Sinusitis in adults is not a rare disease. It makes itself felt especially often during the cold season. This disease is dangerous because, in the absence of proper treatment, it can provoke the development of a chronic form of the disease, and will also be complicated by other ailments. However, it should be noted that with high-quality, timely and effective treatment, it is possible to get rid of sinusitis and stop it in the initial phases of development, preventing the disease from becoming chronic.
Definition of disease
Sinusitis is a pathology in which an inflammatory process occurs in the maxillary (maxillary) sinus. This cavity is steamy, so inflammation can involve one or both parts.
The maxillary sinuses are located on the sides of the nasal passages and are lined with mucous membranes on the inside. They communicate with the nose through small passages. The functional purpose of these sinuses is to cleanse and warm the air entering during nasal inhalation, as well as to form the correct pronunciation of sounds. With sinusitis, all these abilities are distorted.
Depending on the extent of inflammation, unilateral and bilateral sinusitis are distinguished. The following types of illness are distinguished:
- Acute sinusitis. It occurs suddenly and is manifested by nasal congestion and facial soreness. These symptoms last for about 10 days and rarely last more than a month.
- With semi-acute sinusitis, the inflammation process can last about 2 months.
- The chronic form of sinusitis is characterized by persistence of symptoms for more than 2 months.
- Recurrent sinusitis occurs several times a year.
Depending on the nature, acute sinusitis can be catarrhal, allergic, odontogenic and purulent. According to the same indicator, the chronic form is divided into a number of subtypes of sinusitis:
- Polypous;
- Hyperplastic;
- Atrophic;
- Mixed.
Causes
The main cause of sinusitis is considered to be an infection that enters the nasal cavity through the blood or through breathing. Nasal breathing is also impaired by such conditions as:
- Deviation of the nasal septum;
- Vasomotor rhinitis;
- Hypertrophic rhinitis (enlargement of the nasal turbinates).

The cause of sinusitis can be disorders of the immune system, which lead to long-term chronic diseases:
- Parasitosis;
- Allergic conditions;
- untimely or improper treatment of colds, acute respiratory infections, rhinitis.
Modern medicine has identified other causes of sinusitis:
- Injuries to the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses;
- Penetration of viruses and bacteria into the nasopharynx;
- Prolonged stay in a room with very dry air;
- Being in a draft;
- Inhalation of chemical fumes (for example, in hazardous industries);
- Neglected dental condition and poor oral hygiene;
- Past influenza or acute respiratory viral infection;
- Severe hypothermia of the body;
- Disruption of the secretory glands;
- Growth of polyps;
- Allergic reaction of the body to various external irritants;
- Dangerous diseases (tuberculosis, fungal infection of the mucous membrane, radiation sickness, tumors, etc.).
Regular use of vasoconstrictor drops is the main reason for the accumulation of large amounts of mucus in the maxillary sinuses, against which sinusitis develops.
Diagnostics
In most cases, making a diagnosis does not take a long time and the otolaryngologist, in addition to the external symptoms of the disease present in the patient, needs to make sure that his body really reacts negatively to an internal or external stimulus. To do this, the patient is prescribed the following types of tests:
- blood from a vein, which is necessary for isolating in the laboratory a specific type of allergen that provokes inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses;
- morning urine, which gives the doctor detailed information about the general condition of the body, and how serious the inflammation in the upper respiratory tract is;
- bacterial selection of the mucous membrane from the walls of the nasal canals with further bacteriological seeding to make a comparative analysis and exclude the possible presence of infection;
- an immunogram, the results of which reflect the state of the patient’s immune system, as well as how acutely it reacts to allergens entering the body from the external environment;
- X-ray of the maxillary sinuses with identification of areas of epithelial tissue where inflammation is localized.
If necessary, a computed tomography scan of the head may be prescribed if inflammation in the paranasal sinuses, of an allergic nature, has led to the fact that fluid has begun to accumulate inside their cavity, requiring urgent evacuation.
