating the thyroid gland with radioactive iodine.
As a result of scarring of the lesions, the duct can become so closed that it threatens the formation of a ranula cyst.
Why does the parenchyma of the gland under the tongue become inflamed?
Diseases of the tissue of the sublingual salivary gland (sialoadenitis) include:
- processes of a reactive-dystrophic nature;
- chronic and acute inflammatory process;
- tumors;
- cysts.
Gland pathologies of a reactive-dystrophic nature, as a rule, are not an independent disease; they occur with systemic damage to the lacrimal and salivary glands:
- Mikulicz syndrome (benign lymphoid lesion);
- Sjögren's disease (a combination of signs of damage to the lacrimal and salivary glands with autoimmune diseases);
- for endocrine diseases.
Chronic and acute inflammation of the salivary gland
The cause of acute inflammation of the gland under the tongue can be viruses:
- flu;
- mumps;
- ARVI.
Bacterial inflammation occurs due to inattention to oral hygiene standards. The culprits of the infection are staphylococci, streptococci, and in some cases E. coli.
Chronic inflammation is rare. As a rule, it occurs on both sides, and occurs simultaneously with damage to other salivary glands - the parotid, submandibular. In this case, the gland increases slowly, pain appears during exacerbations of the process.
Cysts and tumors
One of the most common pathologies is a cyst, which occurs due to disturbances in the outflow of saliva. This is a connective tissue capsule filled with liquid contents. If the oral mucosa under the tongue is thinned, spontaneous rupture of a benign formation may occur, as a result of which it decreases in size. However, after some time (weeks and months can pass), it recurs and grows again.
Note! A significant increase in the sublingual glands may indicate their tumors, which in 90% of cases are benign.
Among them is an adenoma, which can be single or multiple, developing due to excessive growth of glandular tissue. This formation is benign, but complete removal of the affected salivary gland is recommended, due to the tendency of the adenoma to become malignant.
Symptoms of inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue
When inflammation of the salivary glands under the tongue occurs, symptoms may include the following:
- swelling;
- pain when speaking and chewing;
- decrease in the amount of saliva produced;
- for infectious lesions - symptoms of general intoxication (fever, weakness, headache).
Clinical picture in chronic and acute forms of the disease:
| Form of the disease | Signs |
| Acute inflammation |
|
| Chronic form |
|
Treatment
A doctor can diagnose inflammation of the sublingual gland through a visual examination. He also determines how to treat inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue, depending on the stage of the process and the presence of concomitant pathologies. In particularly difficult cases, or if cancer is suspected, examination can be carried out using the following methods:
- Ultrasound;
- MRI;
- histological examination.
Therapeutic treatment
Conservative methods of treating inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue are used in acute forms of inflammation of a viral and bacterial nature. May be assigned:
- antibiotics;
- antiviral drugs;
- antipyretic drugs;
- painkillers.
In the treatment of chronic inflammation, methods are used to increase the body's resistance and to treat associated pathologies. Locally, in case of exacerbations, novocaine blockade is used.
Forecast
Lumps under the tongue may appear suddenly and for no apparent reason. These bumps often go away on their own without treatment.
Some bumps go away and appear again after a few months or years. Other types of lumps under the tongue go away and never appear again.
People with more serious underlying medical conditions, such as HPV infections and salivary gland cancer, can have a very good prognosis if doctors catch the disease early.
Most HPV infections clear up within 2 years. The relative 5-year survival rate for localized salivary gland cancer is 94% if it has not spread (,).
Surgery
Surgical intervention is required in the following cases:
- Removing stones from ducts. Until recently, stones in the gland were treated by completely removing the gland. Nowadays, with the help of the latest endoscopic equipment, the SG duct is bougienaged and the stone is removed from there. Sometimes it is necessary to first crush the stone so that it can be easily removed from the small duct. Only if this method is ineffective, doctors proceed to surgery and remove the gland.
- If an abscess forms due to acute inflammation of the gland under the tongue, surgical treatment is also indicated.
- When removing cysts and tumors. In the case of a retention cyst, it is opened and emptied; in difficult cases, the cyst is removed along with the salivary gland.
Prevention
To prevent inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract it is necessary:
- undergo annual influenza vaccination;
- carefully monitor the condition and hygiene of the oral cavity;
- promptly treat carious teeth;
- avoid hypothermia;
- strengthen the immune system with hardening procedures.
The most important advice is to have your oral cavity sanitized by a dentist twice a year in order to promptly identify abnormalities in the condition of the salivary glands.
Do I need to follow a diet?
Proper nutrition during treatment is the key to a speedy recovery. Food should be well chopped. Excessive chewing movements will only increase pain and irritate the inflamed area of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. The menu should consist of soups, vegetable and meat purees, and cereals.
Particular attention is paid to the drinking regime. Before starting your meal, you should drink dried fruit compote, fruit drinks or water with lemon juice. This will help stimulate the production of salivary fluid.
How to treat inflammation of the glands under the tongue
- For etiological forms of the disease, sulfonamides and antibiotics are used (for bacterial lesions). They are injected into the salivary duct, taken orally or intramuscularly. For viral infections, Arpetol and Interferon are indicated.
- To increase salivation, use pilocarpine hydrochloride (5 drops three times a day). Among the folk remedies, tincture of wormwood and any acidic foods increase the secretion of saliva.
- For a serous inflammatory process, compresses with a solution of dimexide (30%), oil compresses, and UHF are prescribed.
In order to increase immunity, vitamin complexes are prescribed, as well as desensitizing therapy.
Source: stomach-diet.ru
Folk recipes
The gland under the tongue is inflamed, a photo of which is presented in the article, and no aggravating symptoms are found, then you can use home and folk methods.
Simple remedies to improve salivation:
- Rinse with hot water. Hold the water in your mouth for 10-15 seconds, then rinse your mouth with cold water. The procedure should be performed at least 5 times a day. This helps dissolve the stones.
- Drink pure lemon juice, first holding the liquid in your mouth for 5-7 seconds. The acid is good at removing blockages in the salivary glands.
- Sour sucking candies help increase saliva production.
For sialolithiasis, lotions help:
- Mix 1 tsp. honey, 1 tsp. olive oil, Novocain ampoule. Stir everything and lubricate the inflamed areas.