Symptoms
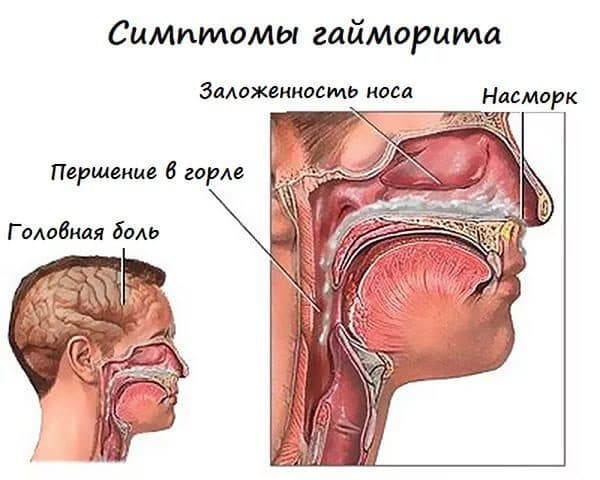
The following manifestations are characteristic of acute sinusitis:
- Increase in body temperature to 38º C;
- General weakness, weakness;
- Prolonged runny nose (discharge is mucous, mucopurulent or purulent in nature);
- Nasal congestion;
- Decreased sense of smell;
- Cough (when nasal secretions flow down the back of the throat into the larynx);
- Putrid odor of discharge (with purulent sinusitis);
- Pain in the area of the bridge of the nose and brow ridges, aggravated by coughing and sneezing, tilting the head down;
- Feeling of pressure in the sinuses and nose;
- There may be swelling of the soft tissues under the eyes.
The clinical picture of chronic sinusitis is more smoothed. Patients are concerned about:
- Slight general weakness;
- Fatigue during intellectual work;
- Mild headaches without clear localization;
- Feeling of heaviness in the head;
- Nasal congestion;
- Deterioration of sense of smell;
- Sore throat, dryness, sore throat when swallowing;
- Swelling of the lower eyelid in the morning is conjunctivitis, indicating involvement of the orbital wall in the pathological process.
The chronic form of sinusitis is characterized by an undulating course, with alternating periods of remissions and exacerbations.
How to recognize allergic sinusitis and treat it?
Allergic sinusitis is one of the types of sinusitis or sinusitis (this is the second, more common name for the disease among people).
Sinusitis in general is an inflammatory process of the maxillary sinuses - the paranasal sinuses, located in the body of the maxillary bone. The frontal, paranasal and ethmoid sinuses are also affected. In other words, the entire area near the wings of the nose, above and below the eyes becomes inflamed.
Sinusitis is one of the most common diseases in the world. It affects men and women, adults and children equally. Residents of literally all countries get sick; neither epidemiologically dangerous nor epidemiologically clean regions with respect to sinusitis are identified.
Causes and nature of sinusitis
Most diagnoses of sinusitis are made against the background of a viral infection complicated by bacterial invasion.
Rhinitis (runny nose) caused by a viral disease, in the absence of treatment or with prolonged or inadequate treatment, creates conditions that are ideal in terms of humidity and temperature for the appearance and spread of pathogenic bacteria in the sinuses.
Sputum accumulates in the sinuses, in which microorganisms thrive - streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci and others. The immune system ceases to cope with the progressively growing number of harmful microbes and an inflammatory process begins, fraught with many complications.
Sometimes bacterial invasion does not occur and sinusitis develops against the background of only a viral disease. This happens when the pathogens are influenza viruses, adenovirus, and parainfluenza.
Less commonly, the cause of sinusitis is fungal infestation.
There have been cases where sinusitis developed against the background of multiple lesions and tooth decay, severe nosebleeds of various etiologies. Getting contaminated water into the nose or mouth when swimming in pools and open water also causes sinusitis.
Sometimes sinusitis is allergic in nature. It can develop against the background of allergic rhinitis, which is not compensated in time. It also happens that allergic sinusitis develops on its own, and not against the background of another disease of an allergic nature.
Symptoms of sinusitis
In the earliest stages, the patient experiences watery, mucous or mucous-watery discharge from the nasal passages. These discharges do not indicate that sinusitis is developing in the body, including allergic sinusitis, but it does indicate the development of rhinitis - inflammation of the nasal mucosa.
If rhinitis is not eliminated in time, the structure, color and density of the discharge changes.
Sinusitis should be suspected in the following cases:
- Rhinitis continues for more than a week and either there is no improvement in the condition or it worsens,
- The discharge becomes thick, acquires a yellow-green color, and is difficult to discharge from the nose,
- In addition to nasal congestion and runny nose, sore and sore throat, irritation, and cough are added, caused by the flow of thick mucus down the back wall of the throat,
- The patient experiences pain around the nose, around the eyes, and in the middle of the forehead. Inhaled air, accumulated thickened sputum, and pus press on the inflamed walls of the affected sinuses, which causes pain. The pain intensifies when tilting the head down, tensing the facial muscles, coughing and sneezing.
- My head hurts and I feel a little dizzy. This is explained by the fact that due to impaired nasal breathing, increasing oxygen starvation occurs in the body, including brain cells.
- A mild toothache is felt. The lower wall of the maxillary sinuses is so thin that accumulated phlegm and pus can flow to the roots of the teeth, causing local inflammation there.
- The temperature rises and remains at approximately 38 degrees.
Allergic sinusitis has the same symptoms and the same treatments as other types of sinusitis.
Treatment of sinusitis
Only an otolaryngologist can competently treat allergic sinusitis and its other types.
He will make a diagnosis based on an examination of the patient and the results of laboratory tests and prescribe the following drugs: antibacterial, antiviral or antifungal to eliminate the infection, antihistamines to extinguish the allergic reaction, decongestants to relieve swelling, vasoconstrictors to reduce secretion, painkillers to relieve pain.
Advanced conditions require surgical treatment, for example, puncture to remove thick mucus from the sinuses.
You should seek medical help in the treatment of allergic sinusitis in the following cases:
- When a runny nose does not stop within a week,
- There was a deterioration in health after the first three days of the disease,
- The temperature remains stable and does not drop,
- Visual and/or hearing impairments have been noted,
- Concerned about severe headaches that cannot be stopped or subside,
- There was a history of sinusitis of any etiology,
- Allergic sinusitis is accompanied by swelling of the nasopharynx, severe difficulty breathing, an allergic rash on the face and neck, and swelling of the face.
If left untreated, sinusitis leads to inflammation of the optic nerve, which can lead to loss of vision, inflammation of the meninges (meningitis), and osteomyelitis (purulent damage to the bones of the skull).
Treatment in adults is easier than in children.
- Firstly, the range of antibacterial agents approved for use by children, especially in the first years of life, is limited.
- Secondly, children do not know how to clear mucus from their nose by blowing their nose, and toileting their nose performed by adults does not guarantee complete cleansing.
- Thirdly, the condition of children deteriorates faster and most often it is difficult to help them at home.
Prevention of sinusitis
Allergic sinusitis is difficult to prevent if allergic reactions have not occurred before.
If a person knows his tendency to immunopathological reactions, he should limit contact with allergens, adhere to a hypoallergenic diet and regularly perform nasal toilets.
In case of allergic rhinitis, it is necessary to prevent the accumulation of mucus in the nasal passages and use anti-allergic drops.
To prevent a runny nose from turning into sinusitis, you need to thin the mucus in the nose. To do this, you need to drink plenty of fluids and regularly irrigate the nasal cavity with seawater sprays.
Facilitate the condition of inhalation with saline solution. The use of herbs and essential oils for unknown causes of allergies is prohibited due to possible complications.
It is necessary to stop smoking at least for a while while you have a runny nose. Smoking irritates the mucous membrane, causing additional mucus secretion. In addition, substances in tobacco smoke are strong allergens and toxins.
It is important not to drink alcohol due to its ability to cause swelling. Against the background of sinusitis, swelling can be very dangerous.
Following the rules of personal hygiene will help prevent infection from entering the sinuses: washing your hands before washing and touching your face, rinsing the nasal passages, using only clean individual handkerchiefs.
Allergic sinusitis
Source: https://allergiu.ru/bolezni/allergicheskij-sinusit.html
Possible complications
In the absence of proper treatment, sinusitis in adults can provoke the development of a chronic form of the disease. Other consequences of sinusitis include the transition of the inflammatory process to the upper jaw, eye socket and teeth. In addition, sinusitis in its chronic form acts as a source of infection, leading to repeated sore throats, pharyngitis, and dental diseases. A closed cavity filled with pus causes an abscess. Acute inflammation of the maxillary sinuses can lead to trigeminal neuritis, which causes facial pain.
With high-quality, timely treatment, in most cases it is possible to get rid of sinusitis and stop it in the initial phases of development, preventing the disease from becoming chronic.
Allergic sinusitis and everything you need to know about the disease

Under the influence of a provoking factor (allergen), an acute reaction . Harmful substances coming with the air flow provoke allergic sinusitis . This is one of the manifestations of hay fever, which without treatment becomes chronic. To completely cure the disease, timely complex therapy is prescribed.
mold and its components;
Treatment
Treatment of sinusitis in adults begins only after receiving the results of additional diagnostics. Symptoms of sinusitis often resemble acute sinusitis, allergic rhinitis and other diseases, therefore, in addition to rhinoscopy, examination of the nasal passages using special mirrors and a general blood test, other types of examinations will be required, such as:
- X-ray of the sinuses;
- Ultrasound of the nasal cavity;
- Computed tomography of the facial region of the skull;
- Puncture of the maxillary sinuses followed by bacteriological examination of the material taken.
By medication
Treatment of acute sinusitis in adults may include:
- Antiviral drugs (Groprinosin, Ingavirin, Amizon). They are prescribed if pus is not detected on the x-ray of the maxillary sinuses, but there is only swelling of the mucous membrane, i.e. i.e. the nature of the disease in this case is viral.
- If pus is detected, antibiotics are indicated: cephalosporins (Cefix, Ceftriaxone), aminopenicillins (Amoxiclav), respiratory fluoroquinolones (Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin). You can achieve a high concentration of an antibacterial drug at the site of inflammation by using local antibiotics in the form of sprays (for example, Bioparox).
- Vasoconstrictor drops and sprays (Otrivin, Nazivin, Sanorin). They are used to restore air exchange between the inflamed sinuses and the nasal cavity.
- The combined drug Rinofluimucil will help relieve swelling from the mucous membrane of the nose and maxillary sinuses, as well as improve the rheological properties of sputum.
- Antipyretics (Nurofen, Imet, Panadol, Solpadeine) are prescribed for elevated temperatures. These drugs will reduce pain and have a mild anti-inflammatory effect.
When signs of inflammation decrease and the acute stage of the disease transitions to subacute, further treatment is carried out using physiotherapy, such as:
- UHF on the maxillary sinuses;
- Sollux;
- Magnetic therapy on the pharynx area;
- Laser therapy.
The course of physiotherapy treatment ranges from 10 to 12 sessions.
Drug therapy during an exacerbation of chronic sinusitis usually includes:
- Vasoconstrictor drugs (Nazivin, Nazol, Otrivin) in short courses;
- Rinsing the paranasal sinuses with disinfectant solutions, followed by the introduction of antibacterial drugs and proteolytic enzymes into the cavity;
- Immunity correctors;
- Antihistamines: Cetrin, Telfast, Erius (in case of allergic inflammation) and hormone-containing sprays (Avamys).
In severe forms of sinusitis, a drainage puncture is performed to restore the patency of the sinus anastomosis. This procedure makes it possible to remove pus from the sinus and introduce antibacterial drugs into the area of inflammation.
With necrotic, purulent-polyposis forms of sinusitis, conservative treatment is often ineffective. In this case, the patient is recommended to undergo surgery – maxillary sinusotomy.
Folk remedies
Treatment of sinusitis can be supplemented with folk remedies, but they will be most effective at the initial stage of inflammation. We offer some of the best recipes:
- Cyclamen horse for sinusitis
Honey, soda and sunflower oil are a very effective remedy for sinusitis. Mix one level teaspoon of soda with the same amount of sunflower oil (it is better to take unrefined) and liquid honey. A mixture of honey, soda and oil in a 1:1:1 ratio has a strong effect on bacteria actively reproducing in the maxillary sinus. Dip a cotton swab into the mixture and gently insert it into your sinus. Apply the solution to one nostril, while lying on the side opposite the nostril into which the medicine was injected. After 15-20 minutes, repeat the procedure by inserting a tampon with the mixture into the other nostril. Don't worry if you feel a slight burning sensation. But after 4-5 daily procedures, sinusitis will leave your body without a trace, eliminating the puncture and relapse of the disease. This product can be stored for a long time (provided you used refined oil), so you can prepare it for several days.
- Treatment of sinusitis with cyclamen juice is considered the most effective method. Cyclamen juice can cure any sinusitis in a matter of days. This is a very unpleasant procedure, not everyone can withstand it, but the result justifies the effort. To achieve the effect, it will take about 2-3 months of daily procedures.
Cyclamen should not be used by people with allergies, as it can cause a severe allergic reaction.
- Propolis is a universal remedy that will also help with sinusitis. Mix 20% propolis tincture in medical alcohol with vegetable oil in a 1:1 ratio. If you have an aqueous solution of propolis, you can simply dilute it with water in a ratio of 1:3 and drip it into your nose.
- Kalanchoe juice is considered an excellent remedy for colds and severe sneezing. Using Kalanchoe juice you can cure acute and chronic sinusitis in adults. For treatment, you need to use the leaves, because they relieve swelling and remove mucus from the nose. Kalanchoe juice in its pure form can be dripped into the nose 3-4 times a day. It causes active and prolonged sneezing, which produces mucus.
- Wash the horseradish root, peel and grate 1/3 cup. Mix the mixture with lemon juice squeezed from 3 lemons. The result is a thick mixture, which should be taken daily in the morning, 0.5 teaspoon 20 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 4 months. After a two-week break, a second course of treatment is carried out. Thus, treatment courses are carried out 2 times - in spring and autumn. After 2 years, attacks of sinusitis will disappear forever.
- Place 3 large bay leaves in the pan. Fill with water and put on fire. As soon as the water boils, turn off the gas. Dip a clean napkin into the water, soak it in the broth, then apply it to the bridge of the nose and forehead. Cover your head with a warm cloth to keep warm longer. When the napkin has cooled, take another one and do the same procedure again. And repeat this until the broth in the pan remains warm (3-4 procedures). It is advisable to carry out the procedures before bedtime. The course of treatment is 6 days.
- Sea buckthorn oil in its pure form can be dripped into each nostril 2 times a day instead of regular nasal drops. For inhalations based on sea buckthorn oil, add 10 drops of oil to a pan of boiling water and inhale the vapors for about 15 minutes.
Signs of allergic sinusitis and its treatment
There are diseases of the nose that are considered to be the most problematic. Allergic sinusitis is considered one of these pathologies. With this disease, the nasal sinuses are damaged and severe swelling of the mucous membranes develops.
Sputum begins to accumulate in the paranasal sinuses and bacteria multiply rapidly. The immune system can no longer cope with the excessive number of microbes.
Over time, if the disease is not treated, complications arise - polyps and purulent inflammation.
Causes of pathology
The main reason is prolonged contact with the allergen. Most often, the irritant enters the nasal mucosa during breathing.
The immune system identifies it as an aggressive compound and activates defense mechanisms. Increased production of immunoglobulin E and the mediator histamine is triggered.
The capillaries expand, resulting in swelling of the nasal tissue and mucus production.
Irritants can be:
- plant pollen;
- house dust;
- pet hair;
- mold;
- food products;
- medicines;
- cosmetics and household chemicals.
Allergic sinusitis develops against the background of other allergic diseases: allergic rhinitis (not compensated in time), hay fever, atopic bronchial asthma. The pathology most often affects adolescents and young people under 20 years of age. People suffering from chronic ENT diseases, as well as smokers, are at risk.
Drug therapy
The doctor may prescribe:
- Antihistamines - Loratadine, Fenistil, Diazolin, Suprastin, Zyrtec, Levocetirizine, Erius, Cetrin, Tavegil, etc.
- Vasoconstrictor drugs - Nazivin, Otrivin, Azelastine, Opatanol, Naphthyzin, etc.
- Glucocorticosteroids in case of severe complications - Hydrocortisone, Flixotide, Afloderm, Prednisolone, etc.
- To eliminate the infection - antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal drugs.
- Eye drops – Azelastine, Cromohexal, Ketotifen, Allergodil, etc.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods can be used during remission.
Applicable:
- darsonvalization;
- medicinal baths;
- ultrasound therapy;
- electrophoresis.
Diet
If the allergen is a food product, it must be removed from the diet. But even if the cause of the disease is not a food allergy, you should adhere to the principles of a healthy diet. They are well known - eat less fatty, starchy, sweet, spicy foods, avoid fast food. You should also reduce your consumption of milk and dairy products: they increase mucus production.
ASIT
This is an effective method of treating allergies. The patient is periodically injected in a minimal dosage with an allergen to which there is an intolerance. The body gradually gets used to it and sensitivity decreases. To get a noticeable positive result, you need to be treated for a long time (several years).
Traditional methods
They can enhance the effectiveness of drug therapy. But they should be used after consulting a doctor, since additional allergic reactions and deterioration of well-being are possible.
Recipes:
- Steam inhalations are effective. You can add 1 tsp to boiling water. propolis infusion, a few drops of fir oil or a crumb of “Zvezdochka” balsam and 1 tsp. soda
- Cyclamen juice relieves inflammation. You need to drop 2 drops into each nostril. Menthol oil drops, rosehip or sea buckthorn oil, aloe juice, and Kalanchoe are also used.
- Useful rinsing of the nose with mineral water, water with added sea salt, green tea, infusions of chamomile, calendula, and currant leaves.
- Pour 20 g of ginger root into 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for half an hour, add a spoonful of honey and drink like regular tea.
- Make a foot bath with dry mustard. After the procedure, your feet should be rinsed, dried and put on thick socks.
- Moisten a woolen cloth with a 10% salt solution and apply it to the forehead, securing it with a terry towel.
- Boil eggs hard and apply hot to your sinuses. Keep until the eggs cool completely.
- You can use turundas - nasal swabs moistened with a special composition. For example, chop the garlic, wrap the pulp in gauze and insert it into one and then into the other nostril for 7-8 minutes. Next, prepare fresh turunda and keep for 3 minutes.
- Chew honey pellets (wax caps of sealed honeycombs) daily.
Prevention
To prevent the development of sinusitis, you must:
- Maintain free passage of the nasal passages (timely correction of the nasal septum, reduction of hypertrophied turbinates, removal of nasal polyps).
- Lead a healthy lifestyle (nutrition, adherence to work and rest, regular physical activity).
- Be outdoors often.
- Treat colds promptly and competently.
- Extinguish foci of chronic infection in the body.
Thermopsis tablets: instructions for use
This article will tell you which syrups for dry cough are prescribed for children of different ages.
How to treat a cough in an infant //drlor.online/diagnostika-lechenie/kashel/u-grudnichkov-doma.html
conclusions
So, sinusitis is a disease that cannot be neglected, otherwise it is difficult to treat.
With timely and correct treatment of sinusitis in adults, the prognosis is favorable: in most cases, the patient makes a full recovery. Unfortunately, getting rid of chronic sinusitis is much more difficult, but stable remission can be achieved. In any case, the disease must be treated to prevent dangerous consequences.
Also read about effective methods of treating specifically chronic sinusitis and what methods can be used to avoid sinus puncture at an advanced stage.
What does traditional medicine advise?
Traditional medicine knows many methods aimed at relieving symptoms or eliminating allergic fungal sinusitis. We have collected the most well-known and effective methods for use in adults.
However, it should be remembered that recipes from alternative medicine serve only as an additional measure to the main treatment, and not as a replacement.
- Take one medium sized onion. Squeeze the juice out of it in any way convenient for you. Mix the resulting liquid with 100 ml of boiling water and add 5–10 g of bee honey. Let the medicine cool and use it to rinse your nose.
- You will need medium-sized, peeled beets. It is necessary to boil it until tender and squeeze out the maximum amount of juice. Treatment occurs by instilling the product into the nasal canals, a few drops once a day.
- The aloe plant is famous for its healing properties. Almost everyone knows that it contains many useful substances. To help yourself with sinusitis, cut a leaf from the stem of a flower and leave it in the refrigerator for two hours. To ensure that the plant retains maximum benefits, wrap it in paper. During cooling, aloe activates the entire supply of necessary substances. After this, you need to chop the leaf into small pieces, extract the juice through a sieve or gauze and bury it in your nose three times a day.
As a rule, allergic rhinosinusitis is a consequence of other allergic diseases - conjunctivitis or dermatitis.
Pathology can manifest itself in a child over 3 years of age, as well as in adults. People who have discovered signs of the disease have a tendency to allergic reactions in general.
In spring and summer, symptoms become most pronounced. A person experiences severe itching throughout the body, watery eyes, and congestion in the ears and nose. The attending physician should try to help the patient as quickly as possible. This will help to avoid the most dangerous complications and eliminate unpleasant symptoms in a short time.